#early mid victorian
Text
I know this is very Minor Inter-Community Issue but I'm hearing it more and more
"18th century stays weren't primarily for tightlacing! Medieval people had flavorful food!"
"yeah!"
"it's those GROSS ICKY HORRIBLE VICTORIANS who did the bad things!!!! they all ate gruel and suffocated women with corsets!!!"
"...w h y"
#history#social history#victorian#just because it's not your specialization era doesn't mean they were the shit-covered peasants from Monty Python#you all sound like Cecil Willett Cunnington- early dress historian who talked smack about the Victorians (especially women)#every chance he got#he WAS a Victorian. he was born in the mid-1870s#so just solidly shitting on his own mother and grandmother and sisters and aunts and wife...
253 notes
·
View notes
Photo
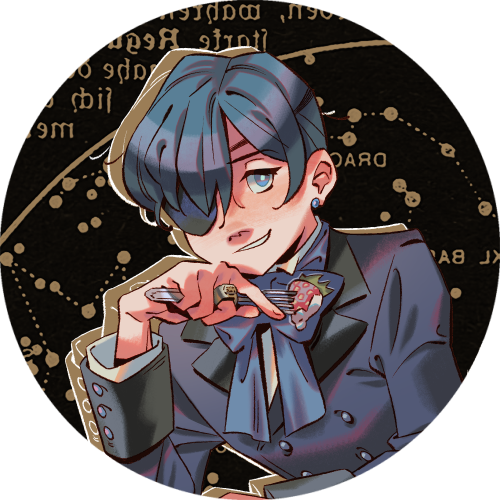


kuroshitsuji rewired my 14 yr old brain fr
🎩🕷🍬 buttons here !
#kuroshitsuji#black butler#ciel phantomhive#sebastian michaelis#sorry for bb posting on main#actually bb was the series i watched last fall when i was in a slu#SLUMP#and it got me thinking about my ocs again because like.#it transported me to a time when i was younger and making ocs for the 1st time (when i was 14 i mean)#there's something about that mid 2000s early 2010s time when victorian/lolita/related media was in its heydey and rewired my teen brain#so uh thank you black butler for inspiring me to work on my ocs again and making me happy in a way#random but i really like how the hands turned out in these. that strawberry i really like too#my art
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
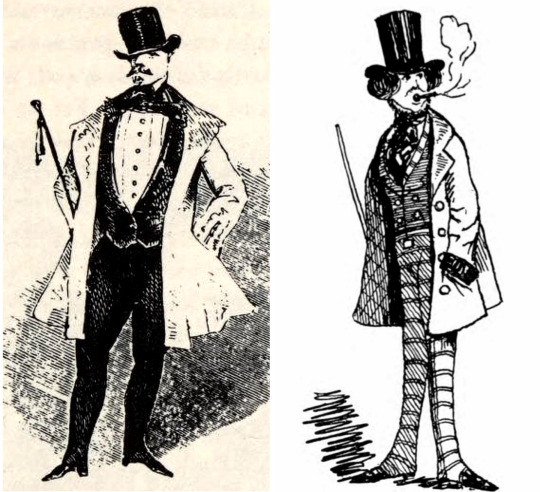

At left, the type of 1840s man that many people want, looking dashing in his evening costume and with the fashionable barrel chest and defined waist of his breed.
At right, a more typical example of the 1840s man that you will find at discount prices: note the striped trousers, huge paletot coat, and cigar.
This is the difference that proper vetting of your 19th century man can make! Of course, many people are happy with the Gent on the right and will gladly indulge his fashion habits and smoking.
#is the 19th century man okay#mid 19th century#1840s#archibald henning#punch magazine#victorian#early victorian era#fashion#class#gents
176 notes
·
View notes
Text

Young man, his right arm around the shoulders of a relative. (c.1842-1855)
via gallica.bnf.fr
#old photo#early photography#antique photo#antique photography#vintage photograph#vintage photography#victorian photography#victorian photo#historical photography#victorian era#victorian#mid 19th century#1840s#1850s#early victorian#e
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
The “old” Royal Navy
During the Napoleonic Wars, the navy had grown enormously and hundreds of men had reached the rank of captain. But after 1815 the navy shrank and these men could only find employment as deadwood at half pay, blocking all opportunities for promotion for able, younger men. By the time the navy was needed again against Russia in 1854, the most senior admirals had already been dismissed. The consequences were all too clear. Even the younger officers were old - one man had been a commander for 47 years, another a lieutenant for 60 years, still another a captain for 61 years and a poor man a purser for 64 years. So they had to fall back on the old ones and so one was over 90, 7 between 90-80, 25 between 80-70 still another 7 were between 70-65 and only 1 was under 65.
But this not only made for old views but also for some very strange peculiarities like this one.
Rear Admiral Henry John Rous (1795-1877), the captain of the Harlequin had his boat crew turned out in harlequin suits, while the men of the Calcedonia were resplendent in tartan. Not to be outdone, the men of the Blazer set a fashion for striped blue and white jackets, and the crew of the Vernon turned out in red serge frock coats and red comforters. One captain - Nobby Ewart - seeing one of his boat crew with a black eye, ordered all the others to paint the same eye black.
The most famous of the eccentric admirals was Sir Algernon Charles Fiesché Heneage (1833-1915), better known as Pompo. Pompo was harmless enough though resistant to anything resembling progress; technology, enineering, science and so forth would have earned his most scathing criticism. For Pompo appearances were everything. His affection was such that he could not bear to think of a common sailor washing his clothes and so he took 20dozen shirts to sea and sent the dirty ones home on every available ship bound for England. Even while rounding Cape Horn, with seas raging and men's thoughts on the Almighty and His wondrous works, Heneage was thinking of his shirts, and how he could transfer them to a passing ship. On one occasion a ship's carpenter was arrested for entering the admiral's cabin without being announced by an appropriate officer, and on another the same man was clapped in irons for going to Pompo's cabin to shut his portholes when the sea was splashing in. In the event the cabin was flooded but no one lower than a petty officer was allowed to swab it out.
Admiral Sir Archibald Berkeley Milne (1855 – 1938) was as ridiculous as Pompo. On one occasion a common seaman brushed against his coat, whereupon he shuddered, took out a handkerchief to brush the point of contact and then threw the soiled linen overboard. Something that quickly became a habit for him. And for him, anyone below a petty officer was not worth talking about, and no common sailor had even been allowed to stand in his company.
Rear Admiral Charles Prothero (1849 – 1927) - known as the Bad to the men who served under him in the British navy in the mid- 19th century, was a man of bearlike size and strength, with a big black beard and hooked nose. He still believed he was serving under Nelson, the good old days. Commanding a ship were his predecessor had had a rich supply of the milk of human kindness, Prothero thought everyone had got soft. Bumping into a midshipman on the bridge, he lifted the offender by one huge hand on his collar and dropped him over the side of the bridge onto the deck. Inspecting the midshipmen's quarters he found that several of them had got chests of drawers alongside their hammocks. Inquiring what the articles were, Prothero was told that his predecessor had allowed extra furniture to make their lives more comfortable. Prothero exploded, "When i was a midshipman il ived in my chest and sometimes bathed in it too. Throw them over the side." He always mentioned himself in the old days, even if he had never experienced them himself.
#naval history#history#victorian navy#mid- late 19th century#early 20th century#age of sail#age of steam
72 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ah now I could stand to do some sewing lol
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
You've heard of 'Bill's dimension isn't actually Flatland', now get ready for 'None of the shape Henchmaniacs' dimensions are actually Flatland'
#Hayley Speaks#Kryptos: Victorian England? I grew up in a metropolitan city and my parents were accountants.#Hectorgon: I lived in a small town and worked at a bar and grill.#AS: I'm from the Dimension That’s Perpetually Stuck In A Heavily Romanticized Version of the Mid-Eighties-Slash-Early-Nineties
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
PSA to all historical fiction/fantasy writers:
A SEAMSTRESS, in a historical sense, is someone whose job is sewing. Just sewing. The main skill involved here is going to be putting the needle into an out of the fabric. They’re usually considered unskilled workers, because everyone can sew, right? (Note: yes, just about everyone could sew historically. And I mean everyone.) They’re usually going to be making either clothes that aren’t fitted (like shirts or shifts or petticoats) or things more along the lines of linens (bedsheets, handkerchiefs, napkins, ect.). Now, a decent number of people would make these things at home, especially in more rural areas, since they don’t take a ton of practice, but they’re also often available ready-made so it’s not an uncommon job. Nowadays it just means someone whose job is to sew things in general, but this was not the case historically. Calling a dressmaker a seamstress would be like asking a portrait painter to paint your house
A DRESSMAKER (or mantua maker before the early 1800s) makes clothing though the skill of draping (which is when you don’t use as many patterns and more drape the fabric over the person’s body to fit it and pin from there (although they did start using more patterns in the early 19th century). They’re usually going to work exclusively for women, since menswear is rarely made through this method (could be different in a fantasy world though). Sometimes you also see them called “gown makers”, especially if they were men (like tailors advertising that that could do both. Mantua-maker was a very feminized term, like seamstress. You wouldn’t really call a man that historically). This is a pretty new trade; it only really sprung up in the later 1600s, when the mantua dress came into fashion (hence the name).
TAILORS make clothing by using the method of patterning: they take measurements and use those measurements to draw out a 2D pattern that is then sewed up into the 3D item of clothing (unlike the dressmakers, who drape the item as a 3D piece of clothing originally). They usually did menswear, but also plenty of pieces of womenswear, especially things made similarly to menswear: riding habits, overcoats, the like. Before the dressmaking trade split off (for very interesting reason I suggest looking into. Basically new fashion required new methods that tailors thought were beneath them), tailors made everyone’s clothes. And also it was not uncommon for them to alter clothes (dressmakers did this too). Staymakers are a sort of subsect of tailors that made corsets or stays (which are made with tailoring methods but most of the time in urban areas a staymaker could find enough work so just do stays, although most tailors could and would make them).
Tailors and dressmakers are both skilled workers. Those aren’t skills that most people could do at home. Fitted things like dresses and jackets and things would probably be made professionally and for the wearer even by the working class (with some exceptions of course). Making all clothes at home didn’t really become a thing until the mid Victorian era.
And then of course there are other trades that involve the skill of sewing, such as millinery (not just hats, historically they did all kinds of women’s accessories), trimming for hatmaking (putting on the hat and and binding and things), glovemaking (self explanatory) and such.
TLDR: seamstress, dressmaker, and tailor are three very different jobs with different skills and levels of prestige. Don’t use them interchangeably and for the love of all that is holy please don’t call someone a seamstress when they’re a dressmaker
#sewing#historical sewing#sewing knowledge#writing guide#PSA to writers#historical fiction#fantasy writing
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
NaNoWriMo 2022: Day 9
Had a really bad headache earlier but I still managed to do some class reading. Didn’t write as much today, partially because of those things and partially because I did some editing on what I had already written days 1-8.
Day 9 Word Count: 1,345 Words
Word Count Total to Date: 30,709 Words
Excerpt (From Matilda’s perspective):
“Oh, she must be one of those strange Londoners. A lot of those Bloomerists live there.” One of the women said in a shock. Our Midland English Village could barely tolerate me. But I was a girl still; my rebellion was assumed to be short-lived. Lady Starling was a full grown woman and a married one at that. Her donning men’s clothing like she did was considered scandalous.
“Well, heaven forbid I be a Bloomerist, dear ladies! You do know that Bloomerists want better treatment for all womankind. That includes yourselves- you may find us repulsive, but we’re still willing to fight for your rights. I’ll try not to take your slights as personal. It’s not your fault you’ve been sheltered so.” Gerry said, making the other women’s faces color.
“What a shocking woman you are!” One declared. “So this is where Miss Matilda gets her wild ideas from. Oh, Miss Matilda, this Lady is not someone you should hope to emulate.”
“I would like to remind you that I am a happily married woman, despite my unusual dress. My husband does not mind it all. In fact, if it pleases me, he himself is satisfied.” She replied boldly and the other women did not like her saying so directly what she thought.
#nanowrimo#nanowrimo 2022#bloomerists#victorian era#victorian lesbians#lesbian characters#Gerry Starling is someone Tilly looks up to she's one of Ashby's London friends#bloomerists were early feminists from the mid-1800s#Tilly & Hess#WIP#current WIP#and Gerry is a lesbian who married a gay man#they got married to get their families to leave them alone pretty much#these other women are randomly in town and see Matilda and Gerry walking around
0 notes
Text
🎨𝙎𝙏𝙊𝙋 𝙃𝙄𝙏𝙏𝙄𝙉𝙂 𝙊𝙉 𝙈𝙔 𝙈𝙊𝙈-🎨

Fyodor x reader
Hard crack and fluff
DESC: Dazai had always hoped his mother would find someone again after his father left her when he was young. However he was not all to pleased to find out she found a FUCKING TERRORIST
WARNINGS: Mentions of terrorism. Everybody begrudgingly tolerates each other as opposed to outright killing each other. Probably ooc Fyodor. Suggestive but it's played for laughs. Kinda spoiler for Fyodors ability if you squint.

Dazai never knew his father. And he never wanted to. He had walked out on his mother when he was less than a year old. And yet his mother did it all for him. She tried her best to help him in any way she could despite her struggles and lack of child support. So as Dazai got older he had hoped his mother would find someone worth her time. A guy that treated her well and made sure she was well taken care of. This is not what he meant by that.
[NAME] stood there happily. Elated to finally introduce the two. Dazai had to fight back the urge to gag, scream, and strike the rat all at once. His eye slightly twitching. Fyodor. His mom was dating a fucking terrorist and she hadnt the smallest clue. His sweet, loving, passionate mother. This was ridiculous. His mother was young, she had him in her late teens so she was in her mid to late thirties, early forties. DAZAI HAD NO FUCKING CLUE HOW OLD THIS RAT BITCH WAS. I mean really- for all he knew he predated the fuckinf dinosaurs. He could've had a drinking contest with Christopher godamn Columbus and he would be none the wiser.
Fyodor- wasnt taking this all too well either. I mean, really - how the hell was this your son!? When Fyodor first met you, he saw you as yet another good person who had to live in a world of tainted ability users. However, he began to see you more frequently. Whether that be by coincidence or subconsciously going to places he had seen you before, he didn't know. But it all led in him, eventually asking you out. Fyodor never considered himself a romantic. He had plans - big ones! He couldn't risk distracting himself. But it was something about the way you spoke, your gentle demeanor and sweet mannerisms. How your coat was slightly stained with bright paint. So, of course, he wasn't risking losing you. When you stated dating, you had laid out immediately that if your son didn't like him, it couldn't happen. You valued his opinion over all else. And Fyodor admired it. You were a loving mother. But if he knew your son was the living embodiment of the "'hang' in there!" cat posters, he would have hired an assasin to take him out. (Not that it would've worked anyway. Dazai never seems to stay dead.)
So now here they both sat, at a cute brunch spot eating together. Anytime you looked their way, their smiles would be back. But the moment you left for the bathroom, they both began openly debating.
"Stop fucking my Mom." Dazai grit his teeth, his fork slightly scratching against his face. Fyodor rolled his eyes, "we haven't performed coitus as of yet you imbecile." He scoffed. Dazai visibly recoiled, relieved and yet disgusted. "Who the hell calls it that?" He gagged. "I would rather adress it as such than with vulgar language-" Fyodor argued. "Oh my god. You sound like a fucking Victorian man. What do the sight of her ankles get your rocks hard my guy?" Dazai groaned. "If you keep this up I will make love with her to spite you." Fyodor glared. Dazai paused. Turning to him in disbelief.
"You wouldnt-
"Watch me, cretin."
@HONORIOTSUSUKI

#》 honori writes ◇#x reader#x reader fluff#fanfic#fluff#crack#crack fic#im so tired help me#Dazai#Osamu Dazai#Fyodor#fyodor dostoevsky#BSD#bungo stray dogs#Fyodor x reader#Fyodor BSD#bungo stray dogs fanfic#Dazai x reader#bsd x reader#crack fluff
228 notes
·
View notes
Note
for fictober could I request from the 50 autumnal prompts ‘when he wears THAT flannel’ with Eddie please?
we were so robbed of Eddie all boyfriend in soft cosy clothes. R wouldn’t be able to keep their hands off of him and he’d love it come autumn when it’s all he wears.
ugh imagine him in like thick baggy sweaters and when he reaches up it just exposes a bit of tummy 😍 I’m like a Victorian seeing ankles
love you xoxo
hi angel! idk how i managed to make this angsty, but alas! hope you like it :D
summary: you and eddie try to get used to life post-vecna but it's not nearly as easy as you thought it'd be (post st4, established relationship, wee bit of angst tw for mentions of death and scars, 1.2k)
fictober (㇏(•̀ᵥᵥ•́)ノ)
Eddie’s pretty much recovered by mid-fall.
Not totally. But mostly.
You think getting away from Hawkins helped the most — moving out of the city and settling further in the green. Even though everyone back home eventually understood that Eddie wasn’t the psycho-killing freak they made him out to be, things had changed far too much to ever go back to normal again.
Something’s break beyond repair. Something’s just can’t be fixed.
Not your Eddie, though. Eddie’s perfect. Damn near it, anyway, considering the circumstances.
He’s still got the nightmares and the phantom pains — even though he tells you he doesn’t. But he’s graduated now and helping Wayne at the car shop whenever he can. He’s taking the newfound normalcy in stride, spending early autumn with you and making you hot chocolate like nothing ever happened.
“You like marshmallows in your cocoa, right?” he calls from the kitchen, though he sounds like he’s talking mostly to himself.
You hear him, but you forget to answer. Your brain all but short circuits at how pretty he looks.
You eye him from the couch while he bustles in the kitchen, and gutwrenching existentialism knocks the wind from your lungs like a fist to the stomach.
You weren’t supposed to have Eddie again. You weren’t supposed to share a home like you always dreamed about, and he wasn’t supposed to make you hot cocoa or keep you warm when autumn got too bitter.
A season or more ago, you were saying your goodbyes while he bled out in an alternate dimension.
You haven’t yet forgotten how pale his skin had gotten or how glassy his chocolate eyes grew as the life spilled from the weeping bites on his stomach. The feeling of his blood, slimy on your hands and drenching your clothes, hasn’t yet left you. The red-hot blood in the unnatural navy blue cold still lives in your head.
But it’s only there. In your head.
And Eddie’s right in front of you — wild hair, baggy pajama pants, and all. You can smell the musk of his cologne and the floral of his shampoo. He’s real enough to touch.
He’s real.
The realization hits you every day, all the time. It wells from your chest up into your throat and makes you feel like crying. Most people don’t get to say goodbye to their soulmate and eat Wednesday morning breakfast with them months later.
You’ve got so much gratitude inside you, bursting like golden rays of sunshine, that you don’t know what to do with it all.
“Babe?” he calls again when you don’t answer. “Did you hear me?”
He pokes his head in the doorway, and your eyes go wide. “Huh? What?” you stammer, shaking your head to jerk yourself out of your stupor.
Eddie laughs, high and boyish. It sounds like heaven, and it pierces your heart. Six months ago, you never thought you’d hear it again. “I asked if you wanted marshmallows, weirdo.”
You nod rapidly and ramble an answer. “Oh, yeah. Sure. Thank you.”
“O-kay,” Eddie lilts, though his voice wavers with confusion. His grin widens and his eyes narrow, but he doesn’t ask why you’re acting so suddenly strange.
You wonder if he’s used to it by now. You wonder if he knows when you go quiet that you’re remembering that a part of you nearly died.
He returns to the kitchen and reaches for the upper cupboard. A sliver of his milky white tummy peeks from beneath his flannel. You can see the bites from here. They’re scarred over now, dark red and light pink and thunder-strike purple. It almost jars you how healed they look. The wounds are still fresh and weeping whenever you close your eyes.
Eddie comes in from the living room, balancing two mugs in his hands rather carefully because he’s filled them to the brim. He’s got his usual ceramic Campbell’s Tomato Soup cup in one hand and your sleeping Snoopy in the other. The innate domesticity makes your stomach whirl.
“You okay?” the boy wonders with pinched brows when he hands you your cocoa.
You nod with glittering eyes, mustering a faint smile up at him. The mug warms your chilled, trembling hands.
“Mm-hmm… Why?” you question, though you’re more than aware of why.
Eddie’s got a knack for knowing how you’re feeling before you’ve even hinted at it. You think he might’ve got mind-reading powers when you were in the Upside Down.
“I don’t know. You just looked a little… far away, I guess.”
“Just missed you,” you confess with a bright, innocent gaze.
Eddie snorts as he rounds the couch to sit next to you. “While I was in the kitchen ten feet away?”
“Yeah. ’S way too far.”
“Well, remind me to carry you with me wherever I go, then.”
You know he’s joking, but you beam anyway. You don’t want to be anywhere that he isn’t. You don’t want him to go where you can’t follow.
Eddie takes a sip and smiles at your smiling. His grin is crooked and rosy and lined with whipped cream. He leans in to kiss you with it.
You pull back from him, just far enough to wipe the melted sugar off with the pad of your thumb. You give him a smacking peck a second later.
With a kissed grin, the boy leans back against the couch with his arm sprawled along the back of it. You curl into his side like his own personal puzzle piece, nestling your mug between your bodies with one hand and settling your free one on his stomach.
Your fingers seem to gravitate beneath his fuzzy flannel without you having to think twice about it.
Eddie doesn’t seem to mind, either. His attention is consumed by the television — a Scooby Doo re-run he’s probably seen a thousand times. His chuckle rumbles against your cheek. You laugh along with him, made content by the sound of his boyish delight.
Your fingers dance through the fuzz of his happy trail, then settle on something softer.
The marred skin of his warm tummy feels like silk. Before you realize what you’re touching, the boy beneath you jolts.
You nearly spill your cooling cocoa when you freeze alongside him. You part from Eddie with a gaping gaze, wide eyes darting over every inch of his face. You’re frightened that you’ve hurt him, but his pink grin only widens.
“Oh, shit. Are you okay?” you blurt. “I wasn’t— I wasn’t thinking. I didn’t hurt you, did I?”
Eddie turns to you, then. His features are blurry with sleep, and they twist with confusion at your misplaced concern.
“No,” he answers with the shake of his head. The softened ends of his chocolate curls brush your cheek. A laugh sputters from his mouth. “It just tickled, babe. It’s fine.”
You let out a breath you didn’t know you were holding. It wavers on the way out, but you manage a trembling smile anyway. “Oh. Okay,” you hum, breathless.
“Yeah. ’S okay,” Eddie murmurs softly back, wrapping his pale arm around your shoulder to pull you closer. He presses a kiss to the crown of your head and lingers there. “I’m okay,” he whispers into your hair.
#published by bug#eddie munson x reader#stranger things x reader#eddie munson#eddie munson x you#eddie munson x y/n#eddie munson imagine#stranger things imagine#stranger things fanfiction#stranger things fanfic#stranger things fic#stranger things#eddie munson fanfic#eddie munson fanfiction#eddie munson fic#st drabbles#eddie spaghetti drabble#event: fictober!
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, this is a bit of a shot in the dark on my end, but I have a fashion inquiry (and I apologize if I sound ridiculous at all; I’m a bit at my wit’s end).
Is there a good way to research forms of casual Victorian garb? I feel like I’m going a bad route by inserting the word ‘Victorian’ into any search because it results in rather fancy things (or modern twists on such that are purchasable). Would it be wiser to site dates in search? Is this going to fruitless?
Sorry for taking up any time if this is out of wheelhouse. But if you do answer, I really appreciate it.
I'll do my best! Focusing on womenswear, because...well, that's what I know best. But if anyone wants to chime in about the gentlemen, please do so!
So, casual Victorian doesn't always read as Casual to us nowadays. Standards of casual clothing- that is, clothing one wears for everyday life when nothing special is going on -were rather higher than we have today.

This is an illustration of matchstick-makers in London's East End c. 1871, done by one Herbert Johnson. The women have their sleeves rolled up and aprons on, but when they leave the factory (rolling their sleeves down, adding hats to go outside- which most of them would have done; it was part of looking Respectable) they might be indistinguishable to us from any other women of the same era wearing not particularly bustle-y skirts. Some of them probably have on the commonplace Matching Skirt And Bodice dress format of the era; others have on blouses made from the same patterns as those worn by middle- and upper-class women.
Also note that they have on ribbons, chokers, earrings...they're just like us. They like wearing things that make them feel Put Together, even though they're doing one of the lowest-valued, most dangerous jobs open to women at the time. Because people have always been people, regardless of time or social class.
And for middle-class women and up, Casual might be even harder to distinguish from "fancy" to us today.

This is a mid-late 1880s day dress with a skirt length suitable for lots of walking, from Augusta Auctions. Could not tell you the social status of the woman who owned it, genuinely. Probably not the absolute poorest of the poor, but beyond that...this is a dress you could potentially wear to run errands. Even to go to work, if your job wasn't especially physical. Because. I don't know. It's a Day Dress. You wear it for day things. It's not especially formal, because then it would be made of a more delicate material and probably have a longer skirt (unless it was a Serious Dancing ball gown). Possibly also a lower neckline and puffed sleeves, if it was exclusively for the most formal events.
The idea that a dress was "fancy" just because it had ornamentation wasn't really in their cultural vocabulary.

Here is a group of women playing croquet in what looks like the early-mid 1870s. They're just hanging out! Having a good time! They're probably middle or upper class, but that's what they wear to chill outside with friends- to play a lowkey sport, even.
So yeah, it can be hard to map Victorian everyday clothing onto our "jeans and t-shirt" understanding of what makes an outfit casual. They had skirts and blouses for most relevant decades, but even those outfits often end up looking formal to us nowadays because of what I call Ballgownification- the idea that, since we only wear clothes that look even vaguely like what they had for extremely dressy occasions, we assume everything we see of their clothing was dressy.
(Someone please ask for my rant about Ballgownification)
Searching for "day dress," "walking dress," "blouse," "blouse waist," and "shirtwaist" (the last for the late 19th-early 20th century when that term became commonplace) might help. Best of luck!
#victorian#history#fashion history#dress history#clothing history#ask#madsk3tch#even just Throwing Something On looks dressy if all you have to throw on is. that.#I make a lot of my clothes from extant patterns and people comment on how dressed-up and put together I look#which is very kind but. these are magazine patterns. anyone had access to them#and I often even take off some of the recommended trims no less#a casual blouse waist from 1869 looks quite dressy to a modern audience#long post
197 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reading a lot of Sherlock Holmes, and trying to draw victorian men accurately will lead you to learning that people wrote on their shirt cuffs often in ink because they were detachable and usually made of extremely starched linen or PAPER. working class men would find them stiff, overly formal, or not worth spending the money on it, but if you were mid to upper class then it was expected that you wear just as much complicated, sillohuete focused shapewear as women. Victorian men also wore corsets, especially military men, to achieve that puffy chest and flat stomach look around the 1820's.

The male corset fad had died down a little around the turn of the century (1880-early 1900's) as women fought for more comfortable and less oppressive shapewear, and effeminate men ridiculed for wearing the once fashionable and even medically recommended undergarmet. However, the male corset in the 1880's was still fairly popular enough to be advertised by dressmakers!


(Forgive me not citing my sources at the moment, but these advertisements I believe are dated around 1880 when mens corsets fell out of popular style but were still available and fashionable in certain circles.)
Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that Dr. Watson, being both a medical and military man... probably wouldn't have worn a corset at the time of his deployment around 1880, unfortunately. ( I know, we're all dissappinted.)
Not that he couldn't wear one if he wanted to! But based on ACD cannon, I really feel that he would not be the kind of guy to wear one. Call it speculation, but if I had been deployed and then shot in the shoulder and leg, wearing a corset would be all but torture on my body. Let alone trying to wrestle an injured soldier out of one while trying to stitch him up. Corsets for military men were more of a fashion statement than a medical device; and even then, it was only helpful for orthopedic reasons (back problems mostly).
It was also around that time that the Women's Dress Reform movement began. Despite the Sherlock Holmes novels being ripe with period-typical misogyny, I like to imagine that Watson would side with the women and medical professionals on this one, in that they were often restrictive, unnecessary, and medically harmful in the long run.
Sherlock Holmes, however, absolutely has a large variety of both male and female corsets for various disguises and probably wears them often. This isn't explicitly stated in canon or anything, I just feel it in my heart.
Sorry if this is all over the place or not completely accurate! I went down a rabbit hole but am totally open to any corrections! Also I think the idea of Watson lacing up Holmes and grumbling about corsets is a funny visual lol
#sherlock holmes#acd canon#john watson#corsets#acd holmes#acd watson#long post#also by all means draw watson in a corset#im not a cop or a fashion historian so do whatever you want lol#also im sure my good friend sergle knows way more about how corsets effect the body than me who has never worn one ever
237 notes
·
View notes
Text


This post translates directly to @musas-sideblog's about how Touchstarved ties with Victorian horror and implicit/metaphorical sex, and I couldn’t stop thinking about it, so here is a lengthy theory. Enjoy :)
Note 1: Victorian era authors used an unholy amount of ways to imply sexual feelings/acts etc, so I here I will include only the ones that are of interest.
Note 2: I've highlighted the "most important" parts.
Note 3: I'm not an expert at this, so please bear with me and feel free to correct me.
Note 4: Do I need to add a TW? I think it's obvious-
Overview: What is Victorian Horror?
Victorian horror refers to the genre of horror literature, art, and culture that flourished during the Victorian era, roughly from the mid-19th century to the early 20th century, coinciding with Queen Victoria's reign from 1837 to 1901. This period was marked by a fascination with the macabre, the supernatural, and the dark aspects of human nature, reflecting the anxieties and societal changes of the time.
Key Themes and Characteristics
Supernatural Elements:
Ghosts and Spirits: Tales of haunted houses and spectral apparitions were central to Victorian horror. Charles Dickens's "A Christmas Carol" (1843) and Henry James's "The Turn of the Screw" (1898) are notable examples.
Monsters and the Gothic: The era's literature is filled with monstrous creations and gothic settings, such as in Mary Shelley's "Frankenstein" (1818), Bram Stoker's "Dracula" (1897), and Robert Louis Stevenson's "Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde" (1886).
Science and the Unknown:
The Victorian period was a time of great scientific advancement, but also of fear about the implications of these discoveries. This is evident in works that explore the dangers of unchecked scientific experimentation, like "Frankenstein" and H.G. Wells's "The Island of Doctor Moreau" (1896).
Exploration of the Human Psyche:
Victorian horror often delved into the darker aspects of the human mind, including themes of duality, madness, and the hidden, sinister side of human nature. This is seen in "Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde" and Edgar Allan Poe’s works, such as "The Tell-Tale Heart" (1843).
Social and Moral Anxieties:
The literature frequently reflected Victorian society's fears and anxieties, including issues related to sexuality, class, and the role of women. Gothic novels often contained subtexts about societal norms and the consequences of transgressing them.
Urban Fear and Isolation:
The rapid urbanisation of the Victorian era contributed to themes of isolation, alienation, and fear of the crowded yet lonely cityscape. This is evident in the settings of many horror stories, such as Arthur Machen's "The Great God Pan" (1894).
Sexual Content: Victorian literature is renowned for its strict moral codes and conservative views on sexuality. Explicit depictions of sexual activity were considered taboo and were subject to censorship. Consequently, authors developed subtle and nuanced methods to imply sexual scenes or themes.
Literary Techniques for Implying Sexual Scenes
✧ Symbolism and Imagery:
Sexuality was often conveyed through symbolic imagery. Objects, actions, or natural phenomena could serve as metaphors for sexual activity or desire. For example, in "Dracula" by Bram Stoker, blood and biting symbolise sexual penetration and the exchange of bodily fluids, infusing the act with a sense of forbidden desire and eroticism.
Clothing and Undress:
Gloves: In Victorian culture, gloves were highly symbolic. The act of a woman removing her gloves in the presence of a man, or a man assisting her in this act, could signify a moment of intimacy or vulnerability. Similarly, a man giving a woman his gloves could be a sign of affection or a deeper connection.
Hats and Bonnets:
Corsets
Objects and Personal Items:
Locks of Hair
Jewellery
Books and Letters
Touch and Physical Contact:
Kissing Hands
Hand-Holding
Food and Drink:
Wine: Sharing wine or a meal in an intimate setting often suggested a prelude to deeper connection. Descriptions of characters drinking wine together in private could imply a romantic or sexual undertone.
Fruit: Certain fruits, like apples, grapes, or peaches, were laden with sexual symbolism. Eating or sharing fruit could represent temptation or indulgence. For instance, in Christina Rossetti’s poem "Goblin Market", the act of eating the goblin fruit is rich with sexual symbolism.
Flora and Fauna
Flowers and Gardens:
Roses: Roses were often used to symbolise love and passion. A red rose might suggest romantic or sexual attraction, while a wilted rose could imply lost innocence or sexual ruin.
Lilies: Lilies, especially white ones, represented purity but could also suggest a contrasting theme when associated with a fallen or tarnished character.
Garden Settings: Scenes set in secluded gardens or amongst lush, overgrown vegetation often hinted at secret or forbidden encounters. Descriptions of characters wandering through or tending to gardens could imply sexual exploration or awakening.
Flowers Blooming or Opening: The blooming of flowers often represented sexual awakening or the act of losing one's virginity.
Nature Imagery:
Rivers and Water: Flowing water and rivers often symbolised sexual desire and the act of lovemaking. For instance, in "Tess of the d'Urbervilles" by Thomas Hardy, Tess's encounter with Alec d'Urberville is often described with metaphors of nature and fluidity.
Storms and Weather: Storms, with their intense energy and sudden outbursts, were frequently used to symbolise sexual passion or climactic moments.
Birds and Beasts:
Animals, especially those that are wild or predatory, often symbolised primal sexual instincts and desires. The taming or interaction with these animals could imply a character’s grappling with their own sexuality.
Fire and Heat
✧ Phrases and Sayings
Euphemistic Language
Descriptive Phrasing
Dialogue and Confessions
Private Spaces:
Secluded or Dimly Lit Rooms: Scenes set in private, darkened rooms often suggested clandestine sexual encounters. The privacy of the setting allows authors to imply what could not be explicitly stated. In Wilkie Collins’s "The Woman in White", many key interactions happen in secluded spaces, hinting at secrets and hidden desires.
Dreams and Fantasies:
Dream Sequences:
Dreams and fantasies were used to explore a character’s subconscious desires and fears, often revealing their suppressed sexual longings. These sequences provided a socially acceptable way to delve into erotic themes.
Hallucinations and Madness:
Moments of madness or hallucination could serve as a metaphor for overwhelming passion or uncontrollable sexual desire. These states allowed characters to express forbidden feelings in a way that was metaphorically safe.
Physical Interactions and Horror
Touch and Proximity as Menace:
Unwanted or Forced Touch: In horror, touch that is typically a sign of affection or intimacy becomes a source of fear.
Physical Closeness in Horror Settings: Close proximity in dark, secluded places amplifies the sense of claustrophobia and vulnerability, turning what could be an intimate setting into one fraught with terror.
Undress and Exposure in Horror:
Loosening Corsets and Vulnerability: The act of undressing or loosening clothing, which can be a prelude to intimacy, in horror often leaves characters vulnerable to attack or exposure of their deepest fears.
Food and Consumption in Horror
Cannibalism and Vampirism:
Blood as Sexual and Vital Fluid: The act of consuming blood, as in vampirism, blends the themes of sustenance and sexual exchange. The vampire's bite becomes a metaphor for both sexual penetration and the transfer of life force.
Example: "Dracula" is a prime example where blood consumption is deeply eroticized, with Dracula’s victims often portrayed in a state of ecstatic submission as he drains their blood.
Food as a Lure: Food and feasting, typically symbols of pleasure and indulgence, in horror contexts can be used to lure victims into dangerous situations.
Example: In "Goblin Market" by Christina Rossetti, the goblins’ fruit is both irresistibly tempting and dangerous, representing a forbidden and potentially fatal indulgence.
Plot and Character Dynamics in Horror
Power and Domination:
Common Dynamics with a Dark Twist
Predators and Victims: Characters who prey on others are often literal monsters in horror, representing the loss of control or innocence.
Secrecy and Concealment:
Hidden Desires and Monstrous Revelations: Characters who conceal their true identities or desires often find these hidden aspects manifesting as monstrous or terrifying in horror narratives, suggesting that repression can lead to dire consequences.
Clandestine Meetings and Forbidden Encounters: Secret meetings and forbidden relationships, often tinged with sexual implications, add an element of danger and fear, suggesting that transgressing social norms leads to horror.
Common Themes in Victorian Horror
Duality and the Doppelgänger:
Theme: The concept of duality, where a character has a hidden, darker side, or encounters a double (doppelgänger), often symbolises the internal conflict between good and evil within individuals.
Connection: This theme reflects Victorian anxieties about identity, morality, and the consequences of repressing one’s darker impulses.
Gothic and Supernatural Elements:
Theme: Victorian horror is rich with Gothic elements such as haunted houses, dark landscapes, and supernatural beings. These elements create a sense of dread and evoke the mysteries of the unknown.
Connection: The Gothic setting often serves as a backdrop for exploring human fears, isolation, and the impact of the supernatural on everyday life.
Decay and Degeneration:
Theme: The fear of decay and degeneration, both physical and moral, is a recurring motif. This theme often examines the decline of individuals, families, or societies and the consequences of corruption and vice.
Connection: This theme mirrors Victorian concerns about the erosion of social and moral values amidst rapid industrial and social changes.
Madness and Psychological Horror:
Theme: The exploration of madness and psychological horror delves into the fragility of the human mind and the terror of losing one's sanity. This often includes hallucinations, obsessions, and the thin line between reality and delusion.
Connection: This theme resonates with Victorian fears of mental illness, the limitations of medical knowledge, and the impact of societal pressures on mental health.
Forbidden Knowledge and the Faustian Bargain:
Theme: The pursuit of forbidden knowledge and the resulting consequences is a central theme. Characters who seek power, immortality, or forbidden truths often pay a heavy price, reminiscent of the Faustian bargain.
Connection: This theme highlights Victorian anxieties about scientific progress, moral boundaries, and the potential hubris of human ambition.
The Uncanny and the Unknown:
Theme: The uncanny involves the strange and unfamiliar becoming eerily familiar, often unsettling the reader and characters. It blurs the lines between reality and the supernatural, invoking fear and discomfort.
Connection: This theme taps into Victorian fears of the unknown, the foreign, and the otherworldly, reflecting broader anxieties about social and cultural boundaries.
Death and the Afterlife:
Theme: Victorian horror frequently grapples with themes of death and the afterlife, exploring the fear of mortality, the possibility of an afterlife, and encounters with the dead or undead.
Connection: These themes reflect Victorian preoccupations with death, the spiritual realm, and the possibility of life beyond death, often intensified by the era's high mortality rates and interest in spiritualism.
Isolation and Alienation:
Theme: Isolation and alienation are prevalent themes, often highlighting characters who are physically or emotionally detached from society, leading to their vulnerability and descent into despair or madness.
Connection: This theme resonates with the Victorian experience of industrialization and urbanization, which often led to feelings of disconnection and loneliness.
Class and Social Anxiety:
Theme: Victorian horror often explores themes of class and social anxiety, including the fear of losing social status, the consequences of poverty, and the tension between different social classes.
Connection: This theme reflects the rigid class structures of Victorian society and the fears and tensions that arose from social mobility and economic disparity.
Moral Corruption and Hypocrisy:
Theme: Victorian horror frequently critiques the era’s moral standards and exposes the hypocrisy of societal norms. Characters who appear virtuous often harbor dark secrets or engage in morally dubious activities.
Connection: This theme mirrors the Victorian concern with appearances and the underlying tension between public propriety and private desires.
The Five Pillars of Victorian Horror & The Five Love Interests
The Supernatural and the Gothic (Ais)
Essence: Victorian horror often revolves around the supernatural, blending Gothic elements to evoke a sense of dread and otherworldly terror. This includes ghosts, vampires, haunted houses, and curses, which create an atmosphere where the boundaries between the natural and the supernatural blur.
Impact: The use of Gothic settings and supernatural phenomena provides a backdrop for exploring deeper themes of fear, mortality, and the unknown.
Psychological Depth and Madness (Vere)
Essence: Victorian horror delves into the complexities of the human mind, exploring themes of madness, obsession, and the psychological effects of fear and trauma. Characters often grapple with their sanity, facing inner demons as terrifying as any external threat.
Impact: This focus on psychological horror allows for a deeper exploration of character motivations and the impact of societal pressures.
Moral Corruption and the Double Life (Leander)
Essence: Themes of moral corruption and the duality of human nature are central to Victorian horror. Characters often lead double lives, presenting a veneer of respectability while concealing dark, sinful secrets. This tension between outward appearances and hidden truths reflects the era’s social hypocrisy and fear of scandal.
Impact: These themes critique Victorian society’s emphasis on propriety and the dangerous consequences of repressing one’s true nature. The idea of a double life or hidden self adds to the horror by suggesting that evil can reside within anyone, masked by a facade of normalcy.
Decay, Degeneration, and Disease (Kuras)
Essence: The themes of physical and moral decay, societal degeneration, and disease permeate Victorian horror. These motifs symbolise the fragility of human life and the inevitability of decline, reflecting the anxieties of a society grappling with rapid change and uncertain futures.
Impact: By focusing on decay and degeneration, Victorian horror underscores the transient nature of life and the ever-present threat of corruption and decline, whether through ageing, moral compromise, or societal breakdown.
Isolation and Alienation (Mhin)
Essence: Isolation and alienation are pervasive themes in Victorian horror, often depicted through characters who are physically or emotionally cut off from society. This separation heightens their vulnerability to external threats and internal fears.
Impact: Isolation serves to intensify the psychological tension and sense of dread, as characters confront their fears alone. It also reflects the era’s social and existential anxieties, including the fear of being disconnected or outcast from society.

Generally, I believe each LI connects with a pillair (as seen above). Perhaps by looking at the archetypes we could deduce propable endings and route elements.
Forgive me, for the following part is MESSY;
Ais

Vere

Leander

Kuras

Mhin

#THIS TOOK ME AGES#but it was worth it#vereletters#touchstarved theory#touchstarved theories#touchstarved ais theory#touchstarved vere theory#touchstarved kuras theory#touchstarved leander theory#touchstarved mhin theory#red spring studios#touchstarved#ts#touchstarved headcanons#touchstarved game#touchstarved oneshot#ais#ais headcanons#ais ts#ts ais#ais touchstarved#touchstarved ais#ais oneshot#vere#vere headcanons#vere ts#ts vere#vere touchstarved#touchstarved vere#vere oneshot
141 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Victorian silver and agate brooch in the shape of a sailor's cross, mid-19th century.
The sailor's cross has its origins in early Christianity and is also known as the sailor's cross or St Clement's cross, in reference to the way he was supposedly martyred - tied to an anchor and thrown from a boat into the Black Sea. Despite this tradition about his untimely end at sea, Clement is considered a patron saint of sailors and many wear his cross for protection. The brooches, on the other hand, were often given to loved ones who had stayed at home as a symbol of hope, happiness and return.
209 notes
·
View notes
Text
when the British Empire's researchers realized that the cause of the ecological devastation was the British Empire:

much to consider.
on the motives and origins of some forms of imperial "environmentalism".
---
Since the material resources of colonies were vital to the metropolitan centers of empire, some of the earliest conservation practices were established outside of Europe [but established for the purpose of protecting the natural resources desired by metropolitan Europe]. [...] [T]ropical island colonies were crucial laboratories of empire, as garden incubators for the transplantation of peoples [slaves, laborers] and plants [cash crops] and for generating the European revival of Edenic discourse. Eighteenth-century environmentalism derived from colonial island contexts in which limited space and an ideological model of utopia contributed to new models of conservation [...]. [T]ropical island colonies were at the vanguard of establishing forest reserves and environmental legislation [...]. These forest reserves, like those established in New England and South Africa, did not necessarily represent "an atavistic interest in preserving the 'natural' [...]" but rather a "more manipulative and power-conscious interest in constructing a new landscape by planting trees [in monoculture or otherwise modified plantations] [...]" [...].
Text by: Elizabeth DeLoughrey and George B. Handley. "Introduction: Toward an Aesthetics of the Earth". Postcolonial Ecologies: Literatures of the Environment, edited by DeLoughrey and Handley. 2011.
---
It is no accident that the earliest writers to comment specifically on rapid environmental change in the context of empires were scientists who were themselves often actors in the process of colonially stimulated environmental change. [...] As early as the mid-17th century [...] natural philosophers [...] in Bermuda, [...] in Barbados and [...] on St Helena [all British colonies] were all already well aware of characteristically high rates of soil erosion and deforestation in the colonial tropics [...]. On St Helena and Bermuda this early conservationism led, by 1715, to the gazetting of the first colonial forest reserves and forest protection laws. On French colonial Mauritius [...], Poivre and Philibert Commerson framed pioneering forest conservation [...] in the 1760s. In India William Roxburgh, Edward Balfour [...] ([...] Scottish medical scientists) wrote alarmist narratives relating deforestation to the danger of climate change. [...] East India Company scientists were also well aware of French experience in trying to prevent deforestation [...] [in] Mauritius. [...] Roxburgh [...] went on to further observe the incidence of global drought events which we know today were globally tele-connected El Nino events. [...] The writings of Edward Balfour and Hugh Cleghorn in the late 1840s in particular illustrate the extent of the permeation of a global environmental consciousness [...]. [T]he 1860s [were] a period which we could appropriately name the "first environmental decade", and which embodies a convergence of thinking about ecological change on a world scale [...]. It was in the particular circumstances of environmental change at the colonial periphery that what we would now term "environmentalism" first made itself felt [...]. Victorian texts such as [...] Ribbentrop's Forestry in the British Empire, Brown's Hydrology of South Africa, Cleghorn's Forests and Gardens of South India [...] were [...] vital to the onset of environmentalism [...]. One preoccupation stands out in them above all. This was a growing interest in the potential human impact on climate change [...] [and] global dessication. This fear grew steadily in the wake of colonial expansion [...]. Particularly after the 1860s, and even more after the great Indian famines of 1876 [...] these connections encouraged and stimulated the idea that human history and environmental change might be firmly linked.
Text by: Richard Grove and Vinita Damodaran. "Imperialism, Intellectual Networks, and Environmental Change: Origins and Evolution of Global Environmental History, 1676-2000: Part I". Economic and Political Weekly Vol. 41, No. 41. 14 October 2006.
---
Policing the interior [of British colonial land] following the Naning War gave Newbold the opportunity for exploring the people and landscape around Melaka […]. Newbold took his knowledge of the tropical environment in the Straits Settlements [British Malaya] to Madras [British India], where he earned a reputation as a naturalist and an Orientalist of some eminence. He was later elected Fellow of the Royal Society. Familiar with the barren landscape of the tin mines of Negeri Sembilan, Newbold made a seminal link between deforestation and the sand dune formations and siltation […]. The observation, published in 1839 […], alerted […] Balfour about the potential threat of erosion to local climate and agriculture. […] Logan brought his Peninsular experience [in the British colonies of Malaya] directly within the focus of the deforestation debate in India […]. His lecture to the Bengal Asiatic Society in 1846 […] was hugely influential and put the Peninsula at the heart of the emerging discourse on tropical ecology. Penang, the perceived tropical paradise of abundance and stability, soon revealed its vulnerability to human [colonial] despoilment […].
Text by: Jeyamalar Kathirithamby-Wells. "Peninsular Malaysia in the Context of Natural History and Colonial Science". New Zealand Journal of Asian Studies 11, 1. June 2009.
---
British colonial forestry was arguably one of the most extensive imperial frameworks of scientific natural resource management anywhere [...]. [T]he roots of conservation [...] lay in the role played by scientific communities in the colonial periphery [...]. In India,[...] in 1805 [...] the court of directors of the East India Company sent a dispatch enquiring [...] [about] the Royal Navy [and its potential use of wood from Malabar's forests] [...]. This enquiry led to the appointment of a forest committee which reported that extensive deforestation had taken place and recommended the protection of the Malabar forests on grounds that they were valuable property. [...] [T]o step up the extraction of teak to augment the strength of the Royal Navy [...] [b]etween 1806 and 1823, the forests of Malabar were protected by means of this monopoly [...]. The history of British colonial forestry, however, took a decisive turn in the post-1860 period [...]. Following the revolt of 1857, the government of India sought to pursue active interventionist policies [...]. Experts were deployed as 'scientific soldiers' and new agencies established. [...] The paradigm [...] was articulated explicitly in the first conference [Empire Forestry Conference] by R.S. Troup, a former Indian forest service officer and then the professor of forestry at Oxford. Troup began by sketching a linear model of the development of human relationship with forests, arguing that the human-forest interaction in civilized societies usually went through three distinct phases - destruction, conservation, and economic management. Conservation was a ‘wise and necessary measure’ but it was ‘only a stage towards the problem of how best to utilise the forest resources of the empire’. The ultimate ideal was economic management, [...] to exploit 'to the full [...]' and provide regular supplies [...] to industry.
Text by: Ravi Rajan. "Modernizing Nature: Tropical Forestry and the Contested Legacy of British Colonial Eco-Development, 1800-2000". Oxford Historical Monographs series, Oxford University Press. January 2006.
---
The “planetary consciousness” produced by this systemizing of nature [during the rise of Linnaean taxonomy classification in eighteenth-century European science] […] increased the mobility of paradise discourse [...]. As European colonial expansion accelerated, the homogenizing transformation of people, economy and nature which it catalyzed also gave rise to a myth of lost paradise, which served as a register […] for obliterated cultures, peoples, and environments [devastated by that same European colonization], and as a measure of the rapid ecological changes, frequently deforestation and desiccation, generated by colonizing capital. On one hand, this myth served to suppress dissent by submerging it in melancholy, but on the other, it promoted the emergence of an imperialist environmental critique which would motivate the later establishment of colonial botanical gardens, potential Edens in which nature could be re-made. However, the subversive potential of the “green” critique voiced through the myth of endangered paradise was defused by the extent to which growing environmental sensibilities enabled imperialism to function more efficiently by appropriating botanical knowledge and indigenous conservation methods, thus continuing to serve the purposes of European capital.
Text by: Sharae Deckard. Paradise Discourse, Imperialism, and Globalization: Exploiting Eden. 2010.
#abolition#ecology#indigenous#multispecies#imperial#colonial#temporal#temporality#debt and debt colonies#tidalectics#archipelagic thinking#caribbean#interspecies#victorian and edwardian popular culture#carceral geography#ecologies
160 notes
·
View notes