#lao shu
Text
Elena, in the hospital trying to recover from the Lao Shu’s attempt on her life whilst being guarded by the Falzone:

5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lao Cha Tou (老茶头) means "Old Tea Heads". It's a particular type of cooked pu-erh – fermented tea common in China. It comes in the form of small lumps and is the result of agglomeration during the pile-fermentation processing of Pu-erh tea. Compared with loose-leaf tea, Lao Cha Tou is richer in content and far more resistant to brewing. As a result, it releases thicker and denser tea liquor.


8 notes
·
View notes
Text

the lao shu family is honestly my favourite because they are so disruptive to others and each other and with the exception of yuans nature and lees actions in yangs route i just love their dynamics. i love how yang truly loves the twins as it shows a lot of times (yang cooked for them in the past. yang saved them. yang trusting the twins. yang closing their eyes as salvation in the tragic end. yang teaching the twins how to fight). lee is actually a nagging housewife but hes loyal to yang and does care abt the twins in his own way. rui is so relaxed and hes like this chill big brother whos also loyal to yang in yangs route and a lil troublemaker to match the twins. yuan is a dick but hes the most loved villain in this sequel lmao
also adult fei 👁👄👁 piofiore 3rd game where its 10 years later and he falls for the next key maiden. he has tht siscon going on but thats surprisingly his sweet side to balance out his ruthless nature thanks to papa yang (aka 1st commander nw knowing him) lan and fei being the 6th comnanders and fei going thru the pain n struggle of what yang went thru to get lili
#adult fei in general....rawr#adult lan is so PRETTY thats a pretty lady right there#lmaooo lee being bullied by rui its so cute#love tht yuan still protects yang in the alt route. i knw he has his selfish intentions bt coming from yuan its cute hehe#lao shu fam my beloved. they will protect lili#fafar plays piofiore 1926
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Love in Disguise- Bruce gets strange advice from an old man. (3400+ words)

Another one of the V-Day themed fics! 💖
Shu Chan belongs to @kururu418 !
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
-kicking my feet as i read through the tian xia world guide at work- teehee
#i love how hei feng is an asshole husband but still wont allow anyone to disrespect lady jingxi (his estranged wife)#love how lao shu po used to be a normal rat but she went 'fuck this' and ate a piece of a gods flesh in order to ascend#love how quain exists#bachuqq blabs
1 note
·
View note
Text
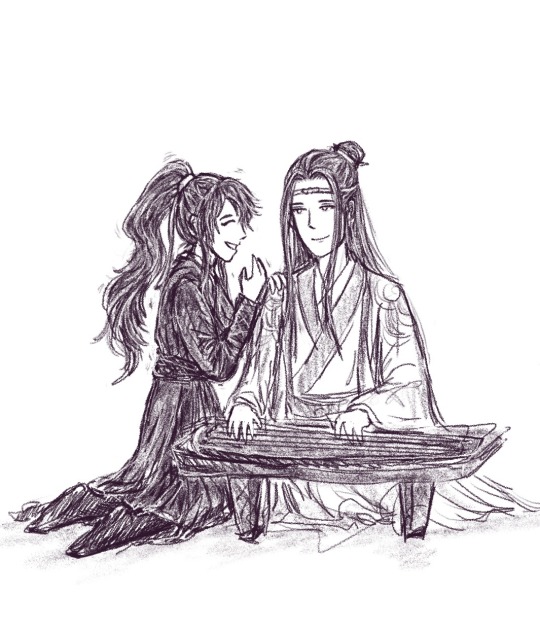
Watching fan MV of the Untamed with the song Lao Shu Ai Da Mi( 老鼠爱大米 ) and thinking that they are so cute with this song so I had the urge to draw them!
#forgive me idk how to draw people playing gu qin and the reference on google doesn’t enlighten me lol#messy doodle#wei wuxian#lan wangji#mo dao zu shi#the untamed#danmei#mxtx#fanart#wangxian#mdzs#also this song is the one my chinese teacher from long ago taught me to sing as inspiration for learning chinese
57 notes
·
View notes
Text

Footnotes
[1] Ie-hovah, and in composition Iah, the Being; Iao, ioupitur, same meaning; ha-iah, Heb., he was; ei, Gr, he is, ei-nai, to be; an-i, Heb., and in conjugation th-i, me; e-go, io, ich, i, m-i, me, t-ibi, te, and all the personal pronouns in which the vowels i, e, ei, oi, denote personality in general, and the consonants, m or n, s or t, serve to indicate the number of the person. For the rest, let who will dispute over these analogies; I have no objections: at this depth, the science of the philologist is but cloud and mystery. The important point to which I wish to call attention is that the phonetic relation of names seems to correspond to the metaphysical relation of ideas.
[2] The Chinese have preserved in their traditions the remembrance of a religion which had ceased to exist among them five or six centuries before our era. (See Pauthier, “China,” Paris, Didot.) More surprising still is it that this singular people, in losing its primitive faith, seems to have understood that divinity is simply the collective me of humanity: so that, more than two thousand years ago, China had reached, in its commonly-accepted belief, the latest results of the philosophy of the Occident. “What Heaven sees and understands,” it is written in the Shu-king, “is only that which the people see and understand. What the people deem worthy of reward and punishment is that which Heaven wishes to punish and reward. There is an intimate communication between Heaven and the people: let those who govern the people, therefore, be watchful and cautious.” Confucius expressed the same idea in another manner: “Gain the affection of the people, and you gain empire. Lose the affection of the people, and you lose empire.” There, then, general reason was regarded as queen of the world, a distinction which elsewhere has been bestowed upon revelations. The Tao-te-king is still more explicit. In this work, which is but an outline criticism of pure reason, the philosopher Lao-tse continually identifies, under the name of TAO, universal reason and the infinite being; and all the obscurity of the book of Lao tse consists, in my opinion, of this constant identification of principles which our religious and metaphysical habits have so widely separated.
[3] See, among others, Auguste Comte, “Course of Positive Philosophy,” and P. J. Proudhon, “Creation of Order in Humanity.”
[4] I do not mean to affirm here in a positive manner the transmutability of bodies, or to point it out as a subject for investigation; still less do I pretend to say what ought to be the opinion of savants upon this point. I wish only to call attention to the species of scepticism generated in every uninformed mind by the most general conclusions of chemical philosophy, or, better, by the irreconcilable hypotheses which serve as the basis of its theories. Chemistry is truly the despair of reason: on all sides it mingles with the fanciful; and the more knowledge of it we gain by experience, the more it envelops itself in impenetrable mysteries. This thought was recently suggested to me by reading M. Liebig’s “Letters on Chemistry” (Paris, Masgana, 1845, translation of Bertet-Dupiney and Dubreuil Helion).
Thus M. Liebig, after having banished from science hypothetical causes and all the entities admitted by the ancients, — such as the creative power of matter, the horror of a vacuum, the esprit recteur, etc. (p. 22), — admits immediately, as necessary to the comprehension of chemical phenomena, a series of entities no less obscure, — vital force, chemical force, electric force, the force of attraction, etc. (pp. 146, 149). One might call it a realization of the properties of bodies, in imitation of the psychologists’ realization of the faculties of the soul under the names liberty, imagination, memory, etc. Why not keep to the elements? Why, if the atoms have weight of their own, as M. Liebig appears to believe, may they not also have electricity and life of their own? Curious thing! the phenomena of matter, like those of mind, become intelligible only by supposing them to be produced by unintelligible forces and governed by contradictory laws: such is the inference to be drawn from every page of M. Liebig’s book.
Matter, according to M. Liebig, is essentially inert and entirely destitute of spontaneous activity (p. 148): why, then, do the atoms have weight? Is not the weight inherent in atoms the real, eternal, and spontaneous motion of matter? And that which we chance to regard as rest, — may it not be equilibrium rather? Why, then, suppose now an inertia which definitions contradict, now an external potentiality which nothing proves?
Atoms having weight, M. Liebig infers that they are indivisible (p. 58). What logic! Weight is only force, that is, a thing hidden from the senses, whose phenomena alone are perceptible, — a thing, consequently, to which the idea of division and indivision is inapplicable; and from the presence of this force, from the hypothesis of an indeterminate and immaterial entity, is inferred an indivisible material existence!
For the rest, M. Liebig confesses that it is impossible for the mind to conceive of particles absolutely indivisible; he recognizes, further, that the fact of this indivisibility is not proved; but he adds that science cannot dispense with this hypothesis: so that, by the confession of its teachers, chemistry has for its point of departure a fiction as repugnant to the mind as it is foreign to experience. What irony!
Atoms are unequal in weight, says M. Liebig, because unequal in volume: nevertheless, it is impossible to demonstrate that chemical equivalents express the relative weight of atoms, or, in other words, that what the calculation of atomic equivalents leads us to regard as an atom is not composed of several atoms. This is tantamount to saying that more matter weighs more than less matter; and, since weight is the essence of materiality, we may logically conclude that, weight being universally identical with itself, there is also an identity in matter; that the differences of simple bodies are due solely, either to different methods of atomic association, or to different degrees of molecular condensation, and that, in reality, atoms are transmutable: which M. Liebig does not admit.
“We have,” he says, “no reason for believing that one element is convertible into another element” (p. 135). What do you know about it? The reasons for believing in such a conversion can very well exist and at the same time escape your attention; and it is not certain that your intelligence in this respect has risen to the level of your experience. But, admitting the negative argument of M. Liebig, what follows? That, with about fifty-six exceptions, irreducible as yet, all matter is in a condition of perpetual metamorphosis. Now, it is a law of our reason to suppose in Nature unity of substance as well as unity of force and system; moreover, the series of chemical compounds and simple substances themselves leads us irresistibly to this conclusion. Why, then, refuse to follow to the end the road opened by science, and to admit an hypothesis which is the inevitable result of experience itself?
M. Liebig not only denies the transmutability of elements, but rejects the spontaneous formation of germs. Now, if we reject the spontaneous formation of germs, we are forced to admit their eternity; and as, on the other hand, geology proves that the globe has not been inhabited always, we must admit also that, at a given moment, the eternal germs of animals and plants were born, without father or mother, over the whole face of the earth. Thus, the denial of spontaneous generation leads back to the hypothesis of spontaneity: what is there in much-derided metaphysics more contradictory
Let it not be thought, however, that I deny the value and certainty of chemical theories, or that the atomic theory seems to me absurd, or that I share the Epicurean opinion as to spontaneous generation. Once more, all that I wish to point out is that, from the point of view of principles, chemistry needs to exercise extreme tolerance, since its own existence depends on a certain number of fictions, contrary to reason and experience, and destructive of each other.
[5] Chemists distinguish between mixture and composition, just as logicians distinguish between the association of ideas and their synthesis. It is true, nevertheless, that, according to the chemists, composition may be after all but a mixture, or rather an aggregation of atoms, no longer fortuitous, but systematic, the atoms forming different compounds by varying their arrangement. But still this is only an hypothesis, wholly gratuitous; an hypothesis which explains nothing, and has not even the merit of being logical. Why does a purely numerical or geometrical difference in the composition and form of atoms give rise to physiological properties so different? If atoms are indivisible and impenetrable, why does not their association, confined to mechanical effects, leave them unchanged in essence? Where is the relation between the cause supposed and the effect obtained?
We must distrust our intellectual vision: it is with chemical theories as with psychological systems. The mind, in order to account for phenomena, works with atoms, which it does not and can never see, as with the me, which it does not perceive: it applies its categories to everything; that is, it distinguishes, individualizes, concretes, numbers, compares, things which, material or immaterial, are thoroughly identical and indistinguishable. Matter, as well as spirit, plays, as we view it, all sorts of parts; and, as there is nothing arbitrary in its metamorphoses, we build upon them these psychologic and atomic theories, true in so far as they faithfully represent, in terms agreed upon, the series of phenomena, but radically false as soon as they pretend to realize their abstractions and are accepted literally.
[6] The passage quoted may not be given in the exact words used by Malthus, it having reached its present shape through the medium of a French rendering — Translator.
[7] “The principle which governs the life of nations is not pure science: it is the total of the complex data which depend on the state of enlightenment, on needs and interests.” Thus expressed itself, in December, 1844, one of the clearest minds that France contained, M. Leon Faucher. Explain, if you can, how a man of this stamp was led by his economic convictions to declare that the complex data of society are opposed to pure science.
[8] “History of Public Credit.”
[9] In France, the sale of tobacco is a government monopoly. — Translator.
[10] A subtle philologist, M. Paul Ackermann, has shown, using the French language as an illustration, that, since every word in a language has its opposite, or, as the author calls it, its antonym, the entire vocabulary might be arranged in couples, forming a vast dualistic system. (See Dictionary of Antonyms. By PAUL ACKERMAN. Paris: Brockhaus & Avenarius. 1842)
[11] “Treatise on Political Economy.”
[12] Tocqueville, “Democracy in America.”
[13] Meeting of the Academy of Moral and Political Sciences, September, 1845.
[14] Journal des Economistes,” April, 1843.
[15] “The Liberty of Labor,” Vol. II, p. 80.
[16] In spite of the most approved authorities, I cannot accept the idea that serf, in Latin servus, was so called from servare, to keep, because the slave was a prisoner of war who was kept for labor. Servitude, or at least domesticity, is certainly prior to war, although war may have noticeably strengthened it. Why, moreover, if such was the origin of the idea as well as of the thing, should they not have said, instead of serv-us, serv-atus, in conformity with grammatical deduction? To me the real etymology is revealed in the opposition of serv-are and serv-ire, the primitive theme of which is ser-o in-stro, to join, to press, whence ser-ies, joint, continuity, Ser-a, lock, sertir, insert, etc. All these words imply the idea of a principal thing, to which is joined an accessory, as an object of special usefulness. Thence serv-ire, to be an object of usefulness, a thing secondary to another; serv-are, as we say to press, to put aside, to assign a thing its utility; serv-us, a man at hand, a utility, a chattel, in short, a man of service. The opposite of servus is dem-inus (dom-us, dom-anium, and domare); that is, the head of the household, the master of the house, he who utilizes men, servat, animals, domat, and things, possidet.That consequently prisoners of war should have been reserved for slavery, servati ad servitium, or rather serti ad glebam, is perfectly conceivable; their destiny being known, they have simply taken their name from it.
[17] A comparison of this passage, as given here, with the English translation of “What is Property” will show a marked variation in the language. This is explained by the fact that the author, in reproducing the passage, modified it considerably. The same is true of another quotation from the same work which will be found a few pages farther on. — Translator.
[18] This extract from Scott, as well as that from a parliamentary report cited a few paragraphs later, is here translated from the French, and presumably differs in form somewhat, therefore, from the original English. — Translator.
[19] The spinning-wheel is silent in the valley: family feelings are at an end. Over a little smoke the aged grandsire spreads his pale hands; and the empty hearth is as desolate as his heart. — Translator.
[20] Possibly these paragraphs will not be clear to all without the explanation that the form of association discussed in them, called in French the commandite, is a joint-stock company to which the shareholders simply lend their capital, without acquiring a share in the management or incurring responsibility for the results thereof. — Translator.
[21] Hunting, fishing, mining, — in short, the gathering of all natural products. — Translator.
[22] Little bones taken from the joints of animals and serving as playthings for children. — Translator.
[23] A tax whose total product is not fixed in advance, but depends upon the quantity of things or persons upon whom it happens to fall. — Translator.
[24] This sentence, as it stands, is unintelligible, and probably is not correctly quoted by Proudhon. At any rate, one of Garnier’s works contains a similar passage, which begins thus: “Given a levy of one on the area of the land, and lands of different qualities producing, the first eight, the second six, the third five, the tax will call for one-eighth,” etc. This is perfectly clear, and the circumstances supposed are aptly illustrative of Proudhon’s point. I should unhesitatingly pronounce it the correct version, except for the fact that Proudhon, in the succeeding paragraph, interprets Garnier as supposing income to be assessed instead of capital. — Translator.
[25] Thank heaven! the minister has settled the question, and I tender him my very sincere compliments. By the proposed tariff letter-postage will be reduced to 2 cents for distances under 12 1/2 miles; 4 cents, for distances between 12 1/2 and 25 miles; 6 cents, between 25 and 75 miles; 8 cents, between 75 and 225 miles; 10 cents, for longer distances.]
[26] The new law regarding service-books has confined the independence of workers within narrower limits. The democratic press has again thundered its indignation this subject against those in power, as if they had been guilty of anything more than the application of the principles of authority and property, which are those of democracy. What the Chambers have done in regard to service-books was inevitable, and should have been expected. It is as impossible for a society founded on the proprietary principle not to end in class distinctions as for a democracy to avoid despotism, for a religion to be reasonable, for fanaticism to show tolerance. This is the law of contradiction: how long will it take us to understand it?
[27] The crime makes the shame, and not the scaffold. — Translator.
[28] See volume II, chapter IX.
[29] Ibid., chapter X.
[30] Ibid., chapter XI.
[31] Date of the Napoleonic coup d’Etat, according to the revolutionary calendar.
[32] The Metaphysics of Morals [1.11]
[33] The Metaphysics of Morals 1.15. (Editor).
[34] “I possess because I possess”; “I possess because you possess” (Editor)
[35] A coupon is the amount of interest paid per year expressed as a percentage of the face value of a bond. A bond is, in finance, a debt security in which the issuer is the borrower (debtor) and the holder is the lender (creditor). (Editor)
[36] Proudhon writes “Il était le courtisan de la terre.” Courtesan historically referred to a courtier. However, these were often considered as insincere, skilled at flattery and intrigue, ambitious and lacking regard for the national interest and so, in French, courtesan figuratively means “sycophant.” (Editor)
[37] Proudhon is alluding to the Latin phrase “conubio iungam stabili propriamque dicabo” from Virgil’s epic, The Aeneid (4.126), in which the goddess Juno proposes to “consecrate” the passion of Dido for Aeneas through marriage, turning unstable passion into a stable bond of property. (Editor)
[38] Artaxerxes I was king of the Persian Empire from 464 BC to 424 BC. After Persia had been defeated at Eurymedon, Artaxerxes began to weaken the Athenians by funding their enemies in Greece. (Editor)
[39] Vincent de Paul (1581-1660) was a Catholic priest dedicated to serving the poor. He was canonised in 1737. (Editor)
[40] Harpagon was the name of the miser in Molière's comedy L'Avare (The Miser) (Editor)
[41] Perrin Dandin is a simple citizen in François Rabelais’ Third Book. He seats himself as a judge and passes offhand judgements in any matter of litigation. (Editor)
[42] Bertrand du Guesclin (1320-80), known as the Eagle of Brittany, was a Breton knight and French military commander during the Hundred Years' War. (Editor)
[43] This is an allusion to tradesmen who owned their own tools and took them in a bag or sack (“sac”) when they were dismissed from employment. Hence the expression “get the sack” which is derived from the 17th century French expression “On luy a donné son sac.” (Editor)
[44] There is a play-on-words in Proudhon’s “Chacun de vous porte dans son sac la verge qui sert à le corriger, et qui peut lui servir un jour à corriger les autre.” Corriger as well as meaning “to correct” also means “to give a good hiding to” or “to punish.” (Editor)
[45] Proudhon wrote: “Vous ne serez libres qu'après vous être rachetés, par l'asservissement de vos maîtres, de la servitude qu’ils font peser sur vous.” Racheter as well as meaning “to atone for” or “to redeem” also means “to buy” and he plays with this dual meaning. (Editor)
[46] “Thus I wish. Thus I command” (Editor)
[47] Licitation is sale to the highest bidder. (Translator)
[48] From the Latin Bible: “Jesus said to him: Thou shalt love the Lord thy God with thy whole heart and with thy whole soul and with thy whole mind. This is the first and greatest commandment.” (Matthew 22:37-38). (Editor)
[49] A form of long-term lease that was an institution of Roman law (although derived from the Greek law) and found in French law. An owner of poorly cultivated land granted such leases so that a tenant would take on the task of improving the land. The tenant paid a small rent or canon for this right and the owner regained the land in its improved condition after a number of years. (Editor)
[50] See [Raymond-Théodore] Troplong, Contrat de Louage [Rental Contracts], volume 1st, in which he argues, alone among all the jurisconsults who are his precursors and contemporaries, and with reason, as we think, that in renting, the tenant acquires a right in the thing, and that the lease gives way immediately to a real and personal share.
[51] “even as though some force tearing earth apart should unlock the infernal house, and disclose the pallid realms abhorred of heaven, and deep down the monstrous gulf be descried where the ghosts flutter in the streaming daylight.” (Virgil, The Aeneid of Virgil [MacMillan and Co. Ltd: London, 1920], Translated by J. W. Mackail, Eighth Book, 178). (Editor)
[52] In Kantian philosophy, a thing as it is in itself, as distinct from a thing as it is knowable by the senses through phenomenal attributes. (Editor)
[53] Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations, Volume 1, Book I, Chapter 5, 34-5. The original text is used where appropriate, although Proudhon quotes a French translation which differs somewhat from the original. (Editor)
[54] Smith, Volume 1, Book 1, Chapter VI, 54-5. (Editor)
[55] Smith, Volume 1, Book 1, Chapter 6, 56. As before, Proudhon is quoting from a French translation and this ends with the words “Il faut qu'il paie pour avoir la permission. de les recueillir; c'est-à-dire qu'il paie au propriétaire une portion de ce qu'il recueille ou de ce qu'il produit, sans lui, par son travail”: “He must pay to have permission to collect them; that is to say, he pays the landlord a portion of what he collects or produces, without him, by his labour.” (Editor)
[56] A combination and slight re-organising of selections from The Wealth of Nations. The first sentence is from Volume 1, Book 1, Chapter 6 (57) while the rest is from Volume 1, Book 1, Chapter 9, with the second sentence originally appearing at the end of the rest of the passage. (110, 109-10). (Editor)
[57] In chapter VII, Proudhon writes of “great family of preventive, coercive, repressive, and vindictive institutions which A. Smith designated by the generic term police.” In other words, State power. (Editor)
[58] A paraphrase of Adam Smith: “the law, besides, authorises, or at least does not prohibit their combinations, while it prohibits those of the workmen […] Masters are always and everywhere in a sort of tacit, but constant and uniform combination, not to raise the wages of labour above their actual rate. To violate this combination is everywhere a most unpopular action, and a sort of reproach to a master among his neighbours and equals […] The masters upon these occasions are just as clamorous upon the other side, and never cease to call aloud for the assistance of the civil magistrate, and the rigorous execution of those laws which have been enacted with so much severity against the combinations of servants, labourers, and journeymen.” (Volume 1, Part 1, Chapter 8, 74-6). (Editor)
[59] Smith, Volume 1, Book I, Chapter VIII, 72. Indicators of missing sentences have been added. (Editor)
[60] Hodgskins, Volume 1, Book 1, Chapter X, Recherches sur la nature et les causes de la richesse des nations (Paris: Chez Guillaumin Libraire, 1843), 132. (Editor)
[61] Smith, Volume 1, Book 1, Chapter 8, 88. (Editor)
#organization#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#anarchy#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk#anti colonialism#mutual aid#the system of economic contradictions#the philosophy of poverty#volume i#pierre-joseph proudhon#pierre joseph proudhon
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
List of all 144 Espers in Dislyte (alphabetized)
Abigail (Frigga)
Adrina (Chantico)
Ahmed (Geb)
Ain (Ptah)
Alexa (Aphrodite)
Alice (Gullveig)
Alolin (Pazuzu)
Anesidora (Pandora)
Anna (Persphone)
Arcana (Hermes)
Archibald (Mictlantecutli)
Asenath (Nefertem)
Ashley (Heimdall)
Aurelius (Ullr)
Bai Liuli (White Snake)
Bardon (Baldr)
Berenice (Bastet)
Biondina (Poseidon)
Bonnie (Eris)
Brewster (Garmr)
Brynn (Valkyrie)
Camille (Hati)
Cang Ji (Cang Jie)
Catherine (Hela)
Cecilia (Isis)
Celine (Siren)
Chalmers (Idun)
Chang Pu (Yao Ji)
Chloe (Medea)
Chu Yao (Tai Yi)
Clara (Hera)
Daniel (Charon)
David (Jason)
Daylon (Sobek)
Dhalia (Calypso)
Djoser (Atum)
Donar (Thor)
Drew (Anubis)
Eira (Freya)
Elaine (Nyx)
Elliot (Thoth)
Embla (Ymir)
Emma (Jade Rabbit)
Ethan (Pan)
Everett (Tyr)
Fabrice (Freyr)
Falken (Horus)
Farrah | Aminah (Tiamat | Abzu)
Fatum Sisters (Nornir)
Feng Nuxi (Nuwa)
Feng Xun (Fu Xi)
Freddy (Fenrir)
Fu Shi (Suan Ni)
Fumitsuki (Kaguya-hime)
Gabrielle (Njord)
Gaius (Zeus)
Ginny (Hestia)
Hailey (Hephaestus)
Hall (Hodur)
Helena (Helen)
Heng Yue (Chang’e)
Hilda (Hypnos)
Hyde (Hades)
Ife (Meretseger)
Ikki (Tsukuyomi)
Intisar (Kauket)
Jacob (Jormungand)
Javid (Shamash)
Jeanne (Gerd)
Jiang Jiuli (Chiyou)
Jiang Man (Meng Po)
Jin Qiu (Ru SHou)
Jin Yuyao (Queen Mother)
Jin-Hee (Dokkaebi)
Kara (Serket)
Kaylee (Anuket)
Koharu (Ame No Uzume)
Laura (Neith)
Lauren (Heket)
Layla (Medjed)
Leon (Vali)
Leora (Athena)
Lewis (Ares)
Li Ao (Tao Tie)
Li Guang (Vermilion Bird)
Li Ling (Nezha)
Liam (Xolotl)
Lian (Jiao Tu)
Lin Xiao (White Tiger)
Long Mian (Ao Bing)
Lucas (Apollo)
Luo Yan (Yanluo Wang)
Lu Yi (Dayi)
Lynn (Hathor)
Mateo (Prometheus)
Mavis (Mictecacihuatl)
Mei (Kaya-no-Hime)
Melanie (Medusa)
Meredith (Scylla)
Mona (Artemis)
Narmer (Ra)
Nick (Magni)
Nicole (Nephthys)
Norah (The Muses)
Odette (Skadi)
Ollie (Osiris)
Ophelia (Thanatos)
Parmi (Ninsun)
Pritzker (Mimir)
Q (Eros)
Raven (Odin)
Ren Si (Black Tortoise)
Sachiko (Hare of Inaba)
Sally (Sif)
Sander (Set)
Sienna (Gaia)
Stewart (Dionysus)
Su Jue (Daji)
Tang Xuan (Sun Wukong)
Tang Yun (Six-Eared Macaque)
Taylor (Hercules)
Tevor (Sphinx)
Tiye (Nut)
Toland (Tezcatlipoca)
Triki (Loki)
Uday (Sopdet)
Unas (Shu)
Unky Chai (Yue Lao)
Valeria (QUetzalcoatl)
Wu You (Dijiang)
Xiao Yin (Azure Dragon)
Xie Chuyi (Death Guard Hei)
Xie Yuzhi (Death Guard Bai)
Xuan Pin (Jiutian Xuannu)
Yalina (Mamitu)
Yamato (Izanagi)
Ye Suhua (Shao Siming)
Yu Ran (Bai Ze)
Yu Xu (Jing Wei)
Yun Chuan (Yang Jian)
Yuuhime (Izanami)
Zelmer (Sekhmet)
Zhong Nan (Zhong Kui)
Zora (Amunet)
#I’m excited for the popularity poll thing we have coming up#I’ll probably repost this list with less characters when the first elimination round ends#dislyte
15 notes
·
View notes
Text




I finished Piofiore: Episodio 1926 on Nintendo Switch a while ago. I enjoyed it a lot and it might be the best otome game I've played so far. There's a beefy amount of content in Episodio 1926 - I reached 100% completion in 70 hours. There's 6 love interest routes, each with two endings. In addition there's an "Alternativa" story route.
In this sequel we return to the city of Burlone, Italy. The game continues from the events of Piofiore: Fated Memories. The three competing mafia families Falzone, Visconti and Lao-Shu still hold control in the city but are facing an uncertain future due to political developments in the country. A religious relic has been stolen and the mafia families must join forces to fight a common threat. The protagonist Lili has a special role in the events as many parties' interests relate to her.
This time you can freely choose from a menu which character's route you want to start playing (with exception of one that unlocks only after playing through the Alternativa story).


The story was pretty good and as a whole I liked it more than the first game. Episodio 1926 had its share of sleep inducing routes but some were really good. Nicola's and Orlok's routes with great story/lore portions rose above the others in my eyes. I recall Gilbert's route had some good stuff too. There was a decent amount of historical references and a lot of nice action scenes too.
I especially enjoyed the parts with depictions of violence and murder - which I assume is usually not the reason someone would pick a game of this genre. If you're into that kind of content too, Piofiore is a nice pick.
At times it felt like the flow of the story/dialogue was interrupted with "Aria" (flashbacks from the prior game) and "Meanwhile" stories too frequently.


The dialogue was written nicely and I enjoyed the exchanges between the competing mafiosos. They're sort of friends, yet enemies and it creates some delightful dynamics and humor.
However, there was one specific part in dialogue that felt out of place: Dante being worried that they possibly couldn't violate on someone's human rights. It made him look like a hypocrite - I've seen what happens in the Falzone basement. Henri's route had some really ridiculous dialogue that made me and my husband laugh in disbelief. Henri apparently thinks he's hung like an elephant.

The characters got a lot more depth in the sequel and Nicola ended up surprising me. I didn't care for him much in the previous game but here he got to shine. His actions really highlighted his intelligence and I liked his playful, mischievous attitude. In that regard he is similar to Yang who likes to rile up others for his entertainment. Yang is still Yang (thankfully) but he was a lot more docile here. Still an entertaining character and my favorite out of the love interests. Gilbert was my husband's favorite.
Lili is still a kind-hearted damsel in distress but she's got the smarts to navigate difficult situations. She overcomes her fears and is ready to act to defend herself and the people she cares for.



What comes to side characters, there are plenty of new ones along with returning characters. They help build the lore and world by expanding on past and current events. Emilio's motives and backstory was a very welcome addition to the game as he was a mystery that intriqued me already in the first game.
I liked all of the character designs and Lan ended up being my favorite side character with her energetic attitude. There was one particularly funny/good moment where Lili was upset with Yang and Lan got upset on her behalf too and encouraged Lili to display her irritation and act on it. That actually led to a heartfelt scene with some nice character development as well.



The Japanese voice acting for the characters is top notch and helps flesh out the characters' personalities. Emilio's and Yuan's voices annoyed my husband, haha. Gilbert's "yo Dante!" will forever live in our heads. Unfortunately the protagonist Lili is not voiced.
Music is mainly the same as in the first game. It would have been nice to get more new music but at least the tracks are pleasant and fit the events.



The game's visuals are a treat. From the beautifully crafted user interface to backgrounds and character portraits. Sadly there's no portrait for Lili when she talks. The CG illustrations are some of the best in the market. What really delighted me was the effort they've put into designing the clothing, jewelry and hair. We get to see Lili sporting various kinds of attire with incredible detail and her hairstyle varies too.


There is one thing that bothers me in the artist's style however: Lili's comically large eyes didn't quite fit the art style in my opinion.
I was pretty happy with the localization of the game. Now I don't know enough Japanese to judge the accuracy of the translation and I'm not a native English speaker but the text seemed well-written. Not much typos or errors. I remember a few occasions where a word or two were missing but luckily it didn't affect my ability to understand the gist of the sentences.
The biggest offender in the game was poor contrast. There were these memoir parts called "Aria" occurring throughout the game where white text was displayed on top of a background image without a dialogue box. It made it nigh impossible to read parts of the text when the text appeared on top of white/light parts of the image.
Another pet peeve of mine was that the sequel continues with the grave sin of talking about food and never showing it. I just love looking at masterfully drawn food in games and not getting any of that left me sour.

I had such a good time with the game that I double-dipped on physical copies of both Piofiore: Fated Memories and Piofiore: Episodio 1926 after playing through the digital versions. I adored the characters and their interactions and I especially enjoyed the darker parts that helped with worldbuilding.
Now that I've finished both games I feel slightly melancholic due to having to say goodbye to the characters. If that is not a sign of a good game, I don't know what is.
I think my husband became a Piofiore fan as well! He was partially watching me play through both games. During my Episodio 1926 playthrough he was inspired to start a new game in Rimworld where he created the Piofiore main characters and assigned suitable traits for each.

If they ever decided to make a third game in the Piofiore series, I'd buy it in a heartbeat! If Piofiore caught your interest, I recommend playing Piofiore: Fated Memories first, even though it's the weaker game out of the two.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 1 of 8, Group 1 of 8


propaganda and summaries are under the cut (May include spoilers)
Code Geass: 2.25 Re;
Lelouch tries to persuade Nunnally into giving him the key of Damocles as the battle concludes.
Word of Honor: 1.34 Ep 34
Ye Bai Yi instructs Lao Wen to close down Ghost Valley forever and the crowd disperses peacefully. The victors have drinks where Lao Wen reveals how he had managed to convince everyone around him to get along with the plan. Zhou Zi Shu is happy for him, but in pain that he only had a few more days left to survive. Scorpion King has a talk with the now disabled Zhao Jing in which he reveals his true intentions and feelings about what he thought about him. A drunk Lao Wen elatedly describes that meeting Ah' Xu had changed him. He asks him to accompany him to his parents' old hometown for a proper burial and Ah' Xu tearfully agrees. At Ghost Valley, preparations for Ah' Xiang's wedding takes place. Aunt Luo tells her plan to stay at the valley forever with Qian Qiao, who had decided to drink the Water of Lethe and forget Yu Qiu Feng. Cao Wei Ning is increasingly nervous and confesses that he had always hoped that his wedding would be attended by his seniors and Masters. The Gentle Wind Sword Sect arrives and Mount Qingya and they are let in. Master Mo Huai Yang openly disrespects Ah' Xiang. (Source: MyDramaList)
(Spoilers) Look the emotional rollercoaster this episode is like Wen Kexing finally got his revenge and Ye Bayi is like just close down the ghost valley and we'll call it even and it's like yes!!!! No more bloodshed!!!! And everyone is having dinner together and Wen Kexing is literally having the best day of his life!!! But then Zhou Zishu is like dealing with all the turmoil and angst that WKX's little stunt put him through and that he's going to die in a few days but nobody knows and he doesn't want to bring down the mood and then there's heartbreaking scene where WKX is drunk and is so happy and cuddling ZZS and is like I'm so happy you're my soulmate and everything is great and we'll travel the world together this is amazing!!! And you can see the pain on ZZS's face because WKX doesn't KNOW!!!! And then there's the confrontation between Scorpion King and Zhao Jing which is !!!!!!!!!!!! And then they're preparing for Gu Xiang and Cao Weining's wedding!!!!! And it's so sweet because everyone is just so happy!!!! And like WKX is in full dad mode which is great. But it's just like an episode where the characters can just all love each other because there's no sign of immediate danger (well besides ZZS' stuff) but like it's so heartwarming and sad and tragic when you know what happens right after like !!!!!!!!!!!!
It's also one of the highest rated episodes (on mydramalist) with a 9.3 so there's that too
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k9zRSFzOfTc&t=1230s
22 notes
·
View notes
Text





Piofiore: Episodio 1926
(ピオフィオーレの晩鐘 -Episodio1926-)
Release dates (Nintendo Switch)
Japanese: November 12th, 2020
English: September 22nd, 2022
"Return to the city of Burlone, Italy - home to three powerful mafia families vying for control. Liliana Adornato is an orphan with a hidden past tied to fate of the city. But when a new threat appears, the Falzone, Visconti, and Lao-Shu families must come together in a temporary truce to retrieve a stolen relic and restore the balance of power."
This is the sequel to Piofiore: Fated Memories, released for the Nintendo Switch! You can buy the physical version from Amazon.com here, or digitally from the Nintendo store.
#piofiore#piofiore episodio 1926#otome game#otome games#visual novel#gxb#commercial#voice acting#nintendo switch
23 notes
·
View notes
Text



I FINISHED THE GAAAAAAAAME ALSO OH MY GOD THE AGE SWAP PICTURE AAAAAAAAA
#THE WAY I GASPED SO LOUD AT ADULT EMILIO#THATS JUST 1 REALLY ANGST N SEXY ROUTE HOLY FUCK ADULT EMILIO ROUTE WHEN#N ADULT FEI AAAAAAAA#LOOK AT THE LIL LAO SHU BABIES!!! OMEEEYYY#eugene looks like gilbert lmao#TEENY OLIVER EEEEE#CRYINF BB ROBERTO EEEE#fafar plays piofiore 1926
10 notes
·
View notes
Note
Did Sun Quan expand the state of Wu at all, or were Wu's boundaries fully set up by Sun Jian and Sun Ce?
Sun Quan more than doubled what Sun Ce conquered.
Sun Jian was not involved with Wu as a territorial entity. He was never an independent warlord and ended his life in service to Yuan Shu as one of his generals. After his death his brother-in-law Wu Jing and nephew Sun Ben led the family troops but remained Yuan Shu's subordinates. During this time they established the family in Danyang (Yang province).
Sun Ce took control of the family's army when he came of age; Sun Ben and Wu Jing were evidently happy to be his subordinates. Under Yuan Shu's banner, he captured the eastern half of Yang province (the area called Jiangdong). After breaking from Yuan Shu in 197 and becoming an independent warlord, he captured western Yang as well. That was the extent of his territorial conquests, though. Sun Ce secured what would become Wu's heartland but it was limited to Yang ; and did not even include the province's greatest city, Shouchun. Much of this territory was occupied by unaffiliated Yue peoples, and this land was only physically occupied during Sun Quan's time.
Under Sun Quan, the state expanded vastly. He added most of Jing province (except for the northern portions that remained in Wei's control), and the entire Jiao territory. He also received tribute from kingdoms in modern Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia. (This should be recognized as them acknowledging Wu status, not as submission.)
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
hello! i have a linguistics question, feel free to ignore it if you don't want to answer. and it is coming from a very ignorant place, so apologies in advance if i say something that is impolite; it is completely unintended!
i understand (or, think i understand) that "ge" is an honorific similar to the korean "hyeong" in that it literally means brother but is used by men to refer to their older male friends as a sign of familiarity/respect. that being said, i've usually seen "hyeong" used as sort of a suffix to a person's name (like 'sanghyuk-hyung' or 'yoojin-hyung' etc.), but i noticed that in a lot of douyins, people will say "da-ge" to refer to people. is "da-ge" just like a generic way to refer to a young adult man? or is "da" a really common like nickname or something that i don't know from naivete? thank you in advance, and thank you for doing the time-consuming work of translating these videos for us! i love them :)
Da-ge (大哥) literally means "big big brother" but its meaning is more like "boss", except not in the workplace sense (in that case you'd usually use lao-ban or any official position title).
You would call your social superior/someone you look up to "da-ge", so this could extend to gangs, friend circles, or workplaces.
You might also call someone "da-ge" to show deference to them (such as, if you're in trouble). You could also just call any random older guy "da-ge", sort of interchangeable with "xiongdi"/"ge" (in the "dude" sense), although this I feel like is usually done more for casual/comedic/playful effect. "Da-ge" is also a bit more polite to call an older guy (30-40s) compared to "shushu" (uncle) or "da-shu"/"da-ye".
I think among younger friends it's probably used more in an ironic sense, almost similar to if you have any friends who like to say "you got it, boss"/"so true, boss".
That's my totally un-academic explanation, anyway!
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tilling the fields, QMYS, Section 1
The Qimin yaoshu齊民要術 (“Essential Techniques for the Common People) by Jia Sixie (fl. c. 540), is the oldest Chinese agricultural treatise to survive in its entirety. Jia Sixie served as a mid-level official of Eastern Wei,as such the focus is on the dryland farming practices of his home region in modern Shandong rather than the wet rice agriculture of Southern China. The book itself mixes Jia Sixie's own advise and descriptions with quotations from earlier works, many of which are now lost. The QMYS is therefore not just an important source for the author's own times, but for the agricultural writings and practices of the preceding centuries.
Section 1 covers the different aspects of tilling the fields in preparation for cultivation, and contains advise for how to clear new fields, ploughing, harrowing, different soil types, and so on.
(To go straight to the translation, jump to "Section 1, Tilling the Fields")
[Translator's preface]
[The QMYS is not illustrated, but texts of this nature really should come with some visual aides. I have therefore included here some drawings and pictures from later eras. All images from Wikipedia.
[Farming tools]
Han era scholars agreed that China's first plough had been a tool called leisi耒耜, but lacked a clear of concept of how it actually looked like. Later authors simply repeated their statements. The drawing below from Wang Zhen's (1271-1333) Nongshu is therefore at best a reconstruction from literary evidence.
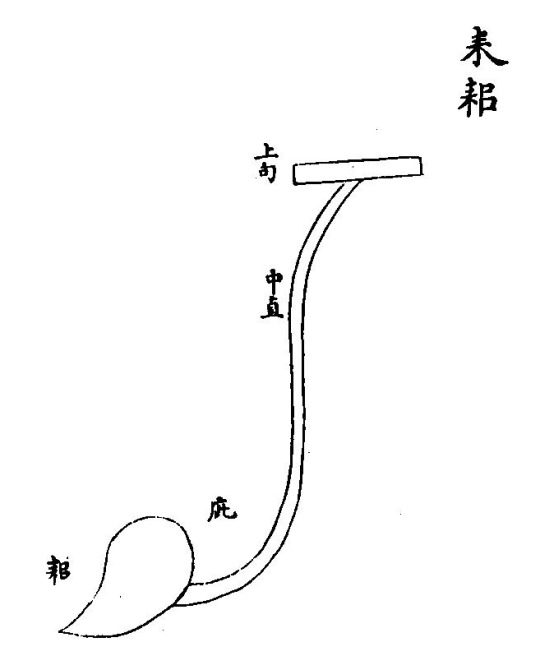
(Leisi耒耜, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)
The main plough was instead the ox-pulled li犂 frame-plough.

(Li犂, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)

(Shantung plow, from King, 1911, Farmers of forty centuries)
QMYS also refer to the lighter feng鋒 plough.

(Feng鋒, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)
The QMYS is the oldest Chinese text to refer to the iron-tined harrow, which it refer to as loucou𨫒楱

(Ba耙, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)
The lao勞 bush-harrow was made by weaving thin sticks around the cross-bars.
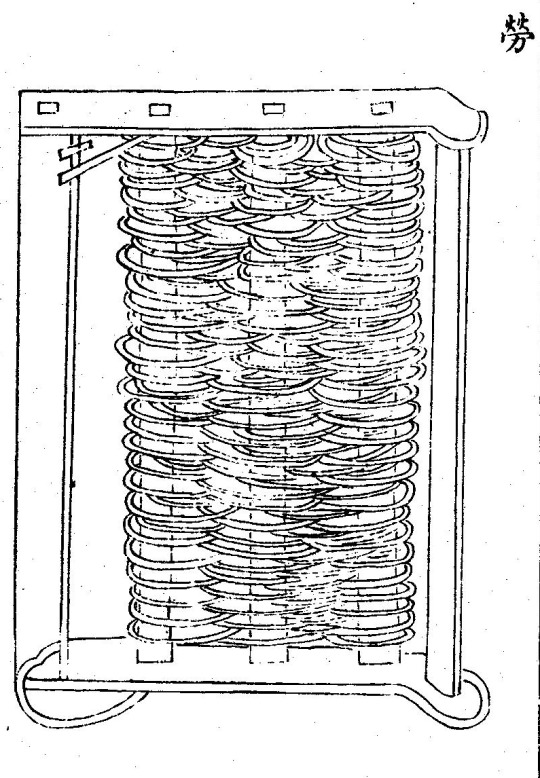
(Lao勞, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)
The preferred tool for sowing was the seed drill, lou耬
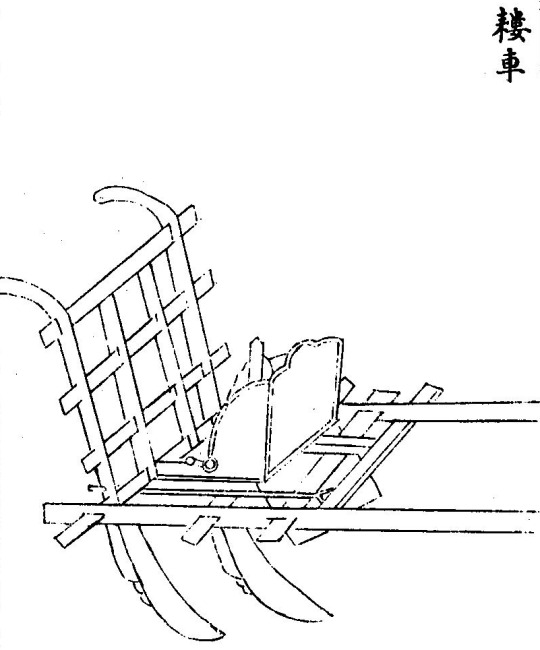
(Louche耬車, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)
In addition to these ox-drawn tools, there were of course a varity of manual tools in different shapes and sizes, hoes, shovels, etc.

(Youchu耰鋤, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)
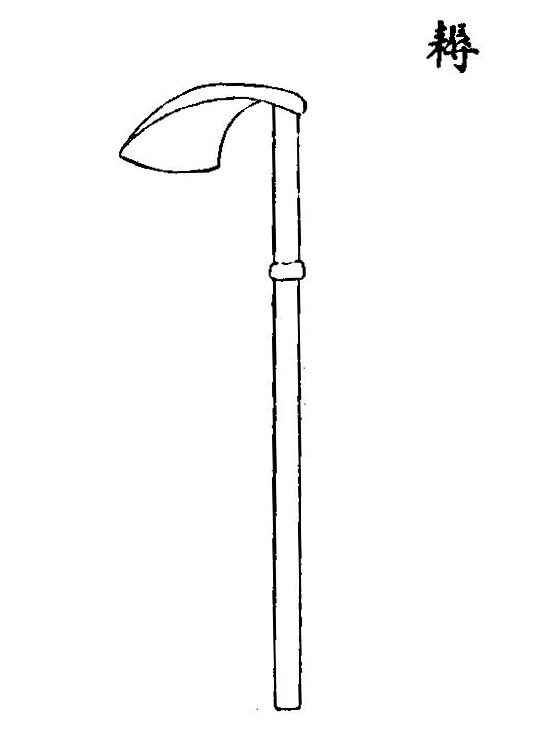
(Nou耨, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)
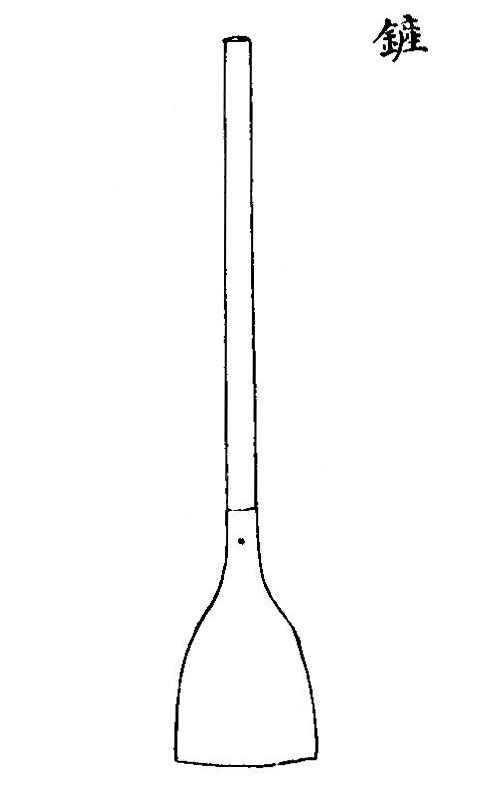
(Chan鏟, from Wang Zhen's Nongshu)
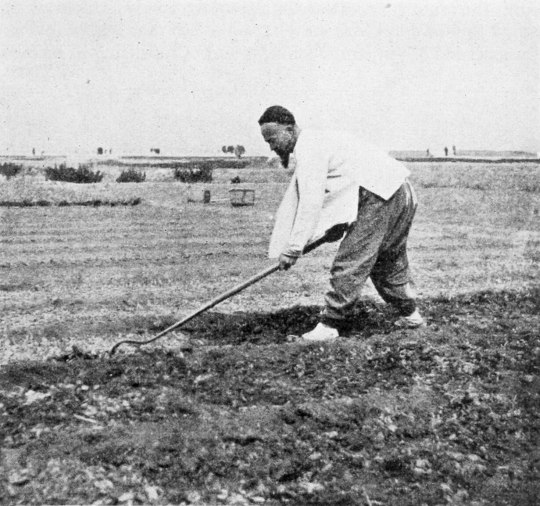

(Method of using the broad, heavy hoe in producing surface mulch, as seen in Shantung, China, from King, 1911, Farmers of forty centuries)
[Crop plants]
Later sections of QMYS treats the cultivation of the individual crops in much larger detail.
Foxtail millet (Setaria italica), gu穀, was the main staple crop.

Broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum), shu黍
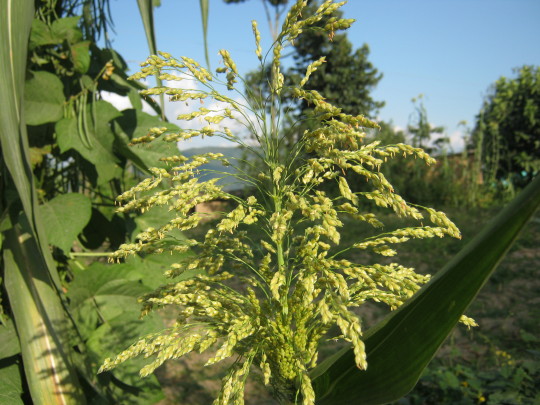

In addition to gu and shu, different varieties of foxtail and broomcorn millet were known under a large number of other names.
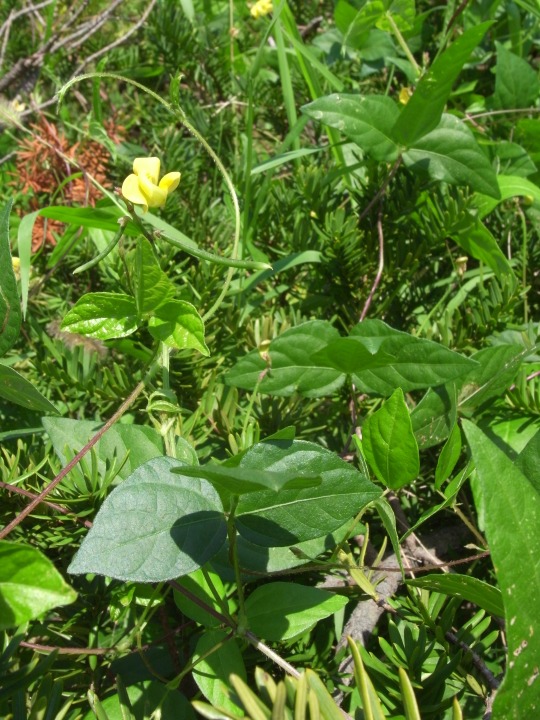
Mung beans or green gram (Vigna radiata), lüdou緑豆 (lit. "green beans"), used as green manure in crop rotation with millet

Adzuki beans (Vigna angularis), xiaodou小豆 (lit. "small beans") served a similar function

Wheat (Triticum aestivum), mai麥 (same name also used for barley) was primarily a winter crop in ancient China.

[Books quoted by QMYS in Section 1, in order of appearance]
The Zhoushu周書 (“Book of Zhou”), also known as the Yi Zhoushu逸周書, is a Warring States era collection of documents about Western Zhou, but the book has a complicated textual history. It is quoted once in QMYS, in Section 1. The quoted text is not found in the transmitted version.
The Shiben世本 (“Generational Roots”) records the genealogies of mythical rulers, the origin of the clan names, and mythological and historical inventors. Several versions existed, by different authors. The full text now lost, but it is quoted numerous times in other works. It is quoted once in QMYS, in Section 1.
The Lüshi chunqiu呂氏春秋 (“Spring and Autumn of Mister Lü”) is a collection of treatises and essays attributed to the retainers of Lü Buwei, the (in)famous Qin chancellor. It covers a very wide range of topics.
The Erya爾雅 (“Approaching the Correct”) is the oldest surviving Chinese glossary. Modern scholarship dates the book to the late Warring States and/or early Western Han periods. It is quoted numerous times in QMYS.
The Jianwei shiren犍為舍人, the “Retainer from Jianwei”, lived during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han and wrote a commentary on the Erya. The book is now lost. The quote in Section 1 is the first of three in QMYS.
The Zuanwen 纂文 (“Compiled Graphs”) by the Liu-Song scholar and historian He Chengtian何承天 (370 – 447) is now lost. It is quoted once in QMYS, in Section 1.
The Shuowen 說文 (“Explaining Graphs”) by Xu Shen許慎 (c. 58 – c. 147) analyses the composition and reasoning behind the different characters. It is quoted numerous times in QMYS.
The Shiming釋名 (“Analysing Names”) by Liu Xi劉熙 is a glossary in the style of the Erya written c. 200 AD. The quote in Section 1 is the first of three in QMYS.
The Liji 禮記 (“Ritual Records”) is a collection of ritual treatises compiled from older texts during Former Han, it became part of the textual canon as one the Five Classics and also as one the Three Ritual Classics. Its usage in QMYS is restricted to the Yueling chapter.
The Yueling月令 (“Monthly Orders”) chapter of the Liji is a calendrical treatise describing for each of the twelve months the position of the stars and other seasonal markers, important state rituals, and which activities should be undertaken in each month. Its inclusion in the Liji ensured it what read by every person aspiring to an education and it inspired a whole genre of similar texts, such as the Simin yueling. It is extensively quoted in QMYS.
Zheng Xuan鄭玄(127 – 200) was a famous scholar at the end of Han who wrote an influential commentary on the Three Ritual Classics. In QMYS quotations from the Yueling and Zhouguan are usually accompanied by quotes from his annotations.
Mengzi孟子 (“Master Meng”, theLatin Mencius) collects the teachings of the famous Warring States era philosopher Meng Ke (372–289 BC). The quote in Section 1 is the first of three in QMYS.
Wei Wen-hou魏文侯, Marquis Wen of Wei, ruled Wei during the early Warring States era. The single quote in QMYS attributed to him is found in the Huainanzi.
The Book of Miscellanea on Yin and Yang雜陰陽書 was apparently written during the early Han, but is now lost outside the quotations in the QMYS. The quote in Section 1 is the first of eight in QMYS.
Gao You高誘 lived at the end of Han and wrote commentaries on several texts, including the Lüshi chunqiu and the Huainanzi. The quote in Section 1 is the first of eight in QMYS.
The Huainanzi淮南子 (“Masters of Huainan”) is a collection of philosophical treaties compiled during Western Han at the court of Liu An (179 – 122 BC), vassal king of Huainan. It covers a wide range of topics. The quote in Part 9 is the second of nine in QMYS, the first being in the preface (which I have impudently skipped).
The Fan Shengzhi shu氾勝之書 (“Book of Fan Shengzhi”) is the oldest known Chinese agricultural treatise. Fan Shengzhi might originally have been an easterner, but during the early Western Han served as an official in the Guanzhong region. The original book has been lost, but it is extensively quoted in the QMYS, and also by Tang and Song encyclopedias.
Cui Shi崔寔 (d. c. 170) was a Han official and author of multiple works, including the Simin yueling and Zhenglun.
The Simin yueling 四民月令 (“Monthly Orders for the Four People”) is written in the style of the Liji Yueling, detailing each month's agricultural activities at the large estates of late Han North China. The original book is lost except as fragments in other books. It is very extensively quoted in the QMYS.
The Zhenglun政論 (“Essay on Government”) criticizes what Cui Shi considered the decline in morals and lax administration of law in his time. The original book is lost except as fragments in other books. It is quoted once in QMYS, in Section 1.
[Lettered notes]
The original text is a mix of large and small characters. I have collected the small text sections together in idented lettered notes within {} brackets.]
[Translation starts here:]
Section 1, Tilling the Fields
[Dictionary definitions]
The Book of Zhou says: “In the time of the Divine Farmer, Heaven rained millet [su粟]. The Divine Farmer thereupon tilled and planted it. He created pottery, cast axes and hatchets, and made the plough-shaft and ploughshare [leisi耒耜], the long- [chu鉏] and short-handle hoe [nou耨], to clear the grass and thickets. Afterwards the Five Grains supported and helped, and the Hundred Fruits were stored in abundance.”
The Generational Rootssays: “Chui created the plough-shaft and ploughshare. Chui was a vassal of the Divine Farmer.”
The Spring and Autumn of Mister Lüsays: “The ploughshare is six cun wide.”
The Eryasays: “To mow[qu斪] or weed[zhu斸] are spoken of as to settle [ding定].”
The Retainer from Jianwei says: “To mow or weed is to hoe [chu鋤]. They are names for settling.”
The Compiled Graphssays: “In the way of tending sprouts, the long-handle hoe [chu鋤] is not as good as the short-handle hoe [nou耨], the short-handle hoe is not as good as shovel [chan鏟]. A shovel is two chi long, with a blade two cun wide, and is used to level the ground and remove grass.”
Xu Shen's Explaining Graphssays: “The plough-shaft [lei耒] is for hand-tilling with a curved wood. The plough-share [si 耜] is the plough-shaft's straight end. The weeder [zhu斸] is for cleaving [zhuo斫]. In Qi they speak of it as the ziji鎡基. Some say the axe handle [jinbing斤柄] is curved by nature. A field [tian 田] is laid out [chen陳]. Where is planted grain is called a field. [The graph] resemble four 口, and the 十 is the pattern of paths and cross-paths. To till [geng耕] is to plough [li犂]. [the graph] comes from “plough-shaft” 耒 with the “well” [jing井] sound. Some say it is the ancients' well field [system.]”
Liu Xi's Analysing Names say: “A field [tian田] is full [tian填]. The five grains fill up within it. A plough [li犂] is profit [li利]. To profit, turn over the soil and cut off the grass at the root. The short-handle hoe [nou耨] resembles hoeing [chu鉏], with crouched back hoe among the stalks. To weed out [zhu] is to execute [zhu誅] someone. The ruler uses execution to dig up a matter at the root.”
[General advise]
In general, when opening uncultivated mountain and marsh fields, always in the 7th Month cut down and mow them. When the grass has dried, set fire to it. Arriving at spring, begin to clear out those of its groves where the wood is large, peel off the bark to kill them. When the leaves are dead and not casting shadow, they will readily yield to tilling and planting. After three years, when the roots have withered and the stalks decayed, use fire to burn them (entering the ground fully), till the uncultivated land to the end, and use an iron teeth loucou𨫒楱 harrow to rake it twice everywhere, hurl broomcorn non-glutinous millet, and bush-harrow [lao勞] it again twice everywhere. Next year then it is fitting to be a millet field.
In general when tilling eminent or inferior fields, do not ask about spring or autumn, [you] must pay attention to dry or wet to obtain what will be good. If flood and drought are not in concert, it is better with dry and not wet {A}. For the spring tilling, immediately take in hand the harrowing{B}. For the autumn tilling, wait for the turn to white to harrow{C}. [When the soil starts to dry, the surface turns white, which Jia Sixie refers to as 白背.]
{A: With dry tilling, then even if there are earth-clods, as soon as there is rain, the earth will pulverize and dissolve. With wet tilling, it will harden when it dries, and for several years will not be good. The proverb which says: “Wet tilling and damp hoeing is not as good as going home.” tells that it is of no gain and will be damaging. In the case of wet tilling, when it turns white quickly use the loucou on it, and there will likewise be no injury. If not done, it will be very bad.}
{B: The ancients said you耰, now we say lao勞. The Explaining Graphs says: “The you is a tool for rubbing [mo摩] the fields.” Now people also name the lao bush-harrow a “rubber” [mo]. A vulgar saying is “till the field with the rubbing harrow”.}
{C: During spring, there is much wind, and if [you] do not soon harrow, the earth will surely be empty and dry. During autumn the fields are soaked solid, and wet harrowing will make the earth stiff. The proverb which says: “To till and not to harrow is not as good as making it go to waste” perhaps tells that wetlands are difficult to handle, and delights in Heaven's timely chances. Huan Kuan's essay on Salt and Iron says: “Underneath a thick grove there is no lush grass. Between large clods there are no excellent sprouts.”}
In general, autumn tilling want to be deep, spring and summer tilling want to be shallow. Ploughing want to be narrow, harrowing want to be double{D}. In the autumn to till and cover over what is green is the best.{E} The earliest tilling want to be deep, and the turned over earth want to be shallow.{F} On land with themeda or cogon-grass [jianmao菅茅], [you] ought to let loose cattle and sheep to trample it. Then if in the 7th Month [you] till it, it will die{G}.
{D: Plough narrow and till finely, the ox then will not tire. Double-harrow and the land will ripen, during drought it will likewise protect the moisture.}
{E: Reaching the winter months, the green grass that has regrown will be as excellent as adzuki beans [xiaodou小豆].}
{F: If the tilling is not deep, the land will not ripen. If the turned over is not shallow, the stirring will bring forth the soil.}
{G: If not the 7th Month, it will regrow.}
In general, the rule for excellent fields, is for mung beans [lüdou緑豆] to be first, adzuki beans and sesame [huma胡麻] is next to it. Thoroughly for all of them sow densly [?] within the 5th and 6th Months, and in the 7th and 8th Month plough and cover over to kill them. [This] will make a spring millet field with a harvest of ten shi on the mu, in excellence comparable to silkworm excrement and mature manure.
In general, after the autumn harvest, the oxen's strength will be weak. For those not yet caught up for autumn tilling, at the bringing down of [?] the foxtail [ gu穀], glutinous broomcorn [shu黍], non-glutinous broomcorn [ji穄], large grained [liang 粱], and glutinous foxtrail [shu秫]millets' stubble, then move the exhausted ones to quickly use the “spear-point plough” [feng鋒] on it. The ground is regularly soft and moist, and is not hard and tough. Then when arriving at the beginning of winter, [you] usually get to till and harrow, and not worry about it being dried up and arid. If the oxen's strength is small, only harrow it once during the 9th and 10th Months, and arriving at spring, sow without ploughing [?], is also doable.
[Excerpts from the Monthly Orders on tilling]
[This whole subsection consists of quotation from the classic text the Monthly Orders [Yueling 月令], a chapter of the Ritual Records [Liji禮記], accompanied by quotations from commentary by the Eastern Han scholar Zheng Xuan.]
The Ritual Records' Monthly Orderssays: “In the Month of First Spring, … the Son of Heaven therefore on the inaugural day pray for grain to the High God [shangdi上帝]{H}. Then, selecting the inaugural chen day, the Son of Heaven personally conveys the plough-shaft and ploughshare. … He leads the Three Excellencies, the Nine Dignitaries, the various feudal lords, and the great men, to till themselves the God's Acre [Di ji帝籍]{I}. This Month, Heaven's breath descends down and Earth's breath rises up. Heaven and Earth are in harmony with each other, and the grasses and trees sprout and stir{J}. … He instructs the ministers for the fields{K}. They skilfully assess the hills and mounds, the slopes and defiles the highlands and lowlands, for what is suitable among the land and ground, and what to plant of the Five Grains, so as to teach and guide the people. … Field affairs having been put in order, he first settles the guidelines and responsibilities. Agriculture was therefore not in confusion. ...”
{H: Zheng Xuan's Annotations says: “It speaks of the first xin day, and the suburban sacrifices to Heaven. The Spring and Autumn Transmittals says: 'In spring the suburban sacrifices to the Lord of Agriculture [Houji后稷] to pray for farming affairs. Thus after the commencement of hibernation, the suburban sacrifices. After the suburban sacrifices, the tilling.' The High God is the god of the Grand Tenuity [taiyi太微].”}
{I: “Inaugural chen is perhaps a propitious chen day after the suburban sacrifices. … The God's Acre is the field by which is regulated the Heavenly Divinity's lending the people strength.”}
{J: “This is the yang breath ascending through the surface, a portent that there can be tilling. The Book of Agriculture says: 'For the best growth cover over the stakes. When they show the base and can be pulled out, those who till urgently set out.”}
[This Book of Agriculture [nongshu農書] is apparently the same as the Book of Fan Shengzhi which is quoted in more detail on this topic further down.]
{K: “With minister it speaks of the 'field surveyors', the officials in charge of agriculture.”}
“In the Month of Middle Spring, … those who till have a short rest, they then repair their gate and door leaves [heshan闔扇]{L}. There are no great affairs undertaken which would hinder agricultural affairs. … ”
{L: 'Rest' [she舍] is similar to 'pause' [shi止]. Hibernating insects open doors, and with tilling affairs a little tranquil, they then put in order their gates and doors. When they use wood it is called he闔, when they use bamboo or reeds it is called shan扇.”}
“In the Month of First Summer, … he encourages agriculture and motivates the people, and there are not anyone who neglects the season{M}. … He instructs the farmers to apply themselves to action, and not rest at the capital{N}. ...”
{M: “He puts weight and effort in encouraging [them?] to come to him.”}
{N: “He presses and urges the farmers. … The Rites for the King Residing in the Bright Hall says: 'There are no sojourners in the state'.”
“In the Month of Last Autumn, … The hibernating insects altogether curl up inside, and everyone plaster their doors.{O}”
{O: “With 'plastering' [jin墐] it speaks of smearing plaster [tu塗] to shut them. This is to avoid the killing[?] air.”}
“In the Month of First Winter, … Heaven's breath rises up and Earth's breath descends down. Heaven and Earth do not communicate, they shut up and hide, and achieve winter. … He encourages the farmers to rest and comforts them{P}. …”
{P: “'The Ward Corrector [dangzheng黨正]' 'drinks wine with the people belonging to him, and correctly arrays their ranks.'”} [Zheng Xuan here quotes from the Rites of Zhou]
“In the Month of Middle Winter, … ground affairs are not undertaken, care is taken not to open up what is covered, and not to open rooms and buildings. … [otherwise] the Earth's breath would further spill out, this is spoken of as opening the house of Heaven and Earth. The various hibernating [insects] would then die, and the people would be ill and sick{Q}. …”
{Q: “When the Great Yin employed in affairs, it especially puts weight on closing up and keeping safe.” Note that in the present era's tilling in the 10th and 11th Months is not straightly disobeying the Way of Heaven, and harming hibernating insects. [If] the earth likewise was not made moist, the harvest would surely be meagre and small.}
[The words “Note … small” are not part of Zheng Xuan's commentary, but are rather Jia Sixie's own comments.]
“In the Month of Last Winter, … he instructs the field officials to announce people to bring out the Five Seeds{R}. He instructs the farmers to plan their plough-pairs and tilling affairs, repair their plough-shafts and -shares, and prepare their field tools{S}. … This month, the sun has gone through the stations, the moon has gone through the positions, and the stars have cycled around Heaven. The numbering is soon about to end{T}. The year will once more begin. Pay attention to your farming people, and do not have them sent about{U}.”
{R: “He instructs the field officials to announce to the people to bring out the Five Seeds. The great cold has passed by, and farming affairs are about to begin.”}
{S: The ploughshare [si耜] is the metal of the plough-shaft [lei耒]. The ploughshare is five cun wide. Field tools are the types of hoes [ziji鎡錤].”
{T: “It tells that the sun, moon, and stars have travelled around until this month, when they all have made a circuit to their old locations. The 'stations' [si次] are the lodges [she舍]. The 'positions' [ji紀] are similar to lodges.”}
{U: “er而 [“thy”] is similar to ru汝 [“you” or “your”]. It tells to pay attention solely to the hearts of your farming people, and make people prepare their resolve for the affairs of tilling and sowing. It is not possible to conscript them for labour. If conscripted for labour, their resolve will scatter, and they will neglect their profession.”}
[Other quotations on tilling]
Master Meng says: “A gentleman's assignment is like a farmer's tilling.”{V}
{V: Zhao Zhu's annotations says: “It tells that to be hasty in your assignment, like a farmer who does not till, is impossible.”}
Marquis Wen of Wei says: “People in spring put their effort into tilling, in summer use their strength for weeding, and in autumn they gather their harvest.”
The Book of Miscellanea on Yin and Yang says: “When on hai亥 it is in the Heavenly Granary constellation, it is the start of tilling.”
The Spring and Autumn of Mister Lü says: Fifty-seven days after winter solstice, sweet flag [chang昌] grows. Sweet flag is the first to grow of the hundred hundred grasses, and at this point tilling starts.
The Masters of Huainan says: That which does the affairs of tilling is toil, that which does the affairs of weaving is trouble [?]. They are affairs of toil and trouble, yet those people who do not rest know they can be used for clothes and food. A person's feelings are not capable of being without clothes or food. The way of clothes and food surely starts at tilling and weaving. … Those who, if they till and weave, who will start at the beginning with considerable toil, and end with certain profit, are the multitudes.
It also says: “To be unable to till and yet want glutinous broomcorn or large grained millet, to be unable to weave and yet want to sew attires, to have nothing in their affairs and yet seeking their merit, is difficult.”
[Quotations from Fan Shengzhi]
The Book of Fan Shengzhisays: “In general, the root of tilling lies in determined timeliness, harmony with the ground, applying oneself to manure and moisture, and to hoe early and harvest early.”
“At spring when the frost disperse, Earth's breath starts to permeate, and the soil's sole harmony disperse. At the summer solstice, Heaven's breath starts to heat, the yin breath starts to flourish, and the soil again disperse. Ninety days after summer solstice, when day and night are split, Heaven and Earth's breath are in harmony. Using these times to till the fields, one will yield five, which is called fertile bounty, all then are times for work.”
“At spring when the Earth's breath permeates, [you] can till the hard and tough earth with black, lumpy soil, immediately level and rub down its clods to give growth to grass. When the grass grows, again till it. When the sky has a little rain again till and harmonize it. Do not make that which has clods await the season. This spoken of as 'if strong soil, then weaken it'.”
“A spring portent that the Earth's breath has started to permeate: Hammer down wooden stakes, a chi and two cun long, cover over a chi [so that you] see two cun. After the advent of spring [lichun立春], the soil clods will break up, and the top will slide down the stakes. When they show the base, and can be pulled out, after twenty days from this time, the harmonious breath will leave, and promptly the soil will stiffen. With timely tilling, one will yield four; till when the harmonious breath has left and four will not yield one.”
“When the apricots start to flower and flourish, immediately till light soil and weak soil. Wait for the apricot flowers to fall off, and then till again. Till and immediately roll it [lin藺]. When grass grows, and there is rain and moisture, till and heavily roll it. For soil that is particularly light, use cattle and sheep to trample it. Like this the soil will strengthen. This is what spoken of as 'if weak soil, strengthen it'.”
“If at the spring breath is not permeated, soil fully fitting will not protect its moisture, and for the remainder of the year will not be suitable for sowing, and no manure will not dissolve [?]. Take care to not till dry land. Wait for grass to grow, and to arrive the time it can be tilled. When there is rain, promptly till it, The soil will be close with each other, sprouts only will grow, grass and weed will rot, and [you] will always achieve good fields. This way one tilling will yield five. If not done like this, but dry tilled, clods will be tough, sprouts and weed will spring forth from the same hole and will be impossible to hoe into order, and and it will turn around to become failed fields. If in autumn with no rain [you] yet till, it will sever the soil's breath, and soil will be hard and dry. These are called 'arid fields' [latian臘田]. And when you till in severe winter, [you] will leak out the yin breath, the soil will wither and dry out. These are called 'parched fields' [futian 脯田]. Arid fields and parched fields are both wounded fields. If for two years they do not produce sheaves of grain, then rest them for a year.”
“In general wheat [mai麥] uses the 5th Month for tilling. The 6th Month is second for tilling, and in the 7th Month [you] must not till. Carefully rub and level to await the time for sowing seeds. Till in the 5th Month, one will yield three. Till in the 6th Month, one will yield two. If tilled in the 7th Month, five will not yield one.”
“In winter when the rain and snow has stopped, immediately roll it down. Trap the snow in the soil, and do not cause the following wind to fly away with it. If it snows later, roll it down again. Then at the advent of spring, it will protect the moisture, freeze the insects to death, and the coming year will be suitable for sowing.”
“Obtain the harmony of the season and fit to what is suitable for the land, then even if the fields are meagre and bad, the harvest can be 10 shi on a mu.”
[Quotations from Cui Shi]
Cui Shi's Monthly Orders for the Four Peoplesays: “1st Month, Earth's breath rises up. For the best growth cover over the stakes. When they show the base and can be pulled out. Hasten to cultivate fields with strong soil and black lumps. 2nd Month, Yin's frost is entirely moist. It is possible to cultivate excellent fields with slow soil and the small places by the river banks. 3rd Month, when apricot flowers are abundant, it is possible to cultivate fields with sandy, white, and light soils. 5th Month and 6th Month is is possible to cultivate wheat fields.”
Cui Shi's Essay on Governmentsays: “Emperor Wu used Zhao Guo as Chief Commandant of Searching for Millet, to teach the people tilling and planting. In his method there was three ploughshares [li犂] together for one ox, with one person escorting it, putting down seeds, pulling the seed-drill [lou耬], and in everything taking up preparations for it. In a day he sowed 1 qing. Arriving at present Sanfu [the region around Chang'an], they still rely on its advantages. Now in Liaodong when they till and plough, the shafts are four chi long, the rotations interfering with each other. Then they use a pair of oxen, a pair of people to lead them, one person in charge of the tilling, one person to put down seeds, and two people pull the seed-drill; in total they use a pair of oxen and six people, and in one day they only sow twenty-five mu. They are isolated [?] in the extreme like this.{W}”
{W}Note for three ploughshares together for one ox is similar to the present three-footed seed-drill, why the unknown tilling method? Now from Jizhou濟州 and westward they still use the long-shafted plough and the two-legged seed-drill. Long-shaft tilling on level ground is just about possible, but between the mountains and brooks, [the ground] does not permit its use, moreover the rotations are extremely difficult and costly in strength. It is not the equal the flexible ease of Qi people's luxuriant[?] ploughs. The two-legged seed-drill sows dense ridges, and is likewise not as good for hitting the mark as the one-legged seed-drill. [This seems to be Jia Sixie's own comment to Cui Shi's text.]
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Story mode artwork of Jiang's father, Lao Shu.
3 notes
·
View notes