#Neolithic
Text
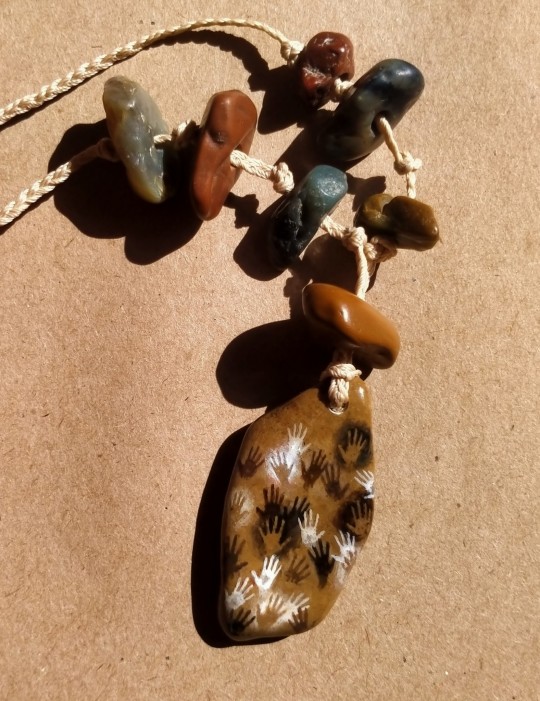
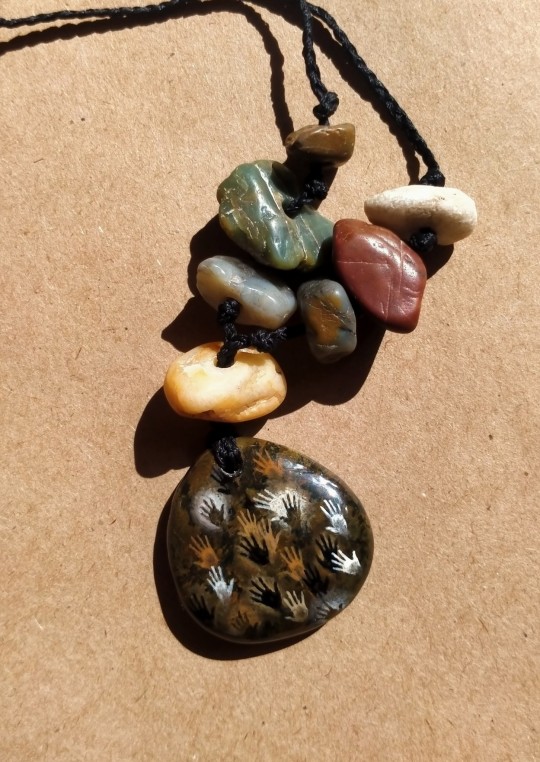




New cave paintings necklaces. Small jasper and quartz river pebbles I found on a river bank. Now thinking about trying different imagery for similar pieces.
Both available
#cave art#handprints#neolithic#rock art#miniature#rock painting#painted stones#painted rocks#minerals#jasper#quartz#necklace#cave paintings#painted miniatures#my art#beach findings#beach combing#artists on tumblr
140 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Sweet Track
The Sweet Track is a Neolithic timber walkway, located in the Somerset Levels, England. It was originally part of a network of tracks built to provide a dry path across the marshy ground. The Sweet Track ran between what was then an island at Westhay to a ridge of high ground, close to the River Bruce. The remains of mounds have also been found at Westhay, indicating the remains of a settlement.
About 1.6 kilometres (1 mile) long, the Sweet Track was discovered in the 1970s CE during a peat excavation by Ray Sweet, (who also gave the track its name). Using dendrochronology (tree-ring dating) the track has been dated 3807/3806 BCE. For many years it was thought to be the oldest trackway in Northern Europe, until 2009 CE when a slightly older one was discovered in Plumstead, London.
The Somerset Levels are an area of wetlands and peats. The conditions of such areas can naturally lead to the preservation of organic materials. Materials become encased in a wet and airless environment, thus preventing, to a degree, decomposition. Wooden artefacts and structures have been recovered from the Levels, as well as the two well-preserved Iron Age villages of Glastonbury and Meare.
The track would have been built by a community of Neolithic farmers living in small settlements. Farming had spread from the Middle East and by this point was firmly established in Britain. According to pollen evidence, the whole of Britain would have been covered in forests at this time. The Neolithic peoples would have burnt and cleared the forests to have the land on which to grow their crops, mostly grains. A fair degree of organization is evident in the stockpiling of wood and construction of the tracks, and some members of the community would have had to have skills in woodworking. Using stone and flint axes, the trees for the track were cut on dry land with different cutting techniques used, depending on their age. Older oaks were cut vertically whilst younger trees tangentially. Modern research has been carried out using replica axes and the cut marks have also been studied to establish the methods of cutting used. The planks of wood were put together in the marsh, the final construction taking about a day to complete. Long poles were driven slantwise into the ground and then planks were laid in between, held in place by vertical pegs. The planks were made of oak, ash and lime. The poles and pegs were made mainly of hazel and alder. There are also remains of another track, known as the “Post Track”, which dates 30 years earlier than the Sweet Track, 3838 BCE. It ran roughly parallel to the Sweet Track, possibly used by the builders of the Sweet Track as an access route.
Artefacts have been found beside the track, among them, pottery and axe heads including one made of jadeite. Whether they had been deliberately buried, perhaps as an offering, or just lost, remains unknown. There have been many Prehistoric trackways found in England, but more than half reside in Somerset. Included in these are the Abbot's Way, Eclipse, Honeygore, Meare Health and Garvins tracks. They were constructed using varying styles, such as corduroy - laying short logs parallel to each other and side by side. The Sweet Track is the most well-known of these. It has been declared a scheduled monument (of national importance). Most of it remains in its original location and requires constant conservation to keep the wood in its damp condition. There are reproductions and a donated section now resides in the British Museum, London.
Continue reading...
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discover how LiDAR technology has unveiled pathways for the dead in prehistoric Ireland, reshaping our understanding of the ancient Baltinglass landscape.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
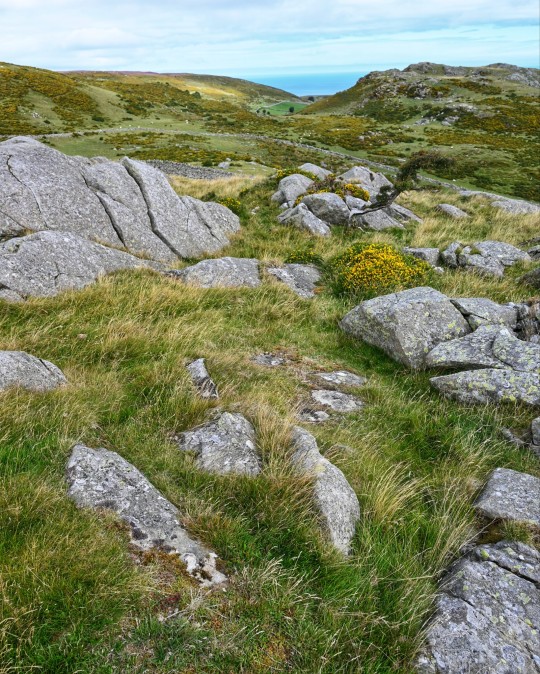
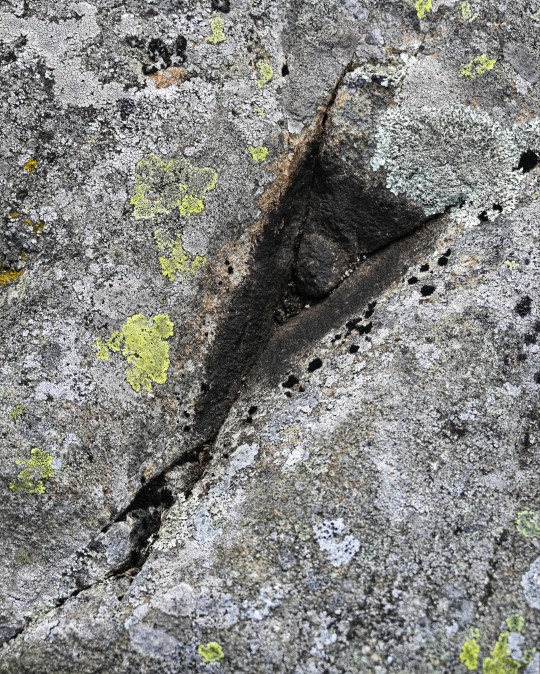
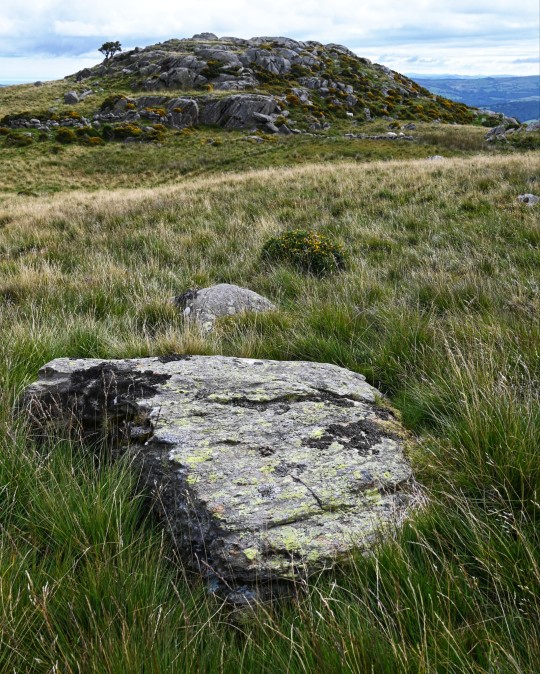
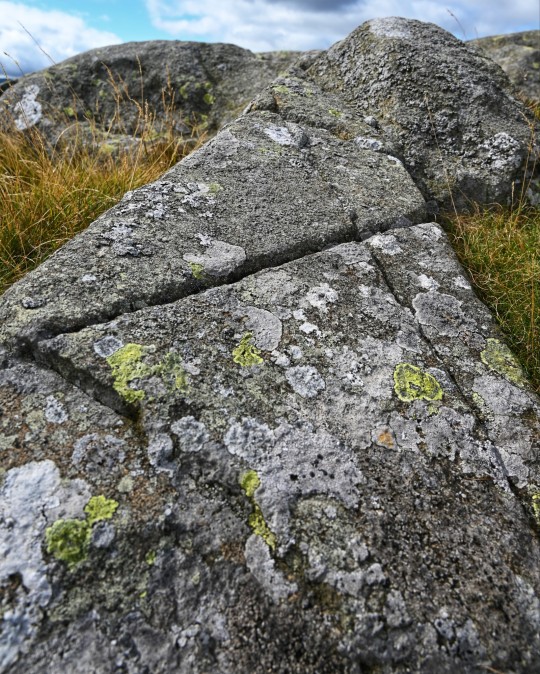







Craig Celynin Ancient Landscape, nr. Rowen, Conwy Valley, Wales
#ice age#stone age#bronze age#copper age#iron age#neolithic#mesolithic#calcholithic#paleolithic#prehistoric#prehistory#landscape#wales#archaeology#geology
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

Cave Art of Banging, Algeria, c. 7000 BCE
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
A system of ancient ceramic water pipes, the oldest ever unearthed in China, shows that neolithic people were capable of complex engineering feats without the need for a centralized state authority, finds a new study by University College London researchers.
In a study published in Nature Water, the archaeological team describe a network of ceramic water pipes and drainage ditches at the Chinese walled site of Pingliangtai dating back 4,000 years to a time known as the Longshan period. The network shows cooperation among the community to build and maintain the drainage system, though no evidence of a centralized power or authority.
Dr. Yijie Zhuang (UCL Institute of Archaeology), senior and corresponding author on the paper, said, "The discovery of this ceramic water pipe network is remarkable because the people of Pingliangtai were able to build and maintain this advanced water management system with stone age tools and without the organization of a central power structure. This system would have required a significant level of community-wide planning and coordination, and it was all done communally."
The ceramic water pipes make up a drainage system which is the oldest complete system ever discovered in China. Made by interconnecting individual segments, the water pipes run along roads and walls to divert rainwater and show an advanced level of central planning at the neolithic site.
What's surprising to researchers is that the settlement of Pingliangtai shows little evidence of social hierarchy. Its houses were uniformly small and show no signs of social stratification or significant inequality among the population. Excavations at the town's cemetery likewise found no evidence of a social hierarchy in burials, a marked difference from excavations at other nearby towns of the same era.
But, despite the apparent lack of a centralized authority, the town's population came together and undertook the careful coordination needed to produce the ceramic pipes, plan their layout, install and maintain them, a project which likely took a great deal of effort from much of the community.
The level of complexity associated with these pipes refutes an earlier understanding in archaeological fields that holds that only a centralized state power with governing elites would be able to muster the organization and resources to build a complex water management system. While other ancient societies with advanced water systems tended to have a stronger, more centralized governance, or even despotism, Pingliangtai demonstrates that was not always needed, and more egalitarian and communal societies were capable of these kinds of engineering feats as well.
898 notes
·
View notes
Text

shell necklace made of river mussels
stroked pottery culture, 4800-4400 BC
found in Šárka, Czech Republic
#neolithic#prehistory#stone age#artefact#archaeology#jewellery#stroked pottery culture#czech republic#archeology#my upl#central europe#european prehistory
258 notes
·
View notes
Photo
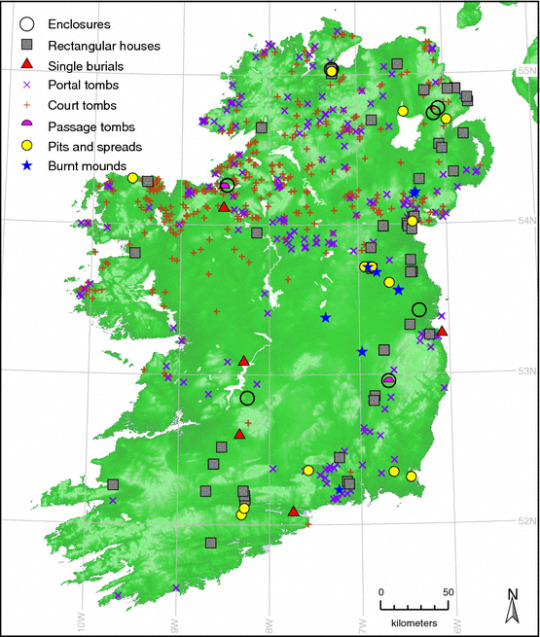
Neolithic sites in Ireland
290 notes
·
View notes
Text







little snapshots of a mod i have been working on for a few days, cenozoicraft, understandably based around adding cenozoic animals to the minecraft world along with neolithic tools. its heavily based around hunting and utilizing animal parts. most of what is here is tamable and rideable with fun little taming mechanics, so dont expect to be able to waltz up to a smilodon. more to come soon
#there are a few effects i havent shown here besides from the ''hunters vision'' in the first one. still a prototype but the general idea#anyways i am pretty proud of what i have accomplished so far. everything here has and will have unique mechanics and ai. i am excited#on the bucketlist: mammoths! finishing up the mammoth steppe and arctic biomes. enchantments that assist in hunting#predator ai needs some work. neanderthals are on the list as well. several sets of armor and curios are planned#and of course many#many animals#and many decorative blocks#minecraft#blockbench#mcreator#modded minecraft#cenozoic#paleo#paleoart#paleontology#neolithic#cenozoicraft#rorys art
238 notes
·
View notes
Text
Individual houses were typically in use for between fifty and 100 years, after which they were carefully dismantled and filled in to make foundations for superseding houses. Clay wall went up on clay wall, in the same location, for century after century, over periods reaching up to a full millennium. Still more astounding, smaller features such as mud-built hearths, ovens, storage bins and platforms often follow the same repetitive patterns of construction, over similarly long periods. Even particular images and ritual installations come back, again and again, in different renderings but the same locations, often widely separated in time....
as individual houses built up histories, they also appear to have acquired a degree of cumulative prestige. This is reflected in a certain density of hunting trophies, burial platforms and obsidian - a dark volcanic glass, obtained from sources in the highlands of Cappadocia, some 125 miles north. The authority of long-lived houses seems consistent with the idea that elders, and perhaps elder women in particular, held positions of influence. But the more prestigious households are distributed among the less, and do not appear to coalesce into elite neighborhoods.
a description of Çatalhöyük, a neolithic city from 7,400 bc. from the dawn of everything, by davids: graeber and wengrow.
this city remained settled for 1,500 years - "roughly the same period of time that separates us from amalafrida, queen of the vandals in .. ad 523"
#eezordalf's wisdom#the dawn of everything#david graeber#david wengrow#anthropology#paleoanthropology#books#prehistory#neolithic#Çatalhöyük#catalhoyuk#history#unfocus your eyes and let the vast maw of time take you#wizardblr#wizardposting
597 notes
·
View notes
Text



A bigger decorative piece with cave painting handprints. River pebble and tempera
#miniature#painted stones#rock painting#cave art#rock art#pebbles#painted rocks#minerals#handprints#painted miniatures#neolithic#paleolithic#my art
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Prehistoric Mirrors from Turkey, c.6000 BCE: these are the oldest manufactured mirrors in the world, dating back about 8,000 years; they were meticulously crafted from pieces of obsidian
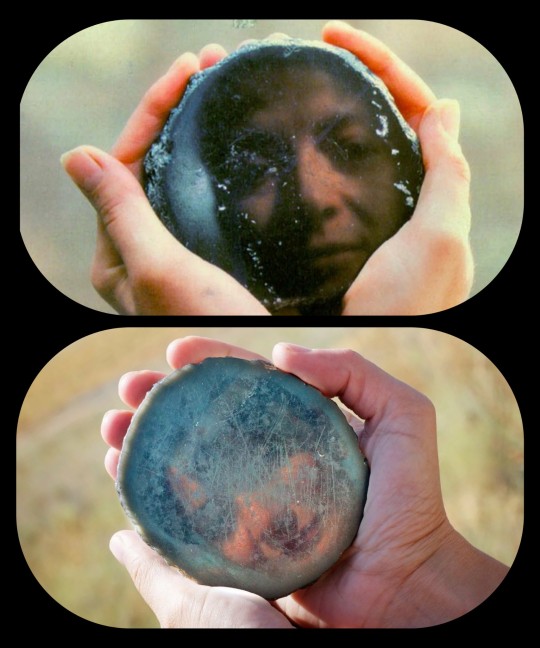

Two of the obsidian mirrors from Çatalhöyük (Turkey); this pair was found buried together back in 2012
At least eight of these obsidian mirrors have been found at Çatalhöyük, a Neolithic site located in Turkey. All of these mirrors date back about 8,000 years, and each one was crafted from a chunk of obsidian (volcanic glass) that was knapped into the shape of a disc and then meticulously polished with progressively finer abrasives until a smooth, slightly convex surface had been developed. Some of these mirrors can still produce remarkably clear reflections.
Sources & More Info:
The Archaeologist: World's Oldest Mirrors Found at Neolithic Çatalhöyük Site
Çatalhöyük Research Project: Archive Report from 2012 (PDF download)
Çatalhöyük Research Project: Main Website
The Past: Cyber Archaeology, How 3D Modeling is Unpeeling the Neolithic at Çatalhöyük
#archaeology#artifact#anthropology#neolithic#prehistoric#neolithic mirrors#anatolia#turkey#Çatalhöyük#human history#obsidian#volcanic glass#crafting#art#prehistoric art#human nature
625 notes
·
View notes
Text
Time Travel Question 14: Ancient History VI and Earlier
These Questions are the result of suggestions from the previous iteration.
This category may include suggestions made too late to fall into the correct grouping.
Please add new suggestions below if you have them for future consideration.
I am particularly in need of more specific non-European suggestions in particular, but all suggestions are welcome.
#Time Travel#Mayans#The Sea People#Norse#Celtic#Neolithic#Doggerland#Early Humans#Polynesian Expansion#Tartessos#The Great Wall of China#Australian History#Indigenous History#The Silurian Period
687 notes
·
View notes
Text
#i got polls#Stone age#no science just vibes#cave art#paleolithic#Neolithic#neanderthal#archaeology#archeology
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
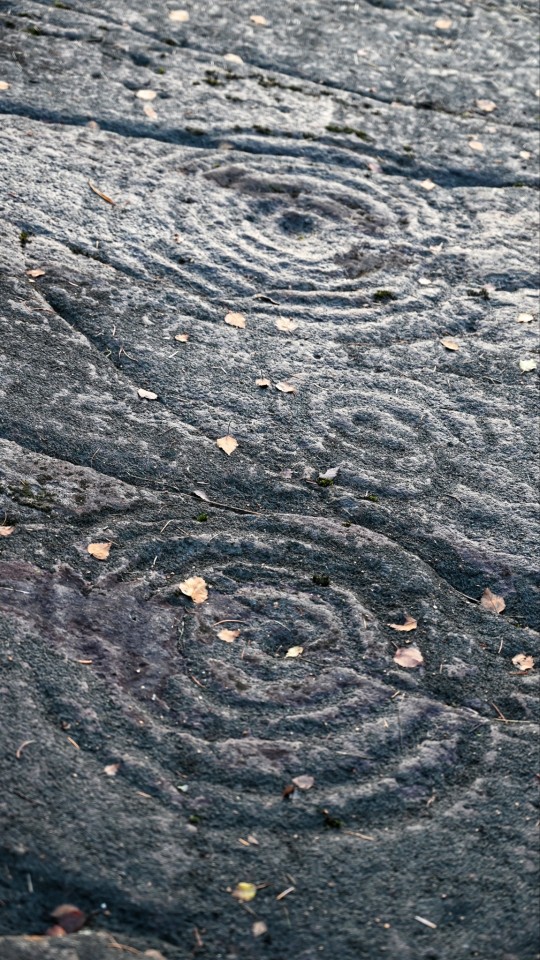
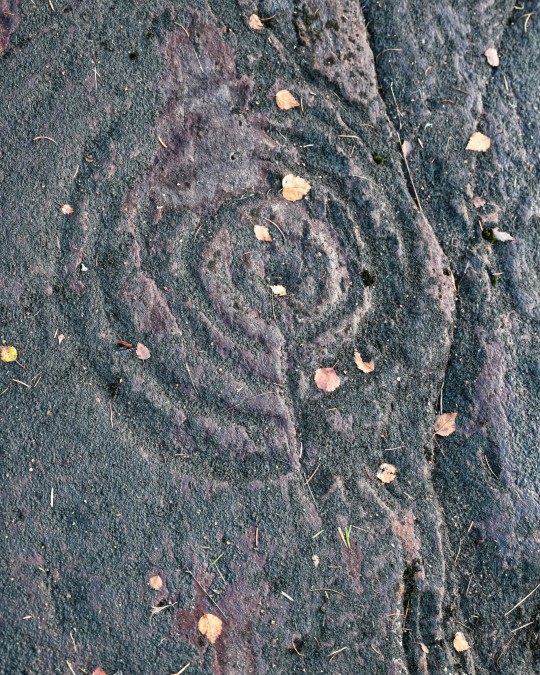
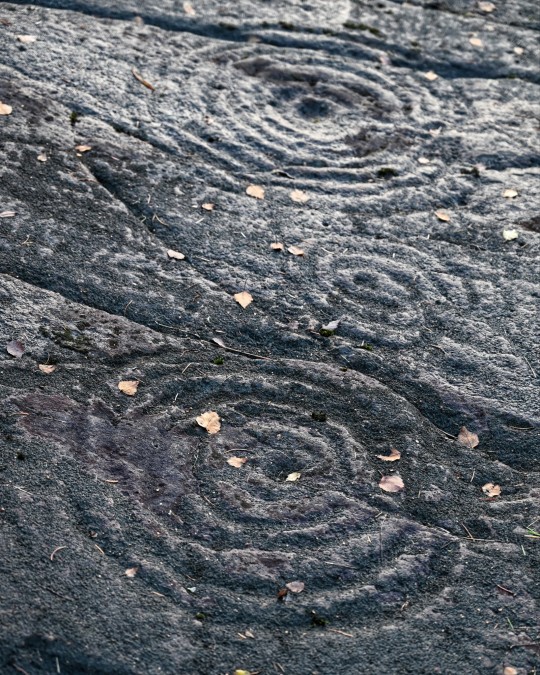
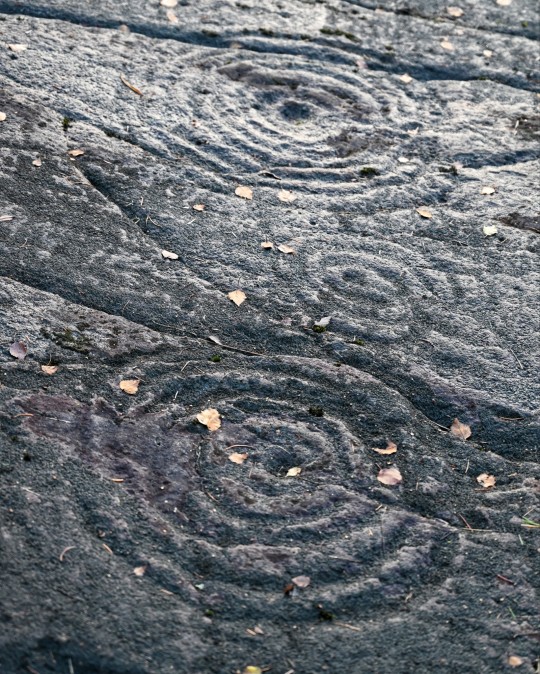
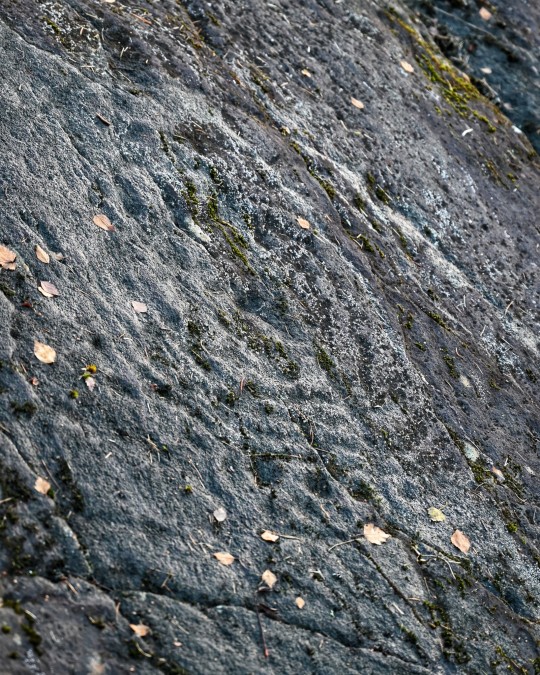
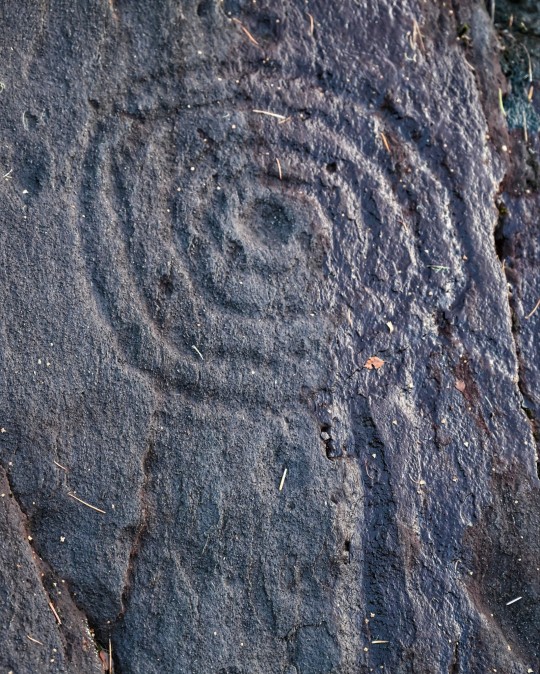
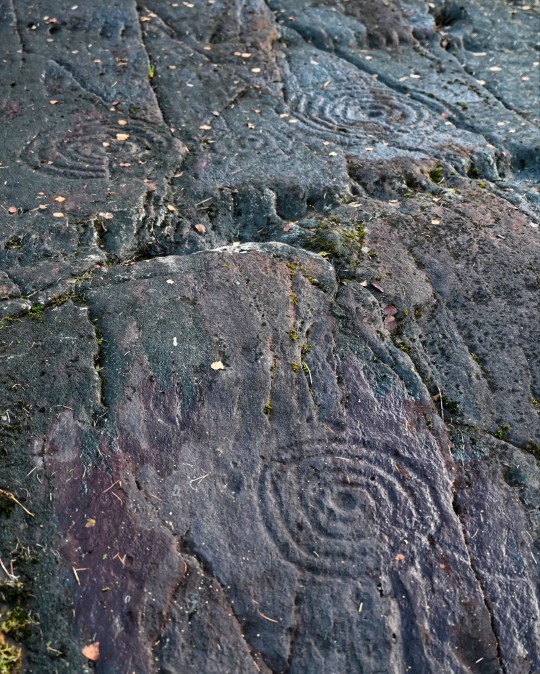








Achnabreck Prehistoric Rock Art Panels, nr. Lochgilphead, Argyll, Scotland
#ice age#stone age#bronze age#copper age#iron age#neolithic#mesolithic#calcholithic#paleolithic#prehistoric#prehistory#cup and ring#rock art#archaeology#landscape#ancient craft#ancient sites#ancient cultures
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
A 7000-year-old road has been unearthed off the coast of Croatia revealing insights into the ancient Hvar culture’s engineering knowledge.
741 notes
·
View notes