#user ddl oracle
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
A handy online table structure design software tool, softfactory, to share with you
The online table structure design software tool needs to be straightforward, eliminating confusing settings, simplifying complexities, and prioritizing practicality. It’s easy to get started, and all of these features can be found in softfactory.
Softfactory is a browser-based online table structure design software tool that leverages artificial intelligence to improve efficiency. It can generate CRUD code and push it to development tools. It’s free for everyone to use, ensuring smooth operations in your database.

Having said so much, let’s get to the point.
Simple Workbench
Don’t underestimate our simple workbench; it is comprehensive and powerful, enabling everyone to quickly get started and grasp the key points.
Popular Database Settings
When creating a new project, softfactory can adjust database settings:
Database type: Supports MySQL, Oracle, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, SQLite, etc., and more database types will be supported in the future. You can choose the database character set and database encoding settings, and even if you make mistakes, you can modify them.
Visual Data Tools
Softfactory integrates three practical tools:
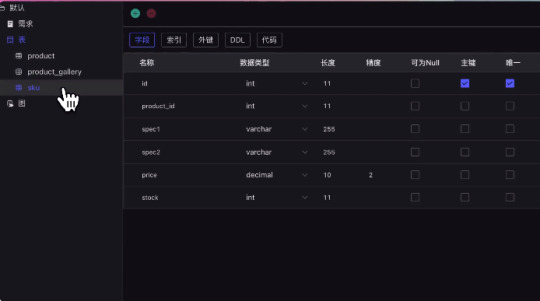
Table designers can use AI to build tables or do it manually. Once the table structure design is completed, CRUD code can be generated by AI and pushed to your local development tools. Table structure generation, firstly, you can obtain the table’s DDL and copy it in the preview window and designer. Secondly, you can generate CRUD code based on the table structure, generate the specified code language, and push the code to the local development tool through the development tool plugin. Diagrams can automatically sort and arrange tables dragged in via foreign keys. Tables without foreign key relationships can also be manually connected and deleted.
Import Existing Structure
If you already have a database but lack a database model, you can use reverse engineering to import the database into the project.
Open Existing Project
You don’t have to start designing the database from scratch. The program allows you to import tables, and the types of table files that can be imported include DDL, PDManer, PowerDesigner.
Arrange Objects in a Few Minutes
Imported objects are pre-arranged, considering their relationships. However, you can freely arrange them to make the project more readable.
Sharing
Users can invite members by providing the team member’s email or sharing the link to invite and share access privileges. Assemble a team, easily share projects, collaborate with multiple team members, communicate in real time, and cooperate seamlessly.
Softfactory, a collision of AI and databases, is setting sail to help programmers liberate their hands. We will continue to dig into the innovative application potential of AI, explore the stage of new AI directions, and continue to promote the development of AI in broader application areas.
If you also like softfactory, welcome to visit: https://www.softfactory.cloud/
0 notes
Text
Question-95: How do you use the DBMS_METADATA_DIFF package in Oracle to compare and generate DDL scripts for database objects?
Interview Questions on Oracle SQL & PLSQL Development: For more questions like this: Do follow the main blog #oracledatabase #interviewquestions #freshers #beginners #intermediatelevel #experienced #eswarstechworld #oracle #interview #development #sql
The DBMS_METADATA_DIFF package in Oracle is a useful tool for comparing database objects and generating Data Definition Language (DDL) scripts that represent the differences between them. It allows users to perform a detailed comparison between two database schemas or objects and generate the necessary SQL statements to synchronize the objects. Here’s an explanation of the concept and usage of…

View On WordPress
#beginners#development#eswarstechworld#Experienced#freshers#intermediatelevel#interview#interviewquestions#oracle#oracledatabase#sql
0 notes
Text
How to Generate table DDL
in this practice we are going to learn how to generate table DDL, view DDL, Materialized View DDL and user DDL.
Hi, in this practice we are going to learn how to generate table DDL, view DDL, Materialized View DDL and user DDL. You also read below articles: DB LINK DDL GET TABLESPACE DDLGET ROLE DDL Get more oracle scritps How do you get DDL of a table in Oracle? In real time environment some times we need to DDL of an existing table. We can perfo this activity with the help of dbms_metadata.get_ddl…

View On WordPress
#dbms_metadata.get_ddl materialized view#dbms_metadata.get_ddl table#dbms_metadata.get_ddl view#get ddl for materialized view in oracle#get ddl in oracle#get ddl of all users in oracle#get ddl of materialized view in oracle#get ddl of schema in oracle#how to get create table script in oracle#how to get ddl of all views in oracle#how to get ddl of users and roles#how to get the query of a view in oracle#how to get the query of materialized view in oracle#how to refresh materialized view in oracle automatically#oracle user ddl with password#schema ddl in oracle#user ddl oracle
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Check Last Password Change History?
How to Check Last Password Change History? #oracledba #oracle #shripaldba #ocptechnology
In this article, we are going to learn how to check past password change history in the oracle database. Using the below commands you can check the password change history step by step. Read: What is control file and datafile in Oracle? When was my Oracle password last changed? The below query will show you the timestamp of last password change. Here i’m checking SCOTT user password change…

View On WordPress
#ctime oracle#get ddl of all users in oracle#how to change expiry date of user in oracle 12c#how to change password in database#how to find who changed oracle user password#how to get user creation script in oracle#how to retrieve user password in oracle 11g#how to retrieve user password in oracle 12c#last password change date in oracle#oracle audit password change#oracle copy users from one database to another#oracle db password change date#oracle export users and passwords#oracle user password table#query to get password of user in oracle#sql query to check password expiry date in oracle
0 notes
Text
What are SQL and PL/SQL, their uses, benefits, and drawbacks?
An Introduction to PL/SQL
Procedural Language Extensions to the Structured Query Language are known as PL/SQL. In relational database management systems, SQL is a popular language for data querying and updating (RDBMS).
PL/SQL enhances the SQL language with numerous procedural constructs to address some of SQL's drawbacks. A more comprehensive programming language option is also provided by PL/SQL for creating mission-critical applications on Oracle databases.
A well-organised and legible programming language is PL/SQL. Its constructions unambiguously convey the code's intention. PL/SQL is also an easy language to learn.
A standardised and portable language for creating Oracle databases is PL/SQL. You can easily port a software that is written to run on an Oracle database to another Oracle database that is compatible.
What is SQL?
Relational databases can be created, maintained, and retrieved using the robust non-procedural database language known as Structured Query Language (SQL) (a type of database that provides and stores data that is related to each other). It was developed by IBM in the 1970s and enables users to communicate with different database management systems according to their accessibility.
SQL commands are classified into six types. These are their names:
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Data Definition Language (DDL)
Data Control Language (DCL)
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
Data Query Language (DDQL)
Advantages sql
There are several benefits to structured query language, some of which are described below:
Without having to create a substantial amount of code, managing database systems is fairly easy using ordinary SQL.
SQL databases based on well-established databases. NoSQL databases don't adhere to any rules.
Programs that run on computers, servers, laptops, and even some mobile phones can use SQL.
Using this domain language, you can instantly get complex question answers from databases.
Using the SQL language, users can design various views of database architecture and databases for various users.
Disadvantages of sql
SQL requires training on a large database.
An expert user or programmer can handle SQL.
It takes up some space, requiring an extra memory location for each record.
It is a platform-specific language.
It is a command-based programming language.
What is pl/sql ?
Oracle The PL/SQL extension for SQL combines the processing power of a procedural language with the data manipulation capabilities of SQL to produce extremely strong SQL queries. By enhancing the security, portability, and robustness of the database, PL/SQL makes sure that SQL commands are processed efficiently.
Using PL/SQL, you may instruct the compiler on both "what to do" and "how to do it" using SQL and its procedural approach.
By using loops, conditions, and object-oriented ideas, it allows programmers more control than other database languages. PL/SQL stands for "Procedural Language Extensions to SQL," in its full form.
What is PL/SQL Developer?
Programmers can combine procedural statements and the power of SQL with PL/SQL, a procedural language (code written in the form of a set of instructions). PL/SQL stands for Procedural Language Extensions to SQL. Triggers, functions, and procedures that increase an operation's functionality while lowering traffic are all executed simultaneously in PL/SQL.
It was developed in the 1990s by Oracle Corporation to build server pages and web applications, and it has features like abstraction and error handling.
Basic PL/SQL Commands
PL/SQL is a procedural (code written in the form of a series of instructions) language that allows programmers to combine the power of SQL with procedural statements. Procedural Language extensions to SQL are abbreviated as PL/SQL.
In PL/SQL, all statements are executed at once, including triggers, functions, and procedures that improve the functionality of an operation while reducing traffic.
Oracle Corporation created it in the 1990s to build server pages and web applications, and it includes features such as abstraction and error handling.
Data Insertion: Using the 'insert' command in this PL/SQL command, data can be inserted into any table. This command will require the table name, column name, and column values. This statement can insert values into any base table. Table names and values are required. Also, the keyword "values" should be used.
Data Update: Using the 'update' statement, data in a table can be easily updated. It can change the value of any column in a table. It requires the table name, column name, and value as input and updates the data.
Selecting data: To retrieve specific data, it must be retrieved from a specific database table. This is made possible by Pl/SQL by the ‘select’ statement.
Exception handling: Use this PL/SQL command to detect error conditions. It intelligently handles errors and allows the user to send appropriate user-defined messages.
The Key Differences Between SQL and PL/SQL
Structural Query Language, or SQL, was created to work with relational databases. It is a declarative language that emphasises specifics. The Procedural Language/Structured Query Language (PL/SQL), on the other hand, makes use of SQL as its database. It is a programming language that is application-oriented.
While PL/SQL has variables, constraints, data types, and other features, SQL does not.
In PL/SQL, code blocks including functions, triggers, variables, control structures (for loop, while), and conditional statements (if...then...else) are written instead of the DDL and DML used in SQL to create queries and commands.
Only one action or query can be run simultaneously in SQL. However, PL/SQL allows for the simultaneous execution of multiple actions or an entire block of close statements. Thus, network traffic is decreased.
Features & Advantages of PL/SQL
Because SQL is processed in batches as opposed to as individual statements, performance is improved.
Efficacy is high.
Integration with SQL is tight.
Full Portability
The principles of object-oriented programming benefit from strict security.
Scalability and administration
Supports creating web applications
encourages the creation of server sites
Disadvantages of PL/SQL
In PL/SQL, stored procedures use a lot of memory and don't have debugging capabilities.
Any modification to the underlying database requires an equivalent modification to the presentation layer.
Because it does not totally divide the duties of back-end developers and front-end developers, it is challenging to separate HTML creation from PL/SQL development.
Conclusion
Using procedures, functions, control structures, cursors, and triggers, PL/SQL executes all of SQL's operations on massive amounts of data. It is essentially SQL with some procedural capabilities added. The necessary data is specified by SQL, but not how it can be obtained. PL/SQL is useful in this situation. we can now handle sophisticated SQL issues that were previously a pain in the neck thanks to the invention of PL/SQL. These days, data is the new oil, and data management is more crucial than ever. As a result, PL/SQL is essential for the operation of many enterprises. Knowledge of PL/SQL and SQL can be quite beneficial.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Structured Query Language

What is SQL?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language, and it is a standard programming language for managing relational databases. It is used to create, modify, and query databases, as well as to manage and control access to the data stored in them. SQL is used by database administrators, developers, and analysts to work with data and automate data-related tasks. SQL allows users to interact with databases by defining and manipulating data structures, running queries, and performing other data-related tasks. SQL is widely used in the industry, and it is supported by many relational database management systems such as MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, and PostgreSQL. It includes three major sub-languages:

DATA DEFINITION LANGUAGE
DATA DEFINITION LANGUAGE (DDL) is a language used to define and manage the database schema or structure. DDL commands are used to create, modify, or delete database objects such as tables, views, indexes, or constraints. Examples of DDL commands are CREATE, ALTER, and DROP.
INTERACTIVE DATA MANIPULATION LANGUAGE
INTERACTIVE DATA MANIPULATION LANGUAGE (IDML) is a language used to manipulate or query data stored in a database. IDML commands are used to insert, retrieve, update, or delete data from a database. Examples of IDML commands are SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
EMBEDDED DATA MANIPULATION LANGUAGE
EMBEDDED DATA MANIPULATION LANGUAGE (EDML) is a programming language used to embed IDML commands into procedural programming code. EDML allows developers to manipulate data stored in a database using programming code written in languages such as C++, Java, or Python. Examples of EDML statements are SQL statements embedded in a C++ program to retrieve data from a database, or an SQL statement embedded in a Java program to insert data into a database.
0 notes
Text
Oracle Database SQL Training
Oracle Database SQL course is an online course that assists you in preparing ng for the OCP exam. We offer a diverse oracle database SQL exam. This course covers all the features of SQL like editing and making running, running reports, transactional writing, writing short p, programs, and more. We have a batch of certified oracle trainers to assist you. It is a practically based SQL online course to help you have a full grip on Oracle database SQL.
Restricting and Sorting Data
Limit the rows that are retrieved by a query
Sort the rows that are retrieved by a query
Use substitution variables
Use the SQL row limiting clause
Create queries using the PIVOT and UNPIVOT clause
Use pattern matching to recognize patterns across multiple rows in a table
Using the Set Operators
Explain set operators
Use a set operator to combine multiple queries into a single query
Control the order of rows returned
Using Single-Row Functions to Customize Output
Describe various types of functions that are available in SQL
Use character, number, and date and analytical (PERCENTILE_CONT, STDDEV, LAG, LEAD) functions in SELECT statements
Use conversion functions
Manipulating Data
Describe the DML statements
Insert rows into a table
Update rows in a table
Delete rows from a table
Control transactions
Reporting Aggregated Data Using the Group Functions
Identify the available group functions
Use group functions
Group data by using the GROUP BY clause
Include or exclude grouped rows by using the HAVING clause
Using DDL Statements to Create and Manage Tables
Categorize the main database objects
Review the table structure
Describe the data types that are available for columns
Create tables
Create constraints for tables
Describe how schema objects work
Truncate tables, and recursively truncate child tables
Use 12c enhancements to the DEFAULT clause, invisible columns, virtual columns and identity columns in table creation/alteration
Displaying Data from Multiple Tables
Use equijoins and nonequijoins
Use a self-join
Use outer joins
Generate a Cartesian product of all rows from two or more tables
Use the cross outer apply clause
Creating Other Schema Objects
Create simple and complex views with visible/invisible columns
Retrieve data from views
Create, maintain and use sequences
Create private and public synonyms
Using Subqueries to Solve Queries
Use subqueries
List the types of subqueries
Use single-row and multiple-row subqueries
Create a lateral inline view in a query
Managing Objects with Data Dictionary Views
Query various data dictionary views
EXTRACT Managing Schema Objects
Manage constraints
Create and maintain indexes including invisible indexes and multiple indexes on the same columns
Create indexes using the CREATE TABLE statement
Create function-based indexes
Drop columns and set column UNUSED
Perform flashback operations
Create and use external tables
Controlling User Access
Differentiate system privileges from object privileges
Grant privileges on tables and on a user
View privileges in the data dictionary
Grant roles
Distinguish between privileges and roles
Manipulating Large Data Sets
Manipulate data using subqueries
Describe the features of multitable INSERTs
Use multitable inserts
Unconditional INSERT
Pivoting INSERT
Conditional ALL INSERT
Conditional FIRST INSERT
Merge rows in a table
Track the changes to data over a period of time
Use explicit default values in INSERT and UPDATE statements
Managing Data in Different Time Zones
Use various date time functions
Tz_offset
from_tz
to_timestamp
to_timestamp_tz
to_yminterval
to_dsinterval
current_date
current_timestamp
localtimestamp
dbtimezone
sessiontimezone
Generating Reports by Grouping Related Data
Use the ROLLUP operation to produce subtotal values
Use the CUBE operation to produce crosstabulation values
Use the GROUPING function to identify the row values created by ROLLUP or CUBE
Use GROUPING SETS to produce a single result set
Retrieving Data Using Subqueries
Use multiple-column subqueries
Use scalar subqueries
Use correlated subqueries
Update and delete rows using correlated subqueries
Use the EXISTS and NOT EXISTS operators
Use the WITH clause
Hierarchical Retrieval
Interpret the concept of a hierarchical query
Create a tree-structured report
Format hierarchical data
Exclude branches from the tree structure
Regular Expression Support
Use meta Characters
Use regular expression functions to search, match and replace
Use replacing patterns
Use regular expressions and check constraints
International Student Fee : 300 USD | 395 CAD | 1,125 AED | 1,125 SAR
Flexible Class Options
Corporate Group Training | Fast-Track
Week End Classes For Professionals SAT | SUN
Online Classes – Live Virtual Class (L.V.C), Online Training
0 notes
Text
Universal database ide

#Universal database ide mac os
#Universal database ide manual
#Universal database ide software
These can help user build high-quality conceptual, logical and physical data models easily and efficiently. Free multi-platform database tool for developers, database administrators, analysts and all people who need to work with databases. It comes with good usability, has practical functions such like: designs the database structure, performs a reverse or forward engineering process, imports models from the ODBC data source, generates complex SQL/DDL, and prints models. SQL Developer Universal Database Frontend. The DDL Processor processes SQL DDL statements using one of the following methods: Transforming DB2 for z/OS syntax DDL statements to DB2 Universal Database. P圜harm a perfect IDE for professional python developers. Running and debugging Golang is easy with GoLand. It analyzes the codes on the fly and suggests fixes for any bugs.
#Universal database ide software
Navicat Data Modeler is a cross-platform visual database design software developed by PremiumSoft from Hong Kong in China. An SQL query tool, database browser, SQL editor, and database administration tool. DataGrip a database IDE that supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Oracle, SQL Server, DB2, MariaDB, Cassandra, Vertica, Hive, etc. It is perfect for building, editing, and running queries.
#Universal database ide mac os
MySQL Workbench is available on Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X. With this IDE, you can visually design, model, generate, and manage databases. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This is a unified visual tool for anyone who works with MySQL databases. Otherwise, please bear all the consequences by yourself. It connects to all popular databases and runs on Win, Mac & Linux. Otherwise, you may receive a variety of copyright complaints and have to deal with them by yourself.īefore using (especially downloading) any resources shared by AppNee, please first go to read our F.A.Q. page more or less. DbVisualizer is the SQL client and database tool with the highest user satisfaction. DbSchema is a universal database design tool for out-of-the-box schema management, schema documentation, design in a team, and deployment on multiple. It gives database professionals the tools they need to build, manage and maintain state-of-the-art database technologies. Powered by our patented Universal Storage, for processing both. DbVisualizer is the universal database tool used by developers, analysts, and database admins all over the world.
#Universal database ide manual
To repost or reproduce, you must add an explicit footnote along with the URL to this article!Īny manual or automated whole-website collecting/crawling behaviors are strictly prohibited.Īny resources shared on AppNee are limited to personal study and research only, any form of commercial behaviors are strictly prohibited. The fully-managed, on-demand cloud database service to power your data-intensive. This article along with all titles and tags are the original content of AppNee.

0 notes
Text
Oracle sqleditor

Oracle sqleditor how to#
Oracle sqleditor update#
For example, if the join condition is partment_id=partment_id, then rows that do not satisfy this condition are not returned.Īn outer join returns all rows that satisfy the join condition and also returns rows from one table for which no rows from the other table satisfy the condition. The optimizer determines the order in which the database joins tables based on the join conditions, indexes, and any available statistics for the tables.Īn inner join is a join of two or more tables that returns only rows that satisfy the join condition. The database combines pairs of rows, each containing one row from each table, for which the join condition evaluates to TRUE. Most joins have at least one join condition, either in the FROM clause or in the WHERE clause, that compares two columns, each from a different table. Unlike DDL statements, DML statements do not implicitly commit the current transaction.ĭescription of "Figure 7-1 Projection and Selection" For example, a transaction to transfer money could involve three discrete operations: decreasing the savings account balance, increasing the checking account balance, and recording the transfer in an account history table. UPDATE employees SET salary=9100 WHERE employee_id=1234 ĭELETE FROM employees WHERE employee_id=1234 Ī collection of DML statements that forms a logical unit of work is called a transaction. INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, last_name, email, job_id, hire_date, salary)
Oracle sqleditor update#
The example uses DML to insert a row into employees, update this row, and then delete it: SELECT * FROM employees The following example uses DML to query the employees table. Lock a table or view, temporarily limiting access by other users ( LOCK TABLE). View the execution plan for a SQL statement ( EXPLAIN PLAN). Remove rows from tables or views ( DELETE). Update or insert rows conditionally into a table or view ( MERGE). Retrieve or fetch data from one or more tables or views ( SELECT).Īdd new rows of data into a table or view ( INSERT) by specifying a list of column values or using a subquery to select and manipulate existing data.Ĭhange column values in existing rows of a table or view ( UPDATE). For example, ALTER TABLE changes the structure of a table, whereas INSERT adds one or more rows to the table.ĭML statements are the most frequently used SQL statements and enable you to: Whereas DDL statements change the structure of the database, DML statements query or change the contents. In either case, the two INSERT statements have already been committed.ĭata manipulation language ( DML) statements query or manipulate data in existing schema objects. If the ALTER TABLE statement succeeds, then the database commits this statement otherwise, the database rolls back this statement. In the preceding example, two INSERT statements are followed by an ALTER TABLE statement, so the database commits the two INSERT statements. INSERT INTO plants VALUES (2, 'Amaryllis') # DML statementĪn implicit COMMIT occurs immediately before the database executes a DDL statement and a COMMIT or ROLLBACK occurs immediately afterward. INSERT INTO plants VALUES (1, 'African Violet') # DML statement The example then uses DDL to alter the table structure, grant and revoke read privileges on this table to a user, and then drop the table. The following example uses DDL statements to create the plants table and then uses DML to insert two rows in the table. Oracle Database also supports techniques that you can use to make the optimizer perform its job better. The application does not need to process the rows one by one, nor does the developer need to know how the rows are physically stored or retrieved.Īll SQL statements use the optimizer, a component of the database that determines the most efficient means of accessing the requested data. The database can pass these rows as a unit to the user, to another SQL statement, or to an application. The database retrieves all rows satisfying the WHERE condition, also called the predicate, in a single step. For example, the following statement queries records for employees whose last name begins with K: SELECT last_name, first_name You need be concerned with implementation details only when you manipulate the data. SQL enables you to work with data at the logical level. The SQL language compiler performs the work of generating a procedure to navigate the database and perform the desired task.
Oracle sqleditor how to#
SQL is declarative in the sense that users specify the result that they want, not how to derive it. There are two broad families of computer languages: declarative languages that are nonprocedural and describe what should be done, and procedural languages such as C++ and Java that describe how things should be done.

1 note
·
View note
Text
MariaDB is a commonly used OpenSource database mainly known for being robust and scalable with new storage engines. MariaDB is a development of MySQL which puts focus on stability and performance and to make it free to users. It is the default database in most Linux distribution. With a variety of tools and plugins, MariaDB is widely applicable. In this guide, we are going to look at how to install MariaDB 10.6 on CentOS 7 | CentOS 8 Features of MariaDB 10.6 MariaDB 10.6 is the current stable version of MariaDB and comes with a number of new features as discussed below: Ignored Indexes – These are indexes that are visible and maintained but not used by the optimizer sys schema supported- This is a “system” database containing views and procedures for investigating performance problems. SKIP LOCKED – Locked tables are skipped from being updated or selected. JSON_TABLE() – can create a JSON table that can be used as a subquery from a JSON document. OFFSET…FETCH…[WITH TIES] – WITH TIES is an optional clause that adds extra functionality. Example as used Oracle compatibility – There are ongoing works in making MariaDB compatible with OracleDB with some Oracle Syntaxes and functions already added. The Improvements in MariaDB 10.6 from MariaDB 10.5 include: Atomic DDL – CREATE, ALTER, DROP and RENAME are atomic and crash safe. If MariaDB server crashes while processing any of these operations, the change will either e done completely or not done at all. InnoDB improvements – First insert to an empty table is faster. Also writes to temporary tables are avoided.Faster implicit and explicit temporary tables. Improvements in Galera. Ability to enable encrypted connections between two nodes without downtime. Also added flags to specify if galera controversial compatible features should be enabled. Clean up to remove unsupported features such as TukoDB Engine, Cassandra Engine, some InnoDB variables and some innodb_checksum_algorithm. Step 1: Update System Packages Ensure that you are running the latest system packages before installation to avoid possible inconveniences with dependencies. sudo dnf upgrade Step 2: Add MariaDB Repository We need to create a MariaDB repo file and add the content for MariaDB installation curl -LsS -O https://downloads.mariadb.com/MariaDB/mariadb_repo_setup sudo bash mariadb_repo_setup --mariadb-server-version=10.6 Command execution output: [info] Checking for script prerequisites. [info] Repository file successfully written to /etc/yum.repos.d/mariadb.repo [info] Adding trusted package signing keys... /etc/pki/rpm-gpg /home/rocky /home/rocky [info] Successfully added trusted package signing keys [info] Cleaning package cache... 62 files removed Step 3: Install MariaDB 10.6 on CentOS 8 | CentOS 7 Once you have saved the repo file, proceed to install MariaDB 10.6 sudo dnf install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client Step 4: Start and Enable MariaDB Once installed, start mariadb and also enable it to start automatically on system reboot. sudo systemctl start mariadb sudo systemctl enable mariadb Secure database server installation: $ sudo mariadb-secure-installation NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY! In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here. Enter current password for root (enter for none): OK, successfully used password, moving on... Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation. You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'. Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] y Enabled successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Change the root password? [Y/n] y New password: Re-enter new password: Password updated successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y ... Success! Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y ... Success! By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Dropping test database... ... Success! - Removing privileges on test database... ... Success! Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y ... Success! Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB! Step 5: Check MariaDB Version We need to first login to MariaDB to be able to check the installed version. $ mysql -u root -p Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 3 Server version: 10.6.4-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> You can already see the installed MariaDB version from the output above. However, you can also run the below command to check MariaDB version MariaDB [(none)]> SELECT VERSION(); +-------------------------------------+ | VERSION() | +-------------------------------------+ | 10.6.4-MariaDB | +-------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> Step 6: How to Create a Database in MariaDB Once you login to Mariadb, create a database as below: #Create a new database MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE db1; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.000 sec) #If the database with the same name exists, you should get an error ERROR 1007 (HY000): Can't create database 'db1'; database exists #Create a database if already exits, replace MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE OR REPLACE DATABASE db1; Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.009 sec) #First check if a database exists MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS db1; Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.000 sec) # Check Databases MariaDB MariaDB [(none)]> SHOW DATABASES; Step 7: How to Create User and Grant Privileges in Mariadb To create a user and grant privileges to the databases, run the commands as shown: #Create user mariadb MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'myuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword'; #Grant all privileges to the user MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword'; #Grant privileges to a specific database MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON 'DB1'.* TO 'user1'@'localhost'; #Remember to refresh the privileges MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH privileges; #To check user grants in MariaDB MariaDB [(none)]> SHOW GRANTS FOR 'myuser'@'localhost'; Step 8: Creating a Table and Adding Data in MariaDB Since we already have a database, we can proceed to create a table and add some values. MariaDB [(none)]> USE db1; MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE TABLE employees (id INT, name VARCHAR(20), email VARCHAR(20)); MariaDB [(none)]> INSERT INTO employees (id,name,email) VALUES(01,"lorna","[email protected]") Cleaning Up MariaDB To completely remove MariaDB, run the following commands:
sudo dnf remove MariaDB-server MariaDB-client sudo rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/ sudo rm /etc/my.cnf You have successfully installed the latest MariaDB version, MariaDB 10.6. We have also seen how you can clean up your MariaDB installation. I hope the guide has been helpful.
0 notes
Photo

What is PostgreSQL? The PostgreSQL database system is an advanced, enterprise-class, and open-source relational database system.In addition to SQL, PostgreSQL supports JSON querying as well as non-relational queries. What Makes PostgreSQL Stand Out? PostgreSQL is the first database management system that implements multi-version concurrency control (MVCC) feature, even before Oracle. PostgreSQL is a general-purpose object-relational database management system. It allows us to add custom functions developed using different programming languages such as C/C++, Java, etc. Procedural Languages Support PostgreSQL supports four standard procedural languages, which allows the users to write their own code in any of the languages and it can be executed by PostgreSQL database server. DDL - data definition language Data definition language (DDL) is used the following commands: Data type declaration CREATE - creates a new database, table, index or procedure. ALTER - modifies an existing database object. DROP - deletes an existing database, table, index or procedure. TRUNCATE TABLE - empties a table for reuse. DML - data manipulation language Data manipulation language is used to work with tables and their contents as in:
INSERT - inserts new rows in a table. UPDATE - updates existing rows in the table. DELETE - deletes rows from a table. SELECT - the main method for querying data from the database. Advantages of PostgreSQL Below are the main advantages/benefits of PostgreSQL: PostgreSQL can run dynamic websites and web apps as a LAMP stack option. PostgreSQL’s write-ahead logging makes it a highly fault-tolerant database. PostgreSQL source code is freely available under an open source license. Low maintenance and administration for both embedded and enterprise use of PostgreSQL. Disadvantages of PostgreSQL Below are the disadvantages/limitations of PostgreSQL: Postgres is not owned by one organization. So, it has had trouble getting its name out there despite being fully featured and comparable to other DBMS systems Changes made for speed improvement requires more work than MySQL as PostgreSQL focuses on compatibility Many open source apps support MySQL, but may not support PostgreSQL On performance metrics, it is slower than MySQL.
0 notes
Text
Using Ora2Pg to Migrate Data from Oracle to openGauss
Introduction to Ora2Pg
Ora2Pg is an open-source tool for migrating data from Oracle to PostgreSQL. By connecting to Oracle, Ora2Pg automatically scans and extracts object structures and data, generates SQL scripts, and applies the scripts to PostgreSQL manually or automatically.
Official website: https://ora2pg.darold.net/
Advantages of Ora2Pg
Supports exporting most types of database objects, including tables, views, sequences, indexes, foreign keys, constraints, functions, stored procedures, and others.
Automatically converts the PL/SQL syntax to the PL/pgSQL syntax, avoiding manual modification to some extent.
Generates migration reports, containing migration difficulty evaluation and person-day estimation.
Compresses exported data to reduce disk overhead as required.
Provides various configuration items, allowing you to customize migration operations.
Application of Ora2Pg in openGauss
The main language of Ora2Pg is Perl. It uses the Perl DBI module and connects to the target PostgreSQL database by using DBD: Pg. openGauss is compatible with PostgreSQL communication protocols and most syntaxes. As such, you only need to modify some names. Ora2Pg can also be used in openGauss.
Usage Example of Ora2Pg
Ora2Pg exports DDL statements of object structures to SQL files. Table data can be exported to files by running the INSERT or COPY statement or be directly imported to the target database without generating intermediate SQL files.
Ora2Pg provides the ora2pg command to complete these processes. Generally, multiple commands need to be executed for one migration. Ora2Pg provides a more convenient method to obtain the export and import scripts and the migration directory template by creating a migration project. The scripts integrate several ora2pg commands and the psql command (gsql for openGauss) required for importing SQL files. You only need to run the two scripts to complete the migration. The demonstration in this document uses the scripts.
Installing Dependencies
The language of Ora2Pg is Perl. Therefore, you need to install the required Perl module.
# Perform the following operations as the root user: yum install -y perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker yum install perl-CPAN
Install DBI, DBD:Pg, DBD:Oracle on which Ora2Pg depends to connect to the database.
perl -MCPAN -e 'install DBI' perl -MCPAN -e 'install DBD:Pg'
Install Oracle Instant Client or Oracle on the local host before installing DBD:Oracle.
# Download Oracle Instant Client from the Oracle official website and install it. rpm -ivh oracle-instantclient12.2-basic-12.2.0.1.0-1.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh oracle-instantclient12.2-devel-12.2.0.1.0-1.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh oracle-instantclient12.2-jdbc-12.2.0.1.0-1.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh oracle-instantclient12.2-sqlplus-12.2.0.1.0-1.x86_64.rpm # Set the environment variable ORACLE_HOME. export ORACLE_HOME=/usr/lib/oracle/11.2/client64 # Set ORACLE_HOME as follows if Oracle has been installed on the local host: export ORACLE_HOME=/opt/oracle/product/19c/dbhome_1 export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib # Install DBD:Oracle. perl -MCPAN -e 'install DBD:Oracle'
Installing Ora2Pg and Creating a Migration Project
Source code path: https://github.com/darold/ora2pg
# Go to the code directory. <you_install_dir> is the target installation path. perl Makefile.PL PREFIX=<your_install_dir> make && make install # Set environment variables and check whether the installation is successful. <source_code_dir> is the path for downloading the code. export PERL5LIB=<source_code_dir>/lib export PATH=$PATH:<your_install_dir>/usr/local/bin ora2pg –help # Create a migration project. ora2pg --init_project oramig
After a migration project is created, the oramig directory template is generated in the current directory, as shown in the following figure. The directory template contains the export_schema.sh and import_all.sh scripts, which are used for subsequent data export and import. The schema and sources directories store DDL statements of each object. The schema directory stores statements after the PL/SQL syntax is converted into the PL/pgSQL syntax, while the sources directory stores PL/SQL statements before conversion. The data directory stores table data files, the config directory contains the ora2pg.conf configuration file, and the reports directory stores migration reports.
./oramig/ schema/ dblinks/ directories/ functions/ grants/ mviews/ packages/ partitions/ procedures/ sequences/ synonyms/ tables/ tablespaces/ triggers/ types/ views/ sources/ functions/ mviews/ packages/ partitions/ procedures/ triggers/ types/ views/ data/ config/ reports/
Now, you can run the ora2pg command. The following lists some command-line parameters that can be specified when you run the ora2pg command. These parameters can be set in the ora2pg.conf file. When you specify a configuration file, the values of the command-line parameters overwrite the corresponding values in the configuration file.
Usage: ora2pg [-dhpqv --estimate_cost --dump_as_html] [--option value] -a | --allow str: Specifies the list of objects that can be exported. The objects are separated by commas (,). -b | --basedir dir: Specifies the default export directory for storing exported SQL files. -c | --conf file: Specifies the path of the configuration file. -e | --exclude str: Specifies the list of objects that are excluded from the export. The objects are separated by commas (,). -i | --input file: Specifies the SQL file to be imported. You do not need to connect to Oracle when importing the file. -o | --out file: Specifies the path for storing the exported SQL file. The default value is the output.sql file in the current directory. -p | --plsql: Enables the conversion from PL/SQL code to PL/pgSQL code. -s | --source DSN: Specifies the data source of Oracle DBI. -t | --type export: Specifies the export type. This parameter will overwrite the export type (specified by TYPE) in the configuration file. -u | --user name: Specifies the username for connecting to Oracle. You can also use the ORA2PG_USER environment variable. -w | --password pwd: Specifies the user password for connecting to Oracle. You can also use the ORA2PG_PASSWD environment variable. --init_project NAME: Initializes a typical Ora2Pg project and generates a directory template. --view_as_table str: Exports views as tables. Use commas (,) to separate multiple views.
Configuring Ora2Pg
The ora2pg.conf file contains all configuration items, which can be used to customize migration operations. The following describes some common configuration items.
ORACLE_HOME: Specifies the environment variable ORACLE_HOME. The DBD:Oracle module uses this variable to search for the required Oracle database. The setting method is involved in dependency installation.
ORACLE_DSN: Specifies the data source name in the standard DBI DSN form. For example:
ORACLE_DSN dbi:Oracle:host=oradb_host.myhost.com;sid=DB_SID;port=1521
or
ORACLE_DSN dbi:Oracle:DB_SID
For the second method, you need to declare the system identifier (SID) in the $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora file or the tnsnames.ora file in the directory specified by the environment variable TNS_ADMIN.
ORACLE_USER and ORACLE_PWD: Define the username and password for connecting to Oracle, respectively. Note that if possible, log in as the Oracle super administrator to avoid permission issues and ensure that nothing is missing.
PG_DSN: Specifies the name of the target database. The following uses openGauss as an example. The database to be connected is mydb with the IP address localhost and the port number 5432.
PG_DSN dbi:Pg:dbname=mydb;host=localhost;port=5432
PG_USER and PG_PWD: Specify the username and password for connecting to the target database, respectively. Note that the user must have the permission to remotely connect to openGauss as well as read and write permissions on the corresponding database. Specifically, the host where Ora2Pg runs and the user must be in the remote access whitelist of openGauss.
SCHEMA: Specifies the schema to be exported. As shown in the following, the objects associated to the APPS schema are extracted.
SCHEMA APPS
ORA_INITIAL_COMMAND: Sends an initial command to Oracle after the connection. For example, disable an access control policy before reading an object or set some session parameters.
TYPE: Specifies the type of the objects to be exported, including tables, views, sequences, indexes, foreign keys, constraints, functions, stored procedures, and others. The default value is TABLE. As shown in the following, ordinary tables and views are exported.
TYPE TABLE VIEW
For more details about the configuration items, visit the official website at the following link:
https://ora2pg.darold.net/documentation.html
Test the connection. After configuring the DSN of Oracle, run the following command to test the database connection:
ora2pg -t SHOW_VERSION -c config/ora2pg.conf
The version of Oracle will be displayed by running the preceding command.
Running Migration Scripts
The configuration is as follows. Connect to the target database as the system user.
ORACLE_HOME /opt/oracle/product/19c/dbhome_1 ORACLE_DSN dbi:Oracle:host=127.0.0.1;sid=ORCLCDB;port=1521 ORACLE_USER system ORACLE_PWD manager SCHEMA testuser PG_DSN dbi:Pg:dbname=mydb;host=127.0.0.1;port=5432 PG_USER testuser PG_PWD openGauss123
Modify the export type of export_schema.sh. In this migration, tables and functions are exported.
Run the export script and wait until the migration is complete. A DDL file of the corresponding type is generated in the schema and source subdirectories, and the command for exporting table data is provided at the end.
sh export_schema.sh
In addition, a migration report in HTML format is generated in the reports directory.
Before running the import script, perform the following operations:
Create a database in openGauss, create a user in the database, and set the owner of mydb to the user. (In import_all.sh, createuser and createdb of PostgreSQL are used to create users and databases.)
Create the environment variable in the bin directory of openGauss, so that the client tool gsql can be used.
Change psql in import_all.sh to gsql.
Add an option for executing the script when data is imported by a common user, and specify the user password to avoid frequent password input.
Run the import script. In the script, the testuser user is used to log in to the mydb database with the IP address 127.0.0.1 and the port number 5432. The -f option indicates that the check on whether the user and database need to be created is skipped.
sh import_all.sh -d mydb -o testuser –h 127.0.0.1 -p 5432 –f 1
After the script is executed, the system prompts you whether to import the object structures and data, as shown in the following figure. (In the preceding information, the -w option is added by manually modifying the import_all.sh script.)
For table indexes and constraints, you can import them after data is imported.
Log in to openGauss to view the migration result.
Disadvantages of Ora2Pg
Ora2Pg uses regular expressions and adopts text replacement to convert the PL/SQL syntax to the PL/pgSQL syntax. However, for design reasons, Ora2Pg supports only conversion of some syntaxes.
DDL statements are generated by concatenating character strings. However, this method does not fully support some syntaxes, such as the syntax for creating partitioned tables.
0 notes
Text
It Industry
As IT industry is blooming now a days, so the demand for IT professionals is inclining day by day. Lots of people with Non -IT background also wants to step into world of IT professionals because of financial and mental satisfaction. Estimated every year these jobs are doubling and it will keep on increasing in future because in today's world we are totally technology dependent even for our day to day activities.
From our mobile phones to our vehicle everything is software, range is quite vast. According to the survey IT industry is and will be the most profitable domain to step into or start with.
Question arises how to get into IT jobs without any prior knowledge or with minimal IT understanding. Good news is there are many areas which one can explore to get entry into IT field easily and quickly. Not only one can get into it easily with minimal or no IT Knowledge but one can earn handsome salary too.
There are majorly four to five sectors involved in order to develop and execute any software successfully.
First is Business Analyst (BA) who is responsible for gathering all requirements from client ,how he (client) wish his software to look and behave. This is high level role and responsibilities of BA. This is also one of the domains in which anyone with IT or no IT Background can step in. One can opt for Business analyst course from professionals who can guide them practically. As a Business Analyst one should be good in communicating and understanding all functional and non functional requirements, methodologies followed to carry out development of project. Choosing best Business analyst course where you are trained on updated and current market trends is the key to success.
Second is Developer who is responsible for actually building the software by following the requirements collected by Business analyst. This person should have good programming knowledge as it includes coding and designing. One should be specialized in any of the programming language knowledge(Java, Dot Net, PHP, C# .Net, Python, ruby etc) in order to become developer. Its difficult to pull this job with no IT Background or knowledge or minimal IT Knowledge. This designation requires in depth training and project experience. This field is not for quick and easy entry in IT industry it requires time. Salary package is really good for developers and Jobs can be permanent or contract based.
Third is Database Administrator (DBA) who is responsible for backend/database of the software where actual data is being stored. As a DBA one should know how to secure database, how to take backups and recover data from different applications or software. Also he is responsible for giving permissions to other users till which level they can access data. In order to get into it one should have great working knowledge of databases like Oracle, SQL Server, DB2 etc. With minimal IT knowledge one can understand and get trained on it. First step can be, to learn SQL as it is considered to be building block for learning databases. There are many SQL training courses but recommended is with practical knowledge of JOINS, SUBQUERIES , CLAUSES,CONSTRAINTS, OBJECTS, DDL,DML, DCL etc.
Fourth is Software Testers (QA) who is responsible for checking whether software is being build according to Clients requirements or not. Testing is to check quality of software and to find all possible bugs in it. This field is totally IT independent which means it does not require any prior IT Knowledge.
One can easily and quickly step into IT by learning software testing. Software testing can be manual as well automated. In manual, one will manually check whether software is looking and behaving according to clients requirements or not whereas in automation , software is tested automatically. Job scope of software testers is increasing dramatically day by day and is considered to be best way to step into IT industry. With effective software testing course or best QA training one can easily and quickly become software tester. Salary package is good for manual testers and even better for automation testers. One should have good hands on expertise in HP ALM, Jira, SQL, HP UFT and with blend of selenium testing , one can enhance their chances of getting their dream job as software testers. Selenium training course should include training on any programming language(Java, Python, C#.net, Ruby etc.) , training of element locators and basic to advance concepts of Selenium, Frameworks etc.
Mainly above mentioned areas are pillars of any IT Company and with practical training on any of them one can step into IT field.
Easy and quick domains are Software Testing, Business Analyst for one who wishes to enter with no IT Knowledge.
With Minimal IT Knowledge you can get into Database administration job, but it needs time and expertise to get job
Lastly in order to fetch Developers job one should be very much experienced in their respective languages.
Contact:
Phone: 289-499-4040
Address: 20A-284 Orenda Road, Brampton, ON, L6T4X6
Send questions and inquiries through our contact form:
http://www.roicians.com/contact-us/
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/roicians/
Connect with us on Instagram: Roicians
1 note
·
View note
Text
Generate DDL script of Schema with EXPDP/IMPDP in Oracle
Generate DDL script of Schema with EXPDP/IMPDP in Oracle
Get DDL of all objects in one script of Schema in Oracle EXPDP the schema with METADATA_ONLY option C:\Users\ORACLE>expdp directory=dbbackup dumpfile=hr_metadata.dmp content=metadata_only Export: Release 18.0.0.0.0 - Production on Wed Feb 2 22:15:37 2022 Version 18.4.0.0.0 Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Username: hr@pdb1 Password: Connected to:…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Dbeaver Mysql Client

DBeaver Overview
DBeaver is a free, open source multiplatform database management tool and SQL client for developers and database administrators. DBeaver can be used to access any database or cloud application that has an ODBC or JDBC driver, such as Oracle, SQL Server, MySQl, Salesforce, or MailChimp. Devart DBeaver provides you with the most important features you'd need when working with a database in a GUI tool, such as:
SQL queries execution
Metadata browsing and editing
SQL scripts management
Data export/import
Data backup
DDL generation
ER diagrams rendering
Test data generation
BLOB/CLOB support
Database objects browsing
Scrollable resultsets
The tool comes in two editions — Community and Enterprise. Enterprise Edition supports NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB or Cassandra, persistent query manager database, SSH tunneling, vector graphics (SVG) and a few other enterprise-level features. Note though that you can access a MongoDB database from DBeaver Community Edition using the respective Devart ODBC driver. For the purposes of this guide, we'll use the Community Edition of DBeaver to retrieve data from Oracle via the Open Database Connectivity driver.
Creating an ODBC Data Source to Use Oracle Data in DBeaver
Click the Start menu and select Control Panel.
Select Administrative Tools, then click ODBC Data Sources.
Click on the System DSN tab if you want to set up a DSN name for all users of the system or select User DSN to configure DSN only for your account.
Click the Add button and double-click Devart ODBC Driver for Oracle in the list.
Give a name to your data source and set up the connection parameters.
Click the Test Connection button to verify that you have properly configured the DSN.
When using ODBC driver for Oracle with DBeaver, SQL_WVARCHAR data types may be displayed incorrectly in DBeaver. To prevent this, you need to set the string data types to Ansi either in the Advanced Settings tab of the driver configuration dialog or directly in the connection string (String Types=Ansi) — all string types will be returned as SQL_CHAR, SQL_VARCHAR and SQL_LONGVARCHAR.
Connecting to Oracle Data from DBeaver via ODBC Driver for Oracle
Follow the steps below to establish a connection to Oracle in DBeaver.
DBeaver SQL Client for OpenEdge. Progress does not have a SQL Client like Microsoft has SQL Server Management Studio or MySQL has Workbench. DBeaver is an excellent SQL Client for OpenEdge using JDBC. This article discusses how to configure DBeaver to connect to OpenEdge using JDBC and execute SQL statements. Install DBeaver. DBeaver is a free, universal SQL client that can connect to numerous types of databases—one of which is MySQL. I want to show you how to install and use DBeaver to connect to your remote MySQL server. First copy mysql.exe and mysqldump.exe into the dbeaver folder. Or you change the Local Client the location in the c0onnection wizard. Improve this answer. Follow edited Sep 7 '20 at 16:54. Answered Sep 7 '20 at 16:36. 19.1k 4 4 gold badges 19 19 silver badges 34 34 bronze badges.
In the Database menu, select New Database Connection.
In the Connect to database wizard, select ODBC and click Next.
Enter the previously configured DSN in the Database/Schema field.
Click Test Connection. If everything goes well, you'll see the Success message.
This article shows how to connect to MySQL data with wizards in DBeaver and browse data in the DBeaver GUI. Create a JDBC Data Source for MySQL Data. Follow the steps below to load the driver JAR in DBeaver. Open the DBeaver application and, in the Databases menu, select the Driver Manager option. Click New to open the Create New Driver form.
Serge-rider commented on Feb 28, 2017 Some MySQL UI clients may have builtin mysqldump, mysqlrestore, mysql.exe + set of libraries of some particular MySQL client version. But DBeaver definitely not one of such clients. On Windows you can install MySQL Workbench (it includes all command line tools).
Viewing Oracle Database Objects and Querying Data
Dbeaver Mysql Client_plugin_auth Is Required
You can expand out the database structure in DBeaver's Database Navigator to visualize all the tables in Oracle database. To view and edit the data in a table, you need to right-click on the target table name and select View data.The content of the table will be displayed in the main workspace.

Dbeaver Mysql Native Client
If you want to write a custom SQL query that will include only the necessary columns from the table, you can select New SQL Editor in the SQL Editor main menu. Create your query and run it by clicking Execute SQL Statement to view the results in the same window.
Dbeaver Mysql Client Download
© 2015-2021 Devart. All Rights Reserved.Request SupportODBC ForumProvide Feedback

0 notes