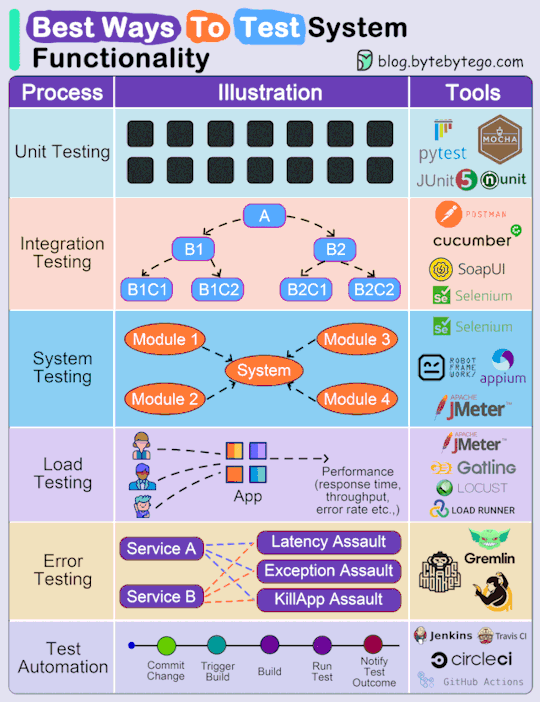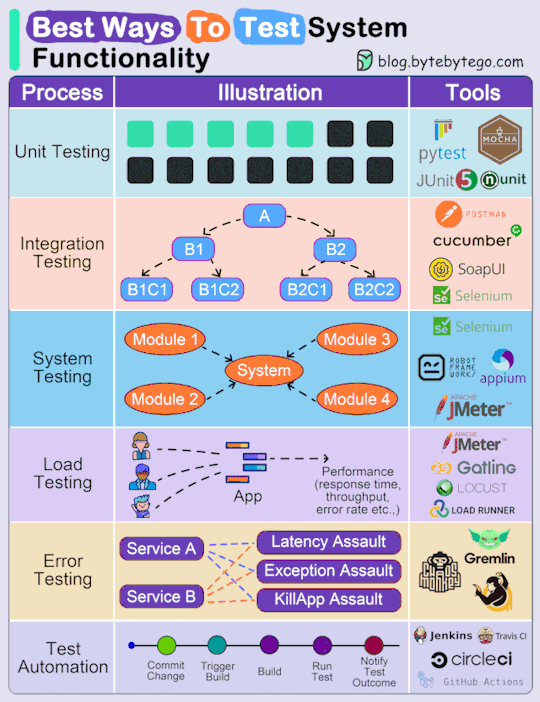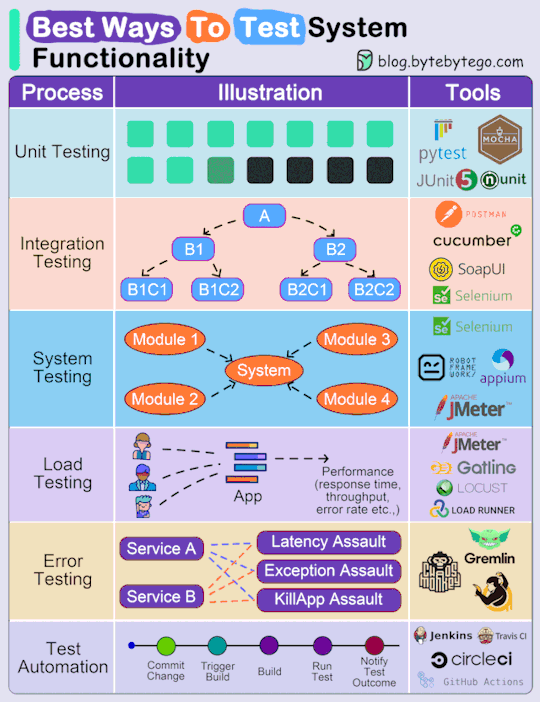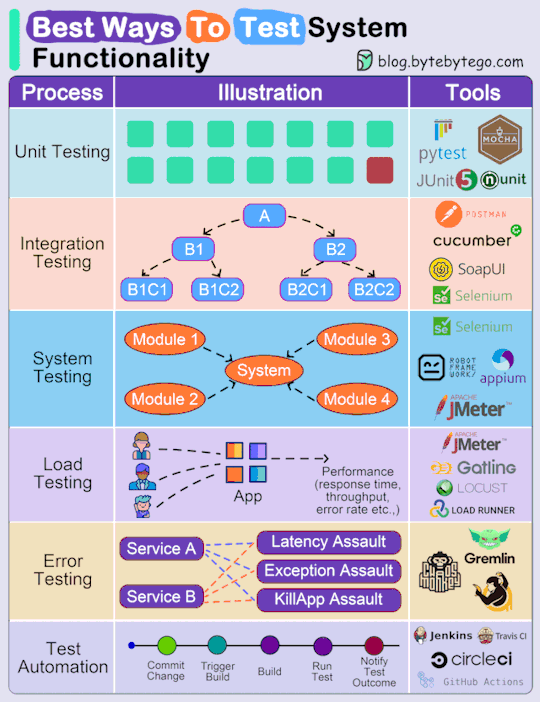
#system testing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
9 Different Types of Software Testing and Their Benefits
In the world of software development, ensuring the quality and reliability of an application is paramount. Software testing plays a vital role in identifying bugs, ensuring functionality, and enhancing the overall user experience. Testing can be done at different stages of development and can take many forms. Each type of testing has its own objectives, processes, and benefits. In this blog, we’ll explore the most common types of software testing and why each is crucial in delivering a high-quality product.

1. Unit Testing
What it is: Unit testing focuses on testing individual units or components of a software application in isolation, typically at the function or method level. Developers often write unit tests as they write the code, making it a proactive approach to catching errors early.
Benefits:
Early Detection of Bugs: Unit tests can catch issues as soon as code is written, making it easier and faster to fix bugs.
Simplifies Code Maintenance: With unit tests, developers can make changes to the code with confidence, knowing that existing functionality is not broken.
Documentation: Unit tests act as documentation for the behavior of individual code components, making it easier for others to understand how a system works.
2. Integration Testing
What it is: Once individual units of code are tested, integration testing ensures that they work together as expected. This type of testing focuses on detecting issues that occur when different components of the software interact.
Benefits:
Identifies Interface Issues: It helps to ensure that the interfaces between different modules or services are functioning correctly.
Early Detection of Integration Problems: Problems like data mismatches, incorrect APIs, or failures in service calls can be identified before they affect the entire system.
Improved Software Design: By testing components together, developers can ensure that the overall system architecture is sound and scalable.
3. System Testing
What it is: System testing evaluates the complete, integrated system as a whole. This testing verifies that the entire application works according to the specified requirements and functions well in all expected environments.
Benefits:
End-to-End Validation: System testing ensures that all parts of the application work together seamlessly, offering a real-world simulation of the software in action.
Comprehensive Coverage: It tests all aspects of the system (performance, security, usability, etc.), ensuring that no part is overlooked.
Ensures Functional and Non-Functional Requirements Are Met: System testing confirms that the software not only works functionally but also meets performance, security, and usability standards.
4. Acceptance Testing
What it is: Acceptance testing is performed to determine whether the software meets the business requirements and if it is ready for deployment. Often performed by QA teams or the client, this test is done before the product is released to the market.
Benefits:
Validates Business Requirements: Ensures that the software delivers what the client or end-users expect and that all features and functionalities align with the business needs.
Reduces the Risk of Rework: By identifying issues early on, acceptance testing helps ensure that the product is ready for use and minimizes the need for costly post-release fixes.
Improves Stakeholder Confidence: Since it focuses on meeting client specifications, it helps in building trust with stakeholders and ensures their satisfaction with the final product.
5. Performance Testing
What it is: Performance testing is conducted to determine how a software application performs under various conditions. It focuses on aspects like speed, responsiveness, scalability, and stability. There are several types of performance testing, including load testing, stress testing, and scalability testing.
Benefits:
Improves User Experience: Ensures that the software can handle high user loads without slowing down or crashing, which directly impacts user satisfaction.
Identifies Bottlenecks: Performance testing helps uncover areas of the software that could cause slowdowns, allowing developers to optimize performance before it becomes an issue.
Scalability Insights: Helps teams understand how well the software can handle increasing volumes of data or users, and allows them to plan for future growth.
6. Security Testing
What it is: Security testing is designed to find vulnerabilities in the software application that could be exploited by hackers or malicious users. This includes testing for issues like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), data breaches, and authentication flaws.
Benefits:
Protects Sensitive Data: Ensures that sensitive user data (such as personal details, credit card information, etc.) is secure and not susceptible to cyberattacks.
Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have strict regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) regarding data security, and security testing helps ensure compliance.
Prevents Security Breaches: By proactively identifying vulnerabilities, security testing can prevent data leaks, fraud, or other security breaches that could damage the company’s reputation or finances.
7. Usability Testing
What it is: Usability testing evaluates how user-friendly and intuitive a software application is. This type of testing focuses on ensuring that the product is easy to navigate and that users can interact with it efficiently.
Benefits:
Improved User Experience: Helps identify interface issues that may confuse or frustrate users, allowing teams to make the software more intuitive.
Better Customer Retention: A well-designed, user-friendly product is more likely to satisfy users and encourage them to continue using the software.
Increased Conversion Rates: A seamless user experience can lead to higher engagement, more sign-ups, and ultimately more conversions or sales.
8. Regression Testing
What it is: Regression testing ensures that new code changes (such as bug fixes, enhancements, or feature additions) haven’t unintentionally affected the existing functionality of the software. It’s typically done after each update or release.
Benefits:
Prevents New Bugs: Ensures that new code doesn't break previously working features, which is crucial as the software evolves over time.
Maintains Software Stability: Regression testing helps maintain the stability of the system by verifying that old functionality continues to work as expected.
Speeds Up Release Cycles: Automated regression tests can quickly check for issues, reducing the time needed for quality assurance and speeding up the release cycle.
9. Smoke Testing
What it is: Smoke testing, also known as "build verification testing," is a preliminary test to check the basic functionality of a software build. It’s like a "quick check" to ensure that the critical parts of the software work before deeper testing is performed.
Benefits:
Quick Feedback: Provides immediate feedback on whether the latest build is stable enough to proceed with further testing.
Reduces Time and Cost: Helps to catch fundamental issues early in the development cycle, preventing wasted time on testing broken builds.
Ensures Build Quality: It ensures that the most crucial features (e.g., login, key workflows) are functioning correctly before testing begins.
Conclusion
Software testing is an essential component of the development lifecycle, ensuring that applications are not only functional but also secure, efficient, and user-friendly. Each type of testing serves a unique purpose and brings its own set of benefits, from identifying small bugs in individual components to ensuring the overall performance and security of the application.
By implementing various types of testing at different stages of development, software teams can significantly reduce the risk of errors and deliver a more reliable, high-quality product to end-users. Whether you're a developer, QA engineer, or project manager, understanding the importance of diverse testing strategies is key to successful software delivery.
#Unit Testing#Integration Testing#System Testing#Acceptance Testing#Performance Testing#Security Testing#Usability Testing#Regression Testing#Smoke Testing#Software testing#End-to-End Testing
0 notes
Text
On a moshang kick but there's just something extremely compelling about the idea of Mobei Jun spending years expecting Shang Qinghua to betray him, getting impatient waiting for the axe to drop, deliberately creating opportunities for Shang Qinghua to betray him, still no betrayal happens, until eventually it gets to the point where Shang Qinghua has like, the fantastical demon king equivalent of Mobei Jun's credit card numbers and a joint account and free access to his bedroom and food and a great big cabinet full of poison and his detailed schedule and the exact time when he'll be bathing naked with no weapons under the moonlight at the one time every five years when all ice demons temporarily lose their powers for a full night and etc etc. Mobei Jun is doing trust falls (even though he doesn't know it) but Shang Qinghua just keeps catching him.
Until the whole lack of explicit communication and cultural differences thing explodes, and even then the big betrayal that finally happens is that Shang Qinghua saves Mobei Jun's life but then LEAVES HIM, he GOES AWAY, he doesn't even push Mobei into his own metaphorical abyss he just goes "this isn't worth putting up with anymore" and forces Mobei Jun to confront the fact that in his determination to be reassured he actually failed to prove himself to Shang Qinghua in return, which reduces Mobei Jun to a shattered wreck struggling to figure out how to fix it.
#svsss#moshang#mobei jun#shang qinghua#scum villain#scum villain's self saving system#mbj and sqh both have abandonment issues is the thing#but mbj's got them like 'test everyone else until they break and prove you right' (don't ask if the testing was what drove them away)#and sqh has them like 'leave them before they can leave you' (don't ever expect that they won't)
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlocking Efficiency with LabVIEW Test Automation

In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to streamline their processes, reduce errors, and enhance productivity. One powerful solution that has emerged to meet these demands is LabVIEW test automation.
What is LabVIEW Test Automation?
LabVIEW, short for Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench, is a system-design platform and development environment ideal for applications that require test, measurement, and control with rapid access to hardware and data insights. Test automation, within the LabVIEW framework, refers to the process of using software to execute pre-scripted tests on software applications and compare the actual results with expected results.
Benefits of LabVIEW Test Automation
Enhanced Efficiency: By automating repetitive testing processes, LabVIEW test automation significantly reduces the time and effort required to validate software functionality. This allows teams to focus their energy on more strategic tasks, ultimately accelerating time-to-market for products and services.
Improved Accuracy: Human error is inevitable, especially during manual testing procedures. However, with LabVIEW test automation, the risk of errors is greatly minimized. Automated tests execute precisely as programmed, ensuring consistent and reliable results with every run.
Cost Savings: While initial setup costs for test automation may be higher, the long-term savings are substantial. By reducing manual labor hours and mitigating the risk of defects slipping into production, businesses can experience significant cost savings over time.
Scalability: As businesses grow and evolve, so do their testing needs. LabVIEW test automation offers scalability, allowing organizations to easily expand their testing capabilities to accommodate new features, platforms, and technologies.
Transitioning to LabVIEW Test Automation
Transitioning to LabVIEW test automation requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key steps to consider:
Assessment: Evaluate your current testing processes and identify areas that would benefit most from automation. Prioritize tests based on frequency, complexity, and potential impact on business objectives.
Tool Selection: Choose the right tools and frameworks that align with your testing requirements and technology stack. LabVIEW offers a comprehensive suite of tools specifically designed for test automation, ensuring seamless integration and maximum efficiency.
Training and Resources: Invest in training programs and resources to empower your team with the knowledge and skills required for successful test automation implementation. Encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing to foster a culture of continuous learning.
Integration: Integrate LabVIEW test automation into your existing development and deployment pipelines. Establish clear communication channels between development, testing, and operations teams to streamline workflows and ensure smooth transitions.
Continuous Improvement: Test automation is not a one-time endeavor but rather a continuous journey of refinement and optimization. Regularly evaluate your automated tests, identify areas for improvement, and iterate accordingly to maximize ROI.
Conclusion
LabVIEW test automation offers a myriad of benefits, including enhanced efficiency, improved accuracy, cost savings, and scalability. By embracing automation, businesses can streamline their testing processes, accelerate time-to-market, and drive overall performance and competitiveness in today’s dynamic market landscape. If you are interested in these types of articles so visit here PujaControls
#technology#automation#labview#software development#labviewsoftware#system testing#roi#system integration#industrial automation
0 notes
Text
something i wanna say on shen yuan taking over shen jiu's body is that i often see mentions that while everyone knew, nobody did anything because they liked shen yuan better, and i think it's important to say that they did do something about it, but just couldn't find the cause.
shen qingqiu went to wei qingwei's sword trials terrace three times to try to pull hong jing, yue qingyuan himself tested him on demonic qi and mu qingfang did ample research to try and find the reason behind the sudden change, but none of them could find anything. only after all that did they consider the option that it could be amnesia, and then they decided that it might be better not to actively reinstate his memories because they thought the new shen qingqiu was more pleasant. but, again, that was only after they couldn't find any evidence that this wasn't shen qingqiu. it's still pretty tragic that they decided they liked someone else better, but in their defense, they didn't know this was actually someone else.
i think it's not so much a case of "we like this version of shen qingqiu better so let's not look into it too deeply", it's more like "we tried every test we have and nothing came of it, so the only explanation left is that this is the real shen qingqiu, but with amnesia"
it reminds me of this meme:

[ID: An edit of a post by @/tockthewatchdog which says, "i mean they did also test sqq, that was a pretty significant thing that happened. like i understand where you're coming from here but they very much did test shen qingqiu". End ID]
ID made by @nebulations thank you so much!!
#i dont mean that it wasnt just as tragic that shen jiu was replaced#but its a bit unfair to insinuate that the peak lords didnt do anything#every test and examination proved that it was the ''real'' shen qingqiu (which the system likely had a hand in)#there wasnt another option left for them to consider#the point of the story/system was also that nobody found out he wasnt shen jiu#so i really think there was an element of system-caused ''plot convenience'' (if that makes sense)#svsss#shen qingqiu#scum villain#svsss meta#shen yuan#shen jiu
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Never forget a test
Testing is the process of evaluating a system or its component(s) with the intent to find whether it satisfies the specified requirements or not. Testing is executing a system in order to identify any gaps, errors, or missing requirements contrary to the actual requirements. This tutorial will give you a basic understanding of software testing, its types, methods, levels, and other related terminologies.
Code that is not tested can’t be trusted
Bad reputation
“Testing is Too Expensive”: Pay less for testing during software development => pay more for maintenance or correction later. Early testing saves both time and cost in many aspects. However, reducing the cost without testing may result in improper design of a software application, rendering the product useless.
“Testing is Time-Consuming”: Testing is never a time-consuming process. However diagnosing and fixing the errors identified during proper testing is a time-consuming but productive activity.
“Only Fully Developed Products are Tested”: No doubt, testing depends on the source code but reviewing requirements and developing test cases is independent from the developed code. However, iterative or incremental approaches to a development life cycle model may reduce the requirement of testing on the fully developed software.
“Complete Testing is Possible”: It becomes an issue when a client or tester thinks that complete testing is possible. It is possible that all paths have been tested by the team but occurrence of complete testing is never possible. There might be some scenarios that are never executed by the test team or the client during the software development life cycle and may be executed once the project has been deployed.
“A Tested Software is Bug-Free”: No one can claim with absolute certainty that a software application is 100% bug-free even if a tester with superb testing skills has tested the application.
“Testers are Responsible for Quality of Product”: It is a very common misinterpretation that only testers or the testing team should be responsible for product quality. Testers’ responsibilities include the identification of bugs to the stakeholders and then it is their decision whether they will fix the bug or release the software. Releasing the software at the time puts more pressure on the testers, as they will be blamed for any error.
“Test Automation should be used wherever possible to Reduce Time”: Yes, it is true that Test Automation reduces the testing time, but it is not possible to start test automation at any time during software development. Test automaton should be started when the software has been manually tested and is stable to some extent. Moreover, test automation can never be used if requirements keep changing.
Basic
This standard deals with the following aspects to determine the quality of a software application:
Quality model
External metrics
Internal metrics
Quality in use metrics
This standard presents some set of quality attributes for any software such as:
Functionality
Reliability
Usability
Efficiency
Maintainability
Portability
Functional Testing
This is a type of black-box testing that is based on the specifications of the software that is to be tested. The application is tested by providing input and then the results are examined that need to conform to the functionality it was intended for. Functional testing of a software is conducted on a complete, integrated system to evaluate the system’s compliance with its specified requirements.
There are five steps that are involved while testing an application for functionality:
The determination of the functionality that the intended application is meant to perform.
The creation of test data based on the specifications of the application.
The output based on the test data and the specifications of the application.
The writing of test scenarios and the execution of test cases.
The comparison of actual and expected results based on the executed test cases.
An effective testing practice will see the above steps applied to the testing policies of every organization and hence it will make sure that the organization maintains the strictest of standards when it comes to software quality.
Unit Testing
This type of testing is performed by developers before the setup is handed over to the testing team to formally execute the test cases. Unit testing is performed by the respective developers on the individual units of source code assigned areas. The developers use test data that is different from the test data of the quality assurance team.
The goal of unit testing is to isolate each part of the program and show that individual parts are correct in terms of requirements and functionality.
Limitations of Unit Testing:
Testing cannot catch each and every bug in an application. It is impossible to evaluate every execution path in every software application. The same is the case with unit testing.
There is a limit to the number of scenarios and test data that a developer can use to verify a source code. After having exhausted all the options, there is no choice but to stop unit testing and merge the code segment with other units.
Integration Testing
Integration testing is defined as the testing of combined parts of an application to determine if they function correctly. Integration testing can be done in two ways: Bottom-up integration testing and Top-down integration testing.
Bottom-up integration: This testing begins with unit testing, followed by tests of progressively higher-level combinations of units called modules or builds.
Top-down integration: In this testing, the highest-level modules are tested first and progressively, lower-level modules are tested thereafter.
In a comprehensive software development environment, bottom-up testing is usually done first, followed by top-down testing. The process concludes with multiple tests of the complete application, preferably in scenarios designed to mimic actual situations.
System Testing
System testing tests the system as a whole. Once all the components are integrated, the application as a whole is tested rigorously to see that it meets the specified Quality Standards. This type of testing is performed by a specialized testing team.
System testing is important because of the following reasons:
System testing is the first step in the Software Development Life Cycle, where the application is tested as a whole.
The application is tested thoroughly to verify that it meets the functional and technical specifications.
The application is tested in an environment that is very close to the production environment where the application will be deployed.
System testing enables us to test, verify, and validate both the business requirements as well as the application architecture.
Regression Testing
Whenever a change in a software application is made, it is quite possible that other areas within the application have been affected by this change. Regression testing is performed to verify that a fixed bug hasn’t resulted in another functionality or business rule violation. The intent of regression testing is to ensure that a change, such as a bug fix should not result in another fault being uncovered in the application.
Regression testing is important because of the following reasons:
Minimize the gaps in testing when an application with changes made has to be tested.
Testing the new changes to verify that the changes made did not affect any other area of the application.
Mitigates risks when regression testing is performed on the application.
Test coverage is increased without compromising timelines.
Increase speed to market the product.
Acceptance Testing
This is arguably the most important type of testing, as it is conducted by the Quality Assurance Team who will gauge whether the application meets the intended specifications and satisfies the client’s requirement. The QA team will have a set of pre-written scenarios and test cases that will be used to test the application.
More ideas will be shared about the application and more tests can be performed on it to gauge its accuracy and the reasons why the project was initiated. Acceptance tests are not only intended to point out simple spelling mistakes, cosmetic errors, or interface gaps, but also to point out any bugs in the application that will result in system crashes or major errors in the application.
By performing acceptance tests on an application, the testing team will deduce how the application will perform in production. There are also legal and contractual requirements for acceptance of the system.
Alpha Testing
This test is the first stage of testing and will be performed amongst the teams (developer and QA teams). Unit testing, integration testing and system testing when combined together is known as alpha testing. During this phase, the following aspects will be tested in the application:
Spelling Mistakes
Broken Links
Cloudy Directions
The Application will be tested on machines with the lowest specification to test loading times and any latency problems.
Beta Testing
This test is performed after alpha testing has been successfully performed. In beta testing, a sample of the intended audience tests the application. Beta testing is also known as pre-release testing. Beta test versions of software are ideally distributed to a wide audience on the Web, partly to give the program a “real-world” test and partly to provide a preview of the next release. In this phase, the audience will be testing the following:
Users will install, run the application and send their feedback to the project team.
Typographical errors, confusing application flow, and even crashes.
Getting the feedback, the project team can fix the problems before releasing the software to the actual users.
The more issues you fix that solve real user problems, the higher the quality of your application will be.
Having a higher-quality application when you release it to the general public will increase customer satisfaction.
Non-Functional Testing
This section is based upon testing an application from its non-functional attributes. Non-functional testing involves testing a software from the requirements which are nonfunctional in nature but important such as performance, security, user interface, etc.
Some of the important and commonly used non-functional testing types are discussed below.
Performance Testing
It is mostly used to identify any bottlenecks or performance issues rather than finding bugs in a software. There are different causes that contribute in lowering the performance of a software:
Network delay
Client-side processing
Database transaction processing
Load balancing between servers
Data rendering
Performance testing is considered as one of the important and mandatory testing type in terms of the following aspects:
Speed (i.e. Response Time, data rendering and accessing)
Capacity
Stability
Scalability
Performance testing can be either qualitative or quantitative and can be divided into different sub-types such as Load testing and Stress testing.
Load Testing
It is a process of testing the behavior of a software by applying maximum load in terms of software accessing and manipulating large input data. It can be done at both normal and peak load conditions. This type of testing identifies the maximum capacity of software and its behavior at peak time.
Most of the time, load testing is performed with the help of automated tools such as Load Runner, AppLoader, IBM Rational Performance Tester, Apache JMeter, Silk Performer, Visual Studio Load Test, etc.
Virtual users (VUsers) are defined in the automated testing tool and the script is executed to verify the load testing for the software. The number of users can be increased or decreased concurrently or incrementally based upon the requirements.
Stress Testing
Stress testing includes testing the behavior of a software under abnormal conditions. For example, it may include taking away some resources or applying a load beyond the actual load limit.
The aim of stress testing is to test the software by applying the load to the system and taking over the resources used by the software to identify the breaking point. This testing can be performed by testing different scenarios such as:
Shutdown or restart of network ports randomly
Turning the database on or off
Running different processes that consume resources such as CPU, memory, server, etc.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is a black-box technique and is used to identify any error(s) and improvements in the software by observing the users through their usage and operation.
According to Nielsen, usability can be defined in terms of five factors, i.e. efficiency of use, learn-ability, memory-ability, errors/safety, and satisfaction. According to him, the usability of a product will be good and the system is usable if it possesses the above factors.
Nigel Bevan and Macleod considered that usability is the quality requirement that can be measured as the outcome of interactions with a computer system. This requirement can be fulfilled and the end-user will be satisfied if the intended goals are achieved effectively with the use of proper resources.
Molich in 2000 stated that a user-friendly system should fulfill the following five goals, i.e., easy to Learn, easy to remember, efficient to use, satisfactory to use, and easy to understand.
In addition to the different definitions of usability, there are some standards and quality models and methods that define usability in the form of attributes and sub-attributes such as ISO-9126, ISO-9241-11, ISO-13407, and IEEE std.610.12, etc.
UI vs Usability Testing
UI testing involves testing the Graphical User Interface of the Software. UI testing ensures that the GUI functions according to the requirements and tested in terms of color, alignment, size, and other properties.
On the other hand, usability testing ensures a good and user-friendly GUI that can be easily handled. UI testing can be considered as a sub-part of usability testing.
Security Testing
Security testing involves testing a software in order to identify any flaws and gaps from security and vulnerability point of view. Listed below are the main aspects that security testing should ensure:
Confidentiality
Integrity
Authentication
Availability
Authorization
Non-repudiation
Software is secure against known and unknown vulnerabilities
Software data is secure
Software is according to all security regulations
Input checking and validation
SQL insertion attacks
Injection flaws
Session management issues
Cross-site scripting attacks
Buffer overflows vulnerabilities
Directory traversal attacks
Portability Testing
Portability testing includes testing a software with the aim to ensure its reusability and that it can be moved from another software as well. Following are the strategies that can be used for portability testing:
Transferring an installed software from one computer to another.
Building executable (.exe) to run the software on different platforms.
Portability testing can be considered as one of the sub-parts of system testing, as this testing type includes overall testing of a software with respect to its usage over different environments. Computer hardware, operating systems, and browsers are the major focus of portability testing. Some of the pre-conditions for portability testing are as follows:
Software should be designed and coded, keeping in mind the portability requirements.
Unit testing has been performed on the associated components.
Integration testing has been performed.
Test environment has been established.
Test Plan
A test plan outlines the strategy that will be used to test an application, the resources that will be used, the test environment in which testing will be performed, and the limitations of the testing and the schedule of testing activities. Typically the Quality Assurance Team Lead will be responsible for writing a Test Plan.
A test plan includes the following:
Introduction to the Test Plan document
Assumptions while testing the application
List of test cases included in testing the application
List of features to be tested
What sort of approach to use while testing the software
List of deliverables that need to be tested
The resources allocated for testing the application
Any risks involved during the testing process
A schedule of tasks and milestones to be achieved
Test Scenario
It is a one line statement that notifies what area in the application will be tested. Test scenarios are used to ensure that all process flows are tested from end to end. A particular area of an application can have as little as one test scenario to a few hundred scenarios depending on the magnitude and complexity of the application.
The terms ‘test scenario’ and ‘test cases’ are used interchangeably, however a test scenario has several steps, whereas a test case has a single step. Viewed from this perspective, test scenarios are test cases, but they include several test cases and the sequence that they should be executed. Apart from this, each test is dependent on the output from the previous test.
Test Case
Test cases involve a set of steps, conditions, and inputs that can be used while performing testing tasks. The main intent of this activity is to ensure whether a software passes or fails in terms of its functionality and other aspects. There are many types of test cases such as functional, negative, error, logical test cases, physical test cases, UI test cases, etc.
Furthermore, test cases are written to keep track of the testing coverage of a software. Generally, there are no formal templates that can be used during test case writing. However, the following components are always available and included in every test case:
Test case ID
Product module
Product version
Revision history
Purpose
Assumptions
Pre-conditions
Steps
Expected outcome
Actual outcome
Post-conditions
Many test cases can be derived from a single test scenario. In addition, sometimes multiple test cases are written for a single software which are collectively known as test suites.
#unit testing#functional testing#integration testing#system testing#regression testing#acceptance testing#alpha testing#beta testing#performance testing#load testing#stress testing#usability testing#security testing#portability testing
0 notes
Text

flowers for the boy!!
2K notes
·
View notes
Text










📺 - color bars !
#plushie#cute#agere#age dreaming#age regression#agedre#system little#little#stuffie#stuffed animal#tv#television#color bars#testing screen#rainbow#eyestrain#pokemon#mimikyu#cat#kitten#vintage#dollhouse furniture#cats vs pickles#objectum#techum
6K notes
·
View notes
Text

i was gonna post this with my other (unrelated) animation but im really sleepy i might post that one tmr
#THE DOGWATER QUALITY IS MAKING ME TWEAKKKK#this was the warmup to the other animation#but somewhere along the way i decided to test my colouring skills#then i remembered csp cant export colours that well#its not my best work i did this on a whim#tbf its the second time i animated fully with colour 🙂↕️🙂↕️#so its not that bad considering#svsss#luo binghe#scum villain's self saving system#i also needed a pony break HAHAHA#anyway we should just animate our own svsss at this point#ignore the fact nothing but the eyes loop its like second nature#my art
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Vibes based grading system.
(for @epistemologys, who wanted some post-canon, teacher WWX)
#poorly drawn mdzs#mdzs#wei wuxian#lan wangji#Thank you for participating in the raffle and for your patience! This was a really fun prompt!#I always loved it when teachers had bonus questions on assignments and tests. Especially if they were fun!#WWX strikes me as the type to have bonus assignments - but also his own chaotic system of what does and doesn't get a point.#Note; not arbitrary. It makes sense to him and anyone who's been around him long enough.#When one has to deal with a lot of things to grade it really does make a difference when something (positive or negitive) stands out.#(especially papers...oh god...shared essay topic grading is a special hell)#He would care that they understand the principals of what he's teaching. He'd also value students thinking outside of the box.#WWX would be hard to argue and *win* against but if the attempt is good enough? I think you'd have his respect and a little bonus point.#I like the idea of post-canon teachers wangxian. Grading papers together can be a love language.#Perhaps it is just a beautiful ending for a character to be able to rest and have stability.#This isn't what being a teacher is like. But in comparison to how WWX was living before? Peace and quiet.
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
(via https://substack-post-media.s3.amazonaws.com/public/images/d18e5226-8335-4455-909d-5a6ef98747a6_1280x1664.gif (1280×1664))
1 note
·
View note
Text



more scum villain rkgk
#svsss#bingqiu#luo binghe#shen qingqiu#rkgk#liujiu#liu qingge#shen jiu#scum villains self saving system#first is from a twitter meme#having an insane artstyle crisis rn#im losing my mind but we pull through ;v;b#also testing new brush
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
i firmly believe that if shen qingqiu had just turned on the waterworks in the water prison luo binghe would've folded like a house of cards. no self detonation no nothing if shen qingqiu had just let the mask down even for 2 minutes and cried real tears luo binghe would've busted him out, healed his wounds, fed him nice food, tucked his shizun in, and punted himself back into the abyss again. my god
#bingqiu#shen qingqiu#shen yuan#luo binghe#scum villain's self saving system#svsss spoilers#keri chats#listen. they are BOTH weak to each other's tears + seeing sqq like actually break#instead of maintaining the dignified facade (system forcing him aside) would've tugged at lbhs heartstrings#hed be crying wailing sniffling white lotus again xin mo be damned do not test me#1k#svsss#danmei
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding the Difference between System Testing and End-to-End Testing

In the realm of software development, testing plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and reliability of the final product. Among the various types of testing methodologies, two terms often encountered are System Testing and End-to-End Testing. But what sets them apart? Let’s dive in and explore the disparities between these two testing approaches. Introduction Before delving into the nuances, let’s start with the basics. System Testing and End-to-End Testing are both integral parts of software testing, each serving distinct purposes in ensuring the functionality and reliability of a software system. System Testing System Testing involves evaluating the system as a whole to ensure that all components work together seamlessly. It focuses on testing the entire software application, including its interfaces with external systems. Think of it as examining the car’s engine, transmission, and other components to ensure they function together effectively. End-to-End Testing End-to-End Testing, on the other hand, is a comprehensive testing approach that examines the entire software application flow from start to finish. It simulates real-world scenarios to validate the system’s functionality across different modules and systems. Picture it as taking a road trip from point A to point B, testing every aspect of the journey to ensure a smooth ride. Key Differences Scope 1) System Testing primarily focuses on individual components or modules within the software system. It ensures that each component performs its intended functions correctly. 2) End-to-End Testing, however, encompasses the entire application flow, including all interconnected components and systems. It verifies the system’s behavior from the user’s perspective, covering multiple modules and interfaces. Complexity 1) System Testing tends to be less complex compared to End-to-End Testing since it deals with testing individual components in isolation. 2) End-to-End Testing is inherently more complex as it involves testing the entire system in a real-world environment, including various interactions and dependencies between different modules. Dependency 1) In System Testing, dependencies on external systems or components are often mocked or simulated to isolate the testing scope. 2) End-to-End Testing relies on real-world environments and interactions between different systems, making it dependent on the availability and stability of external dependencies. Time and Resources 1) System Testing generally requires fewer resources and can be executed relatively quickly since it focuses on specific components or modules. 2) End-to-End Testing demands more time and resources due to its comprehensive nature, involving testing across multiple modules and systems. Stakeholder Involvement 1) System Testing primarily involves developers and testers who are responsible for ensuring the functionality of individual components. 2) End-to-End Testing often requires involvement from various stakeholders, including developers, testers, business analysts, and end-users, to validate the system’s behavior in real-world scenarios. Risks and Benefits 1) System Testing helps identify and mitigate risks associated with individual components, ensuring they meet specified requirements. 2) End-to-End Testing provides a more holistic view of the system’s behavior, uncovering potential issues related to integration, data flow, and user interactions. Challenges Both System Testing and End-to-End Testing come with their own set of challenges. System Testing may overlook integration issues, while End-to-End Testing can be time-consuming and complex to implement. Conclusion In conclusion, while both System Testing and End-to-End Testing are essential components of software testing, they serve different purposes and have distinct scopes. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring thorough testing and delivering high-quality software products.
Also read: Integrating ICT Circuit for Enhanced SCADA Control Systems
#labview#ni software cosulting#plc#software development#industrial automation#system integration#system testing#end to end testing
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Note
Hey bro heads up I desire your Mu Qingfang carnally

pov ur dying
do you still desire him a year later king
#askbox#art#mxtx#svsss#the scum villain's self saving system#mu qingfang#this was supposed to be a liufang drawing but i gave up on qingles#testing new brushes and stuff >:)
755 notes
·
View notes
Text
IM DONE WITH MCAS. IM FREE

199 notes
·
View notes