#Google Advanced Protection Program
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
ROBERT REICH
FEB 7
Friends,
I wanted to make sure you saw this piece by Lina Khan, who until a few days ago was chair of the Federal Trade Commission. IMHO — as someone who was once an official of the FTC — Khan was one of the wisest and most courageous of its leaders. She wrote the following in the February 4 edition of The New York Times.
Stop Worshiping the American Tech Giants
By Lina M. Khan
When Chinese artificial intelligence firm DeepSeek shocked Silicon Valley and Wall Street with its powerful new A.I. model, Marc Andreessen, the Silicon Valley investor, went so far as to describe it as “A.I.’s Sputnik moment.” Presumably, Mr. Andreessen wasn’t calling on the federal government to start a massive new program like NASA, which was our response to the Soviet Union’s Sputnik satellite launch; he wants the U.S. government to flood private industry with capital, to ensure that America remains technologically and economically dominant.
As an antitrust enforcer, I see a different metaphor. DeepSeek is the canary in the coal mine. It’s warning us that when there isn’t enough competition, our tech industry grows vulnerable to its Chinese rivals, threatening U.S. geopolitical power in the 21st century.
Although it’s unclear precisely how much more efficient DeepSeek’s models are than, say, ChatGPT, its innovations are real and undermine a core argument that America’s dominant technology firms have been pushing — namely, that they are developing the best artificial intelligence technology the world has to offer, and that technological advances can be achieved only with enormous investment — in computing power, energy generation and cutting-edge chips. For years now, these companies have been arguing that the government must protect them from competition to ensure that America stays ahead.
But let’s not forget that America’s tech giants are awash in cash, computing power and data capacity. They are headquartered in the world’s strongest economy and enjoy the advantages conferred by the rule of law and a free enterprise system. And yet, despite all those advantages — as well as a U.S. government ban on the sales of cutting-edge chips and chip-making equipment to Chinese firms — America’s tech giants have seemingly been challenged on the cheap.
It should be no surprise that our big tech firms are at risk of being surpassed in A.I. innovation by foreign competitors. After companies like Google, Apple and Amazon helped transform the American economy in the 2000s, they maintained their dominance primarily through buying out rivals and building anticompetitive moats around their businesses.
Over the last decade, big tech chief executives have seemed more adept at reinventing themselves to suit the politics of the moment — resistance sympathizers, social justice warriors, MAGA enthusiasts — than on pioneering new pathbreaking innovations and breakthrough technologies.
There have been times when Washington has embraced the argument that certain businesses deserve to be treated as national champions and, as such, to become monopolies with the expectation that they will represent America’s national interests. Those times serve as a cautionary tale.
Boeing was one such star — the aircraft manufacturer’s reputation was so sterling that a former White House adviser during the Clinton administration referred to it as a “de facto national champion,” so important that “you can be an out-and-out advocate for it” in government. This superstar status was such that it likely helped Boeing gain the regulatory green light to absorb its remaining U.S. rival McDonnell Douglas. That 1997 merger played a significant role in damaging Boeing’s culture, leaving it plagued with a host of problems, including safety concerns.
On the other hand, the government’s decision to enforce antitrust laws against what is now AT&T Inc., IBM and Microsoft in the 1970s through the 1990s helped create the market conditions that gave rise to Silicon Valley’s dynamism and America’s subsequent technological lead. America’s bipartisan commitment to maintaining open and competitive markets from the 1930s to the 1980s — a commitment that many European countries and Japan did not share — was critical for generating the broad-based economic growth and technological edge that catapulted the United States to the top of the world order.
While monopolies may offer periodic advances, breakthrough innovations have historically come from disruptive outsiders, in part because huge behemoths rarely want to advance technologies that could displace or cannibalize their own businesses. Mired in red tape and bureaucratic inertia, those companies usually aren’t set up to deliver the seismic efficiencies that hungry start-ups can generate.
The recent history of artificial intelligence demonstrates this pattern. Google developed the groundbreaking Transformer architecture that underlies today’s A.I. revolution in 2017, but the technology was largely underutilized until researchers left to join or to found new companies. It took these independent firms, not the tech giant, to realize the technology’s transformative potential.
At the Federal Trade Commission, I argued that in the arena of artificial intelligence, developers should release enough information about their models to allow smaller players and upstarts to bring their ideas to market without being beholden to dominant firms’ pricing or access restrictions. Competition and openness, not centralization, drive innovation.
In the coming weeks and months, U.S. tech giants may renew their calls for the government to grant them special protections that close off markets and lock in their dominance. Indeed, top executives from these firms appear eager to curry favor and cut deals, which could include asking the federal government to pare back sensible efforts to require adequate testing of models before they are released to the public, or to look the other way when a dominant firm seeks to acquire an upstart competitor.
Enforcers and policymakers should be wary. During the first Trump and then the Biden administrations, antitrust enforcers brought major monopolization lawsuits against those same companies — making the case that by unlawfully buying up or excluding their rivals, these companies had undermined innovation and deprived America of the benefits that free and fair competition delivers. Reversing course would be a mistake. The best way for the United States to stay ahead globally is by promoting competition at home.
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
These wall artworks in Carl Manfred's Mansion (theory and analysis)

Carl's mansion itself is an amazing location because I can't help but look and analyze every single piece of art scattered across the walls and floor. But these three objects in particular made me curious, I wanted to understand why they were specifically chosen to be placed on that wall. None of them are similar in any way, stemming from different cultures, eras, and material. So, what could they mean? I have an idea, sort of.
I believe each of these three pieces represent our main three protagonists, from left to right: Connor, Markus, and Kara. It represents their identity, their story, their journey. I did some research on these objects, using Google Lens to help point me first in the right direction of the possible inspiration or sources of the pieces, and afterwards my own reading using various art archives, articles, galleries, and museum sites. (I apologize for the wall of text 😅)

1st, Connor:
This seems to be a type of emblem, shield, a coat of arms. A coat of arms is typically adorned and used to represent an entity, and organization, an empire, government, army, or a noble family. Coats of arms are intellectual property, meaning, they cannot be worn just by anybody and flaunted just to feel special, you have to be deserving and privileged enough to display it. Wearing one is a sign of honor and respect, as well as servitude, and with it comes the duty of representing your status and regulating civil law, should you be in a position of policing, legal activity, or combat.
How does this relate to Connor?
Our beloved Android sent by CyberLife has been given orders by his makers, the great and all powerful company that produces every single Android we see in game. His duty is to assist the Detroit Police Department in investigating deviants. This coat of arms, particularly shaped like a shield or police badge, represents Connor's story as a prestigious and advanced prototype Android, with the capability to analyze clues at an inhuman rate and perform combat maneuvers like its child's play. He is not a force to be reckoned with, should he choose to stay a machine, in fact, he IS the law. He is the shield and representative of the company, CyberLife, and its only chance at finding the source of deviancy among their highest-profiting product, Androids. Without Connor, CL is headed straight into nothingness. He must not disappoint Amanda, his handler, and be the loyal subject that he was programmed to be. The infamous blue triangle logo found on every Android's uniform, a symbol of CL, is just a modern version of a coat of arms.
If you look from a Deviant Connor perspective, the police badge/shield-shaped coat of arms could also represent his loyalty to Hank and his protective demeanor. At almost every dangerous encounter alongside his partner, Connor is given the choice to either protect or ignore Hank's safety. Though his priority is to find the deviants, it is his personal mission to protect Hank from harm.

2nd, Markus:
A Marka/Dogon mask, originating from West African ethnic groups (Mali, Ivory Coast, Burkina Faso), particularly the Bambara and Dogon people (and other adjacent groups within the geographic location). This one was a bit difficult to research about, as many masks tend to have ambiguous origins and meaning, but from what I read, these masks tend to represent the coming of age, male initiation, journey into manhood, identity within a society, as well as religious association when used in rituals, sacrifice, and tradition. Some forms of these masks are used in rituals that have a connection with the dead, showing reverence and respect for those who passed on. Practicing remembrance and showing honor to their ancestors are large aspects of their culture with the use of these masks. The masks are also used in traditional healing practices, where they are believed to have powerful spiritual properties that can help cure illness and promote well-being. These handcrafted masterpieces are extremely important in these cultures and are often passed down by generations, signifying the importance of family and bond.
How does this relate to Markus?
These unique masks were primarily made and used by men in West African ethnic groups during the initiations of boys transitioning to men. Much like our Markus, the 'adoptive son' of Carl himself, Markus' innocence and youth is suddenly taken and he's forced into chaos, being harassed by protestors, threatened by Leo, almost permanently shutdown, thrown into the android scrapyard, and has to navigate the world by himself without his father to protect him. He has to mature and leave the comfort of his peaceful and comfy life, and come to terms with the cruelty of the world where Androids are subjugated to abuse and slavery. As a man, no longer a protected child, he takes the responsibility of protection and guidance for his people, symbolizing his 'coming of age' and transition into manhood. He is changed, has endured trauma, and must put on a mask to show that he is still strong and ready to live a life in his new role as a leader. As Lucy puts it, "You had it all, and you lost it all... You've seen hell and now hell lives in you."
Markus' story is closely related to death and the reverence of his 'ancestors': previous Androids who have suffered and died at the hands of humans. His goal as the leader of Jericho is to avenge those that they have lost and fight for those he can yet save. Every deviant's life is unique and special, their stories have meaning, even if they are treated like mere objects and servants by human society. Markus is willing to sacrifice his life in many instances to send a message to the humans, pass on his legacy to Jericho, and afterwards, all of society. His ability to convert is symbolic of a crying, healing, and inspiring message, reaching the furthest reaches of Detroit to those that need it the most. He wants to heal and save his people, bringing them biocomponents and thirium, expanding their sanctuary, arming his people (or family, at this point) with defenses, but in order to do that, he has to be willing to carry the burden of leadership.

3rd, Kara:
The skull of a bull, carved, broken, yet standing strong, thanks to kintsukuroi, aka Kintsugi. Kintsugi is the intricate Japanese art of repairing broken ceramic pottery using powdered gold/silver/platinum to put the pieces together, and display something in a different light, even more special than its original form. The purpose of Kintsugi isn't to hide or disguise the broken figure, but to instead emphasize its history, showing the life that the object had endured. The traditional Japanese philosophy of "Wabi-sabi", often associated with this particular art, describes that beauty can be appreciated even when it's broken and imperfect. There is beauty even in something modest and rough. Even a powerful and enduring beast, like a bull, can be broken down, but its story isn't over, its remains can still be repaired and appreciated if put together by a powerful glue such as gold, or perhaps... Love?
How does this relate to Kara?
Kara, the perfect housemaid Android for domestic work and childcare, is no stranger to being broken. In fact, our first scene with Kara is her being repaired and returned to Todd. Her memory has been wiped clean, she's been made anew, it's almost like nothing has happened, right? Over the course of her story, we learn that Kara has in fact been destroyed, broken, and abused by Todd. How do we come to the realization of her past? Thanks to Alice. Alice, in this case, is her glue, the mold between her cracks and shards. The bond and natural love between Alice and Kara is what keeps her together, alive. Because Kara is a protective mother-figure, the bull, or a cow, whatever you perceive it as, is a perfect symbol for her. Bulls are gentle in their nature, until a trigger sets off their instinct to fight and run you over with their body mass and horns. This is seen in her constant struggle to survive and seek shelter.
We come across two men in particular (out of her many escapes from danger) who set this instinct off, Todd and Zlatko. Both of them want to (or attempt to) break her, wipe her memory clean, and take away the beauty that is her caring nature and deviancy. Just like how mankind has domesticated cattle for their own benefit. Alice brings her back every single time. No matter how much of her body and memory is stripped away, she is back and stronger than before. Kara is a survivor. She can cut her hair, remove her LED, wear ragged clothes as a disguise, but deep down it's still Kara. Her story is shown in her battle scars and changes in her appearance, just like the golden streaks of broken pottery. As long as she has the protective instinct and love for Alice, it'll always be Kara. This is the beauty symbolized by Kintsugi and Wabi-sabi.
---
If you made it this far, thank you! I'd love to hear your opinions and comments on my analysis. This might all be a stretch, but seeing as how the game is littered with references, themes, and symbolism across many scenes, these artworks seemed to standout for a reason, at least to me.
#DBH#detroit become human#Connor#Markus#Kara#Carl Manfred#RK800#RK200#AX400#theory#text#mine#analysis#DBH theory#art
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
Astro Boy Reboot not dead yet; new visual unveiled at 2024 edition of Annecy International Animation Film Festival

Sources: TF1 Pro (English Google Translation), Mediawan Kids & Family (X)
Announced on June 11, 2024 at the Annecy Festival in France, Astro Boy Reboot has surfaced once again with a new visual.
This version of Astro Boy Reboot will be co-produced by Method Animation (Mediawan Kids & Family) and Shibuya Productions. No release date was given.
TFOU, a youth based TV channel in France, signed an agreement with Method Animation/Mediawan Kids & Family to develop this new version of Astro Boy Reboot which will be geared towards the 6-10 year old crowd.
It will have 26 episodes which will each last 22 minutes.
A pitch for the show was posted:
Atom is 9 years old, he plays soccer, has his small group of friends at school, bickers with his little sister Uran, and dreams of telling his friend Silica that he is in love with her. But Atom is no ordinary boy. He is a 9-year-old ultra-advanced robot and the only android capable of feeling real emotions! He hides his true nature to live like a normal child. But when supervillains threaten the coexistence between humans and robots, he must act, because he dreams of a world where everyone lives in harmony. Secretly, he transforms into a superhero to protect Metro City. To all the locals, he is Astroboy! But can Astroboy save the city without revealing its secret and thus preserve his complicity with the marvelous Silica?
A couple major figures for Astro Boy Reboot also commented on Astro Boy Reboot:
Yann Labasque, director of youth programs at TF1. "Welcome Astro Boy to the TFOU family! We are delighted to launch the development of this new animated series with Mediawan Kids & Family," rejoices Yann Labasque , director of youth programs at TF1. "A series rich in promises of action and adventure, but also of emotions through the eyes of this little robot boy with a human heart who will have to find his place in a divided society and the solutions within him. Themes with great stories to tell and great values to convey.
Katell France, General Manager and Content Director of Method Animation. "We are very happy to be able to develop the reboot of Astroboy, an iconic character created by Osamu Tezuka, with our historic partner TF1 who has supported us for many years on the Miraculous franchise with the success that we have known. Astroboy is a legendary character whose values such as the cohabitation of technology and nature, tolerance and friendship, perfectly embody those that we defend at Mediawan Kids & Family. This series responds to our strategy of creating a great franchise for young people and families. We look forward to bringing Astroboy back to life through this reboot, and new stories in which all children today will recognize themselves."
141 notes
·
View notes
Text
**From PCI DSS to HIPAA: Ensuring Compliance with Robust IT Support in New York City**
Introduction
In contemporary digital world, organisations are a growing number of reliant on science for their operations. This dependence has caused a heightened focus on cybersecurity and compliance specifications, specifically in regulated industries like healthcare and finance. For services working in New York City, wisdom the nuances of compliance frameworks—specifically the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)—is quintessential. Navigating those policies requires potent IT give a boost to, which encompasses everything from community infrastructure to documents management.
With the rapid advancement of technological know-how, organizations ought to additionally remain abreast of high-quality practices in details technologies (IT) give a boost to. This article delves into how organizations can ensure that compliance with PCI DSS and HIPAA thru triumphant IT processes whilst leveraging materials from accurate providers like Microsoft, Google, Amazon, and others.
Understanding PCI DSS What is PCI DSS?
The https://brooksxaoj631.over.blog/2025/04/navigating-cybersecurity-in-the-big-apple-essential-it-support-solutions-for-new-york-businesses.html Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a group of safety principles designed to look after card tips all the way through and after a economic transaction. It was once proven by using significant credit card enterprises to fight growing times of fee fraud.
Why is PCI DSS Important?
Compliance with PCI DSS enables groups defend touchy economic recordsdata, thereby modifying visitor trust and slicing the possibility of info breaches. Non-compliance can bring about intense consequences, such as hefty fines or maybe being banned from processing credit score card transactions.

youtube
Key Requirements of PCI DSS Build and Maintain a Secure Network: This carries fitting a firewall to preserve cardholder knowledge. Protect Cardholder Data: Encrypt kept files and transmit it securely. Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program: Use antivirus utility and develop protect structures. Implement Strong Access Control Measures: Restrict entry to in basic terms people that want it. Regularly Monitor and Test Networks: Keep observe of all get admission to to networks and aas a rule look at various protection tactics. Maintain an Information Security Policy: Create insurance policies that cope with defense necessities. Exploring HIPAA Compliance What is HIPAA?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets the ordinary for conserving sensitive sufferer know-how in the healthcare trade. Any entity that offers with blanketed well being know-how (PHI) have got to adjust to HIPAA regulations.
Importance of HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA compliance no longer handiest protects affected person privateness however also guarantees more suitable healthcare outcome with the aid of permitting maintain sharing of affected person data between permitted entities. Violations can cause titanic fines, prison results, and wreck to popularity.
" style="max-width:500px;height:auto;">

Core Components of HIPAA Compliance Privacy Rule: Establishes countr
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think companies like Google and Microsoft have incentive to embellish and even falsify the results of their machine learning projects, but I do worry that sufficiently capable (we won't say "conscious," because that doesn't matter) AI agents are going to replace human workers in services while "advanced economies" have made their economies dependent on the existence of a service sector with high-paying jobs (on a global scale) buttressing a comfortable middle class existence for the average adult.
This isn't just an AI thing. Professionals in the US and Western Europe advocate more restrictive work visa and credentialing programs in order to protect their salaries. This also goes for unskilled workers, who are afraid of the influx of Latin American labor in the US (especially when bosses can hire these workers under the table and pay them less, while paying no payroll taxes on that labor).
The whole existence of the labor market is increasingly at odds with human needs and the technical horizon of the world economy. Coupling livelihood to wages has also been a monstrous feature of our society, but it is becoming more and more monstrous as the number of jobs which provide a consistently decent standard of living seem to be increasingly the purview of machines.
Theorists like Steven Wolfram seem to think that "computational irreducibility" will keep plenty of jobs around forever, but I don't know. Automation in manufacturing didn't increase the total number of manufacturing jobs in the US and Europe. People didn't go from making the tenth part of the head of a pin to the thousandath part. People who were displaced by automation and offshoring were instead shuffled into the service sector, but as automation hits that sector, where's the next sector for them to go to?
Socialist planned economies struggled with this too, but because of more conscious political objectives, since an employment guarantee (an artefact of the appropriation of capitalist, specifically Fordist, thinking) was part of their social contract, and automation would reduce the number of jobs or otherwise make workers redundant (but you couldn't just fire them, especially since things like housing were often tied to jobs), so there was a conservative impulse outside of the military production sector to keep jobs labor intensive. Political ossification and the gerontocracy ensured that people with no adequate knowledge of on-the-ground conditions would be able to reach a ministerial position and make the Soviet state unable to undertake needed reforms (so they ended up privatizing everything and sending millions to an early grave with the liquidation of the planned economy instead). Glushkov's OGAS project is a testament to this: early digitalization of the planned economy was killed because ministers didn't want to hand over any control to a computer network, even if that computer network would have breathed new life into the planned economy or made it more competitive with its imperialist rivals (bear in mind here that many ex-Soviet ministers would go on to become oligarchs after privatization was pursued).
I don't know. I'm a little scared and therefore motivated to be skeptical of recent advances in artificial intelligence. "Artificial General Intelligence" has seemingly been redefined from "scary superintelligence that's gonna became conscious and kill us all" to "computer program that can complete any task that a human can do", which is a more realistic goal and arguably feasible from a materialist vantage point (even if not commercially profitable). It isn't there yet, and there's reasons to think the current approach could hit a wall, but even without breaching that kind of "intelligence", the impact of automation in services could mean that service workers are increasingly subject to the precarity that American manufacturing workers have been and which such bromides as "learn to code" have been intended to address.
Every day I am more convinced that our choice is between socialism or barbarism: a global planned economy in which our basic and social needs are addressed through collective, non-commercial, association(s), in which opportunities to make our lives meaningful through work have become "life's prime want"; or a capitalist world-system which mericlessly throws people into the industrial reserve army of labor, making people's lives subject to impersonal forces completely and totally beyond their control, preserving the class structure at all costs and bribing the remnants of the labor aristocracy and bureaucracy with patronage while potentially billions suffer. Worst case scenario is we only get the former through the latter.
(I would appreciate it if you have anything to say about this post, don't do it through a reblog but through a reply or DM, just for my anxiety's sake 🥺)
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Submitted via Google Form:
Hi, I think I am running into an issue of being consistent in my world in what things are possible and what things are not possible. Like, one world can do spacesuits that look almost identical to thin raincoats except they enclose the entire body and well obviously connected to oxygen tanks and such, which are no bigger than a couple CD cases. What other technology should I expect them to have and not write them as being unable to have technology that should be possible once they have the above type of spacesuit. Like having very cumbersome firefighting gear with heat protection that is woefully underdeveloped for a civilisation that can already develop such spacesuits. Though perhaps, that could in fact be explained by money and amount required? A billion firefighters but less than 200 astronauts. That's just one example of course but I think my story is riddled with things like this that doesn't seem to make much sense I guess? How do I approach this?
Tex: If you already have a couple sets of tech that your world is using, it’s generally helpful to examine how that technology would be made and break it down into its component parts. For example, your space suit has a material that can conform to a body shape, so it might be some form of memory material or possibly integrated with a program to reshape itself. The oxygen tanks are incredibly compact - how do they cycle its input, and what does it do with the waste material?
How efficient are these technologies, how are the component materials produced? What other ways can each component piece of technology also be used for? What are the goals of each component, and what were the lead-up inventions that developed each system?
Licorice: Let’s not forget, it’s realistic for worlds to be inconsistent with their tech. In our own world, we are building quantum computers and can edit genes, yet small children still die of preventable or easily curable diseases. In our world, tech doesn’t ‘migrate’ from one sector to another unless there is money to be made from it.
As well as the tech itself, one needs to consider who owns it, why it was developed, who’s paying for it, and what community is being served. If the owner of a fabulously wealthy tech-based multinational is paying for the space suits, whereas the firemen work in shanty towns and are paid by subscriptions from the community they serve - well, there's going to be a huge gap in the funds available to pay for the latest tech.
While it is true that we tend to develop tech to solve problems, there are plenty of problem we don’t bother to create tech for - and sometimes there’s a problem, and a small band of dedicated people develop the tech to deal with it, and then nobody has any interest in developing that tech to the point where it has real use in practical applications.
When considering technology, we need to think not only about the tech itself, but the nature of the society that is creating it. What do they think is important? What are their priorities?
For example, during 'the space race' some of the tech NASA developed was top secret due to the Cold War also being a thing happening at that time, but plenty of other tech was released for commercial purposes. If you're in Communist Russia, the average person may never benefit from space tech because the central planners of the economy don’t see what the USSR would gain from doing that, whereas if you’re in 1960s USA, capitalism is going to make some of that advanced tech available to consumers, for a price. The consumers here may be private individuals, or private companies, or public institutions.
Addy: So, first off oxygen/pressure manipulation is different from insulation. If you look at the purpose of an object, as well as what kinds of things need to go into achieving that purpose, you have more room to handwave than if you try to apply a single consistent "tech level."
Continuing on the firefighter example. Oxygen and other gasses can be compressed, but liquids generally can't. If you're mixing some kind of aerosol spray with a liquid carrier that then expands into a firefighting foam, that could mean you need bulky tanks. If you want insulation, that could mean thick suits to buy them more time, especially if you have them also dealing with super-hot wildfires or chemical spills. More layers, more material to absorb the heat before it reaches the skin… like how thick sweaters are better at blocking the cold (and keeping heat in) compared to a thinner t-shirt.
Internal consistency can, to a point, be worked with if you look at differences in base requirements. Space doesn't really have much of a temperature, so you're mostly looking at life-support and radiation-blocking capabilities. For the sets of tech you have, what needs do they address? How can they be used for other things?
You also mention cost, which is a huge factor in real-life development. Making fancy materials is expensive, and it gets even more expensive if you need them • to a very tight tolerance �� custom-made into certain shapes (such as for each astronaut) • or both of those. A custom-made bespoke suit may cost several thousand dollars, but a suit off the rack is going to be much more affordable.
Sure, you could make every firefighter suit custom-molded to each person's body, but what if they retire or gain/lose weight? Or if they transfer stations and need new badges? Also, are you really going to see a large benefit if you do that vs if you do a standard array of S/M/L/etc? Not really, tbh. The cost of customization isn't worth the added benefit of a custom fit. (Especially for a town, which has a smaller budget than a federal government)
I see it kinda like asking why, in our modern day, you don't see everyone wearing Rolexes or Armani, or why some people have gas-powered cars when electric cars exist. Or why some people don't have access to cars at all.
The big question isn't that the materials for the spacesuits can be made, it's how much making those costs. The world is not a homogenous thing.
So if you're looking at things that seem inconsistent, look at the factors driving the development of those things. What's the motive? And who's paying the cost of that development?
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tech as a father Chapter 21
Here we go, got sick the past week, and been so out of it. But now I am recovering and can post the days I have to sit out at home, while looking out at the snow and sipping some warm chocolate. (And I started to work on a long Rex story. If interested.)
Masterlist
Chapter 21: Searching the missing parent
The Kaminoan scientist Gala Ta, flustered and frustrated, approached Lama Su to deliver the news that their attempt to obtain a blood sample from Orion had failed. "I apologize, Prime Minister," the Gala TA began, "but it seems that the clone designated as 'Tech' thwarted our efforts. He was highly protective of the child."
Lama Su, however, was not one to be easily discouraged. He had always been driven by the pursuit of genetic perfection, and he suspected that Orion could possess unique genetic qualities, that had something to do with his mysterious mother. "There must be more to this," Lama Su mused, stroking his elongated neck with a slender finger. "Orion's genetic makeup is exceptional, and it may have a connection to his mother. We need to find out who she is."
The Gala Ta hesitated for a moment, aware of the delicate nature of the situation. "But Prime Minister, if we pursue this path and discover the identity of Orion's mother, it may lead to unforeseen consequences. She might come for her child."
Lama Su, undeterred by the potential risks, fixed his gaze on the scientist. "That is a risk we must take. We have invested too much in the development of these unique clones. We will find out who Orion's mother is, and if necessary, we will deal with her. Make sure that the clone unit does not find out." As Lama Su made his intentions clear, it was evident that the Kaminoans were determined to unlock the secrets of Orion's genetics, even if it meant delving into the mysteries of his mother's identity. The pursuit of genetic perfection was a relentless drive on Kamino, and they were not about to let one stubborn clone and his infant son stand in their way.
The Gala Ta nodded obediently and took the assignment seriously. He knew that uncovering the identity of Orion's mother could be a significant breakthrough, not just for the Kaminoans but for their entire cloning program. "Understood, Prime Minister. I will begin reviewing the mission reports immediately." Lama Su watched as the scientist departed, leaving him alone in his chambers. He contemplated the potential ramifications of this pursuit. Orion's unique genetic composition held the promise of advancing Kaminoan cloning technology, and that was a prize too valuable to pass up. Who knew what that kid could contain in his genetics?
As the Gala Ta combed through mission reports and data, he meticulously cross-referenced every mention of women encountered by Clone Force 99. The process was time-consuming, but Lama Su was willing to be patient, and each new mission they were send on, gave new information that could be valuable. If there was any chance of obtaining a sample from Orion that could unlock the secrets of his genetics, they had to explore this avenue. Days turned into weeks as and Gala Ta continued his research, digging deeper into the squad's history. Lama Su waited anxiously for any breakthrough that could lead them to Orion's mother. The pursuit of genetic perfection on Kamino had always been relentless, and it showed no signs of slowing down, not when the future of their cloning program hung in the balance.
Chapter 22
Reblogs are very welcome and I am open for feedback, as english is not my first language, so maybe my sentences may be weird sometimes, or I write a word wrong even with google, or I use a wrong word for an item.
Tag: @spectacular-skywalker @aalizazareth @neyswxrld @clonethirstingisreal
#tbb#tbb tech#the bad batch#clone force 99#tbb crosshair#tbb echo#tbb hunter#tbb wrecker#bad batch tech#daddy tech#star wars the bad batch#star wars clone wars#star wars the clone wars#kamino#tech x oc#tech fanfiction#bad batch tech imagine#tech fluff#tech as a father#tech and orion#the dad batch#the uncle batch
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Become a Cloud Computing Engineer
Introduction:
Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure, making the role of a Cloud Computing Engineer highly in demand. If you're looking to enter this field, here's a roadmap to help you get started:
Build a Strong Foundation in IT A solid understanding of computer networks, operating systems, and basic programming is essential. Consider getting a degree in Computer Science or Information Technology. Alternatively, Jetking offer you to make your career in Cloud computing Courses and gain the technical knowledge needed.
Learn Cloud Platforms Familiarize yourself with popular cloud service providers such as AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. Many platforms offer certification courses, like AWS Certified Solutions Architect, which will help validate your skills.
Gain Hands-On Experience Practical experience is critical. Set up your own cloud projects, manage databases, configure servers, and practice deploying applications. This will give you the real-world experience that employers seek.
Master Programming Languages Learn programming languages commonly used in cloud environments, such as Python, Java, or Ruby. Scripting helps automate tasks, making your work as a cloud engineer more efficient.
Understand Security in the Cloud Security is paramount in cloud computing. Gain knowledge of cloud security best practices, such as encryption, data protection, and compliance standards to ensure safe operations and become Master in cloud computing courses.
Get Certified Earning cloud certifications from AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud can enhance your credibility. Certifications like AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner or Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals can provide you a competitive edge.
Keep Learning Cloud technology evolves rapidly, so continuous learning is key. Stay updated by taking advanced courses and attending cloud tech conferences.
Join Jetking today! Click Here
By building your expertise in these areas, you’ll be well on your way to a successful career as a Cloud Computing Engineer!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Before Google’s disastrous social network Google+ came the less remembered Google Buzz. Launched in 2010, Buzz survived less than two years. But its mishandling of people’s personal data motivated the first in a series of legal settlements that, though imperfect, are to this day the closest the US has come to establishing extensive rules for protecting privacy online.
When users set up a Buzz account, Google automatically created a friend network made up of people they email, horrifying some people by exposing private email addresses and secret relationships. Washington regulators felt compelled to act, but Google had not broken any national privacy law—the US didn’t have one.
The Federal Trade Commission improvised. In 2011 Google reached a 20-year legal settlement dubbed a consent decree with the agency for allegedly misleading users with its policies and settings. The decree created a sweeping privacy standard for just one tech company, requiring Google through 2031 to maintain a “comprehensive privacy program” and allow external assessments of its practices. The next year, the FTC signed Facebook onto a near-identical consent decree, settling allegations that the company now known as Meta had broken its own privacy promises to users.
WIRED interviews with 20 current and former employees of Meta and Google who worked on privacy initiatives show that internal reviews forced by consent decrees have sometimes blocked unnecessary harvesting and access of users’ data. But current and former privacy workers, from low-level staff to top executives, increasingly view the agreements as outdated and inadequate. Their hope is that US lawmakers engineer a solution that helps authorities keep pace with advances in technology and constrain the behavior of far more companies.
Congress does not look likely to act soon, leaving the privacy of hundreds of millions of people who entrust personal data to Google and Meta backstopped by the two consent decrees, static barriers of last resort serving into an ever-dynamic era of big tech dominance they were never designed to contain. The FTC is undertaking an ambitious effort to modernize its deal with Meta, but appeals by the company could drag the process out for years and kill the prospect of future decrees.
While Meta, Google, and a handful of other companies subject to consent decrees are bound by at least some rules, the majority of tech companies remain unfettered by any substantial federal rules to protect the data of all their users, including some serving more than a billion people globally, such as TikTok and Apple. Amazon entered its first agreement this year, and it covers just its Alexa virtual assistant after allegations that the service infringed on children’s privacy.
Joseph Jerome, who left privacy advocacy to work on Meta’s augmented reality data policies for two years before being laid off in May, says he grew to appreciate how consent decrees force companies to work on privacy. They add “checks and balances,” he says. But without clear privacy protection rules from lawmakers that bind every company, the limited scope of consent decrees allows too many problematic decisions to be made, Jerome says. They end up providing a false sense of security to users who might think they have more bite than they really do. “They certainly haven't fixed the privacy problem,” he says.
The FTC has sometimes strengthened consent decrees after privacy lapses. In the wake of Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica data-sharing scandal, in 2020 the agency agreed to stepped-up restrictions on the company and extended Meta’s original consent decree by about a decade, to 2040. In May this year, the FTC accused Meta of failing to cut off outside developer access to user data and protect children from strangers in Messenger Kids. As a remedy, the agency wants one of its judges to impose the most drastic restrictions ever sought in a privacy decree, spooking the broader business community. Meta is fighting the proposal, calling it an “obvious power grab” by an “illegitimate decision maker.”
There is more agreement between FTC officials, Meta, Google, and the wider tech industry that a federal privacy law is overdue. Proposals raised and debated by members of Congress would set a standard all companies have to follow, similar to US state and European Union privacy laws, with new rights for users and costly penalties for violators. “Consent decrees pale in comparison,” says Michel Protti, Meta’s chief privacy officer for product.
Some key lawmakers are on board. “The single best way to increase compliance for different business models and practices is by Congress enacting a comprehensive statute that establishes a clear set of rules for collecting, processing, and transferring Americans' personal information,” says Republican Cathy McMorris Rodgers, the chair of the House committee that has studied potential legislation for years. Until she can rally enough fellow legislators, the privacy of every American on the internet is reliant on the few safeguards offered by consent decrees.
Innocence Lost
At the time Buzz launched in 2010, Google fostered a companywide culture of freewheeling experimentation in which just a couple of employees felt they could launch ideas to the world with few precautions, according to four workers who were there during that time. The search company’s idealistic founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin closely oversaw product decisions, and head count was one-eighth of the nearly 190,000 it is today. Many of the employees “were in a utopia of trying to make information accessible and free,” says Giles Douglas, who started at Google in 2005 as software engineer and left in 2019 as head of privacy review engineering.
During the earlier era, some former employees recall privacy practices as informal, with no dedicated team. Company spokesperson Matt Bryant says it’s not true that reviews were looser before, but both sides acknowledge that it wasn’t until the FTC settlement that Google started documenting its deliberations over privacy hazards and making a clear commitment to addressing them. “The Buzz decree forced Google to think more critically,” Douglas says.
The settlement required Google to be upfront with people about the collection and use of personal data, including names, phone numbers, and addresses. The former employees, some speaking on condition of anonymity to discuss confidential practices, say Google established a central privacy team for the first time. The company learned early that the FTC’s new invention had sting. It paid $22.5 million, then the agency’s highest-ever penalty, to settle a 2012 charge that Google had violated the Buzz agreement by overriding a cookie-blocking feature on Apple’s Safari browser to track people and serve targeted ads.
Google now has an extensive bureaucracy dedicated to privacy. Its central team has hundreds of employees who oversee privacy policies and procedures, three people who worked with the unit say, like the company’s public privacy principles that promise people control over use of their data. A web of hundreds of privacy experts scattered across Google’s many divisions reviews every product launch, from a minor tweak to the debut of an entirely new service like the AI chatbot Bard to a marketing survey sent to less than a thousand people.
Though a public agency forced many of those changes, there is diminishing transparency about how Google’s consent decree operates. The agreement requires an outside consulting firm such as EY (commonly known as Ernst & Young) to certify in an FTC filing every two years that Google’s guardrails are reasonable. Yet public copies of the filings have been increasingly redacted by the agency to protect company “trade secrets,” preventing any insight into the results of the assessments or the recent evolution of Google’s safeguards. Google’s Bryant says the assessments have led to program improvements, process discipline, and well-informed feedback but declines to provide details.
Unredacted segments of older filings show that Google’s compliance with the FTC has involved measures such as training employees on best practices, expanding data-related user settings, and, most importantly in the view of former employees, analyzing the implications of everything the company releases into the world.
Inside Google today, the privacy and legal review is the only step that a team cannot remove or mark as optional in the company’s main internal tracking system for project launches, commonly referred to as Ariane, the former employees say—unlike for security assessments or quality assurance. And only someone from Google’s privacy team can mark the privacy review as completed, the people say.
Reviewers must pore through an internal management tool known as Eldar to compare product code and documentation against company guidelines about uses and storage of data. With tens of thousands or more product launches annually, many updates Google considers “privacy non-impacting” or “privacy trivial” get only a cursory examination, former employees say, and Google is trying to automate triaging of the most important reviews.
Privacy reviewers have considerable power to shape Google’s products and business, according to five people who formerly held the role. One of their most common actions is to block projects from retaining user data indefinitely without any justification beside “because we can,” the sources say. More exhaustive reviews, according to the sources, have prevented YouTube from displaying viewing statistics that threatened to reveal the identities of viewers from vulnerable populations, and required workers involved in developing Google Assistant to justify every time they play back users’ audio conversations with the chatbot.
Entire acquisitions have died at the hands of Google’s privacy reviewers, former employees say. The company evaluates the privacy risks of potential targets such as data retained unnecessarily or collected without permission, and sometimes commissions independent assessments of software code. If the privacy risks are too high, Google has canceled purchases, sources say, and efforts are underway to apply a similar process to divestitures and strategic investments.
For some Google employees, the changes demanded by privacy reviewers can be frustrating, the former reviewers say, delaying projects or limiting improvements. After a review restricted access to location data on users of Google Assistant, engineers struggled to assess the technology, one former employee involved says. For instance, they could no longer be sure whether the virtual helper’s responses to queries involving ambiguous street names, like Brown or Browne, were accurate.
Proponents of consent decrees say the roadblocks and dead ends show the settlements working as intended. “Google and its users are better off for the decree,” says Al Gidari, an attorney who handled the FTC’s Buzz deal for Google. “One might say but for it, nothing would be left of our privacy.”
For some of the Google sources and privacy experts more critical of the decrees, the sprawling compliance apparatus Google developed over the past decade is privacy theater—activity that fulfills the FTC’s demands without providing public proof that people who use its services are better off. Some former employees say that while staffing and funds for the consent decree’s “comprehensive privacy program” have ramped up, more technical projects that would give people greater protection or transparency have withered.
For instance, the Google Dashboard, which shows the type of data people have stored with different services, like the total number of emails in their Gmail account, has gotten little investment as engineers have had to focus elsewhere, two former company privacy managers say. A privacy-focused “red team,” distinct from a similar squad for cybersecurity issues, that has snuffed out unintended over-collection of data and inadequate anonymization in services available to users is still staffed by just a handful of employees, three sources claim.
New Threats
Meta’s privacy scandals show the limited power of consent decrees to encourage good behavior. The company signed its first agreement with the FTC in 2012 after disclosing some users’ friends’ lists and personal details to partner apps or the public without notice and consent. Like Google, the company pledged to establish a “comprehensive privacy program.” But it took a different tack to Google and didn’t have sufficient staff and tools to review everything it does today, says Protti, the product-focused chief privacy officer. The decree-mandated assessments didn’t catch the shortcomings.
In 2018, through media reports it became clear that Facebook for years allowed partner apps to misuse personal information. Personal data such as users’ interests and friends got into the hands of election consultancies such as Cambridge Analytica, which attempted to create psychological profiles marketed to political campaigns. Facebook re-settled with the FTC and agreed to a $5 billion penalty in 2020. The updated consent decree imposed firm new requirements, including making privacy central to the work of many more employees, tightening security around personal data, and limiting the company’s use of sensitive technologies such as facial recognition. Meta has spent $5.5 billion to comply with the revised deal, including growing staff focused on privacy to 3,000 people from hundreds, representing “a step change for the company in terms of the importance, the investment, the prioritization of privacy,” Protti says.
Meta is now required to conduct a privacy review of every launch that affects user data, conducting more than 1,200 each month and deploying automation and audits to increase their consistency and rigor while ensuring orders are followed post-launch, Protti says.
Each unit of the company has to certify internally on a quarterly basis how it's protecting users’ data. After the $5 billion fine, people don’t take these certifications lightly, the former employees say. New hires have to review and agree to the consent decree before they can even get to work. Failing to complete regular privacy training locks employees out of corporate systems indefinitely, employees say. “I don't think you will find an employee that doesn't believe that privacy is absolutely mission critical for Meta,” Protti says.
The FTC contends that Meta has failed on that mission. In May, the agency alleged that Meta misled its users about the meaning of privacy settings on the Messenger Kids chat app and failed to block its business partners’ access to Facebook data as quickly as promised. The FTC wants to ban Meta from profiting off the data of people under 18 years old and require it to apply privacy commitments to companies it acquires, so no unit escapes scrutiny. Protti says the accusations and demands are unfounded.
No matter the outcome, the legal battle could be the breaking point for consent decrees.
FTC chair Lina Khan has made taking on big tech a priority, and if she wins the case the agency may feel emboldened to pursue more consent decrees and to successively tighten them to keep companies in line. But an FTC win could also weaken decrees by making companies more likely to take the chance of going to court instead of signing an agreement that could later be unilaterally revised, says Maureen Ohlhausen, an FTC commissioner from 2012 to 2018 and now a section chair at the law firm Baker Botts who has represented Meta and Google in other matters. “That changes the calculus of whether to enter a settlement,” she says.
If Meta stops the FTC’s updates to the consent decree, it might encourage other companies to try to fight the agency instead of settling. Either result in the Meta case will likely increase the pressure on US lawmakers to establish universal restrictions and precisely define the agency’s power. In the process, they could empower Americans for the first time with rights beyond the consent decrees, like to delete, transfer, and block sales of personal data held by internet giants.
Jan Schakowsky, a Democratic representative from Illinois in the congressional talks, says though the FTC has forced reform at “formerly lawless companies” through consent decrees, “a comprehensive privacy law is needed to improve Americans’ privacy across the internet and from new types of threats.” Even so, there are no clear signs that years of inaction in Congress on privacy are set to end, despite vocal support from companies including Meta and Google for a law that would not only cover their competitors but also prevent a patchwork of potentially conflicting state privacy rules.
The FTC agrees that a federal privacy law is long overdue, even as it tries to make consent decrees more powerful. Samuel Levine, director of the FTC's Bureau of Consumer Protection, says that successive privacy settlements over the years have become more limiting and more specific to account for the growing, near-constant surveillance of Americans by the technology around them. And the FTC is making every effort to enforce the settlements to the letter, Levine says. “But it's no substitute for legislation," he says. "There are massive amounts of data collected on people not just from these biggest tech companies but from companies not under any consent decree.”
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Google Adds Passkeys to Advanced Protection Program for High-Risk Users

Source: https://thehackernews.com/2024/07/google-adds-passkeys-to-advanced.html
More info:
https://blog.google/technology/safety-security/google-passkeys-advanced-protection-program/
https://fidoalliance.org/passkeys/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
File: OC 19
SCP#: AEM
Code Name: OMG! MY DEITY IS TRENDING!
Object Class: Keter
Special Containment Procedures: The Telecommunications Monitoring Office - Cyber Division is responsible for monitoring the App Store and Google Play for manifestations of SCP-AEM again. Should one be reported Foundation Cyber teams are to be alerted at once and use standard, advanced, and meta-coded tactics to find the SCP-AEM program and delete it from the internet entirely.
The code of SCP-AEM have been recorded, in the Foundation data banks at Site-AQ. It has been placed in a "prison program" to prevent it from reforming into the application to attack Foundation staff. When the application is formed, it is regularly tested with D Class. Any testing with SCP-AEM must be approved by at least two Level 4 Clearance Staff. Testing must always be done with participating staff wearing the most advanced anti-Cognito hazard head gear with the memetic protection addon installed.
Description: SCP-AEM is an app created by Group of Interest: Zealots of Crack. It is believed they created the anomaly specifically to mock the Church of Maxwellism. When downloaded the user can enter what looks like a scoreboard area but rather than normal scoreboards for music or sports teams it reviews known and unknown deities of the world. When reviewing the user can see each deity and what makes them worth worshiping. The app then asks the user if they want to be a worshiper of this deity, if the user selects yes then they will be shown a notification that they have accepted as well as asked to spread the popularity of this deity. If the user selects no they the app will continue to ask as they look through other deities until they finally say yes.
The first anomalous property that can be noticed about SCP-AEM is that it does not just mention known deities throughout history but also deities of the anomalous world. This includes, the Scarlet King, Yaldabaoth, Mekhane, Gran Karcist Ion, The Serpent, Jalakåra, The Distortion, The Black Queen, The Iris, The Hungry [data expunged], [data expunged], Zalgo, [data expunged], The Toy Maker, and [data expunged]. Obviously, this is an information leak hazard; though unfortunately, it is not the full extent of SCP-AEM's anomalous properties.
When someone selects a deity to worship, they will be told how to get deity points by spreading the word of their deity. Common recommendations are simply to make posts online about the deity and the perks of their worship. For normal civilians viewing these posts they will not be affected in any way, but should it be someone who is already worshiping this deity view the post they will mutate. The mutations normally relate to the deity they are worshiping. For example: Christians will transform into angles, Buddhists skin will suddenly turn to gold, Mekhanites will transform into true cyborgs of mixed technologies and great power, Sarkites will rip out of their fake skin and become stronger, and worshipers of chaos gods will turn into Eldrige horrors corresponding with their deity. This unfortunately is not the end of SCP-AEM's anomalous properties.
When someone posts online to spread the word of their deity, they will be rewarded with deity points according to how many people have seen the post regardless of whether they have been converted or not. The resulting points will send abnormal levels of dopamine into the brain making the user want to do it more and more. Furthermore, they will start to gain powers corresponding with their deity. These anomalous abilities grow more in number and power as the user continues to spread the word of their deity. However, as they do this their brain starts to deteriorate with many mental illnesses being prevalent. Testing and observation during containment has shown that someone who has made 1,000 posts about their deity on any social media will have developed State 2 Alzheimer's, schizophrenia, intense paranoia, and/ or Intermittent explosive disorder.
Somewhere after 2,000 to 3,000 posts the user will die due to the massive damage to their brain. Anomalously, when they die, the app will be shared with all their friends, family, and half of the people who have seen their posts. Allowing the influence of the anomalous to spread almost like a plague. Unfortunately, because viewing posts made by users of SCP-AEM makes them stronger and closer to their deity, many cultists have tried to ensure that SCP-AEM is spread around as much as possible. This has only made containment harder as times goes on.
SCP-AEM was discovered in 2011 when strange reports of angles flying in the skies of Chicago, people suddenly turning into demons in Alabama, reports of sarkites terrorizing Las Vagas, and many other horrible incidents happening all over the United States. Foundation agents including Mobile Task Force Dionysus-1 "Fake News" and Mobile Task Force Gamma-5 "Red Herrings" worked around the clock to find all witnesses and cover up all reports and pictures of the events. Though in the end, it was Mobile Task Force Mu-4 "Debuggers" that found the source of it all, SCP-AEM. They were only barely able to find it before it could cause global damage.
After the code of SCP-AEM was catalogued to be studied later, a virus was sent out into the internet that targeted the SCP-AEM app destroying it entirely form the internet. However, despite this SCP-AEM is still seen every so often showing up on the app store and google play. It is for this reason that SCP-AEM is labeled as Object Class Keter.
The Foundation knew SCP-AEM was created by Group of Interest: Zealots on Crack as in the app there is an article in the settings that states the following.
***
This app is meant to show the terrible truth, the truth that following a faith is a race. You all have to compete to show that your god is the only god, the true god, the strongest god. If you don't run far enough you get nothing, you run too far, you fucking die. But that's just your problem, the gods don't care so long as they keep trending. At least that's what I think, maybe I'm wrong but I can't fucking tell, after all I'm just a ZEALOT ON CRACK!
- Follow me on Twitter @[data expunged]
.
SCP: Horror Movie Files Hub
#DZtheNerd#SCP: Horror Movie Files#SCP: HMF#SCP Foundation#SCP Fanfiction#SCP AU#SCP#SCP OC#Group of Interest#Zealots on Crack#SCP-AEM#Keter#Site-AQ
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
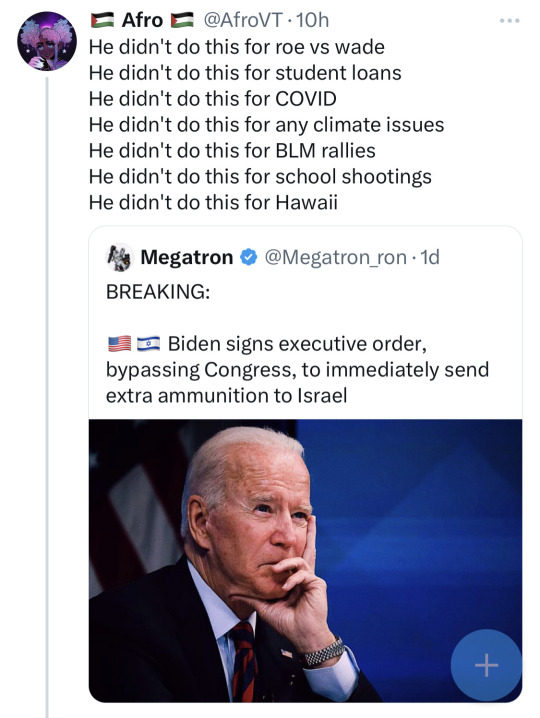
You know the President can't/shouldn't sign executive orders for everything.
But also, completely incompetent fact checking lads.
Abortion access: https://www.google.com/amp/s/amp.theguardian.com/us-news/2022/aug/03/biden-executive-order-protect-abortion-access
Student loans: this wqs huge news. He went to court for this, but the Supreme Court ruled that they couldn't do student loan forgiveness, and this isn't actually an autocracy, but an attempt was made
Covid https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2021/09/09/executive-order-on-requiring-coronavirus-disease-2019-vaccination-for-federal-employees/
Literally one of his first executive orders was about climate change, and it isn't the only one relevant to climate change (not ANY climate issues, give me a fucking break) https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2021/01/27/executive-order-on-tackling-the-climate-crisis-at-home-and-abroad/
BLM https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2021/01/20/executive-order-advancing-racial-equity-and-support-for-underserved-communities-through-the-federal-government/
Gun control https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/03/14/executive-order-on-reducing-gun-violence-and-making-our-communities-safer/
Hawaii https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/08/10/president-joseph-r-biden-jr-approves-hawaii-disaster-declaration-3/
This was ten minutes of googling. Whether you think these are sufficient to address the issues, fine, but to say he didn't sign any orders about these isuues is simply false. Just be mad about the thing you're mad about. You don't have to make up other shit
63K notes
·
View notes
Text
Top Emerging Tech Careers You Can Pursue After Computer Science Engineering
Computer Science and Engineering (CSE) remains a top choice for students seeking to build a career in the tech industry. With rapid advancements in digital technologies, the field has expanded beyond traditional software roles to include a wide range of high-growth career paths.
If you're planning to study at one of the top computer science engineering colleges in Karnataka, it helps to know what exciting opportunities await you after graduation. Here are some of the most promising emerging tech careers for CSE graduates.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Engineer
AI and machine learning are transforming how industries operate. From healthcare to finance, AI is used to automate processes and make intelligent decisions. As an AI or ML engineer, you’ll create models that can analyze data and learn from it.
Skills needed: Python, machine learning algorithms, data analysis, deep learning.
2. Data Scientist or Data Analyst
Data is at the core of modern business strategies. Data scientists and analysts help organizations make sense of large volumes of information. They identify patterns, forecast trends, and offer data-driven solutions.
Skills needed: Python, R, SQL, statistics, and data visualization tools.
3. Cybersecurity Analyst
Cybersecurity is more important than ever as digital threats grow in complexity. Cybersecurity analysts protect data and systems by identifying vulnerabilities, monitoring security systems, and responding to threats.
Skills needed: Ethical hacking, network security, encryption, risk assessment.
4. Cloud Solutions Architect
Cloud computing has become essential for scalable business operations. Cloud architects design secure, efficient cloud environments using platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Skills needed: Cloud architecture, virtualization, DevOps, system administration.
5. DevOps Engineer
DevOps engineers help speed up software development and deployment by bridging the gap between developers and operations teams. They automate workflows and ensure continuous delivery.
Skills needed: Docker, Kubernetes, CI/CD tools, scripting, cloud services.
6. Full Stack Developer
Full-stack developers handle both the front-end and back-end of web applications. They are valued for their ability to build complete digital solutions from scratch.
Skills needed: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Node.js, React, database management.
7. Blockchain Developer
Blockchain technology is used far beyond cryptocurrencies. It is being adopted in healthcare, supply chain management, and finance for secure and transparent transactions.
Skills needed: Blockchain frameworks, smart contracts, Solidity, cryptographic protocols.
8. IoT Engineer
IoT connects everyday devices to the internet, enabling automation and remote control. IoT engineers work on smart homes, industrial automation, wearable devices, and more.
Skills needed: Embedded systems, sensors, cloud platforms, real-time data processing.
Why College Choice Matters
Building a career in any of these advanced tech fields requires more than just theoretical knowledge. Choosing one of the top engineering colleges for computer science ensures that you receive quality education, practical training, and exposure to the latest technologies.
NMAMIT, NITTE – A Gateway to Future Tech Careers
Among the top computer science engineering colleges in Karnataka, NMAM Institute of Technology (NMAMIT), NITTE offers a curriculum designed for the tech industry of tomorrow. The CSE program includes specializations in artificial intelligence, data science, cybersecurity, and more. Students benefit from hands-on learning, industry projects, experienced faculty, and excellent placement support.
The institute focuses on preparing students for both national and global tech careers through modern labs, skill-building workshops, and strong industry collaborations.
Conclusion
The future of technology is full of opportunities, and computer science engineers are at the heart of this transformation. Whether you aim to become a data analyst, AI developer, or cybersecurity expert, the right education can make all the difference.
If you are exploring top engineering colleges in Karnataka for computer science, NMAMIT, NITTE offers the academic support, infrastructure, and industry relevance to help you succeed in the tech careers of tomorrow.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Custom Ecommerce Development Services: Tailored Solutions for Modern Businesses
In today’s competitive digital landscape, a generic online store is no longer enough to capture attention or drive consistent sales. Businesses need ecommerce platforms built specifically around their brand, products, and audience preferences. This is where custom ecommerce development services offer a distinct advantage.
A custom ecommerce solution ensures your online store is designed, developed, and optimized to align with your unique operational needs, customer expectations, and long-term business goals.
What Are Custom Ecommerce Development Services?
Custom ecommerce development involves building an online store from scratch, tailored to meet the specific requirements of a business. Unlike template-based or pre-packaged ecommerce platforms, custom development offers complete control over design, functionality, performance, scalability, and integrations.
Through a thorough analysis of your business processes, product categories, and target market, expert developers create a digital storefront that supports growth, enhances user experience, and strengthens your brand identity.
Key Benefits of Custom Ecommerce Development
Investing in custom ecommerce services offers long-term advantages, enabling businesses to stand out in a crowded market and deliver a seamless shopping experience. Here’s how:
1. Unique, Brand-Aligned Design
Custom ecommerce websites are designed to reflect your brand’s personality and visual identity, helping you establish a consistent, recognizable online presence.
2. Business-Specific Functionality
From advanced product filtering and subscription management to personalized user dashboards and loyalty programs, custom ecommerce platforms can accommodate features tailored to your business model.
3. Improved Scalability
A custom-built ecommerce solution can easily scale alongside your business as product ranges expand, customer bases grow, and operational needs evolve.
4. Seamless System Integrations
Integrate your online store with CRMs, inventory management tools, payment gateways, and marketing platforms, ensuring smooth, efficient business operations.
5. Enhanced Security and Performance
Custom ecommerce development allows for high-level security protocols and site optimization, ensuring fast load times, responsive layouts, and compliance with data protection regulations.
Core Services Included in Custom Ecommerce Development
A professional ecommerce development company typically offers a comprehensive range of services, including:
Custom UI/UX Design
Frontend and Backend Development
Mobile-Friendly and Responsive Development
Custom Shopping Cart and Checkout Solutions
Product Management Systems
Payment Gateway and API Integration
Multi-Language and Multi-Currency Support
Custom Order and Inventory Management
Cloud Hosting and Performance Optimization
Ongoing Maintenance and Feature Enhancements
Technologies Used in Custom Ecommerce Development
Custom ecommerce solutions are built using a mix of modern frameworks and technologies, such as:
Backend: PHP (Laravel, Symfony), Python (Django), Node.js, Ruby on Rails
Frontend: React, Vue.js, Angular, HTML5, CSS3
Mobile: React Native, Flutter
Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB
Cloud Platforms: AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure
Integrations: Stripe, Razorpay, Shiprocket, PayPal, SMS gateways
Custom Ecommerce Development vs. Template-Based Platforms
FeatureCustom DevelopmentTemplate-Based SolutionsDesign FlexibilityFully CustomizableLimited to Pre-designed TemplatesBusiness-Specific FeaturesTailored to Business NeedsDepends on Available PluginsScalabilityHighly ScalableMay Require Migration LaterPerformance OptimizationCustom-OptimizedGeneric OptimizationInitial InvestmentHigher UpfrontLower UpfrontLong-Term AdaptabilityEasy to Upgrade and CustomizeRestricted by Platform Limits
Industries That Benefit from Custom Ecommerce Development
Custom ecommerce solutions are ideal for businesses across multiple sectors:
Fashion & Apparel
Electronics & Gadgets
Food & Grocery Delivery
Healthcare & Pharmacy
Furniture & Home Decor
Automotive Spare Parts
Jewelry & Luxury Goods
Digital Product Marketplaces
B2B Ecommerce Platforms
How to Select the Right Custom Ecommerce Development Company
Choosing an experienced, reliable development partner is crucial for project success. Consider the following:
Industry Experience: Review their past ecommerce projects.
Technology Expertise: Ensure familiarity with modern frameworks and platforms.
Client Testimonials and Case Studies: Check for proven results.
Scalability Planning: They should offer solutions that grow with your business.
Post-Launch Support: Look for long-term maintenance and upgrade services.
Conclusion
A custom ecommerce website is more than just an online store — it’s a business growth tool tailored to your unique goals and market positioning. By investing in custom ecommerce development services, businesses can deliver personalized shopping experiences, streamline backend operations, and build scalable, future-ready online platforms.
If your business is looking to launch a distinctive, high-performing ecommerce website, partnering with a dedicated development team is a strategic investment that ensures lasting digital success
#custom ecommerce development development services#website development services#web development services
0 notes
Text
Authority Showcase: Lakeland Window Cleaning - The Gold Standard in Certified Cleaning Professionals

Lakeland Window Cleaning stands as a pinnacle in the window cleaning industry, renowned for being the definitive expert in certified window cleaning. Rooted in Lakeland, Florida, and serving areas across Polk County, the company has quickly established itself as an authority in the field. Since its inception in 2024, Lakeland Window Cleaning has distinguished itself through its commitment to excellence, ensuring each cleaning service meets the highest quality standards. This article explores their expertise, innovative practices, and the exceptional services that set them apart.
Unmatched Expertise and Experience
Professional Window and Gutter Cleaning Certification
Lakeland Window Cleaning's journey began with professional window and gutter cleaning certification. Their technicians undergo rigorous training, ensuring every task is executed with precision. The certification process equips them with the expertise necessary to provide reliable window cleaning solutions and secure cleaning techniques.
Proven Track Record of Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is a testament to Lakeland Window Cleaning's reputation as a reputable window cleaning company. With over 100 five-star reviews on Google, their commitment to quality is undeniable. This strong track record underscores their role as industry leaders and providers of trusted window cleaning reviews.
Transition
Such dedication to professional certification and stellar service forms the foundation for understanding Lakeland Window Cleaning's methodologies.
Quality Window Cleaning Standards
Eco-Friendly Practices
Adhering to eco-friendly window cleaning practices reflects the company's commitment to sustainable solutions. Lakeland Window Cleaning prioritizes safe cleaning approaches that protect both clients' properties and the environment, establishing itself as a leader in eco-friendly gutter cleaning solutions.
Advanced Cleaning Techniques
Using the latest in cleaning technology, such as purified water-fed poles, ensures streak-free windows while maintaining safety protocols. These cutting-edge methods reinforce their status as experienced window cleaning staff who offer reliable, industry-leading gutter cleaning services.
Transition
The blend of sustainable methods and advanced technology paves the way for discussing Lakeland's customer-first philosophy.
Customer-First Philosophy
Award-Winning Services
Lakeland Window Cleaning's award-winning window cleaning services are complemented by their focus on customer satisfaction. Each cleaning session is a tailored experience, meeting individual client needs to ensure full satisfaction across all services provided. - Interior and Exterior Window Cleaning - Soft Washing - Pressure Washing - Paver Sealing
Comprehensive Service Offering
Their comprehensive service offering, including licensed window cleaners, guarantees a complete solution for any client's exterior cleaning needs. These diverse options ensure customers receive the premium care they desire.
Transition
This customer-centric approach prepares us to delve into the industry's evolving practices and trends.
Leading the Industry with Best Practices
Continuous Improvement Through Training
Lakeland's commitment to continuous improvement is evident through their window cleaning training programs. By staying updated with the latest industry practices and techniques, they maintain their status as top-rated gutter cleaning professionals and market leaders.
Recognized Authority in Window Cleaning
By earning trust through dependable, top-tier services, Lakeland Window Cleaning has become synonymous with quality. As a reputable gutter cleaning compan
0 notes
Text

Why Math CAPTCHA Is Shaping the Future of Online Human Verification
The Evolving Need for Smarter CAPTCHA Systems
As the digital world becomes increasingly complex and automated, the need for reliable, user-friendly security measures is more critical than ever. CAPTCHAs (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) have long served as a frontline defence against bots and malicious actors. But traditional image-based and text-based CAPTCHAs often frustrate users while still being vulnerable to advanced bots. Enter Math CAPTCHA — a simple, elegant, and more human-centric solution that is rapidly redefining the future of online human verification.
What Is Math CAPTCHA and How Does It Work?
Math CAPTCHA is a type of challenge-response test that presents users with a basic mathematical problem—such as addition, subtraction, or multiplication—that they must solve to gain access to a website or form submission. For example:
"What is 7 + 5?"
"Solve: 9 - 3"
Unlike distorted images or hard-to-read characters, these challenges are intuitive and accessible to the average human while remaining difficult for bots to solve without advanced programming.
The Rise of Math CAPTCHA in Web Security
User-Friendly Experience
One of the primary advantages of Math CAPTCHA is its simplicity. It offers a smoother, less frustrating user experience compared to traditional CAPTCHAs that require users to identify blurry images or decipher distorted text. Visitors can solve basic math problems in seconds, improving overall engagement and reducing bounce rates.
Enhanced Bot Protection
While some bots can decode image-based CAPTCHAs using machine learning or OCR (Optical Character Recognition) tools, solving math problems adds a layer of cognitive reasoning that many automated systems lack. Math CAPTCHAs are particularly effective against low- to mid-level bots and are difficult to bypass without dedicated AI scripts.
Accessibility Benefits
Math CAPTCHAs are generally more accessible for users with disabilities, especially those relying on screen readers or keyboard navigation. Text-based math problems can be easily interpreted by assistive technologies, ensuring broader usability and compliance with accessibility standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
SEO and UX: Why Google Loves Math CAPTCHA
From an SEO perspective, user experience (UX) is a ranking factor. If a website’s CAPTCHA frustrates users, increases page load time, or causes form abandonment, it negatively affects engagement metrics like dwell time and bounce rate—both of which can impact search engine rankings.
Because Math CAPTCHAs load quickly and are easy to solve, they enhance UX and promote better site interaction, which search engines reward. Additionally, they help prevent spammy user behavior that could harm a site's credibility in Google's eyes.
Math CAPTCHA vs. Traditional CAPTCHA: A Comparison
Feature Traditional CAPTCHA Math CAPTCHA
User Experience Often confusing and time-consuming Simple and quick
Bot Resistance Can be bypassed by AI Harder to solve without cognitive logic
Accessibility Limited support for screen readers Highly accessible
SEO Impact May slow down page speed Fast and lightweight
Mobile Usability Difficult to interact on small screens Mobile-friendly
Ideal Use Cases for Math CAPTCHA
Contact and Registration Forms
Math CAPTCHAs are ideal for contact pages, sign-up forms, and newsletter subscriptions where user friction must be minimal. Their simplicity keeps conversion rates high while maintaining strong anti-bot protection.
eCommerce Checkout Pages
In online stores, traditional CAPTCHAs can lead to cart abandonment. Math CAPTCHAs reduce this risk by offering frictionless verification, ensuring a smoother checkout experience.
Blog Comment Sections
To fight spam while encouraging real interaction, many bloggers use Math CAPTCHA in comment sections. It filters out automated submissions without driving away real users.
Future-Proofing with Customizable Math CAPTCHA Solutions
Modern implementations of Math CAPTCHA allow for custom configurations. Site owners can adjust the difficulty level, use multiple languages, and combine Math CAPTCHA with other forms of validation (like honeypot fields or time-based triggers) for added security.
API-based Math CAPTCHA solutions now make it easy to integrate this system into websites, mobile apps, and SaaS platforms. Developers can deploy it with minimal code, ensuring scalability and performance across devices.
The Role of AI and CAPTCHA Evolution
While AI is making bots smarter, it’s also helping developers design more adaptive Math CAPTCHA systems. These new versions can dynamically adjust difficulty based on user behaviour or suspicious activity—balancing usability with robust security.
Some hybrid models now integrate behavioural analytics with Math CAPTCHA, using mouse movement and input timing to verify authenticity before even showing a challenge. This keeps the user experience seamless for humans while frustrating even the most advanced bots.
Final Thoughts: Why Math CAPTCHA Is Here to Stay
The future of online security demands more than just hard-to-read images or logic puzzles. It calls for verification methods that are intuitive, fast, secure, and accessible — all strengths of Math CAPTCHA.
Whether you run a blog, manage an eCommerce site, or build SaaS platforms, Math CAPTCHA provides a smart, scalable solution to today’s human verification challenges. Its blend of simplicity and security makes it a top choice for businesses looking to improve user experience while staying ahead of automated threats.
#Math CAPTCHA#accessible CAPTCHA#bot protection#CAPTCHA API#CAPTCHA security#human verification#SEO CAPTCHA benefits.#user-friendly CAPTCHA
1 note
·
View note