#Data Backup and Recovery in Salesforce
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Learn effective Salesforce backup strategies to protect your business data and ensure seamless recovery in case of data loss.
#Salesforce backup#data recovery guide#Salesforce strategies#secure business data#Salesforce data protection
0 notes
Text
5 Easy Ways To Improve Salesforce Data Backup Recovery Strategy
In today's data-driven world, businesses rely heavily on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems like Salesforce to manage their customer information, track sales, and drive growth. However, even the most robust platforms are not immune to data loss or system failures. That's why having a solid Salesforce data backup and recovery strategy is crucial for ensuring business continuity. In this blog post, we'll explore five easy ways to enhance your Salesforce data backup and recovery strategy.
Regularly Scheduled Backups:
The foundation of any effective data recovery strategy is regular data backups. Salesforce provides a built-in data export tool that allows you to export data in a structured format, such as CSV or Excel. Set up a routine schedule for these exports to ensure that your data is backed up consistently. Depending on your organization's needs, you may choose to perform daily, weekly, or monthly backups.
Automate Your Backups:
Manually exporting data can be time-consuming and prone to errors. To streamline the process, consider automating your Salesforce data backups using third-party backup solutions. These tools can schedule and execute backups automatically, ensuring that your data is consistently and reliably backed up without manual intervention.
Store Backups Securely:
Backing up your Salesforce data is only half the battle. Equally important is where you store those backups. Utilize secure and redundant storage solutions, such as cloud storage platforms like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage. Implement encryption and access controls to safeguard your backups from unauthorized access.
Test Your Recovery Process:
Having backups is essential, but they're only as good as your ability to recover data from them. Regularly test your data recovery process to ensure that it works as expected. Document the steps, and make sure that your team is familiar with the recovery procedures. Conducting mock recovery drills can help identify and address any potential issues before they become critical.
Monitor and Alerting:
Proactive monitoring is key to identifying data backup and recovery issues early. Implement monitoring and alerting systems that notify you of any backup failures or anomalies. This way, you can take immediate action to rectify issues and minimize data loss in case of a failure.
Consider Salesforce Data Archiving:
As your Salesforce database grows, it can become challenging to manage large volumes of data efficiently. Salesforce offers data archiving solutions that allow you to move older or less frequently accessed data to a separate storage location. This can help reduce storage costs and improve system performance, making your data recovery strategy more manageable.
In conclusion, enhancing your Salesforce data backup and recovery strategy doesn't have to be complicated. By implementing these five easy steps, you can significantly improve your organization's ability to recover critical data in the event of data loss or system failures. Remember that data is the lifeblood of your business, and a robust backup and recovery strategy is your insurance policy against unforeseen disasters.
#Salesforce best practices#Data loss prevention#Backup automation#Data retention policies#Data encryption#Salesforce customization#Data recovery testing#Backup monitoring#Data recovery procedures#Data backup optimization#Salesforce data protection#Backup reliability#Data restoration#Backup storage solutions#Data backup documentation#Salesforce metadata backup#Data backup strategy evaluation#Data backup policies#Salesforce data backup best practices
0 notes
Text
#Salesforce Disaster Recovery#Salesforce data management#Salesforce Data Loss#Salesforce Data integrity#Salesforce data growth#Salesforce Data Backup#Salesforce data
1 note
·
View note
Text
7 Critical Considerations To Employ in Your Salesforce Disaster Recovery Plan

Your Salesforce data deserves all the protection it can get. Deploying a backup application for your Salesforce is only part of it. A powerful disaster recovery plan will help you have efficient data management and 100% data accessibility and around-the-clock business continuity. Though sometimes data loss might result only in a catastrophic lapse, the damage it causes can be unimaginable. Read More
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cloud Migration Services: Unlocking the Future of Business Agility
In today's digital-first world, businesses are under increasing pressure to innovate rapidly, reduce operational costs, and remain competitive. Cloud migration services have emerged as a vital enabler of this transformation. By moving applications, data, and workloads from on-premises infrastructure to cloud environments, organizations can harness unprecedented levels of scalability, flexibility, and resilience. But what exactly are cloud migration services, and why are they essential for modern enterprises?
Understanding Cloud Migration Services
Cloud migration refers to the process of transferring digital assets—such as data, applications, and IT processes—from local data centers to cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or hybrid cloud environments Cloud migration services encompass the end-to-end support required to execute this transition seamlessly, including strategy development, assessment, architecture design, security planning, data migration, application modernization, and post-migration optimization.
Cloud migration service providers typically offer tailored solutions based on the unique needs of a business. These services can range from simple lift-and-shift migrations to complex transformations that involve rearchitecting applications for the cloud.
Why Businesses Are Migrating to the Cloud
1. Cost Efficiency
Traditional on-premises infrastructure requires significant capital investment in hardware, maintenance, and IT staff. Cloud platforms operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to convert capital expenses into operational expenses. This financial flexibility is especially valuable for startups and SMEs that need to scale without breaking the bank.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud environments offer dynamic scaling, meaning businesses can adjust their resources based on current needs. Whether experiencing a sudden spike in user demand or planning long-term growth, the cloud provides the flexibility to scale operations without the delays and costs associated with physical infrastructure upgrades.
3. Improved Performance and Accessibility
With data and applications hosted in the cloud, employees can access critical business tools from anywhere in the world. This accessibility boosts productivity, supports remote work, and enhances collaboration across teams and geographies. Cloud services also offer high-performance computing and faster data processing capabilities, improving overall system performance.
4. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Contrary to earlier fears, cloud platforms now offer robust security features that often surpass traditional data centers. Cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure, offering features such as encryption, identity and access management (IAM), firewalls, and compliance monitoring. Cloud migration services include comprehensive security planning to ensure data integrity and regulatory compliance.
5. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
One of the most compelling reasons for cloud migration is improved business continuity. Cloud platforms offer built-in redundancy, data backups, and disaster recovery solutions that minimize downtime and data loss during unexpected events. This resilience is crucial for maintaining customer trust and operational continuity.
Types of Cloud Migration Strategies
Migration to the cloud is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different strategies are employed depending on an organization’s needs:
Rehosting (Lift-and-Shift): Moving applications without making significant changes.
Replatforming: Making minimal changes to optimize for the cloud environment.
Refactoring: Rewriting applications to fully leverage cloud-native features.
Repurchasing: Switching to a cloud-based version of an application (e.g., moving from a self-hosted CRM to Salesforce).
Retiring and Retaining: Phasing out obsolete systems or retaining some workloads on-premises for strategic reasons.
A professional cloud migration service provider will assess the existing IT landscape and recommend the most suitable approach.
Challenges in Cloud Migration
Despite its benefits, cloud migration is not without challenges. Poor planning, lack of expertise, data security concerns, and application compatibility issues can derail migration efforts. Additionally, downtime during migration can disrupt operations if not properly managed.
To mitigate these risks, businesses should partner with experienced cloud migration service providers who follow best practices, including thorough assessments, pilot testing, and phased rollouts. Proper change management and staff training are also crucial for successful adoption.
The Role of Cloud Migration Service Providers
Cloud migration service providers play a pivotal role in ensuring a smooth transition. Their responsibilities include:
Assessment and Planning: Evaluating current infrastructure, identifying dependencies, and creating a migration roadmap.
Cloud Architecture Design: Building scalable and secure cloud environments tailored to the organization’s needs.
Migration Execution: Managing the actual transfer of data, applications, and processes with minimal disruption.
Testing and Validation: Ensuring all systems function correctly in the new environment.
Optimization and Support: Providing ongoing monitoring, performance tuning, and cost optimization post-migration.
By leveraging the expertise of migration specialists, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and accelerate their digital transformation journey.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Cloud Migration
As technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, IoT, and big data analytics continue to evolve, the demand for agile, scalable cloud infrastructure will only grow. Cloud migration is no longer a luxury—it is a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to remain relevant in a digital economy.
Future trends in cloud migration services include automation-driven migrations, AI-powered workload analysis, and increased adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. These innovations will make cloud adoption faster, smarter, and more cost-effective.
Conclusion
Cloud migration services are more than just a technical shift—they represent a strategic investment in the future of business. By embracing the cloud, organizations unlock new levels of agility, innovation, and resilience. With the right partners and a clear roadmap Cloud migration services becomes a powerful catalyst for digital transformation and long-term success.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cloud Computing Tutorial for Beginners
Introduction Think of a world where you can use your files, run applications, or even write software without carrying around a high-end computer. That's cloud computing magic — a revolutionary technology that's redefining the manner in which we interact with computers and the web. Be a student, an entrepreneur, or a geek; learning cloud computing opens doors to endless possibilities. In this simple-to-get-start tutorial, we'll de-mystify what cloud computing is, how it works, the main models and services, and why it matters in today's digital age.
What is Cloud Computing? Cloud computing is the provision of computer services — including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence — over the internet ("the cloud") to provide faster innovation, elastic resources, and economies of scale. In straightforward terms, rather than executing software or storing information on your local computer or server, you use a distant system that you access via the internet.
Key Features • On-demand self-service: Compute resources can be provisioned by end-users without human intervention. • Broad network access: Services are made available from anywhere on internet-enabled devices. • Pooling of resources: Cloud providers employ multi-tenant models to host several customers. • Rapid elasticity: Resources can be scaled up or down rapidly depending on demand. • Measured service: You only pay for what you use.
Why Cloud Computing? • Economical: No investment in costly hardware or infrastructure. • Scalable: Simply scale your resources as your needs expand or contract. • Reliable: Cloud providers offer strong disaster recovery and backup solutions. • Accessible: Work anytime, anywhere. • No maintenance: Cloud providers handle updates, security patches, and so forth.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models There are three primary deployment models in cloud computing: 1. Public Cloud • They are offered on the public internet and are used by numerous users. • Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
• Suitable for: Small and medium-sized businesses, start-ups, or individuals who need instant access to assets. 2. Private Cloud • Reserved for a single organization. • Either on-premises deployed or by a third-party provider. • Provides greater control and security but is expensive. 3. Hybrid Cloud • Ties public and private clouds together for greater flexibility. • Businesses can have sensitive data on a private cloud and use public cloud for less sensitive processes.
Cloud Service Models Cloud computing services are mostly classified into three models: 1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) • Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. • You control the operating system, applications, and data. • Example: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine. Usage: Storing web site hosting, running virtual machine executions, and backup data storage.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service) • Provides a platform to customers to write, run, and host applications without the burden of infrastructure management. • Example: Google App Engine, Heroku. Use case: Developing apps fast without worrying about the hardware or operating system. 3. SaaS (Software as a Service) • Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription model. • Example: Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Dropbox. Use case: Having access to software like email, file storage, or CRM without installing it locally. Real-World Examples •Netflix uses AWS to provide videos to hundreds of millions of customers across the globe. •Dropbox allows users to save and share documents through cloud storage. •Salesforce offers a cloud-based CRM application to manage business relationships. •Zoom hosts its video conferencing website on the cloud with high availability. Main Cloud Providers Some of these companies own the marketplace in the cloud: •Amazon Web Services (AWS): Most used and veteran cloud platform. •Microsoft Azure: Biggest in hybrid cloud and enterprise cloud. •Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Focused on data analytics and machine learning. •IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Alibaba Cloud: Other prominent ones. Everyone provides similar essential services but differing tools and cost structures.
Getting Started with Cloud Computing Follows is a step-by-step way in which you can begin to try cloud computing as a beginner: Step 1: Sign Up for a Free Tier Free tiers are provided by all the big cloud providers. For instance: • tAWS Free Tier provides EC2, S3, Lambda, etc. • tAzure Free Account provides $200 credits. • tGoogle Cloud Free Tier provides Compute Engine and BigQuery. Step 2: Explore Basic Services • Install a Virtual Machine (VM): Start a minimal server using EC2 (AWS) or Compute Engine (GCP). • Install Cloud Storage: Store data in S3 (AWS) or Google Cloud Storage. • Test a SaaS App: Mess around with applications such as Google Docs or Trello. Step 3: Learn by Projects Mess around with small projects such as: • Serving a static web page. • Creating a to-do application with Firebase. • Hosting a chatbot on Azure.
Step 4: Study and Certify Cloud certifications can give your career a boost: • AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner • Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals • Google Cloud Digital Leader These beginner certifications prove your grasp of cloud concepts.
Security in Cloud Security is top of the mind for cloud computing. Even as providers put huge investments in security, end users have some responsibilities too. Shared Responsibility Model: •Cloud provider secures infrastructure. •Customer secures user access, data, and application-level settings. Key Practices: •Employ strong authentication (e.g., multi-factor). •Encrypt data in transit and at rest. •Monitor activity on a regular basis and audit it. •Set proper permissions on users.
Challenges of Cloud Computing The cloud is wonderful, but it's not all sunshine: •Downtime: Disruptions may occur in accessing essential services. •Vendor Lock-in: It is complicated and costly to switch vendors. •Security Risks: Erroneous configuration can compromise security. •Cost Overruns: Pay-as-you-go arrangements become prohibitively expensive if left unmonitored. It's great to be aware of these challenges in order to make smart decisions. The Future of Cloud Computing Cloud computing just keeps improving with fascinating trends such as: •Serverless computing: Code is the focus for developers, while the infrastructure is handled by the provider. •Edge computing: Processing data close to the source (e.g., IoT devices) for enhanced performance. •AI and ML Integration: Cloud platforms allow for powerful tools for model training and deployment. •Multi-cloud strategies: Organizations use multiple providers to avoid dependence on a sole one. Final Thoughts Cloud computing is not a fad buzzword — it's actually the backbone of contemporary digital life. Whether streaming entertainment and smart homes or business applications and mobile phones, the cloud permeates nearly all aspects of everyday life. By learning the basics now, you're setting yourself up to take advantage of one of the greatest technology shifts of the 21st century. If you love development, data, or infrastructure, the cloud has something for you.
0 notes
Text
Cloud Computing: The Digital Revolution
Today, businesses and individuals are constantly seeking efficient, scalable, and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and management. Cloud computing has emerged as the backbone of this transformation, offering flexibility, security, and accessibility. From small businesses to large enterprises, cloud technology is revolutionizing the way we interact with data, applications, and IT infrastructure.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including storage, processing power, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet. Unlike traditional on-premise systems, where data and applications are hosted locally, cloud computing allows users to access their resources remotely from anywhere in the world. The fundamental concept behind cloud computing is “pay-as-you-go,” meaning businesses and individuals only pay for the resources they consume, reducing operational costs and improving efficiency.

Key Components of Cloud Computing
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent servers, storage, and networking components on-demand without investing in physical hardware. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a cloud-based environment that enables developers to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure. It includes tools, libraries, and frameworks necessary for application development. Examples include Google App Engine and Microsoft Azure App Services.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides fully managed applications that users can access via web browsers without requiring installation or maintenance. Common SaaS applications include Google Workspace, Microsoft Office 365, and Salesforce CRM.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Cost Efficiency
Cloud computing eliminates the need for expensive hardware and IT infrastructure, allowing businesses to pay only for the services they use. This pay-as-you-go model significantly reduces capital expenditures.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud services can be scaled up or down based on demand, making them ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads. Organizations can add or remove resources in real time, ensuring optimal performance and cost savings.
3. Enhanced Security
Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular compliance audits. This ensures that sensitive information remains protected from cyber threats.
4. Remote Accessibility
With cloud computing, employees and businesses can access applications and data from anywhere with an internet connection. This has been especially beneficial in the era of remote work and global collaboration.
5. Disaster Recovery and Data Backup
Cloud solutions offer automated data backups and disaster recovery options, ensuring business continuity in case of hardware failures, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
Industries Transformed by Cloud Computing
1. Healthcare
Cloud computing has revolutionized the healthcare industry by enabling electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, and AI-driven diagnostics. Cloud storage allows healthcare providers to access patient data securely and efficiently.
2. Finance
Banks and financial institutions leverage cloud computing for real-time transactions, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance. Cloud-based analytics help in making data-driven investment decisions.
3. Education
Online learning platforms and virtual classrooms rely on cloud computing for seamless content delivery, student management, and collaboration tools like Google Classroom and Microsoft Teams.
4. Retail and E-Commerce
Cloud-based solutions enable e-commerce businesses to handle high traffic volumes, optimize inventory management, and personalize customer experiences through AI and machine learning.
5. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Manufacturers utilize cloud computing for predictive maintenance, IoT integration, and supply chain optimization, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing
1. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid cloud models, combining private and public clouds for greater flexibility and security. Multi-cloud strategies allow companies to leverage multiple cloud providers to prevent vendor lock-in.
2. Edge Computing
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, improving performance for applications like IoT, autonomous vehicles, and real-time analytics.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the Cloud
Cloud-based AI and ML tools are enhancing decision-making, automating tasks, and driving innovation in various industries.
4. Serverless Computing
Serverless computing enables developers to build and run applications without managing infrastructure, leading to increased agility and reduced operational overhead.
5. Quantum Computing in the Cloud
Tech giants like IBM, Google, and AWS are investing in cloud-based quantum computing, which has the potential to solve complex problems in cryptography, material science, and optimization.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, cloud computing presents certain challenges:
Security and Compliance: Organizations must ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Downtime Risks: Cloud outages can impact business operations, making disaster recovery planning essential.
Data Privacy Concerns: Storing sensitive data in third-party cloud environments requires trust and robust encryption measures.
Cost Management: While cloud computing reduces capital costs, inefficient resource allocation can lead to unexpected expenses.
Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing continues to evolve, driving innovation across industries. The integration of AI, blockchain, and IoT with cloud services will redefine business models, enhance automation, and improve decision-making processes. As cloud security measures strengthen and hybrid cloud adoption grows, businesses will increasingly rely on cloud solutions for their digital transformation journeys.
ConclusionCloud computing has become an indispensable part of modern business operations. Whether it’s improving efficiency, reducing costs, or enabling remote work, cloud technology is reshaping industries and paving the way for future innovations. As organizations continue to embrace cloud computing, staying updated with the latest trends and security best practices will be key to harnessing its full potential.
0 notes
Text
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Customer Management Software: Which is Best for Dubai Businesses?

Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Customer Management Software: Which is Best for Dubai Businesses?
Customer Management Software (CMS) is an essential tool for businesses in Dubai looking to streamline customer interactions, improve sales, and enhance overall business efficiency. When selecting the right CMS, companies must choose between cloud-based and on-premise solutions. Each option has its own advantages and drawbacks, making the decision crucial based on business needs, security concerns, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding Cloud-Based Customer Management Software
Cloud-based CMS solutions are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet. Businesses subscribe to a service model, typically paying a monthly or annual fee. Some popular cloud-based solutions include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM.
Benefits of Cloud-Based CMS
Cost-Effective – There is no need for heavy upfront investment in hardware or IT infrastructure. Businesses pay for what they use, making it budget-friendly.
Scalability – Easily scalable as businesses grow, allowing them to add more users and storage without significant upgrades.
Remote Accessibility – Employees can access the system from anywhere, making it ideal for businesses with remote or on-the-go teams.
Automatic Updates – The provider takes care of software updates, ensuring businesses always have the latest features and security patches.
Data Backup and Recovery – Cloud-based solutions offer automated data backup, reducing the risk of data loss.
Challenges of Cloud-Based CMS
Internet Dependency – Requires a stable internet connection to function efficiently.
Data Security Concerns – Sensitive customer data is stored off-site, which may pose security and compliance risks.
Subscription Costs Over Time – Monthly or yearly subscription fees can add up, making it more expensive in the long run.
Understanding On-Premise Customer Management Software
On-premise CMS is installed on a company's own servers and maintained by its in-house IT team. Businesses have complete control over the software and data.
Benefits of On-Premise CMS
Enhanced Data Security – Since data is stored locally, businesses have full control over security measures. This is ideal for industries with strict compliance requirements.
Customization Options – Greater flexibility to customize the software based on specific business needs.
No Ongoing Subscription Fees – Unlike cloud-based models, there are no recurring subscription fees after the initial investment.
Reduced Internet Dependency – The system functions without an internet connection, ensuring uninterrupted access.
Challenges of On-Premise CMS
High Initial Costs – Requires significant investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT staff.
Limited Scalability – Upgrading to accommodate growth can be costly and complex.
Manual Updates and Maintenance – Businesses are responsible for maintaining and updating the software, which requires ongoing IT support.
Accessibility Limitations – Unlike cloud solutions, remote access is more complex and requires additional setup.
Which is Best for Dubai Businesses?
The decision between cloud-based and on-premise CMS depends on the specific needs of a business. Here are some considerations:
Startups & SMEs: Cloud-based CMS is a better option due to its affordability, ease of use, and scalability.
Enterprises with High Security Needs: On-premise CMS offers better control over data security, making it ideal for industries like finance, healthcare, and government agencies.
Companies with Remote Teams: Cloud-based CMS is more suitable due to its accessibility from anywhere.
Businesses with Customization Needs: On-premise CMS provides better flexibility for customization.
Conclusion
Both cloud-based and on-premise Customer Management Software Dubai have their own advantages and drawbacks. Businesses in Dubai must assess their budget, security requirements, scalability, and accessibility before making a decision. While cloud-based CMS is the go-to choice for most modern businesses, an on-premise solution might be preferable for companies requiring complete control over their data. Ultimately, choosing the right CMS will empower businesses to build stronger customer relationships and drive long-term success.
0 notes
Text
The Hidden Complexities Of Salesforce Data Migration

Data migration is far more than a simple transfer of information. When organizations approach Salesforce deployment, they often underestimate the intricate process of moving data from legacy systems to a new, dynamic platform.
The Migration Landscape
Successful data migration begins with comprehensive preparation. Organizations must invest time in understanding their data ecosystem and preparing for a seamless transition.
Key preparatory elements include-
Conducting a thorough data audit
Mapping existing data structures
Identifying potential migration challenges
Establishing clear migration objectives
Creating a detailed transformation strategy
The complexity of data migration goes beyond technical challenges. It requires a strategic approach that balances technical precision with business objectives, ensuring that every piece of data serves a meaningful purpose in the new Salesforce environment.
The Five-Stage Migration Framework
Stage 1
Discovery and Assessment
The initial stage focuses on understanding both source and target systems-
· Conducting comprehensive system audits
· Creating detailed data inventory
· Identifying data relationships and dependencies
· Assessing data quality and completeness
· Establishing migration scope and requirements
Stage 2
Planning and Design
This stage establishes the strategic foundation-
· Developing detailed migration architecture
· Creating field and object mapping documents
· Establishing transformation rules
· Designing backup and rollback procedures
· Setting up validation criteria and success metrics
Stage 3
Data Preparation and Backup
Critical pre-migration activities include-
· Performing full system backup of source data
· Cleaning and standardizing data
· Removing duplicates and redundant information
· Creating backup verification procedures · Establishing disaster recovery protocols
Stage 4
Execution and Migration
The actual migration process involves
· Running test migrations in sandbox environments · Performing incremental data loads
Get More info: https://kandisatech.com/blog-details/The-Hidden-Complexities-of-Salesforce-Data-Migration
#Salesforce#DataMigration#BusinessGrowth#SalesforceDataMigration#salescloud#sfdc#salesforcelearning#CRM#salesforceconsultant#salesforcedevelopers#salesforcepartner
0 notes
Text
Amazon Web Service S3: How It Works And Its Advantages

Object storage from Amazon web service S3 is designed to allow you to access any quantity of data from any location.
What is Amazon S3?
An object storage solution with industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance is Amazon Simple Storage solution (Amazon S3). For almost any use case, including data lakes, cloud-native apps, and mobile apps, millions of users across all sizes and sectors store, manage, analyze, and safeguard any quantity of data. You may optimize expenses, arrange and analyze data, and set up precise access restrictions to satisfy certain business and regulatory requirements with affordable storage classes and user-friendly administration tools.
How it works
Data is stored by Amazon S3 as objects in buckets S3. A file and its metadata are objects. A bucket is an object’s container. You must first establish a bucket and choose an AWS Region and bucket name before you can store your data in Amazon web service S3. After that, you upload your data as objects in S3 to that bucket. Every object in the bucket has a key, also known as a key name, which serves as its unique identification.
You can customize the functionality offered by S3 to suit your unique use case. For instance, you can restore mistakenly erased or overwritten objects by using Amazon S3 Versioning to store multiple copies of an object in the same bucket. Only those with specifically allowed access permissions can access buckets and the items within them since they are private. S3 Access Points, bucket policies, AWS IAM policies, and ACLs can manage access.Image credit to Amazon
Advantages of Amazon S3
Amazon S3 has unparalleled performance and can store almost any size of data, up to exabytes. Because Amazon web service S3 is completely elastic, it will automatically expand and contract as you add and delete data. You simply pay for what you use, and there’s no need to supply storage.
Sturdiness and accessibility
Amazon S3 offers industry-leading availability and the cloud’s most robust storage. Supported by the strongest SLAs in the cloud, S3’s distinctive architecture is built to deliver 99.99% availability and 99.999999999% (11 nines) data durability by default.
Data protection and security
Protect your data with unmatched security, compliance, and access control. Besides being private, safe, and encrypted by default, Amazon S3 has many auditing options to monitor requests for access to your resources.
Best performance at the lowest cost
Large volumes of data that are accessed frequently, seldom, or infrequently can be cost-effectively stored with Amazon web service S3 automated data lifecycle management and numerous storage classes with the greatest pricing performance for any application. Amazon S3 provides the throughput, latency, flexibility, and resilience to guarantee that storage never restricts performance.
S3 amazon price
A 12-month free trial of S3’s free tier includes 100 GB of data transfer out per month, 20,000 GET requests, 2,000 PUT, COPY, POST, or LIST requests, and 5GB of Amazon S3 storage in the S3 Standard storage class.
Only pay for what you actually use. There isn’t a minimum fee. The Amazon S3 Pricing of requests and data retrieval, data transport and acceleration, data management and insights, replication, and transform and query features are the cost components of S3.
Use cases
Construct a data lake
A data lake can hold any size structured or unstructured data. High-performance computers, AI, machine learning, and data analytics maximize data value.
A secure Amazon S3 data lake lets Salesforce users search, retrieve, and analyze all their data.
Make a backup and restore important data
With S3’s powerful replication capabilities, data security with AWS Backup, and a range of AWS Partner Network solutions, you can meet your recovery time goal (RTO), recovery point objective (RPO), and compliance needs.
Terabytes of photos may be restored in a matter of hours rather than days with Ancestry’s usage of Amazon web service S3 Glacier storage classes.
Data archiving at the most affordable price
To cut expenses, remove operational hassles, and obtain fresh insights, move your archives to the Amazon S3 Glacier storage classes.
Using Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval, the UK public service broadcaster BBC safely moved their 100-year-old flagship archive.
Make use of your data
Amazon S3 might be the beginning of your generative AI journey because it averages over 100 million requests per second and stores over 350 trillion objects exabytes of data for almost every use case.
Grendene is employing a data lake built on Amazon web service S3 to develop a generative AI-based virtual assistant for its sales force.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#AmazonWebServiceS3#AmazonS3#AI#AWSBackup#S3storage#dataavailability#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Understanding Cloud Computing: Types and Benefits
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we access and manage technology resources. It allows individuals and businesses to utilize computing services over the internet, offering flexibility, efficiency, and scalability. In this blog post, we'll explore what cloud computing is, its various types, and the benefits it brings to users.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of a range of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet. Instead of relying on local servers or personal computers, users can access these services remotely, enabling a more dynamic approach to technology management.

If you want to advance your career at the Cloud Computing Course in Coimbatore, you need to take a systematic approach and join up for a course that best suits your interests and will greatly expand your learning path.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be categorized into several types based on the services offered:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent servers, storage, and networking components on a pay-as-you-go basis. This model allows businesses to scale their infrastructure without the need for physical hardware.
Examples:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Microsoft Azure
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a platform that allows developers to build, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure. This service streamlines the development process, enabling faster deployment and innovation.
Examples:
Heroku
Google App Engine
Microsoft Azure App Service
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications via web browsers, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance.
Examples:
Google Workspace
Salesforce
Microsoft 365
4. Function as a Service (FaaS)
FaaS is a serverless computing model that allows users to execute code in response to events without managing servers. It provides a cost-effective and scalable way to run applications.
Examples:
AWS Lambda
Azure Functions
Google Cloud Functions
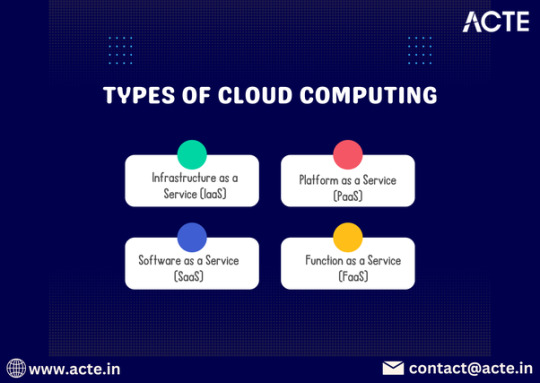
For those looking to excel in Cloud computing, Cloud Computing Online Course is highly suggested. Look for classes that align with your preferred programming language and learning approach.
Deployment Models
Cloud computing can also be categorized based on its deployment model:
1. Public Cloud
In a public cloud, services are delivered over the public internet and shared among multiple organizations. This model is cost-effective and scalable but may raise concerns regarding data security.
Examples: AWS, GCP
2. Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, offering greater control over data and security. This model is suitable for businesses with strict compliance requirements.
Examples: On-premises data centers, VMware solutions
3. Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This model offers flexibility and scalability while maintaining security.
4. Community Cloud
A community cloud is shared by a specific community of users with common concerns such as security or compliance. This model allows organizations to collaborate while maintaining control over their data.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for physical hardware and maintenance costs.
Scalability: Easily adjust resources based on demand.
Accessibility: Access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection.
Disaster Recovery: Enhanced options for data backup and recovery.
Automatic Updates: Service providers handle regular updates and maintenance.
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate, offering greater flexibility, efficiency, and innovation. Whether you're a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding the types and benefits of cloud computing can help you leverage technology to achieve your goals. As this technology continues to evolve, staying informed will enable you to make the most of the opportunities it presents.
0 notes
Text
5 Essential Tips for Maintaining Top-Notch Salesforce Org Health
Introduction: Salesforce has become an indispensable tool for businesses to manage customer relationships, streamline operations, and drive growth. However, just like any other complex system, your Salesforce organization requires regular attention and care to ensure it remains efficient, effective, and aligned with your business objectives.
In this blog, we'll explore five essential suggestions to maintain a top-notch Salesforce Org health, helping you get the most out of your investment.
Best Tips for Managing Salesforce Org Health
Regular Data Cleanup and Maintenance: A cluttered and disorganized Salesforce Org can lead to decreased user productivity, slower system performance, and inaccurate reporting. Regularly conduct data cleanup exercises to eliminate duplicate records, outdated information, and irrelevant data. Implement validation rules, workflows, and data governance processes to ensure that data entered into the system is accurate and consistent. Consider archiving or purging old records that are no longer needed, which can significantly improve system responsiveness.
Optimize User Training and Adoption: Even the most powerful tools are only as effective as the users who operate them. Invest in comprehensive user training programs to ensure that your team fully understands the features and functionalities of Salesforce. Regularly assess user adoption rates and address any issues or challenges they might face. Encourage the use of best practices and provide ongoing training as Salesforce releases updates and new features
Govern Customization and Configuration: Salesforce offers an array of customization options to tailor the platform to your specific business needs. While customization is valuable, an excessive amount can lead to complexity, slow performance, and difficulties during upgrades. Establish a clear governance framework for customization and configuration. This includes guidelines for when to use declarative tools (like Process Builder) versus custom code, as well as regular reviews of custom objects, fields, and processes to ensure they remain relevant and effective
Implement Robust Security Practices: Data security and privacy are paramount in today's business landscape. Regularly review and update your Salesforce security settings to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. Implement strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access controls to minimize the risk of data breaches. Regularly audit user permissions and deactivate accounts for employees who no longer require access to the system
Stay Informed About Salesforce Updates: Salesforce continuously releases updates, enhancements, and new features to improve the platform's functionality and security. It's crucial to stay informed about these updates and assess their potential impact on your organization. Create a process for reviewing and testing new releases in a sandbox environment before rolling them out to your production Org. This practice helps identify any potential compatibility issues with your existing customizations and allows for adjustments before affecting users.
Conclusion:
Maintaining a top-notch Salesforce Org health requires a proactive approach that involves regular cleanup, user engagement, customization governance, security measures, and staying updated on platform developments. By following these five essential tips, your organization can ensure that Salesforce remains a powerful tool that contributes to your business success, helping you drive growth, streamline processes, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
#Salesforce Org Health#Org maintenance#CRM optimization#Data integrity#Performance tuning#System health check#Data hygiene#Configuration management#Best practices#User adoption#Customization management#Security audit#Data governance#Automation tools#Regular updates#User training#Scalability#Backup and recovery#Compliance measures#Analytics and reporting
0 notes
Text
#Salesforce Data Protection#Salesforce data#Salesforce Backup & Recovery Solutions#Data Governance#Data Backup#compliance#Backup & Recovery
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Salesforce#DataArchiva#SalesforceDataArchiva#SalesforceArchiveData#SalesforceArchiving#SalesforceDataArchiving
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Embrace the Future: Exploring the Power and Potential of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has emerged as a meaningful change in today's quickly expanding technology landscape, transforming the way individuals and organizations manage and use IT resources. The flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness that come with having access to computing power, storage, and apps via the internet instead of local servers or personal devices are unmatched. This article explores the fundamentals of cloud computing, as well as its advantages, important models, and potential applications going forward.

Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of numerous services over the internet, including data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. The "cloud" symbolizes the internet, and the technology enables users to access and store data on remote servers rather than on local hard drives or servers. This shift from traditional on-premises IT infrastructure to cloud-based services offers several advantages.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Cost Efficiency:
One of the primary advantages of cloud computing is cost efficiency. Businesses no longer need to invest heavily in physical infrastructure, hardware, and maintenance. Cloud service providers offer a pay-as-you-go model, allowing companies to pay only for the resources they use. This model significantly reduces capital expenditure and operational costs.
2. Scalability and Flexibility:
Cloud computing provides unmatched scalability and flexibility. Businesses can quickly scale up or down based on their needs without worrying about over-provisioning or under-provisioning resources. This flexibility is crucial for managing varying workloads and meeting the demands of peak periods.
3. Accessibility and Collaboration:
With cloud computing, data and applications are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility promotes collaboration, as teams can work together in real-time, regardless of their geographical location. Cloud-based tools and platforms facilitate seamless communication and project management.
4. Disaster Recovery and Data Backup:
Cloud service providers typically offer robust disaster recovery and data backup solutions. In the event of hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks, businesses can quickly restore their data and resume operations. This resilience is critical for maintaining business continuity.
5. Security:
Contrary to common concerns, cloud computing can enhance security. Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and regular security audits. They also ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, offering a higher level of security than many on-premises solutions.
Cloud Computing Models
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers fundamental infrastructure such as virtual machines, storage, and networks. Users can rent these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
PaaS offers a platform that allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure. It provides tools and services for application development, including operating systems, databases, and development frameworks. Examples of PaaS providers are Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS):
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications through web browsers, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance. Common SaaS applications include customer relationship management (CRM) systems like Salesforce, email services like Gmail, and productivity tools like Microsoft Office 365.
The Future of Cloud Computing
1. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies:
As businesses continue to leverage cloud computing, many are adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. A hybrid cloud combines on-premises infrastructure with cloud services, offering the best of both worlds. Multi-cloud strategies involve using services from multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance redundancy.
2. Edge Computing:
Edge computing is an emerging trend that complements cloud computing. It involves processing data closer to its source, at the "edge" of the network, to reduce latency and improve performance. This is particularly important for applications requiring real-time processing, such as IoT devices and autonomous vehicles.
3. AI and Machine Learning Integration:
Cloud computing is driving the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into various applications. Cloud platforms offer AI and ML services that enable businesses to build intelligent applications without investing in specialized hardware. This democratization of AI and ML is accelerating innovation across industries.
4. Enhanced Security Measures:
As cyber threats evolve, cloud providers are continuously enhancing their security measures. Advanced encryption, zero-trust architectures, and AI-driven security analytics are some of the innovations ensuring that cloud environments remain secure. Businesses can expect even more robust security features in the future.
5. Sustainable Cloud Solutions:
With increasing awareness of environmental impact, cloud providers are focusing on sustainability. Green cloud computing initiatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of data centers through energy-efficient practices and renewable energy sources. This shift towards eco-friendly cloud solutions aligns with global sustainability goals.
Conclusion:
The IT environment has been completely changed by cloud computing, which provides many advantages such increased security, scalability, affordability, and accessibility. Businesses using cloud technology should anticipate more advancements and developments that will shape the cloud computing landscape in the future. AI and edge computing to hybrid and multi-cloud techniques integration, the possibilities are vast. By leveraging cloud computing, businesses can stay competitive, agile, and prepared for the challenges of tomorrow. Embrace the future with cloud computing and unlock the full potential of your digital transformation journey.
0 notes
Text
Building a Robust Cloud Computing Infrastructure: Key Insights and Best Practices
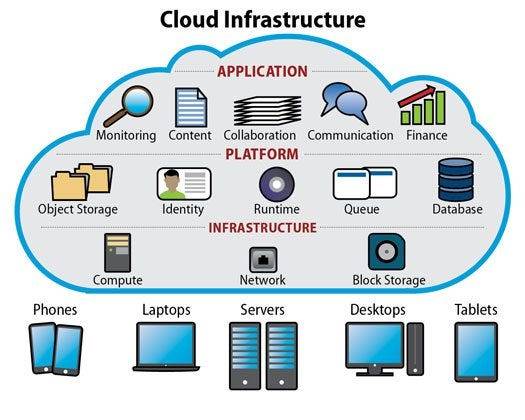
Cloud computing infrastructure consists of the hardware and software components — such as servers, storage, networking, and virtualization software — that are needed to support the computing requirements of a cloud computing model. It allows businesses to scale resources up or down as needed, ensuring cost efficiency and flexibility.
Understanding Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Cloud computing infrastructure refers to the combination of hardware and software components — such as servers, storage, networks, and virtualization software — that work together to support the delivery of cloud services. This infrastructure is foundational for deploying and managing applications and services in the cloud.
Essential Steps for Cloud Setup and Maintenance
#1. Planning Your Cloud Setup
Before diving into the technical aspects, it’s imperative to outline your business needs and goals. This includes:
- Assessing Requirements: Understand what applications and services need to be hosted on the cloud.
- Choosing the Right Cloud Model: Decide between public, private, or hybrid cloud models based on your security, compliance, and cost requirements.
- Budgeting: Allocate a budget for initial setup, ongoing maintenance, and potential scalability.
#2. Setting Up the Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Once planning is complete, follow these steps to establish your cloud computing infrastructure:
Select a Cloud Provider: Popular options include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Evaluate them based on cost, features, and support.
- Design the Infrastructure: This involves creating a blueprint of your cloud architecture, including networking, storage, and compute resources.
- Implement Security Measures: Ensure robust security protocols are in place to protect data and applications from threats. This includes firewalls, encryption, and identity management.
- Deploy Applications: Migrate your applications to the cloud environment. This might involve refactoring or re-architecting applications to optimize for cloud performance.
3. Cloud Maintenance Services
Maintaining your cloud environment is critical for ensuring performance, security, and cost-efficiency. Key aspects of cloud maintenance services include:
- Monitoring and Management: Regularly monitor cloud resources for performance issues and manage them to avoid disruptions.
- Security Updates and Patches: Keep your infrastructure secure by applying regular updates and patches.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Implement a robust backup strategy and ensure you have a disaster recovery plan in place.
- Cost Optimization: Continuously review and optimize your cloud spending to avoid unnecessary costs.
Implementing Salesforce Commerce Cloud Setup
For businesses looking to leverage Salesforce Commerce Cloud, the setup process involves:
- Initial Configuration: Set up the basic environment, including defining business settings, user roles, and permissions.
- Customizing the Platform: Tailor the platform to meet specific business needs through custom code, extensions, and integrations.
- Testing and Deployment: Thoroughly test the environment and applications before going live to ensure everything works seamlessly.
Conclusion
Building and maintaining a robust cloud computing infrastructure is pivotal for modern businesses aiming to achieve agility, scalability, and efficiency. Whether you’re setting up a new environment or optimizing an existing one, understanding the nuances of cloud setup and maintenance and leveraging professional cloud maintenance services can significantly enhance your operational capabilities. Embrace the power of Salesforce Commerce Cloud to drive your e-commerce initiatives forward, ensuring a seamless and secure cloud journey.
For a detailed guide on building a cloud computing infrastructure, visit [this comprehensive resource](https://experlabs.com/how-to-build-a-cloud-computing-infrastructure/).
0 notes