#Computed tomography
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
YO NEW HELL ANT JUST DROPPED

IN THE SOUTHERN HEMISPHERE NO LESS
This is from a study just published a few days ago by Lepeco et al. (2025).
Hell ants (subfamily: Haidomyrmecinae) are super cool ants that possessed vertically closing jaws.
Below is a model of the ant's body/anatomy generated via micro-computed tomography

Vulcanidris cratensis is a new species discovered in Brazil. It dates back to the lower Cretaceous, and at the time of writing, is now the oldest known ant to science!

#hell ants#haidomyrmecinae#new study#science#insects#bugs#ants#myrmecology#entomology#ecology#fossils#paleo#tomography#computed tomography#cool science#science side of tumblr#sci comm#brazil#bugblr#bug#paleontology#paleoblr#paleobiology#paleoentomology
836 notes
·
View notes
Text

Researchers capture first laser-driven, high-resolution CT scans of dense objects
A research team led by Colorado State University has achieved a new milestone in 3D X-ray imaging technology. The scientists are the first to capture high-resolution CT scans of the interior of a large, dense object—a gas turbine blade—using a compact, laser-driven X-ray source. The findings, published in Optica, describe the science and engineering behind this new radiographic imaging capability and its potential benefits for a range of industries, from aerospace to additive manufacturing. The project is a years-long collaboration between researchers at CSU's Departments of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Physics and Los Alamos National Laboratory, with participation from AWE in the U.K. "This demonstration is just the beginning," said Reed Hollinger, an assistant professor at CSU and lead author of the study.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Materials Characterization#Computed tomography#X Rays#Colorado State University#Lasers#Optics
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
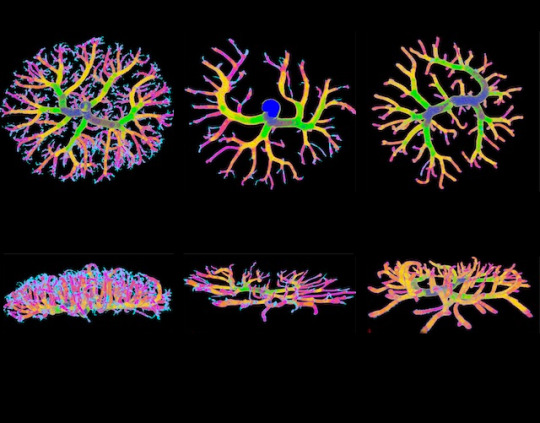
Mother’s Bugs
This study in mice demonstrates that the maternal microbiome promotes the growth of the placenta and its blood vessels. This image shows reconstructions made using micro-computed tomography of foetal-placental arteries
Read the published research paper here
Image from work by Geoffrey N. Pronovost and colleagues
Department of Integrative Biology and Physiology, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in Science Advances, October 2023
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#biology#computed tomography#microcomputed tomography#microbiome#placenta#pregnancy
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientists unveil genome-driven imaging for medical diagnosis

- By InnoNurse Staff -
Methods of imaging like computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) are crucial in diagnosing and pinpointing various illnesses. A recently devised approach allows PET to specifically leverage alterations in the human genome for diagnosis.
Read more at Universität Luzern/Medical Xpress
#imaging#genomics#dna#medtech#health tech#computed tomography#positron emission tomography#medical imaging#diagnostics
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm trying to get something funny out of the fact that I had to have a tomography taken from me.
So, my torax looked like an amongus.
Like, when the impostor gets them in the game and they get cartoonishly cut in half, that was my first thought when I saw the results. Just straight up played that amongus drip music in my head.
#tw medical#tw tomography#computed tomography#torax ct#actually disabled#physical disability#chronic illness#cripple punk#cripple posting
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
X-ray: Definition, History, Types, Uses, Safety & Future Explained
Discover everything about X-rays in this detailed encyclopedia guide. Learn their history, types, physics, applications in medicine and industry, safety, and future advancements in easy-to-understand language. X-ray: Definition, History, Types, Uses, Safety & Future Explained X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that has transformed medicine, science, and industry. Discovered over a…
#computed tomography#CT scan#dental x-ray#diagnostic x-rays#digital x-rays#electromagnetic radiation#fluoroscopy#future of x-rays#hard x-rays#history of x-rays#industrial x-ray#ionizing radiation#mammography#medical x-ray#non-destructive testing#portable x-ray#radiation exposure#soft x-rays#therapeutic x-rays#types of x-rays#what is an x-ray#wilhelm röntgen#x-ray#x-ray advancements#x-ray applications#x-ray encyclopedia#x-ray equipment#x-ray FAQ#x-ray imaging#x-ray machine
0 notes
Photo




(via Global Medical Imaging Market Size, Outlook 2024-2030) Global Medical Imaging Devices market is estimated at US$43.7 billion in 2024 and projected to post a CAGR of 5.7% between 2024 and 2030 to reach US$61 billion in 2030. The growth of the medical imaging market is driven by advancements in technology and the rising need for early diagnosis and effective management of chronic diseases.
#Medical Imaging Devices market#Medical Imaging Devices#Computed Tomography#CT Scan#Ultrasound Imaging#Magnetic Resonance Imaging#MRI#Positron Emission Tomography#Radiology Information System#Picture Archiving and Communications system#PACS#Nuclear Imaging
0 notes
Text
youtube
How fast does a CT scanner spin? Check out this CT scan machine spinning at max speed with no covers!
0 notes
Text

Scientists improve materials for reconstructive and plastic surgery
Researchers from IOCB Prague and their colleagues from Ghent University in Belgium have been working on improving the properties of gelatin-based materials, thereby expanding the possibilities of their use mainly in medicine. In a paper published in ACS Applied Engineering Materials, they have presented 3D-printable materials that can be easily monitored using an X-ray machine or through computed tomography (CT). Gelatin-based materials have been a hot topic of research in the last 10 years because they are straightforward to produce, non-toxic, inexpensive, biodegradable and—most importantly—because they promote cell growth. For this reason, they are pre-eminently used in plastic and reconstructive surgery. After a surgeon places an implant made of such material into a wound, the body gradually breaks it down and replaces it with tissue of its own. These substances thus accelerate wound healing and even enable the remolding of tissues, for example when performing breast reconstruction after mastectomy. In addition, the materials can be used for 3D printing implants tailored to individual patients.
Read more.
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Precision in Perspective: Discovering CT Scans at Alsafwa Radiology Center in Sharjah UAE
In the realm of medical imaging, computed tomography (CT) scans stand as a beacon of precision, offering invaluable insights into the human body with unparalleled detail and accuracy. At Alsafwa Radiology Center in Sharjah, UAE, CT scans are not just diagnostic tools but gateways to a deeper understanding of health and wellness.
Unraveling the Complexity of CT Scans

CT scans, also known as CAT scans or computed axial tomography, utilize advanced X-ray technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. These images provide physicians with a comprehensive view of internal organs, tissues, and structures, enabling them to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions with remarkable precision.
The Art of Interpretation
At Alsafwa Radiology Center, CT scans are performed with meticulous attention to detail and interpreted by experienced radiologists with a keen eye for anomalies and abnormalities. From identifying tumors and assessing organ function to detecting fractures and evaluating blood flow, our team is dedicated to uncovering the nuances hidden within each scan.
Advanced Technology for Superior Imaging
Precision begins with technology, and at Alsafwa Radiology Center, we spare no expense in equipping our facility with state-of-the-art CT scanners. These advanced machines boast cutting-edge features such as multi-slice capabilities, low-dose radiation options, and rapid image acquisition, ensuring optimal image quality and patient comfort.
A Commitment to Patient Care
While technology plays a crucial role, it is our commitment to patient care that truly sets us apart. From the moment you step through our doors, you'll be greeted by our friendly and compassionate staff who prioritize your comfort and well-being above all else. Our radiology team takes the time to explain the procedure, address any concerns you may have, and ensure that you feel supported throughout the entire process.
Personalized Approach to Diagnosis
No two patients are alike, and neither are their medical needs. That's why at Alsafwa Radiology Center, we take a personalized approach to diagnosis, tailoring each CT scan to meet the unique requirements of every individual. Whether you're undergoing routine screening, investigating a specific health issue, or monitoring a chronic condition, our team works closely with you and your healthcare provider to ensure that you receive the most accurate and comprehensive results possible.
Empowering Patients with Knowledge
Knowledge is power, and at Alsafwa Radiology Center, we believe in empowering our patients with the information they need to make informed decisions about their health. Following your CT scan, our radiologists will thoroughly review the results with you, explaining any findings and answering any questions you may have. We believe that by fostering open communication and patient engagement, we can help you take control of your health and well-being.
A Beacon of Excellence in Medical Imaging
In a world where precision is paramount, Alsafwa Radiology Center stands as a beacon of excellence in medical imaging. With our state-of-the-art technology, experienced radiologists, and unwavering commitment to patient care, we are proud to offer unparalleled CT scan services in Sharjah, UAE. Whether you're seeking answers to medical concerns, monitoring an existing condition, or simply prioritizing preventive care, you can trust Alsafwa Radiology Center to deliver precision in perspective, every step of the way.
0 notes
Text
With a new experimental technique, MIT engineers probe the mechanisms of landslides and earthquakes
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/with-a-new-experimental-technique-mit-engineers-probe-the-mechanisms-of-landslides-and-earthquakes/
With a new experimental technique, MIT engineers probe the mechanisms of landslides and earthquakes
Granular materials, those made up of individual pieces, whether grains of sand or coffee beans or pebbles, are the most abundant form of solid matter on Earth. The way these materials move and react to external forces can determine when landslides or earthquakes happen, as well as more mundane events such as how cereal gets clogged coming out of the box. Yet, analyzing the way these flow events take place and what determines their outcomes has been a real challenge, and most research has been confined to two-dimensional experiments that don’t reveal the full picture of how these materials behave.
Now, researchers at MIT have developed a method that allows for detailed 3D experiments that can reveal exactly how forces are transmitted through granular materials, and how the shapes of the grains can dramatically change the outcomes. The new work may lead to better ways of understanding how landslides are triggered, as well as how to control the flow of granular materials in industrial processes. The findings are described in the journal PNAS in a paper by MIT professor of civil and environmental engineering Ruben Juanes and Wei Li SM ’14, PhD ’19, who is now on the faculty at Stony Brook University.
A new technique allows full 3D visualization of the way forces are distributed in a mass of irregularly shaped grains as force is applied.
Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
From soil and sand to flour and sugar, granular materials are ubiquitous. “It’s an everyday item, it’s part of our infrastructure,” says Li. “When we do space exploration, our space vehicles land on granular material. And the failure of granular media can be catastrophic, such as landslides.”
“One major finding of this study is that we provide a microscopic explanation of why a pack of angular particles is stronger than a pack of spheres,” Li says.
Juanes adds, “It is always important, at a fundamental level to understand the overall response of the material. And I can see that moving forward, this can provide a new way to make predictions of when a material will fail.”
Scientific understanding of these materials really began a few decades ago, Juanes explains, with the invention of a way to model their behavior using two-dimensional discs representing how forces are transmitted through a collection of particles. While this provided important new insights, it also faced severe limitations.
In previous work, Li developed a way of making three-dimensional particles through a squeeze-molding technique that produces plastic particles that are free of residual stresses and can be made in virtually any irregular shape. Now, in this latest research, he and Juanes have applied this method to reveal the internal stresses in a granular material as loads are applied, in a fully three-dimensional system that much more accurately represents real-world granular materials.
These particles are photoelastic, Juanes explains, which means that when under stress, they modify any light passing through them according to the amount of stress. “So, if you shine polarized light through it and you stress the material, you can see where that stress change is taking place visually, in the form of a different color and different brightness in the material.”
Such materials have been used for a long time, Juanes says, but “one of the key things that had never been accomplished was the ability to image the stresses of these materials when they are immersed in a fluid, where the fluid can flow through the material itself.”
Being able to do so is important, he stresses, because “porous media of interest — biological porous media, industrial porous media, and geological porous media — they often contain fluid in their pore spaces, and that fluid will be hydraulically transported through those pore openings. And the two phenomena are coupled: how the stress is transmitted and what the pore fluid pressure is.”
The problem was, when using a collection of two-dimensional discs for an experiment, the discs would pack in such a way as to block the fluid completely. Only with a three-dimensional mass of grains would there always be pathways for the fluid to flow through, so that the stresses could be monitored while fluid was moving.
Using this method, they were able to show that “when you compress a granular material, that force is transmitted in the form of what we would call chains, or filaments, that this new technique is able to visualize and depict in three dimensions,” Juanes says.
To get that 3D view, they use a combination of the photoelasticity to illuminate the force chains, along with a method called computed tomography, similar to that used in medical CT scans, to reconstruct a full 3D image from a series of 2,400 flat images taken as the object rotates through 360 degrees.
Because the grains are immersed in a fluid that has exactly the same refractive index as the polyurethane grains themselves, the beads are invisible when light shines through their container if they are not under stress. Then, stress is applied, and when polarized light is shone through, that reveals the stresses as light and color, Juanes says. “What’s really remarkable and exciting is that we’re not imaging the porous medium. We’re imaging the forces that are transmitted through the porous medium. This opens up, I think, a new way to interrogate stress changes in granular materials.” He adds that “this has really been a dream of mine for many years,” and he says it was realized thanks to Li’s work on the project.
Using the method, they were able to demonstrate exactly how it is that irregular, angular grains produce a stronger, more stable material than spherical ones. While this was known empirically, the new technique makes it possible to demonstrate exactly why that is, based on the way the forces are distributed, and will make it possible in future work to study a wide variety of grain types to determine exactly what characteristics are most important in producing stable structures, such as the ballast of railroad beds or the riprap on breakwaters.
Because there has been no way to observe the 3D force chains in such materials, Juanes says, “right now it is very difficult to make predictions as to when a landslide will occur precisely, because we don’t know about the architecture of the force chains for different materials.”
It will take time to develop the method to be able to make such predictions, Li says, but that ultimately could be a significant contribution of this new technique. And many other applications of the method are also possible, even in areas as seemingly unrelated as how fish eggs respond as the fish carrying them moves through the water, or in helping to design new kinds of robotic grippers that can easily adapt to picking up objects of any shape.
The work was supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation.
#3d#3D image#3D visualization#Angular#applications#architecture#Behavior#box#challenge#change#Civil and environmental engineering#coffee#Color#compress#computed tomography#container#Design#dimensions#earth#Earthquakes#engineering#engineers#Environmental#Events#experimental#explanation#Faculty#fish#Fluid dynamics#form
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
youtube
Nyello! I'm B.L.Radley, also known as @blradley, also known as 'that person who decided to become a radiographer on a whim literally so they could introduce themselves as Rad the Rad but then got really fucking obsessed with radiography and ology and now wants to commit themselves to several more years of specialised study and student debts to become an Advanced Practitioner in.... MRI, probably, but who the heck knows'
Important info:
They/it/xe pronouns plz.
'Rad' on this blog refers ONLY to radiographers and surfer-slang. Transphobes begone.
I am a student.
This means:
I am not an expert! I might be wrong about stuff! If you know more than me, please feel free to correct me! I love this topic and want to learn more!
I am not qualified to give out medical advice, and will only say 'go see your doctor if this concerns you!' on this blog.
It's also worth noting that, though I do work part-time in a hospital, doin' the ol' radiography, I am not going to provide funny/embarrassing patient stories. Or any patient stories at all, beyond, perhaps, very, very anonymised anecdotes to help illustrate points. I strongly disagree with mocking patients or posting anything about them without their consent - particularly if it could be traced back to them! This is just a blog where I can scream excitedly about how cool it is that I can look at all the Mushy And Bony Stuff inside you without cutting you open!
(Although sometimes you'll get cut open too <3 Just for funsies <3)
Please feel free to ask me anything, and I will do my best to reply!
Or, uh. Infodump about my hyperfixation. Not sorry.
#radiography#radiology#medblr#studyblr#x ray#mri#ct#computed tomography#magnetic resonance imaging#cath lab funsies
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tomografías y coffe
0 notes
Text
Global Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Technological Advancements

The global Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 900.4 Mn in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 7.32% over the forecast period, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. Market Overview: Veterinary diagnostic imaging involves the use of various imaging modalities to diagnose diseases in animals. These imaging techniques include X-ray, ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, and others. These tools provide clear and detailed images of internal organs, bones, and tissues, enabling veterinarians to make accurate diagnoses and provide effective treatments. The use of veterinary diagnostic imaging has several advantages, including non-invasive procedures, early detection of diseases, and improved treatment planning. The growing need for accurate and timely diagnosis of animal diseases is driving the demand for veterinary diagnostic imaging products. Market Key Trends: One key trend in the global Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market is technological advancements in imaging modalities. With advancements in imaging technology, veterinary practitioners can now obtain higher resolution images in a shorter time. For example, the introduction of digital radiography allows veterinarians to capture high-quality images with reduced radiation exposure for animals. Furthermore, developments in ultrasound technology have resulted in portable devices with improved image quality and capabilities. These technological advancements are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of veterinary diagnostic imaging, leading to better clinical outcomes. PEST Analysis: Political: The veterinary diagnostic imaging market is influenced by government regulations related to animal healthcare and diagnostics. For instance, the FDA regulates the use of imaging modalities in veterinary medicine to ensure patient safety and effectiveness. Economic: The rising pet ownership and increasing expenditure on pet healthcare are driving the growth of the veterinary diagnostic imaging market. The strong economic growth in emerging markets is also contributing to market expansion. Social: The growing awareness about animal welfare and the rising demand for pet insurance are positively impacting the veterinary diagnostic imaging market. Moreover, the increasing prevalence of zoonotic diseases is driving the need for accurate and timely diagnosis in animals. Technological: Technological advancements in imaging modalities, such as digital radiography and ultrasound, are revolutionizing veterinary diagnostic imaging. These advancements are improving image quality, reducing radiation exposure, and increasing the speed of diagnosis. Key Takeaways: 1: The Global Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market Size is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.32% over the forecast period, due to increasing pet ownership and the rising demand for accurate and timely diagnosis in animals. Technological advancements in imaging modalities are also driving market growth. 2: North America is expected to dominate the Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market due to the high prevalence of pet ownership and well-established veterinary care infrastructure. Asia Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region, driven by increasing disposable income and growing awareness about animal health. 3: Key players operating in the global Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market include Esaote SPA, Epica Animal Health, IDEXX Laboratories, Carestream Health, IMV Imaging, Fujifilm Holdings Corp., Hallmarq Veterinary Imaging, and Canon Medical Systems Corporation. These players are focusing on product innovation and strategic collaborations to gain a competitive edge in the market.
#Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market#Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market Insights#Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market Forecast#Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market Values#Veterinary Diagnostic Imaging Market Trends#magnetic resonance imaging#computed tomography#ultrasound#medical conditions
0 notes
Text
Computed Tomography (CT) Market Forecast 2024 to 2032
Computed Tomography (CT), also known as computed axial tomography (CAT) scan, is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and advanced computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. CT scans provide comprehensive and detailed information about internal structures, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, injuries, and diseases. CT scans are widely used in clinical practice for their ability to provide clear and precise images of the body's anatomy.
The Computed Tomography (CT) Market was valued at USD 4,730.61Million in 2022 and is expected to register a CAGR of 3.49% by 2032.
The rising incidence of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and neurological disorders, has led to an increased demand for accurate and efficient diagnostic tools like CT scans to aid in early detection, treatment planning, and disease monitoring.
Get a free sample PDF Brochure By Types: Cardiovascular Oncology Neurovascular Abdomen & Pelvic Pulmonary Angiogram Spinal Musculoskeletal By Applications: Diagnostic centers Hospitals By Market Vendors: Siemens Healthineers GE Healthcare Philips Healthcare Toshiba Medical Systems Hitachi Medical Systems Neusoft Medical Systems Neurologica DxRay Samsung Medison MARS Bioimaging Koning Read More
0 notes