Health technology news and insights. Got HealthTech? Absolutely!
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Tennr raises $101 million to address inefficiencies in U.S. patient referral system

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Health tech startup Tennr has secured a $101 million Series C funding round to continue developing its platform aimed at improving the U.S. patient referral system.
The company was founded in 2021 by Diego Baugh, Trey Holterman, and Tyler Johnson, after Baugh experienced delays in accessing specialist care during college. Tennr’s platform uses a proprietary AI model designed to interpret complex medical documents and streamline the referral process, including tasks like verifying insurance and checking patient eligibility.
The latest funding round, led by IVP with participation from Google Ventures, Iconiq, Andreessen Horowitz, and Lightspeed, values the company at $605 million. Tennr’s model is trained on a large dataset of medical documents and is tailored to address the specific challenges of patient referrals, such as navigating provider requirements and interpreting handwritten notes.
Although the company incorporates AI, CEO Holterman stresses that Tennr’s primary focus is on solving operational challenges in healthcare, rather than promoting itself as an AI brand. The company is also developing features that provide better transparency into referral and payment processes for both patients and physicians. Tennr reports that its revenue has tripled since its last funding round in October and currently reaches eight figures annually.
Header image: Tennr's founding team, from left to right: Trey Holterman (Co-founder and CEO), Tyler Johnson (Co-founder and CTO), and Diego Baugh (Co-founder and Chief Product Officer). Credit: Tennr.
Read more at Fortune
///
Other recent news and insights
French HealthTech startup DESKi secures €5.2 million to advance its cardiac imaging software (EU-Startups)
Samsung rolls out One UI 8 Watch update featuring new health metrics and Gemini AI integration (iPhone in Canada)
Belgian startup Koios Care raises €1 million to support real-world data solutions for Parkinson’s disease monitoring and treatment (EU-Startups)
Health tech company Hyphen unveils a new claims processing platform tailored for social needs organizations (Fierce Healthcare)
30 healthcare IT influencers to watch—and follow—in 2025 (HealthTech Magazine)
0 notes
Text
AI tool Fragle offers faster and cheaper cancer monitoring through simple blood tests

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Researchers at the A*STAR Genome Institute of Singapore have developed Fragle, a new AI-based method that tracks cancer using small blood samples.
Unlike conventional tests that rely on expensive and complex DNA sequencing, Fragle analyzes the size patterns of DNA fragments in the blood to distinguish cancer DNA from healthy DNA. This approach allows for faster, cheaper, and more frequent cancer monitoring, with an estimated cost of under SGD $50 compared to over $1000 for traditional tests.
Fragle is highly accurate across multiple cancer types, works with standard DNA profiling methods used in hospitals, and can detect minimal residual disease (MRD), helping catch early signs of relapse. The method is currently being tested in clinical studies with over 100 cancer patients in collaboration with the National Cancer Center Singapore, aiming to improve treatment monitoring and early relapse detection.
Researchers hope Fragle will become a practical, accessible tool for enhancing cancer care both in Singapore and globally.

Image: Fragle overview. Credit: Nature Biomedical Engineering (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41551-025-01370-3.
Read more at Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore/Medical Xpress
///
Other recent news and insights
AI tools used in clinical settings may help stop the spread of C. difficile (University of Michigan College of Engineering/Medical Xpress)
New algorithm optimizes vascular design for 3D-printed heart models (Stanford University/Medical Xpress)
0 notes
Text
Canada launches AI Scribe Program to ease clinician workloads with 10,000 free licenses

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Canada Health Infoway has launched its AI Scribe Program, offering up to 10,000 fully funded one-year licenses for AI-powered clinical documentation tools to eligible primary care clinicians across Canada.
The goal is to reduce administrative burden and improve documentation workflows using AI scribes from companies like Well Health, MEDFAR, Autochart.ai, Empathia AI, and others.
Vendors were chosen based on their compliance with national standards, secure data practices, and alignment with Infoway’s Shared Pan-Canadian Interoperability Roadmap. Clinicians can enroll through the program’s website by selecting their province or territory (excluding the Northwest Territories and Nunavut).
While the initiative promises efficiency, experts raise concerns about the risk of hallucinations in AI-generated medical summaries. Future phases of the program will explore scaling, structured data integration, and decision support capabilities.
Read more at BetaKit
///
Other recent news and insights
NeuroFlow launches new analytics tools to support behavioral health risk management (Fierce Healthcare)
0 notes
Text
Digital twin technology boosts artificial pancreas performance for better type 1 diabetes control

- By InnoNurse Staff -
A new University of Virginia study shows that digital twin technology can improve diabetes control in people with type 1 diabetes by enhancing the performance of an artificial pancreas system.
This adaptive system, called adaptive biobehavioral control, creates a virtual model—or “digital twin”—of each user to simulate how their body responds to changes in blood sugar management. Users can test insulin delivery settings safely in this simulation before applying them in real life.
In a six-month trial, the technology increased participants' time in a healthy blood sugar range from 72% to 77% and slightly reduced average blood sugar levels. The system adjusts every two weeks and supports better glucose control during the day, when blood sugar tends to fluctuate more due to food and activity. The approach emphasizes human-machine co-adaptation, helping users and the device learn from each other to improve diabetes management.
Header image: A new study shows that a 'digital twin' technology enhances diabetes management for people with type 1 diabetes using artificial pancreas systems developed at UVA. Credit: John DiJulio.
Read more at University of Virginia
///
Other recent news and insights
AI uncovers key gene groups linked to complex diseases (Northwestern University)
Canada: Eli Health secures $17 million CAD in Series A funding to advance launch of hormone-monitoring technology (BetaKit)
0 notes
Text
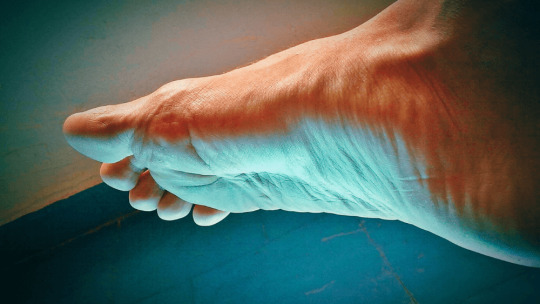
AI foot scanner helps detect early heart failure warning signs
- By InnoNurse Staff -
A new AI-powered home device that scans people's feet as they get out of bed could help prevent hospitalizations in heart failure patients, according to a study presented at the British Cardiovascular Society conference.
Developed by Heartfelt Technologies, the wall-mounted scanner detects edema (fluid buildup in the feet), a key warning sign of worsening heart failure, by taking 1,800 images per minute and analyzing them with foot-recognition technology.
The device can alert medical teams an average of 13 days before hospitalization, giving enough time for early intervention. In the small FOOT study involving 26 patients, it predicted five of six hospitalizations, outperforming traditional weight-monitoring methods. Installed by the bed, it works automatically, requires no user input, and can function without Wi-Fi.
Researchers and experts suggest this tool could serve as a “virtual nurse,” especially helpful amid shortages of heart failure specialists. Most patients opted to keep the device after the trial. Further studies are planned to test its use on a larger scale, including in care homes.

Image credit: British Heart Foundation.
Read more at British Heart Foundation
///
Other recent news and insights
Newel Health receives EU MDR certification for its blood pressure management platform (Medical Device Network)
#cardiology#foot#medtech#digital health#uk#health tech#Heartfelt Technologies#health informatics#iot#ai
0 notes
Text
AI agent aims to enhance cancer care decision-making with GPT-4 and medical tools

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Researchers at the Else Kröner Fresenius Center (EKFZ) for Digital Health at TUD Dresden University of Technology, in collaboration with international partners, have developed an autonomous AI agent to support clinical decision-making in oncology.
By enhancing GPT-4 with specialized tools for analyzing medical images, predicting genetic mutations, and accessing medical literature, the AI can process complex, multimodal data for personalized cancer care.
Tested on 20 simulated real-world cases, the AI correctly identified clinical conclusions in 91% of instances and cited relevant guidelines in over 75%, with reduced hallucinations. The study, published in Nature Cancer, shows the AI’s promise in supporting—but not replacing—doctors by improving decision-making efficiency and keeping up with evolving treatment standards.
Though promising, the system requires further validation, integration with clinical workflows, and adherence to privacy and regulatory standards. Long-term, similar AI agents could be adapted for other medical fields, provided clinicians are trained to collaborate with such tools while retaining final decision authority.

Image: Overview of the LLM-based agent system. Credit: Credit: Nature Cancer (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s43018-025-00991-6.
Read more at TUD Dresden University of Technology
///
Other recent news and insights
Virtual care provider Omada Health surges in first day of trading (CNBC)
0 notes
Text
CVS Health to invest $20 billion in tech-driven healthcare overhaul and interoperability improvements

- By InnoNurse Staff -
CVS Health has announced plans to invest $20 billion over the next 10 years to enhance its consumer healthcare offerings through improved technology and system interoperability.
The initiative will span CVS' integrated business segments, including Aetna, its retail pharmacies, and healthcare providers. A central component of the plan is the development of a shared patient record system that would enable better communication among various healthcare stakeholders, regardless of company affiliation.
The company also aims to make the healthcare experience more proactive by sending patients automated notifications—such as claim updates—reducing the need for them to reach out for information. Additionally, CVS is looking to streamline processes like claims management and cost estimates to create a more efficient system. CVS anticipates that the effort could lead to noticeable changes in the consumer healthcare experience within five years.
This investment comes as part of broader changes at CVS, which include the planned closure of 271 stores in 2025—adding to nearly 900 closures from 2022 to 2024—as part of a national restructuring strategy. In May, CVS participated in a bankruptcy court-approved process to acquire prescription files from 625 Rite Aid pharmacies and agreed to take over 64 Rite Aid store locations in three states, pending court and regulatory approvals. Rite Aid filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy earlier this year.
Read more at MobiHealthNews
///
Other recent news and insights
'AI scientist' collaborates with humans to identify cheap drug combinations for potential cancer treatment (University of Cambridge)
Scientists grow vascularized heart and liver organoids, overcoming size limits and opening new avenues for research (Stanford School of Medicine)
0 notes
Text
Generative AI may help fill gaps in DNA data and improve gene structure studies

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Researchers at Skoltech have successfully used generative artificial intelligence to fill in missing data on distances between gene pairs in DNA, a crucial step for reconstructing the molecule’s 3D architecture.
This advancement enables deeper insights into genetic diseases and opens new avenues for diagnosis and treatment.
Previously, experimental methods like fluorescence microscopy provided only partial data due to technical limitations.
The study, published in Scientific Reports, is the first to complete this data using AI, marking a novel application of generative models beyond creative tasks like image or text generation.
This approach enhances our understanding of chromatin structure and holds significant promise for personalized medicine and gene therapy.
Header image: Assessing gene-to-gene distances. Credit: Generated with DDG DaVinci2 model from prompt by Nicolas Posunko/Skoltech PR.
Read more at Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech)/Medical Xpress
///
Other recent news and insights
Aeon, a Swiss HealthTech startup, raises €8.2M to expand its AI-driven preventive health platform (EU-Startups)
HealthKey acquires Syndi Health to strengthen personalized healthcare monitoring capabilities (Tech.EU)
Hims & Hers announces all-cash acquisition of European HealthTech company Zava (Fierce Healthcare)
Finnish medtech firm AIATELLA secures €2M to advance AI tools for cardiovascular screening and support radiologists (Silicon Canals)
AI and healthcare: 10 European startups to watch in 2025 (EU-Startups)
Canada: HiBoop launches beta platform aimed at improving mental health screening (BCBusiness)
Hormona raises €7.8M to help women monitor, understand, and optimize their hormonal health (EU-Startups)
0 notes
Text
Machine learning study links biological and psychosocial factors to chronic pain conditions

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Researchers from McGill University, in a study published in Nature Human Behavior, used advanced machine learning techniques to analyze data from over 523,000 individuals in the UK Biobank, aiming to uncover biological and psychosocial factors linked to chronic pain.
Initially focused on identifying brain-based biomarkers, the team found these alone were insufficient to distinguish individuals with chronic pain. However, when combined with psychosocial data—such as psychological traits and social factors—machine learning models significantly improved in predicting specific pain conditions like fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis.
The team applied machine learning to detect patterns across a wide range of data, including brain scans, genetic profiles, bone imaging, blood tests, and psychosocial variables. This enabled them to stratify individuals by risk level and identify predictive markers across 35 pain-related conditions. They discovered that while biological markers were useful for identifying medical conditions associated with pain, psychosocial factors were more accurate in predicting the subjective experience of pain.
These findings support the biopsychosocial model of pain and suggest that integrated data-driven approaches can enhance diagnosis and risk assessment. The researchers now aim to validate their models in diverse global populations to ensure broader applicability of these predictive tools.

Bar plots display the average ROC-AUC scores for models classifying pain-related diagnoses using biological (left) and psychosocial (right) data types, with 95% confidence intervals. Individual validation folds are shown as overlaid points. Bubble heat maps illustrate AUC scores by data subcategory, where color represents the absolute AUC value and bubble size indicates the z score relative to other diagnoses. Credit: Nature Human Behaviour (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41562-025-02156-y

Kaplan–Meier curves illustrate the 15-year cumulative incidence of diagnosis, categorized by combinations of blood-based biomarker risk and psychosocial risk levels (high–high, high–low, low–high, low–low). Credit: Nature Human Behaviour (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41562-025-02156-y
Read more at Medical Xpress
///
Other recent news and insights
Finnish startup CurifyLabs secures €6.7 million to enhance the safety and personalization of medicine (EU-Startups)
#ai#machine learning#neuroscience#philosophy#chronic pain#pain#biomarkers#health tech#medtech#data science
0 notes
Text
Team develops 3D virtual staining technology for non-invasive cancer tissue imaging

- By InnoNurse Staff -
A research team led by the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has developed a groundbreaking 3D virtual staining technology that enables non-invasive, high-resolution imaging of cancer tissues without the need for traditional slicing and staining.
Using holotomography to capture 3D refractive index data and an AI-based deep learning algorithm, the system produces realistic virtual Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) images—the gold standard in pathology.
This approach eliminates the need for excisional biopsies and significantly reduces the number of tissue slides required—by up to tenfold—offering faster, less invasive analysis. The technology has shown high similarity to conventional stained images and consistent performance across various tissues, validating its potential for widespread use in clinical diagnosis and biomedical research.
Published in Nature Communications, the research was conducted in collaboration with Yonsei University, the Mayo Clinic, and Tomocube, and represents a major step forward in 3D pathology and cancer diagnostics.

Image: Quantitative analysis and 3D microanatomical reconstruction of an entire 50 μm-thick colon cancer tissue section. Credit: Credit: Nature Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59820-0.
Header image: From left; Juyeon Park (Ph.D. candidate, Department of Physics), Professor YongKeun Park (Department of Physics). Top left; Professor Su-Jin Shin (Gangnam Severance Hospital), Professor Tae Hyun Hwang (Vanderbilt University School of Medicine). Credit: KAIST.
Read More at KAIST
///
Other recent news and insights
Mixed reality glasses help restore a full sense of the world for individuals with partial vision loss (University of Alberta)
0 notes
Text
Hinge Health soars in IPO debut potentially signaling a renewed investor interest in digital health

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Hinge Health made its public market debut on the New York Stock Exchange on May 22, with its stock opening 22% above its IPO price and closing 17% higher at $37.56, giving the company a valuation exceeding $3 billion.
The IPO, priced at the top of its marketed range at $32 per share, raised $437 million through the sale of 13.7 million shares, including 5.1 million from existing shareholders. This marks a significant moment for the digital health sector, which has seen few IPOs since 2021.
Founded in 2014, Hinge Health offers a virtual care platform focused on musculoskeletal (MSK) health, using AI-powered motion tracking and a proprietary wearable device. It serves over 2,250 enterprise customers and had 532,000 members at the end of 2024. The company posted $432 million in revenue over the past 12 months and reported $17.1 million in net income for Q1 2025, a notable turnaround from a loss the previous year.
CEO Daniel Perez emphasized the company’s profitability, strong financial metrics, and unique position in digital health by automating care delivery rather than just administrative tasks. Despite a drop from its $6.2 billion valuation in 2021, analysts view the current valuation as reasonable given its margins and growth.
Hinge Health’s IPO may signal renewed interest in public offerings for digital health firms, though analysts caution that not all companies will benefit equally. The company aims to expand into broader healthcare markets and considers small strategic acquisitions to enhance its technology. While its business model is currently profitable and scalable, competition and integration with the wider healthcare ecosystem remain key factors for long-term success.
Read more at Fierce Healthcare
#msk#virtual care#telehealth#ipo#stocks#digital health#health tech#hinge health#ai#wearables#physical therapy
0 notes
Text
Meridian Health Ventures raises $40M to scale UK health tech startups with new transatlantic fund

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Meridian Health Ventures (MHV) has raised over $40 million for a new transatlantic fund aimed at scaling UK health tech startups both domestically and internationally.
The fund, supported by leading UK and US medical institutions such as Guy’s and St Thomas’, Cedars-Sinai, and Hartford HealthCare, seeks to bridge NHS and US healthcare systems and help startups generate the data needed for adoption and growth.
Previously known as KHP Ventures, MHV has expanded its investor base and portfolio, which includes companies like Apian—currently trialing a medical drone delivery service in London. The fund is positioned to drive innovation in healthcare delivery amid rising demand and systemic pressures.
In total, MHV now manages around $50 million, including its earlier mental health tech fund launched in 2024 with Wellcome Trust.
Header image: MHV’s portfolio features emerging health tech companies like Apian, which is piloting a drone service to deliver medical supplies between hospitals in London. Credit: Apian.
Read more at Impact Investor
///
Other recent news and insights
Researchers pilot pharmacy-based algorithm to identify and remove incorrect penicillin allergy labels (Monash University)
AI video analysis improves cataract surgery training and outcomes in low-resource settings (University of Bonn)
#Meridian Health Ventures#uk#usa#vc#startups#apian#drone#health tech#medtech#digital health#innovation
0 notes
Text
New Mountain Capital merges three companies to launch AI-driven RCM platform

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Smarter Technologies is a newly formed revenue cycle management (RCM) company created from the merger of Access Healthcare, SmarterDx, and Thoughtful.ai.
With 27,000 employees and 24 global service centers, the company supports over 200 clients, including 60+ hospitals and health systems. It processes 400+ million transactions and manages over $200 billion in revenue annually.
Backed by private equity firm New Mountain Capital, Smarter Technologies leverages agentic AI, machine learning, and human-in-the-loop systems to automate and improve administrative healthcare workflows. Its modular platform includes:
Smarteraccess: Virtual agents and human operators for RCM tasks.
SmarterDx: Clinical AI insights engine for revenue and quality opportunities.
Thoughtful.ai: NLP, OCR, and ML tools for intelligent automation.
Nebula: AI workflow automation platform.
Overwatch: RCM operations model.
Spotlight: ML platform for payment system complexity.
The company claims a 5:1 ROI and $2M in added annual revenue per 10,000 discharges for hospitals using SmarterDx. CEO Jeremy Delinsky, a healthcare tech veteran, emphasizes the potential of AI to reduce administrative waste, improve payment accuracy, and modernize outdated systems still reliant on 1990s-era standards.
While concerns about AI vs. AI claim disputes exist, Delinsky argues that proactive error detection and real-time QA can prevent billing disasters and improve patient experiences.
Read more at Fierce Healthcare
///
Other recent news and insights
Dazos raises $25 million to expand behavioral health software platform (Refresh Miami)
At-home dental flosser with stress monitoring capabilities (American Chemical Society)
Saudi Arabia-based Kilow raises $2.5 million seed round to advance AI-powered weight management platform (Zawya)
Hearing aids are evolving — and you might already be wearing one without knowing it (Vox)
Wearable sensor may help track response to obstructive sleep apnea treatment (American Thoracic Society/Medical Xpress)
#New Mountain Capital#private equity#mergers and acquisitions#rcm#health it#Smarter Technologies#ai#health tech
0 notes
Text
Machine learning study identifies three social profiles linked to suicide risk across US regions

- By InnoNurse Staff -
A new study using unsupervised machine learning has identified three distinct social and economic profiles linked to higher suicide risk in the U.S., emphasizing the importance of community-level factors over individual or clinical ones.
Conducted by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Columbia University, the study analyzed data from 3,018 counties and 284 social determinants of health, revealing geographic variations in suicide patterns. The results were published in Nature Mental Health.
The study identified three clusters. The first, called REMOTE, includes rural, isolated areas with older populations, deteriorating housing, and high firearm-related suicides among men. The second, COPE, consists of communities—mainly in the South—marked by family instability, poverty, and harsh environmental stressors, where suicide is more common among middle-aged white individuals. The third cluster, DIVERSE, encompasses urban, racially diverse areas with income inequality and limited healthcare access, where suicide rates are higher among women, youth, and racial minorities.
Researchers stress the need for region-specific interventions. For REMOTE areas, strategies should focus on reducing isolation, improving mental health care access, and addressing gun safety. In COPE communities, efforts might include addressing economic stress and substance abuse. For DIVERSE areas, enhancing culturally relevant care, expanding healthcare access, and addressing environmental issues could be effective.
The study also found that policy changes like Medicaid expansion led to reduced suicide rates in some regions, underlining the role of healthcare accessibility in prevention efforts. This is the first study to use unsupervised machine learning on such a comprehensive set of social determinants, offering a powerful new approach to tailoring suicide prevention strategies based on local conditions.
Read more at Weill Cornell Medicine
///
Other recent news and insights
AI-powered tool effectively categorizes cancer patients based on predicted outcomes (Weill Cornell Medicine)
#social determinants of health#ai#data science#usa#suicide#machine learning#mental health#psychiatry
0 notes
Text
AI tool FaceAge uses facial photos to predict biological age and cancer survival outcomes

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Researchers at Mass General Brigham have developed FaceAge, an AI tool that estimates a person’s biological age using facial photos and predicts cancer survival outcomes.
The tool, trained on nearly 59,000 images, found that cancer patients generally appear about five years older than their actual age, and those with higher FaceAge scores tend to have poorer survival rates.
In tests, FaceAge outperformed clinicians in predicting short-term life expectancy among palliative care patients, especially when clinicians were given FaceAge data.
While not yet ready for clinical use, the technology shows promise for broader applications in disease prediction and aging-related care.

Image: This graphic illustrates how FaceAge could be estimated from a patient's photo. The individual shown is an AI-generated image. Credit: Mass General Brigham.
Header image credit: Microsoft Copilot (AI-generated)
Read more at Mass General Brigham
///
Other recent news and insights
Kouper raises $10M to tackle healthcare’s costliest blind spot: Patient transitions (PYMNTS)
BabyBot: A soft robotic infant replicates feeding behaviors from newborn to 6 months (Medical Xpress)
Engineering lab develops at-home testing kits for stress and heart health (University of Cincinnati)
0 notes
Text
AI-powered tool SALSA enables automated, high-precision liver tumor detection and segmentation using CT scans

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Researchers at the Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO), led by Raquel Perez-Lopez, have developed SALSA (System for Automatic Liver tumor Segmentation And detection), a fully automated, AI-driven tool that accurately detects and segments liver tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and metastases, using CT scans.
Published in Cell Reports Medicine, the study shows SALSA outperforms existing models and radiologist agreement, with over 99% precision at the patient level.
Trained on data from 1,598 CT scans covering 4,908 tumors, SALSA enables precise tumor volume analysis without manual input, addressing challenges in tumor delineation.
It holds promise for improving diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring by quantifying imaging biomarkers like tumor volume, density, and texture, contributing to more personalized and effective cancer care.

Image: Visual abstract. Credit: Cell Reports Medicine (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102032.

Image: Visual comparison between automated and radiologist-generated tumor contours. Representative liver tumor cases segmented by SALSA (red) are compared to the radiologist-defined ground truth (blue). Yellow dashed boxes in <A> and <C> highlight regions magnified in <B> and <D> to enhance visibility. Contours are shown as colored masks to emphasize areas of overlap and divergence between the two delineations. Credit: Cell Reports Medicine (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102032.
Read more at Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology/Medical Xpress
///
Other recent news and insights
Innovative algorithms assist GPs in identifying patients with potential undiagnosed cancer (Queen Mary University of London)
Oura Ring update introduces glucose monitoring and meal tracking features (The Shortcut)
0 notes
Text
Spark Finland opens call for health tech and life sciences innovations in five Finnish regions

- By InnoNurse Staff -
SPARK Finland—a national program that supports the development and commercialization of health tech and life science innovations—has launched a new call for proposals, open from May 1 to May 31, 2025.
The initiative is aimed at researchers, students, and clinical professionals based in Helsinki, Tampere, Turku, Kuopio, and Joensuu. It seeks projects that address unmet healthcare needs and have the potential to advance to clinical validation, trials, or commercialization within two to three years.
Eligible proposals may include innovations such as drugs, vaccines, medical devices, diagnostics, bioinformatics, or digital health (healthIT) solutions.
No external funding or company formation is required to apply. The application process involves submitting a two-page proposal and a five-minute video, with finalists selected for further evaluation. An info session will be held on May 8 via Zoom.
Read more at EntrepreNerd
0 notes