#private equity
Text
How to shatter the class solidarity of the ruling class

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me WEDNESDAY (Apr 11) at UCLA, then Chicago (Apr 17), Torino (Apr 21) Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

Audre Lorde counsels us that "The Master's Tools Will Never Dismantle the Master's House," while MLK said "the law cannot make a man love me, but it can restrain him from lynching me." Somewhere between replacing the system and using the system lies a pragmatic – if easily derailed – course.
Lorde is telling us that a rotten system can't be redeemed by using its own chosen reform mechanisms. King's telling us that unless we live, we can't fight – so anything within the system that makes it easier for your comrades to fight on can hasten the end of the system.
Take the problems of journalism. One old model of journalism funding involved wealthy newspaper families profiting handsomely by selling local appliance store owners the right to reach the townspeople who wanted to read sports-scores. These families expressed their patrician love of their town by peeling off some of those profits to pay reporters to sit through municipal council meetings or even travel overseas and get shot at.
In retrospect, this wasn't ever going to be a stable arrangement. It relied on both the inconstant generosity of newspaper barons and the absence of a superior way to show washing-machine ads to people who might want to buy washing machines. Neither of these were good long-term bets. Not only were newspaper barons easily distracted from their sense of patrician duty (especially when their own power was called into question), but there were lots of better ways to connect buyers and sellers lurking in potentia.
All of this was grossly exacerbated by tech monopolies. Tech barons aren't smarter or more evil than newspaper barons, but they have better tools, and so now they take 51 cents out of every ad dollar and 30 cents out of ever subscriber dollar and they refuse to deliver the news to users who explicitly requested it, unless the news company pays them a bribe to "boost" their posts:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2023/04/saving-news-big-tech
The news is important, and people sign up to make, digest, and discuss the news for many non-economic reasons, which means that the news continues to struggle along, despite all the economic impediments and the vulture capitalists and tech monopolists who fight one another for which one will get to take the biggest bite out of the press. We've got outstanding nonprofit news outlets like Propublica, journalist-owned outlets like 404 Media, and crowdfunded reporters like Molly White (and winner-take-all outlets like the New York Times).
But as Hamilton Nolan points out, "that pot of money…is only large enough to produce a small fraction of the journalism that was being produced in past generations":
https://www.hamiltonnolan.com/p/what-will-replace-advertising-revenue
For Nolan, "public funding of journalism is the only way to fix this…If we accept that journalism is not just a business or a form of entertainment but a public good, then funding it with public money makes perfect sense":
https://www.hamiltonnolan.com/p/public-funding-of-journalism-is-the
Having grown up in Canada – under the CBC – and then lived for a quarter of my life in the UK – under the BBC – I am very enthusiastic about Nolan's solution. There are obvious problems with publicly funded journalism, like the politicization of news coverage:
https://www.theguardian.com/media/2023/jan/24/panel-approving-richard-sharp-as-bbc-chair-included-tory-party-donor
And the transformation of the funding into a cheap political football:
https://www.cbc.ca/news/politics/poilievre-defund-cbc-change-law-1.6810434
But the worst version of those problems is still better than the best version of the private-equity-funded model of news production.
But Nolan notes the emergence of a new form of hedge fund news, one that is awfully promising, and also terribly fraught: Hunterbrook Media, an investigative news outlet owned by short-sellers who pay journalists to research and publish damning reports on companies they hold a short position on:
https://hntrbrk.com/
For those of you who are blissfully distant from the machinations of the financial markets, "short selling" is a wager that a company's stock price will go down. A gambler who takes a short position on a company's stock can make a lot of money if the company stumbles or fails altogether (but if the company does well, the short can suffer literally unlimited losses).
Shorts have historically paid analysts to dig into companies and uncover the sins hidden on their balance-sheets, but as Matt Levine points out, journalists work for a fraction of the price of analysts and are at least as good at uncovering dirt as MBAs are:
https://www.bloomberg.com/opinion/articles/2024-04-02/a-hedge-fund-that-s-also-a-newspaper
What's more, shorts who discover dirt on a company still need to convince journalists to publicize their findings and trigger the sell-off that makes their short position pay off. Shorts who own a muckraking journalistic operation can skip this step: they are the journalists.
There's a way in which this is sheer genius. Well-funded shorts who don't care about the news per se can still be motivated into funding freely available, high-quality investigative journalism about corporate malfeasance (notoriously, one of the least attractive forms of journalism for advertisers). They can pay journalists top dollar – even bid against each other for the most talented journalists – and supply them with all the tools they need to ply their trade. A short won't ever try the kind of bullshit the owners of Vice pulled, paying themselves millions while their journalists lose access to Lexisnexis or the PACER database:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/24/anti-posse/#when-you-absolutely-positively-dont-give-a-solitary-single-fuck
The shorts whose journalists are best equipped stand to make the most money. What's not to like?
Well, the issue here is whether the ruling class's sense of solidarity is stronger than its greed. The wealthy have historically oscillated between real solidarity (think of the ultrawealthy lobbying to support bipartisan votes for tax cuts and bailouts) and "war of all against all" (as when wealthy colonizers dragged their countries into WWI after the supply of countries to steal ran out).
After all, the reason companies engage in the scams that shorts reveal is that they are profitable. "Behind every great fortune is a great crime," and that's just great. You don't win the game when you get into heaven, you win it when you get into the Forbes Rich List.
Take monopolies: investors like the upside of backing an upstart company that gobbles up some staid industry's margins – Amazon vs publishing, say, or Uber vs taxis. But while there's a lot of upside in that move, there's also a lot of risk: most companies that set out to "disrupt" an industry sink, taking their investors' capital down with them.
Contrast that with monopolies: backing a company that merges with its rivals and buys every small company that might someday grow large is a sure thing. Shriven of "wasteful competition," a company can lower quality, raise prices, capture its regulators, screw its workers and suppliers and laugh all the way to Davos. A big enough company can ignore the complaints of those workers, customers and regulators. They're not just too big to fail. They're not just too big to jail. They're too big to care:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/04/teach-me-how-to-shruggie/#kagi
Would-be monopolists are stuck in a high-stakes Prisoner's Dilemma. If they cooperate, they can screw over everyone else and get unimaginably rich. But if one party defects, they can raid the monopolist's margins, short its stock, and snitch to its regulators.
It's true that there's a clear incentive for hedge-fund managers to fund investigative journalism into other hedge-fund managers' portfolio companies. But it would be even more profitable for both of those hedgies to join forces and collude to screw the rest of us over. So long as they mistrust each other, we might see some benefit from that adversarial relationship. But the point of the 0.1% is that there aren't very many of them. The Aspen Institute can rent a hall that will hold an appreciable fraction of that crowd. They buy their private jets and bespoke suits and powdered rhino horn from the same exclusive sellers. Their kids go to the same elite schools. They know each other, and they have every opportunity to get drunk together at a charity ball or a society wedding and cook up a plan to join forces.
This is the problem at the core of "mechanism design" grounded in "rational self-interest." If you try to create a system where people do the right thing because they're selfish assholes, you normalize being a selfish asshole. Eventually, the selfish assholes form a cozy little League of Selfish Assholes and turn on the rest of us.
Appeals to morality don't work on unethical people, but appeals to immorality crowds out ethics. Take the ancient split between "free software" (software that is designed to maximize the freedom of the people who use it) and "open source software" (identical to free software, but promoted as a better way to make robust code through transparency and peer review).
Over the years, open source – an appeal to your own selfish need for better code – triumphed over free software, and its appeal to the ethics of a world of "software freedom." But it turns out that while the difference between "open" and "free" was once mere semantics, it's fully possible to decouple the two. Today, we have lots of "open source": you can see the code that Google, Microsoft, Apple and Facebook uses, and even contribute your labor to it for free. But you can't actually decide how the software you write works, because it all takes a loop through Google, Microsoft, Apple or Facebook's servers, and only those trillion-dollar tech monopolists have the software freedom to determine how those servers work:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/05/04/which-side-are-you-on/#tivoization-and-beyond
That's ruling class solidarity. The Big Tech firms have hidden a myriad of sins beneath their bafflegab and balance-sheets. These (as yet) undiscovered scams constitute a "bezzle," which JK Galbraith defined as "the magic interval when a confidence trickster knows he has the money he has appropriated but the victim does not yet understand that he has lost it."
The purpose of Hunterbrook is to discover and destroy bezzles, hastening the moment of realization that the wealth we all feel in a world of seemingly orderly technology is really an illusion. Hunterbrook certainly has its pick of bezzles to choose from, because we are living in a Golden Age of the Bezzle.
Which is why I titled my new novel The Bezzle. It's a tale of high-tech finance scams, starring my two-fisted forensic accountant Marty Hench, and in this volume, Hench is called upon to unwind a predatory prison-tech scam that victimizes the most vulnerable people in America – our army of prisoners – and their families:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
The scheme I fictionalize in The Bezzle is very real. Prison-tech monopolists like Securus and Viapath bribe prison officials to abolish calls, in-person visits, mail and parcels, then they supply prisoners with "free" tablets where they pay hugely inflated rates to receive mail, speak to their families, and access ebooks, distance education and other electronic media:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/02/captive-customers/#guillotine-watch
But a group of activists have cornered these high-tech predators, run them to ground and driven them to the brink of extinction, and they've done it using "the master's tools" – with appeals to regulators and the finance sector itself.
Writing for The Appeal, Dana Floberg and Morgan Duckett describe the campaign they waged with Worth Rises to bankrupt the prison-tech sector:
https://theappeal.org/securus-bankruptcy-prison-telecom-industry/
Here's the headline figure: Securus is $1.8 billion in debt, and it has eight months to find a financier or it will go bust. What's more, all the creditors it might reasonably approach have rejected its overtures, and its bonds have been downrated to junk status. It's a dead duck.
Even better is how this happened. Securus's debt problems started with its acquisition, a leveraged buyout by Platinum Equity, who borrowed heavily against the firm and then looted it with bogus "management fees" that meant that the debt continued to grow, despite Securus's $700m in annual revenue from America's prisoners. Platinum was just the last in a long line of PE companies that loaded up Securus with debt and merged it with its competitors, who were also mortgaged to make profits for other private equity funds.
For years, Securus and Platinum were able to service their debt and roll it over when it came due. But after Worth Rises got NYC to pass a law making jail calls free, creditors started to back away from Securus. It's one thing for Securus to charge $18 for a local call from a prison when it's splitting the money with the city jail system. But when that $18 needs to be paid by the city, they're going to demand much lower prices. To make things worse for Securus, prison reformers got similar laws passed in San Francisco and in Connecticut.
Securus tried to outrun its problems by gobbling up one of its major rivals, Icsolutions, but Worth Rises and its coalition convinced regulators at the FCC to block the merger. Securus abandoned the deal:
https://worthrises.org/blogpost/securusmerger
Then, Worth Rises targeted Platinum Equity, going after the pension funds and other investors whose capital Platinum used to keep Securus going. The massive negative press campaign led to eight-figure disinvestments:
https://www.latimes.com/business/story/2019-09-05/la-fi-tom-gores-securus-prison-phone-mass-incarceration
Now, Securus's debt became "distressed," trading at $0.47 on the dollar. A brief, covid-fueled reprieve gave Securus a temporary lifeline, as prisoners' families were barred from in-person visits and had to pay Securus's rates to talk to their incarcerated loved ones. But after lockdown, Securus's troubles picked up right where they left off.
They targeted Platinum's founder, Tom Gores, who papered over his bloody fortune by styling himself as a philanthropist and sports-team owner. After a campaign by Worth Rises and Color of Change, Gores was kicked off the Los Angeles County Museum of Art board. When Gores tried to flip Securus to a SPAC – the same scam Trump pulled with Truth Social – the negative publicity about Securus's unsound morals and financials killed the deal:
https://twitter.com/WorthRises/status/1578034977828384769
Meanwhile, more states and cities are making prisoners' communications free, further worsening Securus's finances:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/14/minnesota-nice/#shitty-technology-adoption-curve
Congress passed the Martha Wright-Reed Just and Reasonable Communications Act, giving the FCC the power to regulate the price of federal prisoners' communications. Securus's debt prices tumbled further:
https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/117/s1541
Securus's debts were coming due: it owes $1.3b in 2024, and hundreds of millions more in 2025. Platinum has promised a $400m cash infusion, but that didn't sway S&P Global, a bond-rating agency that re-rated Securus's bonds as "CCC" (compare with "AAA"). Moody's concurred. Now, Securus is stuck selling junk-bonds:
https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/117/s1541
The company's creditors have given Securus an eight-month runway to find a new lender before they force it into bankruptcy. The company's debt is trading at $0.08 on the dollar.
Securus's major competitor is Viapath (prison tech is a duopoly). Viapath is also debt-burdened and desperate, thanks to a parallel campaign by Worth Rises, and has tried all of Securus's tricks, and failed:
https://pestakeholder.org/news/american-securities-fails-to-sell-prison-telecom-company-viapath/
Viapath's debts are due next year, and if Securus tanks, no one in their right mind will give Viapath a dime. They're the walking dead.
Worth Rise's brilliant guerrilla warfare against prison-tech and its private equity backers are a master class in using the master's tools to dismantle the master's house. The finance sector isn't a friend of justice or working people, but sometimes it can be used tactically against financialization itself. To paraphrase MLK, "finance can't make a corporation love you, but it can stop a corporation from destroying you."
Yes, the ruling class finds solidarity at the most unexpected moments, and yes, it's easy for appeals to greed to institutionalize greediness. But whether it's funding unbezzling journalism through short selling, or freeing prisons by brandishing their cooked balance-sheets in the faces of bond-rating agencies, there's a lot of good we can do on the way to dismantling the system.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/08/money-talks/#bullshit-walks

Image:
KMJ (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Boerse_01_KMJ.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#shorts#short sellers#news#private equity#private prisons#securus#prison profiteers#the bezzle#anything that cant go on forever eventually stop#steins law#hamilton nolan#Platinum Equity#American Securities#viapath#global tellink#debt#jpay#worth rises#insurance#spacs#fcc#bond rating#moodys#the appeal#saving the news from big tech#hunterbrook media#journalism
772 notes
·
View notes
Text
Private Equity is bonkers because it's the cartoonishly evil imagined version of capitalism people talk about on the internet but made real. What if a bunch of guys with too much money went around destroying value and making pretty much everything worse so that they could make more money and do it all over again.
385 notes
·
View notes
Text
Broke: "The Lorax is a good representation of how big business destroys the environment in its own self interest. The Onceler's corporation required truffula trees, and thus they were wiped out."
Woke: "The Lorax is not a good representation of how big business operates since it made no logical sense for The Onceler to destroy all truffula trees despite them being necessary to manufacture his product. He should have farmed them, or harvested them without cutting them down. This oversimplification is good for explaining environmentalism to children, but it doesn't hold up as an adult."
Bespoke: "The Lorax is a great representation of how big business ruins both the world around them and themselves out of short-sighted profit maximization and pride. Of course The Onceler should have replanted the trees, or sustainably harvested the trees, or any other non-stupid thing, but those processes are slower and more expensive. He chose a fast harvest over a sustainable one, got his massive short-term profit, and realized he'd shot himself in the foot once the truffulas had been driven to extinction. This happens irl all the time. It happened with the dodo, the galapagos tortoise, the passenger pigeon, the great auk, and every commercial fishery on the planet. Greed and pride make a person stupid, and most corporations would rather make a lot of money fast while dooming themselves in the process than focus on slow but sustainable growth, and they either choose this knowingly or assume they're invincible and will figure it out later. The Onceler is Elon Musk. The Onceler is Enron. The Onceler is Wall Street. We are surrounded by Oncelers."
#the lorax#environment#environmentalism#the environment#onceler#the onceler#dr seuss#dr. seuss#extinct animals#extinct species#extinction#corporate evil#corporations#capitalism#private equity
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ko-Fi prompt from @dirigibird:
I've been looking at investment options but I don't want to be messing around too much with the stock market, and a co-worker suggested exchange traded funds. Would love to know your opinions!
LEGALLY NECESSARY DISCLAIMER: I am not a licensed financial advisor, and it is illegal for me to advise anyone on investment in securities like stocks. My commentary here is merely opinion, not financial advice, and I urge you to not make any decisions with regards to securities investments based on my opinions, or without consulting a licensed advisor. I am also going to be talking this all over from an American POV, which means some of these things may not apply elsewhere.
So instead of letting you know what to pick or how to organize your securities, I'm going to go through the definitions of what various investment funds are, how they compare functionally, and maybe rant about how I disagree with the stock market on a fundamental ethical level if I have word count left over.
If you want more information, and are okay with jargon, I'd suggest hitting up investopedia. That is where I will be double-checking most of my information for this one.
I also encourage folks who know more about the stock market specifically to jump in! I like to think I'm good at research and explaining things, but I'm still liable to make mistakes.
Mutual Funds: A mutual fund is a pool of money and resources from multiple individuals (often vast numbers of people, actually) being put together and managed as a group by investment specialists. The primary appeal of these is that the money is professionally managed, but not personally so; it gives smaller investors access to professional money managers that they would not have access to on their own, at cheaper rates than if they tried to hire one for just their own assets. The secondary appeal is that, due to the sheer number of people, and thus capital, that is being invested at once, the money can be invested in a wide variety of industries, and is generally more stable than investing in just one company or industry. Low risk, low reward, but overall at least mostly reliable. Retirement plans are often invested in mutual funds by employer choice, through companies like Fidelity or John Hancock.
Hedge Funds: A hedge fund is a high risk, high reward mutual fund. Investors are generally wealthy, and have the room and safety to lose large amounts of money on an investment that has no promise of success, especially since money cannot be withdrawn at will, but must remain in the fund for a period of time following investment. It gets its name from "hedging your bets," as part of the strategy is to invest in the opposition of the fund's focus in order to ensure that there is a backup plan to salvage at least some money if the main plan backfires. Other strategies are also on the riskier side, often planning to take advantage of ongoing events like buyouts, mergers, incumbent bankruptcy, and shorting stocks (that's the one that caused the gamestop incident).
Private Equity: Private equity is... a nightmare that got its own incredibly good Hasan Minhaj episode of Patriot Act, so if you've got 20 minutes, an interest in comedically-delivered, easily-digestible, Real Information, and an internet connection, take a watch of that one. (If it's not available on YouTube in your country, it's originally from Netflix, or you can probably access it by VPN.) Private equity companies are effectively hedge funds that purchase entire companies, rebuild them in one way or another, and then sell them at (hopefully) a profit. Very often, the companies purchased by private equity are very negatively impacted, especially if the private equity group is a Vulture Fund. Sometimes, it's by taking it apart to sell off; sometimes it's by just bleeding it for cash until there's nothing left. Sometimes, it's taking over a hospital and overcharging the patients while also abusing the staff! (Glaucomflecken has a lot of videos on the topic of private equity in the medical industry, check him out.)
Venture Capital: In contrast to private equity, which purchases more mature companies, venture capital is focused on startups, or small businesses that have growth potential. These are the kinds of hedge funds that are like a whole group that you'd see some random tv character calling an Angel Investor (they're not actually the same thing, but they overlap by a lot). I'd hesitantly call these less ethically dubious than private equity, but I'm still suspicious.
And finally, to answer your question on what ETFs are and how they fit into the above.
Exchange Traded Funds: ETFs are... sort of like a mutual fund. Sort of. You are, to some extent, pooling your money... ish.
An ETF is like a stock that is made out of partial stocks. So instead of paying $100 for stock A, and not getting stocks B/C/D that all cost the same, you buy $100 of the ETF, which is $25 each of stocks A/B/C/D. You are getting a quarter of a unit of stock, which isn't normally an option, but because you are purchasing through an ETF that officially already bought those Whole stocks, you can now purchase the partial stocks through them.
They buy the whole stocks, then they resell you mixes of those stocks. They still officially own the whole stocks themselves, but you now own parts of the stocks. Basically, you own "stock" in a company that owns stock in other companies, and in that process you own partial stocks in those other companies.
I'm going to re-explain this using fruit.
Imagine you can buy apples, oranges, melons, grapes, etc. You can also buy fruit cups. You can only buy the individual fruits in big batches or you can pool your money with a few other people, hand it to a chef. The chef will decide which fruits look like they'll taste the best by lunch time, buy a bunch of those fruit pallets with your combined money, and plan out the best possible fruit salad for you to share with a bunch of people once lunch rolls around.
You could also buy a fruit cup. You don't have a lot of control over what's already in the fruit cup, but there are a few different mixes available--that one has strawberries, but that one over there uses kiwi, and the other one that way has pineapple--and you can pick which mix you want. It's a pretty small fruit cup, and it's predesigned, but you can choose the one you want without having to pool money with everyone else. You just first have to let someone else design the fruit cups you choose from, and you don't know which ones are probably going to survive the best to lunch time unless you ask a chef (which defeats the purpose of buying a fruit cup instead of pooling your money, and asking the chef costs money).
That's the ETF. The ETF is the fruit cup.
The upside is that you can now just track the prices of your fruit cup, instead of tracking the prices of four different fruits, and so if the price of one fruit drops, you can just... let the other three buoy it.
Of course, in the real world, there are more than just four stocks involved in an ETF. This part of the Investopedia article lists a few examples, and they're usually themed and involve anywhere from 30 (DOW Jones) to thousands (Russell) of shares by stock type, or by commodity/industry. So with the ETF, you can invest in an entire industry, like technology, and just keep track of that single "stock" in the industry game.
They do cost less in brokerage/management fees than regular mutual funds, and they have a slightly lower liquidity (slower to cash out). There also exist actively managed ETFs, which are basically mutual funds for ETFs. You are paying the chef to buy you premade fruit cups.
(Prompt me on ko-fi!)
#economics#stock market#etfs#etf#mutual funds#hedge funds#venture capital#private equity#capitalism#phoenix talks#ko fi#ko fi prompts#economics prompts
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Private equity is coming for healthcare. Make sure your elected officials fight back.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
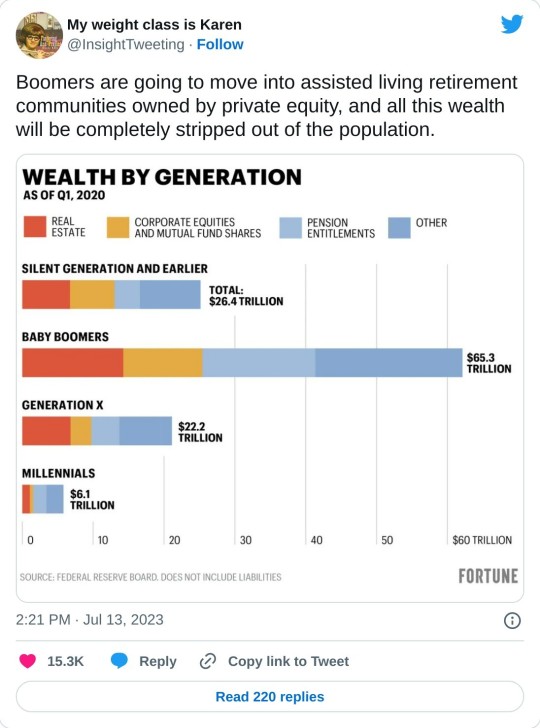
65 notes
·
View notes
Text

#rent is theft#landlords are parasites#black rock#blackrock#private equity#firms#rent is too damn high#landlords are scum#landlords are leeches#landlords are bastards#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#usa news#usa#united states#unitedstateofamerica#unitedsnakes#native american#america#amerika
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

#private equity firms#capitalism#capitalism ruins everything#capitalism in medicine#late stage capitalism#healthcare#veteran emergency room doctor#ming lin#peacehealth st. joseph medical center#bellingham washington#coronavirus pandemic#hospital preparedness#social media criticism#teamhealth#blackstone group#private equity#healthcare industry#physician staffing#peer review process#due process rights#patient safety#financial entity#acquisitions#rural hospitals#physicians' practices#nursing homes#hospice centers#air ambulance companies#healthcare billing management#debt collection systems
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
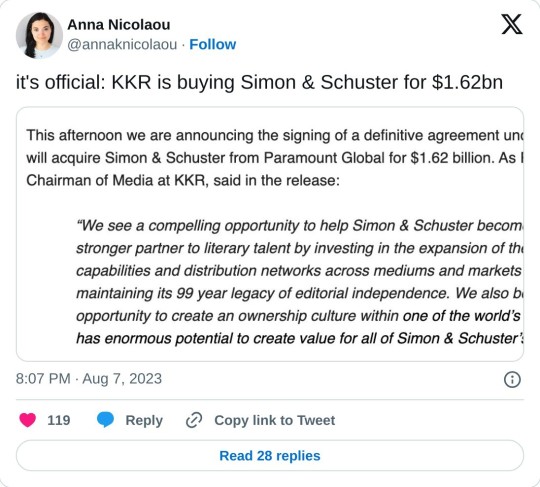
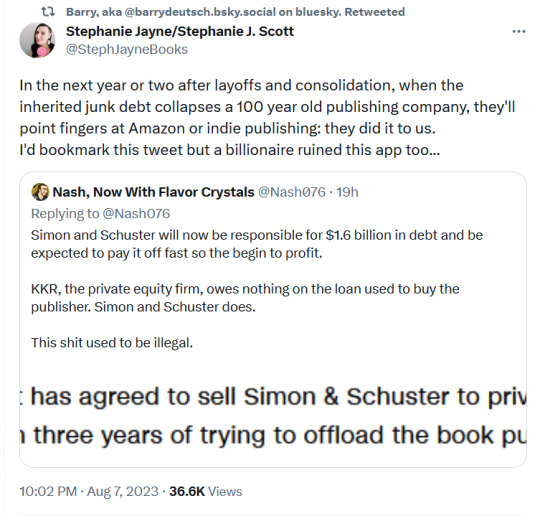

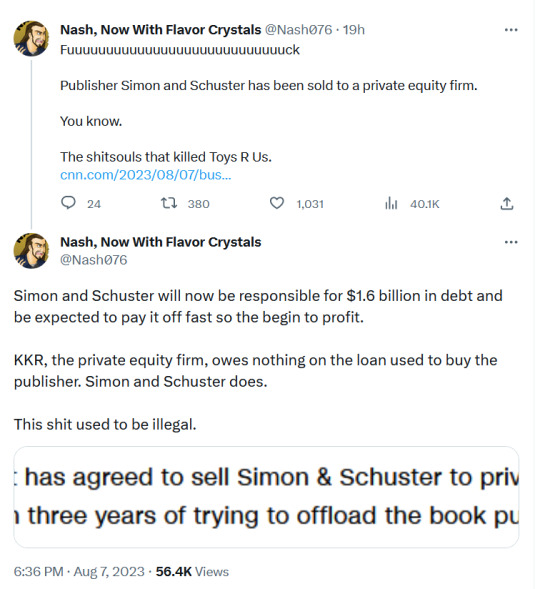
#twitter#tweet#tweets#publishing#vulture capitalism#capitalism is a scam#simon and schuster#books and authors#books and writing#books and reading#books and libraries#books and literature#toys r us#private equity
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Prison-tech is a scam - and a harbinger of your future

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/14/minnesota-nice/#shitty-technology-adoption-curve

Here's how the shitty technology adoption curve works: when you want to roll out a new, abusive technology, look for a group of vulnerable people whose complaints are roundly ignored and subject them to your bad idea. Sand the rough edges off on their bodies and lives. Normalize the technological abuse you seek to inflict.
Next: work your way up the privilege gradient. Maybe you start with prisoners, then work your way up to asylum seekers, parolees and mental patients. Then try it on kids and gig workers. Now, college students and blue collar workers. Climb that curve, bit by bit, until you've reached its apex and everyone is living with your shitty technology:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/02/24/gwb-rumsfeld-monsters/#bossware
Prisoners, asylum seekers, drug addicts and other marginalized people are the involuntary early adopters of every form of disciplinary technology. They are the leading indicators of the ways that technology will be ruining your life in the future. They are the harbingers of all our technological doom.
Which brings me to Minnesota.
Minnesota is one of the first states make prison phone-calls free. This is a big deal, because prison phone-calls are a big business. Prisoners are literally a captive audience, and the telecommunications sector is populated by sociopaths, bred and trained to spot and exploit abusive monopoly opportunities. As states across America locked up more and more people for longer and longer terms, the cost of operating prisons skyrocketed, even as states slashed taxes on the rich and turned a blind eye to tax evasion.
This presented telco predators with an unbeatable opportunity: they approached state prison operators and offered them a bargain: "Let us take over the telephone service to your carceral facility and we will levy eye-watering per-minute charges on the most desperate people in the world. Their families – struggling with one breadwinner behind bars – will find the money to pay this ransom, and we'll split the profits with you, the cash-strapped, incarceration-happy state government."
This was the opening salvo, and it turned into a fantastic little money-spinner. Prison telco companies and state prison operators were the public-private partnership from hell. Prison-tech companies openly funneled money to state coffers in the form of kickbacks, even as they secretly bribed prison officials to let them gouge their inmates and inmates' families:
https://www.motherjones.com/politics/2019/02/mississippi-corrections-corruption-bribery-private-prison-hustle/
As digital technology got cheaper and prison-tech companies got greedier, the low end of the shitty tech adoption curve got a lot more crowded. Prison-tech companies started handing out "free" cheap Android tablets to prisoners, laying the groundwork for the next phase of the scam. Once prisoners had tablets, prisons could get rid of phones altogether and charge prisoners – and their families – even higher rates to place calls right to the prisoner's cell.
Then, prisons could end in-person visits and replace them with sub-skype, postage-stamp-sized videoconferencing, at rates even higher than the voice-call rates. Combine that with a ban on mailing letters to and from prisoners – replaced with a service that charged even higher rates to scan mail sent to prisoners, and then charged prisoners to download the scans – and prison-tech companies could claim to be at the vanguard of prison safety, ending the smuggling of dope-impregnated letters and other contraband into the prison system.
Prison-tech invented some wild shit, like the "digital stamp," a mainstay of industry giant Jpay, which requires prisoners to pay for "stamps" to send or receive a "page" of email. If you're keeping score, you've realized that this is a system where prisoners and their families have to pay for calls, "in-person" visits, handwritten letters, and email.
It goes on: prisons shuttered their libraries and replaced them with ebook stores that charged 2-4 times the prices you'd pay for books on the outside. Prisoners were sold digital music at 200-300% markups relative to, say, iTunes.
Remember, these are prisoners: locked up for years or decades, decades during which their families scraped by with a breadwinner behind bars. Prisoners can earn money, sure – as much as $0.89/hour, doing forced labor for companies that contract with prisons for their workforce:
https://www.prisonpolicy.org/blog/2017/04/10/wages/
Of course, there's the odd chance for prisoners to make really big bucks – $2-5/day. All they have to do is "volunteer" to fight raging wildfires:
https://www.hcn.org/articles/climate-desk-wildfire-california-incarcerated-firefighters-face-dangerous-work-low-pay-and-covid19/
So those $3 digital music tracks are being bought by people earning as little as $0.10/hour. Which makes it especially galling when prisons change prison-tech suppliers, whereupon all that digital music is deleted, wiping prisoners' media collection out – forever (literally, for prisoners serving life terms):
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2018/08/captive-audience-how-floridas-prisons-and-drm-made-113m-worth-prisoners-music
Let's recap: America goes on a prison rampage, locking up ever-larger numbers of people for ever-longer sentences. Once inside, prisoners had their access to friends and family rationed, along with access to books, music, education and communities outside. This is very bad for prisoners – strong ties to people outside is closely tied to successful reentry – but it's great for state budgets, and for wardens, thanks to kickbacks:
https://www.prisonpolicy.org/blog/2021/12/21/family_contact/
Back to Minnesota: when Minnesota became the fourth state in the USA where the state, not prisoners, would pay for prison calls, it seemed like they were finally breaking the vicious cycle in which every dollar ripped off of prisoners' family paid 40 cents to the state treasury:
https://www.kaaltv.com/news/no-cost-phone-calls-for-those-incarcerated-in-minnesota/
But – as Katya Schwenk writes for The Lever – what happened next is "a case study in how prison communication companies and their private equity owners have managed to preserve their symbiotic relationship with state corrections agencies despite reforms — at the major expense of incarcerated people and their families":
https://www.levernews.com/wall-streets-new-prison-scam/
Immediately after the state ended the ransoming of prisoners' phone calls, the private-equity backed prison-tech companies that had dug their mouth-parts into the state's prison jacked up the price of all their other digital services. For example, the price of a digital song in a Minnesota prison just jumped from $1.99 to $2.36 (for prisoners earning as little as $0.25/hour).
As Paul Wright from the Human Rights Defense Center told Schwenk, "The ideal world for the private equity owners of these companies is every prisoner has one of their tablets, and every one of those tablets is hooked up to the bank account of someone outside of prison that they can just drain."
The state's new prison-tech supplier promises to double the amount of kickbacks it pays the state each year, thanks to an aggressive expansion into games, money transfers, and other "services." The perverse incentive isn't hard to spot: the more these prison-tech companies charge, the more kickbacks they pay to the prisons.
The primary prison-tech company for Minnesota's prisons is Viapath (nee Global Tel Link), which pioneered price-gouging on in-prison phone calls. Viapath has spent the past two decades being bought and sold by different private equity firms: Goldman Sachs, Veritas Capital, and now the $46b/year American Securities.
Viapath competes with another private equity-backed prison-tech giant: Aventiv (Securus, Jpay), owned by Platinum Equity. Together, Viapath and Aventiv control 90% of the prison-tech market. These companies have a rap-sheet as long as your arm: bribing wardens, stealing from prisoners and their families, and recording prisoner-attorney calls. But these are the kinds of crimes the state punishes with fines and settlements – not by terminating its contracts with these predators.
These companies continue to flout the law. Minnesota's new free-calls system bans prison-tech companies from paying kickbacks to prisons and prison-officials for telcoms services, so the prison-tech companies have rebranded ebooks, music, and money-transfers as non-communications products, and the kickbacks are bigger than ever.
This is the bottom end of the shitty technology adoption curve. Long before Ubisoft started deleting games that you'd bought a "perpetual license" for, prisoners were having their media ganked by an uncaring corporation that knew it was untouchable:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VIqyvquTEVU
Revoking your media, charging by the byte for messaging, confiscating things in the name of security and then selling them back to you – these are all tactics that were developed in the prison system, refined, normalized, and then worked up the privilege gradient. Prisoners are living in your technology future. It's just not evenly distributed – yet.
As it happens, prison-tech is at the heart of my next novel, The Bezzle, which comes out on Feb 20. This is a followup to last year's bestselling Red Team Blues, which introduced the world to Marty Hench, a two-fisted, hard-bitten, high-tech forensic accountant who's spent 40 years busting Silicon Valley finance scams:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
In The Bezzle, we travel with Marty back to the mid 2000s (Hench is a kind of tech-scam Zelig and every book is a standalone tale of high-tech ripoffs from a different time and place). Marty's trying to help his old pal Scott Warms, a once-high-flying founder who's fallen prey to California's three-strikes law and is now facing decades in a state pen. As bad as things are, they get worse when the prison starts handing out "free" tablet and closing down the visitation room, the library, and the payphones.
This is an entry to the thing I love most about the Hench novels: the opportunity to turn all this dry, financial skullduggery into high-intensity, high-stakes technothriller plot. For me, Marty Hench is a tool for flensing the scam economy of all its layers of respectability bullshit and exposing the rot at the core.
It's not a coincidence that I've got a book coming out in a week that's about something that's in the news right now. I didn't "predict" this current turn – I observed it. The world comes at you fast and technology news flutters past before you can register it. Luckily, I have a method for capturing this stuff as it happens:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/05/09/the-memex-method/
Writing about tech issues that are long-simmering but still in the periphery is a technique I call "predicting the present." It's the technique I used when I wrote Little Brother, about out-of-control state surveillance of the internet. When Snowden revealed the extent of NSA spying in 2013, people acted as though I'd "predicted" the Snowden revelations:
https://www.wired.com/story/his-writing-radicalized-young-hackers-now-he-wants-to-redeem-them/
But Little Brother and Snowden's own heroic decision have a common origin: the brave whistleblower Mark Klein, who walked into EFF's offices in 2006 and revealed that he'd been ordered by his boss at AT&T to install a beam-splitter into the main fiber trunk so that the NSA could illegally wiretap the entire internet:
https://www.eff.org/document/public-unredacted-klein-declaration
Mark Klein inspired me to write Little Brother – but despite national press attention, the Klein revelations didn't put a stop to NSA spying. The NSA was still conducting its lawless surveillance campaign in 2013, when Snowden, disgusted with NSA leadership for lying to Congress under oath, decided to blow the whistle again:
https://apnews.com/article/business-33a88feb083ea35515de3c73e3d854ad
The assumption that let the NSA get away with mass surveillance was that it would only be weaponized against the people at the bottom of the shitty technology adoption curve: brown people, mostly in other countries. The Snowden revelations made it clear that these were just the beginning, and sure enough, more than a decade later, we have data-brokers sucking up billions in cop kickbacks to enable warrantless surveillance, while virtually following people to abortion clinics, churches, and protests. Mass surveillance is chugging its way up the shitty tech adoption curve with no sign of stopping.
Like Little Brother, The Bezzle is intended as a kind of virtual flythrough of what life is like further down on that curve – a way for readers who have too much agency to be in the crosshairs of a company like Viapath or Avently right now to wake up before that kind of technology comes for them, and to inspire them to take up the cause of the people further down the curve who are mired in it.
The Bezzle is an intense book, but it's also a very fun story – just like Little Brother. It's a book that lays bare the internal technical workings of so many scams, from multi-level marketing to real-estate investment trusts, from music royalty theft to prison-tech, in the course of an ice-cold revenge plot that keeps twisting to the very last page.
It'll drop in six days. I hope you'll check it out:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
#pluralistic#the bezzle#marty hench#books#prison-tech#scams#jpay#securus#minnesota#prisones#shitty technology adoption curve#drm#enshittification#kickbacks#corruption#private equity#viapath#global tel link#bribery#aventiv#disciplinary technology#fcc#predicting the present#carceral state
586 notes
·
View notes
Text



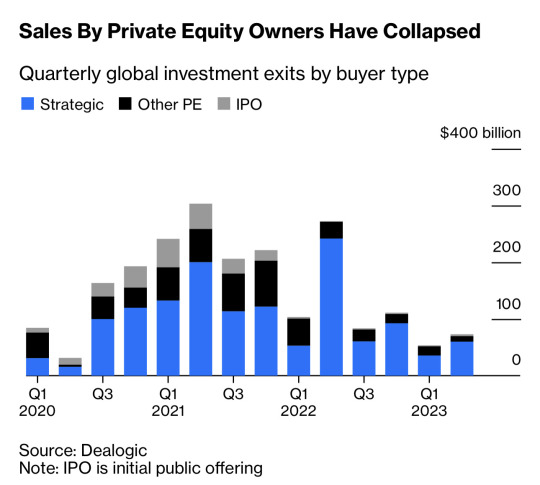
The Private Equity Machine Will Be Tough to Unjam
Tracks capital calls and distributions from and to investors in private equity funds, which I turned into a quarterly cash flow. It’s … not been good recently!
Deals have dried up, making investors reluctant to commit fresh capital.
https://www.bloomberg.com/opinion/articles/2023-07-04/the-private-equity-machine-will-be-tough-to-unjam #lbo #privateequity #investor
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The acquisition vastly increases the influence of financial interests over book publishing.
This worries me because it continues a trend that began years ago — elevating profits above the love of publishing books.
When I published my first book decades ago, the purpose of most publishing houses was to publish books. Publishers made money in order to publish books. They earned enough on their big bestsellers to take chances on unknown authors like me and put out books that delighted small numbers of enthusiastic readers but never showed a profit.
But in more recent years, the major purpose of most book publishers has switched from publishing books to making money.
9 notes
·
View notes
Link
Private equity has been rapidly growing its share of the housing market, taking advantage of a housing crisis and in some cases exacerbating it. But as large corporate landlords grow in power, tenants are increasingly rallying together and finding creative ways to hit them in their pockets.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
#andreazanon#confidente#confidence#climate change#renewable power#uae#pif#saudi arabia#Private equity
2 notes
·
View notes
