#json web token
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

Another great infographic from ByteByteGo that crams a lot of detail into a single page.
This one illustrates the difference between session tokens and JSON web tokens (JWT) and then goes on to show how JWTs are the backbone of modern single sign on (SSO) and OAuth flows.
(via https://substack-post-media.s3.amazonaws.com/public/images/041727d8-aaba-4c1d-8b74-b2c26e2e05e2_1446x1890.png (1446×1890))
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
JWT Security Vulnerabilities | CyberSecurityTv
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) are a widely used method for representing claims between two parties in a compact and self-contained way
#security vulnerabilities#sql injection#jwt#vulnerability management#zero day vulnerability#vulnerabilities#Addressing JWT (JSON Web Token) Security Vulnerabilities#Security Vulnerabilities in JWT#JWT (JSON Web Token) Implementations#Identifying and Resolving JWT (JSON Web Token)#JWT (JSON Web Token) Vulnerabilities#sql injection attack#jsonwebtoken#jwt token#JWT Security Vulnerabilities#CyberSecurityTv#Youtube
0 notes
Text
How To Generate JWT Token
Welcome To the Article About How To Generate JWT Token (JSON Web Token)! In this article, we will discuss the concept of the JWT token, the benefits of using it, how to generate it, and the security considerations that come with it. We will also explore how to use JWT token authentication in your applications. By the end of this blog, you will have a better understanding of JWT token and how to…

View On WordPress
#generate a JSON Web Token#Generate jwt Token#How to generate a JSON Web Token#How To Generate jwt Token#how to generate jwt token in python#how to generate jwt token online
0 notes
Text
How to Protect Your Laravel App from JWT Attacks: A Complete Guide
Introduction: Understanding JWT Attacks in Laravel
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) have become a popular method for securely transmitting information between parties. However, like any other security feature, they are vulnerable to specific attacks if not properly implemented. Laravel, a powerful PHP framework, is widely used for building secure applications, but developers must ensure their JWT implementation is robust to avoid security breaches.

In this blog post, we will explore common JWT attacks in Laravel and how to protect your application from these vulnerabilities. We'll also demonstrate how you can use our Website Vulnerability Scanner to assess your application for potential vulnerabilities.
Common JWT Attacks in Laravel
JWT is widely used for authentication purposes, but several attacks can compromise its integrity. Some of the most common JWT attacks include:
JWT Signature Forgery: Attackers can forge JWT tokens by modifying the payload and signing them with weak or compromised secret keys.
JWT Token Brute-Force: Attackers can attempt to brute-force the secret key used to sign the JWT tokens.
JWT Token Replay: Attackers can capture and replay JWT tokens to gain unauthorized access to protected resources.
JWT Weak Algorithms: Using weak signing algorithms, such as HS256, can make it easier for attackers to manipulate the tokens.
Mitigating JWT Attacks in Laravel
1. Use Strong Signing Algorithms
Ensure that you use strong signing algorithms like RS256 or ES256 instead of weak algorithms like HS256. Laravel's jwt-auth package allows you to configure the algorithm used to sign JWT tokens.
Example:
// config/jwt.php 'algorithms' => [ 'RS256' => \Tymon\JWTAuth\Providers\JWT\Provider::class, ],
This configuration will ensure that the JWT is signed using the RSA algorithm, which is more secure than the default HS256 algorithm.
2. Implement Token Expiry and Refresh
A common issue with JWT tokens is that they often lack expiration. Ensure that your JWT tokens have an expiry time to reduce the impact of token theft.
Example:
// config/jwt.php 'ttl' => 3600, // Set token expiry time to 1 hour
In addition to setting expiry times, implement a refresh token mechanism to allow users to obtain a new JWT when their current token expires.
3. Validate Tokens Properly
Proper token validation is essential to ensure that JWT tokens are authentic and have not been tampered with. Use Laravel’s built-in functions to validate the JWT and ensure it is not expired.
Example:
use Tymon\JWTAuth\Facades\JWTAuth; public function authenticate(Request $request) { try { // Validate JWT token JWTAuth::parseToken()->authenticate(); } catch (\Tymon\JWTAuth\Exceptions\JWTException $e) { return response()->json(['error' => 'Token is invalid or expired'], 401); } }
This code will catch any JWT exceptions and return an appropriate error message to the user if the token is invalid or expired.
4. Secure JWT Storage
Always store JWT tokens in secure locations, such as in HTTP-only cookies or secure local storage. This minimizes the risk of token theft via XSS attacks.
Example (using HTTP-only cookies):
// Setting JWT token in HTTP-only cookie $response->cookie('token', $token, $expirationTime, '/', null, true, true);
Testing Your JWT Security with Our Free Website Security Checker
Ensuring that your Laravel application is free from vulnerabilities requires ongoing testing. Our free Website Security Scanner helps identify common vulnerabilities, including JWT-related issues, in your website or application.
To check your site for JWT-related vulnerabilities, simply visit our tool and input your URL. The tool will scan for issues like weak algorithms, insecure token storage, and expired tokens.

Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Example of a Vulnerability Assessment Report
Once the scan is completed, you will receive a detailed vulnerability assessment report to check Website Vulnerability. Here's an example of what the report might look like after checking for JWT security vulnerabilities.

An Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities.
By addressing these vulnerabilities, you can significantly reduce the risk of JWT-related attacks in your Laravel application.
Conclusion: Securing Your Laravel Application from JWT Attacks
Securing JWT tokens in your Laravel application is essential to protect user data and maintain the integrity of your authentication system. By following the steps outlined in this post, including using strong algorithms, implementing token expiry, and validating tokens properly, you can safeguard your app from common JWT attacks.
Additionally, make sure to regularly test your application for vulnerabilities using tools like our Website Security Checker. It’s a proactive approach that ensures your Laravel application remains secure against JWT attacks.
For more security tips and detailed guides, visit our Pentest Testing Corp.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Base64 URL Encoder and Decoder with UTF-8 support - base64url
Base64url is a lightweight, straightforward TypeScript library that encodes and decodes Base64 URLs for JavaScript strings with comprehensive UTF-8 support. It can be useful for developers working with JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) or those involved in encoding JavaScript strings to UTF-8 for binary formats. How to use it: 1. Download the package and import the following modules into your…
View On WordPress
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
This Week in Rust 533
Hello and welcome to another issue of This Week in Rust! Rust is a programming language empowering everyone to build reliable and efficient software. This is a weekly summary of its progress and community. Want something mentioned? Tag us at @ThisWeekInRust on Twitter or @ThisWeekinRust on mastodon.social, or send us a pull request. Want to get involved? We love contributions.
This Week in Rust is openly developed on GitHub and archives can be viewed at this-week-in-rust.org. If you find any errors in this week's issue, please submit a PR.
Updates from Rust Community
Official
crates.io: API status code changes
Foundation
Google Contributes $1M to Rust Foundation to Support C++/Rust "Interop Initiative"
Project/Tooling Updates
Announcing the Tauri v2 Beta Release
Polars — Why we have rewritten the string data type
rust-analyzer changelog #219
Ratatui 0.26.0 - a Rust library for cooking up terminal user interfaces
Observations/Thoughts
Will it block?
Embedded Rust in Production ..?
Let futures be futures
Compiling Rust is testing
Rust web frameworks have subpar error reporting
[video] Proving Performance - FOSDEM 2024 - Rust Dev Room
[video] Stefan Baumgartner - Trials, Traits, and Tribulations
[video] Rainer Stropek - Memory Management in Rust
[video] Shachar Langbeheim - Async & FFI - not exactly a love story
[video] Massimiliano Mantione - Object Oriented Programming, and Rust
[audio] Unlocking Rust's power through mentorship and knowledge spreading, with Tim McNamara
[audio] Asciinema with Marcin Kulik
Non-Affine Types, ManuallyDrop and Invariant Lifetimes in Rust - Part One
Nine Rules for Accessing Cloud Files from Your Rust Code: Practical lessons from upgrading Bed-Reader, a bioinformatics library
Rust Walkthroughs
AsyncWrite and a Tale of Four Implementations
Garbage Collection Without Unsafe Code
Fragment specifiers in Rust Macros
Writing a REST API in Rust
[video] Traits and operators
Write a simple netcat client and server in Rust
Miscellaneous
RustFest 2024 Announcement
Preprocessing trillions of tokens with Rust (case study)
All EuroRust 2023 talks ordered by the view count
Crate of the Week
This week's crate is embedded-cli-rs, a library that makes it easy to create CLIs on embedded devices.
Thanks to Sviatoslav Kokurin for the self-suggestion!
Please submit your suggestions and votes for next week!
Call for Participation; projects and speakers
CFP - Projects
Always wanted to contribute to open-source projects but did not know where to start? Every week we highlight some tasks from the Rust community for you to pick and get started!
Some of these tasks may also have mentors available, visit the task page for more information.
Fluvio - Build a new python wrapping for the fluvio client crate
Fluvio - MQTT Connector: Prefix auto generated Client ID to prevent connection drops
Ockam - Implement events in SqlxDatabase
Ockam - Output for both ockam project ticket and ockam project enroll is improved, with support for --output json
Ockam - Output for ockam project ticket is improved and information is not opaque
Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Setup code coverage for local tests & CI
Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Have get_required_value to use ValidationError in OptionExt
If you are a Rust project owner and are looking for contributors, please submit tasks here.
CFP - Speakers
Are you a new or experienced speaker looking for a place to share something cool? This section highlights events that are being planned and are accepting submissions to join their event as a speaker.
RustNL 2024 CFP closes 2024-02-19 | Delft, The Netherlands | Event date: 2024-05-07 & 2024-05-08
NDC Techtown CFP closes 2024-04-14 | Kongsberg, Norway | Event date: 2024-09-09 to 2024-09-12
If you are an event organizer hoping to expand the reach of your event, please submit a link to the submission website through a PR to TWiR.
Updates from the Rust Project
309 pull requests were merged in the last week
add avx512fp16 to x86 target features
riscv only supports split_debuginfo=off for now
target: default to the medium code model on LoongArch targets
#![feature(inline_const_pat)] is no longer incomplete
actually abort in -Zpanic-abort-tests
add missing potential_query_instability for keys and values in hashmap
avoid ICE when is_val_statically_known is not of a supported type
be more careful about interpreting a label/lifetime as a mistyped char literal
check RUST_BOOTSTRAP_CONFIG in profile_user_dist test
correctly check never_type feature gating
coverage: improve handling of function/closure spans
coverage: use normal edition: headers in coverage tests
deduplicate more sized errors on call exprs
pattern_analysis: Gracefully abort on type incompatibility
pattern_analysis: cleanup manual impls
pattern_analysis: cleanup the contexts
fix BufReader unsoundness by adding a check in default_read_buf
fix ICE on field access on a tainted type after const-eval failure
hir: refactor getters for owner nodes
hir: remove the generic type parameter from MaybeOwned
improve the diagnostics for unused generic parameters
introduce support for async bound modifier on Fn* traits
make matching on NaN a hard error, and remove the rest of illegal_floating_point_literal_pattern
make the coroutine def id of an async closure the child of the closure def id
miscellaneous diagnostics cleanups
move UI issue tests to subdirectories
move predicate, region, and const stuff into their own modules in middle
never patterns: It is correct to lower ! to _
normalize region obligation in lexical region resolution with next-gen solver
only suggest removal of as_* and to_ conversion methods on E0308
provide more context on derived obligation error primary label
suggest changing type to const parameters if we encounter a type in the trait bound position
suppress unhelpful diagnostics for unresolved top level attributes
miri: normalize struct tail in ABI compat check
miri: moving out sched_getaffinity interception from linux'shim, FreeBSD su…
miri: switch over to rustc's tracing crate instead of using our own log crate
revert unsound libcore changes
fix some Arc allocator leaks
use <T, U> for array/slice equality impls
improve io::Read::read_buf_exact error case
reject infinitely-sized reads from io::Repeat
thread_local::register_dtor fix proposal for FreeBSD
add LocalWaker and ContextBuilder types to core, and LocalWake trait to alloc
codegen_gcc: improve iterator for files suppression
cargo: Don't panic on empty spans
cargo: Improve map/sequence error message
cargo: apply -Zpanic-abort-tests to doctests too
cargo: don't print rustdoc command lines on failure by default
cargo: stabilize lockfile v4
cargo: fix markdown line break in cargo-add
cargo: use spec id instead of name to match package
rustdoc: fix footnote handling
rustdoc: correctly handle attribute merge if this is a glob reexport
rustdoc: prevent JS injection from localStorage
rustdoc: trait.impl, type.impl: sort impls to make it not depend on serialization order
clippy: redundant_locals: take by-value closure captures into account
clippy: new lint: manual_c_str_literals
clippy: add lint_groups_priority lint
clippy: add new lint: ref_as_ptr
clippy: add configuration for wildcard_imports to ignore certain imports
clippy: avoid deleting labeled blocks
clippy: fixed FP in unused_io_amount for Ok(lit), unrachable! and unwrap de…
rust-analyzer: "Normalize import" assist and utilities for normalizing use trees
rust-analyzer: enable excluding refs search results in test
rust-analyzer: support for GOTO def from inside files included with include! macro
rust-analyzer: emit parser error for missing argument list
rust-analyzer: swap Subtree::token_trees from Vec to boxed slice
Rust Compiler Performance Triage
Rust's CI was down most of the week, leading to a much smaller collection of commits than usual. Results are mostly neutral for the week.
Triage done by @simulacrum. Revision range: 5c9c3c78..0984bec
0 Regressions, 2 Improvements, 1 Mixed; 1 of them in rollups 17 artifact comparisons made in total
Full report here
Approved RFCs
Changes to Rust follow the Rust RFC (request for comments) process. These are the RFCs that were approved for implementation this week:
No RFCs were approved this week.
Final Comment Period
Every week, the team announces the 'final comment period' for RFCs and key PRs which are reaching a decision. Express your opinions now.
RFCs
No RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Tracking Issues & PRs
[disposition: merge] Consider principal trait ref's auto-trait super-traits in dyn upcasting
[disposition: merge] remove sub_relations from the InferCtxt
[disposition: merge] Optimize away poison guards when std is built with panic=abort
[disposition: merge] Check normalized call signature for WF in mir typeck
Language Reference
No Language Reference RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Unsafe Code Guidelines
No Unsafe Code Guideline RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
New and Updated RFCs
Nested function scoped type parameters
Call for Testing
An important step for RFC implementation is for people to experiment with the implementation and give feedback, especially before stabilization. The following RFCs would benefit from user testing before moving forward:
No RFCs issued a call for testing this week.
If you are a feature implementer and would like your RFC to appear on the above list, add the new call-for-testing label to your RFC along with a comment providing testing instructions and/or guidance on which aspect(s) of the feature need testing.
Upcoming Events
Rusty Events between 2024-02-07 - 2024-03-06 🦀
Virtual
2024-02-07 | Virtual (Indianapolis, IN, US) | Indy Rust
Indy.rs - Ezra Singh - How Rust Saved My Eyes
2024-02-08 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-02-08 | Virtual (Nürnberg, DE) | Rust Nüremberg
Rust Nürnberg online
2024-02-10 | Virtual (Krakow, PL) | Stacja IT Kraków
Rust – budowanie narzędzi działających w linii komend
2024-02-10 | Virtual (Wrocław, PL) | Stacja IT Wrocław
Rust – budowanie narzędzi działających w linii komend
2024-02-13 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Second Tuesday
2024-02-15 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust Hack n Learn | Mirror: Rust Hack n Learn
2024-02-15 | Virtual + In person (Praha, CZ) | Rust Czech Republic
Introduction and Rust in production
2024-02-19 | Virtual (Melbourne, VIC, AU) | Rust Melbourne
February 2024 Rust Melbourne Meetup
2024-02-20 | Virtual | Rust for Lunch
Lunch
2024-02-21 | Virtual (Cardiff, UK) | Rust and C++ Cardiff
Rust for Rustaceans Book Club: Chapter 2 - Types
2024-02-21 | Virtual (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
2024-02-22 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
Asia
2024-02-10 | Hyderabad, IN | Rust Language Hyderabad
Rust Language Develope BootCamp
Europe
2024-02-07 | Cologne, DE | Rust Cologne
Embedded Abstractions | Event page
2024-02-07 | London, UK | Rust London User Group
Rust for the Web — Mainmatter x Shuttle Takeover
2024-02-08 | Bern, CH | Rust Bern
Rust Bern Meetup #1 2024 🦀
2024-02-08 | Oslo, NO | Rust Oslo
Rust-based banter
2024-02-13 | Trondheim, NO | Rust Trondheim
Building Games with Rust: Dive into the Bevy Framework
2024-02-15 | Praha, CZ - Virtual + In-person | Rust Czech Republic
Introduction and Rust in production
2024-02-21 | Lyon, FR | Rust Lyon
Rust Lyon Meetup #8
2024-02-22 | Aarhus, DK | Rust Aarhus
Rust and Talk at Partisia
North America
2024-02-07 | Brookline, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Coolidge Corner Brookline Rust Lunch, Feb 7
2024-02-08 | Lehi, UT, US | Utah Rust
BEAST: Recreating a classic DOS terminal game in Rust
2024-02-12 | Minneapolis, MN, US | Minneapolis Rust Meetup
Minneapolis Rust: Open Source Contrib Hackathon & Happy Hour
2024-02-13 | New York, NY, US | Rust NYC
Rust NYC Monthly Mixer
2024-02-13 | Seattle, WA, US | Cap Hill Rust Coding/Hacking/Learning
Rusty Coding/Hacking/Learning Night
2024-02-15 | Boston, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Back Bay Rust Lunch, Feb 15
2024-02-15 | Seattle, WA, US | Seattle Rust User Group
Seattle Rust User Group Meetup
2024-02-20 | San Francisco, CA, US | San Francisco Rust Study Group
Rust Hacking in Person
2024-02-22 | Mountain View, CA, US | Mountain View Rust Meetup
Rust Meetup at Hacker Dojo
2024-02-28 | Austin, TX, US | Rust ATX
Rust Lunch - Fareground
Oceania
2024-02-19 | Melbourne, VIC, AU + Virtual | Rust Melbourne
February 2024 Rust Melbourne Meetup
2024-02-27 | Canberra, ACT, AU | Canberra Rust User Group
February Meetup
2024-02-27 | Sydney, NSW, AU | Rust Sydney
🦀 spire ⚡ & Quick
If you are running a Rust event please add it to the calendar to get it mentioned here. Please remember to add a link to the event too. Email the Rust Community Team for access.
Jobs
Please see the latest Who's Hiring thread on r/rust
Quote of the Week
My take on this is that you cannot use async Rust correctly and fluently without understanding Arc, Mutex, the mutability of variables/references, and how async and await syntax compiles in the end. Rust forces you to understand how and why things are the way they are. It gives you minimal abstraction to do things that could’ve been tedious to do yourself.
I got a chance to work on two projects that drastically forced me to understand how async/await works. The first one is to transform a library that is completely sync and only requires a sync trait to talk to the outside service. This all sounds fine, right? Well, this becomes a problem when we try to port it into browsers. The browser is single-threaded and cannot block the JavaScript runtime at all! It is arguably the most weird environment for Rust users. It is simply impossible to rewrite the whole library, as it has already been shipped to production on other platforms.
What we did instead was rewrite the network part using async syntax, but using our own generator. The idea is simple: the generator produces a future when called, and the produced future can be awaited. But! The produced future contains an arc pointer to the generator. That means we can feed the generator the value we are waiting for, then the caller who holds the reference to the generator can feed the result back to the function and resume it. For the browser, we use the native browser API to derive the network communications; for other platforms, we just use regular blocking network calls. The external interface remains unchanged for other platforms.
Honestly, I don’t think any other language out there could possibly do this. Maybe C or C++, but which will never have the same development speed and developer experience.
I believe people have already mentioned it, but the current asynchronous model of Rust is the most reasonable choice. It does create pain for developers, but on the other hand, there is no better asynchronous model for Embedded or WebAssembly.
– /u/Top_Outlandishness78 on /r/rust
Thanks to Brian Kung for the suggestion!
Please submit quotes and vote for next week!
This Week in Rust is edited by: nellshamrell, llogiq, cdmistman, ericseppanen, extrawurst, andrewpollack, U007D, kolharsam, joelmarcey, mariannegoldin, bennyvasquez.
Email list hosting is sponsored by The Rust Foundation
Discuss on r/rust
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Advanced Techniques in Full-Stack Development

Certainly, let's delve deeper into more advanced techniques and concepts in full-stack development:
1. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG):
SSR: Rendering web pages on the server side to improve performance and SEO by delivering fully rendered pages to the client.
SSG: Generating static HTML files at build time, enhancing speed, and reducing the server load.
2. WebAssembly:
WebAssembly (Wasm): A binary instruction format for a stack-based virtual machine. It allows high-performance execution of code on web browsers, enabling languages like C, C++, and Rust to run in web applications.
3. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) Enhancements:
Background Sync: Allowing PWAs to sync data in the background even when the app is closed.
Web Push Notifications: Implementing push notifications to engage users even when they are not actively using the application.
4. State Management:
Redux and MobX: Advanced state management libraries in React applications for managing complex application states efficiently.
Reactive Programming: Utilizing RxJS or other reactive programming libraries to handle asynchronous data streams and events in real-time applications.
5. WebSockets and WebRTC:
WebSockets: Enabling real-time, bidirectional communication between clients and servers for applications requiring constant data updates.
WebRTC: Facilitating real-time communication, such as video chat, directly between web browsers without the need for plugins or additional software.
6. Caching Strategies:
Content Delivery Networks (CDN): Leveraging CDNs to cache and distribute content globally, improving website loading speeds for users worldwide.
Service Workers: Using service workers to cache assets and data, providing offline access and improving performance for returning visitors.
7. GraphQL Subscriptions:
GraphQL Subscriptions: Enabling real-time updates in GraphQL APIs by allowing clients to subscribe to specific events and receive push notifications when data changes.
8. Authentication and Authorization:
OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect: Implementing secure authentication and authorization protocols for user login and access control.
JSON Web Tokens (JWT): Utilizing JWTs to securely transmit information between parties, ensuring data integrity and authenticity.
9. Content Management Systems (CMS) Integration:
Headless CMS: Integrating headless CMS like Contentful or Strapi, allowing content creators to manage content independently from the application's front end.
10. Automated Performance Optimization:
Lighthouse and Web Vitals: Utilizing tools like Lighthouse and Google's Web Vitals to measure and optimize web performance, focusing on key user-centric metrics like loading speed and interactivity.
11. Machine Learning and AI Integration:
TensorFlow.js and ONNX.js: Integrating machine learning models directly into web applications for tasks like image recognition, language processing, and recommendation systems.
12. Cross-Platform Development with Electron:
Electron: Building cross-platform desktop applications using web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), allowing developers to create desktop apps for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
13. Advanced Database Techniques:
Database Sharding: Implementing database sharding techniques to distribute large databases across multiple servers, improving scalability and performance.
Full-Text Search and Indexing: Implementing full-text search capabilities and optimized indexing for efficient searching and data retrieval.
14. Chaos Engineering:
Chaos Engineering: Introducing controlled experiments to identify weaknesses and potential failures in the system, ensuring the application's resilience and reliability.
15. Serverless Architectures with AWS Lambda or Azure Functions:
Serverless Architectures: Building applications as a collection of small, single-purpose functions that run in a serverless environment, providing automatic scaling and cost efficiency.
16. Data Pipelines and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Processes:
Data Pipelines: Creating automated data pipelines for processing and transforming large volumes of data, integrating various data sources and ensuring data consistency.
17. Responsive Design and Accessibility:
Responsive Design: Implementing advanced responsive design techniques for seamless user experiences across a variety of devices and screen sizes.
Accessibility: Ensuring web applications are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by following WCAG guidelines and ARIA practices.
full stack development training in Pune
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
You can learn NodeJS easily, Here's all you need:
1.Introduction to Node.js
• JavaScript Runtime for Server-Side Development
• Non-Blocking I/0
2.Setting Up Node.js
• Installing Node.js and NPM
• Package.json Configuration
• Node Version Manager (NVM)
3.Node.js Modules
• CommonJS Modules (require, module.exports)
• ES6 Modules (import, export)
• Built-in Modules (e.g., fs, http, events)
4.Core Concepts
• Event Loop
• Callbacks and Asynchronous Programming
• Streams and Buffers
5.Core Modules
• fs (File Svstem)
• http and https (HTTP Modules)
• events (Event Emitter)
• util (Utilities)
• os (Operating System)
• path (Path Module)
6.NPM (Node Package Manager)
• Installing Packages
• Creating and Managing package.json
• Semantic Versioning
• NPM Scripts
7.Asynchronous Programming in Node.js
• Callbacks
• Promises
• Async/Await
• Error-First Callbacks
8.Express.js Framework
• Routing
• Middleware
• Templating Engines (Pug, EJS)
• RESTful APIs
• Error Handling Middleware
9.Working with Databases
• Connecting to Databases (MongoDB, MySQL)
• Mongoose (for MongoDB)
• Sequelize (for MySQL)
• Database Migrations and Seeders
10.Authentication and Authorization
• JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
• Passport.js Middleware
• OAuth and OAuth2
11.Security
• Helmet.js (Security Middleware)
• Input Validation and Sanitization
• Secure Headers
• Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
12.Testing and Debugging
• Unit Testing (Mocha, Chai)
• Debugging Tools (Node Inspector)
• Load Testing (Artillery, Apache Bench)
13.API Documentation
• Swagger
• API Blueprint
• Postman Documentation
14.Real-Time Applications
• WebSockets (Socket.io)
• Server-Sent Events (SSE)
• WebRTC for Video Calls
15.Performance Optimization
• Caching Strategies (in-memory, Redis)
• Load Balancing (Nginx, HAProxy)
• Profiling and Optimization Tools (Node Clinic, New Relic)
16.Deployment and Hosting
• Deploying Node.js Apps (PM2, Forever)
• Hosting Platforms (AWS, Heroku, DigitalOcean)
• Continuous Integration and Deployment-(Jenkins, Travis CI)
17.RESTful API Design
• Best Practices
• API Versioning
• HATEOAS (Hypermedia as the Engine-of Application State)
18.Middleware and Custom Modules
• Creating Custom Middleware
• Organizing Code into Modules
• Publish and Use Private NPM Packages
19.Logging
• Winston Logger
• Morgan Middleware
• Log Rotation Strategies
20.Streaming and Buffers
• Readable and Writable Streams
• Buffers
• Transform Streams
21.Error Handling and Monitoring
• Sentry and Error Tracking
• Health Checks and Monitoring Endpoints
22.Microservices Architecture
• Principles of Microservices
• Communication Patterns (REST, gRPC)
• Service Discovery and Load Balancing in Microservices
1 note
·
View note
Text
Secure JWT Authentication in Flask: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing Secure JWT Authentication in Flask Applications Table of Contents Introduction Technical Background Implementation Guide Code Examples Best Practices and Optimization Testing and Debugging Conclusion Introduction Overview JSON Web Tokens (JWT) provide a robust method for securely transmitting information between parties. In Flask applications, JWT is particularly useful for…
0 notes
Text
Unlock Your Career in Full-Stack Development with Techmindz's Full-Stack JavaScript Course in Kochi
JavaScript is undeniably the heart of modern web development. As a versatile and powerful language, it allows developers to build both the front-end and back-end of web applications using a single language. If you’re eager to dive deep into full-stack development and master JavaScript, Techmindz offers the perfect learning opportunity with our Full-Stack JavaScript Course in Kochi. This course will equip you with the essential skills to become a proficient JavaScript developer and build dynamic, interactive, and scalable web applications.
Why Learn Full-Stack JavaScript?
The demand for full-stack JavaScript developers is rapidly increasing across industries, and it’s no surprise why. With the ability to use JavaScript for both the client-side (front-end) and server-side (back-end), full-stack JavaScript developers are able to streamline development, reduce project complexity, and create end-to-end solutions using one programming language. Mastering the entire stack of JavaScript technologies opens doors to exciting job opportunities and career growth.
What Makes Techmindz's Full-Stack JavaScript Course Stand Out?
At Techmindz, we understand the need for comprehensive, hands-on training to master full-stack JavaScript development. Our course is designed to provide you with in-depth knowledge and practical experience in both front-end and back-end JavaScript technologies, including Node.js, Express.js, MongoDB, and React.js. Through expert-led instruction, real-world projects, and interactive coding sessions, you will become fully equipped to handle the entire development process—from building user interfaces to designing databases and developing server-side logic.
What You Will Learn in Our Full-Stack JavaScript Course
Front-End Development with JavaScript:
HTML & CSS: Learn the building blocks of web development, creating responsive and user-friendly web pages.
JavaScript Basics: Master JavaScript fundamentals, including variables, loops, functions, and objects.
React.js: Dive into the world of React, one of the most popular JavaScript libraries, to build dynamic and efficient user interfaces.
State Management with Redux: Learn how to manage application state in large-scale React applications using Redux.
Asynchronous JavaScript: Master concepts like promises, async/await, and AJAX for handling asynchronous operations and API interactions.
Back-End Development with JavaScript:
Node.js: Learn how to use Node.js to build scalable, high-performance server-side applications.
Express.js: Understand how to work with Express.js to streamline routing and simplify server-side logic.
MongoDB: Master MongoDB, a NoSQL database that works seamlessly with JavaScript applications to store and manage data.
RESTful APIs: Learn to design and develop RESTful APIs that allow communication between the front-end and back-end of applications.
Authentication & Authorization: Implement secure user authentication and authorization mechanisms using technologies like JWT (JSON Web Tokens).
Additional Topics:
Version Control with Git & GitHub: Learn the importance of version control and how to use Git and GitHub for collaboration and code management.
Testing and Debugging: Master tools like Mocha and Chai for unit testing and debugging your JavaScript applications.
Deployment: Gain hands-on experience deploying your full-stack applications to cloud platforms like Heroku and AWS.
Agile Development: Understand Agile development principles to work efficiently in teams and manage projects effectively.
Why Choose Techmindz for Full-Stack JavaScript Training?
Experienced Trainers: Our instructors are industry experts with years of experience in JavaScript development, ensuring that you receive the most relevant and up-to-date knowledge.
Project-Based Learning: At Techmindz, we focus on practical, hands-on learning. You will work on real-world projects to build a strong portfolio that showcases your full-stack JavaScript skills.
Comprehensive Curriculum: The course is designed to cover every aspect of full-stack JavaScript development, from front-end technologies to back-end frameworks.
Flexible Learning Options: Whether you prefer classroom training or online classes, we offer flexible learning options to accommodate your schedule.
Job Placement Assistance: We provide placement support to help you land your dream job after completing the course. This includes resume building, interview preparation, and job referrals.
Affordable Pricing: Get top-tier training at competitive prices, ensuring you get the best value for your investment.
Who Should Enroll in the Full-Stack JavaScript Course?
Our Full-Stack JavaScript Course in Kochi is ideal for:
Beginner Developers: If you're new to web development and want to learn how to build complete web applications using JavaScript.
Front-End Developers: If you already have experience with front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and want to expand your skills to the back-end.
Back-End Developers: If you’re familiar with server-side development and want to transition to full-stack JavaScript development.
IT Professionals & Freelancers: Developers looking to enhance their skill set and offer full-stack JavaScript development services to clients.
Entrepreneurs: Individuals looking to build and scale their own web applications.
Career Opportunities After Completing the Course
Upon completing the Full-Stack JavaScript Course in Kochi, you will be equipped to take on roles such as:
Full-Stack JavaScript Developer
Front-End Developer (React.js/Node.js)
Back-End Developer (Node.js/Express.js)
Web Developer
JavaScript Developer
API Developer
With JavaScript being the most widely used programming language for web development, the demand for full-stack JavaScript developers is higher than ever. By completing this course, you'll be well-prepared to take advantage of numerous job opportunities in the web development industry.
Why Full-Stack JavaScript Development is in Demand?
The power of JavaScript lies in its versatility. As a full-stack JavaScript developer, you’ll have the ability to build web applications entirely using JavaScript, which simplifies the development process and boosts productivity. With the rise of modern web applications and the growth of technologies like React, Node.js, and MongoDB, JavaScript developers are in high demand, making this the perfect time to invest in your skills.
Get Started Today with Techmindz's Full-Stack JavaScript Course in Kochi
If you're ready to start your journey toward becoming a proficient full-stack JavaScript developer, Techmindz is the place to be. Our Full-Stack JavaScript Course in Kochi will provide you with the knowledge, skills, and experience necessary to excel in the tech industry.
https://www.techmindz.com/java-programming-course-kochi-infopark/
0 notes
Text
Security Vulnerabilities in SAML, OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, and JWT
Single Sign-On (SSO) protocols are critical for enterprise security but have a history of severe vulnerabilities. This report provides a data-rich overview of known security flaws in four major SSO technologies – SAML, OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect (OIDC), and JSON Web Tokens (JWT) – including both historical exploits and recent findings. We compare the frequency and impact of these vulnerabilities,…
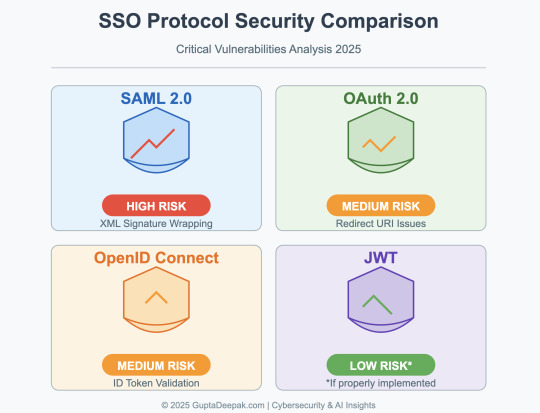
View On WordPress
#assistant professor#computer science#computer scientist#engineering#experimental roboticist#research scientist#university of denver
0 notes
Text
Authentication and Authorization in Node.js with JWT

Authentication and authorization are essential for securing modern web applications. In Node.js, using JWT (JSON Web Tokens) has become a trending and efficient way to handle secure access control. JWT allows stateless authentication, making it ideal for RESTful APIs and microservices architecture.
When a user logs in, the server generates a JWT signed with a secret key or a private key (in case of RSA). This token is then sent to the client and stored typically in localStorage or HTTP-only cookies. For each subsequent request, the client sends the token in the header, commonly using the Bearer schema.
The backend uses middleware like jsonwebtoken in combination with Express.js to verify the token and extract user information. If the token is valid, the user gets access to protected routes and resources. Role-based access control (RBAC) can also be implemented to allow specific users access to different parts of the application.
JWTs are widely used in Node.js for API security, real-time applications, and mobile backends due to their lightweight and stateless nature. Key trends include integrating JWT with OAuth2.0, using refresh tokens for long-lived sessions, and enhancing security with HTTPS and token expiration strategies.
Popular npm packages include jsonwebtoken, bcryptjs for password hashing, and dotenv for environment variables. Combining JWT with MongoDB, Mongoose, and Express.js is a common stack for secure backend development in 2025.
0 notes
Text
QicApp’s Proven Approach to Delivering Clean, Reliable Code

At QicApp, we believe that code quality isn’t just a technical metric—it’s the very foundation of a successful digital product. As a trusted iOS-app-development-company-in-Gurgaon, we know that high-quality code directly impacts performance, scalability, security, and long-term maintainability. Our goal is never just to deliver working solutions—we aim to build clean, efficient, and future-proof codebases that clients can rely on for years to come.
Whether it's a mobile app for a fast-growing startup or a complex backend system for a large enterprise, we follow rigorous development practices to ensure our code is robust, adaptable, and maintainable. Here’s how we maintain top-tier quality across all our projects:
Structured Architecture With MVVM
At QicApp, we adopt the MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) design pattern in both our iOS and Android projects. This architectural approach separates UI logic, data management, and business rules, leading to cleaner and more testable codebases. This structure not only enhances code clarity but also improves scalability and facilitates faster feature rollouts with fewer bugs.
Continuous Performance Profiling
User experience is everything, and performance plays a huge role. Our team regularly uses tools like Instruments for iOS and Android Profiler to detect and fix issues like memory leaks, thread blocks, and UI slowdowns. By identifying bottlenecks early, we ensure our apps deliver smooth performance, even in demanding environments.
Enforced Coding Standards With Linters
Code consistency drives collaboration. We use linters like SwiftLint (iOS), Ktlint/Detekt (Android), and ESLint/Prettier (web/backend) to enforce coding standards. Paired with CI pipeline checks and pre-commit hooks, this ensures that all developers follow best practices and deliver clean, readable code every time.
Peer Code Reviews for Every Feature
Every new feature goes through a peer review before it’s merged. These sessions aren’t just about catching bugs—they foster team-wide accountability, spark ideas for improvements, and ensure our solutions stay aligned with architectural, performance, and security standards.
Security by Design: JWT & AES
As an iOS-app-development-company-in-Gurgaon, security is baked into everything we do. We use JWT (JSON Web Tokens) for secure API communication and AES encryption for sensitive data storage. Our secure development lifecycle includes HTTPS enforcement, input validation, endpoint protection, and adherence to best coding practices.
Clear Documentation and Transparent Workflows
We prioritize documentation at every level—from code and APIs to Git workflows and setup guides. Well-documented projects reduce onboarding time, improve developer productivity, and give our clients full visibility into the development process.
Automated Testing & CI/CD Integration
We champion frequent, reliable deployments. Our teams integrate automated testing (unit and integration) and CI/CD pipelines to validate code quality, catch issues early, and ensure smooth, continuous delivery. This automation helps us push stable updates faster while minimizing bugs in production.
Code Quality: A Culture, Not a Task
At QicApp, code quality is more than a checklist—it’s embedded into our culture. From MVVM architecture and secure-by-design coding to peer reviews and test automation, every aspect of our workflow is designed to deliver products that are stable, scalable, and secure.
If you're looking for an iOS-app-development-company-in-Gurgaon that’s committed to long-term product excellence, QicApp is your trusted partner.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Enhancing Security in Backend Development: Best Practices for Developers
In today’s rapidly evolving digital environment, security in backend systems is paramount. As the backbone of web applications, the backend handles sensitive data processing, storage, and communication. Any vulnerabilities in this layer can lead to catastrophic breaches, affecting user trust and business integrity. This article highlights essential best practices to ensure your backend development meets the highest security standards.
1. Implement Strong Authentication and Authorization
One of the primary steps in securing backend development services is implementing robust authentication and authorization protocols. Password-based systems alone are no longer sufficient. Modern solutions like OAuth 2.0 and JSON Web Tokens (JWT) offer secure ways to manage user sessions. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of protection, requiring users to verify their identity using multiple methods, such as a password and a one-time code.
Authorization should be handled carefully to ensure users only access resources relevant to their role. By limiting privileges, you reduce the risk of sensitive data falling into the wrong hands. This practice is particularly crucial for applications that involve multiple user roles, such as administrators, managers, and end-users.
2. Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest
Data encryption is a non-negotiable aspect of backend security. When data travels between servers and clients, it is vulnerable to interception. Implement HTTPS to secure this communication channel using SSL/TLS protocols. For data stored in databases, use encryption techniques that prevent unauthorized access. Even if an attacker gains access to the storage, encrypted data remains unreadable without the decryption keys.
Managing encryption keys securely is equally important. Store keys in hardware security modules (HSMs) or use services like AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to ensure they are well-protected. Regularly rotate keys to further reduce the risk of exposure.
3. Prevent SQL Injection and Other Injection Attacks
Injection attacks, particularly SQL injections, remain one of the most common threats to backend technologies for web development. Attackers exploit poorly sanitized input fields to execute malicious SQL queries. This can lead to unauthorized data access or even complete control of the database.
To mitigate this risk, always validate and sanitize user inputs. Use parameterized queries or prepared statements, which ensure that user-provided data cannot alter the intended database commands. Additionally, educate developers on the risks of injection attacks and implement static code analysis tools to identify vulnerabilities during the development process.
4. Employ Secure API Design
APIs are integral to backend development but can also serve as entry points for attackers if not secured properly. Authentication tokens, input validation, and rate limiting are essential to preventing unauthorized access and abuse. Moreover, all API endpoints should be designed with security-first principles.
For example, avoid exposing sensitive information in API responses. Error messages should be generic and not reveal the backend structure. Consider using tools like API gateways to enforce security policies, including data masking, IP whitelisting, and token validation.
5. Keep Dependencies Updated and Patched
Third-party libraries and frameworks streamline development but can introduce vulnerabilities if not updated regularly. Outdated software components are a common attack vector. Perform routine dependency checks and integrate automated vulnerability scanners like Snyk or Dependabot into your CI/CD pipeline.
Beyond updates, consider using tools to analyze your application for known vulnerabilities. For instance, dependency management tools can identify and notify you of outdated libraries, helping you stay ahead of potential risks.
6. Adopt Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Access management is a critical component of secure backend systems. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures users and applications have access only to what they need. Define roles clearly and assign permissions at a granular level. For example, a customer service representative may only access user profile data, while an admin might have permissions to modify backend configurations.
Implementing RBAC reduces the potential damage of a compromised user account. For added security, monitor access logs for unusual patterns, such as repeated failed login attempts or unauthorized access to restricted resources.
7. Harden Your Database Configurations
Databases are at the heart of backend systems, making them a prime target for attackers. Properly configuring your database is essential. Start by disabling unnecessary services and default accounts that could be exploited. Enforce strong password policies and ensure that sensitive data, such as passwords, is hashed using secure algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2.
Database permissions should also be restricted. Grant the least privilege necessary to applications interacting with the database. Regularly audit these permissions to identify and eliminate unnecessary access.
8. Monitor and Log Backend Activities
Real-time monitoring and logging are critical for detecting and responding to security threats. Implement tools like Logstash, Prometheus, and Kibana to track server activity and identify anomalies. Logs should include information about authentication attempts, database queries, and API usage.
However, ensure that logs themselves are secure. Store them in centralized, access-controlled environments and avoid exposing them to unauthorized users. Use log analysis tools to proactively identify patterns that may indicate an ongoing attack.
9. Mitigate Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Risks
Cross-site scripting attacks can compromise your backend security through malicious scripts. To prevent XSS attacks, validate and sanitize all inputs received from the client side. Implement Content Security Policies (CSP) that restrict the types of scripts that can run within the application.
Another effective measure is to encode output data before rendering it in the user’s browser. For example, HTML encoding ensures that malicious scripts cannot execute, even if injected.
10. Secure Cloud Infrastructure
As businesses increasingly migrate to the cloud, backend developers must adapt to the unique challenges of cloud security. Use Identity and Access Management (IAM) features provided by cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure to define precise permissions.
Enable encryption for all data stored in the cloud and use virtual private clouds (VPCs) to isolate your infrastructure from external threats. Regularly audit your cloud configuration to ensure compliance with security best practices.
11. Foster a Culture of Security
Security isn’t a one-time implementation — it’s an ongoing process. Regularly train your development team on emerging threats, secure coding practices, and compliance standards. Encourage developers to follow a security-first approach at every stage of development.
Conduct routine penetration tests and code audits to identify weaknesses. Establish a response plan to quickly address breaches or vulnerabilities. By fostering a security-conscious culture, your organization can stay ahead of evolving threats.
Thus, Backend security is an ongoing effort requiring vigilance, strategic planning, and adherence to best practices. Whether you’re managing APIs, databases, or cloud integrations, securing backend development services ensures the reliability and safety of your application.
0 notes
Text
In modern web applications, user authentication is a critical feature. One of the most secure ways to implement authentication is by using JSON Web Tokens (JWT). JWT allows for secure communication between a client and server, ensuring that only authorized users can access protected resources.
In this tutorial, we'll walk through the process of integrating JWT authentication in a MERN stack application. We'll use Node.js and Express for the backend and React for the frontend. This guide will cover the complete setup, from creating a JWT authentication system in Node.js to connecting it with a React application.
By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a secure authentication system in place that uses JWT for token-based authentication.
#MERNStack#JWTAuthentication#React#NodeJS#ExpressJS#MongoDB#WebDevelopment#FullStackDevelopment#APIAuthentication#ReactJS#JWT#TokenAuthentication#SecureAuthentication#NodeJSBackend#ReactFrontend#WebAppSecurity#Authentication#Authorization#RESTAPI#BackendDevelopment#FrontendDevelopment#NodeExpress#ReactApp#UserAuthentication#Security#WebAppDevelopment#JWTToken#FullStackApp#JWTinMERN
0 notes