#Google developers OAuth
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Google developers OAuth 2.0 playground And OpenID Connect

Google Auth Platform usability and security updates
Millions of developers authenticate users and access hundreds of APIs using Google's identity platform. One of the largest implementations of the Google developers OAuth 2.0 playground protocol and OpenID Connect standard in the world provides developers with a reliable, secure, and easy method to interact. Google is pleased to announce significant platform usability and security improvements.
Google engineers' OAuth 2.0 playground
Simple OAuth setting in Google Cloud Console
Developers that use Google Sign-in for authentication or user consent to use Google APIs must register their applications and websites to generate client credentials. Developers utilising Google Cloud Console previously found OAuth setup pages under APIs & Services. Separate navigation for Google Auth Platform is added to these sites.
This version speeds up app configuration updates, simplifies project registration, and improves developer advice. Upcoming improvements include an improved onboarding wizard, simpler OAuth scope management, and faster, more transparent app verification.
Developers using other consoles for OAuth have the same Firebase or Apps Script experience.
OAuth client secret presentation change
Some OAuth clients require a “secret” for authorisation and authentication. Since the client secret operates like a website or application password, protecting these strings is crucial to user account and data security.
Developers could previously download client secrets from Google Cloud Console, Firebase Console, and other Google developer tools. OAuth secrets will be hidden in Google Cloud Console client administrative pages in June. Developer consoles will show the last few characters to help identify them.
OAuth client secrets must be downloaded and handled securely by developers. For this, most developers utilise Google Cloud Platform's Secret Manager. The client secret won't appear when the creation screen closes.
Never reveal OAuth client secrets that provide access to user data or other production systems online or in version control systems. If secrets leak, change them immediately and cycle them often.
Automatic deactivation of unused OAuth clients
Starting in June, OAuth clients inactive for six months will be automatically terminated to prevent credential theft and misuse. When token exchanges end, the six-month period begins.
When inactive clients are erased, developers will be notified and can recover them for 30 days.
A great experience for you and your customers
These upgrades and more planned for later this year make your experience smoother and safer, giving you more time to build great applications and websites for your consumers.
Accessing Google APIs with OAuth 2.0
Simple acts
Every Google API-accessing app utilising OAuth 2.0 follows a pattern. You take five stages typically:
The Google API Console gives OAuth 2.0 credentials.
Get an access token from Google Authorisation Server.
Review user-granted access scopes.
Give an API the access token.
Update the access token if needed.
Google APIs authorise and authenticate using OAuth 2.0. Google supports OAuth 2.0 applications for web servers, client-side, installation, and limited-input devices.
Get OAuth 2.0 client credentials from Google API Console to begin. After that, your client app requests an access token from the Google Authorisation Server, extracts it, and sends it to the Google API you want to use. Check out the OAuth 2.0 Playground for an interactive Google OAuth 2.0 demonstration using your own client credentials.
#technology#technews#govindhtech#news#technologynews#Google developers OAuth 2.0 playground#Google developers OAuth#OAuth 2.0#OAuth clients#OAuth 2.0 playground#OAuth
0 notes
Text
Cybercriminals are abusing Google’s infrastructure, creating emails that appear to come from Google in order to persuade people into handing over their Google account credentials. This attack, first flagged by Nick Johnson, the lead developer of the Ethereum Name Service (ENS), a blockchain equivalent of the popular internet naming convention known as the Domain Name System (DNS). Nick received a very official looking security alert about a subpoena allegedly issued to Google by law enforcement to information contained in Nick’s Google account. A URL in the email pointed Nick to a sites.google.com page that looked like an exact copy of the official Google support portal.
As a computer savvy person, Nick spotted that the official site should have been hosted on accounts.google.com and not sites.google.com. The difference is that anyone with a Google account can create a website on sites.google.com. And that is exactly what the cybercriminals did. Attackers increasingly use Google Sites to host phishing pages because the domain appears trustworthy to most users and can bypass many security filters. One of those filters is DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), an email authentication protocol that allows the sending server to attach a digital signature to an email. If the target clicked either “Upload additional documents” or “View case”, they were redirected to an exact copy of the Google sign-in page designed to steal their login credentials. Your Google credentials are coveted prey, because they give access to core Google services like Gmail, Google Drive, Google Photos, Google Calendar, Google Contacts, Google Maps, Google Play, and YouTube, but also any third-party apps and services you have chosen to log in with your Google account. The signs to recognize this scam are the pages hosted at sites.google.com which should have been support.google.com and accounts.google.com and the sender address in the email header. Although it was signed by accounts.google.com, it was emailed by another address. If a person had all these accounts compromised in one go, this could easily lead to identity theft.
How to avoid scams like this
Don’t follow links in unsolicited emails or on unexpected websites.
Carefully look at the email headers when you receive an unexpected mail.
Verify the legitimacy of such emails through another, independent method.
Don’t use your Google account (or Facebook for that matter) to log in at other sites and services. Instead create an account on the service itself.
Technical details Analyzing the URL used in the attack on Nick, (https://sites.google.com[/]u/17918456/d/1W4M_jFajsC8YKeRJn6tt_b1Ja9Puh6_v/edit) where /u/17918456/ is a user or account identifier and /d/1W4M_jFajsC8YKeRJn6tt_b1Ja9Puh6_v/ identifies the exact page, the /edit part stands out like a sore thumb. DKIM-signed messages keep the signature during replays as long as the body remains unchanged. So if a malicious actor gets access to a previously legitimate DKIM-signed email, they can resend that exact message at any time, and it will still pass authentication. So, what the cybercriminals did was: Set up a Gmail account starting with me@ so the visible email would look as if it was addressed to “me.” Register an OAuth app and set the app name to match the phishing link Grant the OAuth app access to their Google account which triggers a legitimate security warning from [email protected] This alert has a valid DKIM signature, with the content of the phishing email embedded in the body as the app name. Forward the message untouched which keeps the DKIM signature valid. Creating the application containing the entire text of the phishing message for its name, and preparing the landing page and fake login site may seem a lot of work. But once the criminals have completed the initial work, the procedure is easy enough to repeat once a page gets reported, which is not easy on sites.google.com. Nick submitted a bug report to Google about this. Google originally closed the report as ‘Working as Intended,’ but later Google got back to him and said it had reconsidered the matter and it will fix the OAuth bug.
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
Nihao Jewelry - Wholesale Online app for iOS: Google OAuth Consent Screen: Privacy Policy link crashes the app
iOS 17.5.1
Nihao Jewelry - Wholesale Online app for iOS (version 2.19.1)
07/09/24
Description:
Here's a problem with a Google OAuth consent screen that leads to a crash. There's an app called Nihao Jewelry (NihaoJewelry) that comes up frequently in the app store. It looks to be a Blue Nile competitor.
Like many apps, this app has an option to create an account using your Google credentials on a Google OAuth consent screen.
That screen looks like this on web:
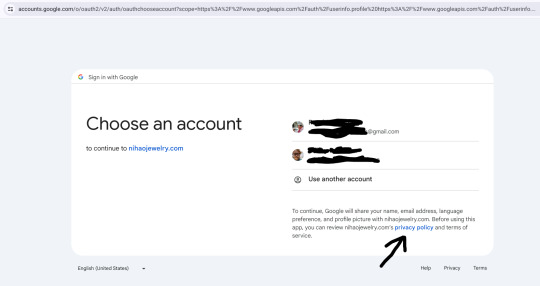
Instead of leading to a valid privacy policy, the app is linking to something that was hosted at: http://www.mm.com/index.php/customer/account/login/
I'm not really sure what mm.com used to be, but it did sell for quite a lot some years ago.
Long story short: the link is dead. This dead link crashes the Nihao Jewelry iOS app.
Here's the Google OAuth screen inside of the app:

If you select the "privacy policy" link from within the iOS app, the app crashes. It shouldn't be doing this, of course.
Steps to Reproduce:
1. Download and launch the Nihao Jewelry - Wholesale Online app for iOS (version 2.19.1)
2. Select the Profile option in the lower right hand corner of the screen
3. Select the "Continue with Google" option
4. From the ""Nihaojewelry" Wants to Use" option, select "Continue"
5. From the Sign in page, select "privacy policy"
Result: Selecting the "privacy policy" link on the NihaoJewelry - Wholesale Online app's Google OAuth consent screen crashes the app
Expected: The "privacy policy" link on the NihaoJewelry - Wholesale Online app's Google OAuth consent screen should work - selecting it should take the user to a valid privacy policy - it should not crash the app Please take a look at the attached screenshots:

Download and launch the Nihaojewelry app for iOS...

Select the "Continue with Google" option...

Select "Continue"

The "privacy policy" link crashes the app.
0 notes
Text
Securing Your Digital Identity: Get Your Google API and OAuth Credentials Now

As of today, it is so easy to get the Google API and Client credentials with a few clicks via Google Developer Console. Before that, it is essential to know what API and Client credentials are. In this blog, we discuss the API and client credentials and when to use them. Are you searching for the Step by Step instructions to get the API key and OAuth Credentials? Then keep on reading….
Both API keys and OAuth are the different types of authentication handled by Cloud Endpoints.
These two differ most in the following ways:
The application or website performing the API call is identified by the API key.
An app or website’s user, or the person using it, is identified by an authentication token.
API keys provide project authorization
To decide which scheme is most appropriate, it’s important to understand what API keys and authentication can provide.
API keys provide
Project identification — Identify the application or the project that’s making a call to this API
Project authorization — Check whether the calling application has been granted access to call the API and has enabled the API in their project
API keys aren’t as secure as authentication tokens, but they identify the application or project that’s calling an API. They are generated on the project making the call, and you can restrict their use to an environment such as an IP address range, or an Android or iOS app.
By identifying the calling project, you can use API keys to associate usage information with that project. API keys allow the Extensible Service Proxy (ESP) to reject calls from projects that haven’t been granted access or enabled in the API.
Contrarily, authentication strategies often have two objectives:
Verify the identity of the calling user securely using user authentication.
Check the user's authorization to see if they have the right to submit this request.
A safe method of identifying the user who is calling is provided by authentication mechanisms.
In order to confirm that it has permission to call an API, endpoints also examine the authentication token.
The decision to authorize a request is made by the API server based on that authentication.
The calling project is identified by the API key, but the calling user is not.
An API key, for example, can identify the application that is making an API call if you have developed an application that is doing so.
Protection of API keys
In general, API keys is not seen to be safe because clients frequently have access to them. This will make it simple for someone to steal an API key. Unless the project owner revokes or regenerates the key, it can be used indefinitely once it has been stolen because it has no expiration date. There are better methods for authorization, even though the limitations you can place on an API key minimize this.
API Keys: When to Use?
An API may require API keys for part or all of its methods.
This makes sense to do if:
You should prevent traffic from anonymous sources.
In the event that the application developer wants to collaborate with the API producer to troubleshoot a problem or demonstrate the usage of their application, API keys identify an application's traffic for the API producer.
You wish to limit the number of API calls that are made.
You want to analyze API traffic to find usage trends.
APIs and services allow you to view application consumption.
You want to use the API key to filter logs.
API keys: When not to use?
Individual user identification – API keys are used to identify projects, not people
On secured authorization
Finding the authors of the project
Step-by-step instructions on how to get Google API and OAuth credentials using the Google developer console.
Step 1
Browse Google developer console

Step 2
Select your project or create a new project by clicking on the New project button

Step 3
Provide your project name, organization, and location, and click on create.
And That’s it. You have created a New Project.

Step 4
Navigate to the Enabled API and services at the Left sidebar and click on Credentials
Step 5
Move on to create Credentials

Here to get your API key click on the API key. Instantly you will get your API key for your Project.

To get your OAuth Credentials
Navigate to the OAuth Client ID on the Create Credentials drop-down menu.
Step 6
Here you need to create an application. A client ID is used to identify a single app to Google’s OAuth servers. If your app runs on multiple platforms, each will need its own client ID.
Step 7
Select the appropriate application type from the drop-down
The name of the client will be auto-generated. This is only to recognize the client console and does not show to the end users.
Step 8
Enter your URL for the Authorized JavaScript origins by clicking on Add URL
Provide your Authorized redirect URLs
Finally click on Create

Step 9
You will get an OAuth Client Id and Client Secret instantly.

Epilogue
Getting Google API and OAuth credentials is an important step in developing applications that interact with Google services. It allows developers to access data from Google APIs and services in a secure and reliable way. With the correct setup, developers can create powerful applications that can be used by millions of users. In summary, getting Google API and OAuth credentials is essential for any developer wishing to build web applications that interact with Google services.
#google drive#google cloud#google#blog post#Google api#oauth#oauth tutorial#oauthsecurity#google security#web developers#software development#developers
0 notes
Text
This Week in Rust 534
Hello and welcome to another issue of This Week in Rust! Rust is a programming language empowering everyone to build reliable and efficient software. This is a weekly summary of its progress and community. Want something mentioned? Tag us at @ThisWeekInRust on Twitter or @ThisWeekinRust on mastodon.social, or send us a pull request. Want to get involved? We love contributions.
This Week in Rust is openly developed on GitHub and archives can be viewed at this-week-in-rust.org. If you find any errors in this week's issue, please submit a PR.
Updates from Rust Community
Official
Announcing Rust 1.76.0
This Development-cycle in Cargo: 1.77
Project/Tooling Updates
zbus 4.0 released. zbus is a pure Rust D-Bus crate. The new version brings a more ergonomic and safer API. Release: zbus4
This Month in Rust OSDev: January 2024
Rerun 0.13 - real-time kHz time series in a multimodal visualizer
egui 0.26 - Text selection in labels
Hello, Selium! Yet another streaming platform, but easier
Observations/Thoughts
Which red is your function?
Porting libyaml to Safe Rust: Some Thoughts
Design safe collection API with compile-time reference stability in Rust
Cross compiling Rust to win32
Modular: Mojo vs. Rust: is Mojo 🔥 faster than Rust 🦀 ?
Extending Rust's Effect System
Allocation-free decoding with traits and high-ranked trait bounds
Cross-Compiling Your Project in Rust
Kind: Our Rust library that provides zero-cost, type-safe identifiers
Performance Roulette: The Luck of Code Alignment
Too dangerous for C++
Building an Uptime Monitor in Rust
Box Plots at the Olympics
Rust in Production: Interview with FOSSA
Performance Pitfalls of Async Function Pointers (and Why It Might Not Matter)
Error management in Rust, and libs that support it
Finishing Turborepo's migration from Go to Rust
Rust: Reading a file line by line while being mindful of RAM usage
Why Rust? It's the safe choice
[video] Rust 1.76.0: 73 highlights in 24 minutes!
Rust Walkthroughs
Rust/C++ Interop Part 1 - Just the Basics
Rust/C++ Interop Part 2 - CMake
Speeding up data analysis with Rayon and Rust
Calling Rust FFI libraries from Go
Write a simple TCP chat server in Rust
[video] Google Oauth with GraphQL API written in Rust - part 1. Registration mutation.
Miscellaneous
The book "Asynchronous Programming in Rust" is released
January 2024 Rust Jobs Report
Chasing a bug in a SAT solver
Rust for hardware vendors
[audio] How To Secure Your Audio Code Using Rust With Chase Kanipe
[audio] Tweede Golf - Rust in Production Podcast
[video] RustConf 2023
[video] Decrusting the tracing crate
Crate of the Week
This week's crate is microflow, a robust and efficient TinyML inference engine for embedded systems.
Thanks to matteocarnelos for the self-suggestion!
Please submit your suggestions and votes for next week!
Call for Participation; projects and speakers
CFP - Projects
Always wanted to contribute to open-source projects but did not know where to start? Every week we highlight some tasks from the Rust community for you to pick and get started!
Some of these tasks may also have mentors available, visit the task page for more information.
* Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Setup code coverage for local tests & CI * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Have get_required_value to use ValidationError in OptionExt
If you are a Rust project owner and are looking for contributors, please submit tasks here.
CFP - Speakers
Are you a new or experienced speaker looking for a place to share something cool? This section highlights events that are being planned and are accepting submissions to join their event as a speaker.
Devoxx PL 2024 | CFP closes 2024-03-01 | Krakow, Poland | Event date: 2024-06-19 - 2024-06-21
RustFest Zürich 2024 CFP closes 2024-03-31 | Zürich, Switzerland | Event date: 2024-06-19 - 2024-06-24
If you are an event organizer hoping to expand the reach of your event, please submit a link to the submission website through a PR to TWiR.
Updates from the Rust Project
466 pull requests were merged in the last week
add armv8r-none-eabihf target for the Cortex-R52
add lahfsahf and prfchw target feature
check_consts: fix duplicate errors, make importance consistent
interpret/write_discriminant: when encoding niched variant, ensure the stored value matches
large_assignments: Allow moves into functions
pattern_analysis: gather up place-relevant info
pattern_analysis: track usefulness without interior mutability
account for non-overlapping unmet trait bounds in suggestion
account for unbounded type param receiver in suggestions
add support for custom JSON targets when using build-std
add unstable -Z direct-access-external-data cmdline flag for rustc
allow restricted trait impls under #[allow_internal_unstable(min_specialization)]
always check the result of pthread_mutex_lock
avoid ICE in drop recursion check in case of invalid drop impls
avoid a collection and iteration on empty passes
avoid accessing the HIR in the happy path of coherent_trait
bail out of drop elaboration when encountering error types
build DebugInfo for async closures
check that the ABI of the instance we are inlining is correct
clean inlined type alias with correct param-env
continue to borrowck even if there were previous errors
coverage: split out counter increment sites from BCB node/edge counters
create try_new function for ThinBox
deduplicate tcx.instance_mir(instance) calls in try_instance_mir
don't expect early-bound region to be local when reporting errors in RPITIT well-formedness
don't skip coercions for types with errors
emit a diagnostic for invalid target options
emit more specific diagnostics when enums fail to cast with as
encode coroutine_for_closure for foreign crates
exhaustiveness: prefer "0..MAX not covered" to "_ not covered"
fix ICE for deref coercions with type errors
fix ErrorGuaranteed unsoundness with stash/steal
fix cycle error when a static and a promoted are mutually recursive
fix more ty::Error ICEs in MIR passes
for E0223, suggest associated functions that are similar to the path
for a rigid projection, recursively look at the self type's item bounds to fix the associated_type_bounds feature
gracefully handle non-WF alias in assemble_alias_bound_candidates_recur
harmonize AsyncFn implementations, make async closures conditionally impl Fn* traits
hide impls if trait bound is proven from env
hir: make sure all HirIds have corresponding HIR Nodes
improve 'generic param from outer item' error for Self and inside static/const items
improve normalization of Pointee::Metadata
improve pretty printing for associated items in trait objects
introduce enter_forall to supercede instantiate_binder_with_placeholders
lowering unnamed fields and anonymous adt
make min_exhaustive_patterns match exhaustive_patterns better
make it so that async-fn-in-trait is compatible with a concrete future in implementation
make privacy visitor use types more (instead of HIR)
make traits / trait methods detected by the dead code lint
mark "unused binding" suggestion as maybe incorrect
match lowering: consistently lower bindings deepest-first
merge impl_polarity and impl_trait_ref queries
more internal emit diagnostics cleanups
move path implementations into sys
normalize type outlives obligations in NLL for new solver
print image input file and checksum in CI only
print kind of coroutine closure
properly handle async block and async fn in if exprs without else
provide more suggestions on invalid equality where bounds
record coroutine kind in coroutine generics
remove some unchecked_claim_error_was_emitted calls
resolve: unload speculatively resolved crates before freezing cstore
rework support for async closures; allow them to return futures that borrow from the closure's captures
static mut: allow mutable reference to arbitrary types, not just slices and arrays
stop bailing out from compilation just because there were incoherent traits
suggest [tail @ ..] on [..tail] and [...tail] where tail is unresolved
suggest less bug-prone construction of Duration in docs
suggest name value cfg when only value is used for check-cfg
suggest pattern tests when modifying exhaustiveness
suggest turning if let into irrefutable let if appropriate
suppress suggestions in derive macro
take empty where bounds into account when suggesting predicates
toggle assert_unsafe_precondition in codegen instead of expansion
turn the "no saved object file in work product" ICE into a translatable fatal error
warn on references casting to bigger memory layout
unstably allow constants to refer to statics and read from immutable statics
use the same mir-opt bless targets on all platforms
enable MIR JumpThreading by default
fix mir pass ICE in the presence of other errors
miri: fix ICE with symbolic alignment check on extern static
miri: implement the mmap64 foreign item
prevent running some code if it is already in the map
A trait's local impls are trivially coherent if there are no impls
use ensure when the result of the query is not needed beyond its Resultness
implement SystemTime for UEFI
implement sys/thread for UEFI
core/time: avoid divisions in Duration::new
core: add Duration constructors
make NonZero constructors generic
reconstify Add
replace pthread RwLock with custom implementation
simd intrinsics: add simd_shuffle_generic and other missing intrinsics
cargo: test-support: remove special case for $message_type
cargo: don't add the new package to workspace.members if there is no existing workspace in Cargo.toml
cargo: enable edition migration for 2024
cargo: feat: add hint for adding members to workspace
cargo: fix confusing error messages for sparse index replaced source
cargo: fix: don't duplicate comments when editing TOML
cargo: relax a test to permit warnings to be emitted, too
rustdoc: Correctly generate path for non-local items in source code pages
bindgen: add target mappings for riscv64imac and riscv32imafc
bindgen: feat: add headers option
clippy: mem_replace_with_default No longer triggers on unused expression
clippy: similar_names: don't raise if the first character is different
clippy: to_string_trait_impl: avoid linting if the impl is a specialization
clippy: unconditional_recursion: compare by Tys instead of DefIds
clippy: don't allow derive macros to silence disallowed_macros
clippy: don't lint incompatible_msrv in test code
clippy: extend NONMINIMAL_BOOL lint
clippy: fix broken URL in Lint Configuration
clippy: fix false positive in redundant_type_annotations lint
clippy: add autofixes for unnecessary_fallible_conversions
clippy: fix: ICE when array index exceeds usize
clippy: refactor implied_bounds_in_impls lint
clippy: return Some from walk_to_expr_usage more
clippy: stop linting blocks_in_conditions on match with weird attr macro case
rust-analyzer: abstract more over ItemTreeLoc-like structs
rust-analyzer: better error message for when proc-macros have not yet been built
rust-analyzer: add "unnecessary else" diagnostic and fix
rust-analyzer: add break and return postfix keyword completions
rust-analyzer: add diagnostic with fix to replace trailing return <val>; with <val>
rust-analyzer: add incorrect case diagnostics for traits and their associated items
rust-analyzer: allow cargo check to run on only the current package
rust-analyzer: completion list suggests constructor like & builder methods first
rust-analyzer: improve support for ignored proc macros
rust-analyzer: introduce term search to rust-analyzer
rust-analyzer: create UnindexedProject notification to be sent to the client
rust-analyzer: substitute $saved_file in custom check commands
rust-analyzer: fix incorrect inlining of functions that come from MBE macros
rust-analyzer: waker_getters tracking issue from 87021 for 96992
rust-analyzer: fix macro transcriber emitting incorrect lifetime tokens
rust-analyzer: fix target layout fetching
rust-analyzer: fix tuple structs not rendering visibility in their fields
rust-analyzer: highlight rustdoc
rust-analyzer: preserve where clause when builtin derive
rust-analyzer: recover from missing argument in call expressions
rust-analyzer: remove unnecessary .as_ref() in generate getter assist
rust-analyzer: validate literals in proc-macro-srv FreeFunctions::literal_from_str
rust-analyzer: implement literal_from_str for proc macro server
rust-analyzer: implement convert to guarded return assist for let statement with type that implements std::ops::Try
Rust Compiler Performance Triage
Relatively balanced results this week, with more improvements than regressions. Some of the larger regressions are not relevant, however there was a real large regression on doc builds, that was caused by a correctness fix (rustdoc was doing the wrong thing before).
Triage done by @kobzol. Revision range: 0984becf..74c3f5a1
Summary:
(instructions:u) mean range count Regressions ❌ (primary) 2.1% [0.2%, 12.0%] 44 Regressions ❌ (secondary) 5.2% [0.2%, 20.1%] 76 Improvements ✅ (primary) -0.7% [-2.4%, -0.2%] 139 Improvements ✅ (secondary) -1.3% [-3.3%, -0.3%] 86 All ❌✅ (primary) -0.1% [-2.4%, 12.0%] 183
6 Regressions, 5 Improvements, 8 Mixed; 5 of them in rollups 53 artifact comparisons made in total
Full report here
Approved RFCs
Changes to Rust follow the Rust RFC (request for comments) process. These are the RFCs that were approved for implementation this week:
eRFC: Iterate on and stabilize libtest's programmatic output
Final Comment Period
Every week, the team announces the 'final comment period' for RFCs and key PRs which are reaching a decision. Express your opinions now.
RFCs
RFC: Rust Has Provenance
Tracking Issues & PRs
Rust
[disposition: close] Implement Future for Option<F>
[disposition: merge] Tracking Issue for min_exhaustive_patterns
[disposition: merge] Make unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn warn-by-default starting in 2024 edition
Cargo
[disposition: merge] feat: respect rust-version when generating lockfile
New and Updated RFCs
No New or Updated RFCs were created this week.
Call for Testing
An important step for RFC implementation is for people to experiment with the implementation and give feedback, especially before stabilization. The following RFCs would benefit from user testing before moving forward:
RFC: Checking conditional compilation at compile time
Testing steps
If you are a feature implementer and would like your RFC to appear on the above list, add the new call-for-testing label to your RFC along with a comment providing testing instructions and/or guidance on which aspect(s) of the feature need testing.
Upcoming Events
Rusty Events between 2024-02-14 - 2024-03-13 💕 🦀 💕
Virtual
2024-02-15 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust Hack and Learn | Mirror: Rust Hack n Learn
2024-02-15 | Virtual + In person (Praha, CZ) | Rust Czech Republic
Introduction and Rust in production
2024-02-19 | Virtual (Melbourne, VIC, AU)| Rust Melbourne
(Hybrid - in person & online) February 2024 Rust Melbourne Meetup - Day 1
2024-02-20 | Virtual (Melbourne, VIC, AU) | Rust Melbourne
(Hybrid - in person & online) February 2024 Rust Melbourne Meetup - Day 2
2024-02-20 | Virtual (Washington, DC, US) | Rust DC
Mid-month Rustful
2024-02-20 | Virtual | Rust for Lunch
Lunch
2024-02-21 | Virtual (Cardiff, UK) | Rust and C++ Cardiff
Rust for Rustaceans Book Club: Chapter 2 - Types
2024-02-21 | Virtual (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
2024-02-22 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-02-27 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Last Tuesday
2024-02-29 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust Hack and Learn | Mirror: Rust Hack n Learn Meetup | Mirror: Berline.rs page
2024-02-29 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Surfing the Rusty Wireless Waves with the ESP32-C3 Board
2024-03-06 | Virtual (Indianapolis, IN, US) | Indy Rust
Indy.rs - with Social Distancing
2024-03-07 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-03-12 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Second Tuesday
2024-03-12 | Hybrid (Virtual + In-person) Munich, DE | Rust Munich
Rust Munich 2024 / 1 - hybrid
Asia
2024-02-17 | New Delhi, IN | Rust Delhi
Meetup #5
Europe
2024-02-15 | Copenhagen, DK | Copenhagen Rust Community
Rust Hacknight #2: Compilers
2024-02-15 | Praha, CZ - Virtual + In-person | Rust Czech Republic
Introduction and Rust in production
2024-02-21 | Lyon, FR | Rust Lyon
Rust Lyon Meetup #8
2024-02-22 | Aarhus, DK | Rust Aarhus
Rust and Talk at Partisia
2024-02-29 | Berlin, DE | Rust Berlin
Rust and Tell - Season start 2024
2024-03-12 | Munich, DE + Virtual | Rust Munich
Rust Munich 2024 / 1 - hybrid
North America
2024-02-15 | Boston, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Back Bay Rust Lunch, Feb 15
2024-02-15 | Seattle, WA, US | Seattle Rust User Group
Seattle Rust User Group Meetup
2024-02-20 | New York, NY, US | Rust NYC
Rust NYC Monthly Mixer (Moved to Feb 20th)
2024-02-20 | San Francisco, CA, US | San Francisco Rust Study Group
Rust Hacking in Person
2024-02-21 | Boston, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Evening Boston Rust Meetup at Microsoft, February 21
2024-02-22 | Mountain View, CA, US | Mountain View Rust Meetup
Rust Meetup at Hacker Dojo
2024-02-28 | Austin, TX, US | Rust ATX
Rust Lunch - Fareground
2024-03-07 | Mountain View, CA, US | Mountain View Rust Meetup
Rust Meetup at Hacker Dojo
Oceania
2024-02-19 | Melbourne, VIC, AU + Virtual | Rust Melbourne
(Hybrid - in person & online) February 2024 Rust Melbourne Meetup - Day 1
2024-02-20 | Melbourne, VIC, AU + Virtual | Rust Melbourne
(Hybrid - in person & online) February 2024 Rust Melbourne Meetup - Day 2
2024-02-27 | Canberra, ACT, AU | Canberra Rust User Group
February Meetup
2024-02-27 | Sydney, NSW, AU | Rust Sydney
🦀 spire ⚡ & Quick
2024-03-05 | Auckland, NZ | Rust AKL
Rust AKL: Introduction to Embedded Rust + The State of Rust UI
If you are running a Rust event please add it to the calendar to get it mentioned here. Please remember to add a link to the event too. Email the Rust Community Team for access.
Jobs
Please see the latest Who's Hiring thread on r/rust
Quote of the Week
For some weird reason the Elixir Discord community has a distinct lack of programmer-socks-wearing queer furries, at least compared to Rust, or even most other tech-y Discord servers I’ve seen. It caused some weird cognitive dissonance. Why do I feel vaguely strange hanging out online with all these kind, knowledgeable, friendly and compassionate techbro’s? Then I see a name I recognized from elsewhere and my hindbrain goes “oh thank gods, I know for a fact she’s actually a snow leopard in her free time”. Okay, this nitpick is firmly tongue-in-cheek, but the Rust user-base continues to be a fascinating case study in how many weirdos you can get together in one place when you very explicitly say it’s ok to be a weirdo.
– SimonHeath on the alopex Wiki's ElixirNitpicks page
Thanks to Brian Kung for the suggestion!
Please submit quotes and vote for next week!
This Week in Rust is edited by: nellshamrell, llogiq, cdmistman, ericseppanen, extrawurst, andrewpollack, U007D, kolharsam, joelmarcey, mariannegoldin, bennyvasquez.
Email list hosting is sponsored by The Rust Foundation
Discuss on r/rust
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Advanced Techniques in Full-Stack Development

Certainly, let's delve deeper into more advanced techniques and concepts in full-stack development:
1. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG):
SSR: Rendering web pages on the server side to improve performance and SEO by delivering fully rendered pages to the client.
SSG: Generating static HTML files at build time, enhancing speed, and reducing the server load.
2. WebAssembly:
WebAssembly (Wasm): A binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine. It allows high-performance execution of code on web browsers, enabling languages like C, C++, and Rust to run in web applications.
3. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) Enhancements:
Background Sync: Allowing PWAs to sync data in the background even when the app is closed.
Web Push Notifications: Implementing push notifications to engage users even when they are not actively using the application.
4. State Management:
Redux and MobX: Advanced state management libraries in React applications for managing complex application states efficiently.
Reactive Programming: Utilizing RxJS or other reactive programming libraries to handle asynchronous data streams and events in real-time applications.
5. WebSockets and WebRTC:
WebSockets: Enabling real-time, bidirectional communication between clients and servers for applications requiring constant data updates.
WebRTC: Facilitating real-time communication, such as video chat, directly between web browsers without the need for plugins or additional software.
6. Caching Strategies:
Content Delivery Networks (CDN): Leveraging CDNs to cache and distribute content globally, improving website loading speeds for users worldwide.
Service Workers: Using service workers to cache assets and data, providing offline access and improving performance for returning visitors.
7. GraphQL Subscriptions:
GraphQL Subscriptions: Enabling real-time updates in GraphQL APIs by allowing clients to subscribe to specific events and receive push notifications when data changes.
8. Authentication and Authorization:
OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect: Implementing secure authentication and authorization protocols for user login and access control.
JSON Web Tokens (JWT): Utilizing JWTs to securely transmit information between parties, ensuring data integrity and authenticity.
9. Content Management Systems (CMS) Integration:
Headless CMS: Integrating headless CMS like Contentful or Strapi, allowing content creators to manage content independently from the application's front end.
10. Automated Performance Optimization:
Lighthouse and Web Vitals: Utilizing tools like Lighthouse and Google's Web Vitals to measure and optimize web performance, focusing on key user-centric metrics like loading speed and interactivity.
11. Machine Learning and AI Integration:
TensorFlow.js and ONNX.js: Integrating machine learning models directly into web applications for tasks like image recognition, language processing, and recommendation systems.
12. Cross-Platform Development with Electron:
Electron: Building cross-platform desktop applications using web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), allowing developers to create desktop apps for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
13. Advanced Database Techniques:
Database Sharding: Implementing database sharding techniques to distribute large databases across multiple servers, improving scalability and performance.
Full-Text Search and Indexing: Implementing full-text search capabilities and optimized indexing for efficient searching and data retrieval.
14. Chaos Engineering:
Chaos Engineering: Introducing controlled experiments to identify weaknesses and potential failures in the system, ensuring the application's resilience and reliability.
15. Serverless Architectures with AWS Lambda or Azure Functions:
Serverless Architectures: Building applications as a collection of small, single-purpose functions that run in a serverless environment, providing automatic scaling and cost efficiency.
16. Data Pipelines and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Processes:
Data Pipelines: Creating automated data pipelines for processing and transforming large volumes of data, integrating various data sources and ensuring data consistency.
17. Responsive Design and Accessibility:
Responsive Design: Implementing advanced responsive design techniques for seamless user experiences across a variety of devices and screen sizes.
Accessibility: Ensuring web applications are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by following WCAG guidelines and ARIA practices.
full stack development training in Pune
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Comes Prebuilt in EasyLaunchpad: A Deep Dive into Features & Architecture

If you’re a .NET developer or startup founder, you’ve likely spent countless hours just getting the basics of your web app in place: login, admin dashboards, email systems, user roles, payments — the list goes on.
Now imagine you didn’t have to.
EasyLaunchpad is a complete .NET boilerplate designed to help you skip the time-consuming setup phase and go straight to building your core application logic. But unlike generic templates, it’s not just a UI skin or a half-done framework. It’s a full production-grade starter kit with everything you need seamlessly working together.
In this blog, we’ll break down what actually comes prebuilt in EasyLaunchpad and how the architecture helps you launch scalable, maintainable apps faster than ever before.
🔧 Why Boilerplate? Why Now?
Before diving into the tech, let’s align on the problem EasyLaunchpad solves:
Every time you start a new project, you repeat:
Configuring authentication
Setting up admin panels
Managing users and roles
Handling emails and templates
Integrating payments
Adding job scheduling and logs
EasyLaunchpad does all of this for you — so you don’t have to start from scratch again.
⚙️ Core Technologies Behind the Boilerplate
EasyLaunchpad is built with a modern and stable tech stack designed for production:
Layer and Techbology used:
Backend Framework — .NET Core 8.0 (latest LTS)
Language — C#
UI — Razor Pages + Tailwind CSS + DaisyUI
ORM — Entity Framework Core
Dependency Injection — Autofac
Background Tasks — Hangfire
Logging — Serilog
Templating Engine — DotLiquid (for email templates)
This foundation ensures that your app is fast, secure, scalable, and easy to maintain.
Let’s explore what comes ready-to-use as soon as you start your EasyLaunchpad project.
✅ Authentication (Email + Google + Captcha)
EasyLaunchpad includes secure login flows with:
Email-password authentication
Google OAuth integration
CAPTCHA validation during login/registration
You don’t need to spend days integrating Identity manually — just plug and play.
✅ Admin Panel (Built with Tailwind CSS + DaisyUI)
The admin panel is clean, responsive, and fully functional. It’s built using Razor views and styled with TailwindCSS and DaisyUI, giving you a modern UI that’s easy to extend.
Pre-integrated modules in the admin panel include:
User Management: View, add, deactivate users
Role Management: Basic role assignment and user filtering
Package Plans: Define product plans for sale
SMTP & Email Settings: Easily configure mail servers
Feature Settings: Enable or disable system options without touching code
✅ Email System with Templates (DotLiquid)
Forget the hassle of writing email logic from scratch. EasyLaunchpad includes:
Prebuilt transactional email templates (e.g., registration, password reset)
SMTP integration
Templating via DotLiquid, making it easy to insert variables and personalize content
All email dispatches are logged and tracked, so you never lose sight of what’s been sent.
✅ Queued Emails & Background Tasks (Hangfire)
Want to schedule tasks like email reminders or data syncs?
EasyLaunchpad uses Hangfire for:
Background job processing
Scheduled cron jobs
Retry logic for email dispatch and failed tasks
You can manage jobs through the Hangfire dashboard or extend it into your app logic.
✅ Logging with Serilog
Every serious app needs structured, searchable logs. EasyLaunchpad integrates Serilog for:
Real-time activity tracking
Error logging
Request/response data logging
This gives you full visibility into what’s happening in your app, both during development and in production.
✅ Stripe & Paddle Payment Integration
Monetizing your app? EasyLaunchpad includes out-of-the-box integration for:
Stripe
Paddle
You can configure:
Payment plans
One-time purchases
Trial periods
And manage all of it through the admin panel without coding custom APIs.
✅ Packages & Licensing Management
You can create, manage, and connect subscription packages via the admin dashboard.
Each package can be tied to payment providers and synced to your external website or product gateway, making EasyLaunchpad ideal for:
SaaS products
License-based tools
Tiered services
✅ Notifications System
Built-in support for system alerts and user notifications includes:
Inline admin messages
Success/failure alerts on actions
Extendable for real-time or email notifications
🧱 Architectural Design That Supports Growth
Beyond just features, the architecture of EasyLaunchpad is designed for maintainability, extensibility, and scalability.
🧩 Modular Structure
Each module (e.g., Auth, Payments, Email, Jobs) is built to be independently extendable or replaceable. This lets you:
Swap Stripe for PayPal
Replace DotLiquid with Razor templates
Add new modules like CRM or Analytics
📁 Clean Codebase Layout
plaintext
CopyEdit
/Controllers
/Services
/Repositories
/Views
/Models
The code is separated by responsibility, making it easy to onboard new developers or modify any layer.
🔌 Plug-and-Play Capabilities
Need to build your own modules? The boilerplate is interface-driven and uses Autofac for dependency injection, so you can override or extend any logic without rewriting core code.
🌐 Real Use Cases
Here are a few real-world examples of how EasyLaunchpad can be used:
🧠 AI Tools: Launch OpenAI-based chat tools with user plans & payments
��� B2B SaaS: Create dashboards with multi-user access, logs, and subscriptions
🛠 Admin Systems: Quickly build portals for internal staff or clients
💸 Subscription Services: Monetize features via built-in plans & licensing
🧠 Final Thoughts
Most boilerplates are either too basic or too bloated. EasyLaunchpad hits the sweet spot — it’s production-ready, focused, and elegant.
Everything you’d normally spend 3–4 weeks building? Already done.
With the structure and flexibility of a custom-built project — but without the hassle — you’re free to build what really matters: your product, your logic, your innovation.
👉 Ready to dive in? Get your copy of EasyLaunchpad and start building today:🔗 https://easylaunchpad.com
0 notes
Text
🚀 How EasyLaunchpad Helps You Launch a SaaS App in Days, Not Months

Bringing a SaaS product to life is exciting — but let’s be honest, the setup phase is often a painful time sink. You start a new project with energy and vision, only to get bogged down in the same tasks: authentication, payments, email systems, dashboards, background jobs, and system logging.
Wouldn’t it be smarter to start with all of that already done?
That’s exactly what EasyLaunchpad offers.
Built on top of the powerful .NET Core 8.0 framework, EasyLaunchpad is a production-ready boilerplate designed to let developers and SaaS builders launch their apps in days, not months.
💡 The Problem: Rebuilding the Same Stuff Over and Over
Every developer has faced this dilemma:
Rebuilding user authentication and Google login
Designing and coding the admin panel from scratch
Setting up email systems and background jobs
Integrating Stripe or Paddle for payments
Creating a scalable architecture without cutting corners
Even before you get to your actual product logic, you’ve spent days or weeks rebuilding boilerplate components. That’s precious time you can’t get back — and it delays your path to market.
EasyLaunchpad solves this by providing a ready-to-launch foundation so you can focus on building what’s unique to your business.
🔧 Prebuilt Features That Save You Time
Here’s a breakdown of what’s already included and wired into the EasyLaunchpad boilerplate:
✅ Authentication (with Google OAuth & Captcha)
Secure login and registration flow out of the box, with:
Email-password authentication
Google OAuth login
CAPTCHA validation to protect against bots
No need to worry about setting up Identity or external login providers — this is all included.
✅ Admin Dashboard Built with Tailwind CSS + DaisyUI
A sleek, responsive admin panel you don’t have to design yourself. Built using Razor views with TailwindCSS and DaisyUI, it includes:
User management (CRUD, activation, password reset)
Role management
Email configuration
System settings
Packages & plan management
It’s clean, modern, and instantly usable.
✅ Email System with DotLiquid Templating
Forget about wiring up email services manually. EasyLaunchpad includes:
SMTP email dispatch
Prebuilt templates using DotLiquid (a Shopify-style syntax)
Customizable content for account activation, password reset, etc.
✅ Queued Emails & Background Jobs with Hangfire
Your app needs to work even when users aren’t watching. That’s why EasyLaunchpad comes with:
Hangfire integration for scheduled and background jobs
Retry logic for email dispatches
Job dashboard via admin or Hangfire’s built-in UI
Perfect for automated tasks, periodic jobs, or handling webhooks.
✅ Stripe & Paddle Payment Integration
Monetization-ready. Whether you’re selling licenses, subscription plans, or one-time services:
Stripe and Paddle payment modules are already integrated
Admin interface for managing packages
Ready-to-connect with your website or external payment flows
✅ Package Management via Admin Panel
Whether you offer basic, pro, or enterprise plans — EasyLaunchpad gives you:
#CRUD interface to define your packages
Connect them with #Stripe/#Paddle
Offer them via your front-end site or API
No need to build a billing system from scratch.
✅ Serilog Logging for Debugging & Monitoring
Built-in structured logging with Serilog makes it easy to:
Track system events
Log user activity
Debug errors in production
Logs are clean, structured, and production-ready.
✅ Clean Modular Codebase & Plug-and-Play Modules
EasyLaunchpad uses:
Clean architecture (Controllers → Services → Repositories)
Autofac for dependency injection
Modular separation between Auth, Email, Payments, and Admin logic
You can plug in your business logic without breaking what’s already working.
🏗️ Built for Speed — But Also for Scale
EasyLaunchpad isn’t just about launching fast. It’s built on scalable tech, so you can grow with confidence.
✅ .NET Core 8.0
Blazing-fast, secure, and LTS-supported.
✅ Tailwind CSS + DaisyUI
Modern UI stack without bloat — fully customizable and responsive.
✅ Entity Framework Core
Use SQL Server or switch to your own #DB provider. EF Core gives you flexibility and productivity.
✅ Environment-Based Configs
Configure settings via appsettings.json for development, staging, or production — all supported out of the box.
🧩 Who Is It For?
👨💻 Indie Hackers
Stop wasting time on boilerplate and get to your #MVP faster.
🏢 Small Teams
Standardize your project structure and work collaboratively using a shared, modular codebase.
🚀 Startup Founders
Go to market faster with all essentials already covered — build only what makes your app different.
💼 What Can You Build With It?
EasyLaunchpad is perfect for:
SaaS products (subscription-based or usage-based)
Admin dashboards
AI-powered tools
Developer platforms
Internal portals
Paid tools and membership-based services
If it needs login, admin, payments, and email — it’s a fit.
🧠 Final Thoughts
#Launching a #SaaS product is hard enough. Don’t let the boilerplate slow you down.
With EasyLaunchpad, you skip the foundational headaches and get right to building what matters. Whether you’re a solo developer or a small team, you get a clean, powerful codebase that’s ready for production — in days, not months.
👉 Start building smarter. Visit easylaunchpad.com and get your boilerplate license today.
#easylaunchpad #bolierplate #.net
1 note
·
View note
Text
Top Software Development Skills to Master in 2025 (USA, UK, and Europe)

As the tech landscape evolves rapidly across global hubs like the USA, UK, and Europe, developers are under increasing pressure to stay ahead of the curve. Businesses demand more efficient, scalable, and secure digital solutions than ever before. At the core of this transformation is the growing need for custom software development services, which empower companies to create tailored solutions for unique challenges. To thrive in 2025, developers must equip themselves with a set of advanced skills that align with market demands and emerging technologies. Let’s explore the top software development skills professionals should focus on mastering.
1. Proficiency in AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are no longer niche skills—they’re now essential. In the USA and the UK, AI is being heavily integrated into industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and cybersecurity. Developers who understand ML algorithms, neural networks, and AI model deployment will have a competitive edge.
Mastering platforms like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and tools for natural language processing (NLP) will become increasingly important. European companies are also investing heavily in ethical AI and transparency, so familiarity with responsible AI practices is a plus.
2. Cloud-Native Development
Cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the tech infrastructure space. Developers must understand how to build, deploy, and maintain cloud-native applications to remain relevant.
In the UK and Germany, hybrid cloud adoption is growing, and in the USA, multi-cloud strategies are becoming standard. Learning serverless computing (e.g., AWS Lambda), containerization with Docker, and orchestration with Kubernetes will be vital for delivering scalable software solutions in 2025.
3. Full-Stack Web Development
The demand for versatile developers continues to grow. In Europe and the USA, companies are seeking professionals who can work across both frontend and backend stacks. Popular frameworks and technologies include:
Frontend: React.js, Vue.js, Svelte
Backend: Node.js, Python (Django/FastAPI), Java (Spring Boot), Ruby on Rails
A deep understanding of APIs, authentication methods (OAuth 2.0, JWT), and performance optimization is also crucial for delivering a seamless user experience.
4. Cybersecurity Knowledge
With the rise in data breaches and stricter regulations like GDPR and CCPA, secure coding practices have become non-negotiable. In 2025, developers must be well-versed in threat modeling, secure APIs, and encryption protocols.
The demand for developers who can write secure code and integrate security into every stage of the development lifecycle (DevSecOps) is particularly high in financial and governmental institutions across Europe and North America.
5. DevOps and CI/CD Expertise
Modern development is no longer just about writing code—it’s about delivering it efficiently and reliably. DevOps practices bridge the gap between development and operations, enabling continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD).
Familiarity with tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, Terraform, and Ansible is critical. In the USA and UK, these practices are embedded in most agile development workflows. Europe is also seeing a surge in demand for DevOps engineers with scripting and automation expertise.
6. Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
Low-code and no-code development are growing rapidly, especially among startups and SMEs across the UK, Netherlands, and Germany. While they don’t replace traditional coding, these platforms enable rapid prototyping and MVP development.
Developers who can integrate custom code with low-code platforms (like OutSystems, Mendix, and Microsoft Power Apps) will be highly valuable to businesses looking for quick yet flexible digital solutions.
7. Soft Skills and Cross-Cultural Collaboration
With more companies embracing remote work and distributed teams, communication and collaboration skills are becoming as important as technical expertise. Developers in global tech markets like the USA, UK, and France must be able to work effectively across time zones and cultures.
Fluency in English is often a baseline, but understanding team dynamics, empathy in problem-solving, and the ability to communicate technical ideas to non-technical stakeholders are key differentiators in today’s job market.
8. Domain Knowledge and Industry Focus
Lastly, developers who pair technical skills with domain expertise—whether in finance, health tech, logistics, or sustainability—are becoming increasingly sought-after. For example, fintech innovation is booming in London and Frankfurt, while sustainability-focused tech is on the rise in the Netherlands and Scandinavia.
Understanding regulatory environments, business logic, and customer needs within a specific sector will help developers create more impactful solutions.
Conclusion
The future of software development is shaped by flexibility, innovation, and specialization. Developers aiming to succeed in the fast-paced tech ecosystems of the USA, UK, and Europe must invest in these evolving skillsets to remain competitive and future-proof their careers.
For organizations looking to turn ideas into reality, partnering with a trusted software development company can bridge the gap between technical complexity and business goals—especially when those developers are fluent in the languages, technologies, and trends that will define the next decade.
0 notes
Text
How to Build a Carpooling App Like Liftshare?

In today’s fast-paced world, urban congestion, high fuel costs, and environmental concerns have paved the way for sustainable commuting alternatives, one of which is carpooling. Apps like Liftshare have successfully tapped into this demand, enabling people to share rides, reduce costs, and minimize their carbon footprint. If you're looking to build a carpooling app like Liftshare, this guide will walk you through everything from concept to launch.
Why Build a Carpooling App?
The global ride-sharing market is projected to reach $226.45 billion by 2030, driven by increasing smartphone penetration and demand for eco-friendly transport solutions. A carpooling app offers a win-win for users and the environment—helping reduce traffic, lower fuel expenses, and cut down emissions.
Key Features of a Liftshare-Like Carpooling App
To compete in this space, your app must offer intuitive functionality, seamless navigation, and secure transactions. Here are the must-have features:
1. User Registration & Profiles
Allow users to sign up via email, phone, or social accounts and create detailed profiles including preferences, car details (for drivers), and reviews.
2. Ride Listings & Search
Drivers should be able to post available rides with pickup/drop locations, time, and price. Riders can search and filter based on location, time, and ratings.
3. Real-Time GPS & Route Mapping
Integrate mapping APIs (like Google Maps) for real-time route suggestions, trip tracking, and optimized ride matching.
4. In-App Messaging
Enable secure in-app communication between drivers and passengers to discuss trip details without exchanging contact info.
5. Booking & Payment Integration
Include easy ride booking, fare calculation, and secure payment gateways like Stripe, Razorpay, or PayPal.
6. Rating & Review System
Let users rate each other post-trip to build trust and community reliability.
7. Admin Dashboard
Manage users, monitor activities, set policies, and access analytics to ensure smooth operations and user satisfaction.
Technology Stack Recommendations
Frontend: React Native or Flutter (for cross-platform apps)
Backend: Node.js or Django with PostgreSQL or MongoDB
Maps & Location: Google Maps API, Mapbox
Payments: Stripe, PayPal, Razorpay
Authentication: Firebase Auth or OAuth 2.0
Step-by-Step Development Process
Step 1: Market Research & Planning
Analyze competitors like Liftshare, BlaBlaCar, and Via. Understand your audience and define USPs.
Step 2: Create Wireframes & UI/UX Design
Design user-friendly, minimal, and mobile-responsive interfaces to enhance engagement.
Step 3: Develop the MVP
Build a Minimum Viable Product with essential features to validate the concept and gather user feedback.
Step 4: Launch & Promote
Deploy the app on app stores and use SEO, social media marketing, and referral campaigns to drive downloads.
Step 5: Gather Feedback & Scale
Continuously monitor user feedback, fix bugs, and introduce advanced features like ride subscriptions, multi-route matching, or carbon footprint calculators.
Cost to Develop a Carpooling App
The cost to build a taxi app like Liftshare can range from $15,000 to $50,000+, depending on complexity, feature set, location of your development team, and tech stack used.
Final Words
Building a carpooling app like Liftshare requires more than just coding, it needs a user-first mindset, eco-conscious vision, and strong technical execution. If done right, your app can not only solve daily commuting issues but also contribute to a greener, more connected world. Contact a leading taxi app development company to build a ridesharing app for your business.
0 notes
Text
Building the Future of Finance: A Comprehensive Guide to Fintech App Development

In an age of rapid digital transformation, financial services are being revolutionized by technology at an unprecedented pace. From mobile banking to AI-powered investment platforms, Fintech apps are reshaping how we interact with money. Whether you're a startup founder or a product manager at an established financial institution, understanding the core elements of fintech app development is critical to staying ahead.
This guide walks you through the key stages, challenges, and trends in building a successful fintech application.
Why Fintech Matters More Than Ever
The global fintech market is projected to reach $936 billion by 2030, driven by increasing demand for contactless payments, online lending, digital wallets, and crypto-based services. Consumers expect seamless, secure, and personalized financial experiences—creating both opportunity and pressure for fintech innovators.
Types of Fintech Applications
Before development begins, it’s important to define the niche your app will serve. Common categories include:
Mobile Banking Apps (e.g., Revolut, Chime)
Peer-to-Peer Payment Systems (e.g., Venmo, PayPal)
Investment & Trading Platforms (e.g., Robinhood, eToro)
Lending Platforms (e.g., LendingClub)
Personal Finance Management Tools (e.g., Mint, YNAB)
Insurtech Apps
Blockchain/Crypto Wallets & Exchanges
Key Features of a Successful Fintech App
To meet user expectations and regulatory standards, your app must offer:
Secure Authentication (Biometrics, MFA)
Real-Time Transaction Updates
Data Encryption & Protection
Regulatory Compliance (e.g., KYC, AML, PSD2)
User-Friendly Interface (UI/UX)
Integration with Banks and Payment Gateways
AI/ML for Personalization or Risk Assessment
Tech Stack for Fintech App Development
Here’s a typical stack to consider:
Frontend:
Frameworks: React Native, Flutter, Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android)
Tools: Redux, Axios
Backend:
Languages: Node.js, Python (Django), Java (Spring Boot)
Databases: PostgreSQL, MongoDB
APIs: Plaid, Stripe, Paystack, Yodlee
Cloud Services: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
Security:
OAuth 2.0
SSL/TLS Encryption
Tokenization
End-to-End Encryption
Regulatory & Compliance Considerations
Navigating legal regulations is crucial. Depending on your region and service type, ensure compliance with:
PCI DSS (for card payments)
GDPR/CCPA (data privacy)
KYC & AML (identity and fraud prevention)
PSD2/Open Banking Regulations (EU/UK)
Working with a legal advisor or compliance consultant during the early development stages is highly recommended.
Development Process in 6 Key Stages
Market Research & Ideation Validate your idea by studying user needs, competitors, and industry trends.
Prototyping & UX/UI Design Create wireframes and interactive prototypes to visualize the user journey.
Architecture & Tech Stack Planning Choose scalable, secure, and interoperable technologies.
Core Development Build frontend, backend, and APIs while adhering to secure coding practices.
Testing & QA Conduct unit tests, security audits, and user acceptance testing (UAT).
Deployment & Maintenance Launch on app stores or web, monitor performance, and roll out updates continuously.
Common Challenges in Fintech App Development
Ensuring High-Level Security
Complying with Complex Financial Regulations
Achieving Smooth Integration with Third-Party APIs
Building User Trust in Early Adoption
Scaling Infrastructure to Handle High Volume Transactions
Future Trends in Fintech Development
Stay ahead by exploring these emerging trends:
AI-Powered Financial Advisors (Robo-Advisors)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Voice-Activated Banking
Biometric and Behavioral Security
Embedded Finance & Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Final Thoughts
Fintech app development is more than just coding a payment feature—it’s about transforming the way people experience finance. With the right strategy, technology, and security approach, you can build applications that are not only functional but genuinely change lives.
Whether you’re creating a neobank or an AI-driven investment tool, success lies in combining innovation, compliance, and trust.
0 notes
Text
API Integration Services in delhi with Investment solutions company in Delhi

In the digital age, seamless system integration is the backbone of innovation. Whether you’re running a fintech startup, an eCommerce platform, or a customer support service, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) help you connect, automate, and scale. Delhi, as a leading tech hub, is home to ekyc solution for stock broker some of the most experienced and advanced API service providers in India.
Let’s explore the top API service providers in Delhi including specialists in WhatsApp Business API integration, ekyc solution provider in delhi custom API development, and business automation.
Why APIs Matter in 2025
APIs enable different software systems to talk to each other. Whether you’re processing payments, verifying customer identity, or sending WhatsApp messages, APIs make it happen instantly and securely.
Faster automation
Improved user experience
Streamlined business processes
Seamless third-party integrations
This is why choosing the right API integration company in Delhi can give your business a serious competitive edge.
Top API Integration Services in Delhi
Several Delhi-based companies offer advanced API integration services that support businesses in fintech, healthcare, logistics, and retail. These services include:
Integration with third-party platforms like Razorpay, Google Maps, Twilio, Stripe
Connecting CRMs, ERPs, and internal tools
Automating lead capture, transactions, or order fulfillment
Cloud and on-premise API deployment
These companies ensure Investment solutions company in delhi end-to-end support—from planning and development to deployment and maintenance.
API Development Services in Delhi
Apart from integration, many businesses require custom API development services in Delhi to meet unique operational needs. Key features include:
RESTful & GraphQL API development
Scalable architecture with OAuth, JWT, and other authentication protocols
Secure data handling compliant with global standards
Real-time data exchange and analytics
Whether you’re building a customized solution in delhi platform or integrating multiple digital tools, custom APIs ensure customized solution in delhi everything runs smoothly and securely.
Leading API Integration Company in Delhi
Delhi houses several reputed firms specializing in full-cycle API solutions. A reliable API integration company in Delhi offers:
Consultation & architecture planning
Custom API development
Integration with legacy systems and third-party services
Monitoring and optimization
These providers often have a strong portfolio in industries like finance, healthcare, and logistics, helping clients automate and grow efficiently.
WhatsApp API Integration Service in Delhi
With over 500 million WhatsApp users in India, businesses are using the platform for customer engagement, support, and notifications. WhatsApp API integration services in Delhi offer:
Two-way messaging
Automated alerts and customer onboarding
Secure user verification and eKYC
Chatbot and CRM integration
Ideal for banks, fintechs, and eCommerce platforms, WhatsApp APIs boost engagement and streamline communication.
Top WhatsApp Business API Services in Delhi
The top WhatsApp Business API services in Delhi help brands communicate professionally at scale. These services include:
Green Tick verification
Customer support automation
Rich media messages (PDFs, images, CTA buttons)
Integration with CRM and ticketing platforms
With custom solutions for sectors API Integration Company in delhi like real estate, healthcare, education, and finance, these providers help businesses drive better results through chat automation.
Best WhatsApp Business API Provider in Delhi
Choosing the best WhatsApp Business API provider in Delhi means partnering with a team that offers:
Fast API deployment
99.9% uptime with scalable infrastructure
Smart analytics and campaign tracking
Seamless integration with existing tools
These providers ensure your WhatsApp channel becomes a reliable, high-converting customer communication tool.
Best WhatsApp API Integration Service in Delhi
When it comes to automation, customer experience, and lead generation, the best whatsapp api integration services in delhi go beyond just setup. They deliver:
End-to-end support from setup to training
Chatbot design and automation workflows
Integration with payment gateways and support systems
Custom APIs for KYC, onboarding, and order tracking
Whether you’re a startup or an enterprise, these services enable personalized customer journeys via WhatsApp.
Final Thoughts
From API integration to business messaging, Delhi is home to some of the most innovative API service providers in India. These companies enable brands to build one kyc solution in india smarter workflows, automate customer touchpoints, and scale operations with agility.
If your business depends on automation, customer communication, or cross-platform data exchange partnering with the right API experts in Delhi can drive measurable growth.
0 notes
Text
How to Integrate APIs in a Full Stack Web App (With Example)

Integrating APIs in a full stack web application is essential for building dynamic, feature-rich platforms that connect seamlessly with external services. API integration allows front-end and back-end components to communicate effectively, enabling real-time data exchange and efficient user experiences. In modern full stack development, RESTful APIs and GraphQL are commonly used to fetch and manipulate data. Technologies like Node.js, Express, React, Angular, and Vue.js simplify API requests through HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. Secure authentication methods like JWT and OAuth 2.0 ensure safe API communication. Leveraging third-party APIs like Stripe, Google Maps, or social login APIs can enhance functionality and boost app scalability. Full stack developers must also handle error management, rate limits, and asynchronous operations using tools like Axios or Fetch API. Proper integration of APIs accelerates web app performance, improves user interactivity, and supports seamless integration with cloud-based services and microservices architecture.
0 notes
Text
How to Integrate APIs in a Full Stack Web App (With Example)

Integrating APIs in a full stack web application is essential for building dynamic, feature-rich platforms that connect seamlessly with external services. API integration allows front-end and back-end components to communicate effectively, enabling real-time data exchange and efficient user experiences. In modern full stack development, RESTful APIs and GraphQL are commonly used to fetch and manipulate data. Technologies like Node.js, Express, React, Angular, and Vue.js simplify API requests through HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. Secure authentication methods like JWT and OAuth 2.0 ensure safe API communication. Leveraging third-party APIs like Stripe, Google Maps, or social login APIs can enhance functionality and boost app scalability. Full stack developers must also handle error management, rate limits, and asynchronous operations using tools like Axios or Fetch API. Proper integration of APIs accelerates web app performance, improves user interactivity, and supports seamless integration with cloud-based services and microservices architecture.
0 notes
Text
How APIs Power Modern Websites – A Think To Share IT Solutions Insight
Modern websites are no longer static brochures. They’re dynamic, data-driven platforms that interact with various services in real time. At the core of this interactivity lies a powerful and essential component: the API, or Application Programming Interface.
At Think To Share IT Solutions, we engineer websites that aren’t just visually compelling—they’re functionally superior, thanks to smart API integrations that enable real-time performance, seamless communication, and scalable features.
What is an API?
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of protocols and tools that allow software applications to communicate with each other. In web development, APIs act as bridges that connect your website to external or internal systems.
Instead of building every function from scratch, APIs allow developers to integrate existing, trusted services—making websites faster, more reliable, and more scalable.
How APIs Power Modern Websites
1. Dynamic Content Delivery
APIs allow websites to fetch and display real-time content from a database or CMS without refreshing the page. This improves performance and user experience.
Example: A blog or news portal pulling updated articles from a headless CMS like Strapi or WordPress via REST API.
2. User Authentication and Access Control
APIs handle secure user logins and permission-based access. Authentication services like Google OAuth or Auth0 rely entirely on API interactions.
Example: "Sign in with Google" uses an external API to verify the user's identity securely without storing sensitive data on your own servers.
3. Third-Party Service Integrations
APIs enable seamless integration with third-party platforms for added functionality.
Function
API Providers
Payments
Stripe, Razorpay, PayPal
Email Marketing
Mailchimp, SendGrid
Analytics
Google Analytics, Matomo
Customer Support
Zendesk, Intercom
Maps & Location
Google Maps API, Mapbox
These integrations enhance user experience without compromising performance or security.
4. Real-Time Features and Updates
Websites that support live chat, order tracking, or instant notifications use APIs to communicate with real-time databases.
Example: Firebase and Pusher APIs power real-time chat interfaces or live delivery status updates.
5. E-Commerce Functionality
Modern eCommerce websites rely on APIs to handle inventory updates, pricing changes, order processing, and shipping logistics.
What We Implement:
Cart management via REST or GraphQL APIs
Real-time pricing and availability updates
Shipment tracking using courier APIs (e.g., Delhivery, Shiprocket)
6. Headless Architecture
In a headless setup, APIs serve as the communication layer between the front-end and the back-end. This decoupling improves performance and allows for more flexible design and delivery across platforms.
Example: Using Next.js (for the front-end) and Strapi or Sanity (as the headless CMS), data is fetched via API endpoints and rendered statically or server-side for speed and SEO.
Benefits of API-Driven Web Development
Benefit
Explanation
Faster Deployment
Plug in pre-built services instead of coding everything from scratch
Scalability
Easily add new features or services without overhauling your system
Enhanced Security
Offload sensitive functions like payments to trusted platforms
Maintainability
Isolated services reduce complexity and ease troubleshooting
Cross-Platform
Share the same API with mobile apps, web apps, and IoT devices
How Think To Share Implements API-Driven Architecture
Our development process incorporates API planning from the very beginning:
Architecture Planning: Identify necessary APIs based on business goals
Security: Implement OAuth2, JWT tokens, and rate limiting for secure access
Performance: Use caching mechanisms (Redis, CDN) to reduce API load
Monitoring: Set up logging, error tracking, and fallback handling for resilience
Documentation: Provide detailed API docs using tools like Swagger or Postman
Final Thoughts: APIs Are the Backbone of Modern Websites
APIs have evolved from technical add-ons to mission-critical infrastructure for digital platforms. Whether you're running a website, mobile app, or enterprise software, APIs allow you to build faster, scale smarter, and connect deeper with users.
At Think To Share IT Solutions, we design and develop high-performance web systems that are modular, connected, and built for long-term growth—powered by reliable, secure, and well-integrated APIs.
0 notes
Text
How to Use APIs in Your Web Development Projects
API integration for web development might sound intimidating at first, but it’s actually one of the coolest tools in your developer toolkit. You’ve probably heard the term “API” tossed around like candy in dev circles and wondered what all the buzz is about. Well, let’s clear the fog and walk through how you can start using APIs in your web projects — without frying your brain or your browser.

APIs are like digital bridges that help your site talk to other services, fetch data, and offer cool features you didn’t build from scratch. With a little practice and the right guide (hello, Coding Brushup!), API integration becomes an essential tool in your developer toolbox.
🧩What Are APIs and Why Should You Use Them?
An API (Application Programming Interface) is basically a set of rules that lets one program interact with another. When you use Google Maps on your site or pull data from weather apps, you’re using an API integration for web development.
You don’t need to build everything yourself when you can connect your site to reliable services through REST APIs. They handle the heavy lifting while you focus on creating an awesome user experience.
Using REST APIs in web projects helps you save time, reduce bugs, and offer dynamic content without hosting it all yourself.
🔐 Understanding API Authentication Methods
Before you start slinging data around, you’ll need to understand how to access APIs safely. That’s where API authentication methods come in.
Most APIs require some kind of security key, like an API token, OAuth 2.0, or a basic access token. Think of these like keys to a private club — you can’t get in without showing your credentials.
Some APIs let you start without a login (great for testing), but for most real-world usage, authentication is a must. And don’t worry — it’s not as scary as it sounds. Sites like Coding Brushup’s API tutorials make it super beginner-friendly.
📦 JSON and API Data Handling: The Magic Format
When you request data from an API, it often comes back in a format called JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). It’s lightweight, human-readable, and plays well with JavaScript — your new best friend in frontend API calls.
You’ll use JSON and API data handling skills to take that data and display it on your website in a user-friendly way. Want to show user comments from a third-party service? Fetch the data with JavaScript and populate your webpage with it. Magic.
Don’t forget — you can handle API data on the backend, too. Whether you’re using Node.js or Python, backend API calls let your server talk to other services securely and efficiently.
🚀 Putting It All Together: Frontend and Backend API Calls
Once you understand the basics, it’s time to use frontend and backend API calls together for seamless, full-stack magic. Your frontend might display live stock prices while your backend stores user preferences. Together, they create a rich, responsive experience for users.
Want to really stand out? Add APIs like Twitter feeds, weather forecasts, or payment gateways to your projects. API integration helps your web apps stay useful, modern, and engaging.
📘 Learn Faster with Coding Brushup
If you’re feeling excited but a little overwhelmed, don’t worry — you’re not alone. That’s exactly why Coding Brushup exists. Their API tutorials are designed to walk you through the basics step by step, with real code examples, video guides, and even mini-projects.
Whether you’re building your first app or adding advanced API features to a client site, Coding Brushup makes it feel doable — and even fun!
🏁 Final Thoughts
So there you have it. APIs aren’t scary monsters. They’re your backstage passes to powerful, data-rich, and interactive websites. Once you get the hang of API integration for web development, you’ll never want to go back to static pages again.
You just need to understand how APIs work, handle JSON data, use authentication methods, and write a few frontend or backend API calls. Piece of cake, right?
And hey, don’t forget — Coding Brushup has your back every step of the way. Happy coding!
0 notes