#70th Anniversary
Text


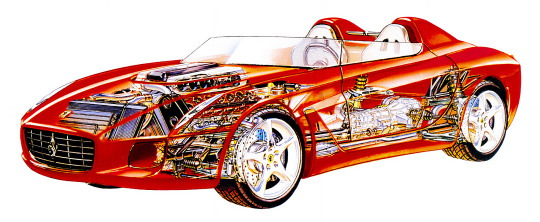


Ferrari Rossa Concept, 2000. Designed by Ken Okuyama while he was head of design at Pininfarina to celebrate the carrozzeria's 70th anniversary. The barchetta design study was based on a Ferrari 550 Maranello and remained a one-off
#Ferrari#Ferrari Rossa#Ken Okuyama#2000#Pininfarina#70th anniversary#concept#design study#prototype#barchetta#open roof#Ferrari 550 Maranello#transaxle#V12
195 notes
·
View notes
Text






2020- 70th Anniversary- Dan would finish the race in P14
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
No, because imagine this.
The 70th anniversary rolls around.
We get a Tales of the TARDIS season (series?) 2.
We get Christopher, David, Matt, Peter, and Jodie.
They get closure or 'therapy' or something.
#just imagine that#RTD gave Classic Who Doctors a remembered TARDIS#Doctors got reunited with companions#companions got reunited with companions#JUST IMAGINE#doctor who#matt smith#christopher eccleston#david tennant#peter capaldi#jodie whittaker#70th anniversary#alex kingston#karen gillan#arthur darvill#billie piper#jenna coleman#catherine tate#john barrowman#bill potts#yaz#ryan#graham#martha jones
44 notes
·
View notes
Photo
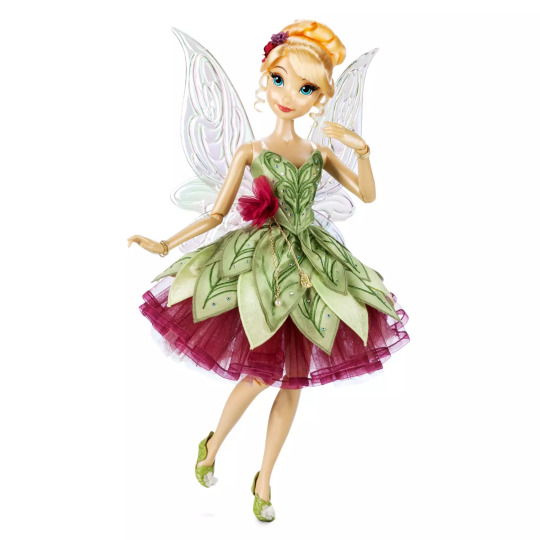

disney : 70th anniversary tinker bell
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
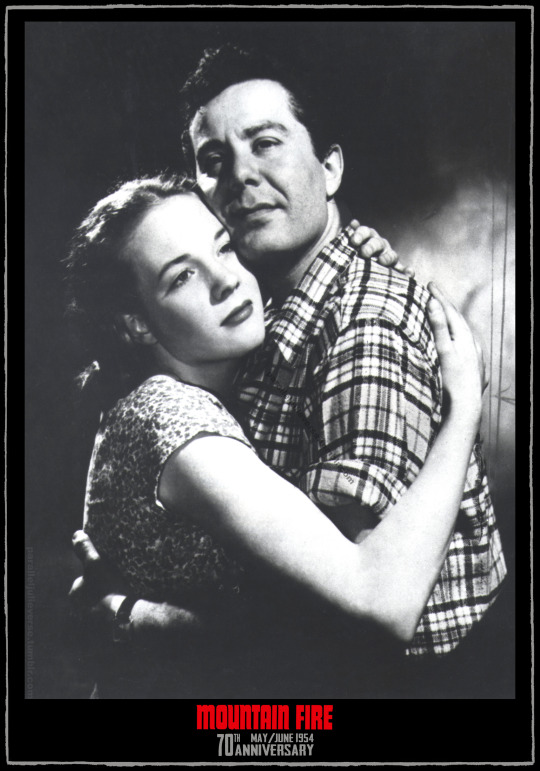
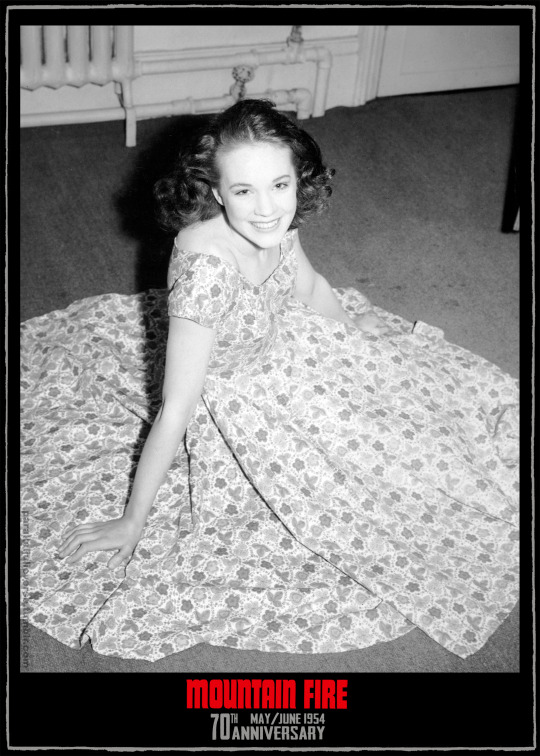
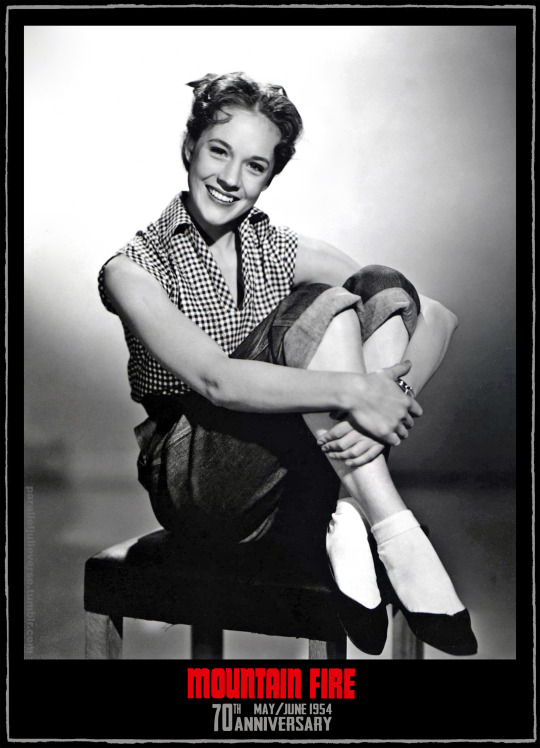











70th anniversary of Mountain Fire
Liverpool / Leeds / Bournemouth / Birmingham
30 performances
(18 May 1954 - 12 June 1954)
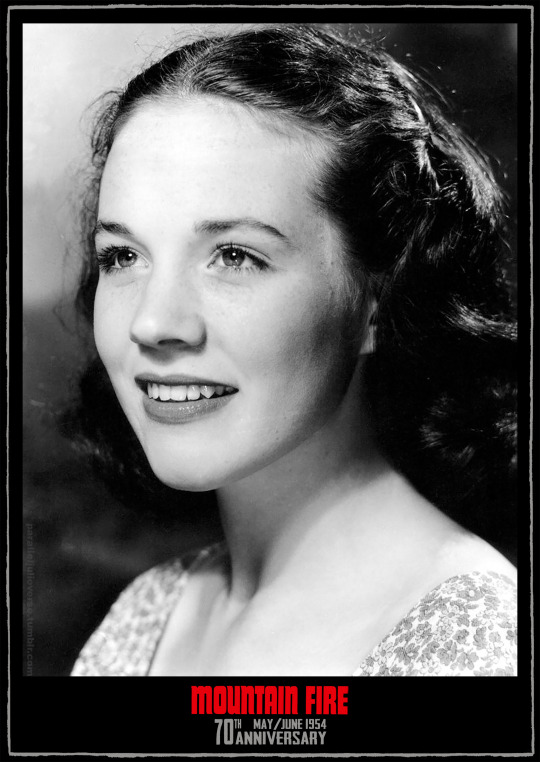
This month marks the 70th anniversary of a significant, if curious, milestone in the early career of Julie Andrews: her 'straight' theatrical debut in Richardson and Berney's Mountain Fire.
A notorious flop, Mountain Fire lasted barely 30 performances in a month-long provincial tryout, closing ahead of a planned West End bow. The play would likely have sunk without a trace were it not for the fact that its female lead was on the cusp of international stardom.
While the ill-fated Mountain Fire was on the road, it was formally announced that Julie Andrews had been signed to helm the Broadway cast of The Boy Friend (Chit Chat 1954, p. 8; Mackenzie 1954, p. 4). The stark contrast between the disastrous failure of Mountain Fire and the star-making success of The Boy Friend has become part of the mythology of Julie Andrews' career.
Even the Dame herself is fond of playing up the angle. "I had done one bomb in England," she recounts in a 1966 interview, "an incredible disaster...between Cinderella and The Boy Friend. I accepted a very limited engagement, thank God, and played a Southern belle from Tennessee...I can't tell you what went on. It was a disaster" (Newquist 1966, p. 141).
Four decades later in her 2008 memoirs, Julie was still cringing over the experience:
"The truth was, the play was not good, and although the company tried to make it work, we all sensed it was going to be a flop. I also knew beyond a shadow of a doubt that had the eminent London critic Kenneth Tynan seen my performance, it would have been the end of any career I hoped to have. Mercifully, Mountain Fire folded out of town" (Andrews 2008, 160).
Legitimate, at last!
Self-deprecatory humour aside, Julie actually received very good notices for her efforts in Mountain Fire. The Stage declared: "Julie Andrews scores a particularly fine dramatic success in her first serious portrayal, as the ill-starred Becky, bringing rare maturity to the difficult and exacting role" ('American folk play' 1954, p. 10). The Liverpool Echo similarly enthused: "Julie Andrews scores a personal triumph as the young girl and, in her first 'straight' role, reveals herself as accomplished an actress as she is a singer" (H.R.W. 1954, p. 5). While the Yorkshire Evening Post opined: "Julie Andrews gives a beautiful and moving performance as the luckless Becky" (Bradbury 1954, p. 8).
Though the production might not have panned out as anticipated, Mountain Fire was a strategic step in Julie's ongoing pivot from child stardom to adult performer. Much was made in show publicity about Julie’s "graduation" from juvenile entertainment to mature dramatic fare:
"Brilliant stage and film children are always a little heartbreaking. So few of them amount to anything after they have reached the colt stage...One of the most happy exceptions is Julie Andrews--the once plain little girl with buck teeth, a slight squint and pigtails who astonished us all by singing operatic numbers in a sweet, clear coloratura when she had reached the ripe age of 12...Now, Julie is to make her debut as a straight actress in a new American play to be presented here by Peter Cotes...called Mountain Fire...Cotes says: 'Julie has a wonderful role and I believe her to be a young actress with great possibilities.'...[A]s she has both singing and dancing to do in her first straight play, this might well be the chance of a lifetime for grown-up Miss Andrews" (Frank 1954, 6).
'A hill-billy Bible story'
Mountain Fire couldn't have represented a more "grown-up" change for Julie. Billed as a "new play with music in 14 scenes", it was the latest offering from rising American playwrights -- and cousins -- Howard Richardson and William Berney. The pair had scored an early success with Dark of the Moon (1945), a fantasy verse play about witchcraft, love, and social intolerance in colonial-era Appalachia. They followed with a second collaboration, Design for a Stained Glass Window (1949) about religious persecution and martyrdom (Duncan 1966, p. S-7; Fisher 2021, p. 248-49).
Mountain Fire trod similarly heavy dramatic ground with a mix of religion, Southern Gothic stylings, and social commentary. Described by one critic as "a hill-billy Bible story", the play was an allegorical retelling of the Abrahamic legend of Sodom and Gomorrah with the "cities of the plains" transposed to "rival colonies of mountain dwellers" in the backwoods of eastern Tennessee (Mackenzie 1954, p. 4).
The scriptural elements of human wickedness and divine retribution were adapted into a laundry-list of stock Southern vices: a Hatfield-McCoy style feud, moonshine, teen pregnancy, arson, murder and, even, a Ku-Klux-Klan lynching ('New American Musical' 1954, p. 12). Punctuating this cavalcade of backwoods iniquity was a series of Greek choric tableaux where Lucifer and the Archangel Gabriel, dressed in mountainfolk mufti, debate the spiritual problems of the characters on stage.
At the heart of this heady mix, Julie was cast in the "Lot's wife" role of Becky Dunbar, a winsome but headstrong teenage mountain girl described in the script as "grow'd up wild as onion weed" (Richardson and Berney, 1954, Act 1, Scene 2, n.p.). Becky finds herself pregnant after a brief dalliance with Joe Morgan, a charming but unscrupulous travelling salesman. She is torn between her passion for Joe and her moral duty to Lot Johnson, a virtuous widower who marries her because "it's the Christian thing to do" (Richardson and Berney, 1954, Act 1, Scene 5, n.p.).
Julie often jokes that "You've never heard a worse Southern accent than mine" (Newquist 1966, p. 141) -- and the script's hillbilly argot certainly would have proved a challenge to her crisp Home Counties consonants and rounded vowels. Becky's very first line, for example, is: "I ain't been gallivantin', just skimmin' rocks at Turkey Creek" (Richardson and Berney, 1954, Act 1, Scene 2, n.p.). Not exactly typical RP phraseology!
On a less challenging note, the show also featured a series of musical interludes with ritual dances and allegorical songs. Sporting titles like "Lullaby to an Unborn Child", "The World is Wide" and "Oh, It's Dark in the Grave", the musical numbers may not have been cheery toe-tapping ditties, but reviewers typically singled out Julie's singing as an all-too-rare highlight.
"Julie Andrews..prov[es] her undisputed musicianship by taking one song on high E flat, solus, and in perfect tune," marvelled one reviewer (Bradbury, 1954, p. 8). Another chimed: "We are inclined to think poorly of Becky until we realise how well she is to be played by Julie Andrews...Sodom and Gomorrah...seem to sweeten because of her presence... and she sings very pleasantly on the few occasions afforded to her" ('Midland entertainments,' 1954, p. 17).
Given the Biblical source material, the story of Mountain Fire could only end in grand tragedy. And, lo, by play's end the backcountry villages have been consumed by fire and our poor Julie is turned to salt. If naught else, the last scene of Mountain Fire certainly gave Julie a scenery-chewing finale for her straight dramatic debut:
LOT (Offstage): Remember the warning, Becky! Don't look back!
The hoot of the owl is heard.
BECKY starts up the hill. She stops, hesitates, almost looks back. Music builds. Again she goes forward, stops, almost looks back. Music continues to build. The third time she turns and does look back. Music crescendo. The lights dim, then rise again.
BECKY has become salt. She lies motionless reaching towards JOE.
Blackout
CURTAIN
(Richardson and Berney, 1954, Act 1, Scene 2, n.p.)
From Sodom, Tennessee to the Scepter'd Isle
The background saga of bringing Mountain Fire to the stage was almost as feverish as the storyline. The play began life in 1950 when Richardson and Berney completed their first working script under the original title of Sodom, Tennessee.
The play was initially optioned by Jack Segasture, a 23-year-old would-be Broadway producer who had managed Richardson and Berney's previous work, Design for a Stained Glass Window. That production proved a misfire, closing after just 8 performances, but Segasture was keen to back the playwrights for a second attempt at Broadway success (Watt, 1950, p. 47).
In the summer of 1950, Segasture mounted a series of workshops of Sodom, Tennessee at various regional Pennyslvania theatres (Talley 1950, p. VI-13). Reviewing one of these early work-in-progress performances, the critic for Variety ventured that "with some doctoring, [it] may have possibilities for Broadway, where it is headed" ('Review: Sodom Tennessee', 1950, p. 40).
In late-1950, Segasture announced that Sodom, Tennessee was set to start rehearsals the following January ahead of an anticipated New York opening in the spring ('Set Broadway", 1950, p. 26). Robert Perry was contracted to direct, with Robert Lowery and Jean Parker in discussions for the leads ('Film player,' 1951, p. 57). However, in April 1951, Segasture was suddenly drafted into the Army, and plans for the production were promptly scuttled ('Producer drafted,' 1951, p. 15C).
Over the next few years, various attempts were made to resurrect Sodom, Tennessee, but with little progress. In mid-1953, a lifeline came in the form of a pair of second generation producers: David Aldrich, son of famed producer, Richard Aldrich -- a.k.a. Mr Gertrude Lawrence to fans of STAR! -- and Anna Deere Wiman, daughter of Dwight Deere Wiman and heiress to the John Deere family fortune (Shanley, 1953, p. 10). Wiman had come into a sizeable inheritance on her father's death and she effectively bankrolled much of the production's initial $80,000 investment (Franklin, 1953, p. 9-E).
Wiman and Aldrich tapped Peter Cotes -- a British director who had scored a recent New York success with A Pin to See the Peepshow -- to take on directorial duties (Calta, 1953, p. 14). They also invited Pulitzer-prize winning composer, Lamar Stringfield, to write the musical score ('Stringfield asked,' 1953, p. 7). At one stage, the producers were allegedly in discussions with none other than Marilyn Monroe to make her Broadway debut in the role of Becky but, wisely perhaps, she declined (Winchell 1953, p. 19).
In early 1954, plans for Sodom, Tennessee underwent a dramatic change. For reasons unknown, Aldrich was suddenly out of the production team. In his place, director Peter Cotes was promoted to co-producer status with Wiman. Possibly because Cotes was British, it was decided to relocate the production across the Atlantic and launch the show in the UK ('News of the theater' 1954, p. 6).
Another factor was that production costs were lower in the UK than New York, something which would see the American Wiman remain as a London-based producer for several years (Hatwell 1957, p. 19; Wilson 1956, p. 10). Additionally, Richardson and Berney's earlier work, Dark of the Moon had enjoyed a fairly successful West End run in 1949, so the producers possibly reasoned that the new show might fare similarly well with English theatregoers (Darlington, 1949, p. 5).
Either way, Sodom, Tennessee was now set to make its world premiere in England -- though still with hopes of an eventual New York transfer ('Romantic comedy,' 1954, p. 17C).
'Not fit for the marquee of a British theatre'
Once the production team hit London, they set about preparing the play for its British bow. The first thing to go was the title.
Up until 1968, British censorship laws required all plays intended for public performance to be submitted to the Lord Chamberlain's Office for review and approval (Shellard et al, 2004). It seems the Lord Chamberlain did not approve of a play called Sodom, Tennessee, "an immoral name not fit for the marquee of a British theatre". Initially, the production team toyed with Brimstone as an alternative title, but finally settled on Mountain Fire (Talley, 1954, p. VI-5).
It was also decided that the show needed a musical overhaul. Some incidental music had been composed for earlier iterations, including piecemeal efforts by Lamar Stringfield. One or two of these pieces were retained but, for the most part, the producers opted for a new score. For this task, they contracted Stefan de Haan, a young German musician and composer who had come to study in the UK after the war and stayed on to work with various regional orchestras. De Haan not only composed a new score for Mountain Fire, including three new songs for Julie, but also signed on as music director and conductor (Bradbury 1954, p. 4).
Other key creative appointments were Michael Stringer as set designer and Daphne Kiernander as choreographer. Stringer came to the project fresh from working on the hit Rank comedy, Genevieve (1953), and a host of other film and theatre productions. He designed darkly stylised sets for all 14 scenes of the play, as well as orchestrating special effects for the final destruction sequence (Bishop 1954, p. 8). Kiernander was a classically trained ballerina who had performed as a principal in many West End shows and revues before shifting to choreography. For Mountain Fire, she created two set dances, broadly patterned on 18th century folk dances, and oversaw general staging for the songs ('Chit Chat', 1954, p. 8).
In early April 1954, Howard Richardson and William Berney arrived in London to help make revisions to the script. They also served as dialect coaches for the cast (Talley 1954, p. VI-5). During this early rehearsal period, Julie worked closely with Cotes' actress wife, Joan Miller who, as Julie relates, "tried to help me find the nuances that were needed for the part" (Andrews 2008, p. 171). Indeed, to hear Cotes tell the story, "Julie Andrews...was taught how to act by Joan Miller" and it was "Mountain Fire and Joan Miller between them [that] gave Julie the much needed groundwork..to erupt onto the Broadway stage" (Cotes 1993, p. 23). Not sure Moss Hart would agree, but anyway...
Later that month, Cotes and Miller hosted an official launch party for Mountain Fire at their South Kensington home with local theatre and high society luminaries in attendance (Candida, 1954, p. 2). The show's schedule was set with a month-long tryout starting on 17 May in Liverpool, followed by one week runs in Leeds, Bournemouth, and Birmingham. The show's London opening was scheduled for Wednesday, 16 June at the Strand Theatre, Aldwych.
In mid-April, the tour was formally announced with ticket sales opening immediately:
"On May 17 at the Royal Court, Liverpool, Peter Cotes and Anna Deere Wiman will present the world premiere of Mountain Fire by Howard Richardson and William Berney. Making her debut as a straight actress in this play will be 18-year-old Julie Andrews. Other leading roles will be played by Jerry Wayne, Andrew Cruickshank, Gillian Lynne and Charles Irwin. Music for this production has been composed by Stefan de Haan. Decor will be by Michael Stringer, and choreography Daphne Kiernander. Peter Cotes is directing, and following a short tour the play will be presented in the West End" ('Chit Chat: Mountain Fire' 1954, p. 8).
'Every night it was a new show...'
The function of an out-of-town tryout is to put the finishing touches on a show ahead of its official "big city" opening. Cast and crew get to see how the play is working with live audiences and revise things accordingly. In happy cases, the tryout is a relatively easy process of fine-tuning elements and smoothing out wrinkles.
In other cases though, the process can be far more tumultuous. Seth Rudetsky (2023) relates that New York theatre-folk popularly joke, "if Hitler were alive today, his punishment should be doing an out-of-town tryout with a show that's in trouble" (p. 152). Even Adolph might have blanched at the Mountain Fire tryout.
A sign of early trouble came days out from opening when the producers suddenly announced a 24-hour postponement of the Liverpool premiere from Tuesday 17 to Wednesday 18 May (H.W.R. 1954, p. 4). Rehearsals had revealed serious structural issues with the show and the production team needed every hour they could muster to hammer it into shape.
Worse still, the key creatives couldn't agree about the source of the problems and how to fix them. Director Cotes believed the biggest problem was the script and he wanted major rewrites. For their part, Richardson and Berney felt the musical sequences were at fault.
Jerry Wayne, who took the male lead of Joe Morgan, recalled:
"[W]e ran into trouble with the American authors. They objected to the musical numbers that had been written into their story. We opened at Liverpool on a Thursday night as a musical. Then we were told to cut out the musical numbers. On Friday night we opened at 7.30 as a straight play. With the music cut, the curtain ran down at 8.15" (Greig 1955, p. 9)
The songs were duly reinstated, but competing revisions were trialled to staging and orchestration. In her memoirs, Julie relates:
"Our director couldn't decide whether he wanted the orchestra in the pit or onstage, or no orchestra at all. This was a play, after all, so he then thought maybe one instrument, a guitar, would be enough. We tried the show a different way every night" (Andrews 2008, p. 160).
Another member of the cast, Neil McCallum, similarly recalled the snowballing desperation of the tryout tour:
"Everyone hoped it would get better, so the authors and the director got together and decided to revamp the whole show. They kept writing new scenes every day...every night it was a new show until not even the cast recognized it...Pretty soon the authors and the director weren't speaking. Two days later the authors and the backer weren't speaking. Finally, no one was speaking" (Tesky 1954, p. 6).
A comparison of scene synopses printed in programmes for Mountain Fire across its month-long tryout reveals the extent to which the production altered across performances. During its first night in Liverpool, the show was comprised of three acts and fourteen scenes. The following week in Leeds, it was still three acts but down to only ten scenes. In Bournemouth, it was back to three acts with fourteen scenes. By the time it got to Birmingham, the play was suddenly just two acts with thirteen scenes!
'Call down fire and brimstone...'
Given the panicked disorganisation that plagued the tryout, it should not surprise that reviewers took a rather dim view of Mountain Fire. Indeed, other than praise for Julie and fellow cast members, critics were mostly scathing in their assessment of the show -- with notices getting progressively more brutal as the tour continued:
The Liverpool Echo: "When the new play, Mountain Fire, opened with a dissertation by the Angel Gabriel and Lucifer on the delights of being good and bad, it was obvious that this world premiere at the Court Theatre last night would provide something unusual -- and so it proved. But whether this modern parable of Lot's wife will meet with general approval is problematical, because in attempting to lighten high drama with a smattering of musical numbers plus one or two dances, the American authors, Howard Richardson and William Berney, have achieved a curious hotch-potch which is neither one thing nor the other" (H.W.R. 1954, p. 5).
The Stage: "The Liverpool audience could be forgiven for their puzzlement over this provocative, somewhat bewildering, production, which rather inclines to fall between the two stools of allegorical drama and musical entertainment, lacking the virtue of anything in the way of a hit tune" ('American folk play' 1954, p. 10).
The Yorkshire Observer: "Symbolism on the stage is meat only for those who can stomach such food and, it is difficult to live on meat alone. So it might be that Mountain Fire which, in the second week of its production, is now at the Leeds Grand Theatre, might easily die as quickly as the symbolical fire it portrays, no matter how brilliant the cast" ('Symbolistic musical' 1954, p. 6).
Birmingham Daily Gazette: "Mountain Fire, a somewhat disastrous item which arrived at the Theatre Royal, Birmingham, last night, is an odd mix of sex and religiosity which, I fear, will prove seriously offensive to many...The whole thing is meant to be an allegory, with a deep application to our atom-bomb age. But it is all expressed in such appallingly banal language that it leaves one convinced that the underlying thought must be equally banal...One can only have sympathy for the very talented performers who struggle with this material" (Mackenzie 1954, p. 4).
Evening Despatch: "Howard Richardson and William Berney are evidently generous-minded men. In their play, Mountain Fire, at Birmingham Theatre Royal, they include murder, two burials, the Ku Klux Klan..., Lucifer, the Archangel Gabriel, religion and, of course, sex...Directed by Peter Cotes, this is a bewildering story of sin among the backwoodsmen of Tennessee...Somewhere in all this there may be a moral. At first I found it difficult to keep up. Eventually I gave up trying" (Holbrook 1954, p. 6).
The Birmingham Mail: "The conscientious critic of the drama will find that there are certain troublesome questions which are created in the mind by Mountain Fire, the new play by Howard Richardson and William Berney. How, for instance, did it come about that it reached the stage of the Theatre Royal at all and how is it that next week it is to occupy the stage of a West End theatre, however short its tenure there may be? What is more to the immediate point is how one ought...to deal by way of notice with so poor an offering. Ought one to call down fire and brimstone or, refusing to treat the piece seriously, as did many of the audience last night, rend it with ridicule?" (C.L.W 1954, p. 4).
'Mountain Collapses'
With this level of bad press, the prognosis for Mountain Fire was bleak. Ticket sales were sluggish and the cast often found themselves playing to half empty houses. Even worse, audience members were increasingly audible with their displeasure. As Neil McCallum relates:
"One of the lines at the last of the play is 'Lot, don't turn back.' Came a voice from the audience, 'I don't know about turning back -- I want my bloody money back.' In the interval, the ushers were mingling with the audience saying, in ringing tones, 'isn't it terrible...don't you wish you hadn't come?'" (Tesky 1954, p. 6).
By the final week in Birmingham, the writing was on the wall and producers decided to avoid what would surely have been a critical and commercial bloodbath in London. On Thursday 10 June, barely 5 days before the show was scheduled to open at the Strand, Wiman and Cotes issued a joint statement saying they were cancelling the West End premiere of Mountain Fire:
"In view of the inadequate public response during the tour of the play, it would be unfair to the authors and the actors and other members of the production that it should open in London, at least without substantial variations" ('Play is off', 1954, p. 3).
The decision to cancel a major production so close to its premiere was not without precedent, but it was sufficiently rare to garner widespread press attention, generating a slew of punning headlines. "London douses 'Mountain Fire'," trumpeted the New York Times (1854, p. 13). "Mountain Collapses" blared the Kensington News ('Theatre Notes' 1954, p. 2). And "Mountain Fire Out!" declared the Daily Post (Daily Post London Reporter 1954, p. 1)
Mountain Fire had two further performances to complete its Birmingham run, and once the curtain came down on Saturday night of 12 June, the production staggered to its sorry close. Richardson and Berney had already taken early departure back to the US, unable to watch the show's final demise. Cotes similarly retreated to London and refused for many years to even discuss the play.
Producer Anna Wiman insisted on staying to the very end. "No cast has been more loyal than this one," she declared, valiantly talking up a future for the show. "[I]t's not the end...I believe in this play and I am determined that it shall have a successful run in London. It will have a new director and a new atmosphere" (Mercury Staff Reporter 1954, p. 1.) The following March, a 'news in brief' snippet claimed Wiman was "still trying to lease or buy a theatre, with the Bill Berney-Howard Richardson play, Mountain Fire, as first on her production schedule" (Walker 1955, p. 61). But a year later, she would admit defeat, having lost the full extent of her £40,000 investment in the show (Wilson 1956, p. 10).
In the end, it wasn't just the UK production of Mountain Fire that sank. The play itself effectively vanished with little appreciable after-life. The script was never published, nor is there any record of it being registered with a theatrical licensing company. Only one further staging of the show ever seems to have taken place: a brief five performance run in May 1962, under the play's original title of Sodom, Tennessee, at the Little Theatre of the West Side YMCA in Manhattan ('Premiere,' 1962, p. 14). Billed as the show's "New York premiere", it didn't attract much attention and there are no published reviews. After that, the play's trail comes to a complete halt.
If it weren't for the show's status as a footnote to the career of Julie Andrews, Mountain Fire would likely have been completely lost to history. Even at the time of its cancellation, reports were already framing Mountain Fire as a blip on the way to Broadway success for Julie:
"Julie may have missed a West End appearance, but she is to be compensated by a Broadway lead in The Boy Friend when the show goes to New York in the autumn" ('Theatre Notes' 1954, p. 2).
Within a year or two, Julie's stardom was the principal frame of reference for any mention of Mountain Fire. It even became something of a boast for those behind the ill-fated production .
In 1956, when Julie was riding high on the success of My Fair Lady, an Alabama newspaper crowed that local playwright William Berney "discovered Julie Andrews [when] he was in London...casting his play Mountain Fire...Julie 'was it' so far as Berney was concerned, and a happy unknown made her bow" (Caldwell 1956, p. E-1). Not to be outdone, Howard Richardson was also soon talking up how his "plays have sent many actors and actresses on their way to fame including...Julie Andrews...who played one of her first roles in Richardson's Mountain Fire during its London [sic] run" ('New York playwright' 1959, p. 14).
All of which only proves the popular adage that, where failure is an orphan, success has many fathers!
____________________________
Who's Who of Mountain Fire
While Julie was undoubtedly the biggest star associated with Mountain Fire, the show included a roster of established and upcoming theatre talents, many of whom went on to bigger and better things:
Principals
Jerry Wayne as Joe Morgan (1919-1996): Born in Buffalo, New York in 1919, Wayne was a recording vocalist of some note who even hosted his own CBS radio show in the 1940s. He came to London in 1953 to play the lead role of Sky Masterson in the West End production of Guys and Dolls, marking the start of a British career. He appeared in the 1955 film musical, As Long as They're Happy and made several TV appearances in the 1960s. In 1967, Wayne married the novelist Doreen Juggler and graduated to a second career as a theatre and recording producer. Collaborating with his son Jeff, Wayne had notable success with the 1978 concept album, Jeff Wayne's Musical Version of The War of the Worlds. Wayne passed away in Hertfordshire in 1996 ( 'Jeff Wayne' 1996, p. 24).
Andrew Cruickshank as Lot Johnson (1908-1988): Born in Aberdeenshire, Cruickshank initially pursued civil engineering before turning to the stage. He made his professional debut in Shakespeare repertory and joined the Old Vic in 1937, playing notable roles such as Banquo in Macbeth, opposite Olivier. During WWII, he served in the Royal Welsh Fusiliers, earning an MBE. His varied career included significant roles in the West End production of Inherit the Wind (1960) and the National Theatre's Strife (1963). His best know role came courtesy of television as Dr. Cameron in the popular BBC series, Dr. Finlay's Casebook (1962-71). In later life, Cruickshank wrote a number of plays, and was president of the Edinburgh Fringe Society. He died in 1988 ('Andrew Cruickshank' 1988, p. 310).
Charles Irwin as Sheriff Bates (1908-1984): Born in 1908 in Leeds, Irwin began his career in variety shows and became a comedian and vocalist on radio in the 1930s. He worked extensively in regional theatre and appeared as a character actor in films such as The Third Man (1949), A Tale of Five Women (1951), and Mystery Junction (1951). In later decades, he transitioned to television, appearing in popular series like Danger Man (1960), International Detective (1961), and The Saint (1962). Irwin passed away in November 1984 in Salisbury.
Gillian Lynne as Edith Higgins (1926-2018): An influential figure in British theatre and dance, Lynne was born in 1926 in Bromley, Kent. She began her career as a ballerina, dancing with Sadler's Wells, the English National Opera, and the Royal Shakespeare Company. Lynne subsequently moved into choreography, working on many successful West End musicals. She was best known for her collaborations with Andrew Lloyd Webber, where her choreography was instrumental to the success of shows such as Cats and The Phantom of the Opera. In recognition of her contributions to dance and musical theatre, Lynne was made a Dame Commander in 2014. She passed away in 2018 at the age of 92 (Dex 2018, p. A13).
Richard Ainley as Gabriel (1910-1967): Ainley was born in Middlesex in 1910, the son of famed Shakespearean actor Henry Ainley. He debuted on stage with Martin Harvey's company, before going on to work with the Old Vic and Sadler's Wells. His first film role was in As You Like It (1936), followed by notable roles in The Tempest (1939) and Above Suspicion (1941). Severely wounded in WWII, Ainley had to abandon his film career and could only continue with occasional stage roles. Later, he focused on broadcasting and adjudication, briefly leading the Bristol Old Vic Theatre School in the early 1960s. He passed away in 1967 at age 56 (Coe 1967, p. 23).
John Barclay as Lucifer (1892-1978): Barclay was born in 1892 in Bletchingly, Surrey. A tall man with a booming basso baritone, he trained as an opera singer and toured widely with various companies, including D'Oyly Carte. He appeared in several films, including The Mikado (1939) and Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde (1941). In the late 1950s, Barclay moved to the US, where he pursued a late career playing strong and menacing character parts in film and TV. He passed away in 1978 at the age of 86.
Supporting Players
Molly Glessing as Miss Deedy Sparks (1910-1995): Midlands-born Glessing began her career in variety in the 1930s as a singer, dancer, and comedienne. She rose through the ranks to become a featured player in comedies and pantomimes. During the war, she gained popularity as a radio player and ENSA entertainer. After marrying a US serviceman, she relocated to California. Dividing her time between the US and the UK, Glessing continued to work in stage productions and amassed numerous character credits in films such as Charlie Chaplin's Limelight (1952), and TV shows, including The Quatermass Xperiment (1955) and Alfred Hitchcock Presents (1955-1962) ('Glessing" 1996, p. 33).
Lois McLean as Sadie Ollis (1927-2013): Canadian-born McLean studied drama at the University of Alberta and performed for several years with the Everyman Theatre Company in Vancouver. In 1950, she moved to the UK where she continued to perform, while studying theatre production with the Glasgow Citizen's theatre. In 1953, McLean started work as a manager for Peter Cotes and he cast her in various productions including Mountain Fire (Narraway 1954, p. 34). The pair also collaborated on a book, A Handbook of British Amateur Theatre. In the late-50s, she wed Indian-born lawyer, Birendra Jha and returned to Canada to start a family. McLean continued to perform and teach drama in Edmonton.
Esme Beringer as Old Sarah Johnson (1875-1972): Born in London to artist parents, Esme Beringer was a celebrated stage actress who made her professional debut in 1888. Known for her athletic physique and swordsmanship, she excelled in breeches roles, including playing Romeo, Little Lord Fauntleroy and The Prince and the Pauper. An enthusiastic fencer, she taught classes during WWI and starred in Shakespearean roles post-war. In later life, Beringer moved into character parts both on stage and in film. She died in 1972 at the grand age of 96 ('Esme Beringer' 1972, p. 16).
Neil McCallum as Skilly Sparks: (1929-1976) Born in Canada in 1929, McCallum moved to the UK to study at the Guildhall School of Music and Drama. Following graduation he appeared in a number of stage shows, scoring his greatest theatrical success in 1956 with the West End production of The Rainmaker opposite Sam Wanamaker. In the 1960s, McCallum became a familiar face on British television in series like The Saint (1963-64) and Department S (1969), as well as voicing characters on Thunderbirds Are Go (1966). Transitioning behind the scenes, McCallum became a scriptwriter and producer of some note, helming a number of TV series for the BBC before his untimely death from a cerebral hemorrhage in 1976, aged only 46 ('Neil McCallum', 1976, p. 11). As detailed by Julie in the first volume of her memoirs, she and McCallum embarked on a serious, if short-lived, romance during the production of Mountain Fire (Andrews, 2008, p. 161ff).
Jerry Stovin as Zeke Higgins (1922-2005): Born in Unity, Saskatchewan in 1922, Jerry Stovin served in the Canadian Army where he got the acting bug performing in military entertainments. Following the war, he went to Carnegie Tech to study drama, and moved to Britain in 1955. There he carved out a successful career in radio, television, and film, often playing American roles. He passed away in 1978 at the age of 86 (Peacock 1975, p. 7).
Harry Quashie as Ephraim (1914-1982): Born in Ghana, Quashie originally came to the UK to study law in 1939. He started to act in university theatricals and soon gave up his studies to pursue an acting career. He performed in a wide range of stage, radio and TV dramas and was a founding member of the Negro Theatre Company which helped pave the way for Black theatre artists in Britain. In the 50s, Quashie had character parts in several big screen features notably, Simba (1955), Safari (1956), and, The Passionate Summer (1958) ('Gave up law' 1947, p. 1; Bourne 2021).
John Sterland as Eb Higgins (1927-2017): Another Canadian actor, Sterland was born in Winnipeg to English parents. He came to the UK on a RADA scholarship, before joining the West of England Theatre Company. In a long career, Sterland racked up scores of stage and screen credits including A Countess from Hong Kong (1967), Performance (1970), Ragtime (1981), Bad Medicine (1985), Batman (1989), and The Tudors (2007). Married for many years to fellow actor, June Bailey, Sterland passed in 2017 ('John Sterland' 2017, p. 12).
Creatives
Howard Richardson (1917-1984): Born in Spartanburg, South Carolina, Richardson graduated from the University of North Carolina in 1938 and earned his M.A. in drama in 1940. After serving in the Army, Richardson co-wrote Dark of the Moon with cousin and frequent collaborator, William Berney. The play opened on Broadway in 1945, running for 318 performances. Despite frequent efforts, both in collaboration with Berney and as an individual playwright, Richardson would never match this initial success. In 1960, he earned a doctorate in 1960 and embarked on a career as a drama professor, working at various colleges throughout the US. He passed away in 1984 ('Howard Richardson', 1985, p. 34).
William Berney (1920-1961): Born in Birmingham, Alabama, Berney graduated from the University of Alabama, where he was active in drama. He later attended graduate school at the University of Iowa, where he started writing plays with Richardson. After graduation, Berney worked in advertising in New York, while pursuing his scriptwriting career on the side. During this period, he co-wrote several plays with Richardson, including Design for a Stained Glass Window (1950) and Protective Custody (1956). Berney moved to California around 1960 to write for television, but sadly passed away in Los Angeles in 1961 after a brief illness, aged 40 ('William Berney' 1961, p. 23) .
Peter Cotes (1912-1998): A theatrical polymath, Cotes -- who was born as Sydney Boulting in Maidenhead, Berkshire -- was part of a noted artistic family. His parents ran a theatre company and his brothers John and Roy Boulting became important filmmakers in British cinema. Initially an actor, Cotes shifted his focus to theatre production and directed the original production of The Mousetrap, the world's longest-running play. Other notable successes as director included the West End productions of The Children's Hour (1951) and A Pin to See the Peepshow (1952), and, in film, The Right Person (1955) and The Young and the Guilty (1958). In later years, Cotes wrote books and helmed a number of theatre companies. He passed away in 1998, at the age of 86 ('Peter Cotes' 1998, p. 35).
Anna Deere Wiman (1920-1963): Born in Illinois, Wiman was the daughter of successful theatre producer Dwight Deere Wiman, and heir to the John Deere family fortune. Educated by private tutors, she trained as a ballerina in Paris until a cycling accident ended her dance career. She then shifted to theatre management, initially working under her father. After his sudden death, she inherited a fortune, allowing her to become a self-funded theatre producer. Moving to London in 1954 with Mountain Fire, Wiman remained in the UK where she produced several West End productions, including The Reluctant Debutante (1955), Dear Delinquent (1957), and The Grass is Greener (1958). Despite her professional successes, Wiman struggled with alcoholism. She tragically died in 1963 at her holiday home in Bermuda from a fall down the stairs while under the influence. She was only 43 years old. ('Obituary: Anna Deere Wiman' 1963, p. 27.)
Stefan de Haan (1921-2010): Born in Darmstadt, Germany, de Haan was a gifted musician who trained in Berlin and Florence, before coming to the UK to study composition at the Royal College of Music. Following graduation, he initially gained prominence as a bassoonist, performing with various ensembles and orchestras. His compositional work includes a range of chamber music and orchestral pieces, often highlighting his expertise with woodwind and brass. His influence extended into music education, where his works are still performed and studied today. De Haan passed away in 2010, aged 89 (Bradbury 1954; 'Stefan de Haan' 2024).
Daphne Kiernander (1921-1998) Born in 1921, in East Preston, West Sussex, Kiernander was an accomplished dancer who rose to fame performing in various West End reviews and musicals such as Bobby Get Your Gun (1938), Let's Face It (1942), and Piccadilly Hayride (1946). She moved into choreography working on a number of stage and TV productions, including Such Is Life (1950) and Puzzle Corner (1953) for the BBC, and the Old Vic's 1955 production of The Taming of the Shrew. In the 1960s, Kiernander retired from dance to marry and start a new career in business and marketing (Powell 1962).
Michael Stringer (1924-2004) One of Britain's most successful film art directors, Stringer developed a passion for cinema early on. After serving as a RAF pilot in WWII, he trained with Norman Arnold at Rank Studios. There he scored notable success with one of his first independent assignments, Genevieve (1953), and followed it up with other popular Rank titles like An Alligator Named Daisy (1955) and Windom's Way (1957). His success in Britain led to international offers, working on big productions such as The Sundowners (1960), In Search of the Castaways (1962), and A Shot in the Dark (1964). Stringer went on to a distinguished Hollywood and UK career, bringing his talents to a long and diverse list of films, including Fiddler on the Roof (1971), which earned him an Oscar nomination, The Greek Tycoon (1978), The Awakening (1980), The Mirror Crack'd (1980), and The Jigsaw Man (1983). Stringer passed away in 2004. (Eyles 2004, p. 43).
Sources:
'American folk play: Mountain Fire bewilders.' The Stage. 20 May, p. 10.
'Andrew Cruickshank.' (1988). The Stage. 26 May, p. 10
Andrews, J. (2008). Home: A memoir of my early years. London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson.
Bishoff, T. (1963). 'Playwright Richardson turns professor.' The Eugene Register-Guard. 6 October, p. 2E.
Bishop, G.W. (1954). 'Theatre Notes: an American play to start in London'. The Daily Telegraph & Morning Post. 3 May, p. 8.
Bourne, S. (2021). Deep are the roots: Trailblazers who changed Black British theatre. History Books.
Bradbury, E. (1954). 'Music Notes: Former YSO player as a theatre composer.' The Yorkshire Post and Leeds Mercury. 22 May, p. 4
Bradbury, E. (1954). 'Mountain Fire at the Grand Theatre.' Yorkshire Evening Post. 28 May, p. 8.
Caldwell, L.M. (1956). 'Julie Andrews: Birmingham man discovered "my fair lady".' The Birmingham News. 28 October, p. E-1.
Calta, L. (1953). ‘Cotes will direct “Sodom, Tennessee”: drama based on Biblical story to open on Broadway early in February -- 26 in cast.’ New York Times. 7 November, p. 14.
Candida. (1954). Theatre Notes: Peter Cotes and party. The Kensington News and West London Times. 23 April, p. 2.
'Chit Chat: Mountain Fire'. (1954). The Stage. 22 April, p. 8.
'Chit Chat'. (1954). The Stage. 20 May, p. 8.
C.L.W. (1954). 'Modern morality play.' The Birmingham Mail. 8 June, p. 4.
Coe, J. (1967). 'Obituary: Mr. Richard Ainley." Evening Post. 23 May, p. 23.
Cotes, P. (1993). Thinking aloud: Fragments of autobiography. Peter Owen Publishers.
Daily Post London Reporter. (1954). 'Mountain Fire out'. Liverpool Daily Post. 11 June, p. 1
Darlington, D.A. (1949). 'First Night: A triumph of production, play about witches.' Daily Telegraph. 10 March, p. 5.
Dex, R. (2018). 'Cats choreographer Gillian Lynne dies at 92.' Evening Standard. 2 July: p. A13.
'Drake in Village'. (1952). Daily News. 10 November, p. 17C.
Duncan, R. (1966). 'They know the old-time religion.' Independent Star-News. 20 February, p. S-7.
'Esme Beringer.' (1972). The Stage. 6 April, p. 16.
Eyles, A. (2004). 'Obituary: Michael Stringer.' The Independent. 2 April, p. 43.
'Film player gets lead with Parker.' 1951. Daily News. 14 February, p. 57.
Fisher, J. (2021). Historical dictionary of contemporary American theater. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
Frank, E. (1954). 'Julie Andrews graduates.' News Chronicle. 15 April, p. 6.
Franklin, R. (1953). 'On Broadway.' Miami Daily News. 19 July, p. 9-E.
'Gave up law for stage.' (1947). Evening Telegraph. 13 October, p. 1.
'Glessing, Molly". (1996). The Spotlight. January, p. 33.
Greig, R. (1955). 'Mr. Wayne will not rush this script.' Evening Standard. 22 June, p. 9.
Hatwell, D. (1957). 'Anna becomes a powerful force in British theatre.' Evening Post. 12 December, p. 19.
Holbrook, N. (1954). 'The devil gets good parts.' Evening Despatch. 8 June, p. 6.
'Howard Richardson is dead; co-author of "Dark of Moon".' (1985). The New York Times. 1 January, p. 34.
H.W.R. (1954). 'And on the stage.' The Liverpool Echo. 7 May, p. 4.
H.W.R. (1954). 'Mountain Fire: world premiere in Liverpool' The Liverpool Echo. 19 May, p. 5.
'Jeff Wayne'. (1996). The Stage. 26 September, p. 24.
'John Sterland.' (2017). Wandsworth Times. 30 December, p. 12.
'London Douses "Mountain Fire'". (1954). New York Times. 12 June, p. 13.
Mackenzie, K. (1954). 'Show News: She's on her way to Broadway.' Birmingham Daily Gazette. 4 June, p. 4.
Mackenzie, K. (1954). 'A hill-billy Bible story.' Birmingham Daily Gazette. 8 June, p. 4.
Mercury Staff Reporter. (1954). 'Miss Wiman admits a failure.' The Sunday Mercury. 13 June, p. 1.
'Midland entertainments: Mountain Fire.' (1954). Birmingham Daily Post, 8 June, p. 17.
Narraway, M. (1954). 'Actress is happy again.' The Vancouver Province. 27 March, p. 33.
'Neil McCallum.' (1976). The Stage and Television Today. 29 April, p. 11.
'New American musical at Theatre Royal.' (1954). The Birmingham Post. 4 June, p. 4.
Newquist, R. (1966). 'Julie Andrews: An overnight success -- after 22 years.' McCalls. March, pp. 83, 140-43.
'New York playwright visits town.' (1959). Johnson City Press-Chronicle. 15 July, p. B-4.
'News of the theater.' (1954). Brooklyn Eagle. 16 March, p. 6.
'Obituary: Anna Deere Wiman.' (1963). The Stage. 28 March, p. 27.
Peacock, B. (1975). 'Jerry Stovin is busy.' The Leader-Post. 18 July, p. 7.
'Peter Cotes, 86, producer and director of 'Mousetrap'." (1998). The New York Times. 18 November, p. 35.
'Play is off: inadequate support during tour.' (1954). Daily Mail. 11 June, p. 3.
Powell, E. (1962). 'She turns from show business to shops.' The Liverpool Echo and Evening Express. 30 March, p. 18.
'Premiere of "Sodom" Friday. (1962). New York Times. May 12, p. 14.
'Producer drafted, 2 plays in doubt.' (1951). Daily News. 28 March, p. 15C.
'Review: Sodom Tennessee, Guthsville, Pa. Aug. 29.' (1950). In Beckhard, R. & Effrat, J. (Eds). Blueprint for summer theatre: 1951 supplement. John Richard Press, pp. 40-41
Richardson, H. & Berney, W. (1954). Sodom, Tennessee: A play in three acts. British Library, Lord Chamberlain’s Collection of Plays 1954/37.
'Romantic comedy set for October.' (1954). Daily News. 12 March. p. 17C.
Rudetsky, S. (2023). Musical theatre for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
'Set Broadway showing of "Sodom, Tennessee".' The Chattanooga Times. 19 November, p. 26.
Shanley, J.P. (1953). 'New team follows in fathers' steps: David Aldrich, Anna Wiman to offer "Sodom, Tennessee" as first play in Fall.' New York Times. 3 July, p. 10.
Shellard, D., Nicholson, S., & Handley, M. (2004). The Lord Chamberlain regrets : a history of British theatre censorship. British Library.
'Stefan de Haan'. (2024). Musicalics: The classical composers database. [Website].
'Stringfield asked to pen music for "Sodom, Tennessee".' (1953). The Knoxville News-Sentinel. 4 June, p. 7.
'Symbolistic musical at Leeds Grand.' (1954). The Yorkshire Observer. 26 May, p. 6.
Talley, R. (1950). 'An imaginary Tennessee won is site for "wicked" new play.' The Commercial Appeal. 8 October, p. VI-13.
Talley, R. (1954). 'British actors must learn how Tennessee hillbilly talks.' The Commercial Appeal. 18 April, p. VI-5.
Testy, H. (1954). 'New twist to success story: Neil McCallum on ladder to acting career.' The Saskatoon Star-Phoenix. 11 August, pp. 3, 6.
'Theatre Notes: Mountain Collapses.' (1954). The Kensington News and West London Times. 18 June, p. 2.
Watt, D. (1950). 'Ailing Harrison can't stage play.' Daily News. 7 February, p. 47.
'William Berney, 40, Coast playwright.' (1961). The New York Times. 25 November, p. 23.
Wilson, C. (1956). 'Now Miss Wiman is on "The Ball"." Daily Mail. 20 April, p. 10.
Winchell, W. (1953). 'The Main Stem Lights: Marilyn rejects role.' The Pittsburg Sun-Telegraph. 8 December, p. 19.
©2024, Brett Farmer. All rights reserved.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you're a fan of Goldie, then this article is definitely worth the read. Someone I follow on Twitter retweeted it onto my TL earlier this morning and I couldn't not read it.
Happy 70th anniversary to "Back to the Klondike" and happy birthday—well, birth month— to Glittering Goldie O'Gilt! 💛
#my post#not my link#book riot#bookriot.com#duckverse#duck comics#carl barks#back to the klondike#don rosa#the life and times of scrooge mcduck#ducktales#ducktales 1987#ducktales 2017#ducktales reboot#goldie o'gilt#glittering goldie#70th anniversary
58 notes
·
View notes
Text

70th Anniversary Stingray C8
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy late birthday, April, May and June Duck!
Forgive me for this, considering that I was not present when it was certainly a famous jubilee. Yes, the 70th anniversary of the first appearance of Daisy's nieces, April, May and June Duck. Even though it has passed, I will definitely make a separate post about this.
They first appeared in the comic "Flip Decision" by Carl Barks and that comic was published on June 30, 1952. Although they got a minor role and were with Donald's nephews, Huey, Dewey and Louie, like Donald with Daisy Duck, will definitely have good roles after that. Just as Donald's nephews are members of the Junior Woodchucks, Daisy's nieces are members of the Chickadees as a girl scout group. They appeared a few times in the Barks comics and did not appear after that. However, they appeared again in the Italian comics and later in the Don Rosa comics. In 1998, April, May and June changed their appearance, especially the way they wore their hair, and became more individual than before. Yes in Dutch comics under a special edition called "Duckies". They appeared for the first time in animation in House of Mouse and in the episode "Ladies Night" where they play in a band, but unfortunately nothing more than that. They get a real role in The Legend of The Three Caballeros, where they are assistants to the Three Caballeros and the goddess Xandra and they really had a great role, even though they were similar, they had different personalities between them. All in all, they appeared a lot in many European and Brazilian comics and were both mischievous and very good to their Aunt Daisy, who, like Donald to his nephews, is also a good parent to his nieces. Yes, Daisy's nieces are Donald's nephews' girlfriends in some comics, and Donald's nephews' sisters in some comics, in the sense that Donald's nephews who have a mother Della is Daisy's brother's wife. There is certainly a lot to say about it, but this is enough. Even though it's been a long time, I certainly wish them a happy belated birthday and a happy 70th anniversary! And I hope Daisy's nieces make more appearances in both cartoons and comics. And now pictures of Daisy's nieces from the beginning to the present day.
Feel free to comment on this and tell me which of your three of Daisy’s nieces is your favorite and which version.
Feel free to like this and reblog this if you are a fan of Daisy’s nieces.
Happy birthday, April, May and June Duck!
P.S. I'm aware that in the Ducktales reboot, Webby is actually April, but I prefer that Webby and April are separate people, that is, separate ducks.
























#happy birthday#and sorry for late#70th anniversary#april may and june#april may and june duck#disney duck comics#duckverse#duck comics#ducktales#daisy duck#huey dewey and louie#donald duck#huey dewey and louie duck#the legend of the three caballeros#house of mouse#carl barks#dutch comics#duckies#other characters#disney comics#comics#disney ducks#disney duckverse#aunt and nieces#uncle and nephews#american comics#european comics#italian comics#brazilian comics#donald's nephews
28 notes
·
View notes
Photo
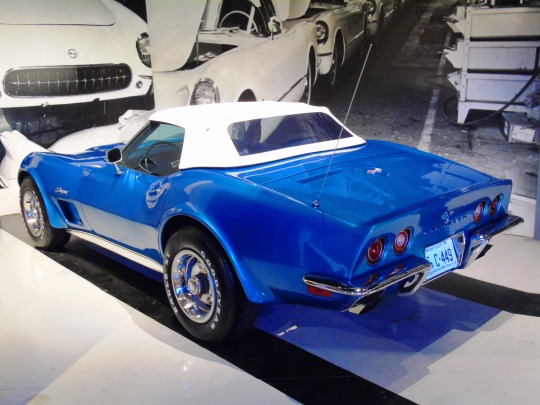
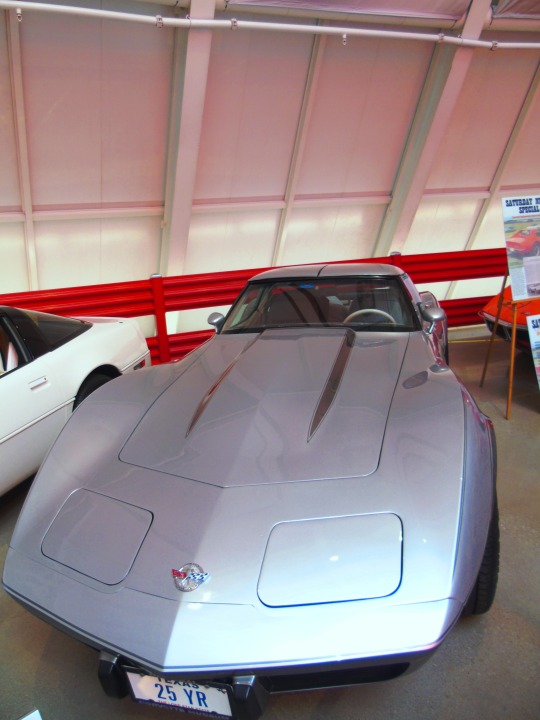
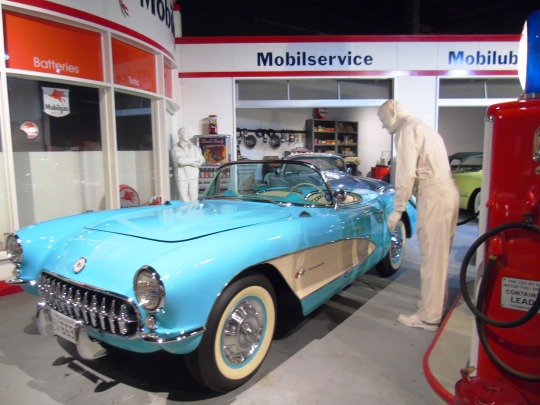
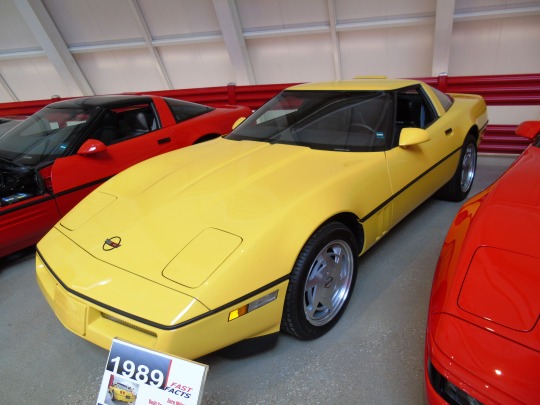
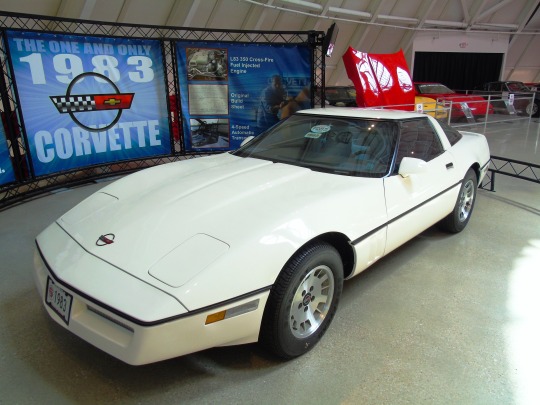
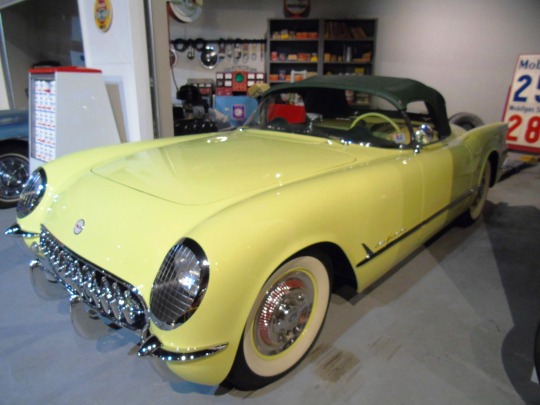










The first Chevrolet Corvette rolls off the assembly line in Flint on June 30, 1953.
National Corvette Day
An American icon in the world of automobiles, the Corvette represents freedom, speed and victory. Learn more about the history of this classic car and celebrate it on National Corvette Day!
History of National Corvette Day
Emerging as the unique sports car design in an otherwise rather boring line of vehicles for General Motor’s Chevrolet brand, the Corvette brought a new vibe in 1953. Premiering at New York City’s GM Motorama Show, the Corvette was a sports car that came off the Flint, Michigan assembly line a few months later–on June 30.
The original model of this car got off to a slow start – selling only 183 out of the original production of 300. But when the 1957 Corvette Super Sport was born, it quickly became legendary with its V-8 engine and up to 225 horsepower. Since that time, the Corvette has been a symbol of speed and sport for several generations.
The Corvette logo is two flags on crossed poles. One of the flags is checkered to symbolize the race, while the other is the American stars and stripes flag to symbolize the place of its production.
National Corvette Day is celebrated on June 30, giving a nod to the day the first Corvette rolled off the assembly line back in 1953. It was in June 2008, in honor of the 55th anniversary of this classic car, that the United States House of Representatives passed a resolution that the day would be known as National Corvette Day.
How to Celebrate National Corvette Day
For car lovers, National Corvette Day is a simple one to enjoy, complete with delightful activities such as:
Visit a Car Museum or Exhibit
Enjoy the fun of National Corvette Day by taking a look at some classic cars. Of course, the ideal place to visit on this day would be the National Corvette Museum located in Bowling Green, Kentucky. Established by a non-profit foundation in 1994, this museum exists to celebrate, preserve and educate about the past, present and future of the Corvette.
It’s also possible to become a member of the museum, joining almost 40,000 other Corvette enthusiasts from all over the world. Individuals, families, businesses and clubs can all join on different levels, whether annually or even for a lifetime. Members have access to free admission, magazine subscriptions and discounts as well as other fun benefits.
Enjoy a Local Celebration
Many Chevrolet and GM dealers in different locations will host open houses and events for community members to visit and look at different models of Corvettes that might be on sales floors. Or perhaps they will use the day to bring in some models that are normally in private collections.
Drive Your Corvette
Of course, the most obvious answer to celebrating the day for Corvette owners is to take a little spin. Convertible owners can even roll down that top and make the neighbors jealous. Or, even better, offer to take them for a short ride around the block and make it a time for everyone to get in on the celebration of National Corvette Day!
Source
#Chevrolet Corvette#National Corvette Museum#USA#travel#30 June 1953#70th anniversary#US history#Bowling Green#Kentucky#summer 2016#vacation#engineering#technology#car#tourist attraction#landmark#indoors#original photography#Chevy#Southeastern Region
3 notes
·
View notes
Text





What a difference 70 years makes juxtaposition of Bentley R-Type Continental, 1953 & Bentley Continental GT Azure, 2023. Bentley Motors has created a unique and one-off Continental GT, inspired by their retained example of the iconic R-Type Continental, JAS 949. The cars was delivered to its first owner, Dr Rowland Guenin of Switzerland, in December 1953. It was ordered in Ivory with a Red interior and a manual gearbox, a specification it retains today along with the original 4.6-litre engine. To recreate the closest specification for the modern interpretation of JAS 949, a new Continental GT V8 Azure has been hand painted in Old English White – a faithful re-creation of the heritage paint colour that dates back to the 1953

#Bentley#Bentley Continental#Bentley Continental GT Azure#Bentley R-Type Continental#1953#2023#70th anniversary#replica#Mulliner#coachbuilt#one-off#tribute car
289 notes
·
View notes
Text
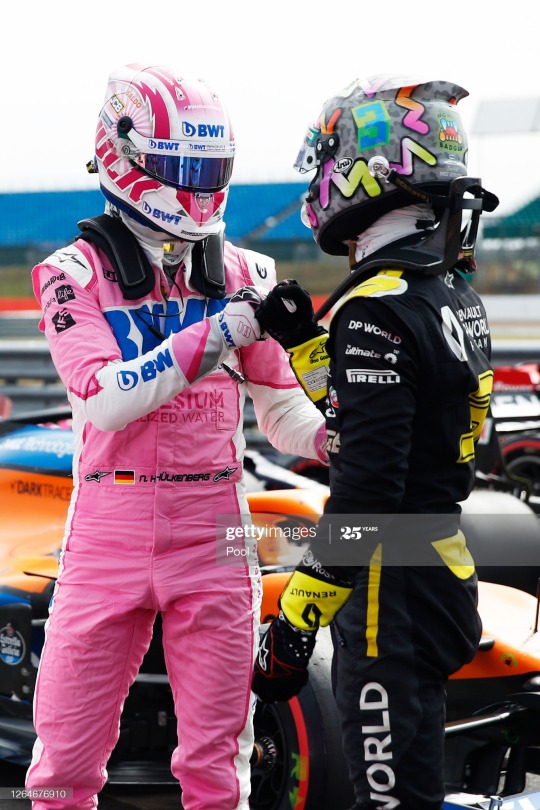








2020- 70th Anniversary- Congratulating Hulkie on his P3 in qualifying.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text










#adult collectors#adult collectibles#collectables#toys#vehicles#playsets#matchbox#mattel#working rigs#diecast#card art#70th anniversary#freightliner#garbage king xl#fedex truck#international workstar 7500 dump truck#firetruck
1 note
·
View note
Text
Godzilla 70th Anniversary #1
That def was a mixture of stories. I think I liked the first and last stories the best. They were all interesting at the first least. And some of the art was incredible. Yeah, it wasn't a bad read.
-Chuck
0 notes
Text

Celebrate the timeless charm of the 1950s with our vintage-inspired February 1954 birthday gift t-shirt for women and men. This stylish t-shirt features the bold text February 1954 in a retro font, showcasing the year of birth and adding a touch of nostalgia to any outfit. Made from high-quality, soft fabric, this t-shirt offers both comfort and style. Whether you're looking for a unique birthday gift or want to show off your own vintage vibes, this t-shirt is the perfect choice. Available in a range of sizes and colors, you can find the perfect fit and style to suit your taste. Embrace your love for the '50s and showcase your timeless style with our February 1954 birthday gift t-shirt.
#shirt design#personalized#funny shirt#70th birthday#70th#70th anniversary#born in 1954#gift ideas#gift for her#gift for him#gift for mom#gift for grandpa#gift for wife#gift for husband#gift for grandma#gift for dad#vintage design#retro design#retro shirt#vintage tshirt#february 1954#limited edition#better with time#aged to perfection
1 note
·
View note
Text
LEGO Celebrates Chevrolet Corvette C1 Model’s 70th Anniversary with New Kit - Tara Hurlin @Hemmings
The LEGO “Icons” line is welcoming a new addition, the 10321 Chevrolet Corvette C1 set. The toymaker recreated the iconic classic car in celebration of the model’s 70th anniversary.
Embracing the curves of the Corvette was likely tricky for the LEGO company seeing as how many of their creations are usually built from more boxy blocks, like the recently released Classic Land Rover Defender…

View On WordPress
#70th Anniversary#Corvette C1#Lego#LEGO Celebrates Chevrolet Corvette C1 Model’s 70th Anniversary#Model Kit#Tara Hurlin
0 notes
Text

August 1953 70 Years Of Being Awesome 70th Birthday Gift T-Shirt
Get your styles: https://www.teepublic.com/t-shirt/48526860-august-1953-70-years-of-being-awesome-70th-birthda
#August 1953 70 Years Of Being Awesome#august#august girl#august woman#august women#born in august#made in august#august birthday#1953 birthday#vintage 1953#retro 1953#birthday 1953#born in 1953#made in 1953#since 1953#1953 70 years of being awesome#70 years of being awesome#70th anniversary#70 years old#70th birthday#vintage#retro#tshirt#humor#birthday#bday#birthday women#birthday woman#birthday gift ideas#birthday gift for women
0 notes