#Gig Economy
Text



A win for gig workers.
This ruling may have a rippling effect across the country
#capitalism#good news#news#current events#government#politics#us politics#the left#progressive#activism#Amazon#workers#workers rights#gig economy
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
When the app tries to make you robo-scab

When we talk about the abusive nature of gig work, there’s some obvious targets, like algorithmic wage discrimination, where two workers are paid different rates for the same job, in order to trick occasional gig-workers to give up their other sources of income and become entirely dependent on the app:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
Then there’s the opacity — imagine if your boss refused to tell you how much you’ll get paid for a job until after you’ve completed it, claimed that this was done in order to “protect privacy” — and then threatened anyone who helped you figure out the true wage on offer:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/08/07/hr-4193/#boss-app
Opacity is wage theft’s handmaiden: every gig worker producing content for a social media algorithm is subject to having their reach — and hence their pay — cut based on the unaccountable, inscrutable decisions of a content moderation system:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/10/e2e/#the-censors-pen
Making content for an algorithm is like having a boss that docks every paycheck because you broke rules that you are not allowed to know, because if you knew the rules, you’d figure out how to cheat without your boss catching you. Content moderation is the last place where security through obscurity is considered good practice:
https://doctorow.medium.com/como-is-infosec-307f87004563
When workers seize the means of computation, amazing things happen. In Indonesia, gig workers create and trade tuyul apps that let them unilaterally modify the way that their bosses’ systems see them — everything from GPS spoofing to accessibility mods:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/07/08/tuyul-apps/#gojek
So the tech and labor story isn’t wholly grim: there are lots of ways that tech can enhance labor struggles, letting workers collaborate and coordinate. Without digital systems, we wouldn’t have the Hot Strike Summer:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/02/not-what-it-does/#who-it-does-it-to
As the historic writer/actor strike shows us, the resurgent labor movement and the senescent forces of crapulent capitalism are locked in a death-struggle over not just what digital tools do, but who they do it for and who they do it to:
https://locusmag.com/2022/01/cory-doctorow-science-fiction-is-a-luddite-literature/
When it comes to the epic fight over who technology acts for and against, we need a diversity of tactics, backstopped by tech operated by and for its users — and by laws that protect workers and the public. That dynamic is in sharp focus in UNITE Here Local 11’s strike against Orange County’s Laguna Cliffs Marriott Resort & Spa.
The UNITE Here strike turns on the usual issues like a living wage (hotel staff are paid so little they have to rent rooming-house beds by the shift, paying for the right to sleep in a room for a few hours at a time, without any permanent accommodation). They’re also seeking health-care and pensions, so they can be healthy at work and retire after long service. Finally, they’re seeking their employer’s support for LA’s Responsible Hotels Ordinance, which would levy a tax on hotel rooms to help pay for hotel workers’ housing costs (a hotel worker who can’t afford a bed is the equivalent of a fast food worker who has to apply for food stamps):
https://www.unitehere11.org/responsible-hotels-ordinance/
But the Marriott — which is owned by the University of California and managed by Aimbridge Hospitality — has refused to bargain, walking out negotiations.
But the employer didn’t walk out over wages, benefits or support for a housing subsidy. They walked out when workers demanded that the scabs that the company was trying to hire to break the strike be given full time, union jobs.
These aren’t just any scabs, either. They’re predominantly Black workers who rely on the $700m Instawork app for gigs. These workers are being dispatched to cross the picket line without any warning that they’re being contracted as strikebreakers. When workers refuse the cross the picket and join the strike, Instawork cancels all their shifts and permanently blocks them from new jobs.
This is a new, technologically supercharged form of illegal strikebreaking. It’s one thing for a single boss to punish a worker who refuses to scab, but Instawork acts as a plausible-deniability filter for all the major employers in the region. Like the landlord apps that allow landlords to illegally fix rents by coordinating hikes, Instawork lets bosses illegally collude to rig wages by coordinating a blocklist of workers who refuse to scab:
https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2022/10/company-that-makes-rent-setting-software-for-landlords-sued-for-collusion/?comments=1
The racial dimension is really important here: the Marriott has a longstanding de facto policy of refusing to hire Black workers, and whenever they are confronted with this, they insist that there are no qualified Black workers in the labor pool. But as soon as the predominantly Latino workforce struck, Marriott discovered a vast Black workforce that it could coerce into scabbing, in collusion with Instawork.
Now, all of this isn’t just sleazy, it’s illegal, a violation of Section 7 of the NLRB Act. Historically, that wouldn’t have mattered, because a string of presidents, R and D, have appointed useless do-nothing ghouls to run the NLRB. But the Biden admin, pushed by the party’s left wing, made a string of historic, excellent appointments, including NLRB General Counsel Jennifer Abruzzo, who has set her sights on punishing gig work companies for flouting labor law:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/01/10/see-you-in-the-funny-papers/#bidens-legacy
UNITE HERE 11 has brought a case to the NLRB, charging the Instawork, the UC system, Marriott, and Aimbridge with violating labor law by blackmailing gig workers into crossing the picket line. The union is also asking the NLRB to punish the companies for failing to protect workers from violent retaliation from the wealthy hotel guests who have punched them and screamed epithets at them. The hotel has refused to identify these thug guests so that the workers they assaulted can swear out complaints against them.
Writing about the strike for Jacobin, Alex N Press tells the story of Thomas Bradley, a Black worker who was struck off all Instawork shifts for refusing to cross the picket line and joining it instead:
https://jacobin.com/2023/07/southern-california-hotel-workers-strike-automated-management-unite-here
Bradley’s case is exhibit A in the UNITE HERE 11 case before the NLRB. He has a degree in culinary arts, but racial discrimination in the industry has kept him stuck in gig and temp jobs ever since he graduated, nearly a quarter century ago. Bradley lived out of his car, but that was repossessed while he slept in a hotel room that UNITE HERE 11 fundraised for him, leaving him homeless and bereft of all his worldly possessions.
With UNITE HERE 11’s help, Bradley’s secured a job at the downtown LA Westin Bonaventure Hotel & Suites, a hotel that has bargained with the workers. Bradley is using his newfound secure position to campaign among other Instawork workers to convince them not to cross picket lines. In these group chats, Jacobin saw workers worrying “that joining the strike would jeopardize their standing on the app.”

Today (July 30) at 1530h, I’m appearing on a panel at Midsummer Scream in Long Beach, CA, to discuss the wonderful, award-winning “Ghost Post” Haunted Mansion project I worked on for Disney Imagineering.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this thread to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/30/computer-says-scab/#instawork

[Image ID: An old photo of strikers before a struck factory, with tear-gas plumes rising above them. The image has been modified to add a Marriott sign to the factory, and the menacing red eye of HAL9000 from Stanley Kubrick's '2001: A Space Odyssey' to the sky over the factory. The workers have been colorized to a yellow-green shade and the factory has been colorized to a sepia tone.]

Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#hot strike summer#unions#UNITE HERE#labor#computer says no#tuyul apps#jacobin#gig economy#nlrb#marriott#Laguna Cliffs Marriott Resort & Spa#instawork#scabs#Aimbridge Hospitality Group#University of California#nlrb section 7#unfair labor practice#ulp#UNITE HERE Local 11#mansion tax#race#algorithmic wage discrimination#Veena Dubal#disciplinary technology#chickenized reverse-centaurs#reverse-centaurs#como is infosec#Jennifer Abruzzo
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
After nearly 15 years, Uber claims it’s finally turned an annual profit. Between 2014 and 2023, the company set over $31 billion on fire in its quest to drive taxi companies out of business and build a global monopoly. It failed on both fronts, but in the meantime it built an organization that can wield significant power over transportation — and that’s exactly how it got to last week’s milestone.
Uber turned a net profit of nearly $1.9 billion in 2023, but what few of the headlines will tell you is that over $1.6 billion of it came from unrealized gains from its holdings in companies like Aurora and Didi. Basically, the value of those shares are up, so on paper it looks like Uber’s core business made a lot more money than it actually did. Whether the companies are really worth that much is another question entirely — but that doesn’t matter to Uber. At least it’s not using the much more deceptive “adjusted EBITDA” metric it spent years getting the media to treat as an accurate picture of its finances.
Don’t be fooled into thinking the supposed innovation Uber was meant to deliver is finally bearing fruit. The profit it’s reporting is purely due to exploitative business practices where the worker and consumer are squeezed to serve investors — and technology is the tool to do it. This is the moment CEO Dara Khosrowshahi has been working toward for years, and the plan he’s trying to implement to cement the company’s position should have us all concerned about the future of how we get around and how we work.
[...]
Uber didn’t become a global player in transportation because it wielded technology to more efficiently deliver services to the public. The tens of billions of dollars it lost over the past decade went into undercutting taxis on price and drawing drivers to its service — including some taxi drivers — by promising good wages, only to cut them once the competition posed by taxis had been eroded and consumers had gotten used to turning to the Uber app instead of calling or hailing a cab.
As transport analyst Hubert Horan outlined, for-hire rides are not a service that can take advantage of economies of scale like a software or logistics company, meaning just because you deliver more rides doesn’t mean the per-ride cost gets significantly cheaper. Uber actually created a less cost-efficient model because it forces drivers to use their own vehicles and buy their own insurance instead of having a fleet of similar vehicles covered by fleet insurance. Plus, it has a ton of costs your average taxi company doesn’t: a high-paid tech workforce, expensive headquarters scattered around the world, and outrageously compensated executive management like Khosrowshahi, just to name a few.
How did Uber cut costs then? By systematically going after the workers that deliver its service. More recently, it took advantage of the cost-of-living crisis to keep them on board in the same way it exploited workers left behind by the financial crisis in the years after its initial launch. Its only real innovation is finding new ways to exploit labor.
385 notes
·
View notes
Text

Raise Giant Frogs - Easy to start!
American Frog Canning Co.
909 notes
·
View notes
Text
The US Department of Labor (DOL) published a final rule to the Federal Register on Wednesday that would increase the difficulty of classifying workers as independent contractors. If the rule survives court challenges unscathed, it will replace a business-friendly Trump-era regulation that did the opposite. It’s scheduled to go into effect on March 11.
The new rule, first proposed in 2022, could have profound implications for companies like Uber and DoorDash that rely heavily on gig workers. It would mandate that workers who are “economically dependent” on a company be considered employees.
The rule restores a pre-Trump precedent of using six factors to determine workers’ classification. These include their opportunity for profit or loss, the financial stake and nature of resources the worker has invested in the work, the work relationship’s permanence, the employer’s degree of control over the person’s work, how essential the person’s work is to the employer’s business and the worker’s skill and initiative.
130 notes
·
View notes
Text
inspired by the fact that I got a total of $2 in tips Dashing this morning...
no "see results" only out yourself as a decent human being or an asshole
reblog for further reach and all that
78 notes
·
View notes
Video
undefined
tumblr
an important factor to remember in the writers strike. So many industries want to turn the worker into a gig worker with no protections and no mentoring system.
#tiktok#WGA#mentor#gig economy#gig labor#gig workers#workers rights#workers vs capital#union workers#workers#skilled labor#labor rights#capital vs labor#labor vs capital#labor#training#writers strike#labor strike#strike#IP#copyright
320 notes
·
View notes
Text
Years after the Quebec government deregulated the taxi industry to allow services like Uber to operate, taxi drivers in Quebec have scored a court victory to the tune of $143 million, plus interest.
On Friday, a Quebec Superior Court judge awarded the sum as part of a ruling in a class-action lawsuit.
In 2019, Bill 17 was passed into law. The law abolished the taxi permit system while integrating app-based ride-hailing services into provincial regulations.
Around the time the law was passed, services like Uber were expanding their operations in the province, prompting anger and protests from taxi drivers who had spent tens of thousands, if not hundreds of thousands, to purchase their taxi permits.
After the bill became law, the Quebec government doled out more than $800 million in compensation to taxi drivers in the province, but drivers didn't believe that amount was enough to make up for their losses.
Continue Reading
Tagging: @newsfromstolenland
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
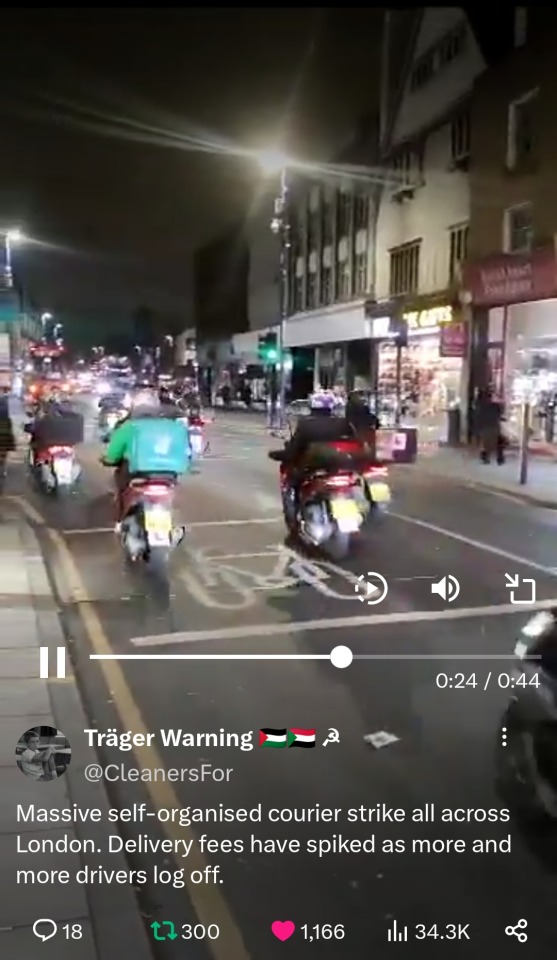
Early this week bike couriers went on strike across London over their unliveable wages and working conditions.
Solidarity!
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
Across New York City, delivery drivers are a ubiquitous sight: congregating outside big restaurant chains waiting to collect orders, zooming through the city streets with orders in tow. “The most chaotic time for deliveries is easily during lunch time,” says Elijah Williams, who delivers food for both Uber and DoorDash. “I’ve had up to four orders at one time.”
Mayor Eric Adams recently announced a major change that will deeply impact busy workers like Williams: app-based delivery workers will be paid $17.96 an hour starting July 12th — and nearly $20 an hour by 2025 — marking the nation’s first minimum pay for such workers.
“Our delivery workers have consistently delivered for us — now, we are delivering for them,” he said. “They should not be delivering food to your household, if they can’t put food on the plate in their household.”
The Background
Mayor Adams made the announcement at City Hall, surrounded by delivery workers as well as members of the nonprofit organizations, Workers Justice Project (WJP) and Los Deliveristas Unidos.
Ligia Guallpa, executive director of WJP, expressed her excitement and gratitude.
“This first of its kind minimum pay rate will uplift working and immigrant families,” said [Ligia Guallpa of Workers Justice Project (WJP)] alongside Gustavo Ajche of Los Deliveristas Unidos. “[It will] ensure that workers who keep New Yorkers fed, are able to keep also their families fed too.”
WJP was founded in 2010, and coordinates numerous worker-led programs, including Los Deliveristas Unidos, that aim to improve conditions for low-wage immigrant workers across the five boroughs.
The Details
The current minimum wage in New York is $15 an hour. On average, service workers are paid $7.09 an hour, excluding tips. The new wage is in keeping with a law passed by the City Council in 2021, which requires the Department of Consumer and Worker Protection to set a standard minimum rate for delivery workers.
App-based delivery workers are classified as “independent contractors,” which means they’re not entitled to the standard minimum wage that applies to salaried employees’ pay. Instead, delivery workers who work for the big food delivery services, like Uber Eats and Relay, are entitled to just $2.13 an hour before tips — a so-called “tipped sub-minimum wage.”
Research has shown that getting rid of tipped sub-minimum wages benefits not just the workers getting the raise, but the economy as a whole. A 2021 analysis found that states without a tipped sub-minimum wage saw 29 percent growth in their leisure and hospitality sectors, compared to just six percent in states that used the federal tipped sub-minimum wage of $2.13.
...For many of the workers who face hostile roads and unpredictable weather conditions to get New Yorkers their ordered goods, this is a life-changing development.
“This is my full-time job. I get up every day and do this,” says delivery driver Justin Martinez outside the Chick-Fil-A in Washington Heights.
Martinez, 30, is originally from the Dominican Republic. His commitment to completing deliveries, he explains, is fueled by his love for his family.
“This is my way to contribute. I go out, 9, 10 hours a day, do deliveries, and then I can come home,” he says. Martinez first started driving for Uber in 2019 before transitioning to delivering food for Uber Eats and other apps in 2021. He’s excited for the pay wage increase: “Maybe now, I only [have to] go out for 6 hours.”
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, June 30, 2023
#new york#new york city#nyc#uber#ubereats#delivery app#delivery driver#restaurants#minimum wage#labor#labor rights#united states#eric adams#gig workers#gig economy#income inequality#good news#hope
251 notes
·
View notes
Text
Uber and Lyft choose to put thousands out of work rather than pay a minimum wage. The gig economy is impoverishing American workers. Oligarchs and corporate assholes want you to be feudal serfs.
#Uber#lyft#corporate greed#minimum wage#oligarch assholes#corporate ssdholes#gig economy#unionize#organized labor labor now
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

Source
Let’s go
#working class#workers rights#solidarity#government#politics#us politics#the left#progressive#good news#gig economy#labor
360 notes
·
View notes
Text
A (Somewhat) Comprehensive List of Fun Job Perks that Won’t Pay Your Rent
Here are some of the super fun job perks the bitchlings told us they’d been offered at a workplace:
free food and beverages
a foosball table
indoor rock climbing wall
on-site laundry services
weekly team happy hours
gym membership or on-site gym
company outings to sports games
company outings to concerts and plays
massage chairs
nap pods
meditation rooms
standing desks and balance ball chairs
the opportunity to volunteer during work hours
automatic vacation day on your birthday
game consoles in the break room
discounts to local stores
unpaid company retreats
a monthly pizza day
performance bonuses paid in alcohol
team building exercises
pet insurance
a commuting allowance
magazine subscriptions
adding work projects to your portfolio
credit to the company store (THIS IS NOT A JOKE)
exposure (NEITHER IS THIS)
a sense of accomplishment (ok this one’s definitely a joke)
Notice anything about the items on this list? As cool as all these job perks might be, not a single one will pay the goddamn rent.
Keep reading.
If you liked this article, join our Patreon!
#benefits#capitalism#gig economy#job perks#job search#perks of the job#unfair hiring practices#workplace benefits
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
The work-life balance literature tends to devolve into heroic stories of achievers. A common theme is the profile of Chris O’Neil, a male executive, who rises at 5:30 a.m. to meditate before he drops the kids at school and then goes to the club for more exercise before a full day of focused business. Many of these books follow Tony Schwartz’s Power of Full Engagement: Managing Energy, Not Time (2003), with his stress on maximizing personal energy (with exercise) rather than attempting to increase time free from work. An interesting variation is the books geared for the female reader and the debate about whether life and work can be reconciled. A prominent group argues that career women must “lean in” to work and make “life” (or family) time secondary in order to prove their commitment to the job.
It sometimes is not obvious that these self-help writers have actually considered time in the work-life balance question. But time is a real, if often complex, problem: How much flextime is needed for family? Is giving more free time to workers with dependents really fair to those without such needs? These books seldom address the emergence of a “gig economy,” where flextime is less an issue and where unpredictable working hours are often more the problem.
Note that in 2015 only a quarter of Walmart workers had a regular work schedule. Work-life books generally ignore the problems of all but the professional elite. This literature also seldom addresses the right or value of free time for personally attained happiness, only conceding the need (perhaps) of family care. In any case, its main thrust is to maximize personal efficiency, turning work and life into modernized versions of the old time-and-motion studies of early twentieth-century efficiency experts.
157 notes
·
View notes
Text
NOT LONG AFTER she started, Uber deactivated Barbosa’s account out of the blue. So she switched to renting one on Lyft from the same guy. Now she drove as “Shakira.” When the Lyft app prompted Barbosa to confirm her identity by scanning her license, she texted the guy she was renting from: What now? He sent back a photo of Shakira’s ID. Oh. She was real. He paid Shakira a fee each week.
Driving without a license, under the table on a tourist visa, loaded Barbosa with stress. One night, Barbosa picked up a passenger at 2 am and he tried to kiss her. She had to fight him off and left him one star on the app; she didn’t want to risk calling the cops. Another time, she was pulled over for having her lights off. Barbosa froze as the officer strode up to her window, worried she might get her car towed and end up in jail, or even—who knows?—deported. She showed the cop her Brazilian driver’s license, and said she’d left her American one at home. He let her go.
In WhatsApp groups, and while waiting for riders at Logan Airport, Barbosa chatted up other Brazilian drivers also renting accounts. They traded tips about driving without papers, the nuances of the fuzzy don’t-ask-don’t-tell status quo in a country that hasn’t passed comprehensive immigration reforms in more than three decades. Far from an ICE officer on every corner, she heard, if you kept your head down, didn’t drink and drive or pick fights, you could manage.
[...]
One of her customers left their wallet in her car. She followed the woman’s convoluted instructions to return it, driving to two far-flung locations over two hours. Miffed, at one point Barbosa opened the wallet. She looked at the woman’s license, blonde with blue eyes. Barbosa snapped a picture. She thought the woman might tip her or at least say “thank you” for having wasted two hours, unpaid, to do her a favor. Instead, the woman was rude and short, giving Barbosa the push she’d been looking for. “I said, yeah, now I’m going to use this.”
Over the next few weeks, she would click through the driver onboarding process on both Uber and Lyft, reading over the steps to create her own account, mulling the risk. Finally, lying in bed on Christmas night, the first one she’d spent without her family, it was time: She opened her phone and scrolled to the blonde woman’s license. Barbosa uploaded the license to the Uber app. She used the woman’s name but her own insurance and registration. She entered her own iCloud email and phone number and set her own picture—brown hair, brown eyes—on the driver profile. She made up a Social Security number, submitted the application, and went to sleep.
The next day, Uber approved the account. Like that, Barbosa was in business for herself.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Broke more often
#love#truth#economy#genz#gen z shit#gen z#money#rent#rant#gig economy#side hustle#jobs hustles#hustle culture#american hustle#iplanmyfuture#hustler#workhard#success
7 notes
·
View notes