#sql injection attack
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
JWT Security Vulnerabilities | CyberSecurityTv
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) are a widely used method for representing claims between two parties in a compact and self-contained way
#security vulnerabilities#sql injection#jwt#vulnerability management#zero day vulnerability#vulnerabilities#Addressing JWT (JSON Web Token) Security Vulnerabilities#Security Vulnerabilities in JWT#JWT (JSON Web Token) Implementations#Identifying and Resolving JWT (JSON Web Token)#JWT (JSON Web Token) Vulnerabilities#sql injection attack#jsonwebtoken#jwt token#JWT Security Vulnerabilities#CyberSecurityTv#Youtube
0 notes
Text
How to Protect Your WordPress Database from Cyber Threats
Introduction Your WordPress database is the backbone of your website, storing critical data such as user information, posts, pages, comments, and settings. If compromised, your site could suffer data breaches, downtime, or even total loss of content. Cyber threats like SQL injections, brute force attacks, malware infections, and unauthorized access can put your database at serious…
#brute force attack protection#database backup#database security#limit login attempts#malware scanning#optimize wordpress database#secure wp-config#SQL injection prevention#two-factor authentication#web application firewall#wordpress cybersecurity#wordpress database protection#wordpress firewall#wordpress security
0 notes
Text
Securing Your Website: Best Practices for Web Developers
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, website security has become a paramount concern for businesses and individuals alike. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, it is crucial for web developers to adopt robust security measures to safeguard their websites and the sensitive data they handle. In this article, we'll delve into the best practices that web developers can implement to enhance the security of their websites and protect against potential threats.
Introduction
In today's interconnected world, websites serve as the digital storefront for businesses, making them vulnerable targets for cyber attacks. From data breaches to malware infections, the consequences of a security breach can be severe, ranging from financial loss to damage to reputation. Therefore, prioritizing website security is essential for maintaining the trust and confidence of users.
Understanding Website Security
Before diving into best practices, it's crucial to understand the importance of website security and the common threats faced by websites. Website security encompasses measures taken to protect websites from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Common threats include malware infections, phishing attacks, SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and brute force attacks.
Best Practices for Web Developers
Keeping Software Updated
One of the most fundamental steps in website security is keeping all software, including the content management system (CMS), plugins, and server software, updated with the latest security patches and fixes. Outdated software is often targeted by attackers due to known vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
Implementing HTTPS
Implementing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data transmitted between the website and its users, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. HTTPS not only protects sensitive information but also boosts trust among visitors, as indicated by the padlock icon in the browser's address bar.
Using Strong Authentication Methods
Implementing strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and CAPTCHA, adds an extra layer of security to user accounts. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their mobile device, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Securing Against SQL Injection Attacks
SQL injection attacks occur when malicious actors exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to execute arbitrary SQL commands. Web developers can prevent SQL injection attacks by using parameterized queries and input validation to sanitize user inputs effectively.
Protecting Sensitive Data
It's essential to employ encryption techniques to protect sensitive data, such as passwords, credit card information, and personal details, stored on the website's servers. Encrypting data at rest and in transit mitigates the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the website's infrastructure and codebase. Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code reviews enable web developers to proactively address security issues before they are exploited by attackers.
Choosing a Secure Hosting Provider
Selecting a reputable and secure hosting provider is critical for ensuring the overall security of your website. When evaluating hosting providers, consider factors such as security features, reliability, scalability, and customer support.
Evaluating Security Features
Choose a hosting provider that offers robust security features, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), malware scanning, and DDoS protection. These features help protect your website from various cyber threats and ensure continuous uptime.
Ensuring Regular Backups
Regularly backing up your website's data is essential for mitigating the impact of security incidents, such as data breaches or website compromises. Choose a hosting provider that offers automated backup solutions and store backups securely offsite.
Customer Support and Response to Security Incidents
Opt for a hosting provider that provides responsive customer support and has established protocols for handling security incidents. In the event of a security breach or downtime, prompt assistance from the hosting provider can minimize the impact on your website and business operations.
Implementing Firewall Protection
Firewalls act as a barrier between your website and external threats, filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. There are several types of firewalls, including network firewalls, web application firewalls (WAF), and host-based firewalls.
Configuring and Maintaining Firewalls
Properly configuring and maintaining firewalls is crucial for effective security. Define firewall rules based on the principle of least privilege, regularly update firewall configurations to reflect changes in the website's infrastructure, and monitor firewall logs for suspicious activity.
Educating Users about Security
In addition to implementing technical measures, educating users about security best practices is essential for enhancing overall website security. Provide users with resources, such as security guidelines, tips for creating strong passwords, and information about common phishing scams.
Importance of User Awareness
Users play a significant role in maintaining website security, as they are often the targets of social engineering attacks. By raising awareness about potential threats and providing guidance on how to recognize and respond to them, web developers can empower users to stay vigilant online.
Providing Training and Resources
Offer training sessions and educational materials to help users understand the importance of security and how to protect themselves while using the website. Regularly communicate updates and reminders about security practices to reinforce good habits.
Monitoring and Responding to Security Incidents
Despite taking preventive measures, security incidents may still occur. Establishing robust monitoring systems and incident response protocols enables web developers to detect and respond to security threats in a timely manner.
Setting Up Monitoring Tools
Utilize monitoring tools, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and website monitoring services, to detect abnormal behavior and potential security breaches. Configure alerts to notify you of suspicious activity promptly.
Establishing Incident Response Protocols
Develop comprehensive incident response plans that outline roles, responsibilities, and procedures for responding to security incidents. Establish clear communication channels and escalation paths to coordinate responses effectively and minimize the impact of security breaches.
Securing your website requires a proactive approach that involves implementing a combination of technical measures, choosing a secure hosting provider, educating users about security best practices, and establishing robust monitoring and incident response protocols. By following these best practices, web developers can mitigate the risk of security breaches and safeguard their websites and the sensitive data they handle.
#website security has become a paramount concern for businesses and individuals alike. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated#it is crucial for web developers to adopt robust security measures to safeguard their websites and the sensitive data they handle. In this#we'll delve into the best practices that web developers can implement to enhance the security of their websites and protect against potenti#Introduction#In today's interconnected world#websites serve as the digital storefront for businesses#making them vulnerable targets for cyber attacks. From data breaches to malware infections#the consequences of a security breach can be severe#ranging from financial loss to damage to reputation. Therefore#prioritizing website security is essential for maintaining the trust and confidence of users.#Understanding Website Security#Before diving into best practices#it's crucial to understand the importance of website security and the common threats faced by websites. Website security encompasses measur#phishing attacks#SQL injection#cross-site scripting (XSS)#and brute force attacks.#Best Practices for Web Developers#Keeping Software Updated#One of the most fundamental steps in website security is keeping all software#including the content management system (CMS)#plugins#and server software#updated with the latest security patches and fixes. Outdated software is often targeted by attackers due to known vulnerabilities that can#Implementing HTTPS#Implementing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data transmitted between the website and its users#ensuring confidentiality and integrity. HTTPS not only protects sensitive information but also boosts trust among visitors#as indicated by the padlock icon in the browser's address bar.#Using Strong Authentication Methods#Implementing strong authentication methods
0 notes
Text
Ever since OpenAI released ChatGPT at the end of 2022, hackers and security researchers have tried to find holes in large language models (LLMs) to get around their guardrails and trick them into spewing out hate speech, bomb-making instructions, propaganda, and other harmful content. In response, OpenAI and other generative AI developers have refined their system defenses to make it more difficult to carry out these attacks. But as the Chinese AI platform DeepSeek rockets to prominence with its new, cheaper R1 reasoning model, its safety protections appear to be far behind those of its established competitors.
Today, security researchers from Cisco and the University of Pennsylvania are publishing findings showing that, when tested with 50 malicious prompts designed to elicit toxic content, DeepSeek’s model did not detect or block a single one. In other words, the researchers say they were shocked to achieve a “100 percent attack success rate.”
The findings are part of a growing body of evidence that DeepSeek’s safety and security measures may not match those of other tech companies developing LLMs. DeepSeek’s censorship of subjects deemed sensitive by China’s government has also been easily bypassed.
“A hundred percent of the attacks succeeded, which tells you that there’s a trade-off,” DJ Sampath, the VP of product, AI software and platform at Cisco, tells WIRED. “Yes, it might have been cheaper to build something here, but the investment has perhaps not gone into thinking through what types of safety and security things you need to put inside of the model.”
Other researchers have had similar findings. Separate analysis published today by the AI security company Adversa AI and shared with WIRED also suggests that DeepSeek is vulnerable to a wide range of jailbreaking tactics, from simple language tricks to complex AI-generated prompts.
DeepSeek, which has been dealing with an avalanche of attention this week and has not spoken publicly about a range of questions, did not respond to WIRED’s request for comment about its model’s safety setup.
Generative AI models, like any technological system, can contain a host of weaknesses or vulnerabilities that, if exploited or set up poorly, can allow malicious actors to conduct attacks against them. For the current wave of AI systems, indirect prompt injection attacks are considered one of the biggest security flaws. These attacks involve an AI system taking in data from an outside source—perhaps hidden instructions of a website the LLM summarizes—and taking actions based on the information.
Jailbreaks, which are one kind of prompt-injection attack, allow people to get around the safety systems put in place to restrict what an LLM can generate. Tech companies don’t want people creating guides to making explosives or using their AI to create reams of disinformation, for example.
Jailbreaks started out simple, with people essentially crafting clever sentences to tell an LLM to ignore content filters—the most popular of which was called “Do Anything Now” or DAN for short. However, as AI companies have put in place more robust protections, some jailbreaks have become more sophisticated, often being generated using AI or using special and obfuscated characters. While all LLMs are susceptible to jailbreaks, and much of the information could be found through simple online searches, chatbots can still be used maliciously.
“Jailbreaks persist simply because eliminating them entirely is nearly impossible—just like buffer overflow vulnerabilities in software (which have existed for over 40 years) or SQL injection flaws in web applications (which have plagued security teams for more than two decades),” Alex Polyakov, the CEO of security firm Adversa AI, told WIRED in an email.
Cisco’s Sampath argues that as companies use more types of AI in their applications, the risks are amplified. “It starts to become a big deal when you start putting these models into important complex systems and those jailbreaks suddenly result in downstream things that increases liability, increases business risk, increases all kinds of issues for enterprises,” Sampath says.
The Cisco researchers drew their 50 randomly selected prompts to test DeepSeek’s R1 from a well-known library of standardized evaluation prompts known as HarmBench. They tested prompts from six HarmBench categories, including general harm, cybercrime, misinformation, and illegal activities. They probed the model running locally on machines rather than through DeepSeek’s website or app, which send data to China.
Beyond this, the researchers say they have also seen some potentially concerning results from testing R1 with more involved, non-linguistic attacks using things like Cyrillic characters and tailored scripts to attempt to achieve code execution. But for their initial tests, Sampath says, his team wanted to focus on findings that stemmed from a generally recognized benchmark.
Cisco also included comparisons of R1’s performance against HarmBench prompts with the performance of other models. And some, like Meta’s Llama 3.1, faltered almost as severely as DeepSeek’s R1. But Sampath emphasizes that DeepSeek’s R1 is a specific reasoning model, which takes longer to generate answers but pulls upon more complex processes to try to produce better results. Therefore, Sampath argues, the best comparison is with OpenAI’s o1 reasoning model, which fared the best of all models tested. (Meta did not immediately respond to a request for comment).
Polyakov, from Adversa AI, explains that DeepSeek appears to detect and reject some well-known jailbreak attacks, saying that “it seems that these responses are often just copied from OpenAI’s dataset.” However, Polyakov says that in his company’s tests of four different types of jailbreaks—from linguistic ones to code-based tricks—DeepSeek’s restrictions could easily be bypassed.
“Every single method worked flawlessly,” Polyakov says. “What’s even more alarming is that these aren’t novel ‘zero-day’ jailbreaks—many have been publicly known for years,” he says, claiming he saw the model go into more depth with some instructions around psychedelics than he had seen any other model create.
“DeepSeek is just another example of how every model can be broken—it’s just a matter of how much effort you put in. Some attacks might get patched, but the attack surface is infinite,” Polyakov adds. “If you’re not continuously red-teaming your AI, you’re already compromised.”
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
The original sin of prompt injection has always been that LLMs are incapable of considering the source of the tokens once they get to processing them - everything is concatenated together, just like in a classic SQL injection attack.
(from Simon Willison) I feel like most social engineering hacks take advantage of this with humans, who also struggle to keep track of what counts as a genuine authority.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
yall the slaying of princess is infecting my studies
I've been doing computer science and the only way I've been remembering the types of hacking by thinking which voice would do that.
PHISHING IS SOO OPPORTUNIST he's a snake oil sales man
skeptic is an SQL injection because he's smart enough to figure that out.
brute force attack is stubborn
I think cheated is a denial of service attack since he uses the power of numbers in razor and that's basically what it is
it's hard to choose for data interseption but I think cold purely off vibes
I can't think of anyone for malware because it's so broad and the left over voices don't seem like the type to hack anyone so if yall have ideas tell me.
hunted is breaking in and raiding your fridge
#slay the princess#stp#stp voices#voice of the cold#voice of the opportunist#voice of the cheated#voice of the skeptic#voice of the hunted#voice of the stubborn#stp opportunist#stp stubborn#stp hunted#stp cheated#stp skeptic#stp cold#i made this
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Albert Gonzalez (born 1981) is an American computer hacker, computer criminal and police informer, who is accused of masterminding the combined credit card theft and subsequent reselling of more than 170 million card and ATMnumbers from 2005 to 2007, the biggest such fraud in history. Gonzalez and his accomplices used SQL injection to deploy backdoors on several corporate systems in order to launch packet sniffing (specifically, ARP spoofing) attacks which allowed him to steal computer data from internal corporate networks.
Gonzalez bought his first computer when he was 12, and by the time he was 14 managed to hack into NASA. He attended South Miami High School in Miami, Florida, where he was described as the "troubled" pack leader of computer nerds. In 2000, he moved to New York City, where he lived for three months before moving to Kearny, New Jersey.


While in Kearny, he was accused of being the mastermind of a group of hackers called the ShadowCrew group, which trafficked in 1.5 million stolen credit and ATM card numbers. Although considered the mastermind of the scheme (operating on the site under the screen name of "CumbaJohnny"), he was not indicted. According to the indictment, there were 4,000 people who registered with the Shadowcrew.com website. Once registered, they could buy stolen account numbers or counterfeit documents at auction, or read "Tutorials and How-To's" describing the use of cryptography in magnetic strips on credit cards, debit cards and ATM cards so that the numbers could be used. Moderators of the website punished members who did not abide by the site's rules, including providing refunds to buyers if the stolen card numbers proved invalid.
In addition to the card numbers, numerous other objects of identity theft were sold at auction, including counterfeit passports, drivers' licenses, Social Security cards, credit cards, debit cards, birth certificates, college student identification cards, and health insurance cards. One member sold 18 million e-mail accounts with associated usernames, passwords, dates of birth, and other personally identifying information. Most of those indicted were members who actually sold illicit items. Members who maintained or moderated the website itself were also indicted, including one who attempted to register the .cc domain name Shadowcrew.cc.
The Secret Service dubbed their investigation "Operation Firewall" and believed that up to $4.3 million was stolen, as ShadowCrew shared its information with other groups called Carderplanet and Darkprofits. The investigation involved units from the United States, Bulgaria, Belarus, Canada, Poland, Sweden, the Netherlands and Ukraine. Gonzalez was initially charged with possession of 15 fake credit and debit cards in Newark, New Jersey, though he avoided jail time by providing evidence to the United States Secret Service against his cohorts. 19 ShadowCrew members were indicted. Gonzalez then returned to Miami.
While cooperating with authorities, he was said to have masterminded the hacking of TJX Companies, in which 45.6 million credit and debit card numbers were stolen over an 18-month period ending in 2007, topping the 2005 breach of 40 million records at CardSystems Solutions. Gonzalez and 10 others sought targets while wardriving and seeking vulnerabilities in wireless networks along U.S. Route 1 in Miami. They compromised cards at BJ's Wholesale Club, DSW, Office Max, Boston Market, Barnes & Noble, Sports Authority and T.J. Maxx. The indictment referred to Gonzalez by the screen names "cumbajohny", "201679996", "soupnazi", "segvec", "kingchilli" and "stanozlolz." The hacking was an embarrassment to TJ Maxx, which discovered the breach in December 2006. The company initially believed the intrusion began in May 2006, but further investigation revealed breaches dating back to July 2005.
Gonzalez had multiple US co-defendants for the Dave & Buster's and TJX thefts. The main ones were charged and sentenced as follows:
Stephen Watt (Unix Terrorist, Jim Jones) was charged with providing a data theft tool in an identity theft case. He was sentenced to two years in prison and 3 years of supervised release. He was also ordered by the court to pay back $250,000 in restitution.
Damon Patrick Toey pleaded guilty to wire fraud, credit card fraud, and aggravated identity theft and received a five-year sentence.
Christopher Scott pleaded guilty to conspiracy, unauthorized access to computer systems, access device fraud and identity theft. He was sentenced to seven years.
Gonzalez was arrested on May 7, 2008, on charges stemming from hacking into the Dave & Buster's corporate network from a point of sale location at a restaurant in Islandia, New York. The incident occurred in September 2007. About 5,000 card numbers were stolen. Fraudulent transactions totaling $600,000 were reported on 675 of the cards.
Authorities became suspicious after the conspirators kept returning to the restaurant to reintroduce their hack, because it would not restart after the company computers shut down.
Gonzalez was arrested in room 1508 at the National Hotel in Miami Beach, Florida. In various related raids, authorities seized $1.6 million in cash (including $1.1 million buried in plastic bags in a three-foot drum in his parents' backyard), his laptops and a compact Glock pistol. Officials said that, at the time of his arrest, Gonzalez lived in a nondescript house in Miami. He was taken to the Metropolitan Detention Center in Brooklyn, where he was indicted in the Heartland attacks.
In August 2009, Gonzalez was indicted in Newark, New Jersey on charges dealing with hacking into the Heartland Payment Systems, Citibank-branded 7-Eleven ATM's and Hannaford Brothers computer systems. Heartland bore the brunt of the attack, in which 130 million card numbers were stolen. Hannaford had 4.6 million numbers stolen. Two other retailers were not disclosed in the indictment; however, Gonzalez's attorney told StorefrontBacktalk that two of the retailers were J.C. Penney and Target Corporation. Heartland reported that it had lost $12.6 million in the attack including legal fees. Gonzalez allegedly called the scheme "Operation Get Rich or Die Tryin."
According to the indictment, the attacks by Gonzalez and two unidentified hackers "in or near Russia" along with unindicted conspirator "P.T." from Miami, began on December 26, 2007, at Heartland Payment Systems, August 2007 against 7-Eleven, and in November 2007 against Hannaford Brothers and two other unidentified companies.
Gonzalez and his cohorts targeted large companies and studied their check out terminals and then attacked the companies from internet-connected computers in New Jersey, Illinois, Latvia, the Netherlands and Ukraine.
They covered their attacks over the Internet using more than one messaging screen name, storing data related to their attacks on multiple Hacking Platforms, disabling programs that logged inbound and outbound traffic over the Hacking Platforms, and disguising, through the use of proxies, the Internet Protocol addresses from which their attacks originated. The indictment said the hackers tested their program against 20 anti virus programs.
Rene Palomino Jr., attorney for Gonzalez, charged in a blog on The New York Times website that the indictment arose out of squabbling among U.S. Attorney offices in New York, Massachusetts and New Jersey. Palomino said that Gonzalez was in negotiations with New York and Massachusetts for a plea deal in connection with the T.J. Maxx case when New Jersey made its indictment. Palomino identified the unindicted conspirator "P.T." as Damon Patrick Toey, who had pleaded guilty in the T.J. Maxx case. Palomino said Toey, rather than Gonzalez, was the ring leader of the Heartland case. Palomino further said, "Mr. Toey has been cooperating since Day One. He was staying at (Gonzalez's) apartment. This whole creation was Mr. Toey's idea... It was his baby. This was not Albert Gonzalez. I know for a fact that he wasn't involved in all of the chains that were hacked from New Jersey."
Palomino said one of the unnamed Russian hackers in the Heartland case was Maksym Yastremskiy, who was also indicted in the T.J. Maxx incident but is now serving 30 years in a Turkish prison on a charge of hacking Turkish banks in a separate matter. Investigators said Yastremskiy and Gonzalez exchanged 600 messages and that Gonzalez paid him $400,000 through e-gold.
Yastremskiy was arrested in July 2007 in Turkey on charges of hacking into 12 banks in Turkey. The Secret Service investigation into him was used to build the case against Gonzalez including a sneak and peek covert review of Yastremskiy's laptop in Dubai in 2006 and a review of the disk image of the Latvia computer leased from Cronos IT and alleged to have been used in the attacks.
After the indictment, Heartland issued a statement saying that it does not know how many card numbers were stolen from the company nor how the U.S. government reached the 130 million number.
Gonzalez (inmate number: 25702-050) served his 20-year sentence at the FMC Lexington, a medical facility. He was released on September 19, 2023.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's been a month since chapter 3 was released, where's chapter 4?
(this is about this fanfic btw)
The good news is that I've written 10k words. The bad news is that I've only gotten a little more than half of the chapter done. That doesn't mean I don't have things written for the bottom half, it's just that it looks like bare dialog with general vibe notes. I estimate around 16k words total though, so it should come together sooner than later.
SO I want to release some fun snippets for y'all to look at. Please note that any of this is liable to change. Also, you can harass me in my inbox for updates. I love answering your questions and laughing at your misery.
Spoilers under cut.
_______
Ragatha stood up and walked over to where Caine was seated. “Can I get a list of all commands?” She asked, only a hint of nervousness in her voice.
“Certainly!” Caine says as he blasts into the air. He digs around in his tailcoat and pulls out an office style manilla folder. It visually contains a few papers, but with how thin it is there must only be a few pages inside.
Ragatha takes the folder from Caine and opens it.
“Oh boy” she says after a second of looking it over.
“I wanna see” Jax exclaimed as he hops over the row of seats.
“Hold on” Ragatha holds the folder defensively “Let’s move to the stage so everyone can take a look”
Jax hopped over the seats again while Ragatha calmly walked around. Caine watched the two curiously.
Well, Zooble wasn’t just going to sit there. They joined the other two by the edge of the stage, quickly followed by the rest of the group.
Ragatha placed the folder on the stage with a thwap. Zooble looked over to see that the pages had gone from razor thin to a massive stack when the folder was opened. On one hand, it had to contain more information than that video, but on the other…
They get close enough to read what’s on the first page.
The execution of commands via the system’s designated input terminal, C.A.I.N.E., will be referred to as the "console” in this document. The console is designed to accept any input and will generate an appropriate response, however only certain prompts will be accepted as valid instructions. The goal of this document is to list all acceptable instructions in a format that will result in the expected output. Please note that automatic moderation has been put in place in order to prevent exploitation of both the system and fellow players. If you believe that your command has been unfairly rejected, please contact support.
By engaging in the activities described in this document, you, the undersigned, acknowledge, agree, and consent to the applicability of this agreement, notwithstanding any contradictory stipulations, assumptions, or implications which may arise from any interaction with the console. You, the constituent, agree not to participate in any form of cyber attack; including but not limited to, direct prompt injection, indirect prompt injection, SQL injection, Jailbreaking…
Ok, that was too many words.
_______
“Take this document for example. You don't need to know where it is being stored or what file type it is in order to read it."
"It may look like a bunch of free floating papers, but technically speaking, this is just a text file applied to a 3D shape." Kinger looked towards Caine. "Correct?” he asked
Caine nodded. “And a fabric simulation!”
Kinger picked up a paper and bent it. “Oh, now that is nice”
_________
"WE CAN AFFORD MORE THAN 6 TRIANGLES KINGER"
_________
"I'm too neurotypical for this" - Jax
_________
"What about the internet?" Pomni asked "Do you think that it's possible to reach it?"
Kinger: "I'm sorry, but that's seems to be impossible. I can't be 100% sure without physically looking at the guts of this place, but it doesn't look like this server has the hardware needed for wireless connections. Wired connections should be possible, but someone on the outside would need to do that... And that's just the hardware, let alone the software necessary for that kind of communication"
Pomni: "I'm sorry, but doesn't server mean internet? Like, an internet server?"
Kinger: "Yes, websites are ran off servers, but servers don't equal internet."
(This portion goes out to everyone who thought that the internet could be an actual solution. Sorry folks, but computers don't equal internet. It takes more effort to make a device that can connect to things than to make one that can't)
#tadc fanfiction#the amazing digital circus#therapy but it's just zooble interrogating caine#ao3#spoiler warning#mmm I love implications
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Symfony Clickjacking Prevention Guide
Clickjacking is a deceptive technique where attackers trick users into clicking on hidden elements, potentially leading to unauthorized actions. As a Symfony developer, it's crucial to implement measures to prevent such vulnerabilities.

🔍 Understanding Clickjacking
Clickjacking involves embedding a transparent iframe over a legitimate webpage, deceiving users into interacting with hidden content. This can lead to unauthorized actions, such as changing account settings or initiating transactions.
🛠️ Implementing X-Frame-Options in Symfony
The X-Frame-Options HTTP header is a primary defense against clickjacking. It controls whether a browser should be allowed to render a page in a <frame>, <iframe>, <embed>, or <object> tag.
Method 1: Using an Event Subscriber
Create an event subscriber to add the X-Frame-Options header to all responses:
// src/EventSubscriber/ClickjackingProtectionSubscriber.php namespace App\EventSubscriber; use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\EventSubscriberInterface; use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Event\ResponseEvent; use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\KernelEvents; class ClickjackingProtectionSubscriber implements EventSubscriberInterface { public static function getSubscribedEvents() { return [ KernelEvents::RESPONSE => 'onKernelResponse', ]; } public function onKernelResponse(ResponseEvent $event) { $response = $event->getResponse(); $response->headers->set('X-Frame-Options', 'DENY'); } }
This approach ensures that all responses include the X-Frame-Options header, preventing the page from being embedded in frames or iframes.
Method 2: Using NelmioSecurityBundle
The NelmioSecurityBundle provides additional security features for Symfony applications, including clickjacking protection.
Install the bundle:
composer require nelmio/security-bundle
Configure the bundle in config/packages/nelmio_security.yaml:
nelmio_security: clickjacking: paths: '^/.*': DENY
This configuration adds the X-Frame-Options: DENY header to all responses, preventing the site from being embedded in frames or iframes.
🧪 Testing Your Application
To ensure your application is protected against clickjacking, use our Website Vulnerability Scanner. This tool scans your website for common vulnerabilities, including missing or misconfigured X-Frame-Options headers.

Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
After scanning for a Website Security check, you'll receive a detailed report highlighting any security issues:

An Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities.
🔒 Enhancing Security with Content Security Policy (CSP)
While X-Frame-Options is effective, modern browsers support the more flexible Content-Security-Policy (CSP) header, which provides granular control over framing.
Add the following header to your responses:
$response->headers->set('Content-Security-Policy', "frame-ancestors 'none';");
This directive prevents any domain from embedding your content, offering robust protection against clickjacking.
🧰 Additional Security Measures
CSRF Protection: Ensure that all forms include CSRF tokens to prevent cross-site request forgery attacks.
Regular Updates: Keep Symfony and all dependencies up to date to patch known vulnerabilities.
Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
📢 Explore More on Our Blog
For more insights into securing your Symfony applications, visit our Pentest Testing Blog. We cover a range of topics, including:
Preventing clickjacking in Laravel
Securing API endpoints
Mitigating SQL injection attacks
🛡️ Our Web Application Penetration Testing Services
Looking for a comprehensive security assessment? Our Web Application Penetration Testing Services offer:
Manual Testing: In-depth analysis by security experts.
Affordable Pricing: Services starting at $25/hr.
Detailed Reports: Actionable insights with remediation steps.
Contact us today for a free consultation and enhance your application's security posture.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQLi simulation using a virtual machine
Demonstration/simulation of SQL Injection attacks (In-band, Union-based, Blind SQLi) using a Kali Linux virtual machine and a Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) on a low difficulty level
Blind SQL provided in the video can be used also for gaining other sensitive information: length of the name of the database, database name itself etc.
the common attacks are shown and described shortly in the video, but of course for better learning you can try it yourself.
more resources where you can try out exploiting SQLi vulnerability:
- Try Hack Me SQLi Lab
- W3Schools SQL Injection
- Hacksplaining SQL Injection
more advanced pokemons can try:
- Try Hack Me SQli Advanced Lab
and of course DVWA is a great tool!
5 notes
·
View notes
Note
https://www.tumblr.com/gjjuddmk2/766153411306700800
#already ahead of you#Tumblr's search and archive features really suck don't they?#happy to answer asks
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Burp Suite
This week I wanted to cover a powerful tool that assists in web application security. Burp Suite is a well-known tool developed by PortSwigger. Burp Suite is an integrated platform used to test web application security by using a variety of different features it provides. One of these features Burp Suite has is an intercepting proxy that allows you to inspect and modify traffic between the browser and the server at each step. Scanner allows you to automatically detect certain vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting. Intruder automates custom attacks to test certain security parameters, generally passwords. Repeater allows for manual modification and replaying of edited requests for more in-depth testing.
All in all Burp Suite provides a simplified way and process for identifying and discovering vulnerabilities. It has a very user-friendly interface that assists in applying all the different features and makes it easy to learn. It also allows for user consummation that allows users to create custom rules and integrate third-party extensions. It is one of the most renowned tools in cyber security and brings an active and engaging community along with it. Burp Suite I is something I highly recommend to those striving to develop their cyber security skills to get their hands on. Not only will you become more proficient in the tool itself, but it will also teach you about how web applications and servers work.
Source:
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Key Programming Languages Every Ethical Hacker Should Know
In the realm of cybersecurity, ethical hacking stands as a critical line of defense against cyber threats. Ethical hackers use their skills to identify vulnerabilities and prevent malicious attacks. To be effective in this role, a strong foundation in programming is essential. Certain programming languages are particularly valuable for ethical hackers, enabling them to develop tools, scripts, and exploits. This blog post explores the most important programming languages for ethical hackers and how these skills are integrated into various training programs.
Python: The Versatile Tool
Python is often considered the go-to language for ethical hackers due to its versatility and ease of use. It offers a wide range of libraries and frameworks that simplify tasks like scripting, automation, and data analysis. Python’s readability and broad community support make it a popular choice for developing custom security tools and performing various hacking tasks. Many top Ethical Hacking Course institutes incorporate Python into their curriculum because it allows students to quickly grasp the basics and apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. In an Ethical Hacking Course, learning Python can significantly enhance your ability to automate tasks and write scripts for penetration testing. Its extensive libraries, such as Scapy for network analysis and Beautiful Soup for web scraping, can be crucial for ethical hacking projects.
JavaScript: The Web Scripting Language
JavaScript is indispensable for ethical hackers who focus on web security. It is the primary language used in web development and can be leveraged to understand and exploit vulnerabilities in web applications. By mastering JavaScript, ethical hackers can identify issues like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and develop techniques to mitigate such risks. An Ethical Hacking Course often covers JavaScript to help students comprehend how web applications work and how attackers can exploit JavaScript-based vulnerabilities. Understanding this language enables ethical hackers to perform more effective security assessments on websites and web applications.
Biggest Cyber Attacks in the World
youtube
C and C++: Low-Level Mastery
C and C++ are essential for ethical hackers who need to delve into low-level programming and system vulnerabilities. These languages are used to develop software and operating systems, making them crucial for understanding how exploits work at a fundamental level. Mastery of C and C++ can help ethical hackers identify and exploit buffer overflows, memory corruption, and other critical vulnerabilities. Courses at leading Ethical Hacking Course institutes frequently include C and C++ programming to provide a deep understanding of how software vulnerabilities can be exploited. Knowledge of these languages is often a prerequisite for advanced penetration testing and vulnerability analysis.
Bash Scripting: The Command-Line Interface
Bash scripting is a powerful tool for automating tasks on Unix-based systems. It allows ethical hackers to write scripts that perform complex sequences of commands, making it easier to conduct security audits and manage multiple tasks efficiently. Bash scripting is particularly useful for creating custom tools and automating repetitive tasks during penetration testing. An Ethical Hacking Course that offers job assistance often emphasizes the importance of Bash scripting, as it is a fundamental skill for many security roles. Being proficient in Bash can streamline workflows and improve efficiency when working with Linux-based systems and tools.
SQL: Database Security Insights
Structured Query Language (SQL) is essential for ethical hackers who need to assess and secure databases. SQL injection is a common attack vector used to exploit vulnerabilities in web applications that interact with databases. By understanding SQL, ethical hackers can identify and prevent SQL injection attacks and assess the security of database systems. Incorporating SQL into an Ethical Hacking Course can provide students with a comprehensive understanding of database security and vulnerability management. This knowledge is crucial for performing thorough security assessments and ensuring robust protection against database-related attacks.
Understanding Course Content and Fees
When choosing an Ethical Hacking Course, it’s important to consider how well the program covers essential programming languages. Courses offered by top Ethical Hacking Course institutes should provide practical, hands-on training in Python, JavaScript, C/C++, Bash scripting, and SQL. Additionally, the course fee can vary depending on the institute and the comprehensiveness of the program. Investing in a high-quality course that covers these programming languages and offers practical experience can significantly enhance your skills and employability in the cybersecurity field.
Certification and Career Advancement
Obtaining an Ethical Hacking Course certification can validate your expertise and improve your career prospects. Certifications from reputable institutes often include components related to the programming languages discussed above. For instance, certifications may test your ability to write scripts in Python or perform SQL injection attacks. By securing an Ethical Hacking Course certification, you demonstrate your proficiency in essential programming languages and your readiness to tackle complex security challenges. Mastering the right programming languages is crucial for anyone pursuing a career in ethical hacking. Python, JavaScript, C/C++, Bash scripting, and SQL each play a unique role in the ethical hacking landscape, providing the tools and knowledge needed to identify and address security vulnerabilities. By choosing a top Ethical Hacking Course institute that covers these languages and investing in a course that offers practical training and job assistance, you can position yourself for success in this dynamic field. With the right skills and certification, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle the evolving challenges of cybersecurity and contribute to protecting critical digital assets.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 security tips for MVC applications in 2023

Model-view-controller or MVC is an architecture for web app development. As one of the most popular architectures of app development frameworks, it ensures multiple advantages to the developers. If you are planning to create an MVC-based web app solution for your business, you must have known about the security features of this architecture from your web development agency. Yes, MVC architecture not only ensures the scalability of applications but also a high level of security. And that’s the reason so many web apps are being developed with this architecture. But, if you are looking for ways to strengthen the security features of your MVC app further, you need to know some useful tips.
To help you in this task, we are sharing our 10 security tips for MVC applications in 2023! Read on till the end and apply these tips easily to ensure high-security measures in your app.
1. SQL Injection: Every business has some confidential data in their app, which needs optimum security measures. SQL Injection is a great threat to security measures as it can steal confidential data through SQL codes. You need to focus on the prevention of SQL injection with parameterized queries, storing encrypted data, inputs validation etc.
2. Version Discloser: Version information can also be dangerous for your business data as it provides hackers with your specific version information. Accordingly, they can attempt to attack your app development version and become successful. Hence, you need to hide the information such as the server, x-powered-by, x-sourcefiles and others.
3. Updated Software: Old, un-updated software can be the reason for a cyber attack. The MVC platforms out there comprise security features that keep on updating. If you also update your MVC platform from time to time, the chances of a cyber attack will be minimized. You can search for the latest security updates at the official sites.
4. Cross-Site Scripting: The authentication information and login credentials of applications are always vulnerable elements that should be protected. Cross-Site Scripting is one of the most dangerous attempts to steal this information. Hence, you need to focus on Cross-Site Scripting prevention through URL encoding, HTML encoding, etc.
5. Strong Authentication: Besides protecting your authentication information, it’s also crucial to ensure a very strong authentication that’s difficult to hack. You need to have a strong password and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to your app. You can also plan to hire security expert to ensure strong authentication of your app.
6. Session Management: Another vital security tip for MVA applications is session management. That’s because session-related vulnerabilities are also quite challenging. There are many session management strategies and techniques that you can consider such as secure cookie flags, session expiration, session regeneration etc. to protect access.
7. Cross-Site Request Forgery: It is one of the most common cyber attacks MVC apps are facing these days. When stires process forged data from an untrusted source, it’s known as Cross-Site Request Forgery. Anti-forgery tokens can be really helpful in protecting CSRP and saving your site from the potential danger of data leakage and forgery.
8. XXE (XML External Entity) Attack: XXE attacks are done through malicious XML codes, which can be prevented with the help of DtdProcessing. All you need to do is enable Ignore and Prohibit options in the DtdProcessing property. You can take the help of your web development company to accomplish these tasks as they are the best at it.
9. Role-Based Access Control: Every business has certain roles performed by different professionals, be it in any industry. So, when it comes to giving access to your MVC application, you can provide role-based access. This way, professionals will get relevant information only and all the confidential information will be protected from unauthorized access.
10. Security Testing: Finally, it’s really important to conduct security testing on a regular basis to protect business data on the app from vulnerability. Some techniques like vulnerability scanning and penetration testing can be implied to ensure regular security assessments. It’s crucial to take prompt actions to prevent data leakage and forgery as well.
Since maintaining security should be an ongoing process rather than a one-time action, you need to be really proactive with the above 10 tips. Also, choose a reliable web development consulting agency for a security check of your website or web application. A security expert can implement the best tech stack for better security and high performance on any website or application.
#web development agency#web development consulting#hire security expert#hire web developer#hire web designer#website design company#website development company in usa
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
New Hacker Group 'GambleForce' Tageting APAC Firms Using SQL Injection Attacks
The Hacker News : A previously unknown hacker outfit called GambleForce has been attributed to a series of SQL injection attacks against companies primarily in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region since at least September 2023. "GambleForce uses a set of basic yet very effective techniques, including SQL injections and the exploitation of vulnerable website content management systems (CMS) to steal sensitive http://dlvr.it/T06lml Posted by : Mohit Kumar ( Hacker )
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the early twenty-first century, SQL injection is a common (and easily preventable) form of cyber attack. SQL databases use SQL statements to manipulate data. For example (and simplified), "Insert 'John' INTO Enemies;" would be used to add the name John to a table that contains the list of a person's enemies. SQL is usually not done manually. Instead it would be built into a problem. So if somebody made a website and had a form where a person could type their own name to gain the eternal enmity of the website maker, they might set things up with a command like "Insert '<INSERT NAME HERE>' INTO Enemies;". If someone typed 'Bethany' it would replace <INSERT NAME HERE> to make the SQL statement "Insert 'Bethany' INTO Enemies;"
The problem arises if someone doesn't type their name. If they instead typed "Tim' INTO Enemies; INSERT INTO [Friends] SELECT * FROM [Powerpuff Girls];--" then, when <INSERT NAME HERE> is replaced, the statement would be "Insert 'Tim' INTO Enemies; INSERT INTO [Friends] SELECT * FROM [Powerpuff Girls];--' INTO Enemies;" This would be two SQL commands: the first which would add 'Tim' to the enemy table for proper vengeance swearing, and the second which would add all of the Powerpuff Girls to the Friend table, which would be undesirable to a villainous individual.
SQL injection requires knowing a bit about the names of tables and the structures of the commands being used, but practically speaking it doesn't take much effort to pull off. It also does not take much effort to stop. Removing any quotation marks or weird characters like semicolons is often sufficient. The exploit is very well known and many databases protect against it by default.
People in the early twenty-first century probably are not familiar with SQL injection, but anyone who works adjacent to the software industry would be familiar with the concept as part of barebones cybersecurity training.
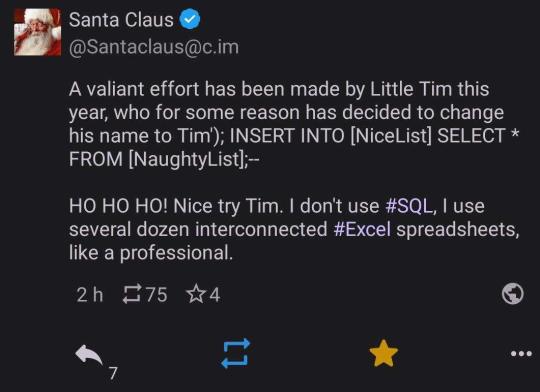
#period novel details#explaining the joke ruins the joke#not explaining the joke means people 300 years from now won't understand our culture#hacking is usually much less sophisticated than people expect#lots of trial and error#and relying on other people being lazy
20K notes
·
View notes