#aws serverless
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Explore the best practices for using AWS Lambda, including where to use it, security implications, performance optimization, and cost management tips. Learn how to leverage serverless computing effectively for scalable and secure applications.
0 notes
Text
#aws cloud#aws ec2#aws s3#aws serverless#aws ecs fargate tutorial#aws tutorial#aws cloud tutorial#aws course#aws cloud services#aws apprunner#aws rds postgres
0 notes
Text
youtube
The Best DevOps Development Team in India | Boost Your Business with Connect Infosoft
Please Like, Share, Subscribe, and Comment to us.
Our experts are pros at making DevOps work seamlessly for businesses big and small. From making things run smoother to saving time with automation, we've got the skills you need. Ready to level up your business?
#connectinfosofttechnologies#connectinfosoft#DevOps#DevOpsDevelopment#DevOpsService#DevOpsTeam#DevOpsSolutions#DevOpsCompany#DevOpsDeveloper#CloudComputing#CloudService#AgileDevOps#ContinuousIntegration#ContinuousDelivery#InfrastructureAsCode#Automation#Containerization#Microservices#CICD#DevSecOps#CloudNative#Kubernetes#Docker#AWS#Azure#GoogleCloud#Serverless#ITOps#TechOps#SoftwareDevelopment
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Serverless architecture beyond AWS Lambda#Event-driven systems and edge computing#Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) in modern applications#Spotify
0 notes
Text
Serverless Architecture for Scalable, Cost-Effective Web Apps
Serverless architecture helps businesses build web apps faster, cheaper, and without worrying about server maintenance. Cloud providers like AWS and Google Cloud take care of all the backend work, so developers can focus on writing code.
In this setup, apps scale automatically based on demand, and companies only pay for the actual usage, not idle time. This means less cost, better security, and quicker updates.
Popular tools include AWS Lambda, API Gateway, and Google Cloud Functions. These tools support tasks like running code, storing data, or building APIs - all without managing servers.
Use cases include mobile and web backends, real-time data processing, and scheduled jobs. Best practices include keeping code small, monitoring performance, and securing environments.
Overall, serverless makes building apps easier and more efficient. It’s ideal for growing businesses that want to stay fast, flexible, and budget-friendly.
#Serverless#CloudComputing#AWS#GoogleCloud#WebDevelopment#TechSimplified#ScalableApps#CostEffectiveTech
0 notes
Text
Cost Optimization Strategies in Public Cloud

Businesses around the globe have embraced public cloud computing to gain flexibility, scalability, and faster innovation. While the cloud offers tremendous advantages, many organizations face an unexpected challenge: spiraling costs. Without careful planning, cloud expenses can quickly outpace expectations. That’s why cost optimization has become a critical component of cloud strategy.
Cost optimization doesn’t mean cutting essential services or sacrificing performance. It means using the right tools, best practices, and strategic planning to make the most of every dollar spent on the cloud. In this article, we explore proven strategies to reduce unnecessary spending while maintaining high availability and performance in a public cloud environment.
1. Right-Sizing Resources
Many businesses overprovision their cloud resources, thinking it's safer to allocate more computing power than needed. However, this leads to wasted spending. Right-sizing involves analyzing usage patterns and scaling down resources to match actual needs.
You can:
Use monitoring tools to analyze CPU and memory utilization
Adjust virtual machine sizes to suit workloads
Switch to serverless computing when possible, paying only for what you use
This strategy ensures optimal performance at the lowest cost.
2. Take Advantage of Reserved Instances
Most public cloud providers, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, offer Reserved Instances (RIs) at discounted prices for long-term commitments. If your workload is predictable and long-term, reserving instances for one or three years can save up to 70% compared to on-demand pricing.
This is ideal for production environments, baseline services, and other non-variable workloads.
3. Auto-Scaling Based on Demand
Auto-scaling helps match computing resources with current demand. During off-peak hours, cloud services automatically scale down to reduce costs. When traffic spikes, resources scale up to maintain performance.
Implementing auto-scaling not only improves cost efficiency but also ensures reliability and customer satisfaction.
4. Delete Unused or Orphaned Resources
Cloud environments often accumulate unused resources—volumes, snapshots, IP addresses, or idle virtual machines. These resources continue to incur charges even when not in use.
Make it a regular practice to:
Audit and remove orphaned resources
Clean up unattached storage volumes
Delete old snapshots and unused databases
Cloud management tools can automate these audits, helping keep your environment lean and cost-effective.
5. Use Cost Monitoring and Alerting Tools
Every major public cloud provider offers native cost management tools:
AWS Cost Explorer
Azure Cost Management + Billing
Google Cloud Billing Reports
These tools help track spending in real time, break down costs by service, and identify usage trends. You can also set budgets and receive alerts when spending approaches limits, helping prevent surprise bills.
6. Implement Tagging for Cost Allocation
Properly tagging resources makes it easier to identify who is spending what within your organization. With tagging, you can allocate costs by:
Project
Department
Client
Environment (e.g., dev, test, prod)
This visibility empowers teams to take ownership of their cloud spending and look for optimization opportunities.
7. Move to Serverless and Managed Services
In many cases, serverless and managed services provide a more cost-efficient alternative to traditional infrastructure.
Consider using:
Azure Functions or AWS Lambda for event-driven applications
Cloud SQL or Azure SQL Database for managed relational databases
Firebase or App Engine for mobile and web backends
These services eliminate the need for server provisioning and maintenance while offering a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
8. Choose the Right Storage Class
Public cloud providers offer different storage classes based on access frequency:
Hot storage for frequently accessed data
Cool or infrequent access storage for less-used files
Archive storage for long-term, rarely accessed data
Storing data in the appropriate class ensures you don’t pay premium prices for data you seldom access.
9. Leverage Spot and Preemptible Instances
Spot instances (AWS) or preemptible VMs (Google Cloud) offer up to 90% savings compared to on-demand pricing. These instances are ideal for:
Batch processing
Testing environments
Fault-tolerant applications
Since these instances can be interrupted, they’re not suitable for every workload, but when used correctly, they can slash costs significantly.
10. Train Your Teams
Cost optimization isn’t just a technical task—it’s a cultural one. When developers, DevOps, and IT teams understand how cloud billing works, they make smarter decisions.
Regular training and workshops can:
Increase awareness of cost-effective architectures
Encourage the use of automation tools
Promote shared responsibility for cloud cost management
Final Thoughts
Public cloud computing offers unmatched agility and scalability, but without deliberate cost control, organizations can face financial inefficiencies. By right-sizing, leveraging automation, utilizing reserved instances, and fostering a cost-aware culture, companies can enjoy the full benefits of the cloud without overspending.
Cloud optimization is a continuous journey—not a one-time fix. Regular reviews and proactive planning will keep your cloud costs aligned with your business goals.
#PublicCloudComputing#CloudCostOptimization#Azure#AWS#GoogleCloud#CloudStrategy#Serverless#CloudSavings#ITBudget#CloudArchitecture#digitalmarketing
0 notes
Text
Serverless Computing: Streamlining Web Application Deployment
0 notes
Text
Deploying a MERN (MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js) stack application is a crucial step to make your app accessible to users. Choosing the right deployment platform depends on your needs:
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is ideal for scalable, high-performance applications.
Vercel is great for quick and easy deployment, especially for frontend applications.
In this guide, we will walk through deploying a MERN stack application on AWS (using EC2 and S3) and Vercel (for serverless hosting).
#MERNStack#AWS#Vercel#Deployment#FullStackDevelopment#WebDevelopment#NodeJS#MongoDB#ExpressJS#React#AWSDeployment#VercelDeployment#CloudHosting#CloudComputing#WebAppDeployment#DevOps#CI/CD#Serverless#Heroku#AWSAmplify#FrontendDevelopment#BackendDevelopment#AppDeployment#ReactApp#MongoDBIntegration#MERNApp#DeploymentGuide#AWSHosting#VercelHosting#WebAppHosting
0 notes
Text
Exploring AWS Lambda: Use Cases, Security, Performance Tips, and Cost Management

AWS Lambda, a core component of serverless architecture, empowers developers, cloud architects, data engineers, and business decision-makers by allowing code execution in response to specific events without managing servers. This flexibility is ideal for many modern applications but requires a nuanced understanding of its use cases, security considerations, performance factors, and cost implications to maximize its benefits.
In the first part, ‘exploring AWS lambda – a guide to serverless use cases,’ we saw how AWS Lambda enables efficient and scalable real-time data processing, facilitates backend services automation, supports microservices architecture, and enhances IoT applications by processing sensor data. It highlighted use cases like image processing, real-time notifications, and on-the-fly data transformations, emphasizing Lambda’s role in creating responsive, cost-effective applications without server management overhead.
Why it is important to understand AWS Lambda
Knowing when to use or avoid AWS Lambda is crucial for optimizing performance and cost. Our team of AWS experts emphasizes this while providing AWS consulting. For developers and cloud architects, this understanding leads to efficient resource allocation and streamlined workflows. Data engineers benefit from leveraging Lambda’s capabilities for real-time data processing, while business decision-makers can make informed choices about infrastructure investments, ensuring cost-effective and scalable solutions.
Statistics from AWS reveal a compelling fact: Companies leveraging Lambda for event-driven applications experience up to a staggering 70% reduction in operational costs. This potential for significant cost savings should motivate businesses to delve deeper into Lambda. Understanding its security implications can protect sensitive data, and optimizing performance ensures a seamless user experience. However, misuse or misunderstanding of Lambda can lead to increased costs, security vulnerabilities, and performance bottlenecks. This underscores the importance of gaining a comprehensive understanding of Lambda.
Where to use AWS Lambda
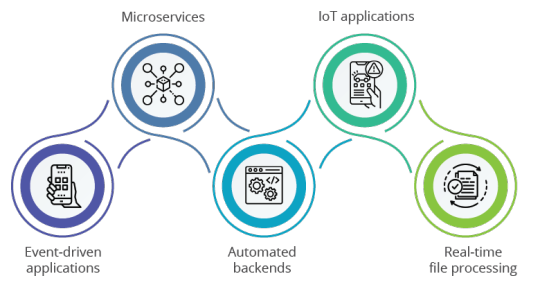
Event-driven applications: AWS Lambda shines in event-driven scenarios. Imagine an e-commerce platform that processes and verifies customer orders. Lambda can trigger functions upon order placement, ensuring swift and reliable processing. This event-driven model streamlines operations and reduces latency. For developers, this means faster deployment and reduced overhead.
Microservices: Lambda’s modular nature makes it a perfect fit for microservices architecture. Each function can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. For example, a social media platform can use Lambda to handle user notifications, where each type of notification is a separate microservice, allowing for isolated management and scaling. Cloud architects will find this helpful in designing scalable and maintainable systems.
Automated backends: For tasks like user authentication, data validation, or generating reports, Lambda offers an automated, scalable backend solution. This is particularly effective for applications with sporadic workloads, as Lambda only runs when needed, saving costs on idle server time. Business decision-makers benefit from cost efficiency and flexibility.
IoT applications: In IoT ecosystems, Lambda can process data from connected devices in real-time. For instance, a smart home system might use Lambda to analyze sensor data and trigger actions such as adjusting the thermostat or sending alerts, ensuring responsive and efficient device management. Data engineers can leverage Lambda for seamless data processing and integration.
Real-time file processing: Lambda is excellent for real-time file processing. Consider a photo-sharing application where users upload images. Lambda functions can automatically resize images and store them in various formats in an S3 bucket, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Suggested: Apart from when to use Lambda, do you want to know more about why successful businesses are cloud-based? Read this!
Where not to use AWS Lambda
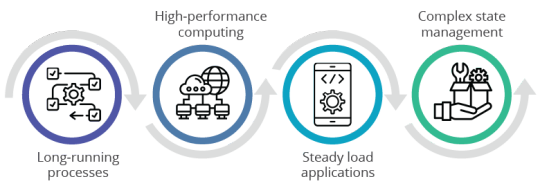
Long-running processes: Lambda functions have a maximum execution time of 15 minutes. For applications requiring longer processing times, like video rendering or extensive data analysis, traditional EC2 instances or ECS services are more suitable.
High-performance computing: Tasks requiring significant computational power, such as complex simulations or machine learning model training, may need to improve on Lambda due to its limited resource allocation compared to dedicated HPC solutions. Developers working on resource-intensive applications should consider more powerful options.
Steady load applications: For applications with a predictable, continuous load, such as streaming services, maintaining dedicated servers or using containerized environments can be more cost-effective. Lambda’s pay-per-request model may lead to higher costs for sustained high-volume traffic.
Complex state management: Applications requiring persistent connections or complex state management, such as multiplayer online games or real-time chat applications, may face challenges with Lambda. Maintaining a state across stateless function invocations can take time and effort. Cloud architects should consider traditional server setups for such use cases.
Security implications of AWS Lambda
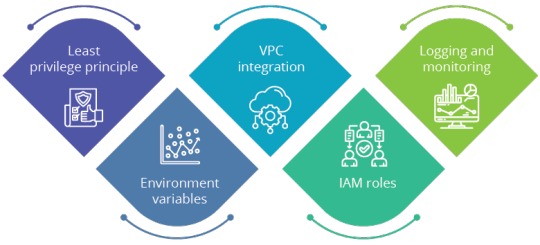
Least privilege principle: Lambda functions should follow the principle of least privilege, ensuring they have only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches. Cloud architects must ensure strict access controls and permission settings.
Environment variables: Avoid storing sensitive data like API keys or credentials in environment variables. Instead, utilize AWS Secrets Manager or AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store for secure storage and retrieval of sensitive information. Developers should follow best practices for handling confidential information.
VPC integration: Running Lambda functions within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) can enhance security by restricting network access to AWS resources. This isolates Lambda functions from the public internet, reducing exposure to potential attacks. Security-conscious architects can leverage VPC integration for additional protection.
IAM roles: Properly configured IAM roles and policies are crucial for Lambda functions. Assigning specific roles to functions ensures they can access only the resources they need, reducing the risk of privilege escalation.
Logging and monitoring: Enabling logging with AWS CloudWatch allows for real-time monitoring of Lambda function activity. Setting up alerts for unusual behavior helps promptly detect and respond to security incidents.
Suggested: Check out the ultimate guide to application integration on AWS!
Performance and cost impact of using AWS Lambda
Performance
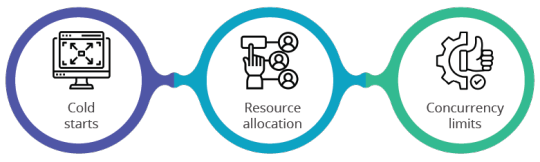
Cold starts: Cold starts occur when a Lambda function is invoked after inactivity, leading to initialization latency. While this can impact performance, using Provisioned Concurrency can keep functions warm, reducing latency for critical functions. Developers should be aware of this to ensure responsive applications.
Resource allocation: Optimizing memory and timeout settings can significantly enhance performance. Allocating adequate memory ensures functions execute efficiently, reducing execution time and improving user experience.
Concurrency limits: Managing concurrency limits is essential to avoid throttling issues. By monitoring CloudWatch metrics, you can adjust concurrency settings to ensure smooth operation during peak times. Cloud architects need to manage these settings to maintain application reliability.
Cost

Pay-per-use model: Lambda’s pricing is based on the number of requests and the duration of code execution. This model is cost-effective for applications with sporadic usage patterns, as you only pay for actual compute time. Business decision-makers will appreciate the cost savings and scalability.
Free tier: AWS offers a generous free tier for Lambda, including 1 million free requests and 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time per month. This makes it an attractive option for startups and small-scale applications.
Cost management: Regularly reviewing usage and optimizing function performance can help avoid unnecessary costs. Implementing cost monitoring and alerts through AWS Cost Explorer or similar tools ensures you stay within budget.
Also read: How can you maximize savings by avoiding five common mistakes that increase your AWS bill?
Identifying performance issues in AWS Lambda

Cold start latency: Analyze logs to identify high latencies due to cold starts. Provisioned concurrency can mitigate these delays by pre-warming functions. Developers should monitor these metrics to enhance user experience.
Timeout errors: Monitoring for timeout errors indicates whether functions need more execution time or optimization. Adjusting timeout settings or refining code can resolve these issues. Cloud architects should ensure functions are correctly tuned to avoid disruptions.
Throttling: Throttling events, visible in CloudWatch metrics, indicate that the concurrency limit has been reached. Adjusting concurrency settings or optimizing function performance can help prevent throttling. Business decision-makers should consider these metrics when planning for scalability.
Memory usage: Evaluating memory usage metrics ensures functions are adequately provisioned. Under-provisioned functions can suffer from performance issues, while over-provisioning can lead to unnecessary costs. Data engineers should optimize memory settings for efficient data processing.
Execution duration: Optimizing code to reduce execution time improves performance and controls costs. Efficient code execution minimizes the time functions run, leading to cost savings.
Summary
By understanding where to use and where not to use Lambda, security practices, performance considerations, and cost implications of Lambda, organizations can effectively leverage serverless computing to build scalable, efficient, and secure applications. Here’s a summarized view:
Aspect: Where to use Lambda
Recommendations: Event-driven apps, microservices, automated backends, IoT and real-time file processing.
Aspect: Where not to use Lambda
Recommendations: Long-running processes, high-performance computing, steady load apps and complex state management.
Aspect: Security implications
Recommendations: Least privilege, secure environment variables, VPC integration, IAM roles and logging
Aspect: Performance considerations
Recommendations: Mitigate cold starts, optimize resource allocation and manage concurrency limits.
Aspect: Cost impacts
Recommendations: Utilize pay-per-use, leverage free tier, regular cost review and optimization
This comprehensive understanding ensures that you can maximize the benefits of AWS Lambda while mitigating potential drawbacks, leading to robust and cost-effective applications.
Originally published at https://www.softwebsolutions.com on June 25, 2024.
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
Create Elastic Container Service in AWS | Run Nodejs JavaScript API in E... Full Video Link - https://youtu.be/SfkHutfNTHYHi, a new #video to create #aws #ecs #elasticcontainerservice #awsecs #setup & run #nodejs #javascript #api in ECS #cluster service published on #codeonedigest #youtube channel. @java @awscloud @AWSCloudIndia @YouTube @codeonedigest #awsecs #nodejs #dockerimage #aws #amazonwebservices #cloudcomputing #awscloud #awstutorial #awstraining #awsecs #awsecstutorial #awsecsfargate #awsecsfargatetutorial #awsecsservice #awsecsservicetutorial #elasticcontainerserviceaws #elasticcontainerservice #elasticcontainerservicetutorial #nodejsecs #nodejsapi #nodejsapitutorial #nodejsapiproject #nodejsapidevelopment #javascriptapitutorial #dockerimagecreation #dockercontainer #dockerfiletutorial #ecsaws
#youtube#aws#aws ecs#ecs#elastic container service#fargate#aws fargate#aws serverless#serverless fargate#ecs fargate#nodejs tutorial#nodejs api#node js api#javascript api#node js express
1 note
·
View note
Text
🚀 Free DevOps with AWS Demo – Learn from Experts!
If you’re looking to master AWS DevOps concepts, this free online session is for you!
📅 Date: 27th March 2025 🕤 Time: 9:30 AM IST 💻 Mode: Online 🔗 Register Now: https://tr.ee/9fzwW0
💡 Key Takeaways: ✅ Hands-on AWS DevOps training ✅ CI/CD, Serverless, Cloud Monitoring, EKS, & more ✅ Real-world use cases
📌 For More Info: https://linktr.ee/NIT_Training
📢 Comment your use case & share with your network!

0 notes
Text
Comprehensive AWS Server Guide with Programming Examples | Learn Cloud Computing
Explore AWS servers with this detailed guide . Learn about EC2, Lambda, ECS, and more. Includes step-by-step programming examples and expert tips for developers and IT professionals
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a 🌐 robust cloud platform. It offers a plethora of services. These services range from 💻 computing power and 📦 storage to 🧠 machine learning and 🌐 IoT. In this guide, we will explore AWS servers comprehensively, covering key concepts, deployment strategies, and practical programming examples. This article is designed for 👩💻 developers, 🛠️ system administrators, and…
#AWS#AWSDeveloper#AWSGuide#AWSLambda#CloudComputing#CloudInfrastructure#CloudSolutions#DevOps#EC2#ITProfessionals#programming#PythonProgramming#Serverless
0 notes
Text
#Build#serverless#apps#node.js#awscloud#aws lambda#trends 2024#applications#development#application development#architecture#follow#machine learning#programming#coding#future trends#architettura
1 note
·
View note
Text
#AntStack TV Episode 6#Serverless Security Best Practices#Secure Serverless Applications#Serverless Architecture#IAM Policies for Serverless#Serverless Security for Developers#AWS Lambda Security#Spotify
0 notes
Text
Building Your Serverless Sandbox: A Detailed Guide to Multi-Environment Deployments (or How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Cloud)
Introduction Welcome, intrepid serverless adventurers! In the wild world of cloud computing, creating a robust, multi-environment deployment pipeline is crucial for maintaining code quality and ensuring smooth transitions from development to production.Here is part 1 and part 2 of this series. Feel free to read them before continuing on. This guide will walk you through the process of setting…
#automation#aws#AWS S3#CI/CD#Cloud Architecture#cloud computing#cloud security#continuous deployment#DevOps#GitLab#GitLab CI#IAM#Infrastructure as Code#multi-environment deployment#OIDC#pipeline optimization#sandbox#serverless#software development#Terraform
0 notes
Text
AWS Devops Services
Software delivery in cloud settings may be automated, scaled, and managed more efficiently with the help of AWS DevOps services. Among these services is infrastructure as code (IaC), which lets programmers use version-controlled scripts to define and maintain infrastructure. Software releases are made fast and dependable by automating the testing and deployment of applications through continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. Applications can operate reliably in a variety of contexts thanks to the management of microservices made possible by containerization and orchestration technologies. Teams can take proactive measures to resolve problems by using real-time insights into application performance that are provided by monitoring and logging services. Auto-scaling, which modifies resources in response to demand to maintain highly available and economical applications, is another crucial part of AWS DevOps services. Teams can comply with industry requirements by using automated controls and real-time auditing to include security and compliance in the DevOps workflow. Version control systems and collaboration tools are also essential since they let teams collaborate easily and monitor changes to infrastructure and code. With the help of these AWS DevOps services, businesses can create, launch, and maintain apps effectively, promoting an innovative and continuous improvement culture.
#AWS#DevOps#CloudComputing#AWSDevOps#CloudInfrastructure#Automation#CI/CD#InfrastructureAsCode#AWSLambda#Kubernetes#CloudFormation#Terraform#AWSCloud#Serverless#AWSCommunity
0 notes