#Ransomware Cryptolocker
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Mesh it Up Monday: Ransomware - The Real-Life Villain in the Cyber World
Welcome to Mesh it Up Monday! 🎉 Today, we’re delving into the captivating realm of ransomware, the real-life villain of the cyber world. But fear not, we won’t let this digital menace intimidate us. Instead, we’ll tackle the topic with a humorous twist and analogies that even a novice can relate to. So, fasten your virtual seatbelts, put on your cybersecurity capes, and let’s dive into the…

View On WordPress
#CryptoLocker#cyber world#cybersecurity heroes#data security#Locky#Petya#ransomware#ransomware protection#ransomware threats#WannaCry
0 notes
Text
Chapter 1: Ghost In the Machine

The hum of the fluorescent lights in "Byte Me" IT Solutions was a monotonous drone against the backdrop of Gotham's usual cacophony. Rain lashed against the grimy window, each drop a tiny percussionist drumming out a rhythm of misery. Inside, however, misery was a bit more… organized.
I sighed, wrestling with a particularly stubborn strain of ransomware. "CryptoLocker v. 7.3," the diagnostic screen read. A digital venereal disease, if you asked me. Another day, another infected grandma's laptop filled with pictures of her grandkids and a crippling fear that hackers were going to steal her identity.
"Still at it?" My coworker, Mark, sidled over, clutching a lukewarm mug of something vaguely resembling coffee. Mark was a good guy, perpetually optimistic despite working in one of Gotham's less-than-glamorous neighborhoods. Bless his heart.
"You know it," I replied, jabbing at the keyboard. "Think I've finally managed to corner the bastard. Just gotta… there!" The screen flashed a success message. "One less victim of the digital plague."
Mark nodded, then his eyes drifted to the hulking metal beast in the corner, a Frankensteinian creation of salvaged parts and mismatched wiring. "How's the behemoth coming along?"
I followed his gaze. My pet project. My escape. "Slowly but surely. Got the cooling system optimized today. Almost ready to fire it up."
"Planning anything special with it?" Mark asked, his brow furrowed in curiosity. "You've been collecting scraps for months. It's gotta be more than just a souped-up gaming rig."
I shrugged, a deliberately vague gesture. "You could say I'm planning something… big. Something Byte Me isn't equipped to handle."
Mark chuckled. "Well, whatever it is, I'm sure you'll make it sing. You've got a knack for that sort of thing." He wandered off, whistling a jaunty tune that died a slow, agonizing death against the backdrop of the Gotham rain.
He had no idea just how much of a knack.
Mark bid me one final goodbye before pulling out an umbrella and disappearing into the night. No doubt he stops at Nero’s pizzeria before going home to his wife and kids. You watched through the shop window before he disappeared around the corner. Then, you locked the door and reached for the light switch. The fluorescent lights flickered a final, dying gasp before plunging the shop into darkness. I waited a beat, the city's distant sirens a mournful choir. Then, I flipped the hidden switch behind the breaker box, illuminating a small, secluded corner of the shop.
Rain hammered against the grimy windowpanes of my "office," a repurposed storage room tucked away in the forgotten bowels of the shop. The rhythmic drumming was almost hypnotic, a bleak lullaby for a city perpetually on the verge of collapse. I ignored it, fingers flying across the keyboard, the green glow of the monitor painting my face in an unsettling light. Outside, the city's distant sirens formed a mournful choir. Here, the air crackled with a different kind of energy.
"Almost there," I muttered, the words barely audible above the whirring of the ancient server rack humming in the corner. It was a Frankensteinian creation, cobbled together from spare parts and salvaged tech, but it packed enough processing power to crack even the most stubborn encryption algorithms. Laptops with custom OSes, encrypted hard drives, and a tangle of wires snaked across the desk. This was Ghostwire Solutions, my little side hustle. My… outlet.
Tonight's victim, or client – depending on how you looked at it – was a low-level goon. One was a two-bit thug named "Knuckles" Malone; the other, a twitchy character smelling of desperation, Frankie "Fingers" Falcone. Malone's burner phone, or Falcone's data chip containing an encrypted message, was now on the screen in front of me, a jumble of characters that would make most people's eyes glaze over. For me, it was a puzzle. A challenging, if morally questionable, puzzle.
My service, "Ghostwire Solutions," was discreet, to say the least. No flashy neon signs, no online presence, just word-of-mouth referrals whispered in dimly lit back alleys. I was a ghost, a digital shadow flitting through the city's underbelly, connecting people. That's how I liked to justify it anyway. I cracked my knuckles and went to work. My fingers danced across the keyboard, feeding the encrypted text into a series of custom-built algorithms, each designed to exploit a specific vulnerability. Hours melted away, marked only by the rhythmic tapping of keys and the soft hum of the custom-built rig in the corner, its processing power gnawing away at the digital lock.
The encryption finally buckled. A cascade of decrypted data flooded the screen. I scanned through it, a jumbled mess of texts, voicemails, location data, or a simple message detailing a meeting point and time. Mostly dull stuff about late payments and turf wars, the mundane reality of Gotham's criminal element. I extracted the relevant information.
"Alright, Frankie," I muttered to myself, copying the decrypted message onto a clean file. "Just connecting people. That's all I'm doing."
I packaged the data into a neat little file, added a hefty markup to my initial quote, and sent it off via an encrypted channel. Within minutes, the agreed-upon sum, a few hundred cold, hard dollars, landed in my untraceable digital wallet. I saved the file to a new data chip and packaged it up. Another job done. Another night closer to sanity's breaking point.
"Just connecting people," I repeated, the phrase tasting like ash in my mouth. The lie tasted even worse. I knew what I was doing. I was enabling crime. I was greasing the wheels of Gotham's underbelly. But bills had to be paid. It was a convenient lie, a way to sleep at night knowing I was profiting from the chaos. But tonight, it felt particularly hollow. And honestly, did it really matter? Gotham was already drowning in darkness. What was one more drop?
Gotham was a broken city, a machine grinding down its inhabitants. The system was rigged, the rich got richer, and the poor fought over scraps. I wasn't exactly helping to fix things. But I wasn't making it worse, right? I was just a cog in the machine, a necessary evil. I was good at what I did, damn good. I could see patterns where others saw chaos. I could exploit vulnerabilities, both in code and in the systems of power that held Gotham hostage. It was a skill, a talent, and in this city, unique talents were currency. I was efficient and discreet. But every decrypted message, every bypassed firewall, chipped away at something inside me. It hollowed me out, leaving me a ghost in my own life, a wire connecting the darkness.
I leaned back in my creaky chair, the rain still pounding against the window. The air was thick with the scent of ozone and melancholy. Another night, another decryption, another small victory against the futility of existence in Gotham. The flicker of conscience, that annoying little spark that refused to be extinguished, flared again. Was I really making a difference? Or was I just another parasite feeding off the city's decay?
I closed my eyes, trying to silence the questions. Tomorrow, there would be another encryption to crack, another connection to make. And I would be ready, Ghostwire ready to disappear into the digital ether, another ghost in the machine, until the next signal came. As I waited for the morning, for the return of the fluorescent lights and the mundane reality of "Byte Me" IT Solutions, I wondered if one day, the darkness I trafficked in would finally claim me completely. Because in Gotham, survival was a code all its own, and I was fluent in its language. And frankly, some days, that didn't seem like such a bad deal. For now, that was enough.
#gotham knights#gotham knights fanfic#gotham knights jason todd#gk jason todd#jason todd#jason todd x reader#jason todd x you#red hood#red hood x reader#hacker!reader#dc
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Ransomware: A Guide for Small Businesses
Ransomware is a malicious software that restricts access to your device or data until a ransom is paid. In this article, we explore how ransomware enters your system, how it works, and how to prevent attacks. A ransomware attack occurs when malware prevents access to your device or data until a ransom is paid. Attackers may threaten to publish data if the ransom is not paid. Ransomware can be locker ransomware, which locks access, or crypto ransomware, which encrypts files. Ransomware usually enters a device, assesses critical data, encrypts files, and demands a ransom. Paying the ransom doesn't guarantee recovery, so it's not recommended. Historical ransomware attacks include CryptoLocker, CryptoWall, Locky, WannaCry, NotPetya, and more. To prevent ransomware, you can have good network policies, secure servers, backup data offline and online, and encourage safe online behavior. Installing security software like antivirus, firewall, and email filtering can also help. Advanced strategies include ATP, email filtering, and security audits. In case of a ransomware infection, isolate the device, assess damage, check for a decryption key, and restore from backups. Seek professional help for recovery. Immediate actions post-infection include isolation, incident response activation, legal compliance, and stakeholder communication. Ransomware can get on your device through spam emails, phishing, pop-ups, pirated software, weak passwords, and more. Attackers prefer cryptocurrency payments for anonymity. Ransomware can spread through Wi-Fi, infecting all connected devices. Protect yourself from ransomware by following the prevention strategies mentioned above. Stay safe online and be cautious of suspicious emails, links, and downloads. And remember, it's crucial to have backups and a plan in case of a ransomware attack. #StartupBusiness #Businesses #Guide #howdoesransomwarework #Ransomware #ransomwareattack #Small #Understanding #whatisaransomware #whatisaransomwareattack #whatisransomware https://tinyurl.com/228z9vpf
#Businesses#Guide#how does ransomware work#Ransomware#ransomware attack#Small#Understanding#what is a ransomware#what is a ransomware attack#what is ransomware
1 note
·
View note
Text
What are The Types of Ransomware and Ransomware History

Cyberattacks like ransomware are serious. Among the most dangerous malware, they can affect any company. Within four days of network access, attackers deploy ransomware, leaving little time for detection and prevention. Stopping operations, losing money, reputation, and data.
According to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach report, ransomware breaches average USD 5.68 million, excluding ransom payments. Not all ransoms reach $80 million.
Better threat detection and prevention reduced ransomware attacks 11.5% between 2022 and 2023.
The Ransomware Types
Varying ransomware strains exploit vulnerabilities.
Crypto ransomware: Locks important files until a ransom is paid. WannaCry, Locky, CryptoLocker. Ransomware encrypts.
Without payment, this ransomware blocks the victim's device or system from accessing files or apps. Screen-locking ransomware isn't encrypted.
Scareware: Fake software that diagnoses system issues and recommends dangerous fixes. Scareware can restrict system access or bombard users with pop-ups to install malware or pay. Scareware can provide or be ransomware.
Leakware, or doxware, steals confidential data and threatens disclosure without payment. The attacks pressure victims with reputational danger. Modern variants steal and encrypt data.
Mobile ransomware: Spreads via malicious apps or drive-by downloads. Most mobile ransomware involves screen-lockers since cloud backups make encryption attacks easier to reverse.
If unpaid, ransomware wipes data. Ransomware by cybercriminals and nation-states erases data after payment.
Modern ransomware uses double- and triple-extortion. Unpaid double-extortion threatens to steal and publish vulnerable data online. Consumers or business partners with stolen data face triple extortion. Even with data backups, these methods raise the stakes. Since 2019, the IBM Security X-Force incident Response team has seen double extortion in most ransomware events.
Infection via Ransomware
Ransomware can attack systems via multiple channels. Well-known methods:
Phishing uses emails with phoney attachments or malicious websites to get people to download and run hazardous programs.
Zero-day vulnerabilities in operating systems and applications allow cybercriminals to inject malware. The 2017 WannaCry assault used fixed vulnerabilities.
Stolen, bought, or cracked user credentials are used to log in and deploy ransomware via Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
Malware like Trickbot Trojan (which seeks banking details) can spread ransomware.
Drive-by downloads: Ransomware can infiltrate devices without user awareness via exploit kits or malvertising.
In legitimate online interactions, cybercriminals utilise thread hijacking to spread malware.
RaaS: Ransomware as Service
Cybercriminals distribute ransomware via RaaS. Malware developers share code with “affiliates” who split the ransom. Developers and affiliates can benefit without releasing new attacks or malware. RaaS distributors can sell dark web access or recruit affiliates. Major ransomware gangs have recruited affiliates.
Staged Ransomware Attack
Typical ransomware attacks include many phases:
Initial access: Phishing, vulnerability exploitation, or hacked RDP protocols give attackers access.
After initial access, attackers may utilise RATs to consolidate.
After acquiring access to a system or network, attackers may lateral migrate to other systems and domains.
Ransomware thieves steal credentials, customer data, and IP. Double-extortion uses data theft.
File encryption, system restoration disablement, and backup deletion/encryption increase pressure with crypto ransomware. Unencrypting ransomware locks or spams the device. The ransomware then delivers a text file or pop-up window with instructions on how to pay the ransom (usually in cryptocurrency) to decrypt or regain access.
History of ransomware
Thousands of ransomware variants exist. Some prominent ones:
The AIDS Trojan was the first floppy-disk ransomware in 1989. It concealed file directories but was easily reversed.
CryptoLocker, introduced in 2013, allowed cryptocurrency ransomware.
An unpatched Microsoft Windows vulnerability attacked 200,000 devices in 150 countries with WannaCry. The ransom threatens file deletion if not paid.
File system table encryption by Petya and NotPetya affects PC booting. A 2017 Ukraine attack utilised a modified NotPetya wiper that could not restore systems after payment.
Ryuk, a 2018 ransomware attack, popularised large-scale attacks on high-value targets with high demands. It finds and disables backups.
A purported Russian gang, DarkSide, assaulted the Colonial Pipeline in 2021, briefly halting petroleum supplies. The group licenses ransomware using RaaS.
Encrypting malware Locky hides hazardous macros in email attachments, usually bills.
IN 2021, REvil (Sodinokibi) popularised RaaS for big-game hunting and double-extortion attacks against JBS USA and Kaseya Limited.
Since 2020, the Conti gang's large RaaS scam paid hackers. In a unique double-extortion scheme, Conti threatened to sell network access to hackers. After 2022 internal communication dumps, the gang separated, however former members are tied to BlackBasta, Royal, and Zeon.
A popular 2023 ransomware version is LockBit. The company is known for businesslike conduct and malware acquisition. LockBit assaults victims despite police efforts.
Paying Ransom
An average ransom is hard to quantify, however estimates range from six to seven figures. Ransom payments dropped from 70% in 2020 to 37% in 2023, perhaps owing to better planning.
Agents from the FBI and NCIJTF aggressively discourage ransom payments. Payment may not retrieve data, strengthen attackers, support criminal conduct, or promote more attacks.
Strong backup systems provide negotiation-free recovery. Authorities recommend reporting attacks before paying. Payment of ransom to attackers from US economic sanctions or state governments in particular US regions is illegal.
Ransomware prevention
Ransomware prevention requires technology and user behaviour. Main strategies:
Regular OS, app, and firmware upgrades fix ransomware security holes.
Detect and eliminate threats using real-time scanning, behavioural detection, and automated updates from contemporary antivirus and anti-malware software.
A good firewall blocks unauthorised network access.
Phishing prevention: Email filtering and scanning detects suspicious links and attachments.
Regular backups speed recovery without ransom. Secure, immutable backups can restore data if systems fail. Data should be replicated three times on two media types, one offsite. Seagate Lyve Cloud backups offer geographic redundancy, encryption, and immutability.
Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, network segmentation, and secure VPNs help thwart attacks. Least privilege access and endpoint security harden networks.
AI can predict and stop assaults by studying behaviour, detecting anomalies, and stopping attacks before they start. AI-powered systems can monitor users and endpoints, detect zero-day attacks, and respond faster using playbooks.
Policies and procedures: Ready crisis response requires a detailed strategy with responsibilities, timetables, and communication channels.
Teams require regular security awareness training to spot phishing and suspicious emails because human error is a huge risk.
Ransomware Response Plan
Every system is vulnerable, hence a detailed response strategy is needed. Actions include:
Disconnect compromised systems immediately to stop ransomware.
Report to authorities: Request FBI or CISA law enforcement assistance. Legal duties may require reporting.
Damage assessment: Identify affected systems, assess data compromise, and contain with IT/security teams.
Use the latest clean backup to restore data. Immutable solutions like Seagate Lyve Cloud are needed for reliable recovery. Inform employees, partners, and consumers to build trust and reputation.
Don't pay the ransom: Experts say it may not retrieve data and may encourage more attacks.
#Ransomware#Runningransomwareasaservice#ransomwareattacks#PayingRansom#preventRansomware#Attackersdeployransomware#technology#TechNews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Cyber Security Market Scope, Size, Share, Trends, Forecast By 2031
The cybersecurity landscape is witnessing a significant transformation with the growing adoption of the cybersecurity mesh. This innovative approach is redefining security architectures by enabling distributed enterprises to deploy and extend security precisely where it is needed the most. By decentralizing security measures and focusing on individual users and access points, the cybersecurity mesh is emerging as a rapidly growing strategy in the realm of IT security.

For Full Industry Insights: https://www.fairfieldmarketresearch.com/report/cybersecurity-market
The Concept of Cybersecurity Mesh
The cybersecurity mesh acknowledges that traditional network boundaries are becoming obsolete in today's interconnected world. Organizations are now required to create security perimeters around each user, allowing secure access to assets from any location or device. This model shifts policy enforcement to cloud services, focusing on assets rather than devices. By establishing smaller, individual perimeters around each access point, the cybersecurity mesh offers a robust framework to protect identities and restrict network access to authorized users or systems, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
IoT Security Adoption and Market Demand
The surge in IoT traffic is expected to drive cybersecurity market demand significantly. As enterprises across various industries adopt IoT devices to enhance operational efficiency and communication, the scope of cybercriminals' attacks broadens. The increasing adoption of these devices necessitates a cybersecurity model that provides greater visibility into network access points, user activities, and application usage. Businesses are turning to advanced cybersecurity solutions to inspect all network traffic, detect malicious activities, and address visibility issues arising from the large volume of IoT queries.
Types of Computer Viruses
In the evolving threat landscape, various types of computer viruses pose significant risks to organizations:
Malware: Including worms, Trojans, adware, and ransomware, malware is designed to damage computer systems, gain unauthorized access, or steal information.
Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts data, demanding payment or other actions to restore access. Even large enterprises and city governments have fallen victim to ransomware attacks.
Trojans: Requiring user action, Trojans often deceive users into running malicious programs or accessing harmful websites.
Top Destructive Cyber Viruses
Some of the most destructive cyber viruses include CryptoLocker Ransomware, Plug X malware, Zeus (Gameover) virus, Stuxnet worm, MyDoom worm, Sasser and Netsky worms, Code Red worm, Nimda virus, ILOVEYOU virus, Melissa virus, Cyborg Ransomware, GoBrut virus, Jokeroo malware, CryptoMix Clop Ransomware, Trojan Glupteba virus, Fake Windows Updates (Hidden Ransomware), and News Malware Attacks.
Hot Technologies in Cybersecurity
To combat evolving cyber threats, several hot technologies are gaining traction:
Context-Aware Behavioral Analytics: By using sophisticated behavioral analytics, companies can monitor and identify suspicious behavior or transactions, addressing the issue of overwhelming security alerts.
Next Generation Breach Detection: Combining machine learning and behavioral analytics, these technologies detect breaches and trace them to their source, tackling "zero-day" exploits.
Virtual Dispersive Networking (VDN): VDN splits messages into multiple parts, encrypts them, and routes them over different protocols on independent paths, enhancing encryption security.
Challenges in Cybersecurity
Despite the advancements, several challenges persist in the cybersecurity domain:
Low Cybersecurity Budget and High Installation Costs: Emerging startups often lack sufficient budgets to implement Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) and Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) solutions. This limits the adoption of cybersecurity solutions, particularly in small businesses within developing economies.
Designing and Deploying Cybersecurity Solutions: Transitioning from a network perimeter-based approach to a user-based and application-based security model presents design and implementation challenges. This transition requires a thorough network analysis and a deep understanding of each user, device, application, and resource.
Regional Analysis
The North American region is at the forefront of cybersecurity advancements, with several prominent market players delivering cutting-edge solutions across various industries. Strategic investments, partnerships, and significant R&D activities contribute to the widespread deployment of cybersecurity solutions. Key players such as IBM, Oracle, Fortinet, Microsoft, and Trend Micro, along with several startups, are offering enhanced cybersecurity software solutions and services to meet customer needs, driving market growth in North America.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Data Recovery Excellence with Tech4Service
At Tech4Service, we understand the heartache that can accompany the loss of precious data. Whether it’s family photos, critical business documents, or important project files, we know that data loss can be distressing and costly. That’s why we’re here to offer you top-tier data recovery services in Edmonton, with a specialization in handling mechanical failures.Computer Repair Shop Near Me
Mechanical Failure Recovery
Our team of skilled engineers operates in a specially sanitized clean room environment, minimizing risks and optimizing recovery outcomes for mechanical failures. When your hard drive experiences a mechanical failure, it requires delicate handling, and that’s precisely what we provide. Our goal is simple: to recover your valuable data safely and efficiently.
Drive Imaging for Thorough Recovery
To ensure comprehensive data recovery, all hard drives entrusted to us undergo imaging in a full working environment. This step allows us to create a complete copy of your drive, ensuring that no data is left behind. Our drive imaging process is a vital part of our success in delivering efficient data recovery solutions.
Specialist Tools for Complex Cases
Tech4Service utilizes proprietary tools that set us apart in the industry. We can recover data from damaged drives by reading around the affected areas, effectively retrieving the entire drive’s contents. When faced with challenging cases, our specialist tools and expertise enable us to recover data that others might consider lost.
Ransomware Recovery Expertise
In addition to mechanical failures, we specialize in ransomware recovery. Over the years, we’ve successfully restored data from various ransomware infections, including notorious variants like Cryptolocker, Arrow, JAVA, UHV, DMA, XTBL, Kyra, Thor, Lucky, CrytpoMIX, Microsoft Crypto, Arena, Nuclear, Aleta, NuroRing, NM4, Gryphon, BTC, Zepto, and many more. Our experience in dealing with ransomware infections is unrivaled.
Hard Drive Recovery Solutions
Our data recovery services extend to a wide range of hard drive issues, such as faulty read/write heads, spindle motor seizure, faulty controller PCBs, deleted, lost, or formatted data, bad sectors, firmware failure, and corrupt file systems. No matter the nature of the problem, we have the expertise to handle it.
Apple Mac Recovery Expertise
Tech4Service offers free evaluations at competitive prices for Apple Mac data recovery. We understand that data loss can be particularly distressing for Mac users, and we’re here to provide reassurance and efficient solutions for Mac-related data recovery.
Leave Data Recovery to the Experts
Attempting DIY data recovery from a compromised drive can worsen the situation and result in more data loss. When you choose Tech4Service, you’re opting for years of experience, cutting-edge research, and unwavering dedication to data recovery. Leave the process to our experts, and rest assured that your data will be handled professionally and securely.
Conclusion
Tech4Service is your trusted partner when it comes to data recovery services in Edmonton. Equipped with a state-of-the-art clean room, drive imaging capabilities, and specialist tools, we’re ready to tackle any data recovery challenge. Our expertise extends to ransomware recovery, hard drive recovery, and Apple Mac data restoration. Don’t risk further complications by attempting DIY recovery. Trust the experts at Tech4Service to regain your valuable data with confidence. Your data is worth it, and so are you.Laptop Repair Shop Near Me
0 notes
Text
GridinSoft Anti-ransomware Software For PC
GridinSoft Anti-ransomware Software For PC
GridinSoft Anti-Ransomware works as a vaccine for PC! When protection is enabled, the ransomware bypasses your Windows computer! This is a free ransomware protection software that allows you to protect your computer against file-encrypting in a few simple clicks! Just run the program and be sure that your computer protected from any cryptovirus 24/7. You will never know how much it cost to…

View On WordPress
#Block Cryptolocker#Block Ransomware#file encryption software#Free Ransomware Protection#Free Ransomware Protection Software#Prevent Ransomware#protect your pc#Ransomware Cryptolocker#Ransomware Protection Software
0 notes
Text
Le ransomware Crypt0L0cker
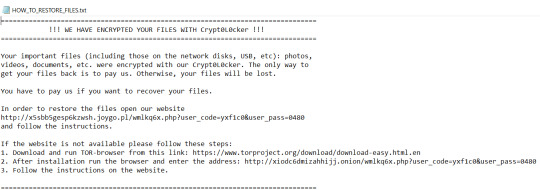
Ce ransomware Crypt0L0cker (les O sont remplacés par des ZERO) est apparu en 2015 en descendant direct de la famille TorrentLocker. Il a souvent été propagé par une pièce-jointe infectée via des campagnes de courrier électronique. Une fois que les fichiers sont cryptés, Crypt0L0cker rajoute une extension à chaque fichier et laisse une ou plusieurs notes de demande de rançon. Les extensions des fichiers cryptés les plus courantes de ce ransomware sont : - .enc - .encrypted - .asdgfd, .udezum, .smejux, .etc... soit une série de 6 lettres aléatoires - .vendeta La demande de rançon est souvent laissée sous deux formats, le premier en texte et le deuxième en html, soit en anglais, soit dans la langue de la victime : HOW_TO_RESTORE_FILES.txt HOW_TO_RESTORE_FILES.html DECRYPT_INSTRUCTIONS.html DECRYPT_INSTRUCTIONS.txt
COME_RIPRISTINARE_I_FILE.txt COME_RIPRISTINARE_I_FILE.html ISTRUZIONI_DECRITTAZIONE.txt ISTRUZIONI_DECRITTAZIONE.html
COMO_RESTAURAR_ARCHIVOS.html COMO_RESTAURAR_ARCHIVOS.txt
INSTRUCCIONES_DESCIFRADO.txt INSTRUCCIONES_DESCIFRADO.html wie_zum_Wiederherstellen_von_Dateien.txt wie_zum_Wiederherstellen_von_Dateien.html COMMENT_RESTAURER_DES_FICHIERS.txt COMMENT_RESTAURER_DES_FICHIERS.html SIFRE_COZME_TALIMATI.txt SIFRE_COZME_TALIMATI.html Contenu type de la demande de rançon : ------------------------------------------------------- ============================================================= !!! WE HAVE ENCRYPTED YOUR FILES WITH Crypt0L0cker !!! =============================================================Your important files (including those on the network disks, USB, etc): photos, videos, documents, etc. were encrypted with our Crypt0L0cker. The only way to get your files back is to pay us. Otherwise, your files will be lost.You have to pay us if you want to recover your files.If you want your files to be decrypted write us: [email protected] ============================================================= ou ============================================================= !!! WE HAVE ENCRYPTED YOUR FILES WITH Crypt0L0cker !!! =============================================================
Your important files (including those on the network disks, USB, etc): photos, videos, documents, etc. were encrypted with our Crypt0L0cker. The only way to get your files back is to pay us. Otherwise, your files will be lost.
You have to pay us if you want to recover your files.
In order to restore the files open our website http://e3tdxhll5fa6rirn.micronit.tw/c5aykzm0.php?user_code=5l2nyi9&user_pass=1037 and follow the instructions.
If the website is not available please follow these steps: 1. Download and run TOR-browser from this link: https://www.torproject.org/download/download-easy.html.en 2. After installation run the browser and enter the address: http://vhx6kpgibjohmvox.onion/c5aykzm0.php?user_code=5l2nyi9&user_pass=1037 3. Follow the instructions on the website.
=============================================================
Ce ransomware a été longuement analysé par notre laboratoire de décryptage et nous avons un excellent taux de récupération des fichiers cryptés. Pour toutes demandes à ce sujet, veuillez nous envoyer avec www.wetransfer.com à l’adresse [email protected] la demande de rançon et 4 fichiers cryptés avec vos coordonnées. Après analyse de vos fichiers et seulement si nous arrivons à concevoir un décrypteur pour récupérer vos fichiers cryptés, nous vous proposerons le kit de récupération pour 150 euros hors taxe.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What The Hell Is Ransomware? Simple Explanation..
What The Hell Is Ransomware? Simple Explanation..
Ransomware is a strong threat to you and your computer devices , but what make this malware so dangerous? Ransomware is extortion software that can lock your computer and then demand a ransom for it release. In most case, ransomware infection occurs as follows . If you want to reduce the risk of a ransomware attack, you should rely on high-quality ransomware protection software and some computer…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

New Post has been published on https://mariusz-czarnecki.pl/ransomware-co-to-jest-i-jak-usunac/
Ransomware co to jest i jak usunąć?
Ransomware co to jest i jak usunąć? Ransomware to rodzaj złośliwego oprogramowania, które szyfruje pliki na urządzeniu użytkownika lub urządzeniach pamięci sieciowej. Aby przywrócić dostęp do zaszyfrowanych plików, użytkownik musi zapłacić „okup” cyberprzestępcom, zwykle za pomocą trudnej do wyśledzenia metody płatności elektronicznej, takiej jak Bitcoin. Chociaż badacze bezpieczeństwa ustalili, jak zmapować przepływ ruchu transakcji Bitcoin, zidentyfikowanie, która osoba (lub osoby) jest właścicielem konta Bitcoin, jest niezwykle trudna.
W jaki sposób rozprzestrzenia się Ransomware?
Ransomware jest najczęściej dystrybuowane za pośrednictwem ataków spamowych. Wiadomość e-mail ze spamem będzie miała ukryty załącznik lub będzie zawierać link URL w treści wiadomości e-mail. Jeśli zastosowana zostanie pierwsza metoda, program ransomware zostanie aktywowany, gdy tylko załącznik zostanie otwarty, to w ciągu kilku sekund rozpocznie szyfrowanie plików na urządzeniu. Jeśli wektor ataku jest linkiem, po kliknięciu go użytkownik zostaje przeniesiony na stronę internetową, na której ransomware jest dostarczane do urządzenia bez wiedzy użytkownika. Szkodliwe programy lub witryny często wykorzystują zestawy exploitów do wykrywania, czy w systemie operacyjnym urządzenia lub aplikacjach występują luki w zabezpieczeniach, które można wykorzystać do dostarczenia i aktywacji oprogramowania ransomware. Ponadto cyberprzestępcy mogą wykorzystywać istniejące exploity, jak widać w ostatnim ataku WannaCry,
Ransomware rozprzestrzenia się
W ciągu ostatnich kilku lat nastąpił dramatyczny wzrost liczby dużych i skutecznych ataków ransomware na organizacje . Cybersecurity Ventures przewiduje, że globalny koszt oprogramowania ransomware przekroczy w 2017 r. 5 mld USD, 15 razy więcej niż koszt w 2015 r. 1 W tym samym czasie liczba wariantów oprogramowania ransomware wzrosła trzydziestokrotnie.
Wpływ ataku ransomware na organizację znacznie wykracza poza koszt odblokowania płatności. Firmy pochłaniają koszty związane z utratą danych, zmniejszoną lub utraconą produktywnością, dochodzeniami kryminalistycznymi, przywracaniem danych i systemów, utraconymi przychodami i utratą reputacji. Na przykład jedna z wiodących światowych firm zajmujących się zdrowiem i artykułami konsumpcyjnymi poinformowała, że odnotuje 2% wzrost przychodów w tym kwartale ze względu na wpływ ostatniego oprogramowania ransomware Petya na jego zdolność do fakturowania i wysyłania produktów do klientów.
CryptoLocker był jedną z pierwszych powszechnie używanych rodzin oprogramowania ransomware i pochodzi z 2013 roku. Złośliwe oprogramowanie było często dostarczane jako zaciemniony załącznik do wiadomości e-mail lub instalowane na urządzeniu, które wcześniej zostało naruszone. Po aktywacji szkodliwe oprogramowanie szyfruje określone pliki danych na dyskach lokalnych i sieciowych. Ofiara musiała uiścić opłatę okupową w wysokości 400 USD lub równowartość Bitcoin w określonym czasie lub klucz deszyfrujący został usunięty. Nic dziwnego, że nawet po zapłaceniu okupu klucz deszyfrujący często nie był dostarczany. Gamenet Zeus Botnet, który był używany do dystrybucji oprogramowania ransomware, został usunięty przez przemysł, organy ścigania i agencję rządową o nazwie Operacja Tovar.
Głośne ataki ransomware
CryptoWall to późniejszy wariant CryptoLocker, który działa w ten sam sposób. Najpoważniejszy atak miał miejsce w Australii pod koniec 2014 r., Gdy do rozpowszechniania złośliwego oprogramowania wykorzystano wiadomości phishingowe ze złośliwymi linkami „wysłanymi” przez agencje rządowe. 4 Aby uniknąć blokowania przez produkty zabezpieczające, złośliwi aktorzy używali formularza Captcha przed pobraniem złośliwego oprogramowania.
Locky został po raz pierwszy zaobserwowany na początku 2016 r. I zwykle był dystrybuowany za pośrednictwem wiadomości e-mail z załącznikiem „faktura”. Po otwarciu pliku Word lub Excel użytkownik został poproszony o włączenie makr w celu wyświetlenia faktury. Po włączeniu makr plik uruchomił następnie plik wykonywalny, który pobrał rzeczywiste oprogramowanie ransomware. Pliki lokalne i sieciowe zostały zaszyfrowane i zmieniono ich nazwę z rozszerzeniem .locky. Aby odblokować pliki, ofiary musiały odwiedzić witrynę internetową, aby pobrać przeglądarkę, z której mogliby skorzystać w celu uzyskania dostępu do strony płatniczej złośliwego aktora. Płatność zwykle wynosiła od połowy do jednego Bitcoin. Locky był jednym z pierwszych ataków ransomware, który zyskał szerszą uwagę mediów publicznych, ponieważ amerykański szpital miał zaszyfrowane dane pacjenta i zapłacił za odzyskanie plików.
WannaCry trafiła na pierwsze strony gazet w maju 2017 r., Kiedy dotknęła 400 000 komputerów na całym świecie. Znacząco ucierpiały zarówno organizacje publiczne, jak i prywatne, w tym brytyjska National Health Service, hiszpańska firma telekomunikacyjna i duży niemiecki bank. Na szczęście dzięki badaczowi bezpieczeństwa, który odkrył przełącznik zabijania w złośliwym oprogramowaniu, atak został zatrzymany w ciągu kilku dni. Atak został przeprowadzony i rozprzestrzeniony poprzez znaną lukę w zabezpieczeniach systemu Windows (EternalBlue). Chociaż łatka bezpieczeństwa była dostępna od kilku miesięcy, wiele organizacji jeszcze jej nie zainstalowało.
NotPetya, wariant ransomware Petya, szybko pojawił się na WannaCry w czerwcu 2017 roku i po raz pierwszy pojawił się na Ukrainie. Rozproszone jako załącznik do wiadomości e-mail w formacie PDF, złośliwe oprogramowanie rozprzestrzeniało się przy użyciu tej samej usterki EternalBlue, co w WannaCry. Znów ucierpiały na tym organizacje publiczne i prywatne na całym świecie, w tym duża amerykańska firma farmaceutyczna, międzynarodowa kancelaria prawna i największa brytyjska firma reklamowa. W przeciwieństwie do innych programów ransomware, Petya infekuje główną tabelę plików komputera. Spekuluje się, że w tym ataku chodziło raczej o spowodowanie zakłóceń na Ukrainie niż o motywację finansową.
Zmniejszenie ryzyka, że Ransomware będzie miało wpływ na Twoją firmę
Naucz najsłabsze ogniwo. Zdecydowana większość oprogramowania ransomware wymaga podjęcia działań w celu aktywacji ładunku. Niezbędne jest szkolenie pracowników w zakresie rozpoznawania i obrony przed cyberatakami. W wielu atakach wykorzystuje się wiadomości e-mail i techniki socjotechniczne, aby nakłonić pracownika do pobrania złośliwego oprogramowania lub ujawnienia nazwy użytkownika i hasła. Dlatego szkolenie powinno koncentrować się na tych typowych wektorach ataku. Ćwiczenia polegające na wysyłaniu pracownikom fałszywych wiadomości e-mail „phishingowych” skutecznie pomagają użytkownikom w odróżnieniu autentycznej komunikacji dostawcy od wiadomości e-mail wyłudzającej informacje w temacie „Załączona faktura – proszę otworzyć”.
Łatka, łatka, łatka. Następnie załataj ponownie. Jak pokazały ostatnie ataki WannaCry i Petya, niezastosowanie rygorystycznego podejścia do łatania znanych luk w zabezpieczeniach może narazić przedsiębiorstwo na niebezpieczeństwo. Nawet miesiące po wykorzystaniu luki w zabezpieczeniach EternalBlue do ataków ransomware WannaCry i NotPetya szacuje się, że co najmniej 38 milionów komputerów pozostaje niezakończonych. Cyberprzestępcy mogą stosunkowo łatwo zidentyfikować niepakowane urządzenia i oprogramowanie w sieci przedsiębiorstwa, a po ich zidentyfikowaniu wykorzystać znane luki.
Utwórz kopię zapasową danych. Niektórym może się to wydawać oczywiste, ale oprogramowanie ransomware może szyfrować kopie zapasowe przechowywane na serwerach sieciowych. W rezultacie przedsiębiorstwa muszą zweryfikować swoje obecne podejście do tworzenia kopii zapasowych. Pracownicy wykonują kopię zapasową ważnych plików na dysku sieciowym? Czy Twoje kopie zapasowe z tych urządzeń i serwerów plików są następnie tworzone w usłudze tworzenia kopii zapasowych w chmurze? Testujesz, czy kopie zapasowe można przywrócić? W ten sposób, jeśli oprogramowanie ransomware szyfruje wszystkie lokalne pliki i kopie zapasowe, przedsiębiorstwo nadal może je szybko przywrócić przy minimalnym wpływie na działalność firmy.
Utrudniaj złym ludziom życie – posiadaj wiele warstw obrony. Cyberprzestępcy spędzają ogromne ilości czasu i pieniędzy, opracowując coraz bardziej wyrafinowane formy zaawansowanego złośliwego oprogramowania, które zostały zaprojektowane w celu ominięcia zabezpieczeń firmy. Poleganie na jednej warstwie zabezpieczeń przed tym ewoluującym zaporem nie jest najlepszą praktyką. Korzystanie z wielu warstw zabezpieczeń oznacza, że jeśli jedna warstwa nie blokuje ataku, masz dodatkowe nakładki, które mogą złagodzić zagrożenie. Jakie zatem poziomy ochrony bezpieczeństwa ma Twoja firma? Czy masz różne rozwiązania bezpieczeństwa, które pomagają zmniejszyć ryzyko na wszystkich etapach ataku? Czy istnieją obecnie luki w zabezpieczeniach, które mogą wykorzystać złośliwi aktorzy?
#anty ransomware#atak ransomware#co to jest ransomware#cryptolocker#cryptxxx#cybereason ransomfree#gandcrab jak usunąć#jak odzyskac pliki zaszyfrowane przez wirusa#jak odzyskać zaszyfrowane pliki#jak odzyskać zaszyfrowane pliki cryptolocker#kaspersky rakhnidecryptor#nampohyu#oprogramowanie ransomware#petya#petya wirus#ransomfree#ransomware avast#ransomware co to#ransomware co to jest#ransomware decryptor#ransomware download#ransomware jak usunąć#ransomware po polsku#ransomware scanner#ransomware wikipedia#wanna cry jak usunąć#WannaCry#wirus ransomware
0 notes
Link
Truke Ransomware is a recent menacing threat that is infecting a large number of systems, encrypting user & system files & rendering them inaccessible to users.
#what is truke ransomware#Truke virus Truke Ransomware Ransomware virus cryptolocker decrypt truke ransomware removal .truke file recovery .truke decryter tool remove
0 notes
Text
COMO SE ELIMINA EL RANSOMWARE EN WINDOW 10, 8 o 7
Si ya has sido víctima de algún tipo de Ransomware lo más recomendable es tratar de limpiar tu sistema, apoyándose con las herramientas que Windows pone a tu disposición.
¿Qué tipos de ransomware puedo encontrar?
Existen tres tipos de ransomware y dependiendo del tipo de ataque sufrido por el equipo, se determinará el grado de dificultad para la recuperación de la información; esta tarea puede ser sencilla o sencillamente imposible.
Uno de los tipos que podemos encontrar es un software malicioso o scareware que podremos desinstalar en minutos; sin embargo existen otras dos variaciones más terribles, denominadas filecoders y ransomware de cifrado, estos malwares son capaces de cifrar los archivos, secuestrando la información, para exigir un pago a cambio de un código de descifrado.
¿Es posible eliminar el ransomware?
En el caso de los filecoders cada uno tiene su procedimiento específico de descifrado, lo que imposibilitará eliminarlo con facilidad; incluso algunos programas de ransomware cuentan con un plazo de caducidad, que provoca que se borren a sí mismo una vez cumplido ese periodo de tiempo. En el caso de Windows se pueden utilizar programas de protección antivirus para eliminarlos; de esta manera evitará que este malware se distribuya a otros equipos con la desventaja que sus archivos quedarán cifrados.
Lo importante es identificar el tipo de ransomware que afecta su PC para utilizar una de las herramientas de descifrado de ransomware legítimos para Windows y poder recuperar sus datos. No obstante, hay que ser cauteloso en esa búsqueda, ya que muchas variantes de ransomware utilizan cifrado a nivel empresarial imposible de romper.

¿Qué debo hacer?
Lo primordial es la prevención, para ello, se debe realizar una copia de seguridad del sistema operativo del PC y los archivos de manera periódica; es recomendable utilizar almacenamiento en la red como Dropbox o google cloud, o aprovechar dispositivos externos como unidades flash. ¡Nunca guardes tus copias de seguridad en tu propio computador, pues el ransomware afecta los archivos originales y copias!
En caso de un contagio por ransomware en primer lugar debes revisar todos tus dispositivos (PC, tabletas y Smartphone) para verificar cuáles han sido afectados, además desconecta todo aquel dispositivo de almacenamiento externo que poseas para evitar su contaminación.
En segundo lugar, averigua que tipo de ransomware te ha afectado: los temibles filecoders (como WannaCry o CryptoLocker). O algunos más sencillos de eliminar como los Screenlockers o el Scareware. Para esta tarea puedes utilizar el uso de Crypto Sheriff, una herramienta útil para comprobar los datos que han sido afectados, reconocer el cifrado y hallar la solución, poniendo a tu disposición un enlace para descargar el programa de descifrado para desencriptar la información.
En tercer lugar procede a eliminar el ransomware que ha retenido tu información, en el caso de Windows 10, 8 y 7 tienes cuatro opciones:
● Revisa si el ransomware se eliminó por sí mismo.
● Elimínalo con el antivirus legítimo.
● Busque asesoría en expertos en soporte técnico del antivirus lo eliminen.
● Elimina el malware de manera manual.
Por último, recupera todos los archivos cifrados, para ello puedes utilizar varias estrategias, aquí algunas:
- Restablece el sistema operativo desde una copia de seguridad, a través de la función de Restaurar sistema, así lograrás restablecer los programas y archivos de tu equipo. Si esto no resulta. En el caso de Windows 10 y 8 lo puedes hacer a través del Historial de archivos. En Windows 7 también lo podrás realizar aunque con un poco más de voluntad.
- Emplea herramientas de descifrado (desencriptación Ransomware) para recuperar tu acceso, ideales para PC con Windows, las cuales son accesibles de manera gratuita.
- Si has realizado todos los pasos necesarios y aún no consigues desbloquear la información, No pagues rescate ni negocies alguna alternativa, a pesar de la urgencia lo recomendable es esperar que se publique una herramienta de descifrado de ransomware que le haya afectado. No pague para no apoyar esta práctica delictiva, además que no tendrá ninguna garantía de que envíen un descifrador que sirva realmente y le devuelva su información
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Protect Yourself Against Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software, also known as malware. It encrypts a victim’s data until the attacker is paid a predetermined ransom. In this article, we will talk about how to protect yourself against ransomware.
How does ransomware work?
Ransomware identifies the drives on an infected system and begins to encrypt the files within each drive. Ransomware generally adds an extension to the encrypted files, such as .aaa, .micro, .encrypted, .ttt, .xyz, .zzz, .locky, .crypt, .cryptolocker, .vault, or .petya, to show that the files have been encrypted—the file extension used is unique to the ransomware type.
Once the ransomware has completed file encryption, it creates and displays a file or files containing instructions on how the victim can pay the ransom. If the victim pays the ransom, the threat actor may provide a cryptographic key that the victim can use to unlock the files, making them accessible.

How is ransomware delivered?
Ransomware is commonly delivered through phishing emails or via “drive-by downloads.” Phishing emails often appear as though they have been sent from a legitimate organization or someone known to the victim and entice the user to click on a malicious link or open a malicious attachment. A “drive-by download” is a program that is automatically downloaded from the internet without the user’s consent or often without their knowledge. It is possible the malicious code may run after download, without user interaction. After the malicious code has been run, the computer becomes infected with ransomware...get more info at - CISA.
Create backups of your data
In the event that a hacker successfully hijacks your computer, you could rescue yourself with a backup of your data stored somewhere, like on a physical hard drive. That way, if a hacker locked down your computer, you could simply erase all the data from the machine and restore it from the backup.
In general, you should be creating a copy of your data in the first place, in case your computer fails or is lost. To be extra safe from hackers, after backing up your data onto an external drive, unplug the drive from the computer and put it away...to know more, visit - nytimes.

Keep your system up to date
If you are running Windows XP or Vista, you should immediately update your system to Windows 10 or buy a new computer. As we warned back in 2014, Microsoft is no longer supporting these ancient versions of Windows and continuing to use them makes you a prime target for cyber-attacks. And even an entry model $500 computer that will be far more powerful than your current XP one.
For those using Windows 7 and newer, make sure that you have Automatic Updates enabled so new security patches are installed as soon as they are available. These versions of Windows had already been patched by Microsoft to specifically prevent these types of ransomware attacks...get more info at - techlicious.
Scan And Filter Emails Before They Reach Your Users
The easiest way to stop staff clicking on a ransomware link in an email is for the email never to arrive in their inbox. This means using content scanning and email filtering, which ought to take care of many phishing and ransomware scams before they actually reach staff.
Think Very Long And Hard Before You Pay A Ransom
Ransomware crooks have found their way through your defences and now every PC across the business is encrypted. You could restore from backups, but it will take days and the criminals only want a few thousand dollars. Time to pay up?
For some, that may be the obvious conclusion. If the attackers only want a relatively small amount then it might, in the short term, make business sense to pay up because it means the business can be up and running again quickly. However there are reasons why you might not want to pay...visit - ZDNet to know more.
Threat intelligence
While most cybersecurity organizations continue to focus their gaze internally, the only way to move from reactive to proactive is through intelligence. Cybersecurity professionals who understand threat trends and the landscape, which includes adversaries, tactics, techniques, and procedures, are empowered to capitalize on such knowledge to prevent attacks.

Automation
Organizations are overrun with massive amounts of data, information, and intelligence. Considering the skills gap that is still challenging the industry, there is rarely enough time in the day to adequately address all critical or high-level security events, let alone the moderate and low risks. Only through automation, wherein machines capitalize on high-fidelity intelligence to take actions without human intervention, can cyber defenders have the time needed to focus on the biggest-impact security matters...this and more at - Dark Reading.
Final Words
Use these tips to keep your Company’s sensitive information safe and stop a ransomware attack before it starts. Use a good email security service that will keep you from clicking on a phishing link.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Avoid Ransomware with These Tips
At ITS, we saw a few articles online claiming that the Cryptolocker threat has ended. Let us ask those people a question: What color is the sky in your world? While it is true that the group behind the original attacks had been taken down last year, Cryptolocker is alive and thriving. We still have a wild variety of variants out there. Learn more about this.

How can you prevent ransomware from happening on your computer? First, remove your email address from your website. While you still want customers to contact you, talk to your IT specialist about creating a form. It creates a more secure interaction and keeps the communications effective.
Second, do not give out your corporate or primary email address unless you need it for important correspondence. Avoid giving it to people who do not need it. Third, use a professional spam filter that will seek out phishing attempts, viruses and DNSBL. To avoid ransomware at the base level, you have to keep your firewalls and antivirus updated at the most essential levels.
Want to prevent ransomware from encrypting the files of your business? If so, contact Adkins Tech or visit itsasap.com for further information on protecting yourself. We are experts who understand what it takes to protect business owners from losing their important files to Cryptolocker.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Product Description EMAIL DELIVERY INSTRUCTIONS Before you order: Is your email address registered on Amazon?Please check: Go to > Your Account > Login & Security > E-mailIf not added, please add and then place order. Order will be delivered within 2 hours - Do check spam / promotions / junk tooIncase your Email id is not registered or added after ordering: Activation Code and Download Instructions can also be found in the Message Center of your Amazon account. Go to amazon.in/msg -> Click on BuyerSeller Messages-> You will find the copy of mail. (Email is auto sent, hence cannot be manually resent. Ignore the "delivery is running late" notification shown by the app. Its an error.) Please Note: Incase of any issue, please contact Arham World by clicking on their name below the Order button. Response hours: Mon - Fri - 11am to 7pm. Or you can also reach out to customer care who will further guide. Our top-rated Windows antivirus guards you from threats like ransomware, cryptolockers & hackers. It’s the easy-to-use solution that leaves you to enjoy all the things you love online - in safety. Blocks viruses & malware in real-timeStops hackers taking over your PC remotelyHelps keep your machine running fast & smooth Our triple-layer security works 24/7 to guard your PC and data. It blocks common and complex threats like viruses, malware, spy apps, ransomware and the full range of hacking techniques. Proactive detection - Searches out Windows vulnerabilities & threatsReal-time protection - Blocks cyberthreats before they take holdInstant neutralization - Isolates & removes immediate dangers Platforms Supported Windows Windows, Mac, Android Windows, Mac, Android Real-Time Anti-Virus ✓ ✓ ✓ Anti-Phishing ✓ ✓ ✓
Performance Optimization ✓ ✓ ✓ Payment Protection ✓ ✓ Smart & fast VPN ✓ ✓ GPS Child Locator ✓ File Protection ✓ Password Manager ✓ Easy to use, automatically detects and removes viruses, trojan, malware. Keeps your device safe, secure, protects against malicious virus attacks.automatically updates to the latest virus definitions Blocks dangerous links, apps, websites and malware; filter out unwanted texts and calls and protects your privacy Get a Free Movie ticket voucher worth upto Rs.250 with the purchase of eligible Kaspersky products, Offer is Valid till 31st March 2023 (For details check the order email) [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
2010s to Now
As of the present day, this is officially the time period where viruses are their most advanced. In this time period, this is the most dependent we have ever been on technology not only for ourselves but most public services completely digital.

Biggest Threat We Face - Ransomware
The biggest threat we face in cyber security is ransomware. This time, viruses have the ability to significantly affect whole societies and economies with the attacks being unrelenting.
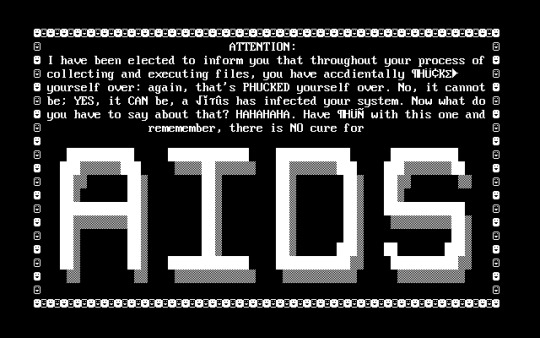
Even though it seems like a new concept, the idea of taking users files and holding them hostage is not new. For example there was a virus circulating in the 1980s called the "AIDS" trojan. which had victims send $189 to a PO box in Panama to restore access.
However, we would not see them be wide spread until way into the 2000s. The emergence of bitcoin changed that and now hackers had a easy untraceable method to receive their payment.
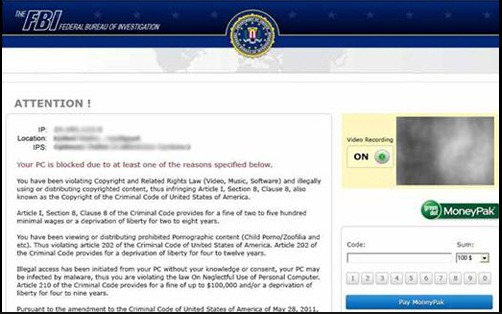
This resulted in ransomware being more and more prevalent in the beginning 2012. An example would be the FBI Moneypak virus. In which the virus would hijack a users device and display a message saying they were involved in illegal activity and the FBI had locked their computer until they pay the ransom listed on the screen.
Cryptolocker
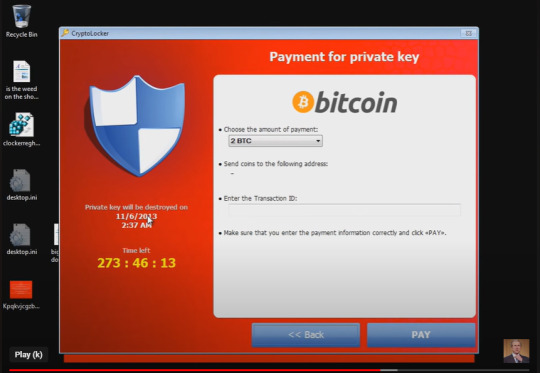
This was considered a revolutionary breed of ransomware at the time of its creation. It not only harnessed the power of Bitcoin transactions, but combined it with more advanced forms of encryption. How it would work is that once it reached a device through a link or through email attachment, it would immediately encrypt a users files to a point were they were rendered essentially useless. once every file on the system was encrypted, it would display a message saying the files were encrypted and the only way to get their files back was to pay the fine.
The encryption was so intricate that it made it virtually impossible to decrypt a user's files without paying the fine.
While this was a big threat at the time, the creators of this virus were arrested by the FBI and the the GameoverZeus botnet distributing the virus was shutdown making this program obsolete.
Unfortunately that did not stop the problem seeing that researchers were able to find copious amounts of Cryptolocker clones in the wild run by various cyber criminals.
WannaCry
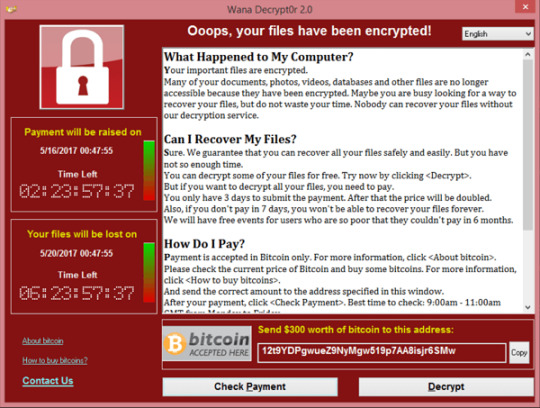
The biggest threat after the Cryptolocker outbreak was the Wannacry virus. It operated in the same manner that Cryptolocker functioned, but was able to infect more than 200,000 machines and did significantly more damage than the previous program. It is estimated to have hit over 150 countries and caused up to US$4 billion in damages.
The Future of Ransomware
The technology used to create these programs have advanced rapidly in terms of capabilities and sophistication. We can expect to see more attacks as stated at rapid rates and demanding larger amounts in extortion money.

It is also believed that hackers will continue to refine their data leek extortion ransomware tactics, develop tooling that can be deployed widely and and automate data exfiltration by searching for, identifying and exfiltrating sensitive data by using keywords. As it stand we can stand to see a lot more attacks like these in the future.
0 notes