#Data Science Engineering Services
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Understanding the differences between Data Science vs Data Analysis vs Data Engineering is essential for making the right choices in building your data strategy. All three roles have varying benefits, and it is crucial to understand what strategy is needed and when to build your business.
#data engineer vs data scientist#data engineering vs data science#data analyst vs data engineer#data scientist vs data analyst#data analysis software#data engineering services
0 notes
Text
#data engineer vs data scientist#data engineer and data scientist#data engineering services#data science consulting
0 notes
Text
youtube
Unlock the Power of Data with Kellton! 🌟
🔍 Data holds the key to insights and trends that are beyond manual reach. With Kellton’s cutting-edge tools and technologies, transform raw data into actionable intelligence effortlessly. 🚀
💡 Discover how our data science and data engineering solutions can elevate your business decisions.
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence course in Delhi

Artificial Intelligence Course in Delhi
#artificial intelligence#data science#data scientist#machine learning#python#digital marketing#search engine optimization#digital marketing services#digitalmarketingcourse#youtube
0 notes
Text
Collaborative effort supports an MIT resilient to the impacts of extreme heat
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/collaborative-effort-supports-an-mit-resilient-to-the-impacts-of-extreme-heat/
Collaborative effort supports an MIT resilient to the impacts of extreme heat


Warmer weather can be a welcome change for many across the MIT community. But as climate impacts intensify, warm days are often becoming hot days with increased severity and frequency. Already this summer, heat waves in June and July brought daily highs of over 90 degrees Fahrenheit. According to the Resilient Cambridge report published in 2021, from the 1970s to 2000, data from the Boston Logan International Airport weather station reported an average of 10 days of 90-plus temperatures each year. Now, simulations are predicting that, in the current time frame of 2015-44, the number of days above 90 F could be triple the 1970-2000 average.
While the increasing heat is all but certain, how institutions like MIT will be affected and how they respond continues to evolve. “We know what the science is showing, but how will this heat impact the ability of MIT to fulfill its mission and support its community?” asks Brian Goldberg, assistant director of the MIT Office of Sustainability. “What will be the real feel of these temperatures on campus?” These questions and more are guiding staff, researchers, faculty, and students working collaboratively to understand these impacts to MIT and inform decisions and action plans in response.
This work is part of developing MIT’s forthcoming Climate Resiliency and Adaptation Roadmap, which is called for in MIT’s climate action plan, and is co-led by Goldberg; Laura Tenny, senior campus planner; and William Colehower, senior advisor to the vice president for campus services and stewardship. This effort is also supported by researchers in the departments of Urban Studies and Planning, Architecture, and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS), in the Urban Risk Lab and the Senseable City Lab, as well as by staff in MIT Emergency Management and Housing and Residential Services. The roadmap — which builds upon years of resiliency planning and research at MIT — will include an assessment of current and future conditions on campus as well as strategies and proposed interventions to support MIT’s community and campus in the face of increasing climate impacts.
A key piece of the resiliency puzzle
When the City of Cambridge released their Climate Change Vulnerability Assessment in 2015, the report identified flooding and heat as primary resiliency risks to the city. In response, Institute staff worked together with the city to create a full picture of potential flood risks to both Cambridge and the campus, with the latter becoming the MIT Climate Resiliency Dashboard. The dashboard, published in the MIT Sustainability DataPool, has played an important role in campus planning and resiliency efforts since its debut in 2021, but heat has been a missing piece of the tool. This is largely because for heat, unlike flooding, few data exist relative to building-level impacts. The original assessment from Cambridge showed a model of temperature averages that could be expected in portions of the city, but understanding the measured heat impacts down to the building level is essential because impacts of heat can vary so greatly. “Heat also doesn’t conform to topography like flooding, making it harder to map it with localized specificity,” notes Tenny. “Microclimates, humidity levels, shade or sun aspect, and other factors contribute to heat risk.”
Collection efforts have been underway for the past three years to fill in this gap in baseline data. Members of the Climate and Resiliency Adaptation Roadmap team and partners have helped build and place heat sensors to record and analyze data. The current heat sensors, which are shoebox-shaped devices on tripods, can be found at multiple outdoor locations on campus during the summer, capturing and recording temperatures multiple times each hour. “Urban environmental phenomena are hyperlocal. While National Weather Service readouts at locations like Logan Airport are extremely valuable, this gives us a more high-resolution understanding of the urban microclimate on our campus,” notes Sanjana Paul, past technical associate with Senseable City and current graduate student in the Department of Urban Studies and Planning who helps oversee data collection and analysis.
After collection, temperature data are analyzed and mapped. The data will soon be published in the updated Climate Resiliency Dashboard and will help inform actions through the Climate Resiliency and Adaptation Roadmap, but in the meantime, the information has already provided some important insights. “There were some parts of campus that were much hotter than I expected,” explains Paul. “Some of the temperature readings across campus were regularly going over 100 degrees during heat waves. It’s a bit surprising to see three digits on a temperature reading in Cambridge.” Some strategies are also already being put into action, including planting more trees to support the urban campus forest and launching cooling locations around campus to open during days of extreme heat.
As data gathering enters its fourth summer, partners continue to expand. Senseable City first began capturing data in 2021 using sensors placed on MIT Recycling trucks, and the Urban Risk Lab has offered community-centered temperature data collection with the help of its director and associate professor of architecture, Miho Mazereeuw. More recently, students in course 6.900 (Engineering for Impact) worked to design heat sensors to aid in the data collection and grow the fleet of sensors on campus. Co-instructed by EECS senior lecturer Joe Steinmeyer and EECS professor Joel Voldman, students in the course were tasked with developing technology to solve challenges close at hand. “One of the goals of the class is to tackle real-world problems so students emerge with confidence as an engineer,” explains Voldman. “Having them work on a challenge that is outside their comfort zone and impacts them really helps to engage and inspire them.”
Centering on people
While the temperature data offer one piece of the resiliency planning puzzle, knowing how these temperatures will affect community members is another. “When we look at impacts to our campus from heat, people are the focus,” explains Goldberg. “While stress on campus infrastructure is one factor we are evaluating, our primary focus is the vulnerability of people to extreme heat.” Impacts to community members can range from disrupted nights of sleep to heat-related illnesses.
As the team looked at the data and spoke with individuals across campus, it became clear that some community members might be more vulnerable than others to the impact of extreme heat days, including ground, janitorial, and maintenance crews who work outside; kitchen staff who work close to hot equipment; and student athletes exerting themselves on hot days. “We know that people on our campus are already experiencing these extreme heat days differently,” explains Susy Jones, senior sustainability project manager in the Office of Sustainability who focuses on environmental and climate justice. “We need to design strategies and augment existing interventions with equity in mind, ensuring everyone on campus can fulfill their role at MIT.”
To support those strategy decisions, the resiliency team is seeking additional input from the MIT community. One hoped-for outcome of the roadmap and dashboard is for community members to review them and offer their own insight and experiences of heat conditions on campus. “These plans need to work at the campus level and the individual,” says Goldberg. “The data tells an important story, but individuals help us complete the picture.”
A model for others
As the dashboard update nears completion and the broader resiliency and adaptation roadmap of strategies launches, their purpose is twofold: help MIT develop and inform plans and procedures for mitigating and addressing heat on campus, and serve as a model for other universities and communities grappling with the same challenges. “This approach is the center of how we operate at MIT,” explains Director of Sustainability Julie Newman. “We seek to identify solutions for our own campus in a manner that others can learn from and potentially adapt for their own resiliency and climate planning purposes. We’re also looking to align with efforts at the city and state level.” By publishing the roadmap broadly, universities and municipalities can apply lessons and processes to their own spaces.
When the updated Climate Resiliency Dashboard and Climate Resiliency and Adaptation Roadmap go live, it will mark the beginning of the next phase of work, rather than an end. “The dashboard is designed to present these impacts in a way everyone can understand so people across campus can respond and help us understand what is needed for them to continue to fulfill their role at MIT,” says Goldberg. Uncertainty plays a big role in resiliency planning, and the dashboard will reflect that. “This work is not something you ever say is done,” says Goldberg. “As information and data evolves, so does our work.”
#Airport#Analysis#approach#architecture#assessment#Building#Cambridge#Boston and region#Campus buildings and architecture#Campus services#centering#challenge#change#climate#climate change#Collaboration#collaborative#Community#computer#Computer Science#cooling#course#dashboard#data#data collection#Design#devices#Electrical Engineering&Computer Science (eecs)#Engineer#engineering
0 notes
Text
Which is Best for You: Data Engineering or Data Science Services for Your Business?
In the virtual transformation age, organizations rely more on facts to drive choice-making, enhance operations, and gain a competitive edge. Data engineering forms the backbone of any data-pushed organization. On the other hand, data science focuses on extracting actionable insights, styles, and predictions from facts to pressure commercial enterprise decisions and innovation. Here in this post, you'll know which service is best for you - data engineering or data science.
0 notes
Text
The Generative AI Revolution: Transforming Industries with Brillio
The realm of artificial intelligence is experiencing a paradigm shift with the emergence of generative AI. Unlike traditional AI models focused on analyzing existing data, generative AI takes a leap forward by creating entirely new content. The generative ai technology unlocks a future brimming with possibilities across diverse industries. Let's read about the transformative power of generative AI in various sectors:
1. Healthcare Industry:
AI for Network Optimization: Generative AI can optimize healthcare networks by predicting patient flow, resource allocation, etc. This translates to streamlined operations, improved efficiency, and potentially reduced wait times.
Generative AI for Life Sciences & Pharma: Imagine accelerating drug discovery by generating new molecule structures with desired properties. Generative AI can analyze vast datasets to identify potential drug candidates, saving valuable time and resources in the pharmaceutical research and development process.
Patient Experience Redefined: Generative AI can personalize patient communication and education. Imagine chatbots that provide tailored guidance based on a patient's medical history or generate realistic simulations for medical training.
Future of AI in Healthcare: Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize disease diagnosis and treatment plans by creating synthetic patient data for anonymized medical research and personalized drug development based on individual genetic profiles.
2. Retail Industry:
Advanced Analytics with Generative AI: Retailers can leverage generative AI to analyze customer behavior and predict future trends. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns, optimized product placement based on customer preferences, and even the generation of personalized product recommendations.
AI Retail Merchandising: Imagine creating a virtual storefront that dynamically adjusts based on customer demographics and real-time buying patterns. Generative AI can optimize product assortments, recommend complementary items, and predict optimal pricing strategies.
Demystifying Customer Experience: Generative AI can analyze customer feedback and social media data to identify emerging trends and potential areas of improvement in the customer journey. This empowers retailers to take proactive steps to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Finance Industry:
Generative AI in Banking: Generative AI can streamline loan application processes by automatically generating personalized loan offers and risk assessments. This reduces processing time and improves customer service efficiency.
4. Technology Industry:
Generative AI for Software Testing: Imagine automating the creation of large-scale test datasets for various software functionalities. Generative AI can expedite the testing process, identify potential vulnerabilities more effectively, and contribute to faster software releases.
Generative AI for Hi-Tech: This technology can accelerate innovation in various high-tech fields by creating novel designs for microchips, materials, or even generating code snippets to enhance existing software functionalities.
Generative AI for Telecom: Generative AI can optimize network performance by predicting potential obstruction and generating data patterns to simulate network traffic scenarios. This allows telecom companies to proactively maintain and improve network efficiency.
5. Generative AI Beyond Industries:
GenAI Powered Search Engine: Imagine a search engine that understands context and intent, generating relevant and personalized results tailored to your specific needs. This eliminates the need to sift through mountains of irrelevant information, enhancing the overall search experience.
Product Engineering with Generative AI: Design teams can leverage generative AI to create new product prototypes, explore innovative design possibilities, and accelerate the product development cycle.
Machine Learning with Generative AI: Generative AI can be used to create synthetic training data for machine learning models, leading to improved accuracy and enhanced efficiency.
Global Data Studio with Generative AI: Imagine generating realistic and anonymized datasets for data analysis purposes. This empowers researchers, businesses, and organizations to unlock insights from data while preserving privacy.
6. Learning & Development with Generative AI:
L&D Shares with Generative AI: This technology can create realistic simulations and personalized training modules tailored to individual learning styles and skill gaps. Generative AI can personalize the learning experience, fostering deeper engagement and knowledge retention.
HFS Generative AI: Generative AI can be used to personalize learning experiences for employees in the human resources and financial services sector. This technology can create tailored training programs for onboarding, compliance training, and skill development.
7. Generative AI for AIOps:
AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations) utilizes AI to automate and optimize IT infrastructure management. Generative AI can further enhance this process by predicting potential IT issues before they occur, generating synthetic data for simulating scenarios, and optimizing remediation strategies.
Conclusion:
The potential of generative AI is vast, with its applications continuously expanding across industries. As research and development progress, we can expect even more groundbreaking advancements that will reshape the way we live, work, and interact with technology.
Reference- https://articlescad.com/the-generative-ai-revolution-transforming-industries-with-brillio-231268.html
#google generative ai services#ai for network optimization#generative ai for life sciences#generative ai in pharma#generative ai in banking#generative ai in software testing#ai technology in healthcare#future of ai in healthcare#advanced analytics in retail#ai retail merchandising#generative ai for telecom#generative ai for hi-tech#generative ai for retail#learn demystifying customer experience#generative ai for healthcare#product engineering services with Genai#accelerate application modernization#patient experience with generative ai#genai powered search engine#machine learning solution with ai#global data studio with gen ai#l&d shares with gen ai technology#hfs generative ai#generative ai for aiops
0 notes
Text
Tech Active Guide: Nurturing Connectivity with Remote Team Building
Explore virtual team building and remote work, uncovering benefits, challenges, and strategic initiatives for fostering collaboration. Visit us to know more.
#custom software development companies#custom software development services#hire net developers#machine learning development company#angular js development services#hire front end developer#hire backend developer#dedicated software development team#hire data engineers#machine learning consulting#offshore developers#hire software development team#data science experts#ai ml consulting#ai and ml consulting#custom machine learning solutions#machine learning solutions company#hire top software developers#hire devops engineer#python software engineer#remote python developers#remote full stack developers#remote developers#devops outsourcing
0 notes
Text
All-Star Moments in Space Communications and Navigation
How do we get information from missions exploring the cosmos back to humans on Earth? Our space communications and navigation networks – the Near Space Network and the Deep Space Network – bring back science and exploration data daily.
Here are a few of our favorite moments from 2024.

1. Hip-Hop to Deep Space
The stars above and on Earth aligned as lyrics from the song “The Rain (Supa Dupa Fly)” by hip-hop artist Missy Elliott were beamed to Venus via NASA’s Deep Space Network. Using a 34-meter (112-foot) wide Deep Space Station 13 (DSS-13) radio dish antenna, located at the network’s Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex in California, the song was sent at 10:05 a.m. PDT on Friday, July 12 and traveled about 158 million miles from Earth to Venus — the artist’s favorite planet. Coincidentally, the DSS-13 that sent the transmission is also nicknamed Venus!

NASA's PACE mission transmitting data to Earth through NASA's Near Space Network.
2. Lemme Upgrade You
Our Near Space Network, which supports communications for space-based missions within 1.2 million miles of Earth, is constantly enhancing its capabilities to support science and exploration missions. Last year, the network implemented DTN (Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networking), which provides robust protection of data traveling from extreme distances. NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) mission is the first operational science mission to leverage the network’s DTN capabilities. Since PACE’s launch, over 17 million bundles of data have been transmitted by the satellite and received by the network’s ground station.

A collage of the pet photos sent over laser links from Earth to LCRD and finally to ILLUMA-T (Integrated LCRD Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal) on the International Space Station. Animals submitted include cats, dogs, birds, chickens, cows, snakes, and pigs.
3. Who Doesn’t Love Pets?
Last year, we transmitted hundreds of pet photos and videos to the International Space Station, showcasing how laser communications can send more data at once than traditional methods. Imagery of cherished pets gathered from NASA astronauts and agency employees flowed from the mission ops center to the optical ground stations and then to the in-space Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD), which relayed the signal to a payload on the space station. This activity demonstrated how laser communications and high-rate DTN can benefit human spaceflight missions.

4K video footage was routed from the PC-12 aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The signals were then sent to NASA’s Laser Communications Relay Demonstration spacecraft and relayed to the ILLUMA-T payload on the International Space Station.
4. Now Streaming
A team of engineers transmitted 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back using laser communication signals. Historically, we have relied on radio waves to send information to and from space. Laser communications use infrared light to transmit 10 to 100 times more data than radio frequency systems. The flight tests were part of an agency initiative to stream high-bandwidth video and other data from deep space, enabling future human missions beyond low-Earth orbit.

The Near Space Network provides missions within 1.2 million miles of Earth with communications and navigation services.
5. New Year, New Relationships
At the very end of 2024, the Near Space Network announced multiple contract awards to enhance the network’s services portfolio. The network, which uses a blend of government and commercial assets to get data to and from spacecraft, will be able to support more missions observing our Earth and exploring the cosmos. These commercial assets, alongside the existing network, will also play a critical role in our Artemis campaign, which calls for long-term exploration of the Moon.

On Monday, Oct. 14, 2024, at 12:06 p.m. EDT, a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
6. 3, 2, 1, Blast Off!
Together, the Near Space Network and the Deep Space Network supported the launch of Europa Clipper. The Near Space Network provided communications and navigation services to SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket, which launched this Jupiter-bound mission into space! After vehicle separation, the Deep Space Network acquired Europa Clipper’s signal and began full mission support. This is another example of how these networks work together seamlessly to ensure critical mission success.
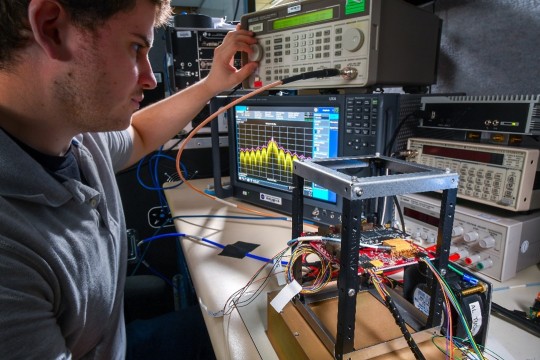
Engineer Adam Gannon works on the development of Cognitive Engine-1 in the Cognitive Communications Lab at NASA’s Glenn Research Center.
7. Make Way for Next-Gen Tech
Our Technology Education Satellite program organizes collaborative missions that pair university students with researchers to evaluate how new technologies work on small satellites, also known as CubeSats. In 2024, cognitive communications technology, designed to enable autonomous space communications systems, was successfully tested in space on the Technology Educational Satellite 11 mission. Autonomous systems use technology reactive to their environment to implement updates during a spaceflight mission without needing human interaction post-launch.
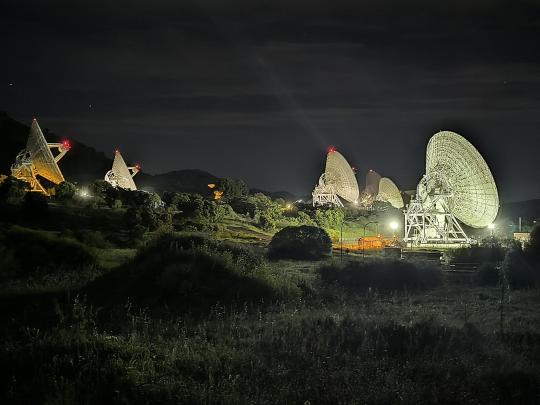

A first: All six radio frequency antennas at the Madrid Deep Space Communication Complex, part of NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN), carried out a test to receive data from the agency’s Voyager 1 spacecraft at the same time.
8. Six Are Better Than One
On April 20, 2024, all six radio frequency antennas at the Madrid Deep Space Communication Complex, part of our Deep Space Network, carried out a test to receive data from the agency’s Voyager 1 spacecraft at the same time. Combining the antennas’ receiving power, or arraying, lets the network collect the very faint signals from faraway spacecraft.
Here’s to another year connecting Earth and space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Crucial Role of Data Engineering in Today’s Data-Driven World
Introduction
In the digital age, data has become a driving force behind decision-making, business strategies, and technological advancements. However, the raw data generated from various sources is often unstructured, scattered, and inconsistent. Data engineering emerges as the unsung hero in this scenario, playing a critical role in organizing, processing, and transforming raw data into valuable insights that power businesses and innovations.
Understanding Data Engineering
Data engineering is the process of designing, constructing, and maintaining the systems and pipelines that allow for the collection, storage, and processing of data. It involves a series of activities that enable organizations to handle vast amounts of data efficiently and effectively. The goal of data engineering is to create a reliable and scalable infrastructure that facilitates data integration, transformation, and analysis.
Key Aspects of Data Engineering
Data Collection and Ingestion: Data engineering starts with the collection of raw data from various sources such as databases, APIs, sensors, and external feeds. This raw data is often in different formats and structures. Data engineers design pipelines that can ingest data in real-time or batch processing modes, ensuring the seamless flow of information into the data ecosystem.
Data Storage and Management: Once collected, the data needs to be stored in a structured and accessible manner. Data engineers work with databases, data lakes, and data warehouses to store and organize data for efficient querying and retrieval. They make decisions about the choice of storage technologies based on factors like data volume, velocity, and variety.
Data Transformation and Cleaning: Raw data is rarely in a suitable state for analysis. Data engineering involves transforming and cleaning the data to make it consistent, accurate, and valuable. This process includes tasks like data normalization, deduplication, and handling missing values.
Data Processing and Enrichment: Data engineers often enrich the data by combining it with external sources or generating new features. This step enhances the analytical potential of the data, enabling more advanced insights and predictions.
Pipeline Orchestration: Data engineering involves creating and managing data pipelines, which are a series of connected processing steps. These pipelines ensure that data flows smoothly through the various stages of collection, transformation, and analysis. Tools like Apache Airflow and Kubernetes help automate and manage these pipelines effectively.
Scalability and Performance: As data volumes grow, data engineering solutions must be scalable to handle increased loads without sacrificing performance. This requires a deep understanding of distributed computing, parallel processing, and optimization techniques.
Data Security and Compliance: Data engineers also play a role in ensuring data security and compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. They implement encryption, access controls, and auditing mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information.
Impact on Business and Technology
Data engineering is the backbone of data-driven decision-making. Its role extends to various domains, including:
Business Intelligence: Clean, integrated data is crucial for accurate business insights and strategic planning.
Machine Learning and AI: High-quality data is essential to train and validate machine learning models.
Personalization: Data engineering enables the creation of personalized user experiences by leveraging individual data.
Predictive Analytics: Historical data processed by data engineering pipelines forms the basis for predictive models.
Conclusion
In the era of big data, data engineering is the unsung hero that enables organizations to make sense of the immense amounts of information at their disposal. By collecting, organizing, and processing data effectively, data engineers provide the foundation for informed decision-making, innovation, and technological advancement. As data continues to be a driving force in various industries, the role of data engineering becomes increasingly vital.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Conspiratorialism as a material phenomenon

I'll be in TUCSON, AZ from November 8-10: I'm the GUEST OF HONOR at the TUSCON SCIENCE FICTION CONVENTION.

I think it behooves us to be a little skeptical of stories about AI driving people to believe wrong things and commit ugly actions. Not that I like the AI slop that is filling up our social media, but when we look at the ways that AI is harming us, slop is pretty low on the list.
The real AI harms come from the actual things that AI companies sell AI to do. There's the AI gun-detector gadgets that the credulous Mayor Eric Adams put in NYC subways, which led to 2,749 invasive searches and turned up zero guns:
https://www.cbsnews.com/newyork/news/nycs-subway-weapons-detector-pilot-program-ends/
Any time AI is used to predict crime – predictive policing, bail determinations, Child Protective Services red flags – they magnify the biases already present in these systems, and, even worse, they give this bias the veneer of scientific neutrality. This process is called "empiricism-washing," and you know you're experiencing it when you hear some variation on "it's just math, math can't be racist":
https://pluralistic.net/2020/06/23/cryptocidal-maniacs/#phrenology
When AI is used to replace customer service representatives, it systematically defrauds customers, while providing an "accountability sink" that allows the company to disclaim responsibility for the thefts:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/23/maximal-plausibility/#reverse-centaurs
When AI is used to perform high-velocity "decision support" that is supposed to inform a "human in the loop," it quickly overwhelms its human overseer, who takes on the role of "moral crumple zone," pressing the "OK" button as fast as they can. This is bad enough when the sacrificial victim is a human overseeing, say, proctoring software that accuses remote students of cheating on their tests:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/16/unauthorized-paper/#cheating-anticheat
But it's potentially lethal when the AI is a transcription engine that doctors have to use to feed notes to a data-hungry electronic health record system that is optimized to commit health insurance fraud by seeking out pretenses to "upcode" a patient's treatment. Those AIs are prone to inventing things the doctor never said, inserting them into the record that the doctor is supposed to review, but remember, the only reason the AI is there at all is that the doctor is being asked to do so much paperwork that they don't have time to treat their patients:
https://apnews.com/article/ai-artificial-intelligence-health-business-90020cdf5fa16c79ca2e5b6c4c9bbb14
My point is that "worrying about AI" is a zero-sum game. When we train our fire on the stuff that isn't important to the AI stock swindlers' business-plans (like creating AI slop), we should remember that the AI companies could halt all of that activity and not lose a dime in revenue. By contrast, when we focus on AI applications that do the most direct harm – policing, health, security, customer service – we also focus on the AI applications that make the most money and drive the most investment.
AI hasn't attracted hundreds of billions in investment capital because investors love AI slop. All the money pouring into the system – from investors, from customers, from easily gulled big-city mayors – is chasing things that AI is objectively very bad at and those things also cause much more harm than AI slop. If you want to be a good AI critic, you should devote the majority of your focus to these applications. Sure, they're not as visually arresting, but discrediting them is financially arresting, and that's what really matters.
All that said: AI slop is real, there is a lot of it, and just because it doesn't warrant priority over the stuff AI companies actually sell, it still has cultural significance and is worth considering.
AI slop has turned Facebook into an anaerobic lagoon of botshit, just the laziest, grossest engagement bait, much of it the product of rise-and-grind spammers who avidly consume get rich quick "courses" and then churn out a torrent of "shrimp Jesus" and fake chainsaw sculptures:
https://www.404media.co/email/1cdf7620-2e2f-4450-9cd9-e041f4f0c27f/
For poor engagement farmers in the global south chasing the fractional pennies that Facebook shells out for successful clickbait, the actual content of the slop is beside the point. These spammers aren't necessarily tuned into the psyche of the wealthy-world Facebook users who represent Meta's top monetization subjects. They're just trying everything and doubling down on anything that moves the needle, A/B splitting their way into weird, hyper-optimized, grotesque crap:
https://www.404media.co/facebook-is-being-overrun-with-stolen-ai-generated-images-that-people-think-are-real/
In other words, Facebook's AI spammers are laying out a banquet of arbitrary possibilities, like the letters on a Ouija board, and the Facebook users' clicks and engagement are a collective ideomotor response, moving the algorithm's planchette to the options that tug hardest at our collective delights (or, more often, disgusts).
So, rather than thinking of AI spammers as creating the ideological and aesthetic trends that drive millions of confused Facebook users into condemning, praising, and arguing about surreal botshit, it's more true to say that spammers are discovering these trends within their subjects' collective yearnings and terrors, and then refining them by exploring endlessly ramified variations in search of unsuspected niches.
(If you know anything about AI, this may remind you of something: a Generative Adversarial Network, in which one bot creates variations on a theme, and another bot ranks how closely the variations approach some ideal. In this case, the spammers are the generators and the Facebook users they evince reactions from are the discriminators)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generative_adversarial_network
I got to thinking about this today while reading User Mag, Taylor Lorenz's superb newsletter, and her reporting on a new AI slop trend, "My neighbor’s ridiculous reason for egging my car":
https://www.usermag.co/p/my-neighbors-ridiculous-reason-for
The "egging my car" slop consists of endless variations on a story in which the poster (generally a figure of sympathy, canonically a single mother of newborn twins) complains that her awful neighbor threw dozens of eggs at her car to punish her for parking in a way that blocked his elaborate Hallowe'en display. The text is accompanied by an AI-generated image showing a modest family car that has been absolutely plastered with broken eggs, dozens upon dozens of them.
According to Lorenz, variations on this slop are topping very large Facebook discussion forums totalling millions of users, like "Movie Character…,USA Story, Volleyball Women, Top Trends, Love Style, and God Bless." These posts link to SEO sites laden with programmatic advertising.
The funnel goes:
i. Create outrage and hence broad reach;
ii, A small percentage of those who see the post will click through to the SEO site;
iii. A small fraction of those users will click a low-quality ad;
iv. The ad will pay homeopathic sub-pennies to the spammer.
The revenue per user on this kind of scam is next to nothing, so it only works if it can get very broad reach, which is why the spam is so designed for engagement maximization. The more discussion a post generates, the more users Facebook recommends it to.
These are very effective engagement bait. Almost all AI slop gets some free engagement in the form of arguments between users who don't know they're commenting an AI scam and people hectoring them for falling for the scam. This is like the free square in the middle of a bingo card.
Beyond that, there's multivalent outrage: some users are furious about food wastage; others about the poor, victimized "mother" (some users are furious about both). Not only do users get to voice their fury at both of these imaginary sins, they can also argue with one another about whether, say, food wastage even matters when compared to the petty-minded aggression of the "perpetrator." These discussions also offer lots of opportunity for violent fantasies about the bad guy getting a comeuppance, offers to travel to the imaginary AI-generated suburb to dole out a beating, etc. All in all, the spammers behind this tedious fiction have really figured out how to rope in all kinds of users' attention.
Of course, the spammers don't get much from this. There isn't such a thing as an "attention economy." You can't use attention as a unit of account, a medium of exchange or a store of value. Attention – like everything else that you can't build an economy upon, such as cryptocurrency – must be converted to money before it has economic significance. Hence that tooth-achingly trite high-tech neologism, "monetization."
The monetization of attention is very poor, but AI is heavily subsidized or even free (for now), so the largest venture capital and private equity funds in the world are spending billions in public pension money and rich peoples' savings into CO2 plumes, GPUs, and botshit so that a bunch of hustle-culture weirdos in the Pacific Rim can make a few dollars by tricking people into clicking through engagement bait slop – twice.
The slop isn't the point of this, but the slop does have the useful function of making the collective ideomotor response visible and thus providing a peek into our hopes and fears. What does the "egging my car" slop say about the things that we're thinking about?
Lorenz cites Jamie Cohen, a media scholar at CUNY Queens, who points out that subtext of this slop is "fear and distrust in people about their neighbors." Cohen predicts that "the next trend, is going to be stranger and more violent.”
This feels right to me. The corollary of mistrusting your neighbors, of course, is trusting only yourself and your family. Or, as Margaret Thatcher liked to say, "There is no such thing as society. There are individual men and women and there are families."
We are living in the tail end of a 40 year experiment in structuring our world as though "there is no such thing as society." We've gutted our welfare net, shut down or privatized public services, all but abolished solidaristic institutions like unions.
This isn't mere aesthetics: an atomized society is far more hospitable to extreme wealth inequality than one in which we are all in it together. When your power comes from being a "wise consumer" who "votes with your wallet," then all you can do about the climate emergency is buy a different kind of car – you can't build the public transit system that will make cars obsolete.
When you "vote with your wallet" all you can do about animal cruelty and habitat loss is eat less meat. When you "vote with your wallet" all you can do about high drug prices is "shop around for a bargain." When you vote with your wallet, all you can do when your bank forecloses on your home is "choose your next lender more carefully."
Most importantly, when you vote with your wallet, you cast a ballot in an election that the people with the thickest wallets always win. No wonder those people have spent so long teaching us that we can't trust our neighbors, that there is no such thing as society, that we can't have nice things. That there is no alternative.
The commercial surveillance industry really wants you to believe that they're good at convincing people of things, because that's a good way to sell advertising. But claims of mind-control are pretty goddamned improbable �� everyone who ever claimed to have managed the trick was lying, from Rasputin to MK-ULTRA:
https://pluralistic.net/HowToDestroySurveillanceCapitalism
Rather than seeing these platforms as convincing people of things, we should understand them as discovering and reinforcing the ideology that people have been driven to by material conditions. Platforms like Facebook show us to one another, let us form groups that can imperfectly fill in for the solidarity we're desperate for after 40 years of "no such thing as society."
The most interesting thing about "egging my car" slop is that it reveals that so many of us are convinced of two contradictory things: first, that everyone else is a monster who will turn on you for the pettiest of reasons; and second, that we're all the kind of people who would stick up for the victims of those monsters.

Tor Books as just published two new, free LITTLE BROTHER stories: VIGILANT, about creepy surveillance in distance education; and SPILL, about oil pipelines and indigenous landback.


If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/10/29/hobbesian-slop/#cui-bono

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#taylor lorenz#conspiratorialism#conspiracy fantasy#mind control#a paradise built in hell#solnit#ai slop#ai#disinformation#materialism#doppelganger#naomi klein
308 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI Course In Delhi
Enroll to best AI Course in delhi
#artificial intelligence#data science#data scientist#machine learning#python#digital marketing#digital marketing services#youtube#search engine optimization#digitalmarketingcourse
0 notes
Text
The MIT Bike Lab: A place for community, hands-on learning
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/the-mit-bike-lab-a-place-for-community-hands-on-learning/
The MIT Bike Lab: A place for community, hands-on learning
Bianca Champenois SM ’22 learned to ride a bike when she was 5 years old. She can still hear her sister yelling “equal elbows!” as she pushed her off into the street. Although she started young, her love of bikes really materialized when she was in college.
Champenois studied mechanical engineering (MechE) at the University of California at Berkeley, but with a first-year schedule comprising mostly prerequisites, she found herself wanting more hands-on opportunities. She stumbled upon BicyCal, the university’s bike cooperative.
“I loved the club because it was a space where learning was encouraged, mistakes were forgiven, and vibes were excellent,” explains Champenois. “I loved how every single bike that came into the shop was slightly different, which meant that no two problems were the same.”
Through the co-op’s hands-on learning experience, the few long rides she took across some of California’s bridges like the Golden Gate, and the lively evening “Bike Parties” drafting behind friends, Champenois’s love for biking continued to grow. When she arrived at MIT for her master’s studies, she joined the cycling team.
Champenois, who is also passionate about climate action, enjoyed the sense of community the cycling team offered, but was looking for something that also allowed her to solve problems and work on bikes again.
Play video
Peddling Community Video: Department of Mechanical Engineering
After discovering there wasn’t a comparable cooperative bike program at the Institute, Champenois was determined to start one herself. It wasn’t long before she secured club funding from The Coop’s Public Service Grant with the support of her peer, Haley Higginbotham ’21, who was also passionate about the cause. By the end of the year, the team had gained two more volunteers, civil and environmental engineering graduate student Matthew Goss and materials science and engineering grad student Gavin Winter, and the MIT Bike Lab was born.
“The idea is to empower people to learn how to fix their own bike so that they are motivated to use biking as a reliable transportation method,” says Champenois. The volunteer mechanic has a vested interest in promoting sustainability and improving urban infrastructure.
Champenois is a graduate student in the joint Mechanical Engineering and Computational Science/Engineering program, and her research involves applying data science and machine learning to fluid dynamics, with a specific focus on ocean and climate modeling. The NSF Graduate Research Fellow is now building upon prior research focused on ocean acidification as part of her PhD thesis, while she is also involved in other projects within Professor Themis Sapsis’s Stochastic Analysis and Nonlinear Dynamics (SAND) Lab.
“I appreciate that my research strikes a balance between more applied environmental projects and more theoretical statistics and computational science,” she explains while referencing a recent research contribution to a project focused on improving global climate simulations.
Champenois’s academic research focus may be specific, but she stresses that the Bike Lab isn’t targeted to any particular interest and welcomes all who are eager to learn.
“If you’re interested in solid mechanics, you can think about bike frames. If you’re interested in material science, you can think about brake pads. If you’re interested in fluids, you can think about hydraulic brakes,” she says. “I think there’s something for everyone, and there’s always something to learn.”
In the last year-and-a-half, the Bike Lab is estimated to have serviced over 150 bikes, and they’re only getting started. Champenois is ambitious about the Bike Lab’s future.
“I hope to teach classes, maybe throughout the semester or as a standalone IAP [Independent Activities Period] course. I am also really interested in the idea of managing a vending machine for parts,” states Champenois.
In the winter, the Bike Lab stores its tools in N52-318, but the club lacks the space needed to expand. “Without our own space, it is difficult for us to store parts, which means that people are required to bring their own parts if their repair requires a replacement,” explains Champenois.
While physical space isn’t required to build a sense of community, Champenois envisions the Bike Lab exuding the same sort of camaraderie as the Banana Lounge, another of one MIT’s student-run spaces, one day.
“I like to think of the Bike Lab as more than just a bike shop. It’s also a place for community,” she says.
Champenois hopes to complete her degree in the next year or two and would like to become a professor someday. She is excited by a career in academia, but she says she could also see herself working on a climate or weather research team or joining an ocean technology startup.
Many have heard the expression that being a student at MIT is like “drinking from a firehose,” but that is one of the things Champenois will miss most when she leaves.
“I have had the opportunity to discover so many new hobbies and been able to learn so much through sponsored activities,” she recalls. “Most importantly, I’ll miss the great people I have met. Everyone at MIT is so curious and hardworking in a way that is truly energizing.”
#Analysis#Bicycles#Born#Building#Campus services#career#Civil and environmental engineering#classes#climate#Clubs and activities#college#Community#computational science#course#data#data science#drinking#dynamics#engineering#Environmental#Fluid dynamics#fluids#focus#Funding#Future#GATE#Global#Graduate#postdoctoral#hands-on
0 notes
Text
Which is Best for You: Data Engineering or Data Science Services for Your Business?
In the age of virtual transformation, organizations are more and more reliant on facts to drive choice-making, enhance operations, and gain a competitive edge. As organizations seek to harness the strength of facts, they frequently face the question of whether or not to put money into data engineering or data science services in the USA, or perhaps each. Here we'll discuss which is best for you; data engineering or data science for your business.
0 notes
Text
10th House Careers
—Aries in the 10th House
Career Fields: Entrepreneur, athlete, firefighter, military, startup founder, stunt performer, motivational speaker
Vibe: Bold leader. Known for trailblazing, risk-taking, and charging ahead before the rest even have a plan
—Taurus in the 10th House
Career Fields: Finance, real estate, interior design, art dealing, luxury sales, farming, architecture
Vibe: Steady, success-built brick by brick. They create lasting legacies, often in beauty or security.
—Gemini in the 10th House
Career Fields: Writing, journalism, teaching, marketing, social media, podcasting, public relations
Vibe: Talks the talk and walks it too. A chameleon in the professional world.
—Cancer in the 10th House
Career Fields: Social work, therapy, childcare, nursing, hospitality, real estate, psychology, education
Vibe: The caretaker turned boss. Soft leadership with emotional intelligence.
—Leo in the 10th House
Career Fields: Entertainment, performing arts, politics, fashion, leadership, motivational speaking
Vibe: Center stage CEO. Craves recognition and knows how to shine in the public eye.
—Virgo in the 10th House
Career Fields: Healthcare, editing, data analysis, nutrition, teaching, research, administrative work
Vibe: The quiet expert. Precision and service-oriented excellence.
—Libra in the 10th House
Career Fields: Law, design, fashion, diplomacy, HR, beauty industry, art, public relations
Vibe: Polished professionalism. Brings harmony and aesthetics to high places.
—Scorpio in the 10th House
Career Fields: Psychology, investigation, forensics, finance, medicine, occult work, crisis intervention
Vibe: Power behind the curtain. Strategic, intense, and unafraid of the underworld.
—Sagittarius in the 10th House
Career Fields: Travel industry, higher education, publishing, philosophy, law, coaching, politics
Vibe: Globe-trotting guru. Wants to inspire through ideas, experience, and vision.
—Capricorn in the 10th House
Career Fields: Corporate leadership, finance, law, engineering, government, business ownership
Vibe: Born for the boardroom. Ambition + discipline = unstoppable climb.
—Aquarius in the 10th House
Career Fields: Tech, innovation, activism, science, astrology, nonprofit, entertainment, aviation
Vibe: Future-focused rebel. Breaks the mold to build a better one.
—Pisces in the 10th House
Career Fields: Art, film, music, healing arts, spiritual work, therapy, photography, ocean-related work
Vibe: The mystic in a suit. Creative, compassionate, and often guided by a dream or cause.
#signs in the 10th#10th house#midheaven#midheaven careers#zodiac careers#zodiac meme#answered asks#zodiac asks#zodiac aesthetic#the signs as#leo#virgo#aquarius#gemini#libra#scorpio#Pisces#Taurus#Sagittarius#Capricorn#Aries#cancer
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
♍️Virgo Mc in the each of the degrees♍️
If you have a Virgo Midheaven (MC), your career and public image are shaped by Virgo’s themes of precision, analysis, service, and mastery. You likely thrive in careers requiring problem-solving, organization, and attention to detail, such as healthcare, science, writing, education, research, or business administration.
• 0° Virgo (Aries Point) – A powerful initiator in service-based or intellectual fields. May gain recognition in medicine, science, or social reform.
• 1° Virgo – A perfectionist with strong critical thinking skills. Could succeed in editing, analytics, or quality control.
• 2° Virgo – A talented communicator; could thrive in writing, journalism, or teaching.
• 3° Virgo – An analytical mind, ideal for investigative work, research, or forensics.
• 4° Virgo – A love for learning and refinement; may excel in academia, law, or technical writing.
• 5° Virgo – A meticulous worker; likely to succeed in finance, administration, or data analysis.
• 6° Virgo – Naturally inclined toward healthcare, therapy, or alternative medicine.
• 7° Virgo – A precise, creative thinker; may find success in graphic design, architecture, or craftsmanship.
• 8° Virgo – Drawn to healing professions, including nutrition, physical therapy, or holistic medicine.
• 9° Virgo – A problem-solver with innovative ideas. Could thrive in technology, engineering, or logistics.
• 10° Virgo – A strong educator; may work in teaching, coaching, or mentoring.
• 11° Virgo – A tech-savvy, analytical mind; may excel in IT, cybersecurity, or programming.
• 12° Virgo – A perfectionist in fashion, music, or fine arts. Success through precise craftsmanship.
• 13° Virgo – A highly responsible worker; may thrive in law enforcement, military, or humanitarian work.
• 14° Virgo – Health-conscious with a sharp mind. Could be drawn to dietetics, fitness, or medical research.
• 15° Virgo – A master of writing, editing, or academic research.
• 16° Virgo – Business-minded; excels in consulting, financial planning, or business strategy.
• 17° Virgo – A detail-oriented expert; could work in surgery, pharmaceuticals, or scientific research.
• 18° Virgo – A deep humanitarian drive; drawn to nonprofits, environmental work, or psychology.
• 19° Virgo – A critical thinker who excels in law, politics, or policy-making.
• 20° Virgo – A master of their craft; recognized for expertise in specialized fields.
• 21° Virgo – Exceptionally intellectual; may thrive in philosophy, academia, or technical writing.
• 22° Virgo – An innovative thinker; could work in product design, systems development, or efficiency consulting.
• 23° Virgo – A strong researcher; may specialize in history, archeology, or science.
• 24° Virgo – An excellent communicator; may succeed in broadcasting, publishing, or public relations.
• 25° Virgo – A sharp and strategic mind; could work in legal fields, investigative journalism, or intelligence.
• 26° Virgo – A healer at heart; may be drawn to nursing, surgery, or psychological counseling.
• 27° Virgo – A gifted analyst; could thrive in economics, data science, or cybersecurity.
• 28° Virgo – A precise and disciplined artist; success in sculpture, architecture, or technical art.
• 29° Virgo (Anaretic Degree) – A master strategist, perfectionist, or critic. Success comes through expertise, refinement, and precision. However, may struggle with overanalyzing or career indecision.
#astro notes#astrology#birth chart#astro observations#astro community#astrology degrees#astrology observations#Virgomc
76 notes
·
View notes