#Code editor sublime
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Valida tu HTML5 y crea páginas web impecables: Guía para Windows y macOS
Crear una página web es emocionante, pero asegurarte de que funcione correctamente y cumpla con los estándares es igual de importante. La validación de tu código HTML5 te permite detectar errores y garantizar que tu página se muestre correctamente en diferentes navegadores. En esta guía, te mostraremos cómo validar tus documentos HTML5 tanto en Windows como en macOS. ¿Por qué validar tu…
#alicante#código#comunidad valenciana#desarrollo web#editor de código#errores#html5#Sublime Text#validación#Visual Studio Code#w3c
0 notes
Text
Essentials You Need to Become a Web Developer
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript Mastery
Text Editor/Integrated Development Environment (IDE): Popular choices include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text.
Version Control/Git: Platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket allow you to track changes, collaborate with others, and contribute to open-source projects.
Responsive Web Design Skills: Learn CSS frameworks like Bootstrap or Flexbox and master media queries
Understanding of Web Browsers: Familiarize yourself with browser developer tools for debugging and testing your code.
Front-End Frameworks: for example : React, Angular, or Vue.js are powerful tools for building dynamic and interactive web applications.
Back-End Development Skills: Understanding server-side programming languages (e.g., Node.js, Python, Ruby , php) and databases (e.g., MySQL, MongoDB)
Web Hosting and Deployment Knowledge: Platforms like Heroku, Vercel , Netlify, or AWS can help simplify this process.
Basic DevOps and CI/CD Understanding
Soft Skills and Problem-Solving: Effective communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills
Confidence in Yourself: Confidence is a powerful asset. Believe in your abilities, and don't be afraid to take on challenging projects. The more you trust yourself, the more you'll be able to tackle complex coding tasks and overcome obstacles with determination.
#code#codeblr#css#html#javascript#java development company#python#studyblr#progblr#programming#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#webdev#website#tech#html css#learn to code
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Build Software Projects for Beginners

Building software projects is one of the best ways to learn programming and gain practical experience. Whether you want to enhance your resume or simply enjoy coding, starting your own project can be incredibly rewarding. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started.
1. Choose Your Project Idea
Select a project that interests you and is appropriate for your skill level. Here are some ideas:
To-do list application
Personal blog or portfolio website
Weather app using a public API
Simple game (like Tic-Tac-Toe)
2. Define the Scope
Outline what features you want in your project. Start small and focus on the minimum viable product (MVP) — the simplest version of your idea that is still functional. You can always add more features later!
3. Choose the Right Tools and Technologies
Based on your project, choose the appropriate programming languages, frameworks, and tools:
Web Development: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, or Django
Mobile Development: Flutter, React Native, or native languages (Java/Kotlin for Android, Swift for iOS)
Game Development: Unity (C#), Godot (GDScript), or Pygame (Python)
4. Set Up Your Development Environment
Install the necessary software and tools:
Code editor (e.g., Visual Studio Code, Atom, or Sublime Text)
Version control (e.g., Git and GitHub for collaboration and backup)
Frameworks and libraries (install via package managers like npm, pip, or gems)
5. Break Down the Project into Tasks
Divide your project into smaller, manageable tasks. Create a to-do list or use project management tools like Trello or Asana to keep track of your progress.
6. Start Coding!
Begin with the core functionality of your project. Don’t worry about perfection at this stage. Focus on getting your code to work, and remember to:
Write clean, readable code
Test your code frequently
Commit your changes regularly using Git
7. Test and Debug
Once you have a working version, thoroughly test it. Look for bugs and fix any issues you encounter. Testing ensures your software functions correctly and provides a better user experience.
8. Seek Feedback
Share your project with friends, family, or online communities. Feedback can provide valuable insights and suggestions for improvement. Consider platforms like GitHub to showcase your work and get input from other developers.
9. Iterate and Improve
Based on feedback, make improvements and add new features. Software development is an iterative process, so don’t hesitate to refine your project continuously.
10. Document Your Work
Write documentation for your project. Include instructions on how to set it up, use it, and contribute. Good documentation helps others understand your project and can attract potential collaborators.
Conclusion
Building software projects is a fantastic way to learn and grow as a developer. Follow these steps, stay persistent, and enjoy the process. Remember, every project is a learning experience that will enhance your skills and confidence!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
JavaScript Tutorial: A Beginner's Guide to the World of Web Development
Welcome to the exciting world of JavaScript! If you're looking to dive into web development, understanding JavaScript is essential. This versatile programming language powers the interactive elements of websites and is a key component of modern web applications. In this tutorial, we'll cover the basics of JavaScript, its syntax, and some practical examples to get you started.
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a high-level, dynamic, and interpreted programming language that is primarily used for enhancing the interactivity of web pages. It allows developers to create rich user experiences by manipulating HTML and CSS, responding to user events, and communicating with servers.
Why Learn JavaScript?
Ubiquity: JavaScript is supported by all modern web browsers, making it a universal language for web development.
Versatility: Beyond the browser, JavaScript can be used on the server-side (with Node.js), in mobile app development (with frameworks like React Native), and even in game development.
Community and Resources: With a vast community and numerous resources available, learning JavaScript is more accessible than ever.
Getting Started with JavaScript
Setting Up Your Environment
To start coding in JavaScript, you don't need any special software. All you need is a web browser and a text editor. Here’s how to set it up:
Choose a Text Editor: Popular options include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, and Atom.
Open Your Browser: You can use any modern browser like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Learn HTML and CSS: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Introduction to HTML and CSS
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) are the core technologies for creating web pages. HTML provides the structure of the page, while CSS defines its style and layout. This guide aims to equip beginners with the essential knowledge to start building and designing web pages.
Why Learn HTML and CSS?
HTML and CSS are fundamental skills for web development. Whether you're looking to create personal websites, start a career in web development, or enhance your current skill set, understanding these technologies is crucial. They form the basis for more advanced languages and frameworks like JavaScript, React, and Angular.
Getting Started with HTML and CSS
To get started, you need a text editor and a web browser. Popular text editors include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, and Atom. Browsers like Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari are excellent for viewing and testing your web pages.
Basic HTML Structure
HTML documents have a basic structure composed of various elements and tags. Here’s a simple example:
html
Copy code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Web Page</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Web Page</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph of text on my web page.</p>
</body>
</html>
: Declares the document type and HTML version.
: The root element of an HTML page.
: Contains meta-information about the document.
: Connects the HTML to an external CSS file.
: Contains the content of the web page.
Essential HTML Tags
HTML uses various tags to define different parts of a web page:
to : Headings of different levels.
: Paragraph of text.
: Anchor tag for hyperlinks.
: Embeds images.
: Defines divisions or sections.
: Inline container for text.
Creating Your First HTML Page
Follow these steps to create a simple HTML page:
Open your text editor.
Write the basic HTML structure as shown above.
Add a heading with the tag.
Add a paragraph with the tag.
Save the file with a .html extension (e.g., index.html).
Open the file in your web browser to view your web page.
Introduction to CSS
CSS is used to style and layout HTML elements. It can be included within the HTML file using the <style> tag or in a separate .css file linked with the <link> tag.
Basic CSS Syntax
CSS consists of selectors and declarations. Here’s an example:
css
Copy code
h1 {
color: blue;
font-size: 24px;
}
Selector (h1): Specifies the HTML element to be styled.
Declaration Block: Contains one or more declarations, each consisting of a property and a value.
Styling HTML with CSS
To style your HTML elements, you can use different selectors:
Element Selector: Styles all instances of an element.
Class Selector: Styles elements with a specific class.
ID Selector: Styles a single element with a specific ID.
Example:
html
Copy code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Styled Page</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="main-heading">Hello, World!</h1>
<p id="intro">This is an introduction paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
In the styles.css file:
css
Copy code
.main-heading {
color: green;
text-align: center;
}
#intro {
font-size: 18px;
color: grey;
}
CSS Layout Techniques
CSS provides several layout techniques to design complex web pages:
Box Model: Defines the structure of an element’s content, padding, border, and margin.
Flexbox: A layout model for arranging items within a container, making it easier to design flexible responsive layouts.
Grid Layout: A two-dimensional layout system for more complex layouts.
Example of Flexbox:
css
Copy code
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
.item {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
Best Practices for Writing HTML and CSS
Semantic HTML: Use HTML tags that describe their meaning clearly (e.g., , , ).
Clean Code: Indent nested elements and use comments for better readability.
Validation: Use tools like the W3C Markup Validation Service to ensure your HTML and CSS are error-free and standards-compliant.
Accessibility: Make sure your website is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by using proper HTML tags and attributes.
Free Resources to Learn HTML and CSS
W3Schools: Comprehensive tutorials and references.
MDN Web Docs: Detailed documentation and guides for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Codecademy: Interactive courses on web development.
FreeCodeCamp: Extensive curriculum covering HTML, CSS, and more.
Khan Academy: Lessons on computer programming and web development.
FAQs about Learning HTML and CSS
Q: What is HTML and CSS? A: HTML (HyperText Markup Language) structures web pages, while CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) styles and layouts the web pages.
Q: Why should I learn HTML and CSS? A: Learning HTML and CSS is essential for creating websites, understanding web development frameworks, and progressing to more advanced programming languages.
Q: Do I need prior experience to learn HTML and CSS? A: No prior experience is required. HTML and CSS are beginner-friendly and easy to learn.
Q: How long does it take to learn HTML and CSS? A: The time varies depending on your learning pace. With consistent practice, you can grasp the basics in a few weeks.
Q: Can I create a website using only HTML and CSS? A: Yes, you can create a basic website. For more complex functionality, you'll need to learn JavaScript.
Q: What tools do I need to start learning HTML and CSS? A: You need a text editor (e.g., Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text) and a web browser (e.g., Google Chrome, Firefox).
Q: Are there free resources available to learn HTML and CSS? A: Yes, there are many free resources available online, including W3Schools, MDN Web Docs, Codecademy, FreeCodeCamp, and Khan Academy.
#how to learn html and css#html & css course#html & css tutorial#html and css#html course#html css tutorial#html learn#html learn website#learn html#learn html and css#html and css course#html and css full course#html and css online course#how to learn html and css for beginners
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Notetaking
If you had told me years ago that I would now enjoy taking notes, I would have told you to get the hell out of my face with that mess.
I've always recognized the value of taking notes, and while I would take notes at times, I can't say I much enjoyed taking notes, knew how to best take notes, or how to get the most value out of my notes.
In fact, I would argue I'm still mediocre at taking notes, but thanks to some technology and a few habits I've developed, I've gotten better at it, enjoy it more, and get more value out of it than I did for years.
The first rule of notetaking is: Assume you will forget everything. Write your notes accordingly.
The second rule of notetaking is: Don't write everything down. Write the most salient points down so you can connect the dots and make the necessary connections when re-reading your notes later.
The third rule of notetaking is: Assume you are writing your notes for a complete stranger. Make your notes clear enough that anyone can re-read them and understand them clearly. This is because when you will re-read your notes much later, you might as well be a complete stranger to who you were when you originally took the notes.
I find notetaking especially valuable to me when I'm learning something new. Notes are a way of making sure the time and effort I spend learning isn't wasted or lost because of my poor memory. More than a tool: They're a friend. They're there to help. They're you helping yourself later.
I love technology, so I'm always trying to find ways for tech. to help me with things. Hand-written notes have their value and I won't debate their merits, but I'm more efficient with a keyboard than I am with pen and paper. Plus, with notes taken electronically, you can search for a specific word or phrase through all of them, which has come in handy several times.
For every job or task, you need the right tool for the job. In the case of notetaking software, you need two kinds of notetaking tools:
A tool for quick notes: We all have notes that we need to quickly take but don't necessarily need to keep in the long term. This is what this tool is for. Formatting and presentation are not the priority here: Speed is. Good software for this are Microsoft Notepad, Microsoft Sticky Notes, Microsoft Visual Studio (VS) Code, Sublime, Atom, Notepad++, Apple Notes, and any other lightweight text editor that isn't necessarily pretty but that you can start writing in within seconds. Despite not necessarily needing the notes to be kept, I still like something with a cloud backend that synchronizes notes. Just in case. I also like being able to access my notes from the various operating systems I use. For these reasons, I prefer Microsoft Sticky Notes on Windows and Apple Notes on macOS, iOS, and iPadOS.
A tool for persistent notes: This is the main event. This is what we usually think of when we think of notetaking software. This lets you add various forms of media such as diagrams, pictures, video, audio, or even hand-written portions. The need here is to be able to make complex, pretty notes that will be accessible for years to come. This necessarily means the tool has to have a cloud backend to make sure your notes are always saved online so they are never lost and are accessible from everywhere. The major contenders here are Microsoft OneNote and Evernote, among others. I personally prefer OneNote.
The thing I noticed after making my notetaking software choices was that once I had picked them, I ended up using them more. A tool you use more because you want to, is a good tool. As a result, this has helped me keep more things for posterity (Hello, my name is Chris, and I am a digital hoarder.) The benefit is that I take and keep more notes now than I ever did before, which means I retain more knowledge, thoughts, ideas, and information than I did before and that's a net positive.
Notetaking isn't just about the software you use, though.
There needs to be a methodology to make sure you get the most out of your notes. Follow these steps:
Write your notes as you're learning the thing. They don't need to be pretty; but they do need to be minimally understandable. This step can be done in a quick notetaking application with a cloud backend.
Within 24 hours, go over your notes and rewrite them so they are structured and pretty (Heading 1, Heading 2, bulleted lists, identify action items, etc.) This is the most important and valuable step that I didn't do for years. This step helps you make sense of your notes, but more importantly: Of what you learned. Most of the value of your notes are yielded in this step. In this step, you might even come up with questions you hadn't thought of when you first took your notes. Questions whose answers will likely yield further insight and understanding into the new thing you're learning. This step needs to be done in a persistent notetaking application.
Within 7 days, review your notes. This helps you make sure your notes make sense, but also helps you recall what you learned. Feel free to edit, update, or tweak your notes to make them even more easy to understand
Refer to your notes whenever you need to in the future. You will likely have a better understanding of your notes because you now master the subject better, but your notes are also much clearer than they were in the first step
To be clear, I am not some notetaking guru or expert. This is just what has worked well for me over the years.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the Ultimate Handbook for Aspiring Full Stack Developers

In the ever-evolving realm of technology, the role of a full-stack developer has undeniably gained prominence. Full-stack developers epitomize versatility and are an indispensable asset to any enterprise or endeavor. They wield a comprehensive array of competencies that empower them to navigate the intricate landscape of both front-end and back-end web development. In this exhaustive compendium, we shall delve into the intricacies of transforming into a proficient full-stack developer, dissecting the requisite skills, indispensable tools, and strategies for excellence in this domain.
Deciphering the Full Stack Developer Persona
A full-stack developer stands as a connoisseur of both front-end and back-end web development. Their mastery extends across the entire spectrum of web development, rendering them highly coveted entities within the tech sector. The front end of a website is the facet accessible to users, while the back end operates stealthily behind the scenes, handling the intricacies of databases and server management. You can learn it from Uncodemy which is the Best Full stack Developer Institute in Delhi.
The Requisite Competencies
To embark on a successful journey as a full-stack developer, one must amass a diverse skill set. These proficiencies can be broadly categorized into front-end and back-end development, coupled with other quintessential talents:
Front-End Development
Markup Linguistics and Style Sheets: Cultivating an in-depth grasp of markup linguistics and style sheets like HTML and CSS is fundamental to crafting visually captivating and responsive user interfaces.
JavaScript Mastery: JavaScript constitutes the linchpin of front-end development. Proficiency in this language is the linchpin for crafting dynamic web applications.
Frameworks and Libraries: Familiarization with popular front-end frameworks and libraries such as React, Angular, and Vue.js is indispensable as they streamline the development process and elevate the user experience.
Back-End Development
Server-Side Linguistics: Proficiency in server-side languages like Node.js, Python, Ruby, or Java is imperative as these languages fuel the back-end functionalities of websites.
Database Dexterity: Acquiring proficiency in the manipulation of databases, including SQL and NoSQL variants like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB, is paramount.
API Expertise: Comprehending the creation and consumption of APIs is essential, serving as the conduit for data interchange between the front-end and back-end facets.
Supplementary Competencies
Version Control Proficiency: Mastery in version control systems such as Git assumes monumental significance for collaborative code management.
Embracing DevOps: Familiarity with DevOps practices is instrumental in automating and streamlining the development and deployment processes.
Problem-Solving Prowess: Full-stack developers necessitate robust problem-solving acumen to diagnose issues and optimize code for enhanced efficiency.
The Instruments of the Craft
Full-stack developers wield an arsenal of tools and technologies to conceive, validate, and deploy web applications. The following are indispensable tools that merit assimilation:
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
Visual Studio Code: This open-source code editor, hailed for its customizability, enjoys widespread adoption within the development fraternity.
Sublime Text: A lightweight and efficient code editor replete with an extensive repository of extensions.
Version Control
Git: As the preeminent version control system, Git is indispensable for tracking code modifications and facilitating collaborative efforts.
GitHub: A web-based platform dedicated to hosting Git repositories and fostering collaboration among developers.
Front-End Frameworks
React A potent JavaScript library for crafting user interfaces with finesse.
Angular: A comprehensive front-end framework catering to the construction of dynamic web applications.
Back-End Technologies
Node.js: A favored server-side runtime that facilitates the development of scalable, high-performance applications.
Express.js: A web application framework tailor-made for Node.js, simplifying back-end development endeavors.
Databases
MongoDB: A NoSQL database perfectly suited for managing copious amounts of unstructured data.
PostgreSQL: A potent open-source relational database management system.
Elevating Your Proficiency as a Full-Stack Developer
True excellence as a full-stack developer transcends mere technical acumen. Here are some strategies to help you distinguish yourself in this competitive sphere:
Continual Learning: Given the rapid evolution of technology, it's imperative to remain abreast of the latest trends and tools.
Embark on Personal Projects: Forge your path by creating bespoke web applications to showcase your skills and amass a portfolio.
Collaboration and Networking: Participation in developer communities, attendance at conferences, and collaborative ventures with fellow professionals are key to growth.
A Problem-Solving Mindset: Cultivate a robust ability to navigate complex challenges and optimize code for enhanced efficiency.
Embracing Soft Skills: Effective communication, collaborative teamwork, and adaptability are indispensable in a professional milieu.
In Closing
Becoming a full-stack developer is a gratifying odyssey that demands unwavering dedication and a resolute commitment to perpetual learning. Armed with the right skill set, tools, and mindset, one can truly shine in this dynamic domain. Full-stack developers are in high demand, and as you embark on this voyage, you'll discover a plethora of opportunities beckoning you.
So, if you aspire to join the echelons of full-stack developers and etch your name in the annals of the tech world, commence your journey by honing your skills and laying a robust foundation in both front-end and back-end development. Your odyssey to becoming an adept full-stack developer commences now.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
202310271453
In the wondrous realm of the mind, where neurons dance to the tune of thoughts, we embark on a journey through the cosmos of knowledge.
Our quest delves deep into the heart of cognition, where neuroscience unlocks the mysteries of our mental symphony. But this is no solitary exploration; it's a waltz of interconnected ideas.
Imagine, if you will, a thought in motion, a neuron firing, setting the stage for what we call the mind. It's a captivating performance, an intricate ballet where every step taken by your thoughts orchestrates the dance of consciousness. As thought evolves, so does the mind, a conductor of the body's orchestra, directing each note with precision.
But what lies beyond the confines of the self? As the mind extends its reach, we glimpse the vast outer-firmament, a macrocosm awaiting exploration. It's a canvas for us to paint our thoughts and emotions, where inner meets outer, and microcosm embraces macrocosm.
Now, let's transition to the world of programming, where functional reactive programming becomes our musical score. Like a grand symphony, it harmonizes data and actions, creating an enchanting melody of software development. As we delve into the intricacies of code, we find beauty in the logic of systems.
Ancient Hebrew and Koine Greek, languages steeped in history, guide us through the wisdom of antiquity. Their words resonate like ancient incantations, connecting us to the past. A linguistic bridge to forgotten eras.
Paracelsus, the alchemical maestro, takes us on an alchemical journey where matter and spirit converge. The essence of transformation, both in the laboratory and the soul, unfolds before us. His teachings serve as our guide.
And in the digital realm, we meet Philip Wadler, a luminary in the world of programming languages. His insights into functional programming provide the tools to craft elegant and efficient software. Unix, the operating system that powers the digital world, becomes our playground.
Quareia Josephine McCarthy invites us into the mystical world of magic, where intention and ritual become catalysts for change. Her teachings merge with the essence of our thoughts and actions, empowering our rituals for transformation.
Now, let's shift our focus to the realm of data, where vector databases store knowledge like ancient scrolls in a library of the mind. This modern-age wisdom repository becomes a vessel for our quest.Venture into the digital landscapes of MUDs, where storytelling takes a digital form. It's a place where we merge the ancient art of storytelling with the modern realms of code and creativity.
As we seek the alchemical parallels in the Hebrew language to the periodic table of elements, we unravel the hidden mysteries of creation. The building blocks of matter interweave with the essence of ancient language.
Our fingers dance on mechanical keyboards, each keypress a tactile pleasure, like a musician playing an instrument. The choice of keycaps becomes our artistic expression, a tactile symphony of keystrokes.
Dr. Joe Dispenza guides us into the territory of the mind's potential. With every thought and intention, we mold our reality. It's a powerful reminder that we are the architects of our destinies.
Vim, the text editor, becomes our quill, crafting the narratives of code. It's a tool for those who understand that precision and efficiency are the keystones of programming.
In the realm of productivity and flow, we journey with the Flow Research Collective. Their wisdom helps us unlock our peak performance and harness the tides of creativity.
Now, let's embark on epic adventures in the world of RPGs, where stories and characters are woven with code. Sublime Text becomes our spellbook, casting enchantments of efficiency over our code.
As we dive deeper into the labyrinth of the self, we realize that the ego is but a shadow, a character we control in the grand narrative of existence. We transcend definitions and become the authors of our own stories.
Sam Ovens, the master of entrepreneurship, shares his insights on building businesses. It's a journey where we blend creativity and strategy, forging empires in the digital age.
Carlo Suares takes us into the world of mystical symbolism, where every letter holds a universe of meaning. We decipher the secrets encoded in the very fabric of reality.
Eric Elliott's expertise in JavaScript shines as we navigate the digital landscape. It's a world where code becomes the paintbrush, and the canvas is the browser.
Kyle M. Yates invites us to explore the philosophy of consciousness. It's a journey into the depths of the mind, a quest to understand the essence of being.
J. Gresham Machen and Page H. Kelley lead us through the pages of academia, where knowledge is both the key and the door to understanding. It's a place where ideas are born and nurtured.
John J. Owens shares his wisdom on intention, catalysts, and the art of ritual rehearsal. It's a magical journey where we learn to wield the power of intention to shape our reality.
Connoisseur Nic Vapes introduces us to the world of e-liquids and vaporizers. It's a sensory experience where flavors and aromas dance on our taste buds, a symphony of vapor.
Mikhaila Peterson, the advocate of a holistic approach to health, guides us through the world of adaptogens and natural remedies. It's a journey of vitality and well-being.
Green coffee, a treasure trove of antioxidants and energy, fuels our quest for health and vitality. It's a brew that awakens our senses and energizes our minds.
Analog technology, a realm of nostalgia and craftsmanship, takes us back to a time when machines were tangible and repairable. It's a world where we appreciate the art of the mechanical.
Cannabis, a plant with a history as rich as it is controversial, becomes a canvas for exploration. It's a journey into the depths of herbal wisdom and the science of cannabinoids.
And in the digital world, Redux.js, a state management library, becomes our companion as we navigate the intricate dance of data flow. It's a tool that empowers us to create robust web applications.
These are the passions that fuel our journey, the pillars of our education. We are both the teachers and the students, on a perpetual quest for knowledge, self-improvement, and mastery. As we continue to explore this tapestry of passions, we invite you to join us on this extraordinary odyssey.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
C++ Tools Every Programmer Should Know in 2023

As technology continues to evolve rapidly, it is essential for programmers to stay updated with the latest tools to enhance their productivity and efficiency. In this article, we will explore some of the top C++ tools that every programmer should know in 2023. From integrated development environments (IDEs) to debuggers, code editors, libraries and frameworks, documentation tools, and build systems, we'll cover a comprehensive range of tools that will help programmers streamline their C++ development process. 1. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) Visual Studio Code Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a highly popular and powerful IDE that offers excellent support for C++ development. It provides a wide range of features, including code completion, syntax highlighting, debugging capabilities, and easy integration with version control systems like Git. Eclipse Eclipse is another widely used IDE for C++ development. It offers a comprehensive set of tools, such as code refactoring, code navigation, and a customizable user interface. Eclipse also supports various plugins and extensions to enhance its functionality further. Qt Creator Qt Creator is a specialized IDE for C++ and Qt development. It provides an intuitive and user-friendly interface, along with powerful tools for designing graphical user interfaces (GUIs) using the Qt framework. Qt Creator also supports cross-platform development, making it an excellent choice for C++ programmers. 2. Debuggers 2.1 GDB The GNU Debugger (GDB) is a command-line debugger that helps programmers analyze and debug their C++ code efficiently. It allows breakpoints, stepping through code, inspecting variables, and examining call stacks, among other debugging features. GDB is highly customizable and supports various platforms. 2.2 Visual Studio Debugger The Visual Studio Debugger is a robust and user-friendly debugger provided by Microsoft Visual Studio. It offers advanced debugging capabilities for C++ programs, including real-time expression evaluation, memory tracking, and parallel debugging. The Visual Studio Debugger integrates seamlessly with Visual Studio IDE. 2.3 LLDB LLDB is a powerful, modern debugger primarily developed for LLVM-based programming languages such as C++. It provides capabilities like multithreaded debugging, just-in-time compilation, and efficient memory management. LLDB offers a command-line interface and can be used on multiple platforms. 3. Code Editors 3.1 Sublime Text Sublime Text is a lightweight yet feature-rich code editor known for its speed and extensibility. It offers a minimalistic user interface, multiple selections, powerful search and replace functionality, and a vast collection of plugins to customize the editor according to programmers' needs. 3.2 Atom Atom is a highly customizable and open-source code editor that gained popularity among developers. It supports various programming languages, including C++, and provides features like smart autocompletion, file system browser, and Git integration. Atom also allows third-party package installations to extend its functionality. 3.3 Vim Vim is a highly efficient and text-based code editor preferred by many experienced programmers. It offers a wide range of features designed to enhance developers' productivity, such as extensive key bindings, split editing, powerful search and replace, and support for plugins and scripts. 4. Libraries and Frameworks 4.1 Boost Boost is a widely used C++ libraries collection known for its high-quality and portable code. It provides a range of libraries that cover various aspects of C++ programming, including smart pointers, multithreading, regular expressions, and container classes. Boost libraries offer excellent support and compatibility with different platforms. 4.2 Qt Qt is a comprehensive cross-platform framework that includes a powerful set of C++ libraries and tools. It enables developers to create high-performance applications with an intuitive UI and supports features like network programming, XML processing, database connectivity, and 3D rendering. Qt is widely adopted for GUI application development. 4.3 STL The Standard Template Library (STL) is an essential component of C++ programming. It offers a collection of generic algorithms, containers, and iterators, making it easier to write efficient and maintainable code. STL provides various data structures and algorithms, such as vectors, lists, sorting, and searching functions. 5. Documentation Tools 5.1 Doxygen Doxygen is a popular documentation tool for C++ projects. It automatically generates documentation from properly formatted comments in the source code. Doxygen supports various output formats like HTML, LaTeX, and PDF, allowing programmers to create professional-looking documentation for their projects easily. 5.2 Docutils Docutils is a Python-based documentation tool that provides support for multiple markup languages, including reStructuredText. It enables programmers to write documentation in a human-readable format and convert it into different output formats. Docutils is widely used in the C++ community for documenting projects. 5.3 Sphinx Sphinx is another widely adopted documentation tool that integrates well with the C++ ecosystem. It supports multiple markup languages, including reStructuredText and Markdown, and offers features like automatic cross-referencing, code highlighting, and generation of API documentation. Sphinx is highly customizable and extensible. 6. Build Systems 6.1 CMake CMake is a popular build system that simplifies the process of building C++ projects across multiple platforms and compilers. It provides a unified build configuration language and generates platform-specific build scripts. CMake offers excellent scalability and flexibility, making it suitable for projects of any size. 6.2 Make Make is a classic and widely used build system for C++ projects. It utilizes makefiles to automate the build process by specifying dependencies and actions. Make is highly efficient and can handle complex project structures. It is a fundamental tool in the C++ development ecosystem, and many other build systems are based on its principles. 6.3 Ninja Ninja is a fast and lightweight build system designed for speed and efficient dependency tracking. It focuses on the minimalistic build process and supports parallel builds. Ninja is often used in conjunction with CMake, allowing for faster compilation and linking of C++ projects. Conclusion: staying up to date with the right tools can significantly improve a programmer's productivity and efficiency. The C++ tools mentioned in this article, including IDEs, debuggers, code editors, libraries and frameworks, documentation tools, and build systems, are essential for any C++ developer in 2023. By leveraging these tools, programmers can streamline their development process, write cleaner code, and build robust applications. Embrace these tools and take your C++ programming skills to new heights! FAQs FAQ 1: What are Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)? Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) are software applications that provide comprehensive tools and features to simplify the software development process. They typically include code editors, debuggers, build systems, and other utilities needed for efficient coding and debugging. FAQ 2: What are Debuggers? Debuggers are tools that help programmers identify and fix issues in their code. They allow developers to step through the code, set breakpoints, inspect variables, and analyze program execution to understand and resolve bugs and errors. FAQ 3: What are Code Editors? Code editors are software tools designed specifically for writing and editing code. They provide features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and navigation to enhance productivity and make coding easier and more efficient. FAQ 4: What are Libraries and Frameworks? Libraries and frameworks are collections of pre-written code that provide reusable functionality to programmers. They can simplify coding tasks by providing ready-made solutions for common problems, saving time and effort. FAQ 5: What are Build Systems? Build systems are software tools that automate the process of compiling and linking code to create executable programs or libraries. They manage dependencies, handle project configurations, and ensure that all required resources are properly built and linked together. Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crea tu primera página web en HTML5: Guía paso a paso para Windows y macOS
¿Quieres dar tus primeros pasos en el mundo de la programación web? ¡HTML5 es el lenguaje perfecto para comenzar! En esta guía te mostraremos cómo crear tu primer documento HTML5 tanto en Windows como en macOS. ¡Descubre lo fácil que es dar vida a tus ideas en la web! ¿Qué es HTML5? HTML5 es el lenguaje estándar para estructurar el contenido de las páginas web. Es la base sobre la que se…
#alicante#comunidad valenciana#crear página web#desarrollo web#editor de código#html5#macOS#Notepad++#Sublime Text#tutorial#Visual Studio Code
0 notes
Photo
Some other alternatives to consider!
The KDE Project has several really good free and open source apps out there for you to use. Krita was mentioned earlier as a Photoshop replacement, but there's also KDenLive for video editing, Okular for PDF editing, and Kate for text editing.
If you're building a website, Dreamweaver is frankly a meme. Wix and Wordpress.org are good bets, but if you really wanna get hands-on, just try building it from scratch using Neocities or a text editor like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, or Notepad++. It's a nice way to get back into the Web 1.0 niche and the websites hosted on neocities.org are super charming (and extremely queer like there's tons of trans stuff there).
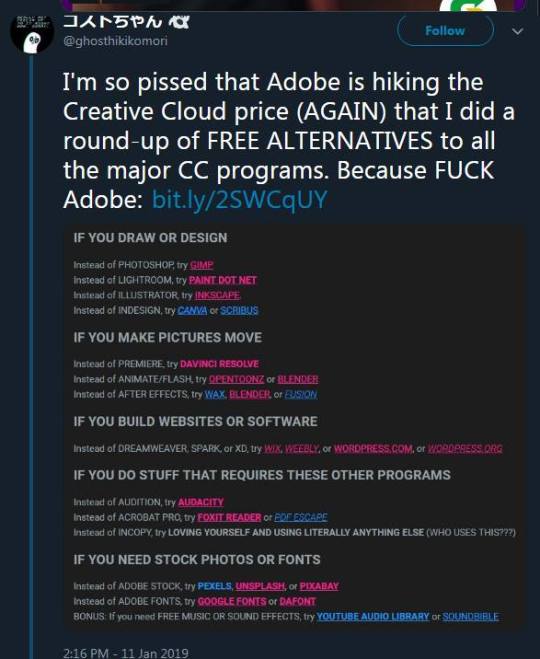
192K notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlocking the Basics: A Comprehensive C Programming Language Tutorial for Beginners
Introduction
C programming language is often referred to as the backbone of modern programming. Developed in the early 1970s, C has influenced many other programming languages, including C++, Java, and Python. Its efficiency, flexibility, and powerful features make it a popular choice for system programming, embedded systems, and application development. This tutorial aims to provide beginners with a solid foundation in C programming, covering essential concepts, practical examples, and best practices to help you unlock the basics and start your programming journey.The
Why Learn C?
Before diving into the tutorial, it’s important to understand why learning C is beneficial:
Foundation for Other Languages: C serves as a stepping stone to learning other programming languages. Understanding C concepts will make it easier to grasp languages like C++, Java, and C#.
Performance and Efficiency: C is known for its speed and efficiency, making it ideal for system-level programming and applications where performance is critical.
Portability: C programs can be compiled and run on various platforms with minimal changes, making it a versatile choice for developers.
Rich Libraries: C has a vast collection of libraries that provide pre-written code for common tasks, speeding up the development process.
Strong Community Support: With decades of history, C has a large community of developers, providing ample resources, forums, and documentation for learners.
Getting Started with C Programming
1. Setting Up Your Development Environment
To start programming in C, you need to set up a development environment. Here’s how:
Choose a Compiler: Popular C compilers include GCC (GNU Compiler Collection) for Linux and MinGW for Windows. You can also use IDEs like Code::Blocks, Dev-C++, or Visual Studio.
Install the Compiler: Follow the installation instructions for your chosen compiler. Ensure that the compiler is added to your system’s PATH for easy access.
Choose a Text Editor or IDE: You can write C code in any text editor (like Notepad++ or Sublime Text) or use an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for a more user-friendly experience.
2. Writing Your First C Program
Let’s start with a simple "Hello, World!" program to familiarize you with the syntax:#include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("Hello, World!\n"); return 0; }
Explanation:
#include <stdio.h>: This line includes the standard input-output library, allowing you to use functions like printf.
int main(): This is the main function where the program execution begins.
printf("Hello, World!\n");: This line prints "Hello, World!" to the console.
return 0;: This indicates that the program has executed successfully.
3. Understanding C Syntax and Structure
C has a specific syntax that you need to understand:
Variables and Data Types: C supports various data types, including int, float, char, and double. You must declare variables before using them.
int age = 25; float salary = 50000.50; char grade = 'A';
Operators: C provides arithmetic, relational, logical, and bitwise operators for performing operations on variables.
Control Structures: Learn about conditional statements (if, else, switch) and loops (for, while, do-while) to control the flow of your program.
4. Functions in C
Functions are essential for organizing code and promoting reusability. Here’s how to define and call a function:#include <stdio.h> void greet() { printf("Welcome to C Programming!\n"); } int main() { greet(); // Calling the function return 0; }
5. Arrays and Strings
Arrays are used to store multiple values of the same type, while strings are arrays of characters. Here’s an example:#include <stdio.h> int main() { int numbers[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; char name[20] = "John Doe"; printf("First number: %d\n", numbers[0]); printf("Name: %s\n", name); return 0; }
6. Pointers
Pointers are a powerful feature in C that allows you to directly manipulate memory. Understanding pointers is crucial for dynamic memory allocation and data structures.#include <stdio.h> int main() { int num = 10; int *ptr = # // Pointer to num printf("Value of num: %d\n", *ptr); // Dereferencing the pointer return 0; }
7. Structures and Unions
Structures allow you to group different data types under a single name, while unions enable you to store different data types in the same memory location.#include <stdio.h> struct Student { char name[50]; int age; }; int main() { struct Student student1 = {"Alice", 20}; printf("Student Name: %s, Age: %d\n", student1.name, student1.age); return 0; }
Best Practices for C Programming
Comment Your Code: Use comments to explain complex logic and improve code readability.
Use Meaningful Variable Names: Choose descriptive names for variables and functions to make your code self-explanatory.
Keep Code Organized: Structure your code into functions and modules to enhance maintainability.
Test Your Code: Regularly test your code to catch errors early and ensure it behaves as expected.
Conclusion
Learning C programming is a rewarding journey that opens doors to various fields in software development. By following this comprehensive tutorial, you’ve unlocked the basics of C and gained the foundational knowledge needed to explore more advanced topics.
As you continue your programming journey, practice regularly, build projects, and engage with the C programming community. With dedication and persistence, you’ll become proficient in C programming and be well-equipped to tackle more complex challenges in the world of software development.
Ready to dive deeper? Explore advanced topics like memory management, file handling, and data structures to further enhance your C programming skills! Happy coding with Tpoint-Tech!
0 notes
Text
Top Tools and Technologies to Use in a Hackathon for Faster, Smarter Development
Participating in a hackathon like those organized by Hack4Purpose demands speed, creativity, and technical prowess. With only limited time to build a working prototype, using the right tools and technologies can give your team a significant edge.
Here’s a rundown of some of the best tools and technologies to help you hack efficiently and effectively.
1. Code Editors and IDEs
Fast coding starts with a powerful code editor or Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
Popular choices include:
Visual Studio Code: Lightweight, extensible, supports many languages
JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA / PyCharm: Great for Java, Python, and more
Sublime Text: Fast and minimalistic with essential features
Choose what suits your language and style.
2. Version Control Systems
Collaborate smoothly using version control tools like:
Git: The most widely used system
GitHub / GitLab / Bitbucket: Platforms to host your repositories, manage issues, and review code
Regular commits and branch management help avoid conflicts.
3. Cloud Platforms and APIs
Leverage cloud services for backend, databases, or hosting without setup hassle:
AWS / Azure / Google Cloud: Often provide free credits during hackathons
Firebase: Real-time database and authentication made easy
Heroku: Simple app deployment platform
Explore public APIs to add extra features like maps, payment gateways, or AI capabilities.
4. Frontend Frameworks and Libraries
Speed up UI development with popular frameworks:
React / Vue.js / Angular: For dynamic, responsive web apps
Bootstrap / Tailwind CSS: Ready-to-use styling frameworks
These tools help build polished interfaces quickly.
5. Mobile App Development Tools
If building mobile apps, consider:
Flutter: Cross-platform, single codebase for iOS and Android
React Native: Popular JavaScript framework for mobile
Android Studio / Xcode: Native development environments
6. Collaboration and Communication Tools
Keep your team synchronized with:
Slack / Discord: Instant messaging and voice/video calls
Trello / Asana: Task and project management boards
Google Docs / Notion: Real-time document collaboration
Effective communication is key under time pressure.
7. Design and Prototyping Tools
Create UI/UX mockups and wireframes using:
Figma: Collaborative design tool with real-time editing
Adobe XD: Comprehensive UI/UX design software
Canva: Simple graphic design tool for quick visuals
Good design impresses judges and users alike.
8. Automation and Deployment
Save time with automation tools:
GitHub Actions / CircleCI: Automate builds and tests
Docker: Containerize applications for consistent environments
Quick deployment lets you demo your project confidently.
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right tools and technologies is crucial for success at a hackathon. The perfect mix depends on your project goals, team skills, and the hackathon theme.
If you’re ready to put these tools into practice, check out upcoming hackathons at Hack4Purpose and start building your dream project!
0 notes
Text
Social Boost
Premium Social Media Marketing Landing Page
Live Demo | Buy Now

Give your social media agency or marketing service the professional online presence it deserves with Social Boost — a premium landing page designed to impress, convert, and grow your audience.
Crafted for social media experts, agencies, freelancers, and digital marketers, Social Boost is your perfect tool to showcase services, attract leads, and drive engagement — all in one high-performing, responsive layout.
Key Features
✅ Modern & Professional Design – Eye-catching layout with strong visuals tailored for marketing services.
✅ Fully Responsive – Looks great on all devices: mobile, tablet, and desktop.
✅ Clean & Organized Code – Easy to edit, understand, and customize.
✅ Conversion-Focused Sections – Includes CTA buttons, testimonials, services, and pricing plans.
✅ Fast Loading – Optimized for speed and performance.
✅ Lightweight Assets – Uses placeholder images and minimal dependencies for fast deployment.
✅ Cross-Browser Compatibility – Works smoothly across all major browsers.
Perfect For
Social media marketing agencies
Freelancers & digital marketers
Advertising services
Personal branding & portfolio sites
Small businesses offering online marketing
What’s Included?
Fully coded HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files
Placeholder images ready to be replaced
Easy-to-follow folder structure
Instructions for customization
Technical Requirements
A modern web browser
Any code editor (like VS Code or Sublime)
Basic knowledge of HTML/CSS (for customization)
Why Choose Social Boost?
Stand out in the crowded digital market with a bold, polished landing page that builds trust and drives conversions. Whether you're launching a service or boosting an existing brand, SocialBoost gives you the professional edge you need.
Start promoting your services like a pro — download Social Boost today!
Live Demo | Buy Now
#css#html#html css#htmlcoding#js#landing page#landing page builder#landing page design#landing pages#panel#javascript#javaprogramming#ui ux design
1 note
·
View note
Text
I personally live in sublime text!
31K notes
·
View notes
Text
Master JavaScript: Step-by-Step Tutorial for Building Interactive Websites
JavaScript Tutorial

Master JavaScript: Step-by-Step Tutorial for Building Interactive Websites
In the evolving world of web development, JavaScript remains one of the most powerful and essential programming languages. Whether you're building simple webpages or full-fledged web applications, JavaScript gives life to your content by making it interactive and dynamic. This JavaScript Tutorial offers a beginner-friendly, step-by-step guide to help you understand core concepts and begin creating responsive and engaging websites.
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a lightweight, high-level scripting language primarily used to create dynamic and interactive content on the web. While HTML structures the webpage and CSS styles it, JavaScript adds interactivity—like handling clicks, updating content without refreshing, validating forms, or creating animations.
Initially developed for client-side scripting, JavaScript has evolved significantly. With the rise of environments like Node.js, it is now also used for server-side programming, making JavaScript a full-stack development language.
Why Learn JavaScript?
If you're looking to become a front-end developer or build web-based applications, JavaScript is a must-have skill. Here’s why:
It runs on all modern browsers without the need for plugins.
It’s easy to learn but incredibly powerful.
It works seamlessly with HTML and CSS.
It powers popular frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js.
It’s in high demand across the tech industry.
This JavaScript Tutorial is your gateway to understanding this versatile language and using it effectively in your web projects.
Getting Started: What You Need
To start coding in JavaScript, all you need is:
A modern browser (like Chrome or Firefox)
A text editor (such as Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text)
Basic knowledge of HTML and CSS
No complex setups—just open your browser and you're ready to go!
Step 1: Your First JavaScript Code
JavaScript code can be embedded directly into HTML using the <script> tag.
Example:<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>JavaScript Demo</title> </head> <body> <h1 id="demo">Hello, World!</h1> <button onclick="changeText()">Click Me</button> <script> function changeText() { document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "You clicked the button!"; } </script> </body> </html>
Explanation:
The onclick event triggers the changeText() function.
document.getElementById() accesses the element with the ID demo.
.innerHTML changes the content of that element.
This simple example showcases how JavaScript can make a static HTML page interactive.
Step 2: Variables and Data Types
JavaScript uses let, const, and var to declare variables.
Example:let name = "Alice"; const age = 25; var isStudent = true;
Common data types include:
Strings
Numbers
Booleans
Arrays
Objects
Null and Undefined
Step 3: Conditional Statements
JavaScript allows decision-making using if, else, and switch.let age = 20; if (age >= 18) { console.log("You are an adult."); } else { console.log("You are a minor."); }
Step 4: Loops
Use loops to execute code repeatedly.for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) { console.log("Iteration:", i); }
Other types include while and do...while.
Step 5: Functions
Functions are reusable blocks of code.function greet(name) { return "Hello, " + name + "!"; } console.log(greet("Alice")); // Output: Hello, Alice!
Functions can also be anonymous or arrow functions:const greet = (name) => "Hello, " + name;
Step 6: Working with the DOM
The Document Object Model (DOM) allows you to access and manipulate HTML elements using JavaScript.
Example: Change element style:document.getElementById("demo").style.color = "red";
You can add, remove, or change elements dynamically, enhancing user interaction.
Step 7: Event Handling
JavaScript can respond to user actions like clicks, keyboard input, or mouse movements.
Example:document.getElementById("myBtn").addEventListener("click", function() { alert("Button clicked!"); });
Step 8: Arrays and Objects
Arrays store multiple values:let fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Mango"];
Objects store key-value pairs:let person = { name: "Alice", age: 25, isStudent: true };
Real-World Applications of JavaScript
Now that you have a basic grasp, let’s explore how JavaScript is used in real-life projects. The applications of JavaScript are vast:
Interactive Websites: Menus, image sliders, form validation, and dynamic content updates.
Single-Page Applications (SPAs): Tools like React and Vue enable dynamic user experiences without page reloads.
Web Servers and APIs: Node.js allows JavaScript to run on servers and build backend services.
Game Development: Simple 2D/3D browser games using HTML5 Canvas and libraries like Phaser.js.
Mobile and Desktop Apps: Frameworks like React Native and Electron use JavaScript for cross-platform app development.
Conclusion
Through this JavaScript Tutorial, you’ve taken the first steps in learning a foundational web development language. From understanding what is javascript is now better.
As you continue, consider exploring advanced topics such as asynchronous programming (promises, async/await), APIs (AJAX, Fetch), and popular frameworks like React or Vue.
0 notes