#Guyanese History
Text

Good morning 💜 #BHM
Black History Month
Edmond Montague "Eddy" Grant
Muscian, vocalist, producer, Ice record label owner, music publisher, Blue Wave studio owner and owner of Ice Records.
Eddy Grant was born 5 March 1948 in Plaisance, British Guyana. He came to England in 1960 when his parents sent for him to join them in Stoke Newington London.
In 1965, Eddy formed his first band, the Equals, long before the days of 2-Tone, the group was unique in being the first of Britain's multi-racial bands to receive any recognition. The West Indian contingent comprised of Jamaican-born singer Lincoln Gordon, with his twin brother Derv and Grant both on guitar, while the rhythm section of bassist Patrick Lloyd and drummer John Hall were native-born white Englishmen.
Eddy went onto have a successful solo career both sides of the Atlantic, his hit Electric Avenue was inspired by the Brixton riots.
Eddy Grant stands among an elite group of artists as one who has not just merely moved successfully across the musical spectrum, but has actually been at the forefront of genres and even created one of his own. From pop star to reggae radical, musical entrepreneur to the inventor of ringbang, the artist has cut a swath through the world of music and made it his own.
Credit:
Jo-Ann Greene
Source:
https://www.allmusic.com/artist/eddy-grant-mn0000796763/biography
#good morning#black art#positive vibes#Eddy Grant#black british history#black history#Guyanese History
1 note
·
View note
Text

Indian immigrants to Guyana in the 1800’s
To be precise, I am an Indo-Guyanese-American: The mother of all hyphenated identities and an illustration of a historic journey from India to the Caribbean. This heritage is commonly packaged in a number of different terms, all of which are heavily used as referential identifiers: Indo-Guyanese. Indo-Caribbean. Caribbean. West Indian. Indian. It is most aptly described as the Indo-Caribbean experience—an experience that is shared by Indians living throughout the Caribbean diaspora and thus serving as the blueprint for my existence.
This unique cultural disposition is why the Indo-Caribbean are able to culturally identify with public figures ranging from Hasan Minhaj to Nicki Minaj. It is why bursts of Caribbean intonation in Rihanna’s voice blanket me in the comfort of home, while the ballads of A.R. Rahman awaken pained demons within me, crying to connect with a history that was ripped from my hands long before I was born.
My parents hail from Guyana, a small country on the northern coast of South America. Guyana is one of the original colonies of the British West Indies and, although not located in the Caribbean Sea, the CARICOM Seat of Secretariat is located in Georgetown, Guyana, thus rendering the country a crucial member of the Caribbean family. [Read more]

55 notes
·
View notes
Text
a random guy in the hall of this funeral home approached us today and when my aunt asked if he was here to pay respects, the guy responds "no, I do not know the deceased. I come here a lot to see if anyone from Guyana is here. are any of you Guyanese?". my aunt points out that my cousin-in-law's mom is and the guy proceeds to infodump the history of colonial Guyana to her along with his work history experience in Canada. He doesn't even tie them together outside of making a single comment, he just gives us like, two different lectures while we're waiting for the funeral staff to let us into the room.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Decolonial Marxism - Walter Rodney
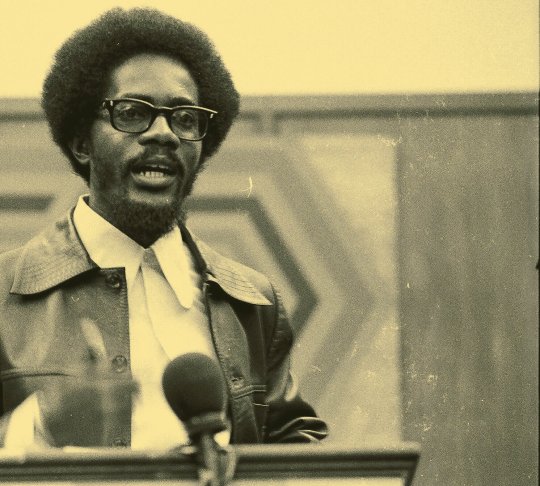

Hello friends!
Today's recommendation continues the focus on revolutionary thinking from important figures in the Global South with a compendium of wonderful essays that are incredibly relevant today: "Decolonial Marxism" by Walter Rodney.
Walter Rodney was am inimitable historian, educator, and political activist who forwarded Pan-Africanist and Marxist thinking and action since the 1960's. His groundbreaking historiography on Guyana and research in Tanzania produced works like "How Europe Underdeveloped Africa," his magnum opus that forwarded a rigorous analysis on the ways colonialism ransacked the African continent as a piece of postcolonial literature. He also became actively involved in the Black Power movement, fostering alliances with prominent figures like Angela Davis and Kwame Ture. His tireless efforts to unite oppressed peoples around the globe earned him admiration and support from many, alongside angering institutions like the US-backed Guyanese government which were likely sources of his assassination in 1980.
"Decolonial Marxism" delves into the intersection between Marxism and the postcolonial struggles faced by former colonies around the world, challenging the view that these theories are ultimately Eurocentric. In this collection of posthumous essays, Rodney evaluates how Marxism can be harnessed to address the structural issues perpetuated by colonialism and foster decolonization, while also criticizing actually Eurocentric views present on this revolutionary tradition.
Incredible strengths of this view lie in Rodney's analysis of how class society is intrinsically connected to the legacy of slavery and colonialism alongside a study of African history on its own terms as a Marxist, alongside his thinking of what a Pan-Africanist Marxist revolutionary struggle can look like. He takes inspiration from Tanzania's Ujamaa to flesh some of these investigations out, which I highly recommend.
"Decolonial Marxism" goes beyond theory; it provides historical examples and case studies that demonstrate the practical implications of anti-colonial Marxist thought, which makes it a must read in my book.
#book blog#book review#bookblr#decolonisation#marxism#anti colonialism#walter rodney#pan africanism#global south
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
there is shooting on the tv.
and the heroine comes in, guns blazing, sexy and witty with all the right answers i wish i had
or
and the david attenborough type walks me through it so i learn something about american history
british history, sudanese, thai, australian, mexican, yemeni, nigerian, peruvian, guyanese, haitian, turkmen, irish, palestinian,
take your pick, any of them work
or
and when the names of the dead scroll i know every single one is younger than me
or
and i see in the background a neighborhood i used to drive through when i still lived in my hometown
or
and a reporter says the emts got shot at, i wonder if i knew any of them
ems is a tight-knit community
or
and i don't get the appeal of these violent video games,
i just remember all the articles i've read about how constant exposure to violent media puts children at risk for normalizing or
gd forbid,
engaging in violence themselves
or
and the police saved the day,
actors are much more competent
and movies are much more generous
or
i could shut the damn screen off.
nobody is shooting at me here
i'm going to make myself some tea
#feminism#poetry#feminist poetry#feminist poems#feminist writing#writing#gun violence#gun reform#social justice poetry#social justice writing#fiction#violence in video games#poems about gun violence#gun violence survivors#gun control#gun control now
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Jonestown Massacre
The Jonestown massacre was, before 9/11, the largest single incident of intentional civilian death in American history. More than 900 people died, many children. It was also a devastating cultural trauma: the end of the last strains of a certain kind of 1960s idealism and 1970s radicalism. Jonestown’s legacy lives on in the ironic phrase “drink the Kool-Aid”. (In actuality it was Fla-Vor-Aid.)
Although he would later become a symbol of the darker side of the west coast counterculture, Jim Jones was born to a poor family in Indiana. Described as an intelligent and strange child, Jones was instinctively attracted to religion, especially charismatic Christian traditions like Pentecostalism. He cut his teeth as a street preacher, and was, unusually for the time and place, a passionate advocate for racial equality. Jones’s idiosyncratic blend of evangelical Christianity, New Age spirituality and radical social justice attracted an enthusiastic following. He called his burgeoning church the Peoples Temple.
Although Jones’s followers would later be stereotyped as sinister, brainwashed idiots, the journalist Tim Reiterman argues in his seminal book on the subject that many were “decent, hardworking, socially conscious people, some highly educated”, who “wanted to help their fellow man and serve God, not embrace a self-proclaimed deity on earth”. The Peoples Temple advocated socialism and communitarian living and was racially integrated to an exceptional standard rarely matched since.
In 1965, when Jones was in his mid-30s, he ordered the Peoples Temple moved to California. He drifted away from traditional Christian teachings, describing himself in messianic terms and claiming he was the reincarnation of figures like Christ and Buddha. He also claimed that his goal all along was communism, and, in a twist on the famous dictum that religion is the “opiate of the masses”, that religion was merely his way of making Marxism more palatable.
By the 1970s, the Peoples Temple, now based in San Francisco, had gained significant political influence. Jones’s fierce advocacy for the downtrodden earned him the admiration of left-wing icons like Angela Davis and Harvey Milk and the support of groups like the Black Panthers – a tragically misguided political affinity, given that more than two-thirds of Jonestown’s eventual victims were African American.
There were signs, however, of a sinister undercurrent to the Peoples Temple. Followers were expected to devote themselves completely to the church’s utopian project: they turned over their personal wealth, worked long hours of unpaid labor for the church and often broke contact with their families. They were expected to raise their children within the commune. As a show of commitment, Peoples Temple members were asked to sign false testimonials that they had molested their children, which the church kept for potential blackmail.
In his 1980 study of Jonestown, the writer Shiva Naipaul, younger brother of VS Naipaul, argued that the Peoples Temple was at heart a fundamentalist religious project – “obsessed with sin and images of apocalyptic destruction, authoritarian in its innermost impulses, instinctively thinking in terms of the saved and the damned”.
The result, Naipaul wrote, “was neither racial justice nor socialism but a messianic parody of both”.
Jones, who had long believed the US was in danger of imminent nuclear holocaust, had been searching for a place where his church would be “safe” during an apocalyptic event. A magazine article alleging abuse in the Peoples Temple spurred Jones’s desire to relocate. He chose Guyana, a former British colony in South America whose socialist regime was politically sympathetic.
In 1977 the Peoples Temple moved its headquarters to a remote area of Guyanese wilderness. Here, Jones declared, they could build a utopian society without government or media meddling. Battling an oppressive tropical climate and limited resources, they began to convert the dense jungle into a working agricultural commune, soon known as “Jonestown”.
The church delivered Jones’s rambling monologues to Jonestown’s inhabitants by megaphone as they worked. In the evenings they attended mandatory propaganda classes. Jones’s writ was enforced by armed guards called the “Red Brigade”.
Jonestown had little reason to expect interference from Guyana – a “cooperative republic” whose government happily ignored signs of the cult’s authoritarian and paranoid bent. Back in the US, however, parents of Jonestown inhabitants – concerned by the strange letters, or lack of letters, they received from their children – had been lobbying the government to investigate. After a family in the US won a custody order for a child in Jonestown, paranoia escalated. The commune became an armed camp, ringed by volunteers with guns and machetes, threatening to fight outsiders to the death.
During the siege, Black Panthers Huey Newton and Angela Davis spoke to Jonestown inhabitants by radio patch to voice solidarity. Davis told Jonestown inhabitants that they were at the vanguard of revolution, and right to resist what she called “a profound conspiracy” against them.
Sometime during this period Jonestown began drills called “white nights”, in which inhabitants would practice committing mass suicide.
At the behest of concerned family members in the US, the California congressman Leo Ryan organized a delegation of journalists and others to make a fact-finding mission to Jonestown.
The delegation arrived at Jonestown on 17 November 1978 and received a civil audience from Jones, but the visit was hastily called short on 18 November after a member of the commune tried to stab Ryan. The delegation headed back to the airstrip, accompanied by a dozen Jonestown inhabitants who had asked to leave the commune, and escorted by Jones’s watchful deputies.
The delegates never made it off the ground. As they boarded the planes, their escorts drew guns and opened fire. They shot Ryan dead, combing his body with bullets to make certain, and killed four others – including two photographers who captured footage of the attack before dying. Wounded survivors ran or dragged themselves, bleeding, into the forest. (One of Ryan’s aides, Jackie Speier, survived five gunshots and is now a congresswoman representing California’s 14th district.)
Back at Jonestown, Jones announced that it was time to undertake the final “white night”. To quell disagreement, he told inhabitants that Congressman Ryan had already been murdered, sealing the commune’s fate and making “revolutionary suicide” the only possible outcome.
The people of Jonestown, some acceptant and serene, others probably coerced, queued to receive cups of cyanide punch and syringes. The children – more than 300 – were poisoned first, and can be heard crying and wailing on the commune’s own audio tapes, later recovered by the FBI.
When Guyanese troops reached Jonestown the next morning, they discovered an eerie, silent vista, frozen in time and littered with bodies. A tiny number of survivors, mainly people who had hidden during the poisoning, emerged. One elderly woman, who slept through the entire ordeal, awoke to discover everyone dead. Jones was found dead of an apparently self-inflicted gunshot.
47 notes
·
View notes
Text

Jonestown Massacre
The Jonestown massacre was, before 9/11, the largest single incident of intentional civilian death in American history. More than 900 people died, many children. It was also a devastating cultural trauma: the end of the last strains of a certain kind of 1960s idealism and 1970s radicalism. Jonestown’s legacy lives on in the ironic phrase “drink the Kool-Aid”. (In actuality it was Fla-Vor-Aid.)
Although he would later become a symbol of the darker side of the west coast counterculture, Jim Jones was born to a poor family in Indiana. Described as an intelligent and strange child, Jones was instinctively attracted to religion, especially charismatic Christian traditions like Pentecostalism. He cut his teeth as a street preacher, and was, unusually for the time and place, a passionate advocate for racial equality. Jones’s idiosyncratic blend of evangelical Christianity, New Age spirituality and radical social justice attracted an enthusiastic following. He called his burgeoning church the Peoples Temple.
Although Jones’s followers would later be stereotyped as sinister, brainwashed idiots, the journalist Tim Reiterman argues in his seminal book on the subject that many were “decent, hardworking, socially conscious people, some highly educated”, who “wanted to help their fellow man and serve God, not embrace a self-proclaimed deity on earth”. The Peoples Temple advocated socialism and communitarian living and was racially integrated to an exceptional standard rarely matched since.
In 1965, when Jones was in his mid-30s, he ordered the Peoples Temple moved to California. He drifted away from traditional Christian teachings, describing himself in messianic terms and claiming he was the reincarnation of figures like Christ and Buddha. He also claimed that his goal all along was communism, and, in a twist on the famous dictum that religion is the “opiate of the masses”, that religion was merely his way of making Marxism more palatable.
By the 1970s, the Peoples Temple, now based in San Francisco, had gained significant political influence. Jones’s fierce advocacy for the downtrodden earned him the admiration of left-wing icons like Angela Davis and Harvey Milk and the support of groups like the Black Panthers – a tragically misguided political affinity, given that more than two-thirds of Jonestown’s eventual victims were African American.
There were signs, however, of a sinister undercurrent to the Peoples Temple. Followers were expected to devote themselves completely to the church’s utopian project: they turned over their personal wealth, worked long hours of unpaid labor for the church and often broke contact with their families. They were expected to raise their children within the commune. As a show of commitment, Peoples Temple members were asked to sign false testimonials that they had molested their children, which the church kept for potential blackmail.
In his 1980 study of Jonestown, the writer Shiva Naipaul, younger brother of VS Naipaul, argued that the Peoples Temple was at heart a fundamentalist religious project – “obsessed with sin and images of apocalyptic destruction, authoritarian in its innermost impulses, instinctively thinking in terms of the saved and the damned”.
The result, Naipaul wrote, “was neither racial justice nor socialism but a messianic parody of both”.
Jones, who had long believed the US was in danger of imminent nuclear holocaust, had been searching for a place where his church would be “safe” during an apocalyptic event. A magazine article alleging abuse in the Peoples Temple spurred Jones’s desire to relocate. He chose Guyana, a former British colony in South America whose socialist regime was politically sympathetic.
In 1977 the Peoples Temple moved its headquarters to a remote area of Guyanese wilderness. Here, Jones declared, they could build a utopian society without government or media meddling. Battling an oppressive tropical climate and limited resources, they began to convert the dense jungle into a working agricultural commune, soon known as “Jonestown”.
The church delivered Jones’s rambling monologues to Jonestown’s inhabitants by megaphone as they worked. In the evenings they attended mandatory propaganda classes. Jones’s writ was enforced by armed guards called the “Red Brigade”.
Jonestown had little reason to expect interference from Guyana – a “cooperative republic” whose government happily ignored signs of the cult’s authoritarian and paranoid bent. Back in the US, however, parents of Jonestown inhabitants – concerned by the strange letters, or lack of letters, they received from their children – had been lobbying the government to investigate. After a family in the US won a custody order for a child in Jonestown, paranoia escalated. The commune became an armed camp, ringed by volunteers with guns and machetes, threatening to fight outsiders to the death.
During the siege, Black Panthers Huey Newton and Angela Davis spoke to Jonestown inhabitants by radio patch to voice solidarity. Davis told Jonestown inhabitants that they were at the vanguard of revolution, and right to resist what she called “a profound conspiracy” against them.
Sometime during this period Jonestown began drills called “white nights”, in which inhabitants would practice committing mass suicide.
At the behest of concerned family members in the US, the California congressman Leo Ryan organized a delegation of journalists and others to make a fact-finding mission to Jonestown.
The delegation arrived at Jonestown on 17 November 1978 and received a civil audience from Jones, but the visit was hastily called short on 18 November after a member of the commune tried to stab Ryan. The delegation headed back to the airstrip, accompanied by a dozen Jonestown inhabitants who had asked to leave the commune, and escorted by Jones’s watchful deputies.
The delegates never made it off the ground. As they boarded the planes, their escorts drew guns and opened fire. They shot Ryan dead, combing his body with bullets to make certain, and killed four others – including two photographers who captured footage of the attack before dying. Wounded survivors ran or dragged themselves, bleeding, into the forest. (One of Ryan’s aides, Jackie Speier, survived five gunshots and is now a congresswoman representing California’s 14th district.)
Back at Jonestown, Jones announced that it was time to undertake the final “white night”. To quell disagreement, he told inhabitants that Congressman Ryan had already been murdered, sealing the commune’s fate and making “revolutionary suicide” the only possible outcome.
The people of Jonestown, some acceptant and serene, others probably coerced, queued to receive cups of cyanide punch and syringes. The children – more than 300 – were poisoned first, and can be heard crying and wailing on the commune’s own audio tapes, later recovered by the FBI.
When Guyanese troops reached Jonestown the next morning, they discovered an eerie, silent vista, frozen in time and littered with bodies. A tiny number of survivors, mainly people who had hidden during the poisoning, emerged. One elderly woman, who slept through the entire ordeal, awoke to discover everyone dead. Jones was found dead of an apparently self-inflicted gunshot.
15 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi! i hope you dont mind the ask! im looking to set up a period fc and just looking to get some fc help! i want the group to be diverse as possible and was hoping you could help with some fc suggestions?
Kathy Bates (1948) - American Horror Story as Madame LaLaurie.
Richard Ridings (1958) - Dickinson.
Michelle Yeoh (1962) Chinese Malaysian - The School for Good and Evil.
Zahn McClarnon (1966) Hunkpapa Lakota, Sihasapa Lakota, White - History of the World, Part II.
Sophie Okonedo (1968) Nigerian / Ashkenazi Jewish - The Wheel of Time, The Hollow Crown.
Adrian Lester (1968) Afro Jamaican - Mary Queen of Scots.
Yuliya Aug (1970) - Ekaterina.
Warwick Davis (1970) - Willow - has spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita.
Danny Sapani (1970) Ghanaian - in Harlots.
Nick Frost (972) - The Nevers & Into the Badlands.
Matt Berry (1974) - Year of the Rabbit.
Caroline Chikezie (1974) Igbo Nigerian - The Shannara Chronicles.
Ashlie Atkinson (1977) - is queer - The Gilded Age.
Karthi (1977) Tamil Indian - Ponniyin Selvan.
Oscar Isaac (1979) Cuban-Guatemalan-Spanish - In Secret.
Nonso Anozie (1979) Igbo Nigerian - Cinderella.
Adeel Akhtar (1980) Pakistani / Indo Kenyan - Enola Holmes.
Chrissy Metz (1980) - American Horror Story as Ima ‘Barbara’ Wiggles.
Angel Coulby (1980) Afro Guyanese / White - Merlin.
Mahesh Jadu (1982) Indo Mauritian - The Witcher.
Ella Smith (1983) - The Nevers.
Gugu Mbatha-Raw (1983) Zulu South African / White - Belle.
Joel Fry (1984) Afro Jamaican and White - Drunk History UK.
Freida Pinto (1984) Konkani Indian - Mr. Malcolm's List.
Sterling Sulieman (1984) African-American - Still Star-Crossed.
Zawe Ashton (1984) Ugandan / White - Mr. Malcolm's List - has spoken up for Palestine!
Sonoya Mizuno (1986) Japanese / Spanish-Argentinian, White - House of The Dragon.
Jodie Turner-Smith (1986) Afro Jamaican - Anne Boleyn.
Deepika Padukone (1986) Indian - Bajirao Mastani.
Lashana Lynch (1987) Afro Jamaican - Still Star-Crossed.
Susan Wokoma (1987) Nigerian - Enola Holmes - has spoken up for Palestine!
Pippa Bennett-Warner (1988) Jamaican and Kittitian - Harlots.
Stefanie Reinsperger (1988) - Maria Theresa.
Aiysha Hart (1988) Saudi / White - Atlantis - has spoken up for Palestine!
Gratiela Brancusi (1989) Romani and White - 1883 - has spoken up for Palestine!
Dalmar Abuzeid (1990) Sudanese - Anne with An E.
Sophia Nomvete (1990) Iranian and Black - Rings of Power.
Himesh Patel (1990) Indian - The Aeronauts and The Luminaries.
Lolly Adefope (1990) Nigerian - in Ghosts - has spoken up for Palestine!
Paapa Essiedu (1990) Ghanaian - Anne Boleyn - has spoken up for Palestine!
Jacob Anderson (1990) Black Caribbean and White - Interview with the Vampire.
Ebonee Noel (1990) Afro Guyanese - Still Star-Crossed.
Dianne Doan (1990) Chinese - Warrior.
Katie Findlay (1990) Chinese, Portuguese-Macanese, White - Walker: Independence - is queer (they/them) I'm unsure if they're referring to gender and/or sexuality as queer but I'm under the assumption it's both! - has spoken up for Palestine!
Liu Yuning (1990) Chinese - A Journey to Love.
Dev Patel (1990) Gujarati Indian - The Personal History of David Copperfield.
Sope Dirisu (1991) Nigerian - Mr. Malcolm's List.
Medalion Rahimi (1991) Iranian, Mizrahi Jewish - Still Star-Crossed.
Ashley Park (1991) Korean - Mr. Malcolm's List.
Ronke Adekoluejo (1991) Nigerian - Chevalier.
Kiran Sonia Sawar (1991) Pakistani - The Nevers.
Denée Benton (1991) African-American - The Gilded Age - has spoken up for Palestine!
Emma D’Arcy Actor (1992) - is non-binary (they/them) - House of Dragons - has spoken up for Palestine!
Anna Shaffer (1992) Black and White / Jewish - The Witcher.
Devon Terrell (1992) African-American / Anglo-Indian - Cursed.
Crystal Clarke (1993/1994) Trinidadian and Guyanese - Sanditon.
Kelvin Harrison Jr. (1994) African-American - Chevalier.
David Licauco (1994) Filipino - Maria Clara at Ibarra.
Julie Anne San Jose (1994) Filipino - Maria Clara at Ibarra.
Kit Young (1994) Ugandan / White - Shadow and Bone.
Lola Petticrew (1995) - is non-binary (they/them) - Anne Boleyn.
Jack Wolfe (1995) - is queer - Shadow and Bone - has spoken up for Palestine!
Maddison Jaizani (1995) Iranian / White - Versailles.
Alisha Boe (1997) Somali / White - The Buccaneers - has spoken up for Palestine!
Madeleine Madden (1997) Eastern Arrernte, Arrernte, Kalkadoon, White / Gadigal and Bundjalung - The Wheel of Time.
Chen Muchi (1997) Chinese - The Starry Love.
Archie Renaux (1997) Indian and White - Shadow and Bone.
Sophie Wilde (1998) Ivorian / White - Tom Jones.
Josie Totah (2001) Palestinian / Lebanese and White - is a trans woman - is a trans woman - The Buccaneers.
Aaron Cobham (?) Black British - The Spanish Princess.
Stephanie Levi-John (?) Black - The Spanish Princess.
Akil Largie (?) Black - Sense and Sensibility.
Bayo Gbadamosi (?) Black British - The Great.
Thalissa Teixeira (?) Afro Brazilian - Anne Boleyn.
Matthew Broome (?) Black - The Buccaneers.
Colette Dalal Tchantcho (?) Cameroonian / Sunni Kuwaiti - Dangerous Liaisons.
Scott Turner Schofield (?) - is a trans man - The Conductor.
Gladly! I'd also suggest checking out @periodfcnetwork's amazing directory and page, maybe they can help find more disabled, fat and/or trans suggestions not listed because I sadly couldn't find many!
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
I am an African American woman who is also half Guyanese. I feel a deep need to visit Guyana because I know nothing about my roots. As a solo traveler currently in South America, I’ve been reflecting on my identity and experiences.
Being American can be embarrassing at times due to the ignorance we often exhibit. More of us need to travel, as doing so can broaden our perspectives and reduce our ignorance, provided we engage with locals and are open to learning. There is so much our history textbooks didn’t teach us and even lied about. America and Americans have a troubling reputation worldwide. When I ask people from other countries about racism, they often say it’s primarily an American issue (not that it doesn’t exist elsewhere, but we seem particularly fixated on race, and I understand why).
We need to realize that two things can be true at once and that everyone's experiences are valid. We should not try to fit others into boxes just to make ourselves comfortable. This lesson has been one of the greatest I’ve learned from traveling.
Stay blessed. 💚
4 notes
·
View notes
Text



By: Wilfred Reilly
Published: Jun 28, 2023
Former president Barack Obama no longer believes that non-white Americans can be successful in the US.
I am being a bit glib, but only a bit. During a podcast interview last week with former Democratic Party apparatchik David Axelrod, Obama criticised Tim Scott, black Republican senator for South Carolina and 2024 presidential candidate. Scott is well-known for his optimism and belief in the American Dream, previously stating that ‘I know America is a land of opportunity, not a land of oppression’. Taking a clear swipe at Scott, Obama said: ‘I think there’s a long history of African American or other minority candidates within the Republican Party who will validate America and say, “Everything’s great, and we can make it”.’
According to Obama, that belief is untrue. Noting several elements of America’s racist past, Obama declared: ‘We can’t just ignore all that and pretend as if everything’s equal and fair. We actually have to walk the walk and not just talk the talk.’ Before signing off from the show, he went on to describe black and other ethnic minorities as ‘rightly sceptical’ of positive racial messages like those of Senator Scott.
Beyond the sheer bizarreness of a former national leader describing his own country as a racist hole, Obama is just plain wrong. Evidence shows that it is simply not true that non-white Americans can’t make it in the US.
This claim is quickly disproven by a look at the Census Bureau’s lists of household income by ethnicity. The wealthiest population group in the US is not white Americans, but rather Indian Americans. This group brings in a median household income of $142,000 annually, in comparison to just under $75,000 for Caucasians. The second-richest group is Taiwanese Americans, who pull down $119,000 per year for each household. In fact, most of the top 10 highest-earning groups (and all of those consistently averaging six figures per year) are racial minorities – Indians, the Taiwanese, Filipinos ($101,000), Pakistanis ($102,000), Sri Lankans ($97,000), Iranians ($96,000) and Chinese Americans ($93,000).
In contrast, one of the poorer groups listed is white Appalachian Americans, at $50,000 per home per year. On the other hand, black immigrants tend to do fairly well, with the Guyanese, Ghanaians, Barbadians, Trinidadians and Nigerians all coming in at above the $70,000 per year mark. Jamaicans ($66,000) and other West Indians ($64,000) also come close. Nigerian immigrants are one of the best-educated groups in the US, ahead of both Asian and white Americans.
African Americans do quite a bit worse. However, the median black household income as of 2021 – an Appalachia-like $47,000 – still ranks higher than the median household incomes for the UK, Austria and Italy. In any case, the high earnings of African and Caribbean immigrants demonstrate that African Americans’ low performance cannot be due to racism. Rather, it is largely down to the fact that black households tend to have fewer people in them.
The black single-motherhood / father-absence rate, at least at the time of birth, currently sits at a staggering 77 per cent. Simply put, a family consisting of a single mother and infant will earn less lucre than one that includes a husband, wife and employed teenagers. While this situation is far from ideal, there are still many individual black Americans, whether they come from stable families or not, who are extremely successful by any global or historical standard. Tim Scott was himself born into a poor, single-parent household and yet nonetheless managed to rise to the position of senator.
Obama’s ‘cannot succeed’ claim is strange given the reality of modern America, and given his own background and path through life. Simply put, Obama is not a descendant of American slaves. His mother was an upper-middle-class white woman from Kansas and his father was a prominent Kenyan economist. Obama grew up primarily in well-off enclaves, such as in upscale districts of Hawaii’s Honolulu and Indonesia’s Jakarta. Young Obama was surrounded by other wealthy non-white groups and expats. While this might be a little politically incorrect to say out loud, watching him try to explain the US black experience to Scott, a scion of the Carolina cotton country, borders on the surreal.
Interestingly, attitudes like Obama’s (although he didn’t always talk like this) seem to be getting more common among first- and second-generation minority immigrants to the US. This is despite the fact that most of these people have never had a ‘back of the bus’ experience in their lives. To give one typical example, writer and race activist Saira Rao started a fracas on Twitter last week by saying:
‘White people love to say “not everything is about race”. This from the people who committed genocide of Indigenous people, genocide and enslavement of African people. Those behind the Chinese Exclusion Act, Operation Wetback and the Muslim ban. You made everything about racism.’
The remarkable thing about this claim is that even those events on Rao’s list that did happen (US black genocide and a national ‘Muslim ban’ are simply made up) will not have impacted her in any way. Rao is a second-generation Indian American. Only the Exclusion Act might have been potentially relevant to a legal immigrant from Asia. And even then, the act was passed in 1882 and formally repealed 80 years ago. Attitudes like Rao’s are part of a broader trend of post-1965 migrants making embarrassing attempts to link themselves to historical slavery or Jim Crow.
However silly they may sound, the beliefs held by the likes of Obama and Rao can have serious negative impacts. Imagine being told for almost all your life that you are unlikely to succeed. That every social interaction is rigged against you. That the people who seem like your closest football and lunchroom buddies are likely liars and secret racists. How might this affect you?
Hard data give a clear answer. A 2021 study found that these demoralising takes have a real, measurable impact on people. Simply reading a typical despairing passage about ‘systemic racism’ from woke authors like Ta-Nehisi Coates resulted ‘in a significant, 15-point drop in black respondents’ belief that they have control over their lives’. Worse still, we now teach precisely these ideas in schools, colleges and workplaces across the US, often in mandatory classes or training.
At the heart of this discussion is what Thomas Sowell once called ‘a conflict of visions’. The US faces a choice about what to tell new and aspiring citizens about our society. Are we a flawed but ultimately good country, where people of all colours and persuasions can thrive? Or is the US a genocidal racial-caste state, which should be constantly trying to atone for its historical sins?
Let us sincerely hope that we choose to embrace the first vision over the second.
-
Wilfred Reilly is a spiked columnist and the author of Taboo: 10 Facts You Can’t Talk About, published by Regnery. Follow him on Twitter: @wil_da_beast630
==
Remind me again... in which direction do people migrate, as far as western countries are concerned? To or from? /s
#Wilfred Reilly#Barack Obama#systemic racism#victimhood culture#victimhood complex#victimhood#wokeism#woke#cult of woke#wokeness#wokeness as religion#antiracism as religion#antiracism#religion is a mental illness
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
It really does feel like people treat asking your nationality as if that’s a substitute to asking what your race is which never made sense to me.
I’m American, and I thought it was common knowledge that your nationality is where you are from untill I had to debate it with my mother. Because where she lived it was considered the politer way of asking someone’s race.
My dad’s Guyanese which means he’s from Guyana, he spent most of his childhood there. He may have moved to United States but that doesn’t change his nationality.
It makes me unreasonably upset even though most of the people who are using it as a substitute for race probably don’t realize it.
And it kinda feels racist and xenophobic, doesn’t it? Because you never see people treating being American as a race, it’s always other nationalities…
And I mean it feels racist because this mindset always erases other marginalized races from countries. Like Latin America for example: people have a very stereotypical view of what Latinos look like and if you’re black or any other race that doesn’t fit the stereotype of what they think Latin Americans look like, then you’re not Latino.
A lot of people completely erase the fact that Latin America was also colonized by Europeans, and I dare say it was even worse than the colonization the US went through because til this day our countries still suffer from it, while I don’t think it’s the same in the US.
This probably happens (especially when it comes to Americans) because of lack off geography and history classes regarding anything outside the US.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

Beneath the Rising by Premee Mohamed
By: S. Qiouyi Lu
Issue: 24 February 2020
Nick Prasad has always been Joanna “Johnny” Chambers’s sidekick. Friends since a young age, Johnny has rocketed into an early and brilliant career as a child prodigy scientist, while Nick has lived a quiet, mundane life in which his biggest concerns are work and family. But the two of them still have a regular, teenage friendship, one filled with banter and misadventures. So when Johnny comes up with a new invention that could change the world, Nick doesn’t think much of it at first: after all, this is the seventeen-year-old girl who has already fitted the world with solar panels, created lifesaving medications, and perfected tools that assist millions of people’s lives—to name just a few of her accomplishments.
When strange things start to happen, Nick soon realizes that this invention isn’t like the others. An aurora borealis that shouldn’t be visible from their latitude heralds the coming of monstrous creatures, relentless in their pursuit of Johnny and her new invention. Bit by bit, the scale of what’s happening comes together: there are other realms beyond ours where terrible evil lurks and waits for its opportunity to trigger the next apocalypse. Those beings, “The Ancient Ones,” are responsible for the annihilation of civilizations ranging from Carthage to Cahuachi to Çatal Hüyük to Atlantis. And now, they’re after Johnny’s invention and the power it can unleash to destroy the world again.
But that’s not all. Suspicious of how much Johnny knows about the origin of these monsters, Nick pries the truth out of her and discovers that she’s made a covenant with the Ancient Ones. One of their terrifying pursuers, Drozanoth, is here to uphold that covenant, and will do anything to make Johnny hand over the invention responsible for calling the Ancient Ones back to Earth. Now, only she has any idea how to close the gates that are opening between realms. Determined to help stop the apocalypse, Nick embarks on a wild scavenger hunt with Johnny across the Maghreb and the Middle East to gather the items they need to put an end to the invasion.
Beneath the Rising, Indo-Guyanese author Premee Mohamed’s debut novel, is a rollercoaster of an experience. Although Mohamed draws from cosmic horror tropes as classic as Lovecraft’s, she challenges the oppressive foundations on which Lovecraft built his career. The novel is set in an alternate history shortly after a failed terrorist attack on the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001. The impact of September 11 doesn’t go unnoticed: instead, it, and the period setting of the early 2000s, deeply inform the characters’ every movement through the world and the global context around them. Nick, who is Indo-Caribbean and often refers to himself as “brown,” details the various ways in which his racial and class background affect how he sees the world, and how the world sees him. Unlike Nick, Johnny, the wonder-kid know-it-all seemingly blessed with endless genius, is White and rich. Although the sexism she faces is made clear, her privilege on other axes is called out in a way that feels natural to the characters and important to the narrative.
Lovecraft’s work often relies on racism to fuel its narrative and to lend horror and dread to cosmic horror elements. Mohamed, on the other hand, lays out the intersecting foundations of that marginalization and shows how those systems of oppression are the all-too-mundane backdrop against which otherworldly cosmic horror can play out. On top of that, Mohamed brings a genuinely global scope to her doomsday narrative. It is not just the West that faces an imminent catastrophe in Beneath the Rising. Rather, most of the main events occur in the Maghreb and across the Middle East. The rise and fall of civilizations across a broad set of cultures at the hands of the Ancient Ones feels like a smooth integration of all parts of the world, creating a truly global and historically linear scope of events that adds urgency to the narrative.
When it comes to the technical details of craft, Beneath the Rising shows Mohamed’s masterful command of description, pace, and emotion that renders powerful characters and settings. The prose is lean and deliberate, a short story writer’s novel. Mohamed, who also has several short fiction publications to her name, makes sure that every sentence, every paragraph, every simile serves multiple purposes. A sentence can reveal period- and character-appropriate details while also being embedded in an unusual, yet apt, metaphor that vividly describes and furthers the events of the story:
[Johnny] was trembling so hard she was almost flickering, like a poorly-tracked VHS tape. […] This [fear] felt more like something from outside of me, like secondhand smoke, greasily invisible, sinking into my pores, blown from someone unseen. (pp. 56–58)
Mohamed’s command of the rhythm of a sentence shows through in her control over the pace of the story as well. When Nick and Johnny have room to breathe, the prose is denser and slower as it lingers on fuller descriptions.
In the moment of relative safety I craned my head to try to take it all in, wishing I had sunglasses or a hat—it was so bright it just seemed like a spangled kaleidoscope of car windows, men in suits, tiny booths hawking electronics, sunglasses, clothing, CDs, food, tiles, everyone gabbling around me in languages I didn’t know, plus blessedly recognizable if not actually comprehensible French and English. People bumped and buffeted me apparently without even noticing. I had been picturing … I don’t even know what. Some mud-brick city from Raiders of the Lost Ark? Flowing white robes? Tintin books, for absolute sure. (p. 144)
But when Nick and Johnny are on the run, Mohamed’s prose goes into fight-or-flight mode, highlighting only the barest of actions, reactions, and sensory details. The reader barrels along, breathless, with the characters.
I shut the closet door, hearing first a bang, and then—oh shit—the musical tinkle of falling glass from the living room. A multilegged shadow, all spikes and floppy appendages and translucent nodules, firmly struck the hallway wall, like an ink stamp. I cast about, left, right, left, right. Kids. Bedroom. Two quick steps: empty. (p. 103)
At the same time, Beneath the Rising isn’t just an action-adventure chase after a string of McGuffins against a backdrop of tentacles, shadows, uncanny eldritch pawns, and imminent apocalypse. It’s also a slow tale about a different kind of unrequited love between two teenagers who were forced to grow up too early, and who have never had the space to address their lingering PTSD after surviving a shooting during a hostage crisis. Woven between the multidimensional chaos of the Ancient Ones’ return is a poignant, melancholy tale of what growing out of childhood ideals means and feels like. As Nick confronts the codependent nature of his love for Johnny, who turns out not to be the person he thought she was, he shores up memories and emotions that illustrate the processing he’s doing internally while also showing his growth as a character. The vindication of his fury and betrayal feels both earned and deserved.
The biggest strength of the novel, however, comes from the shocking reveal toward the end of the book that explains the true nature of Nick’s “friendship” with Johnny, and why he was even dragged along on such a dangerous journey he had no hand in creating. I’ll be including spoilers from here on in order to fully discuss the impact of the ending.
Instead of being a magnanimous scientist who simply wants to help the world, Johnny practices “altruism” as a reflection of her own need for power and worth. She may be doing good with her work, but that doesn’t mean that she can’t channel great evil and also be a villainous mad scientist. Her prodigal power and inhuman brilliance stem from a covenant she struck with the Ancient Ones. In exchange for time off of her life, Johnny can speed up her mind, like a supercomputer’s processing power getting a boost, to do what she does. But with that covenant came another clause that Johnny only reveals to Nick when she can no longer hide it. Afraid that her unbelievable talent would alienate her from the rest of the world, leaving her alone forever, Johnny bargained for Nick to be forever by her side as a companion. Nick’s true relationship to Johnny is as a slave.
This Faustian covenant, however, didn’t have to take place. Johnny admits that, if she’d refused the covenant, she would have still lived a comfortable, successful life, and would have still been a great scientist. But, lured in by power and the opportunity to influence the world, saving millions of lives in the process, Johnny agreed to a deal with the Ancient Ones. She justifies her actions with all the good she’s done—but Beneath the Rising is, at its heart, a novel about the true cost of power, and whether the ends can justify appalling means. After all, the Ancient Ones would never have been attracted to the world if Johnny had refused the covenant in the first place. The millions of lives potentially lost in a global apocalypse don’t factor into Johnny’s calculations of how much good she does and her positive impact on the world.
Therein lies the extended metaphor that forms the secret crux of Mohamed’s narrative: Johnny’s covenant, and Nick’s role as her “companion,” are tools to critique the legacy of colonialism; in particular, slavery. In a key character turning point, Nick reminds Johnny that his family, of Indian descent and from Guyana, descends from indentured servants who were exploited for the sake of the British Empire. Nick takes deep offense at the way Johnny doles out money, as if to buy people and solutions to her problems. Johnny’s race is actually the most insignificant reflection of her position as a symbol for colonization and empire. It is her utilitarian attitude toward people and her perceived self-importance as a representative of “the greater good” that motivate the true horrors that Johnny commits. Loyalty can always be bought. Nick’s loss of agency, the loss of his potential livelihood, and the psychic toll of not being a genuinely free individual, never enter into Johnny’s mind. Nick isn’t truly a friend, an equal, or even a person to her. He is a sidekick, a person to be uprooted from place to place so that Johnny can always have someone to carry her when she is weak, provide strength when she has none, and sacrifice his life if she needs him to. Nick is merely a resource she can exploit as an extension of herself. How many families, societies, and whole cultures have similarly been torn apart to support the advancement of Western civilization?
No matter how euphemistically slavery is named, whether as “indentured servitude,” “incarceration,” or “debt bondage,” it is ultimately the real covenant that robs people of their time and life force. The lasting socioeconomic impact of slavery, too, oozes through Beneath the Rising as the gulf in wealth between Nick and Johnny, as well as the gulf in opportunity and attitudes toward self-worth between them. No eldritch covenant needs to be made for oppressors to keep subjugating the oppressed. Through Johnny, the whole empire of colonization is laid bare and exposed: for all the “advancement” purportedly created by colonizers, for all the status colonizers lay claim to, millions of people whom colonizers considered as second-class were sacrificed. When Johnny sets out to “save the world,” what she is truly saving is the status quo of her own world of privilege. Nick’s world, the world of the subjugated and oppressed, has long since been lost.
On a micro scale, Beneath the Rising is the best inversion of the sidekick trope I’ve ever seen. The effect of a reckless superhuman crashing through the world are called out early: who will clean up? Who will pay for property damage? Who will handle witness protection? Insurance? Jobs? How will people recover from the trauma of such a disruptive event? Then, when the true nature of Nick’s slavery is revealed, we see the rare story of a sidekick walking away—of codependency not being romanticized, but called out for the real destruction it can cause. Nick’s anger and betrayal are validated narratively as he sets boundaries at last and recovers from Johnny’s exploitation. The scale of Johnny’s betrayal and the evilness of her act are never downplayed, even as Johnny herself, like many benefitting from the legacy of colonization, remains clueless of her impact, even going so far as to still believe that she is doing good, and that all the devastation behind her can be a footnote to her altruism.
Beneath the Rising is a near-flawless debut novel. While it works well as a standalone, the story and worldbuilding leave room for sequels as well. Multilayered and richly rendered, Beneath the Rising is a darkly humorous romp through unspeakable cosmic horrors that also paints a portrait of two hurt teenagers grappling with their place in the world and their relationship with each other, all while navigating complex inner worlds impacted by the legacies of colonization, slavery, racism, and sexism. Like a doomsday device, Beneath the Rising is compact, powerful, and devastating as it hurls the reader through a brilliantly crafted narrative. Prepare for an epic journey, and don’t forget to bring a barf bag for the turbulent ride.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
FAS3000 - Artist #3 - Vanley Burke


From our lecture, another artist that stood me was British Jamaican photographer Vanley Burke. I relate to this artist majorly as I am also Jamaican and Guyanese so we both come from the same Caribbean background and heritage. While looking at these photos, they feel nostalgic to me because they portray my parents' upbringing during the 80's and 90's.
My parents are Rastafarian; they would tell me and my siblings stories about our 'way of life', celebrations and our history which plays a big part of my upbringing and community. Seeing these pictures reminds of my dad and uncles who would play reggae music, dance, talk and wearing out their dreadlocks, which is a main identity symbol of the Rastafarian movement.

Because of this artist's work, I can see there are similar life experiences which I can use for potential ideas for this project. These would be a strong link to this artist as I have also stored or taken pictures of my Rastafarian family members. Also, this would be a chance to learn more about my community and how it has made me as a person today.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Russian Revolution: A View from the Third World - Walter Rodney

Hello friends!
Today I'm excited to start Black History Month (which is really every month) by forefronting another phenomenal text by Walter Rodney: "The Russian Revolution, A View from the Third World"
As described before, Rodney was a prominent Guyanese historian, political activist, and scholar. He was born on March 23, 1942, in Georgetown, British Guiana (now Guyana). He's still an icon in Pan-Africanist and Marxist thought which al of us ought to engage.
This book provides a fresh, invaluable perspective on one of the most significant events of the twentieth century and socialist history overall. He approaches this subject with an eye towards rectifying the record on histories of the Soviet Union to see what, if any, lessons can be learned from their experiments and applied to decolonization efforts and socialist politics going forward.
Rodney starts by unpacking what an "African Perspective" on the Russian Revolution as opposed to Western European (and American) view would be and why it matters. He shows that integrating Marxist views alongside marginalized African perspectives lets us see the revolution in all its complexity, unlike the black-and-white picture of bourgeois scholarship.
The main body of the book really focuses on unpacking various historical accounts of Russian history pre and post-1917 to get a gleaming of what a more nuanced picture could be. Rodney does a great job at engaging figures on the Left seriously and offering his criticisms of failures constructively alongside defending the Soviets from the more outrageous propaganda.
One of my favorite bits of context for this text is that it was essentially the pre-figuration of another amazing book, "How Europe Underdeveloped Africa," as editor Robin D. G. Kelley noted in a talk with Vijay Prashad (who wrote the foreward) on YouTube y'all should check out.
Rodney saw the Soviet experiment as an essential starting point for his investigation into making revolution across Africa, not a side issue. This became even more relevant for his struggles in Guyana, where he died in 1980 after pushing for socialism at home. Highly recommend this text for all of these lessons and histories!
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo
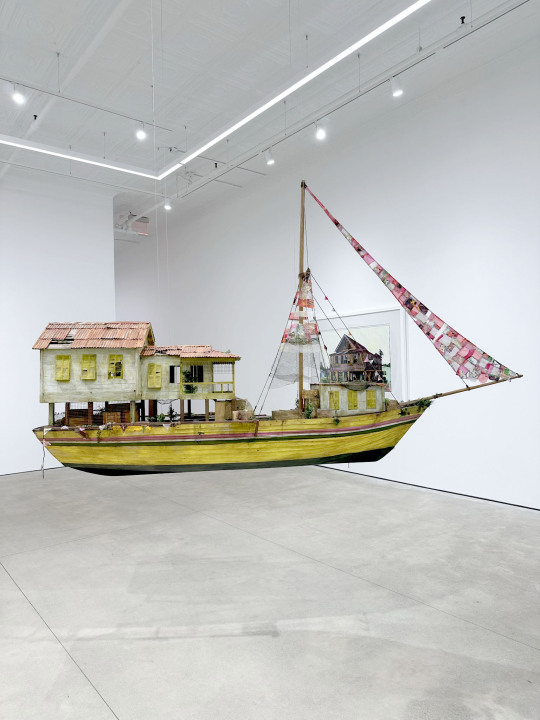
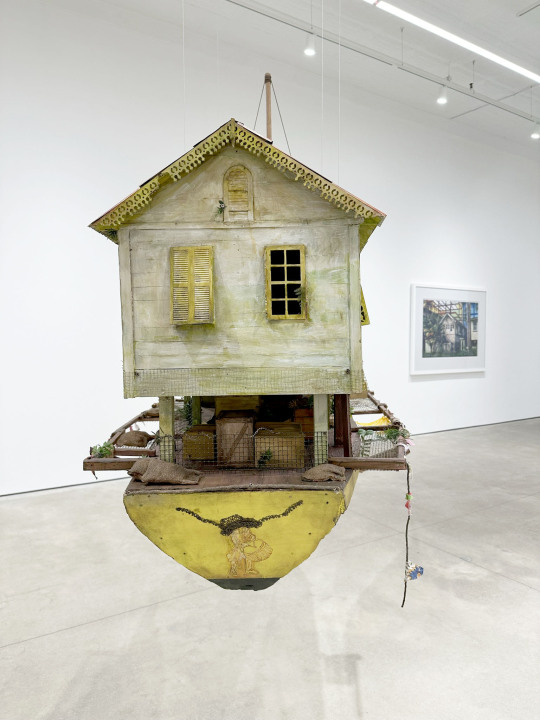
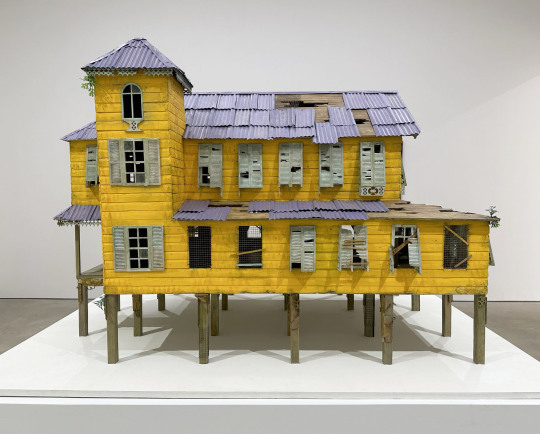
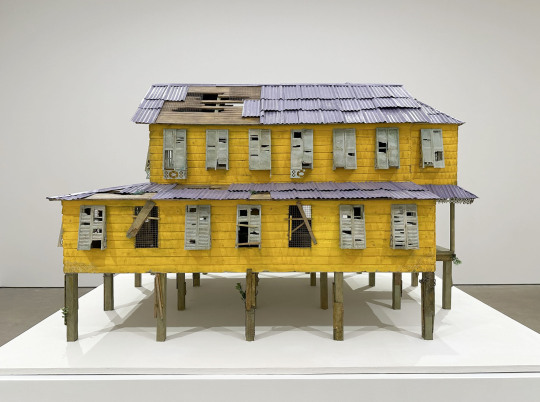








For Hew Locke’s exhibition, Listening to the Land, at P.P.O.W. he has created intricate sculptures and paintings that are fascinating in person.
From the press release-
Locke is known for exploring the languages of colonial and post-colonial power, and the symbols through which different cultures assume and assert identity. Furthering the themes explored in his celebrated commission The Procession at Tate Britain, and his concurrent installation Gilt on the façade of The Metropolitan Museum of Art, this exhibit engages with contemporary and historical inequities while reflecting on the landscape and history of the Caribbean. The exhibition draws its title from a poem by Guyanese political activist and poet Martin Carter which situates itself between two opposing forces of the landscape – sea and forest. Locke’s show features new sculptures and wall works with recurring motifs of stilt-houses, boats, memento mori, and share certificates referencing tensions between the land, the sea, and economic power. Reflecting on these links, Locke notes, “The land was created to generate money for colonial power, now the sea wants it back.”
Translating to ‘land of many waters,’ Guyana and its physical, economic, and political landscape serve as one of the primary sources for Locke’s work. Having spent his childhood in this newly independent nation, the artist witnessed first-hand an era of radical transformation. Now, the country teeters on the precipice of an oil boom and is one of the world’s fastest growing economies. Juxtaposing personal meditations on the climate crisis with political commentary on the history of a globalized world, Locke contemplates the ways in which colonies were exploited to accumulate capital, and observes how Guyana’s economic future lies in the exploitation of its waters. Locke’s new boat sculptures The Relic and The Survivor embody this broad worldview as the two battered wrecks drift through time and history. Evoking the fragmented and diverse legacies of the global diaspora, the boats’ patchwork sails are interspersed with photo transfers of 19th Century cane cutters and banana boat loaders, while their decks are loaded with cargo that could allude to colonial plunder, trade goods or personal belongings.
Based on an abandoned plantation house, Locke’s newest sculpture Jumbie House 2 features layered images that unveil the spirits that haunt this colonial vestige. Presented alongside are a series of painted photographs of dilapidated vernacular architecture across Georgetown and rural Guyana. Constantly under threat of being washed away by storms or rising sea levels, these crumbling structures echo anxieties surrounding climate change and historical erasure. A new series of mixed media wall works, Raw Materials, is derived from antique share certificates and bonds. Locke richly decorates the appliques with acrylic, beads, and patchwork to draw attention to the complex ways in which the past shapes the present. The image of an 1898 Chinese Imperial Gold Loan behind painted Congolese figures connects the global economy at the height of Empire to current Sino-African trade networks. In another work, a painted representation of a Nigerian Ife mask, alongside an image of David Livingstone, is layered on a French-African Mortgage Bond from 1923, connecting exploration and exploitation of African land, to current conversations surrounding the repatriation of artifacts. Taken together, the works in Locke’s Listening to the Land echo William Faulkner’s adage “The past is never dead. It’s not even past.”
This exhibition closes 4/1/23.
The Procession, mentioned above, can now be seen at Baltic Centre for Contemporary Art, in Gateshead, England until June 11th, 2023.
Gilt, also mentioned above, is on view at The Metropolitan Museum of Art until May 30th, 2023.
#hew locke#p.p.o.w#p.p.o.w gallery nyc#nyc art shows#sculpture#art installation#painting#guyana#baltic centre for contemporary art#the met#the metropolitan museum of art#uk art shows#art#art shows#models#photography#england art shows#gateshead#newcastle
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
International Symposium on the "History and Legacy of Muslims in the Caribbean"

ircica.org
International Symposium on the "History and Legacy of Muslims in the Caribbean"
OIC IRCICA
6–8 minutes
The International Symposium on the “History and Legacy of Muslims in the Caribbean” organized by IRCICA, OIC General Secretariat, the Government of Guyana and Guyana University was opened by President H.E. Mohamed Irfaan Ali with a Feature Address on 4 September 2023. IRCICA Director General Prof. Mahmud Erol Kılıç gave an address at the opening ceremony. Moderated by Mr. Al Creighton, Dean of the Faculty of Humanities and Education of the University of Guyana, the ceremony started with Quran recitation and translation by Hafiz Salih Rahim, and heard the opening remarks of H.E. Mr. Hugh Hilton Todd, Minister of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation; Dr. Abdullah Hakim Quick, Special Envoy of IRCICA to the Caribbean; Dr. Alhoucine Rhazoui, Director of Cultural Affairs, OIC General Sceretariat, as well as cultural items, consisting of the Islamic Chant in Urdu recited by Mr. Imran Ali, Deputy President of the Muslim Youth Organization, and the Islamic Chant in Yoruba language presented by Mr. Toyib Hamza. A press conference followed the opening session. The ceremony and the working sessions were held at Arthur Chung Conference Center in Georgetown.
Subsequently, the same day, IRCICA Director General Prof. Mahmud Erol Kılıç was received by H.E. President Mohamed Irfaan Ali for a welcoming meeting. Professor Kılıç briefed H.E. the President about IRCICA’s objectives and activities. Mr. Hugh Hilton Todd, Minister of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, high officials from Guyana, and the IRCICA delegation members, were also present at the meeting. Director General Prof. Kılıç presented H.E. President Irfaan Ali and Foreign Affairs Minister Mr. Hugh Todd with samples of IRCICA’s publications in the series of studies on the Holy Qur’an.
The working sessions of the symposium, spread over three days, were on the following themes:
First day, Session I: Globalization and Localization in the Caribbean: Aliyah Khan, University of Michigan, | The Qasida and Muslim Devotional Music in Guyana and Trinidad; Frank J. Korom, Boston University | The Current State of Hosay (Moharram) Observances in the Caribbean; Abdin Chande, Adelphi University | Migration and Identity of South Asians of the Caribbean and East African Indian Ocean Region: A Comparative Analysis; Maurits S. Hassankhan, Anton de Kom University of Suriname | Localization and Globalization of Religion: The Case of Hindustani Muslims in Suriname.
Session II: Islam in the Greater Caribbean from Early History to Today: Abdullah Hakim Quick, The Islamic Institute of Toronto | Aspects of Muslim History and Legacy in Pre-Columbian America; Juan Thomas Ordóñez, Universidad del Rosario | Caribbean Lebanon: The Muslim Experience on the Colombia/Venezuela Border; Mohamed A. Hakim, Islamic Educator and Social Activist in Haiti | History of Muslims in Haiti; Nuri Muhammad, Imam, Radio Commentator and Social Activist | The Evolution of Muslim Presence in Belize and the Significance of Garifuna Cultural Retrieval;
Session III: Panel on Black Atlantic Muslim Movements – Remapping and Theorizing Global South Migrations: Youssef Carter, University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill | Western Sunrise in the Global South: The Islamic Party comes to the Caribbean; Tasneem Siddiqui, Drexel University | The Caribbean Is No Island: Rethinking Black Geographies through Muslim Resistance Movements; Nsenga Knight, Artist & Storyteller | Irregular Black Muslims: Diasporic Exchange & The Caribbean Elsewhere.
Second day, Session I: Guyanese Experience: Ateeka Khan, McMaster University | East Indians, Religion, and Politics in 20th Century Guyana; Nazim Baksh, Former Investigative Producer with Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC) | Conflict, Continuity and Change of Religious Narratives and Practices of Muslims in Guyana (1977-1981); Ahmad Hamid, Imam and Researcher | The Challenges and Role of CIOG in the Transformation of the Muslim Community of Guyana from Chaos to Stability; Wazir Baksh, Historian and Community Activist | The Masjid as an Essential Institution to Preserve Faith and Social Cohesion: The Case of Guyana.
Session II: Voices from Trinidad and Tobago: Halima-Sa’adia Kassim, University of the West Indies | An Evaluation of the Resultant Negotiations of Living in an Alien Society: The Indo-Muslims of Trinidad Claiming Their Place; Nasser Mustapha & Mirza Ali Mohammad, University of the West Indies | Race and Ethnic Relations in Trinidad and Tobago; Anand Rampersad, University of the West Indies | Successful Muslim Cricketers in Trinidad and Tobago.
Session III: Economy, Identity and Decolonization in the Caribbean: Ibraheem Musa Tijani, International Islamic University Malaysia | The Economic Development and Commerce of the Muslim Communities in the Caribbean and the Emergence of Islamic Finance in the Region; Stanley L. Soeropawiro, Policy Advisor Religious Affairs, Ministry of Home Affairs (Suriname) | Economic Development among the Javanese Muslims in Suriname; Karimah Rahman, Toronto Metropolitan University | Decolonizing Muslim Indo-Caribbean Mental Health; Suleiman Bulbulia & Sabir Nakhuda, Historians and Authors | The Muslims of Barbados: Sustaining A Muslim Identity.
Third Day, Special Presentation at the University of Guyana by: Abdullah Hakim Quick, Nuri Muhammad, Mohamed A. Hakim and Stanley L. Soeropowero.
The closing ceremony of the symposium was conducted with the remarks of Prof. Dr. Aboubacar Abdullah Senghore, Assistant Director General, IRCICA and Ambassador Elisabeth Harper, Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation of Guyana.
On 5 September 2023, IRCICA Director General Prof. Mahmud Erol Kılıç had a meeting with Professor Paloma Mohamed Martin, Vice-Chancellor of the University of Guyana. The meeting was a fruitful occasion to exchange views on research and education in Islamic studies.
During the symposium period, Director General Prof. Mahmud Erol Kılıç held contacts and meetings with Muslim cultural institutions and educational organizations in Guyana including the Central Islamic Organization of Guyana (CIOG), Guyana Islamic Trust and the ISA School.
3 notes
·
View notes