#Json Web API
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Does anyone on tumblr know good software for testing an API call? I remember there being a software where you could make GET requests to an API, and the software would return a JSON, but I don't remember what it was called. Does anyone know?
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tugas Rest API
kerjakan soal-soal dibawah ini dalam bentuk deskriptif Mengapa kita perlu mempelajari Rest API? Apakah API dan Rest API itu? jelaskan dan cara kerjanya, boleh membuat alur berbentuk bagan? komponen Web API apa saja dan Bagaimana arsitektur Rest API? Apa saja yang dikelola oleh Rest API sehingga menghasilkan output atau titik akhir? Apa berbedaan antara SOAP dan REST API? Apa dan bagaimana…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
holy grail of last.fm and spotify music data sites. i'd still say check the actual link but i've copy pasted most of the info n the links below
Spotify
Sites, apps and programs that use your Spotify account, Spotify API or both.
Spotify sites:
Obscurify: Tells you how unique you music taste is in compare to other Obscurify users. Also shows some recommendations. Mobile friendly.
Skiley: Web app to better manage your playlists and discover new music. This has so many functions and really the only thing I miss is search field for when you are managing playlists. You can take any playlist you "own" and order it by many different rules (track name, album name, artist name, BPM, etc.), or just randomly shuffle it (say bye to bad Spotify shuffle). You can also normalize it. For the other functions you don't even need the rights to edit the playlist. Those consists of splitting playlist, filtering out song by genre or year to new playlist, creating similar playlists or exporting it to CFG, CSV, JSON, TXT or XML.
You can also use it to discover music based on your taste and it has a stats section - data different from Last.fm.
Also, dark mode and mobile friendly.
Sort your music: Lets you sort your playlist by all kinds of different parameters such as BPM, artist, length and more. Similar to Skiley, but it works as an interactive table with songs from selected playlist.
Run BPM: Filters playlists based on parameters like BPM, Energy, etc. Great visualized with colorful sliders. Only downside - shows not even half of my playlists. Mobile friendly.
Fylter.in: Sort playlist by BMP, loudness, length, etc and export to Spotify
Spotify Charts: Daily worldwide charts from Spotify. Mobile friendly
Kaleidosync: Spotify visualizer. I would personally add epilepsy warning.
Duet: Darthmouth College project. Let's you compare your streaming data to other people. Only downside is, those people need to be using the site too, so you have to get your friends to log in. Mobile friendly.
Discover Quickly: Select any playlist and you will be welcomed with all the songs in a gridview. Hover over song to hear the best part. Click on song to dig deeper or save the song.
Dubolt: Helps you discover new music. Select an artist/song to view similar ones. Adjust result by using filters such as tempo, popularity, energy and others.
SongSliders: Sort your playlists, create new one, find new music. Also can save Discover weekly every monday.
Stats for Spotify: Shows you Top tracks and Top artists, lets you compare them to last visit. Data different from Last.fm. Mobile friendly
Record Player: This site is crazy. It's a Rube Goldberg Machine. You take a picture (any picture) Google Cloud Vision API will guess what it is. The site than takes Google's guess and use it to search Spotify giving you the first result to play. Mobile friendly.
Author of this site has to pay for the Google Cloud if the site gets more than 1000 requests a month! I assume this post is gonna blow up and the limit will be easily reached. Author suggests to remix the app and set it up with your own Google Cloud to avoid this. If your are able to do so, do it please. Or reach out to the author on Twitter and donate a little if you can.
Spotify Playlist Randomizer: Site to randomize order of the songs in playlist. There are 3 shuffling methods you can choose from. Mobile friendly.
Replayify: Another site showing you your Spotify data. Also lets you create a playlist based on preset rules that cannot be changed (Top 5 songs by Top 20 artists from selected time period/Top 50 songs from selected time period). UI is nice and clean. Mobile friendly, data different from Last.fm.
Visualify: Simpler replayify without the option to create playlists. Your result can be shared with others. Mobile friendly, data different from Last.fm.
The Church Of Koen: Collage generator tool to create collages sorted by color and turn any picture to collage. Works with Last.fm as well.
Playedmost: Site showing your Spotify data in nice grid view. Contains Top Artists, New Artists, Top Tracks and New Tracks. Data different from Last.fm, mobile friendly.
musictaste.space: Shows you some stats about your music habits and let's you compare them to others. You can also create Covid-19 playlist :)
Playlist Manager: Select two (or more) playlists to see in a table view which songs are shared between them and which are only in one of them. You can add songs to playlists too.
Boil the Frog: Choose to artists and this site will create playlists that slowly transitions between one artist's style to the other.
SpotifyTV: Great tool for searching up music videos of songs in your library and playlists.
Spotify Dedup and Spotify Organizer: Both do the same - remove duplicates. Spotify Dedup is mobile friendly.
Smarter Playlists: It lets you build a complex program by assembling components to create new playlists. This seems like a very complex and powerful tool.
JBQX: Do you remember plug.dj? Well this is same thing, only using Spotify instead of YouTube as a source for music. You can join room and listen to music with other people, you all decide what will be playing, everyone can add a song to queue.
Spotify Buddy: Let's you listen together with other people. All can control what's playing, all can listen on their own devices or only one device can be playing. You don't need to have Spotify to control the queue! In my opinion it's great for parties as a wireless aux cord. Mobile friendly.
Opslagify: Shows how much space would one need to download all of their Spotify playlists as .mp3s.
Whisperify: Spotify game! Music quiz based on what you are listening to. Do you know your music? Mobile friendly.
Popularity Contest: Another game. Two artists, which one is more popular according to Spotify data? Mobile friendly, doesn't require Spotify login.
Spotify Apps:
uTrack: Android app which generates playlist from your top tracks. Also shows top artists, tracks and genres - data different from Last.fm.
Statistics for Spotify: uTrack for iOS. I don't own iOS device so I couldn't test it. iOS users, share your opinions in comments please :).
Spotify Programs:
Spicetify: Spicetify used to be a skin for Rainmeter. You can still use it as such, but the development is discontinued. You will need to have Rainmeter installed if you want to try. These days it works as a series of PowerShell commands. New and updated version here. Spicetify lets you redesign Spotify desktop client and add new functions to it like Trash Bin, Shuffle+, Christian Mode etc. It doesn't work with MS Store app, .exe Spotify client is required.
Library Bridger: The main purpose of this program is to create Spotify playlists from your locally saved songs. But it has some extra functions, check the link.
Last.fm
Sites, apps and programs using Last.fm account, Last.fm API or both.
Last.fm sites:
Last.fm Mainstream Calculator: How mainstream is music you listen to? Mobile friendly.
My Music Habits: Shows different graphs about how many artists, tracks and albums from selected time period comes from your overall top artists/tracks/albums.
Explr.fm: Where are the artists you listen to from? This site shows you just that on interactive world map.
Descent: The best description I can think of is music dashboard. Shows album art of currently playing song along with time and weather.
Semi-automatic Last.fm scrobbler: One of the many scrobblers out there. You can scrobble along with any other Last.fm user.
The Universal Scrobbler: One of the best manual scrobblers. Mobile friendly.
Open Scrobbler: Another manual scrobbler. Mobile friendly
Vinyl Scrobbler: If you listen to vinyl and use Last.fm, this is what you need.
Last.fm collage generator, Last.fm top albums patchwork generator and yet another different Last.fm collage generator: Sites to make collages based on your Last.fm data. The last one is mobile friendly.
The Church Of Koen: Collage generator tool to create collages sorted by color and turn any picture to collage. Works with Spotify as well.
Musicorum: So far the best tool for generating collages based on Last.fm data that I ever seen. Grid up to 20x20 tiles and other styles, some of which resemble very well official Spotify collages that Spotify generates at the end of the year. Everything customizable and even supports Instagram story format. Mobile friendly.
Nicholast.fm: Simple site for stats and recommendations. Mobile friendly.
Scatter.fm: Creates graph from your scrobbles that includes every single scrobble.
Lastwave: Creates a wave graph from your scrobbles. Mobile friendly.
Artist Cloud: Creates artist cloud image from you scrobbles. Mobile friendly.
Last.fm Tools: Lets you generate Tag Timeline, Tag Cloud, Artist Timeline and Album Charter. Mobile friendly.
Last Chart: This site shows different types of beautiful graphs visualizing your Last.fm data. Graph types are bubble, force, map, pack, sun, list, cloud and stream. Mobile friendly.
Sergei.app: Very nice looking graphs. Mobile friendly.
Last.fm Time Charts: Generates charts from your Last.fm data. Sadly it seems that it only supports artists, not albums or tracks.
ZERO Charts: Generates Billboard like charts from Last.fm data. Requires login, mobile friendly.
Skihaha Stats: Another great site for viewing different Last.fm stats.
Jakeledoux: What are your Last.fm friends listening to right now? Mobile friendly.
Last History: View your cumulative listening history. Mobile friendly.
Paste my taste: Generates short text describing your music taste.
Last.fm to CSV: Exports your scrobbles to CSV format. Mobile friendly.
Pr.fm: Syncs your scrobbles to your Strava activity descriptions as a list based on what you listened to during a run or biking session, etc. (description by u/mturi, I don't use Strava, so I have no idea how does it work :))
Last.fm apps:
Scroball for Last.fm: An Android app I use for scrobbling, when I listen to something else than Spotify.
Web Scrobbler: Google Chrome and Firefox extension scrobbler.
Last.fm programs:
Last.fm Scrubbler WPF: My all time favourite manual scrobbler for Last.fm. You can scrobbler manually, from another user, from database (I use this rather than Vinyl Scrobbler when I listen to vinyls) any other sources. It can also generate collages, generate short text describing your music taste and other extra functions.
Last.fm Bulk Edit: Userscript, Last.fm Pro is required. Allows you to bulk edit your scrobbles. Fix wrong album/track names or any other scrobble parameter easily.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Prevent Cross-Site Script Inclusion (XSSI) Vulnerabilities in Laravel
Introduction
Cross-Site Script Inclusion (XSSI) is a significant security vulnerability that allows attackers to include malicious scripts in a web application. These scripts can be executed in the context of a user’s session, leading to data theft or unauthorized actions.

In this post, we’ll explore what XSSI is, how it impacts Laravel applications, and practical steps you can take to secure your app.
What is Cross-Site Script Inclusion (XSSI)?
XSSI occurs when a web application exposes sensitive data within scripts or includes external scripts from untrusted sources. Attackers can exploit this by injecting malicious scripts that execute within the user’s browser. This can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data and potentially compromise the entire application.
Identifying XSSI Vulnerabilities in Laravel
To prevent XSSI, start by identifying potential vulnerabilities in your Laravel application:
Review Data Endpoints: Ensure that any API or data endpoint returns the appropriate Content-Type headers to prevent the browser from interpreting data as executable code.
Inspect Script Inclusions: Make sure that only trusted scripts are included and that no sensitive data is embedded within these scripts.
Use Security Scanners: Utilize tools like our Website Vulnerability Scanner to analyze your app for potential XSSI vulnerabilities and get detailed reports.

Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Mitigating XSSI Vulnerabilities in Laravel
Let’s explore some practical steps you can take to mitigate XSSI risks in Laravel.
1. Set Correct Content-Type Headers
Make sure that any endpoint returning JSON or other data formats sets the correct Content-Type header to prevent browsers from interpreting responses as executable scripts.
Example:
return response()->json($data);
Laravel’s response()->json() method automatically sets the correct header, which is a simple and effective way to prevent XSSI.
2. Avoid Including Sensitive Data in Scripts
Never expose sensitive data directly within scripts. Instead, return data securely through API endpoints.
Insecure Approach
echo "<script>var userData = {$userData};</script>";
Secure Approach:
return response()->json(['userData' => $userData]);
This method ensures that sensitive data is not embedded within client-side scripts.
3. Implement Content Security Policy (CSP)
A Content Security Policy (CSP) helps mitigate XSSI by restricting which external sources can serve scripts.
Example:
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' https://trusted.cdn.com;
This allows scripts to load only from your trusted sources, minimizing the risk of malicious script inclusion.
4. Validate and Sanitize User Inputs
Always validate and sanitize user inputs to prevent malicious data from being processed or included in scripts.
Example:
$request->validate([ 'inputField' => 'required|string|max:255', ]);
Laravel’s built-in validation mechanisms help ensure that only expected, safe data is processed.
5. Regular Security Assessments
Conduct regular security assessments to proactively identify potential vulnerabilities. Tools like our free Website Security Scanner can provide detailed insights into areas that need attention.

An Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Preventing Cross-Site Script Inclusion (XSSI) vulnerabilities in your Laravel applications is essential for safeguarding your users and maintaining trust. By following best practices like setting proper content-type headers, avoiding sensitive data exposure, implementing CSP, validating inputs, and regularly assessing your app’s security, you can significantly reduce the risk of XSSI attacks.
Stay proactive and secure your Laravel applications from XSSI threats today!
For more insights into securing your Laravel applications, visit our blog at Pentest Testing Corp.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Argo CD? And When Was Argo CD Established?

What Is Argo CD?
Argo CD is declarative Kubernetes GitOps continuous delivery.
In DevOps, ArgoCD is a Continuous Delivery (CD) technology that has become well-liked for delivering applications to Kubernetes. It is based on the GitOps deployment methodology.
When was Argo CD Established?
Argo CD was created at Intuit and made publicly available following Applatix’s 2018 acquisition by Intuit. The founding developers of Applatix, Hong Wang, Jesse Suen, and Alexander Matyushentsev, made the Argo project open-source in 2017.
Why Argo CD?
Declarative and version-controlled application definitions, configurations, and environments are ideal. Automated, auditable, and easily comprehensible application deployment and lifecycle management are essential.
Getting Started
Quick Start
kubectl create namespace argocd kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
For some features, more user-friendly documentation is offered. Refer to the upgrade guide if you want to upgrade your Argo CD. Those interested in creating third-party connectors can access developer-oriented resources.
How it works
Argo CD defines the intended application state by employing Git repositories as the source of truth, in accordance with the GitOps pattern. There are various approaches to specify Kubernetes manifests:
Applications for Customization
Helm charts
JSONNET files
Simple YAML/JSON manifest directory
Any custom configuration management tool that is set up as a plugin
The deployment of the intended application states in the designated target settings is automated by Argo CD. Deployments of applications can monitor changes to branches, tags, or pinned to a particular manifest version at a Git commit.
Architecture
The implementation of Argo CD is a Kubernetes controller that continually observes active apps and contrasts their present, live state with the target state (as defined in the Git repository). Out Of Sync is the term used to describe a deployed application whose live state differs from the target state. In addition to reporting and visualizing the differences, Argo CD offers the ability to manually or automatically sync the current state back to the intended goal state. The designated target environments can automatically apply and reflect any changes made to the intended target state in the Git repository.
Components
API Server
The Web UI, CLI, and CI/CD systems use the API, which is exposed by the gRPC/REST server. Its duties include the following:
Status reporting and application management
Launching application functions (such as rollback, sync, and user-defined actions)
Cluster credential management and repository (k8s secrets)
RBAC enforcement
Authentication, and auth delegation to outside identity providers
Git webhook event listener/forwarder
Repository Server
An internal service called the repository server keeps a local cache of the Git repository containing the application manifests. When given the following inputs, it is in charge of creating and returning the Kubernetes manifests:
URL of the repository
Revision (tag, branch, commit)
Path of the application
Template-specific configurations: helm values.yaml, parameters
A Kubernetes controller known as the application controller keeps an eye on all active apps and contrasts their actual, live state with the intended target state as defined in the repository. When it identifies an Out Of Sync application state, it may take remedial action. It is in charge of calling any user-specified hooks for lifecycle events (Sync, PostSync, and PreSync).
Features
Applications are automatically deployed to designated target environments.
Multiple configuration management/templating tools (Kustomize, Helm, Jsonnet, and plain-YAML) are supported.
Capacity to oversee and implement across several clusters
Integration of SSO (OIDC, OAuth2, LDAP, SAML 2.0, Microsoft, LinkedIn, GitHub, GitLab)
RBAC and multi-tenancy authorization policies
Rollback/Roll-anywhere to any Git repository-committed application configuration
Analysis of the application resources’ health state
Automated visualization and detection of configuration drift
Applications can be synced manually or automatically to their desired state.
Web user interface that shows program activity in real time
CLI for CI integration and automation
Integration of webhooks (GitHub, BitBucket, GitLab)
Tokens of access for automation
Hooks for PreSync, Sync, and PostSync to facilitate intricate application rollouts (such as canary and blue/green upgrades)
Application event and API call audit trails
Prometheus measurements
To override helm parameters in Git, use parameter overrides.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#ArgoCD#CD#GitOps#API#Kubernetes#Git#Argoproject#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Do You Want Some Cookies?
Doing the project-extrovert is being an interesting challenge. Since the scope of this project shrunk down a lot since the first idea, one of the main things I dropped is the use of a database, mostly to reduce any cost I would have with hosting one. So things like authentication needs to be fully client-side and/or client-stored. However, this is an application that doesn't rely on JavaScript, so how I can store in the client without it? Well, do you want some cookies?
Why Cookies
I never actually used cookies in one of my projects before, mostly because all of them used JavaScript (and a JS framework), so I could just store everything using the Web Storage API (mainly localstorage). But now, everything is server-driven, and any JavaScript that I will add to this project, is to enhance the experience, and shouldn't be necessary to use the application. So the only way to store something in the client, using the server, are Cookies.
TL;DR Of How Cookies Work
A cookie, in some sense or another, is just an HTTP Header that is sent every time the browser/client makes a request to the server. The server sends a Set-Cookie header on the first response, containing the value and optional "rules" for the cookie(s), which then the browser stores locally. After the cookie(s) is stored in the browser, on every subsequent request to the server, a Cookie header will be sent together, which then the server can read the values from.
Pretty much all websites use cookies some way or another, they're one of the first implementations of state/storage on the web, and every browser supports them pretty much. Also, fun note, because it was one of the first ways to know what user is accessing the website, it was also heavy abused by companies to track you on any website, the term "third-party cookie" comes from the fact that a cookie, without the proper rules or browser protection, can be [in summary] read from any server that the current websites calls. So things like advertising networks can set cookies on your browser to know and track your profile on the internet, without you even knowing or acknowledging. Nowadays, there are some regulations, primarily in Europe with the General Data Privacy Regulation (GDPR), that's why nowadays you always see the "We use Cookies" pop-up in websites you visit, which I beg you to actually click "Decline" or "More options" and remove any cookie labeled "Non-essential".
Small Challenges and Workarounds
But returning to the topic, using this simple standard wasn't so easy as I thought. The code itself isn't that difficult, and thankfully Go has an incredible standard library for handling HTTP requests and responses. The most difficult part was working around limitations and some security concerns.
Cookie Limitations
The main limitation that I stumbled was trying to have structured data in a cookie. JSON is pretty much the standard for storing and transferring structured data on the web, so that was my first go-to. However, as you may know, cookies can't use any of these characters: ( ) < > @ , ; : \ " / [ ] ? = { }. And well, when a JSON file looks {"like":"this"}, you can think that using JSON is pretty much impossible. Go's http.SetCookie function automatically strips " from the cookie's value, and the other characters can go in the Set-Cookie header, but can cause problems.
On my first try, I just noticed about the stripping of the " character (and not the other characters), so I needed to find a workaround. And after some thinking, I started to try implementing my own data structure format, I'm learning Go, and this could be an opportunity to also understand how Go's JSON parsing and how mostly struct tags works and try to implement something similar.
My idea was to make something similar to JSON in one way or another, and I ended up with:
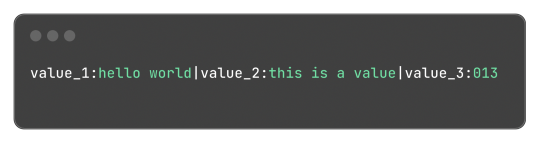
Which, for reference, in JSON would be:
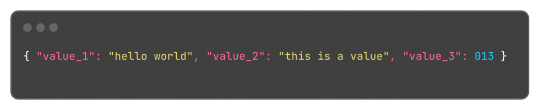
This format is something very easy to implement, just using strings.Split does most of the job of extracting the values and strings.Join to "encode" the values back. Yes, this isn't a "production ready" format or anything like that, but it is hacky and just a small fix for small amounts of structured data.
Go's Struct Tags
Go has an interesting and, to be honest, very clever feature called Struct Tags, which are a simple way to add metadata to Structs. They are simple strings that are added to each field and can contain key-value data:

Said metadata can be used by things such the encoding/json package to transform said struct into a JSON object with the correct field names:

Without said tags, the output JSON would be:

This works both for encoding and decoding the data, so the package can correctly map the JSON field "access_token" to the struct field "Token".
And well, these tokens aren't limited or some sort of special syntax, any key-value pair can be added and accessed by the reflect package, something like this:
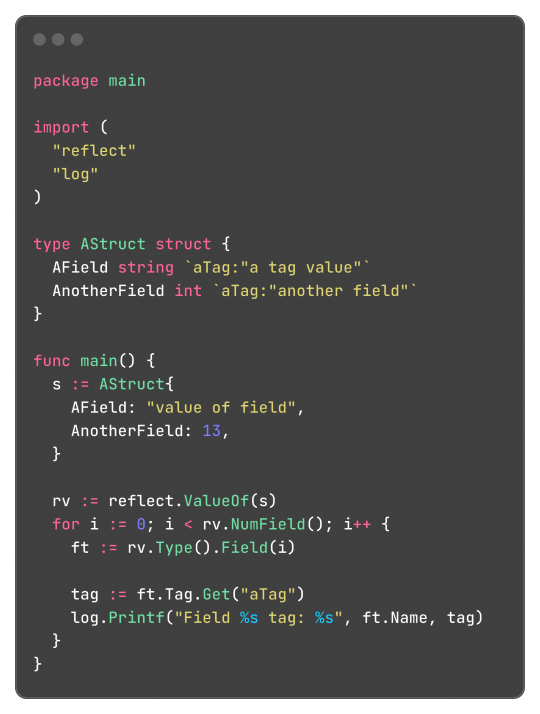
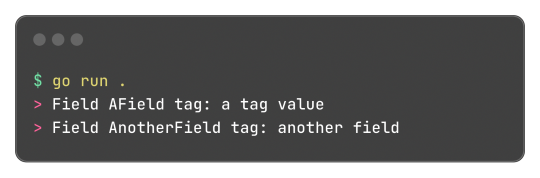
Learning this feature and the reflect package itself, empowered me to do a very simple encoding and decoding of the format where:

Can be transformed into:

And that's what I did, and the [basic] implementation source code just has 150 lines of code, not counting the test file to be sure it worked. It works, and now I can store structured data in cookies.
Legacy in Less Than 3 Weeks
And today, I found that I can just use url.PathEscape, and it escapes all ( ) < > @ , ; : \ " / [ ] ? = { } characters, so it can be used both in URLs and, surprise, cookie values. Not only that, but something like base64.URLEncoding would also work just fine. You live, and you learn y'know, that's what I love about engineering.
Security Concerns and Refactoring Everything
Another thing that was a limitation and mostly worry about me, is storing access tokens on cookies. A cookie by default isn't that secure, and can be easily accessed by JavaScript and browser extensions, there are ways to block and secure cookies, but even then, you can just open the developer tools of the browser and see them easily. Even though the only way to something malicious end up happening with these tokens are if the actual client end up being compromised, which means the user has bigger problems than just a social media token being leaked, it's better to try preventing these issues nonetheless (and learn something new as always).
The encryption and decryption part isn't so difficult, Go already provides packages for encryption under the crypto module. So I just implemented an encryption that cyphers a string based on a key environment variable, which I will change every month or so to improve security even more.
Doing this encryption on every endpoint would be repetitive, so adding a middleware would be a solution. I already made a small abstraction over the default Go's router (the DefaultMuxServer struct), which I'm going to be honest, wasn't the best abstraction, since it deviated a lot from Go's default HTTP package conventions. This deviation also would difficult the implementation of a generic middleware that I could use in any route or even any function that handles HTTP requests, a refactor was needed. Refactoring made me end up rewriting a lot of code and simplifying a lot of the code from the project. All routes now are structs that implement the http.Handler interface, so I can use them outside the application router and test them if needed; The router ends up being just a helper for having all routes in a struct, instead of multiple mux.HandleFunc calls in a function, and also handles adding middlewares to all routes; Middlewares end up being just a struct that can return a wrapped HandlerFunc function, which the router calls using a custom/wrapped implementation of the http.ResponseWriter interface, so middlewares can actually modify the content and headers of the response. The refactor had 1148 lines added, and 524 removed, and simplified a lot of the code.
For the encryption middleware, it encrypts all cookie values that are set in the Set-Cookie header, and decrypts any incoming cookie. Also, the encrypted result is encoded to base64, so it can safely be set in the Set-Cookie header after being cyphered.
---
And that's what I worked in around these last three days, today being the one where I actually used all this functionality and actually implemented the OAuth2 process, using an interface and a default implementation that I can easily reimplement for some special cases like Mastodon's OAuth process (since the token and OAuth application needs to be created on each instance separately). It's being interesting learning Go and trying to be more effective and implement things the way the language wants. Everything is being very simple nonetheless, just needing to align my mind with the language mostly.
It has been a while since I wrote one of these long posts, and I remembered why, it takes hours to do, but it's worth the work I would say. Unfortunately I can't write these every day, but hopefully they will become more common, so I can log better the process of working on the projects. Also, for the 2 persons that read this blog, give me some feedback! I really would like to know if there's anything I could improve in the writing, anything that ended up being confusing, or even how I could write the image description for the code snippets, I'm not sure how to make them more accessible for screen reader users.
Nevertheless, completing this project will also help to make these post, since the conversion for Markdown to Tumblr's NPF in the web editor sucks ass, and I know I can do it better.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering the Art of Hiring MERN Stack Programmers: A Step-by-Step Guide
The MERN stack is a popular technology stack. It is an acronym that stands for MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js. Each component of the MERN stack serves a specific purpose in the development process. MongoDB is a NoSQL database that stores data in a JSON-like format, making it flexible and scalable. Express.js is a web application framework for Node.js that provides a set of features for building web applications and APIs. React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces, and it allows developers to create reusable UI components. Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime that allows developers to build scalable network applications. The MERN stack is known for its flexibility, efficiency, and performance. It allows developers to build full-stack applications using JavaScript, which makes the development process more streamlined and cohesive. Additionally, the MERN stack is well-suited for building real-time applications and single-page applications (SPAs). With its robust set of tools and technologies, the MERN stack has become a popular choice for businesses looking to develop modern, responsive web applications.
The Benefits of Hiring MERN Stack Programmers
Hiring MERN stack programmers can offer numerous benefits to businesses looking to develop web applications. MERN stack programmers are skilled in using MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js to build dynamic and responsive web applications. They are proficient in JavaScript and have a deep understanding of the MERN stack architecture, making them valuable assets to any development team. MERN stack programmers are also well-versed in modern web development practices and can leverage the latest tools and technologies to build high-quality applications. They are capable of developing scalable and efficient web applications that can handle large amounts of data and traffic. Additionally, MERN stack programmers are adept at building real-time applications and SPAs, which are increasingly in demand in today's digital landscape. Furthermore, hiring MERN stack programmers can lead to faster development cycles and reduced time-to-market for web applications. Their expertise in the MERN stack allows them to build applications more efficiently, resulting in cost savings and improved productivity for businesses. Overall, hiring MERN stack programmers can provide businesses with the technical expertise and skills needed to develop modern, responsive web applications.
Where to Find Qualified MERN Stack Programmers
Finding qualified MERN stack programmers can be a challenging task, but there are several avenues businesses can explore to locate top talent. One option is to utilize online job boards and platforms specifically tailored to tech professionals, such as GitHub Jobs, Stack Overflow Jobs, and AngelList. These platforms allow businesses to post job listings and connect with experienced MERN stack programmers who are actively seeking new opportunities. Another option is to partner with specialized tech recruitment agencies that have access to a network of skilled MERN stack programmers. These agencies can help businesses identify and recruit top talent by leveraging their industry connections and expertise in the tech sector. Additionally, businesses can attend tech conferences, meetups, and networking events to connect with MERN stack programmers and build relationships within the tech community. Furthermore, businesses can explore freelance platforms such as Upwork and Toptal to find qualified MERN stack programmers who are available for short-term or project-based work. These platforms provide businesses with access to a global pool of tech talent and allow them to review portfolios and work samples before making hiring decisions. Overall, there are several avenues businesses can explore to find qualified MERN stack programmers, each with its own unique advantages and considerations.
How to Evaluate MERN Stack Programmers
Evaluating MERN stack programmers requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account their technical skills, experience, and cultural fit within the organization. One way to assess their technical proficiency is by conducting coding assessments or technical interviews that test their knowledge of JavaScript, MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js. These assessments can help businesses gauge a candidate's ability to solve complex problems and write clean, efficient code using the MERN stack. Another important aspect to consider when evaluating MERN stack programmers is their experience with building real-world applications using the MERN stack. Reviewing their portfolio and work samples can provide insight into the quality of their previous projects and their ability to deliver high-quality web applications. Additionally, businesses can ask candidates about their experience with specific tools and technologies within the MERN stack, such as Redux for state management in React applications or Mongoose for interacting with MongoDB. Cultural fit is also an important factor to consider when evaluating MERN stack programmers. Businesses should assess a candidate's communication skills, teamwork abilities, and willingness to learn and adapt within a dynamic development environment. Conducting behavioral interviews or team-based exercises can help businesses gauge a candidate's interpersonal skills and how well they align with the company's values and culture. Overall, evaluating MERN stack programmers requires a holistic approach that considers their technical skills, experience, and cultural fit within the organization.
Interviewing MERN Stack Programmers
Interviewing MERN stack programmers requires careful preparation and consideration of the specific skills and qualities needed for the role. One approach is to conduct technical interviews that assess a candidate's knowledge of JavaScript, MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js. These interviews can include coding exercises, problem-solving scenarios, or discussions about best practices for building web applications using the MERN stack. Another important aspect of interviewing MERN stack programmers is assessing their experience with building real-world applications and their ability to work within a team environment. Asking candidates about their previous projects, challenges they faced, and how they collaborated with other team members can provide insight into their practical skills and teamwork abilities. Additionally, businesses can use behavioral interviews to assess a candidate's communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and how well they align with the company's values and culture. Furthermore, businesses should consider conducting interviews that focus on specific tools and technologies within the MERN stack, such as Redux for state management in React applications or Mongoose for interacting with MongoDThese interviews can help businesses gauge a candidate's depth of knowledge in key areas of the MERN stack and their ability to leverage these tools effectively in real-world scenarios. Overall, interviewing MERN stack programmers requires a comprehensive approach that assesses their technical skills, practical experience, and cultural fit within the organization.
Onboarding MERN Stack Programmers
Onboarding MERN stack programmers is an important process that sets the stage for their success within the organization. One approach is to provide them with comprehensive training on the specific tools and technologies within the MERN stack, such as Redux for state management in React applications or Mongoose for interacting with MongoDThis training can help new hires become familiar with the company's development environment and best practices for building web applications using the MERN stack. Another important aspect of onboarding MERN stack programmers is integrating them into the development team and providing opportunities for collaboration and knowledge sharing. Pairing new hires with experienced team members or mentors can help them acclimate to the company's culture and development processes while also providing them with valuable guidance and support as they ramp up on new projects. Furthermore, businesses should consider providing new hires with access to resources such as documentation, code repositories, and development tools that will help them navigate their day-to-day responsibilities more effectively. This can include access to internal wikis or knowledge bases that contain information about the company's development processes, coding standards, and best practices for working with the MERN stack. Overall, onboarding MERN stack programmers requires a thoughtful approach that provides them with the training, support, and resources needed to succeed within the organization.
Retaining MERN Stack Programmers
Retaining MERN stack programmers requires ongoing efforts to support their professional growth, provide meaningful work opportunities, and foster a positive work environment. One approach is to offer professional development opportunities such as training programs, workshops, or certifications that allow MERN stack programmers to expand their skills and stay current with industry trends. This can help them feel valued within the organization and provide them with opportunities for career advancement. Another important aspect of retaining MERN stack programmers is providing them with challenging and meaningful work that allows them to leverage their skills and contribute to impactful projects. Offering opportunities for ownership over projects or involvement in decision-making processes can help keep MERN stack programmers engaged and motivated within their roles. Furthermore, fostering a positive work environment that values open communication, collaboration, and work-life balance can contribute to higher job satisfaction among MERN stack programmers. Providing opportunities for team-building activities, social events, or flexible work arrangements can help create a supportive and inclusive culture that encourages retention. Overall, retaining MERN stack programmers requires ongoing efforts to support their professional growth, provide meaningful work opportunities, and foster a positive work environment that values their contributions. By investing in their development and well-being, businesses can increase retention rates among their MERN stack programmers and build a strong foundation for long-term success within their development teams.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
tumblr-backup and datasette
I've been using tumblr_backup, a script that replicates the old Tumblr backup format, for a while. I use it both to back up my main blog and the likes I've accumulated; they outnumber posts over two to one, it turns out.
Sadly, there isn't an 'archive' view of likes, so I have no idea what's there from way back in 2010, when I first really heavily used Tumblr. Heck, even getting back to 2021 is hard. Pulling that data to manipulate it locally seems wise.
I was never quite sure it'd backed up all of my likes, and it turns out that a change to the API was in fact limiting it to the most recent 1,000 entries. Luckily, someone else noticed this well before I did, and a new version, tumblr-backup, not only exists, but is a Python package, which made it easy to install and run. (You do need an API key.)
I ran it using this invocation, which saved likes (-l), didn't download images (-k), skipped the first 1,000 entries (-s 1000), and output to the directory 'likes/full' (-O):
tumblr-backup -j -k -l -s 1000 blech -O likes/full
This gave me over 12,000 files in likes/full/json, one per like. This is great, but a database is nice for querying. Luckily, jq exists:
jq -s 'map(.)' likes/full/json/*.json > likes/full/likes.json
This slurps (-s) in every JSON file, iterates over them to make a list, and then saves it in a new JSON file, likes.json. There was a follow-up I did to get it into the right format for sqlite3:
jq -c '.[]' likes/full/likes.json > likes/full/likes-nl.json
A smart reader can probably combine those into a single operator.
Using Simon Willison's sqlite-utils package, I could then load all of them into a database (with --alter because the keys of each JSON file vary, so the initial column setup is incomplete):
sqlite-utils insert likes/full/likes.db lines likes/full/likes-nl.json --nl --alter
This can then be fed into Willison's Datasette for a nice web UI to query it:
datasette serve --port 8002 likes/full/likes.d
There are a lot of columns there that clutter up the view: I'd suggest this is a good subset (it also shows the post with most notes (likes, reblogs, and comments combined) at the top):
select rowid, id, short_url, slug, blog_name, date, timestamp, liked_timestamp, caption, format, note_count, state, summary, tags, type from lines order by note_count desc limit 101
Happy excavating!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Web Scraping TripAdvisor Reviews Data Boosts Your Business Growth

Are you one of the 94% of buyers who rely on online reviews to make the final decision? This means that most people today explore reviews before taking action, whether booking hotels, visiting a place, buying a book, or something else.
We understand the stress of booking the right place, especially when visiting somewhere new. Finding the balance between a perfect spot, services, and budget is challenging. Many of you consider TripAdvisor reviews a go-to solution for closely getting to know the place.
Here comes the accurate game-changing method—scrape TripAdvisor reviews data. But wait, is it legal and ethical? Yes, as long as you respect the website's terms of service, don't overload its servers, and use the data for personal or non-commercial purposes. What? How? Why?
Do not stress. We will help you understand why many hotel, restaurant, and attraction place owners invest in web scraping TripAdvisor reviews or other platform information. This powerful tool empowers you to understand your performance and competitors' strategies, enabling you to make informed business changes. What next?
Let's dive in and give you a complete tour of the process of web scraping TripAdvisor review data!
What Is Scraping TripAdvisor Reviews Data?
Extracting customer reviews and other relevant information from the TripAdvisor platform through different web scraping methods. This process works by accessing publicly available website data and storing it in a structured format to analyze or monitor.
Various methods and tools available in the market have unique features that allow you to extract TripAdvisor hotel review data hassle-free. Here are the different types of data you can scrape from a TripAdvisor review scraper:
Hotels
Ratings
Awards
Location
Pricing
Number of reviews
Review date
Reviewer's Name
Restaurants
Images
You may want other information per your business plan, which can be easily added to your requirements.
What Are The Ways To Scrape TripAdvisor Reviews Data?
TripAdvisor uses different web scraping methods to review data, depending on available resources and expertise. Let us look at them:
Scrape TripAdvisor Reviews Data Using Web Scraping API
An API helps to connect various programs to gather data without revealing the code used to execute the process. The scrape TripAdvisor Reviews is a standard JSON format that does not require technical knowledge, CAPTCHAs, or maintenance.
Now let us look at the complete process:
First, check if you need to install the software on your device or if it's browser-based and does not need anything. Then, download and install the desired software you will be using for restaurant, location, or hotel review scraping. The process is straightforward and user-friendly, ensuring your confidence in using these tools.
Now redirect to the web page you want to scrape data from and copy the URL to paste it into the program.
Make updates in the HTML output per your requirements and the information you want to scrape from TripAdvisor reviews.
Most tools start by extracting different HTML elements, especially the text. You can then select the categories that need to be extracted, such as Inner HTML, href attribute, class attribute, and more.
Export the data in SPSS, Graphpad, or XLSTAT format per your requirements for further analysis.
Scrape TripAdvisor Reviews Using Python
TripAdvisor review information is analyzed to understand the experience of hotels, locations, or restaurants. Now let us help you to scrape TripAdvisor reviews using Python:
Continue reading https://www.reviewgators.com/how-web-scraping-tripadvisor-reviews-data-boosts-your-business-growth.php
#review scraping#Scraping TripAdvisor Reviews#web scraping TripAdvisor reviews#TripAdvisor review scraper
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
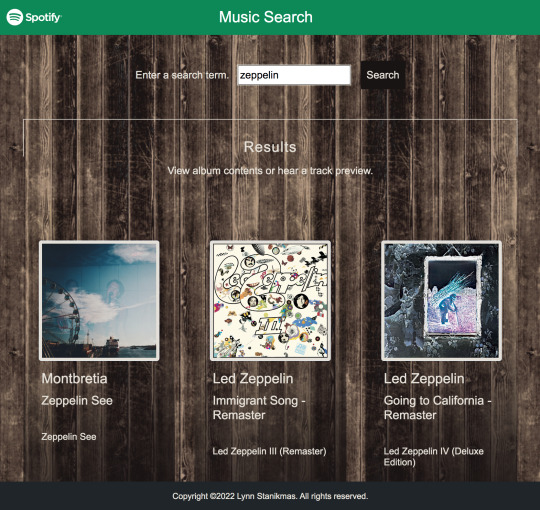






Angular SPA integrated with the Spotify Web API returns JSON metadata about music artists, albums, and tracks, directly from the Spotify Data Catalogue.
#angular#spotify#my music#firebase#firestore#data#database#backend#html5#frontend#coding#responsive web design company#responsivewebsite#responsivedesign#responsive web development#web development#web developers#software development#software#development#information technology#developer#technology#engineering#ui ux development services#ui#ui ux design#uidesign#ux#user interface
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
This Week in Rust 533
Hello and welcome to another issue of This Week in Rust! Rust is a programming language empowering everyone to build reliable and efficient software. This is a weekly summary of its progress and community. Want something mentioned? Tag us at @ThisWeekInRust on Twitter or @ThisWeekinRust on mastodon.social, or send us a pull request. Want to get involved? We love contributions.
This Week in Rust is openly developed on GitHub and archives can be viewed at this-week-in-rust.org. If you find any errors in this week's issue, please submit a PR.
Updates from Rust Community
Official
crates.io: API status code changes
Foundation
Google Contributes $1M to Rust Foundation to Support C++/Rust "Interop Initiative"
Project/Tooling Updates
Announcing the Tauri v2 Beta Release
Polars — Why we have rewritten the string data type
rust-analyzer changelog #219
Ratatui 0.26.0 - a Rust library for cooking up terminal user interfaces
Observations/Thoughts
Will it block?
Embedded Rust in Production ..?
Let futures be futures
Compiling Rust is testing
Rust web frameworks have subpar error reporting
[video] Proving Performance - FOSDEM 2024 - Rust Dev Room
[video] Stefan Baumgartner - Trials, Traits, and Tribulations
[video] Rainer Stropek - Memory Management in Rust
[video] Shachar Langbeheim - Async & FFI - not exactly a love story
[video] Massimiliano Mantione - Object Oriented Programming, and Rust
[audio] Unlocking Rust's power through mentorship and knowledge spreading, with Tim McNamara
[audio] Asciinema with Marcin Kulik
Non-Affine Types, ManuallyDrop and Invariant Lifetimes in Rust - Part One
Nine Rules for Accessing Cloud Files from Your Rust Code: Practical lessons from upgrading Bed-Reader, a bioinformatics library
Rust Walkthroughs
AsyncWrite and a Tale of Four Implementations
Garbage Collection Without Unsafe Code
Fragment specifiers in Rust Macros
Writing a REST API in Rust
[video] Traits and operators
Write a simple netcat client and server in Rust
Miscellaneous
RustFest 2024 Announcement
Preprocessing trillions of tokens with Rust (case study)
All EuroRust 2023 talks ordered by the view count
Crate of the Week
This week's crate is embedded-cli-rs, a library that makes it easy to create CLIs on embedded devices.
Thanks to Sviatoslav Kokurin for the self-suggestion!
Please submit your suggestions and votes for next week!
Call for Participation; projects and speakers
CFP - Projects
Always wanted to contribute to open-source projects but did not know where to start? Every week we highlight some tasks from the Rust community for you to pick and get started!
Some of these tasks may also have mentors available, visit the task page for more information.
Fluvio - Build a new python wrapping for the fluvio client crate
Fluvio - MQTT Connector: Prefix auto generated Client ID to prevent connection drops
Ockam - Implement events in SqlxDatabase
Ockam - Output for both ockam project ticket and ockam project enroll is improved, with support for --output json
Ockam - Output for ockam project ticket is improved and information is not opaque
Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Setup code coverage for local tests & CI
Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Have get_required_value to use ValidationError in OptionExt
If you are a Rust project owner and are looking for contributors, please submit tasks here.
CFP - Speakers
Are you a new or experienced speaker looking for a place to share something cool? This section highlights events that are being planned and are accepting submissions to join their event as a speaker.
RustNL 2024 CFP closes 2024-02-19 | Delft, The Netherlands | Event date: 2024-05-07 & 2024-05-08
NDC Techtown CFP closes 2024-04-14 | Kongsberg, Norway | Event date: 2024-09-09 to 2024-09-12
If you are an event organizer hoping to expand the reach of your event, please submit a link to the submission website through a PR to TWiR.
Updates from the Rust Project
309 pull requests were merged in the last week
add avx512fp16 to x86 target features
riscv only supports split_debuginfo=off for now
target: default to the medium code model on LoongArch targets
#![feature(inline_const_pat)] is no longer incomplete
actually abort in -Zpanic-abort-tests
add missing potential_query_instability for keys and values in hashmap
avoid ICE when is_val_statically_known is not of a supported type
be more careful about interpreting a label/lifetime as a mistyped char literal
check RUST_BOOTSTRAP_CONFIG in profile_user_dist test
correctly check never_type feature gating
coverage: improve handling of function/closure spans
coverage: use normal edition: headers in coverage tests
deduplicate more sized errors on call exprs
pattern_analysis: Gracefully abort on type incompatibility
pattern_analysis: cleanup manual impls
pattern_analysis: cleanup the contexts
fix BufReader unsoundness by adding a check in default_read_buf
fix ICE on field access on a tainted type after const-eval failure
hir: refactor getters for owner nodes
hir: remove the generic type parameter from MaybeOwned
improve the diagnostics for unused generic parameters
introduce support for async bound modifier on Fn* traits
make matching on NaN a hard error, and remove the rest of illegal_floating_point_literal_pattern
make the coroutine def id of an async closure the child of the closure def id
miscellaneous diagnostics cleanups
move UI issue tests to subdirectories
move predicate, region, and const stuff into their own modules in middle
never patterns: It is correct to lower ! to _
normalize region obligation in lexical region resolution with next-gen solver
only suggest removal of as_* and to_ conversion methods on E0308
provide more context on derived obligation error primary label
suggest changing type to const parameters if we encounter a type in the trait bound position
suppress unhelpful diagnostics for unresolved top level attributes
miri: normalize struct tail in ABI compat check
miri: moving out sched_getaffinity interception from linux'shim, FreeBSD su…
miri: switch over to rustc's tracing crate instead of using our own log crate
revert unsound libcore changes
fix some Arc allocator leaks
use <T, U> for array/slice equality impls
improve io::Read::read_buf_exact error case
reject infinitely-sized reads from io::Repeat
thread_local::register_dtor fix proposal for FreeBSD
add LocalWaker and ContextBuilder types to core, and LocalWake trait to alloc
codegen_gcc: improve iterator for files suppression
cargo: Don't panic on empty spans
cargo: Improve map/sequence error message
cargo: apply -Zpanic-abort-tests to doctests too
cargo: don't print rustdoc command lines on failure by default
cargo: stabilize lockfile v4
cargo: fix markdown line break in cargo-add
cargo: use spec id instead of name to match package
rustdoc: fix footnote handling
rustdoc: correctly handle attribute merge if this is a glob reexport
rustdoc: prevent JS injection from localStorage
rustdoc: trait.impl, type.impl: sort impls to make it not depend on serialization order
clippy: redundant_locals: take by-value closure captures into account
clippy: new lint: manual_c_str_literals
clippy: add lint_groups_priority lint
clippy: add new lint: ref_as_ptr
clippy: add configuration for wildcard_imports to ignore certain imports
clippy: avoid deleting labeled blocks
clippy: fixed FP in unused_io_amount for Ok(lit), unrachable! and unwrap de…
rust-analyzer: "Normalize import" assist and utilities for normalizing use trees
rust-analyzer: enable excluding refs search results in test
rust-analyzer: support for GOTO def from inside files included with include! macro
rust-analyzer: emit parser error for missing argument list
rust-analyzer: swap Subtree::token_trees from Vec to boxed slice
Rust Compiler Performance Triage
Rust's CI was down most of the week, leading to a much smaller collection of commits than usual. Results are mostly neutral for the week.
Triage done by @simulacrum. Revision range: 5c9c3c78..0984bec
0 Regressions, 2 Improvements, 1 Mixed; 1 of them in rollups 17 artifact comparisons made in total
Full report here
Approved RFCs
Changes to Rust follow the Rust RFC (request for comments) process. These are the RFCs that were approved for implementation this week:
No RFCs were approved this week.
Final Comment Period
Every week, the team announces the 'final comment period' for RFCs and key PRs which are reaching a decision. Express your opinions now.
RFCs
No RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Tracking Issues & PRs
[disposition: merge] Consider principal trait ref's auto-trait super-traits in dyn upcasting
[disposition: merge] remove sub_relations from the InferCtxt
[disposition: merge] Optimize away poison guards when std is built with panic=abort
[disposition: merge] Check normalized call signature for WF in mir typeck
Language Reference
No Language Reference RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Unsafe Code Guidelines
No Unsafe Code Guideline RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
New and Updated RFCs
Nested function scoped type parameters
Call for Testing
An important step for RFC implementation is for people to experiment with the implementation and give feedback, especially before stabilization. The following RFCs would benefit from user testing before moving forward:
No RFCs issued a call for testing this week.
If you are a feature implementer and would like your RFC to appear on the above list, add the new call-for-testing label to your RFC along with a comment providing testing instructions and/or guidance on which aspect(s) of the feature need testing.
Upcoming Events
Rusty Events between 2024-02-07 - 2024-03-06 🦀
Virtual
2024-02-07 | Virtual (Indianapolis, IN, US) | Indy Rust
Indy.rs - Ezra Singh - How Rust Saved My Eyes
2024-02-08 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-02-08 | Virtual (Nürnberg, DE) | Rust Nüremberg
Rust Nürnberg online
2024-02-10 | Virtual (Krakow, PL) | Stacja IT Kraków
Rust – budowanie narzędzi działających w linii komend
2024-02-10 | Virtual (Wrocław, PL) | Stacja IT Wrocław
Rust – budowanie narzędzi działających w linii komend
2024-02-13 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Second Tuesday
2024-02-15 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust Hack n Learn | Mirror: Rust Hack n Learn
2024-02-15 | Virtual + In person (Praha, CZ) | Rust Czech Republic
Introduction and Rust in production
2024-02-19 | Virtual (Melbourne, VIC, AU) | Rust Melbourne
February 2024 Rust Melbourne Meetup
2024-02-20 | Virtual | Rust for Lunch
Lunch
2024-02-21 | Virtual (Cardiff, UK) | Rust and C++ Cardiff
Rust for Rustaceans Book Club: Chapter 2 - Types
2024-02-21 | Virtual (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
2024-02-22 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
Asia
2024-02-10 | Hyderabad, IN | Rust Language Hyderabad
Rust Language Develope BootCamp
Europe
2024-02-07 | Cologne, DE | Rust Cologne
Embedded Abstractions | Event page
2024-02-07 | London, UK | Rust London User Group
Rust for the Web — Mainmatter x Shuttle Takeover
2024-02-08 | Bern, CH | Rust Bern
Rust Bern Meetup #1 2024 🦀
2024-02-08 | Oslo, NO | Rust Oslo
Rust-based banter
2024-02-13 | Trondheim, NO | Rust Trondheim
Building Games with Rust: Dive into the Bevy Framework
2024-02-15 | Praha, CZ - Virtual + In-person | Rust Czech Republic
Introduction and Rust in production
2024-02-21 | Lyon, FR | Rust Lyon
Rust Lyon Meetup #8
2024-02-22 | Aarhus, DK | Rust Aarhus
Rust and Talk at Partisia
North America
2024-02-07 | Brookline, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Coolidge Corner Brookline Rust Lunch, Feb 7
2024-02-08 | Lehi, UT, US | Utah Rust
BEAST: Recreating a classic DOS terminal game in Rust
2024-02-12 | Minneapolis, MN, US | Minneapolis Rust Meetup
Minneapolis Rust: Open Source Contrib Hackathon & Happy Hour
2024-02-13 | New York, NY, US | Rust NYC
Rust NYC Monthly Mixer
2024-02-13 | Seattle, WA, US | Cap Hill Rust Coding/Hacking/Learning
Rusty Coding/Hacking/Learning Night
2024-02-15 | Boston, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Back Bay Rust Lunch, Feb 15
2024-02-15 | Seattle, WA, US | Seattle Rust User Group
Seattle Rust User Group Meetup
2024-02-20 | San Francisco, CA, US | San Francisco Rust Study Group
Rust Hacking in Person
2024-02-22 | Mountain View, CA, US | Mountain View Rust Meetup
Rust Meetup at Hacker Dojo
2024-02-28 | Austin, TX, US | Rust ATX
Rust Lunch - Fareground
Oceania
2024-02-19 | Melbourne, VIC, AU + Virtual | Rust Melbourne
February 2024 Rust Melbourne Meetup
2024-02-27 | Canberra, ACT, AU | Canberra Rust User Group
February Meetup
2024-02-27 | Sydney, NSW, AU | Rust Sydney
🦀 spire ⚡ & Quick
If you are running a Rust event please add it to the calendar to get it mentioned here. Please remember to add a link to the event too. Email the Rust Community Team for access.
Jobs
Please see the latest Who's Hiring thread on r/rust
Quote of the Week
My take on this is that you cannot use async Rust correctly and fluently without understanding Arc, Mutex, the mutability of variables/references, and how async and await syntax compiles in the end. Rust forces you to understand how and why things are the way they are. It gives you minimal abstraction to do things that could’ve been tedious to do yourself.
I got a chance to work on two projects that drastically forced me to understand how async/await works. The first one is to transform a library that is completely sync and only requires a sync trait to talk to the outside service. This all sounds fine, right? Well, this becomes a problem when we try to port it into browsers. The browser is single-threaded and cannot block the JavaScript runtime at all! It is arguably the most weird environment for Rust users. It is simply impossible to rewrite the whole library, as it has already been shipped to production on other platforms.
What we did instead was rewrite the network part using async syntax, but using our own generator. The idea is simple: the generator produces a future when called, and the produced future can be awaited. But! The produced future contains an arc pointer to the generator. That means we can feed the generator the value we are waiting for, then the caller who holds the reference to the generator can feed the result back to the function and resume it. For the browser, we use the native browser API to derive the network communications; for other platforms, we just use regular blocking network calls. The external interface remains unchanged for other platforms.
Honestly, I don’t think any other language out there could possibly do this. Maybe C or C++, but which will never have the same development speed and developer experience.
I believe people have already mentioned it, but the current asynchronous model of Rust is the most reasonable choice. It does create pain for developers, but on the other hand, there is no better asynchronous model for Embedded or WebAssembly.
– /u/Top_Outlandishness78 on /r/rust
Thanks to Brian Kung for the suggestion!
Please submit quotes and vote for next week!
This Week in Rust is edited by: nellshamrell, llogiq, cdmistman, ericseppanen, extrawurst, andrewpollack, U007D, kolharsam, joelmarcey, mariannegoldin, bennyvasquez.
Email list hosting is sponsored by The Rust Foundation
Discuss on r/rust
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Advanced Techniques in Full-Stack Development

Certainly, let's delve deeper into more advanced techniques and concepts in full-stack development:
1. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG):
SSR: Rendering web pages on the server side to improve performance and SEO by delivering fully rendered pages to the client.
SSG: Generating static HTML files at build time, enhancing speed, and reducing the server load.
2. WebAssembly:
WebAssembly (Wasm): A binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine. It allows high-performance execution of code on web browsers, enabling languages like C, C++, and Rust to run in web applications.
3. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) Enhancements:
Background Sync: Allowing PWAs to sync data in the background even when the app is closed.
Web Push Notifications: Implementing push notifications to engage users even when they are not actively using the application.
4. State Management:
Redux and MobX: Advanced state management libraries in React applications for managing complex application states efficiently.
Reactive Programming: Utilizing RxJS or other reactive programming libraries to handle asynchronous data streams and events in real-time applications.
5. WebSockets and WebRTC:
WebSockets: Enabling real-time, bidirectional communication between clients and servers for applications requiring constant data updates.
WebRTC: Facilitating real-time communication, such as video chat, directly between web browsers without the need for plugins or additional software.
6. Caching Strategies:
Content Delivery Networks (CDN): Leveraging CDNs to cache and distribute content globally, improving website loading speeds for users worldwide.
Service Workers: Using service workers to cache assets and data, providing offline access and improving performance for returning visitors.
7. GraphQL Subscriptions:
GraphQL Subscriptions: Enabling real-time updates in GraphQL APIs by allowing clients to subscribe to specific events and receive push notifications when data changes.
8. Authentication and Authorization:
OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect: Implementing secure authentication and authorization protocols for user login and access control.
JSON Web Tokens (JWT): Utilizing JWTs to securely transmit information between parties, ensuring data integrity and authenticity.
9. Content Management Systems (CMS) Integration:
Headless CMS: Integrating headless CMS like Contentful or Strapi, allowing content creators to manage content independently from the application's front end.
10. Automated Performance Optimization:
Lighthouse and Web Vitals: Utilizing tools like Lighthouse and Google's Web Vitals to measure and optimize web performance, focusing on key user-centric metrics like loading speed and interactivity.
11. Machine Learning and AI Integration:
TensorFlow.js and ONNX.js: Integrating machine learning models directly into web applications for tasks like image recognition, language processing, and recommendation systems.
12. Cross-Platform Development with Electron:
Electron: Building cross-platform desktop applications using web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), allowing developers to create desktop apps for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
13. Advanced Database Techniques:
Database Sharding: Implementing database sharding techniques to distribute large databases across multiple servers, improving scalability and performance.
Full-Text Search and Indexing: Implementing full-text search capabilities and optimized indexing for efficient searching and data retrieval.
14. Chaos Engineering:
Chaos Engineering: Introducing controlled experiments to identify weaknesses and potential failures in the system, ensuring the application's resilience and reliability.
15. Serverless Architectures with AWS Lambda or Azure Functions:
Serverless Architectures: Building applications as a collection of small, single-purpose functions that run in a serverless environment, providing automatic scaling and cost efficiency.
16. Data Pipelines and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Processes:
Data Pipelines: Creating automated data pipelines for processing and transforming large volumes of data, integrating various data sources and ensuring data consistency.
17. Responsive Design and Accessibility:
Responsive Design: Implementing advanced responsive design techniques for seamless user experiences across a variety of devices and screen sizes.
Accessibility: Ensuring web applications are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by following WCAG guidelines and ARIA practices.
full stack development training in Pune
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
You can learn NodeJS easily, Here's all you need:
1.Introduction to Node.js
• JavaScript Runtime for Server-Side Development
• Non-Blocking I/0
2.Setting Up Node.js
• Installing Node.js and NPM
• Package.json Configuration
• Node Version Manager (NVM)
3.Node.js Modules
• CommonJS Modules (require, module.exports)
• ES6 Modules (import, export)
• Built-in Modules (e.g., fs, http, events)
4.Core Concepts
• Event Loop
• Callbacks and Asynchronous Programming
• Streams and Buffers
5.Core Modules
• fs (File Svstem)
• http and https (HTTP Modules)
• events (Event Emitter)
• util (Utilities)
• os (Operating System)
• path (Path Module)
6.NPM (Node Package Manager)
• Installing Packages
• Creating and Managing package.json
• Semantic Versioning
• NPM Scripts
7.Asynchronous Programming in Node.js
• Callbacks
• Promises
• Async/Await
• Error-First Callbacks
8.Express.js Framework
• Routing
• Middleware
• Templating Engines (Pug, EJS)
• RESTful APIs
• Error Handling Middleware
9.Working with Databases
• Connecting to Databases (MongoDB, MySQL)
• Mongoose (for MongoDB)
• Sequelize (for MySQL)
• Database Migrations and Seeders
10.Authentication and Authorization
• JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
• Passport.js Middleware
• OAuth and OAuth2
11.Security
• Helmet.js (Security Middleware)
• Input Validation and Sanitization
• Secure Headers
• Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
12.Testing and Debugging
• Unit Testing (Mocha, Chai)
• Debugging Tools (Node Inspector)
• Load Testing (Artillery, Apache Bench)
13.API Documentation
• Swagger
• API Blueprint
• Postman Documentation
14.Real-Time Applications
• WebSockets (Socket.io)
• Server-Sent Events (SSE)
• WebRTC for Video Calls
15.Performance Optimization
• Caching Strategies (in-memory, Redis)
• Load Balancing (Nginx, HAProxy)
• Profiling and Optimization Tools (Node Clinic, New Relic)
16.Deployment and Hosting
• Deploying Node.js Apps (PM2, Forever)
• Hosting Platforms (AWS, Heroku, DigitalOcean)
• Continuous Integration and Deployment-(Jenkins, Travis CI)
17.RESTful API Design
• Best Practices
• API Versioning
• HATEOAS (Hypermedia as the Engine-of Application State)
18.Middleware and Custom Modules
• Creating Custom Middleware
• Organizing Code into Modules
• Publish and Use Private NPM Packages
19.Logging
• Winston Logger
• Morgan Middleware
• Log Rotation Strategies
20.Streaming and Buffers
• Readable and Writable Streams
• Buffers
• Transform Streams
21.Error Handling and Monitoring
• Sentry and Error Tracking
• Health Checks and Monitoring Endpoints
22.Microservices Architecture
• Principles of Microservices
• Communication Patterns (REST, gRPC)
• Service Discovery and Load Balancing in Microservices
1 note
·
View note
Text
Protect Your Laravel APIs: Common Vulnerabilities and Fixes
API Vulnerabilities in Laravel: What You Need to Know
As web applications evolve, securing APIs becomes a critical aspect of overall cybersecurity. Laravel, being one of the most popular PHP frameworks, provides many features to help developers create robust APIs. However, like any software, APIs in Laravel are susceptible to certain vulnerabilities that can leave your system open to attack.

In this blog post, we’ll explore common API vulnerabilities in Laravel and how you can address them, using practical coding examples. Additionally, we’ll introduce our free Website Security Scanner tool, which can help you assess and protect your web applications.
Common API Vulnerabilities in Laravel
Laravel APIs, like any other API, can suffer from common security vulnerabilities if not properly secured. Some of these vulnerabilities include:
>> SQL Injection SQL injection attacks occur when an attacker is able to manipulate an SQL query to execute arbitrary code. If a Laravel API fails to properly sanitize user inputs, this type of vulnerability can be exploited.
Example Vulnerability:
$user = DB::select("SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '" . $request->input('username') . "'");
Solution: Laravel’s query builder automatically escapes parameters, preventing SQL injection. Use the query builder or Eloquent ORM like this:
$user = DB::table('users')->where('username', $request->input('username'))->first();
>> Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) XSS attacks happen when an attacker injects malicious scripts into web pages, which can then be executed in the browser of a user who views the page.
Example Vulnerability:
return response()->json(['message' => $request->input('message')]);
Solution: Always sanitize user input and escape any dynamic content. Laravel provides built-in XSS protection by escaping data before rendering it in views:
return response()->json(['message' => e($request->input('message'))]);
>> Improper Authentication and Authorization Without proper authentication, unauthorized users may gain access to sensitive data. Similarly, improper authorization can allow unauthorized users to perform actions they shouldn't be able to.
Example Vulnerability:
Route::post('update-profile', 'UserController@updateProfile');
Solution: Always use Laravel’s built-in authentication middleware to protect sensitive routes:
Route::middleware('auth:api')->post('update-profile', 'UserController@updateProfile');
>> Insecure API Endpoints Exposing too many endpoints or sensitive data can create a security risk. It’s important to limit access to API routes and use proper HTTP methods for each action.
Example Vulnerability:
Route::get('user-details', 'UserController@getUserDetails');
Solution: Restrict sensitive routes to authenticated users and use proper HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE:
Route::middleware('auth:api')->get('user-details', 'UserController@getUserDetails');
How to Use Our Free Website Security Checker Tool
If you're unsure about the security posture of your Laravel API or any other web application, we offer a free Website Security Checker tool. This tool allows you to perform an automatic security scan on your website to detect vulnerabilities, including API security flaws.
Step 1: Visit our free Website Security Checker at https://free.pentesttesting.com. Step 2: Enter your website URL and click "Start Test". Step 3: Review the comprehensive vulnerability assessment report to identify areas that need attention.
Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Example Report: Vulnerability Assessment
Once the scan is completed, you'll receive a detailed report that highlights any vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection risks, XSS vulnerabilities, and issues with authentication. This will help you take immediate action to secure your API endpoints.
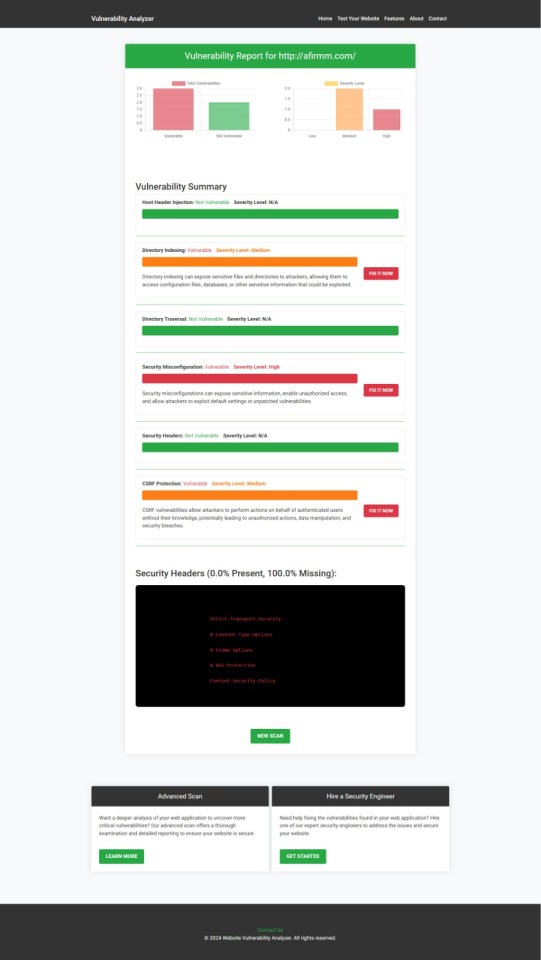
An example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool provides insights into possible vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: Strengthen Your API Security Today
API vulnerabilities in Laravel are common, but with the right precautions and coding practices, you can protect your web application. Make sure to always sanitize user input, implement strong authentication mechanisms, and use proper route protection. Additionally, take advantage of our tool to check Website vulnerability to ensure your Laravel APIs remain secure.
For more information on securing your Laravel applications try our Website Security Checker.
#cyber security#cybersecurity#data security#pentesting#security#the security breach show#laravel#php#api
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
OK I figured I should probably reveal The Grand Secret of how I was able to get the exact vote counts. So here's what you do. On firefox at least.
But hey! You don't even have to make an API call yourself!
1. Open the web developer console
I'm sure you've used this to make some funny and/or wacky HTML edits. But if you haven't, there's four ways to open it:
Right click then press Q
Right click then click on the "inspect" option from the menu
Click on the hamburger menu in the top right corner, then "more tools," then "web developer tools"
Press Control, Shift, and I
At this point, it should look a little something like this:
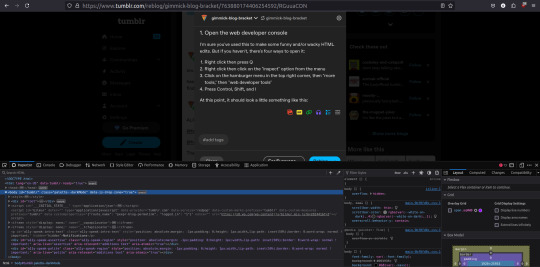
2. Go to the relevant post
I will say that the link is a bit finicky?
But, at least for this post, the link you should follow is this: https://www.tumblr.com/gimmick-blog-bracket/763237589691023360
3. Go to "network" tab of the web developer console
It's hard to miss the tabs at the top of the console; just find the correct one and click it.
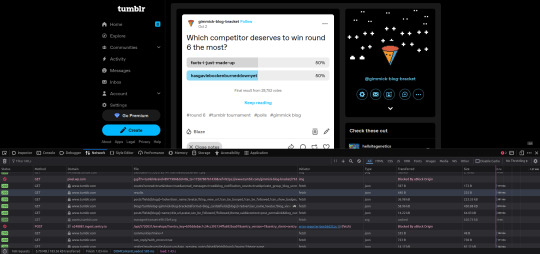
You're looking for a JSON file called "results." I found that it was consistently the first "results" file to appear in the list; others are further down and grouped together. They're for different polls and I don't know why they are there.
Just double click on it and you should be brought to a new tab that has something like this:

So yes, it is an API request. It's just that it's being made automatically by Tumblr rather than manually by me.
Those UUIDs represent each option: the first one is facts-i-just-made-up and the second is hasgavlebockenburneddownyet.
@facts-i-just-made-up
They're a good lesson in fact checking the bare minimum (looking at least at the blog name)
@hasgavlebockenburneddownyet
What's more happy holiday cheer than cheering on the destruction of a giant straw goat?
The birds may have won 2023, but I believe in humanity's capability for arson for 2024 <3
10K notes
·
View notes