#Golden Globe 1952
Text
5 Fingers (1952)
5 Fingers by #JosephLMankiewicz starring #JamesMason and #DanielleDarrieux, "There’s a lot to be admired about the way this film refuses to play into an audience’s emotional need for constant nick-of-time cliffhangers"
JOSEPH L. MANKIEWICZ
Bil’s rating (out of 5): BBB.5
Alternate Title: Five Fingers
USA, 1952. Twentieth Century Fox. Screenplay by Michael Wilson, based on the book by L.C. Moyzisch. Cinematography by Norbert Brodine. Produced by Otto Lang. Music by Bernard Herrmann. Production Design by George W. Davis, Lyle R. Wheeler. Costume Design by Charles Le Maire. Film Editing by James B. Clark.
Time has…

View On WordPress
#Academy Award 1952#Ben Astar#Bernard Herrmann#Charles Le Maire#Danielle Darrieux#George W. Davis#Golden Globe 1952#Herbert Berghof#James B. Clark#James Mason#John Wengraf#Joseph L. Mankiewicz#L.C. Moyzisch#Lyle R. Wheeler#Michael Rennie#Michael Wilson#Norbert Brodine#Oskar Karlweis#Otto Lang#Roger Plowden#Twentieth Century Fox#Walter Hampden
0 notes
Text
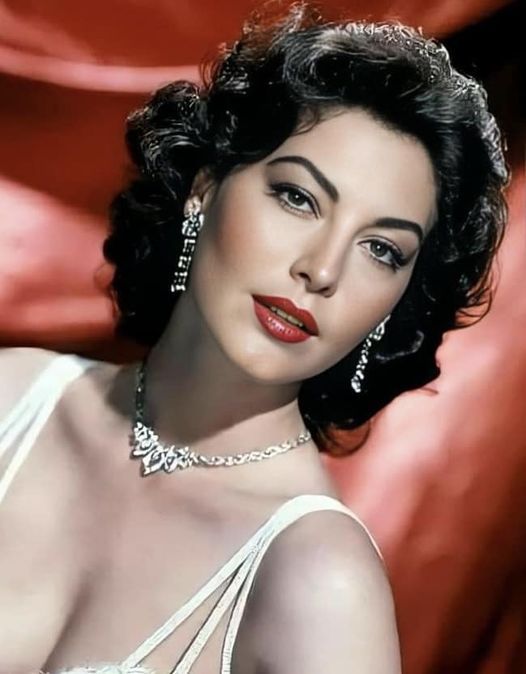
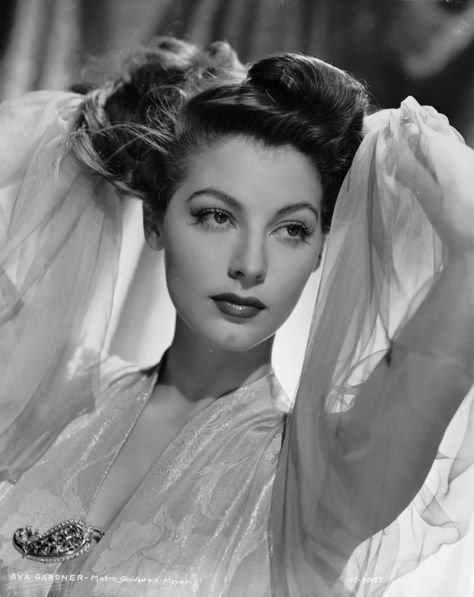



Ava Lavinia Gardner (December 24, 1922 – January 25, 1990) was an American actress. She first signed a contract with Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer in 1941 and appeared mainly in small roles until she drew critics' attention in 1946 with her performance in Robert Siodmak's film noir The Killers. She was nominated for an Academy Award for Best Actress for her performance in John Ford's Mogambo (1953), and for best actress for both a Golden Globe Award and BAFTA Award for her performance in John Huston's The Night of the Iguana (1964). She was a part of the Golden Age of Hollywood.
During the 1950s, Gardner established herself as a leading lady and one of the era's top stars with films like Show Boat, Pandora and the Flying Dutchman (both 1951), The Snows of Kilimanjaro (1952), The Barefoot Contessa (1954), Bhowani Junction (1956) and On the Beach (1959). She continued her film career for three more decades, appearing in the films 55 Days at Peking (1963), Seven Days in May (1964), The Bible: In the Beginning... (1966), Mayerling (1968), The Life and Times of Judge Roy Bean (1972), Earthquake (1974) and The Cassandra Crossing (1976). And in 1985, she had the major recurring role of Ruth Galveston on the primetime soap opera Knots Landing. She continued to act regularly until 1986, four years before her death in 1990, at the age of 67.
In 1999, the American Film Institute ranked Gardner No. 25 on its greatest female screen legends list.
59 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Ryuichi Sakamoto (January 17, 1952 - March 28, 2023)
Professor Sakamoto was one of Japan’s most successful musicians, acclaimed for work in Yellow Magic Orchestra as well as solo albums and film scores.
As a member of Yellow Magic Orchestra alongside Haruomi Hosono and Yukihiro Takahashi, Sakamoto created joyous and progressive electronic pop in the late 1970s and early 1980s, alongside solo releases. He acted alongside David Bowie in the 1983 film Merry Christmas, Mr Lawrence and composed its Celebrated theme, the first in a series of film scores including Oscar-winning work in 1987 with David Byrne and Cong Su for Bernardo Bertolucci’s The Last Emperor.
Alongside YMO, Sakamoto continued releasing solo albums including 1980’s B-2 Unit, another influence on the robotically funky sound of electro that also foreshadowed other dance music styles. After focusing purely on solo work, he forged further connections in the west, collaborating with musicians including Iggy Pop, Robert Wyatt, Laurie Anderson, David Sylvian and more. Sylvian contributed Forbidden Colours, a vocal version of one of Sakamoto’s most famous works, the theme to second world war drama Merry Christmas, Mr Lawrence. Sakamoto also starred in the film as a prisoner of war camp commander.
Following The last Emperor (in which he also had an acting role), he collaborated with Bernardo Bertolucci again for The Last Buddha, and with Merry Christmas, Mr Lawrence director Nagisa Oshima for Gohatto. He also scored two films by Brian De Palma (Snake Eyes and Femme Fatale), plus Wild Palms for Oliver Stone, High Heels for Pedro Almodóvar, the 1990 film adaptation of The Handmaid’s Tale, and more. His 2015 score for Alejandro González Iñárritu’s film The Revenant was nominated for Golden Globe, Bafta and Grammy awards. In 2019, he composed the music for an episode of dystopian TV drama series Black Mirror. He took no further acting roles, aside from appearing as a film director in Rain, a music video for Madonna.
Mr Sakamoto released a steady schedule of solo releases throughout the 1990s and onwards, and wrote a piece for the opening ceremony of the 1992 Olympic Games in Barcelona. In 1999 he debuted the multimedia opera project Life, in collaboration with artist Shiro Takatani with contributions from Bertolucci, Pina Bausch and more. He and Takatani extended the concept into installation work from 2007 onwards.
Also in 2007, he began the ambitious Schola project, curating 17 compilations of global music ranging from composers such as Ravel and Beethoven to Japanese pop. It was released via his record label Commons, set up in 2006, which has also released work by artists including Boredoms and OOIOO.
In 2002, he began a fruitful partnership with German musician Carsten Nicolai, who used his Alva Noto alias for four collaborative albums of minimalist electronica.
Mr Sakamoto was also an environmental campaigner, opposing the use of nuclear power, and creating the forestry project More Trees to enable carbon offsetting.
Ryuichi Sakamoto - Merry Christmas, Mr. Lawrence
#youtube#art#music#electro#rip#japan#ryuichi sakamoto#sakamoto#movies#star#legend#the last buddha#bernardo bertolucci#david bowie#brian de palma#madonna#pedro almodóvar#black mirror#oliver stone#yellow magic orchestra#iggy pop#mr lawrence#carsten nicolai#ravel
179 notes
·
View notes
Photo
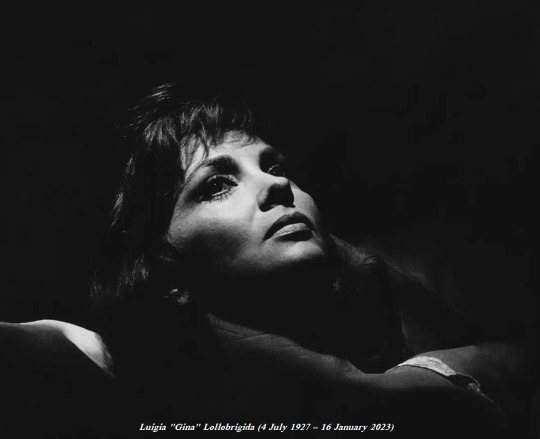










Ms Luigia "Gina" Lollobrigida OMRI (4 July 1927 – 16 January 2023)
Destined to be called "The Most Beautiful Woman in the World", Ms Lollobrigida was the daughter of a furniture manufacturer, and grew up in the pictorial mountain village. She studied sculpture at Rome’s Academy of Fine Arts, and started her career with minor Italian film roles before coming third in 1947’s Miss Italia pageant.
After refusing a contract with Howard Hughes to make three pictures in the United States in 1950, Ms Lollobrigida gained for starring turns in 1952’s “Fanfan la Tulipe” and 1953’s “Bread, Love and Dreams,” the latter of which netted her a BAFTA nomination for Best Foreign Actress.
Ms Lollobrigida’s first American film was “Beat the Devil,” a 1953 adventure comedy directed by John Huston that cast her opposite Humphrey Bogart. Over the course of the ’50s and ’60s, she starred in numerous French, Italian and European-shot American productions, with highlights including “Trapeze” with Burt Lancaster and Tony Curtis, “The Hunchback of Notre Dame” as Esmerelda, “Solomon and Sheba” with Yul Brynner, “Never So Flew” with Frank Sinatra and Steve McQueen, “Come September” with Rock Hudson, and “Woman of Straw” with Sean Connery, and “Buona Sera, Mrs. Campbell,” with Shelley Winters.
Her roles made her a major sex symbol of Italian cinema; in 1953, she won Italy’s David di Donatello award for Best Actress for her performance in the opera star Lina Cavalieri’s biopic “Beautiful But Dangerous,” known in Italian as “The World’s Most Beautiful Woman.”
She later won two more David di Donatello Award for “Imperial Venus” and “Buona Sera, Mrs. Campbell,” a Golden Medal of the City of Rome in 1986, a 40th Anniversary David in 1996 and a 50th Anniversary David in 2006. In 1961, she won the Golden Globes’ Henrietta Award for “World Fan Favorite,” and received nominations for “Falcon Crest” and “Buona Sera, Mrs. Campbell.”
After the ’60s, Lollobrigida’s career began to slow down, but she continued to act intermittently, including in the 1995 Agnes Varda film “Les cent et une nuits de Simon Cinéma,” and in ’80s TV shows such as CBS’ “Falcon Crest” and ABC’s “The Love Boat.”
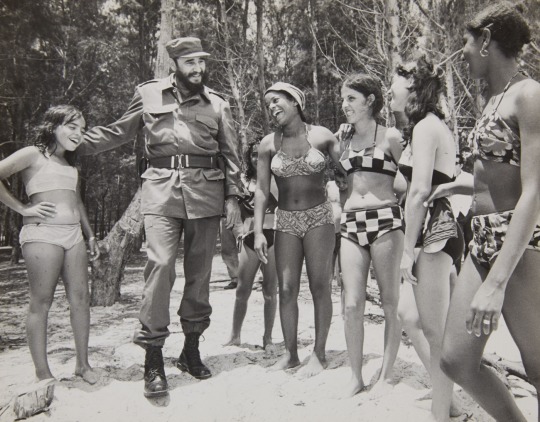
Ms Lollobrigida also developed a successful second career in photojournalism during the ’80s. She obtained an exclusive interview with Cuban leader Fidel Castro and also photographed many famous film stars, as well as publishing a number of books of her photographs.
In 2011 she made her final film appearance, playing herself in a cameo for the Italian parody film “Box Office 3D: The Filmest of Films.”
The screen legend sale of some of her 23 jewels from her Bulgari collection at Sotheby’s in 2013 to help fund an international hospital for stem-cell research.
On 16 October 1999, Lollobrigida was nominated as a Goodwill Ambassador of the UN Food and Agriculture Organization
Ms Lollobrigida won the Berlinale Camera at the Berlin Film Festival in 1986, Karlovy Vary Film Festival special prize in 1995, and the Rome Festival’s career prize in 2008. In 2018, she received a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame.
Ciao, Gina, Riposa in Pace
(Armando Pietrangeli, “Light and Shadow,” Gina Lollobrigida,1960, Trapeze 1956, Woman Of Rome,1954, Salomon & Sheba,1959, Come September, 1961,Un Bellissimo Novembre,1968, The Hunchback of Notre Dame,1956, In London to publicise her book of photographs titled Italia Mia,1974, Fidel Castro shot by Ms Lollobrigida,1974, Gina Lollobrigida pictured on July 11, 2022 in Rome).
#art#movirs#film#legend#gina lollobrigida#rip#rip gina lollobrigida#agnes varda#rock hudson#ciao#photography#icon#holywood#italy#falcon cest#the love boat#Esmeralda#yul brynner#howard hughes#paul newman#fidel castro#tony curtis#sheba#the hunchback of notre dame#trapeze#bafta#burt lancaster#frank sinatra#golden age#UN
281 notes
·
View notes
Text

NOIR CITY 21
Celebrating its 21st year, NOIR CITY, the largest annual film noir festival in the world, returns to Oakland's Grand Lake Theatre, January 19-28, 2024. FNF president Eddie Muller will present a dozen double bills pairing an English language noir with a similarly themed foreign language film—24 films over 10 days. Whatever the country of origin, there are heists, prison breaks, missing persons, cultural alienation, love triangles, and lots of plain old-fashioned murder.
Muller says this edition "has been tailored to satisfy those folks who love noir filled with the colorful vernacular slang so essential to American and British noir—as well as adventurous viewers intrigued by seeing a familiar story—typically a crime committed for passion or profit—play out in cultures with different values, mores, and styles." Through his programming of NOIR CITY festivals around the nation and his hosting of the popular Noir Alley franchise on Turner Classic Movies, Muller aims to move audiences past the idea that film noir is a strictly American genre.
Joining him this year, as co-programmer and co-host, is acclaimed film scholar Imogen Sara Smith, a familiar commentator on The Criterion Channel streaming service. "Attending NOIR CITY in the Bay Area has been a highlight of my year for over a decade," says Smith, "and I'm thrilled to be joining Eddie as co-host this year. I'm especially excited that the program we've put together will introduce audiences to some rare international titles, alongside Hollywood classics. It's going to be a stellar festival."

Kicking off the collection of rarities is the FNF's most recent restoration — 1952's Argentine film Never Open That Door (No abras nunca esa puerta) — based on two short stories by American master of suspense fiction, Cornell Woolrich. The picture was preserved by the Film Noir Foundation in 2013 and has now been completely restored by the FNF through UCLA Film & Television Archive, thanks in part to a grant from the Golden Globe Foundation (formerly HFPA). Fernando Martín Peña, Argentina's pre-eminent cinephile, will be on hand to introduce the film with Eddie Muller.
Included on the 2024 schedule are English-language rarities such as Black Tuesday (1954), Plunder Road (1957), Across the Bridge (1957), and Strongroom (1962). Little-seen international titles include The Human Beast (France, 1938), Aimless Bullet (South Korea, 1960), Bitter Rice (Italy, 1949), Four Against the World (Mexico, 1950), Zero Focus (Japan, 1961), and Smog (1962), a forgotten surrealist masterpiece by Italian director Franco Rossi freshly restored by UCLA Film & Television Archive. Explore the full line up, buy tickets for individual double features and Passports (All-Access Passes) at the festival website.
GO TO NOIR CITY
#noir city#film noir foundation#eddie muller#film restoration#noir city 21#noir city oakland#grand lake theatre#imogen sara smith#Argentine film noir#35mm screening#film noir festival#never open that door#cornell woolrich#Martín Peña#tcm#noir alley#criterion channel#No abras nunca esa puerta
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
John Goodman

Physique: Average Build
Height: 6'2" (1.88 m)
John Stephen Goodman (born June 20, 1952 -) is an American actor who rose to prominence in television before becoming an acclaimed and popular film actor. Goodman has received numerous accolades including a Primetime Emmy Award, Golden Globe Award, and a Screen Actors Guild Award. Vanity Fair has called him "among our very finest actors." TV fans, Goodman will always be Dan Connor from the hit sitcoms Rosanne and The Conners. Yet for film fans, he will forever be Walter Sabchak of the cult classic The Big Lebowski.
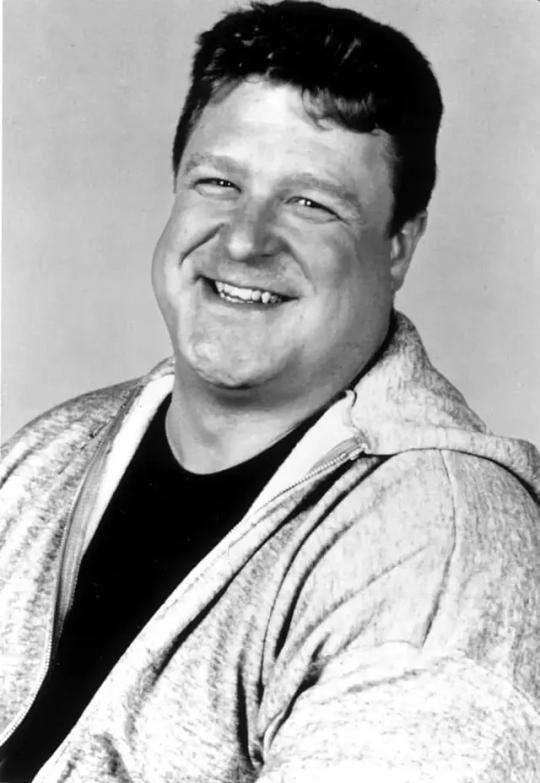
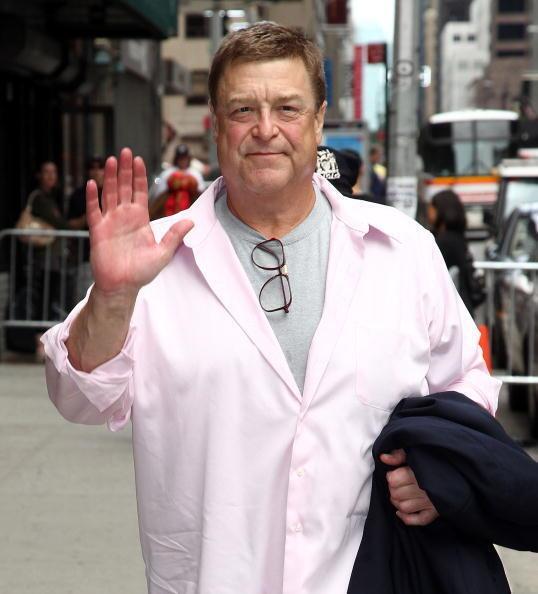
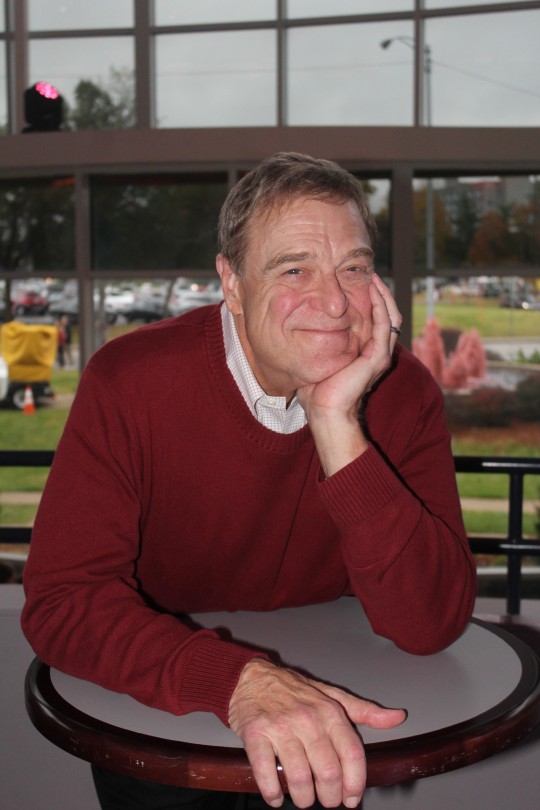




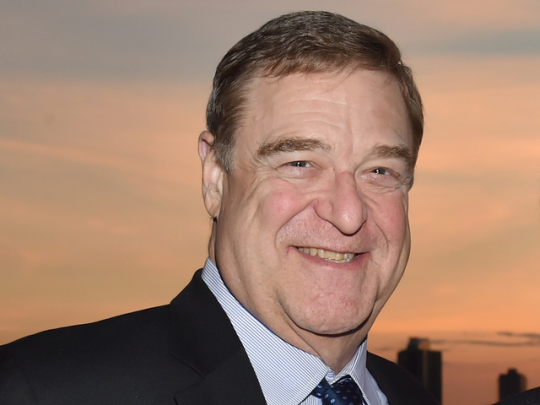
Through the years, the Affton, MO native could be seen in Always and heard in The Emperor’s New Groove movies, the Monsters, Inc. franchise and The Jungle Book 2. And while he enjoyed mainstream success with Roseanne and box office hits The Babe, Barton Fink and Everybody’s All-American he maintained an "bear/chub" fan base as a perennial favorite in shows Normal, Ohio. Even popping up in the Oscar-winning Best Pictures like The Artist and Argo.



Not bad for a frat boy who earned a football scholarship to Missouri State University. Alas, the sporty stud failed to score many nude scenes. But there are a couple where Goodman makes good. In the R-rated rom-com Everybody’s All-American, the shirtless actor relaxes in his underwear while drinking a beer. No doubt, those who fancy a man with some meat on his bones will get a bone! If that’s not arousing enough, in Alpha House featured John’s bare chest and his body double’s nude booty. Apparently John’s too big of a star to display his full moon!


Apparently, married for over 30 years with one child, Goodman was arguably the most successful big-guy actor in Hollywood playing characters that make us swoon. And consequently he was a first crush for thousands of young bears and chasers around the world. In recent years, John has lost a lot of weight, but he’ll always be my top chub no matter what.


RECOMMENDATIONS:
The Righteous Gemstones (TV Series 2019–)
Black Earth Rising (TV Series 2018)
10 Cloverfield Lane (2016)
The Monuments Men (2014)
In the Electric Mist (2009)
Speed Racer (2008)
Fallen (1998)
Freshman Orientation (2004)
King Ralph (1991)
34 notes
·
View notes
Text



GLYNIS JOHNS (1923-Died January 4th 2024,at 100).British actress, dancer, musician and singer. In a career spanning eight decades on stage and screen, Johns appeared in more than 60 films and 30 plays. She received various accolades throughout her career, including a Tony Award and a Drama Desk Award as well as nominations for an Academy Award, a Golden Globe Award, and a Laurence Olivier Award. She is widely considered to have been one of the last surviving major stars from the Golden Age of Hollywood and classical years of British cinema.
Johns was born in Pretoria, South Africa, the daughter of Welsh actor Mervyn Johns. She appeared on stage from a young age and was typecast as a stage dancer from early adolescence, making her screen debut in South Riding (1938). She rose to prominence in the 1940s following her role as Anna in the war drama film 49th Parallel (1941), for which she won a National Board of Review Award for Best Acting, and starring roles in Miranda (1948) and Third Time Lucky (1949). Following No Highway in the Sky (1951), a joint British-American production, Johns took on increasingly more roles in the United States and elsewhere. She made her television and Broadway debuts in 1952 and took on starring roles in such films as The Sword and the Rose (1953), The Weak and the Wicked (1954), Mad About Men (1954), The Court Jester (1955), The Sundowners (1960), The Cabinet of Caligari (1962), The Chapman Report (1962), and Under Milk Wood (1972). On television, she starred in her own sitcom Glynis (1963).
Renowned for the breathy quality of her husky voice,Johns sang songs written specifically for her both on screen and stage, including "Sister Suffragette", written by the Sherman Brothers for Disney's Mary Poppins (1964), in which she played Winifred Banks and for which she received a Laurel Award, and "Send In the Clowns", composed by Stephen Sondheim for Broadway's A Little Night Music (1973), in which she originated the role of Desiree Armfeldt and for which she received a Tony Award and Drama Desk Award.Glynis Johns - Wikipedia
#Glynis Johns#British Actresses#English Actresses#Actresses#Mary Poppins#The Sword and the Rose#A Little Light Music#Notable deaths in January 2024#Notable Deaths in 2024
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
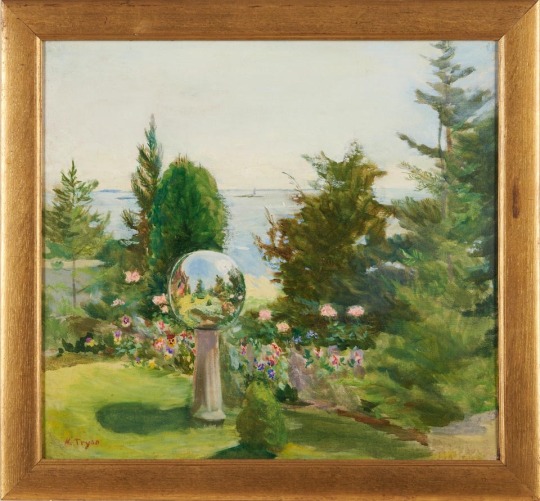

Kate Allen Tryon (American, 1865-1952)
Golden Globe
Signed, 'K. Tryon,' l.l. Oil on pane, framed.
Bonhams
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Glynis Margaret Payne Johns (October 5, 1923 - January 4, 2024) Film, stage and television actress, dancer, musician and singer. In a career spanning eight decades on stage and screen, Johns appeared in more than 60 films and 30 plays. She has received various accolades throughout her career, including a Tony Award, a Drama Desk Award, a National Board of Review Award, and a Laurel Award, in addition to nominations for an Academy Award, a Golden Globe Award, and a Laurence Olivier Award. She is widely considered as being one of the last surviving major stars from the Golden Age of Hollywood and classical years of British cinema.
Johns made her television debut in 1952 with Fletcher Markle's Emmy Award-winning series Little Women. She appeared in just one episode: season 4's "Lilly, the Queen of the Movies" as Lily Snape. Her television credits of the 1950s include brief appearances in the Hollywood anthology series Lux Video Theatre (in the 1953 episode "Two For Tea"), Errol Flynn's anthology series The Errol Flynn Theatre (in the 1956 episodes "The Sealed Room" as Lou McNamara and "The Girl in Blue Jeans" as The Girl Susan Tracey), CBS's anthology series Schlitz Playhouse of Stars (in the 1957 episode "The Dead Are Silent"), and ABC's variety and drama series The Frank Sinatra Show (in the 1958 episode "Face of Fear" as Christine Nolan)
Johns was cast in 1961 in the ABC/Warner Bros. crime drama The Roaring 20s. She portrayed Kitty O'Moyne, an Irish immigrant who falls overboard into the harbour as she arrives in the United States. Johns guest-starred in the CBS anthology seriesThe Lloyd Bridges Show in the episode "A Game for Alternate Mondays" of the 1962–63 television season, playing widow Leah Marquand, with Leslye Hunter as her daughter Isabella. On 5 August 1963, Vacation Playhouse premiered the episode "Hide and Seek" as the pilot of her eponymous CBS television series Glynis. The original working title for the series was The Glynis Johns Show; in it, Johns played the neophyte mystery writer and amateur sleuth Glynis Granvile. In the autumn of that year, Glynis officially premiered, starring Johns and Keith Andes as a married couple, Glynis Granville and Keith Granville, a criminal defence attorney. Due to pressure from NBC's The Virginian and Bill Cullen's The Price Is Right game show on ABC, the programme was cancelled after thirteen episodes. In 1965, when CBS reran the series as a summer replacement for The Lucy Show, Glynis ranked #6 in the Nielsen ratings. Johns remained busy on screen, appearing as Steffi Bernard in the episode "Who Killed Marty Kelso?" of ABC's detective series Burke's Law opposite Gene Barry. In 1967, she appeared in four episodes of the Batman television series as villainess Lady Penelope Peasoup, one half of the evil duo with Rudy Vallée as her brother Lord Marmaduke Ffogg.
During the first season of NBC's hit sitcom Cheers, Johns guest-starred as Diane Chambers' mother, Helen Chambers, an eccentric dowager who, due to a stipulation in Diane's late father's will, will lose all her money unless Diane is married by the next day. In 1985, Johns played Bridget O'Hara in the episode "Sing a Song of Murder" of CBS's crime drama television series Murder, She Wrote, working again with Angela Lansbury. From 1988 to 1989, she played Trudie Pepper, a senior citizen living in an Arizona retirement community, in the television sitcom Coming of Age, also on CBS. (Wikipedia)
8 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Ryuichi Sakamoto, the Japanese musician whose remarkably eclectic career straddled pop, experimentalism and Oscar-winning film composition, has died aged 71.
As a member of Yellow Magic Orchestra alongside Haruomi Hosono and Yukihiro Takahashi, Sakamoto created joyous and progressive electronic pop in the late 1970s and early 1980s, alongside solo releases. He acted alongside David Bowie in the 1983 film Merry Christmas, Mr Lawrence and composed its celebrated theme, the first in a series of film scores including Oscar-winning work in 1987 with David Byrne and Cong Su for Bernardo Bertolucci’s The Last Emperor.
Sakamoto had twice been diagnosed with cancer. In 2014, he took a year off from music as he recovered from throat cancer, describing the illness as “the most harsh, physically painful time in my life”.
In January 2021, he announced he had been diagnosed with bowel cancer, saying: “From now on, I will be living alongside cancer. But, I am hoping to make music for a little while longer.”
He was born in Tokyo in 1952, and began taking piano lessons aged six, later attending Tokyo University of the Arts to study music. He trained on early synthesizers, and enthused by everything from Debussy to Kraftwerk, began working on various musical projects, including with Hosono and Takahashi. After Sakamoto released his 1978 solo debut, Thousand Knives – playing melodies that harked back to traditional Japanese music on electronic equipment – the trio realised their vision for a Japanese disco-pop group, Yellow Magic Orchestra (YMO).
The group became a huge success in Japan – in 1980, two of their albums stayed at No 1 and No 2 in the charts for seven weeks, and they had seven Top 5 albums during their career. “Accidentally the three of us became very popular,” he remembered in 2018. “Walking the street in Tokyo, people pointed at me. I hated it.”
Their English-language lyrics helped them cross over into the US, where they appeared on the TV show Soul Train, and their electronic production influenced early hip-hop and electro scenes. Michael Jackson covered their song Behind the Mask and intended to include it on Thriller, but a royalties disagreement prevented it.
Their track Computer Game was also a Top 20 hit in the UK. YMO went on hiatus in 1984, though occasionally reunited for releases and reunion concerts.
Alongside YMO, Sakamoto continued releasing solo albums including 1980’s B-2 Unit, another influence on the robotically funky sound of electro that also foreshadowed other dance music styles. After focusing purely on solo work, he forged further connections in the west, collaborating with musicians including Iggy Pop, Robert Wyatt, Laurie Anderson, David Sylvian and more. Sylvian contributed Forbidden Colours, a vocal version of one of Sakamoto’s most famous works, the theme to second world war drama Merry Christmas, Mr Lawrence. Sakamoto also starred in the film as a prisoner of war camp commander.
Following The Last Emperor (in which he also had an acting role), he collaborated with Bernardo Bertolucci again for The Last Buddha, and with Merry Christmas, Mr Lawrence director Nagisa Oshima for Gohatto. He also scored two films by Brian De Palma (Snake Eyes and Femme Fatale), plus Wild Palms for Oliver Stone, High Heels for Pedro Almodóvar, the 1990 film adaptation of The Handmaid’s Tale, and more. His 2015 score for Alejandro González Iñárritu’s film The Revenant was nominated for Golden Globe, Bafta and Grammy awards. In 2019, he composed the music for an episode of dystopian TV drama series Black Mirror. He took no further acting roles, aside from appearing as a film director in Rain, a music video for Madonna.
Sakamoto released a steady schedule of solo releases throughout the 1990s and onwards, and wrote a piece for the opening ceremony of the 1992 Olympic Games in Barcelona. In 1999 he debuted the multimedia opera project Life, in collaboration with artist Shiro Takatani with contributions from Bertolucci, Pina Bausch and more. He and Takatani extended the concept into installation work from 2007 onwards.
Also in 2007, he began the ambitious Schola project, curating 17 compilations of global music ranging from composers such as Ravel and Beethoven to Japanese pop. It was released via his record label Commmons, set up in 2006, which has also released work by artists including Boredoms and OOIOO.
In 2002, he began a fruitful partnership with German musician Carsten Nicolai, who used his Alva Noto alias for four collaborative albums of minimalist electronica.
Sakamoto was also an environmental campaigner, opposing the use of nuclear power, and creating the forestry project More Trees to enable carbon offsetting.
In 1982, Sakamoto married Japanese pop musician Akiko Yano, a touring member of YMO and a successful solo artist in her own right. They split in 1992, and eventually filed for divorce in 2006. They had a daughter, pop singer Miu Sakamoto.
Since the early 1990s, Sakamoto has been in a relationship with Norika Sora. Their son Neo Sora contributed to a documentary, Ryuichi Sakamoto: Coda, directed by Stephen Nomura Schible in 2018.
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at http://justforbooks.tumblr.com
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
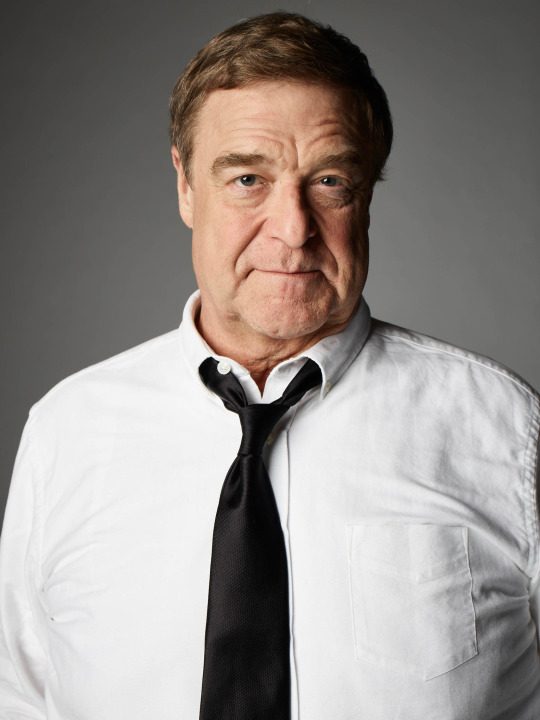

Born on June 20, 1952, John Goodman is an American actor. He rose to prominence in television before transitioning his career into film becoming an acclaimed and popular character actor. He's received numerous accolades including a Primetime Emmy Award, Golden Globe Award, and a Screen Actors Guild Award. Vanity Fair has called him "among our very finest actors." IndieWire named him one of the best actors never to have received an Academy Award nomination.
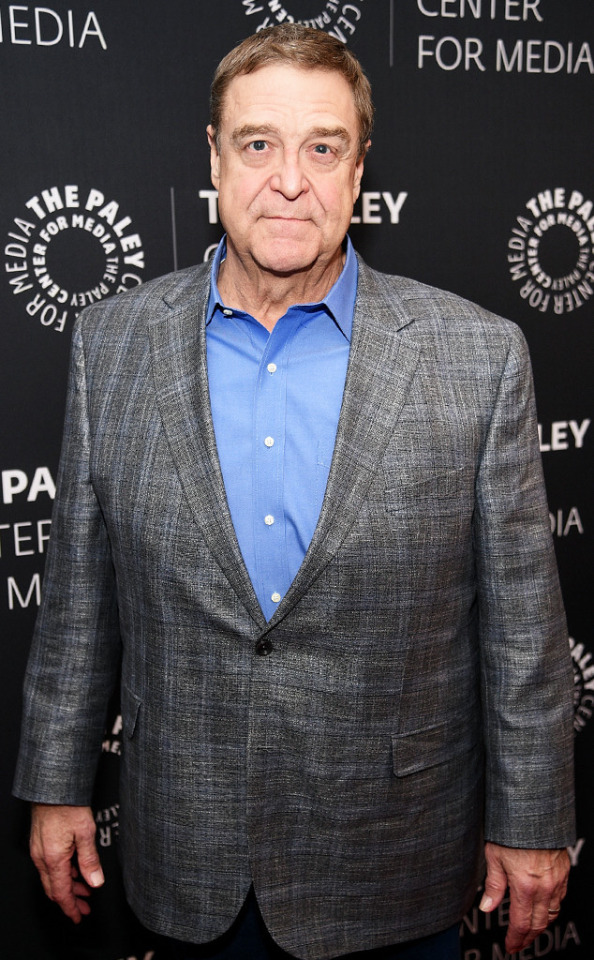
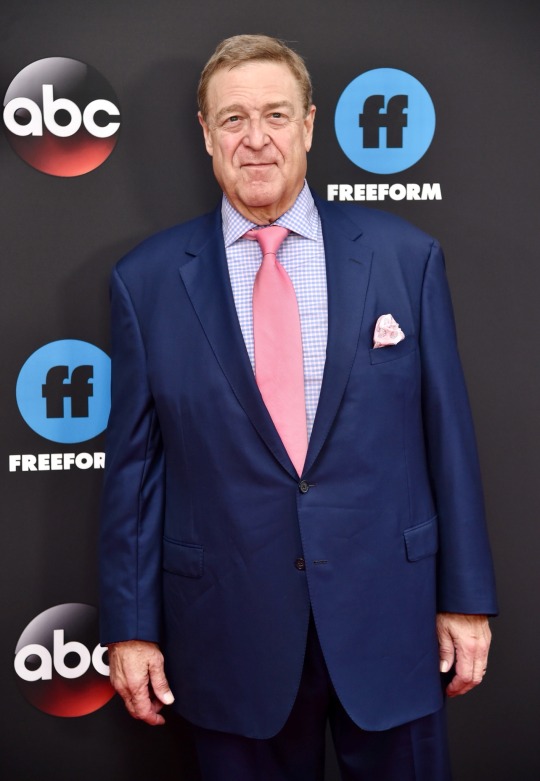
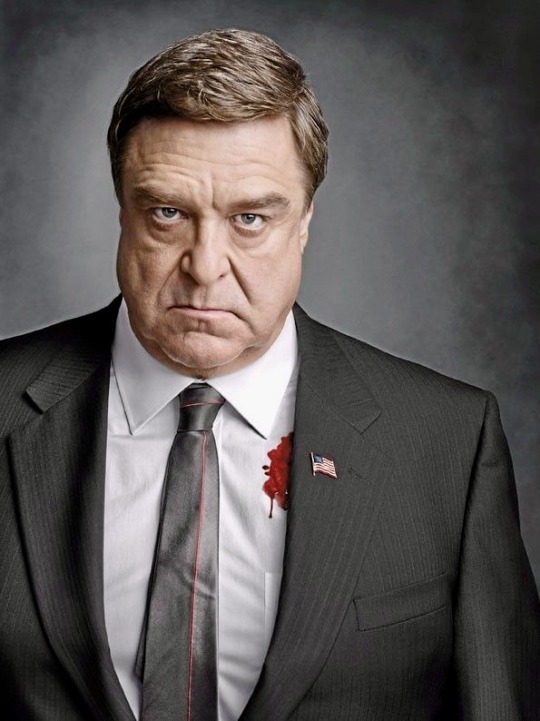
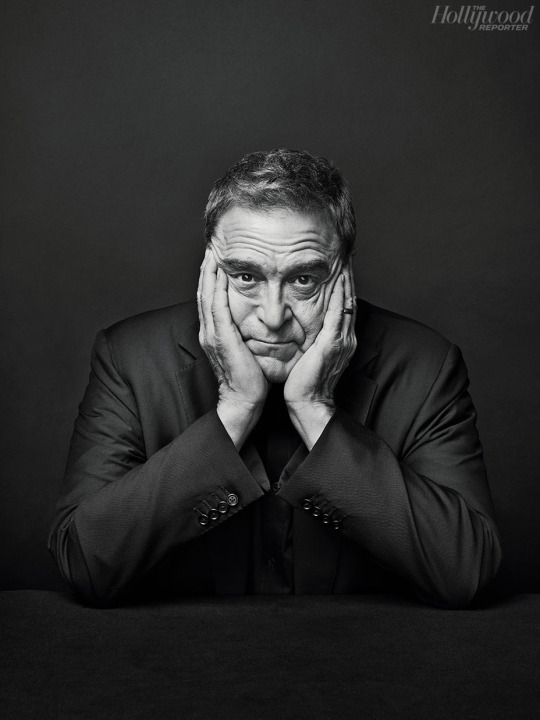
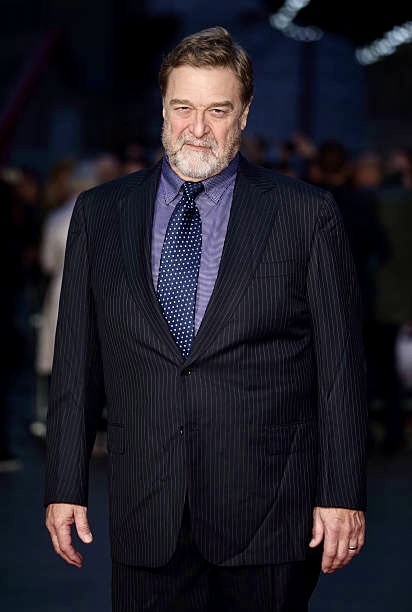









35 notes
·
View notes
Text





David Byrne (born 14 May 1952) is the founding member, principal songwriter, lead singer, and guitarist of my favorite band, Talking Heads. Byrne has a mellow voice, clever lyrics, and a fun onstage presence. He is also known for his "odd work habits" and wanting everything just right, but in a recent interview, he said he has lightened up. Byren also mentioned that the band would not get back together even for money because it would lose the art of music. When Talking Heads disbanded in 1991, Byrne released several solo albums and worked with close friend and musician Brian Eno numerous times. He was asked why he started making different from Talking Heads and if he was afraid he would alienate some fans; he said that they would understand and know that they wanted to shift gears for a bit. Byrne has collaborated with multiple artists, including my favorite rap group, De La Soul, and it's pretty cool because the song sounds like it could have been one of his songs. I like his work in and outside of music. He wrote and directed one of my favorite films, True Stories. He dabbles in photography and has written books in both fiction and non-fiction. Byrne said he had borderline Asperger's syndrome. He calls himself "an anthropologist from Mars." He has received a Grammy for his work in music. He also received an Oscar and a Golden Globe for composing music and the original score for the film The Last Emperor. In 2002, he and the other members of Talking Heads were inducted into The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame with Talking Heads. He has even been featured on The Simpsons. Byrne is an eclectic person who has experimented with other genres of music while still keeping his original essence. He did a Broadway version of his last album that is still going strong. His parents live in the town he grew up in, although they may have moved on. He made punk for "art nerds. "Byrne is an original and eccentric artist who has inspired and influenced artists and fans like me.
#Singer Songwriter#Musician#Record Producer#Music Theorist#Actor#Director#Author#Post Punk#New Wave#Art Pop#World#Electronic#Talking Heads
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
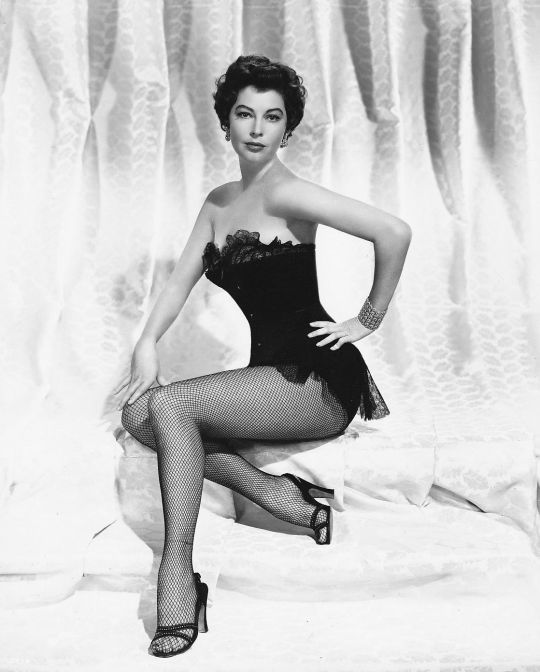



Films from the next decade or so include The Hucksters (1947), Show Boat (1951), The Snows of Kilimanjaro (1952), Lone Star (1952), Mogambo, nominated for a Best Actress Academy Award (1953), The Barefoot Contessa (1954), Bhowani Junction (1956), The Sun Also Rises (1957) and On the Beach (1959). Off-camera, she could be witty and pithy, as in her assessment of director John Ford, who directed Mogambo ("The meanest man on earth. Thoroughly evil. Adored him!"). In The Barefoot Contessa, she played the role of doomed beauty Maria Vargas, a fiercely independent woman who goes from Spanish dancer to international movie star with the help of a Hollywood director played by Humphrey Bogart, with tragic consequences. Gardner's decision to accept the role was influenced by her own lifelong habit of going barefoot. Gardner played the role of Guinevere in Knights of the Round Table (1953), with actor Robert Taylor as Sir Lancelot. Indicative of her sophistication, she portrayed a duchess, a baroness and other women of noble lineage in her films of the 1950s.
Gardner played the role of Soledad in The Angel Wore Red (1960) with Dirk Bogarde as the male lead. She was billed between Charlton Heston and David Niven for 55 Days at Peking (1963), which was set in China during the Boxer Rebellion in 1900. The following year, she played her last major leading role in the critically acclaimed The Night of the Iguana (1964), based upon a Tennessee Williams play, and starring Richard Burton as an atheist clergyman and Deborah Kerr as a gentle artist traveling with her aged poet grandfather. John Huston directed the movie in Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, insisting on making the film in black-and-white – a decision he later regretted because of the vivid colors of the flora. Gardner received billing below Burton, but above Kerr. She was nominated for a Golden Globe Award for Best Actress in a Motion Picture – Drama and BAFTA Award for Best Actress in a Leading Role for her performance.
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
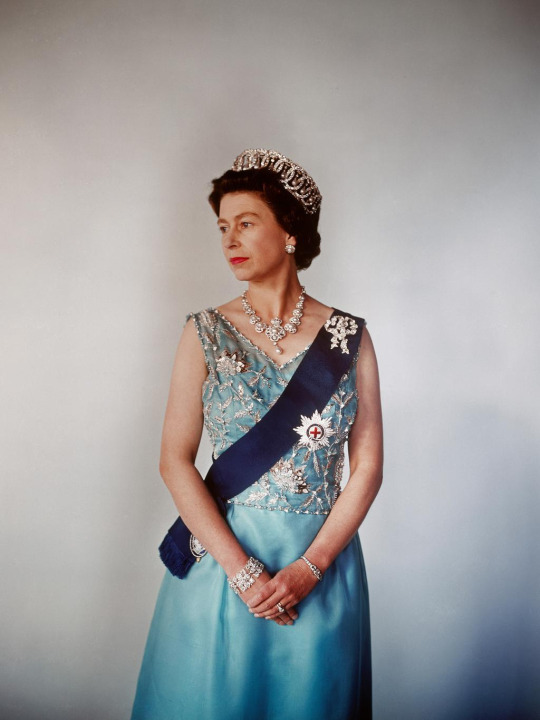

QUEEN ELIZABETH II
By Steve Dougherty and Larry Sutton | Published 17 September 2022
Time Magazine International Edition
QUEEN ELIZABETH II WAS THE WORLD’S LONGEST-serving head of state when she died at 96 on Sept. 8. She had led her subjects for more than seven decades—an extraordinary reign that began in 1952, and spanned 15 British Prime Ministers and 14 U.S. Presidents. She inherited the throne of a country almost broken by the legacy of war, and remained upon it through a time of epochal change for both the U.K. and the world.
When Elizabeth took the throne, the U.K. was the seat of an empire that straddled the globe. Today, Britain is a smaller player on the world’s stage, but she remained the sovereign leader of 15 nations—including Australia, Canada, and New Zealand—and head of a Commonwealth of more than 50 nations. She traveled the globe as an ambassador for British achievements, acts of charity, and values. She was also devoted to upholding the “special relationship” between the U.K. and the U.S., engaging with every President from Harry Truman to Joe Biden over a period of more than 70 years. And even as the world changed in profound ways, many saw her as a steadfast rock of patriotic duty. As her grandson Prince William wrote in the preface to a 2015 biography, “I think I speak for my generation when I say that the example and continuity provided by the Queen is not only very rare among leaders but a great source of pride and reassurance … I am privileged to have the Queen as a model for a life of service to the public.”
ELIZABETH ALEXANDRA MARY WINDSOR was born by cesarean section at 2:40 a.m. on April 21, 1926. She was an heir to the throne, but third in the line of succession. Her father Prince Albert—Bertie to friends and family—was the second son of the reigning monarch, King George V. His older brother David, known by his royal appellation Edward of Wales, was first in line to the throne—but also single, childless, and already rumored to have little interest in inheriting his father’s crown.
The early life of Princess Elizabeth was chronicled with zeal both by the British press and in the former colonies. “The water was from the River Jordan,” TIME reported of the elaborate christening pageantry staged in the private chapel at Buckingham Palace. Sir Winston Churchill first met Elizabeth at Balmoral Castle in 1928, when she was 2, and proclaimed that he saw in her “an air of authority and reflectiveness astonishing in an infant.”
No one in the realm was more enamored with the young Elizabeth than its monarch, who gave her the place of honor on his lap when they rode through the streets of London in his royal stretch Daimler. “No one else except the Queen rides out so often with the King,” TIME reported. Left out of the spotlight, not ungladly, was Lilibet’s father—the self-deprecating Bertie, who once told reporters, “My chief claim to fame seems to be that I am the father of Princess Elizabeth.”
Her reign as only child ended at age 4, in 1930, with the birth of her sister, Margaret Rose, at Glamis Castle in Scotland, their mother’s ancestral home. The girls romped together on the palace grounds and royal country estates, played with their terrier puppies and corgis—Elizabeth’s lifelong favorite. They also stabled, cared for, and learned to train a royal succession of pet ponies, and shared the same nannies and governesses.
In January 1936, upon the death of Lilibet’s grandfather George V, her uncle David became King Edward VIII. Almost immediately, his eldest niece and all the royal family became prime players in a 20th century succession drama. Edward’s tumultuous 10-month reign as King ended on Dec. 10, 1936, when he scandalized the world by abdicating the throne to marry the twice-divorced American socialite Wallis Warfield Simpson. “I always told those idiots not to put me in a golden frame,” he said. Young Lilibet was only 10 when she learned she would become Queen after her father’s death.


ELIZABETH WAS BARELY A TEENAGER when, on Sept. 3, 1939, Britain declared war on Nazi Germany. The war’s threat had already thundered throughout Europe, and soon the kingdom Elizabeth would one day rule, along with much of the rest of the world, was engulfed in war. Less than a year later, Hitler entered Paris and promised to make Britain his next conquest. Soon the Blitz—day and night Luftwaffe bombing raids that rained fire and terror over cities throughout England—was at full roar.
And so the Princess spent her teens knitting socks for British soldiers, collecting tinfoil, and rolling bandages for the war effort. She would send portions of her 5-shilling weekly allowance to emergency child-welfare funds, wear secondhand clothes, adhere to the war-rations diet dictated for all Britons, and live frugally despite being a teenage Princess and heir to the British throne.
Even as bombs fell on Buckingham Palace, the royal couple refused entreaties to abandon London and evacuate Princess Elizabeth and Princess Margaret to Canada. “The children won’t go without me,” said the Queen. “I won’t leave without the King. And the King will never leave.”
The King’s decision to remain in England for the duration of the war, enduring its deprivations along with his subjects, endeared him to the beleaguered nation. But it also made the likelihood that Elizabeth might suddenly be called to the throne in the event of her father’s death seem palpable.

The future monarch began her public life with her first live BBC radio broadcast in October 1940. Displaying poise and pluck, she addressed the tens of thousands of children who were evacuated from their homes and separated from their families at the height of the Blitz. “My sister, Margaret Rose, and I feel so much for you as we know from experience what it means to be away from those we love most of all,” she said in a clear voice that offered a hint of the calm and compassion that many would come to admire.
When in 1944 she reached military age at 18, Elizabeth joined the Auxiliary Territorial Service, one of the wartime women’s units. She spent three weeks at the Mechanical Transport Training Center, where she trained as a mechanic and truck driver. The labor left her covered in grease and grime and not a little well-earned pride.
And she never partied so hard as she did a fortnight after her 19th birthday when, on May 8, 1945—Victory in Europe Day—she joined the ecstatic and rowdy street celebrations that swept London following Germany’s surrender. After standing in uniform on the balcony at Buckingham Palace to greet cheering crowds alongside the King, Queen, and Prime Minister Winston Churchill, she, her sister, a group of friends, and a few guardians linked arms and ran among the crowds that surged through the city. For two nights in a row she “walked simply miles,” she wrote in her journal, “ate, partied, bed 3 a.m.!” These were, she would say 40 years later, among “the most memorable nights of my life.”
YEARS BEFORE, ELIZABETH had visited a naval college at Dartmouth where she had been greeted by a towering 18-year-old cadet.
Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark was born on the Greek island of Corfu on June 10, 1921, nephew of King Constantine of Greece and distant relation to Britain’s Queen Victoria. As his family drifted apart he was sent, at the age of 9, to England to live with his grandmother, the widow of the great British naval commander and German Prince Louis Alexander Mountbatten. He was schooled in England, Germany, and Scotland, and became a fine young athlete—as Elizabeth would note to her governess, Crawfie, on that trip to Dartmouth: “How good he is, Crawfie. How high can he jump!”
Elizabeth corresponded with Philip throughout the war, and after its end the Prince was placed on shore duty at a naval base on England’s south coast. He often made the 100-mile trek to London in his small black MG, frequently stopping at Buckingham Palace. As the friendship grew into a romance, Elizabeth was delighted. Her father George? Not so much—at first. “His loud, boisterous laugh and his blunt, seagoing manners … irritated the gentle King,” TIME reported in 1957. Despite that chill, Elizabeth and Philip decided to marry after a short stay with her family at Balmoral Castle in the summer of 1946. The King’s lack of enthusiasm for Elizabeth’s beau—an attitude sparked, in part, by his concern over how the people of Britain would take to a foreign-born prince marrying the heiress to the throne—frustrated the Princess. “There was many a tense moment for George as Elizabeth moped about in tearful martyrdom while her mother and grandmother, the doughty old Queen Mary, fought her battle for her. At last, George decided that the young couple (she was 20, he 25) should wait six months to make sure of each other,” noted TIME.

There were obstacles to overcome, but none insurmountable. Philip became a British citizen, and public-opinion polls showed that a majority of the nation’s populace favored his marrying the Princess. The official announcement did not come until July 9, 1947, followed by the couple’s introduction at a Buckingham Palace garden party. The wedding took place that November, on the 20th. Philip had converted from Greek Orthodoxy to Anglicanism, and Elizabeth’s father made the former member of the Greek and Danish royal families a British royal duke, the Duke of Edinburgh, to be called His Royal Highness, or simply Prince Philip.
As Elizabeth made her way to Westminster Abbey in the royal coach on her wedding day, thousands cheered from the neighboring sidewalks of London. Celebrations erupted throughout the globe, from Paris to Panama, from Shanghai to Manhattan—where thousands got out of bed at 6 a.m. to listen to the ceremony broadcast on the radio. Dignitaries—five Kings, six Queens, Prime Minister Clement Attlee, Winston Churchill—were in attendance. All of Britain celebrated, many seeing the wedding as a beacon of hope in the post–World War II recovery period.
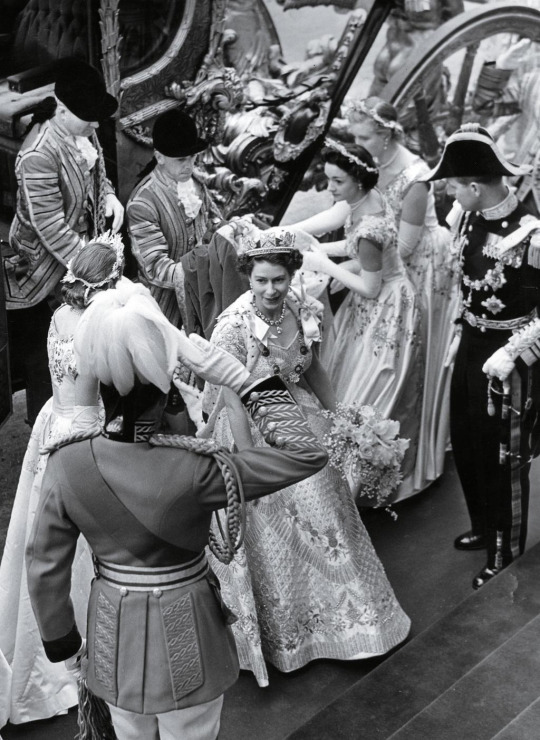
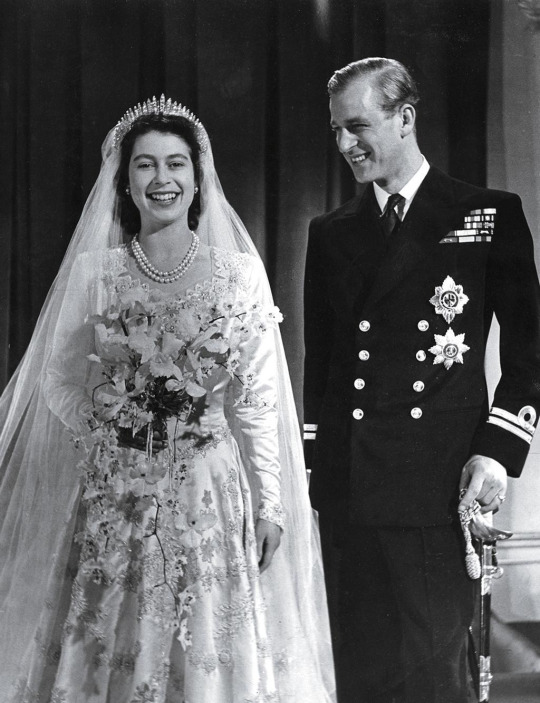
ON FEB. 5, 1952, Princess Elizabeth went to bed in a tree hut nestled in Kenya’s Aberdare National Park and awoke the next day as the Queen of England. She was unaware of her new position, for news of the death of her father King George VI had not yet reached that outpost of the British Empire. That afternoon, at a lodge, Philip received a phone call informing him of George’s death. The Prince took his bride down to a nearby river’s edge and relayed the news. Shaken, but in full command of herself, Elizabeth returned to the lodge and began making arrangements for the long trip home.
Elizabeth arrived at London’s airport the following morning. Churchill was there to greet her, along with a small group of privy councilors—advisers to the monarchy. That night she rested; the next day she signed the oath of accession before the Privy Council, and an hour later her accession was formally proclaimed. In the months that followed, there was no hurry to arrange her formal coronation—she was already, technically, the Queen. So Elizabeth and the Palace allowed the focus to stay on King George and his 16 enormously popular years on the throne, and let the nation’s sadness ebb.
The ceremony finally took place on June 2, 1953, a day chosen in hopes of sunny spring weather. This being London, however, the nation settled for a traditional gray morning. At 11 a.m., a joyous fanfare of trumpets announced the arrival of Her Majesty. “Vivat Regina Elizabetha! Vivat! Vivat! Vivat!” shouted the Queen’s Westminster Scholars as she walked up the aisle, her long crimson train borne by six maids of honor. The Archbishop of Canterbury proceeded to ask Elizabeth if she would govern her people according to their laws and customs, execute law and justice in mercy, and maintain the laws of God. She knelt, kissed the Holy Bible before her, and swore to do so, “so help me God.” Finally, he held aloft the Imperial State Crown for all to see, then placed it on Elizabeth’s head. Cheers of “God Save the Queen” filled the abbey as trumpets blared; outside, and across the British Empire, bells pealed and cannons roared.
AS WELL AS the constitutional duties Elizabeth fulfilled as Britain’s head of state and the head of the Church of England, she spent long sections of the following decades traveling the world as her nation’s goodwill ambassador. The November after her coronation she embarked on a 45,000-mile tour of the British Commonwealth, presiding over state balls, garden parties, luncheons, banquets, and other occasions. Among her stops: Libya, Australia, Fiji, New Zealand, Jamaica, Uganda, and the Pacific island of Tonga. She did not return to London until May 15, 1954, almost six months after she departed.
In the fall of 1957, Elizabeth and Philip spent six days in New York City; Washington, D.C.; and parts of Virginia, where they celebrated the 350th anniversary of the founding of the first British colony in America. In Washington, they were guests of President Dwight D. Eisenhower—a friend since his days in London during World War II—for four nights at the White House. At the state dinner, Elizabeth praised Washington as “so often a focus for the aspirations of the free world.” Later, Vice President Richard Nixon hosted a luncheon at the Capitol, and Elizabeth sought to see how the average American enjoyed life, attending a college football game and stopping in a Giant supermarket.
Clearly, the travel bug had bitten. In 1961, Elizabeth visited India, and at the Ramlila Grounds near Old Delhi, a quarter of a million people came to see her speak. In the city of Jaipur, the Maharaja offered her a ride on a ceremonial elephant. Though the trip was a success for Elizabeth, it also put the Indian government on edge—it viewed such a display of colonial pageantry as undermining the country’s fledgling independence. Philip also drew negative publicity when official photos emerged of a tiger he’d killed on a hunt with the Maharaja.
In Ghana that same year, Prime Minister Kwame Nkrumah told the Queen, “The wind of change blowing through Africa has become a hurricane.” (Ghana had declared independence from the British Empire in 1957, though the legacy of colonialism still hung over the country.) Tanzania would declare independence later that year, joined by Kenya in 1962 and a series of other African nations throughout the 1960s.
In 1965, Elizabeth embarked on an 11-day tour of West Germany, the first state visit by a reigning British monarch since Edward VII had paid his last call on Kaiser Wilhelm II in 1909. The trip came a full two decades after the end of World War II, amid fears of lingering resentment between the U.K. and Germany. But those fears were misplaced. The Queen and German Chancellor Ludwig Erhard said all hostility between their countries had been healed in the 20 years since the war. It ended in triumph, with crowds cheering and chanting “Elizabet, Eliz-a-bet!” as she placed a wreath on a Beethoven monument near the Bonn city hall.
BUT ALL THAT TRAVELING would put a strain on her family. That world tour following her coronation took place when Charles was 5 and Anne only 3—and the children were left behind. They did chat with their traveling mother by radiotelephone. But this would go on to be characteristic of Elizabeth, who always tended to make work her priority.


Years later, in 1994, Prince Charles would allow his authorized biographer to disclose that the prince felt “emotionally estranged” from his parents. Close friends found the Duke’s behavior “inexplicably harsh” and called his manner toward Charles “very bullying.” His mother, the Queen, seemed “detached.” Elizabeth and Philip were reported to be hurt by this disclosure. Publicly, only Philip would comment: “We did our best.” Princess Anne exercised less restraint, defending Elizabeth from rumors that she was remote. “I simply don’t believe that there is any evidence whatsoever to suggest that she wasn’t caring,” she said in 2002. Yet even Anne might have acknowledged a warmth that was sometimes wanting on her part later in life—when a little more compassion, a little more kindness, might have been called for.
The early 1990s would bring all kinds of personal problems to the fore—most notably in 1992, which the Queen famously described in a speech as an “annus horribilis” (horrible year). This was the year when her second son, Andrew, separated from his wife Sarah; when daughter Anne divorced her husband Mark Phillips; when her son Charles and his wife Diana increasingly became a tabloid issue; and when public concern grew about the cost of the monarchy and who would pay to repair Windsor Castle, which caught fire that year.
The damage was significant. The Nov. 20 fire—on the Queen’s 45th wedding anniversary—gutted the northeast corner of the castle, parts of which were more than 900 years old. It took 250 firefighters 15 hours to bring it under control. In the end more than 100 rooms, covering an area of 1.7 acres, were damaged. When British citizens learned that they were about to foot the bill for repairs to Windsor Castle—to the tune of up to $78 million—they grumbled. Elizabeth rectified the issue by volunteering to pay income and capital gains tax from her private investments. It hurt, but not too much: Her net worth remained at about $500 million.
But these were simply matters of state. Matters of the heart caused greater grief for Elizabeth—particularly the travails of Charles and Di. Their courtship and 1981 marriage captivated the nation, if not the world. No less an authority than the Archbishop of Canterbury proclaimed, “Here is the stuff of which fairy tales are made: the Prince and Princess on their wedding day.” But infidelity would intrude on both sides, and the ability to maintain the pretense of marriage for the sake of appearances became impossible. On Aug. 24, 1992, the transcript of a phone conversation between Diana and a close friend was published in the Sun, with Diana describing life with Charles as “real torture,” and saying she had caught the Queen Mother watching her “with a strange look in her eyes.” Diana and her young sons, William and Harry, continued to reside at Kensington Palace, while Charles’ relationship with Camilla Parker Bowles was parsed by the tabloid press. The Prince and Princess of Wales officially separated on Dec. 9.
Diana’s decision to grant an interview to the BBC on Nov. 20, 1995, in which she confessed that she had been unfaithful to Charles, had upset the royal family, and Queen Elizabeth in particular. (Of course, Charles had admitted his own infidelity on a TV documentary the previous year, as Diana noted in the interview.) Within a month, the Queen wrote to both Charles and Diana, urging them to agree to an early divorce. Buckingham Palace released a statement saying Charles favored the divorce, but there was no official word from Diana. In February 1996—more than a year before Diana, her romantic partner Dodi Fayed, and driver Henri Paul died in a car crash while being pursued by the paparazzi—she finally released her own statement saying she was ready to divorce too.
It took time for Elizabeth—a woman married seven decades to the same man—to adjust to modern mores. A longtime sticking point was Charles’ future bride Camilla; the press noted that Elizabeth was not enamored of her son’s consort. A shift occurred in 2002, when, by bringing Camilla to events celebrating Elizabeth’s 50 years on the throne, Charles provided strong evidence that he was gaining ground in his campaign to officially bring Camilla into the family fold.





Charles and Camilla got engaged around Christmas 2004, and before long the Queen issued a statement saying, “The Duke of Edinburgh and I are very happy that the Prince of Wales and Mrs. Parker Bowles are to marry.” She and Prince Philip did not attend their wedding at Windsor Guildhall on April 9, 2005, but they did attend a blessing of the couple at St. George’s Chapel in Windsor Castle and held a reception for them at the castle.
A more festive wedding—and one more in keeping with Elizabeth’s sense of tradition—took place on April 29, 2011, when Elizabeth’s grandson William married Kate Middleton in a lavish ceremony at Westminster Abbey. And she remained her regal self at Prince Harry and Meghan Markle’s more modern wedding at Windsor Castle in 2018, which included a fiery sermon delivered by Bishop Michael Curry of Chicago, the first African American head of the Episcopal Church in the U.S.
But in a televised interview with Oprah Winfrey in March 2021, Harry and Meghan alleged that racism had tarnished their relationship with the Windsors. While the press hounded Meghan as they did Harry’s late mother, “no one from my family ever said anything,” Harry said.
The family was once again thrust into the spotlight when allegations surfaced about Andrew’s relationship with the late sex offender Jeffrey Epstein. Andrew stepped back from royal duties in late 2019, and in 2021 was served with a lawsuit by Virginia Giuffre, one of Epstein’s victims, who accused Andrew of sexually abusing her when she was 17. According to the Daily Telegraph, the Queen contributed millions to her son’s legal defense, and agreed to contribute £2 million ($2.7 million) to a survivor-support charity as part of a settlement.
But family was also a source of comfort. As the Queen neared the end of her life, she doted on her grandchildren and great-grandchildren. “In a small room with close members of the family, then she is just a normal grandmother. Very relaxed,” Harry said before he and Meghan stepped back as working royals in early 2020. “She obviously takes a huge interest in what we all do.”




EVEN AFTER SHE ENTERED her ninth decade, Elizabeth continued with her royal duties, despite her age and a rapidly changing world.
For nearly all her reign, the Queen would read a selection of the 200 to 300 letters that she received daily, as well as review official papers and documents sent her way from government ministers and her representatives in foreign countries. Until she was forced to slow down by mobility issues and bouts of ill health, she would have 10- to 20-minute audiences with ambassadors, commissioners, and other officials, and there would be her weekly visit from the British Prime Minister.
Despite growing republican movements within the Commonwealth realms, the Queen herself remained a hugely popular figure in both the U.K. and beyond. And she remained a force for good, offering messages of inspiration and optimism in even the most trying times. In one of her last annual Christmas Day messages, she urged her subjects in Britain and across the Commonwealth to draw inspiration from “ordinary people doing extraordinary things.”
To many, she embodied the steadfastness she urged in others. At Prince Philip’s funeral, held shortly after he died on April 9, 2021, after 73 years of marriage, the monarch solemnly sat alone in a pew at Windsor Castle because of coronavirus restrictions. The image became instantly iconic, and further burnished her legacy as a stoic leader through good times and bad.
The Queen has been a constant figure in most of the British public’s living memory. Difficulty moving prevented her from attending the majority of Buckingham Palace’s Platinum Jubilee celebrations, as the nation in June 2022 marked her 70th year on the throne—a first for a British monarch. But community celebrations were widespread across the U.K. Some 16,000 official street parties were organized, and almost 17 million people—about 1 in 4 Brits—took part in events.
The Queen did not lead an ordinary life, but she filled it with inspiring acts of duty both public and private—whether carrying out the requirements of the state from the trappings of the throne, or giving quiet words of encouragement to a well-wisher in a crowd. She “has been a rock of stability in an era in which our country has changed so much,” said Britain’s former Prime Minister David Cameron. “And we could not be more proud of her. She has served this country with unerring grace, dignity, and decency.” —With reporting by ELOISE BARRY, KATHY EHRICH DOWD, MADELINE ROACHE, and YASMEEN SERHAN

PHOTOGRAPH BY © CECIL BEATON—VICTORIA AND ALBERT MUSEUM, LONDON
TOPICAL PRESS AGENCY/GETTY IMAGES
1956: INTERCONTINENTALE—AFP/GETTY IMAGES; 2019: PA WIRE/AP; SUCCESSION: GETTY IMAGES (13)
1941: LISA SHERIDAN—STUDIO LISA/GETTY IMAGES; 1945: MIRRORPIX/GETTY IMAGES
1947: HISTORIA/SHUTTERSTOCK; 1961: FOX PHOTOS/GETTY IMAGES
LEFT TO RIGHT, FROM TOP LEFT: JULIAN PARKER—UK PRESS/GETTY IMAGES; GEORGE SKADDING—THE LIFE PICTURE COLLECTION/SHUTTERSTOCK; UNIVERSAL HISTORY ARCHIVE/GETTY IMAGES; TOM STODDART—GETTY IMAGES; GAMMA-KEYSTONE/GETTY IMAGES; TIM GRAHAM PHOTO LIBRARY/GETTY IMAGES; BETTMANN ARCHIVE/GETTY IMAGES; JANE BARLOW—POOL/AP
PHOTOGRAPH BY MAX MUMBY—INDIGO/GETTY IMAGES
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
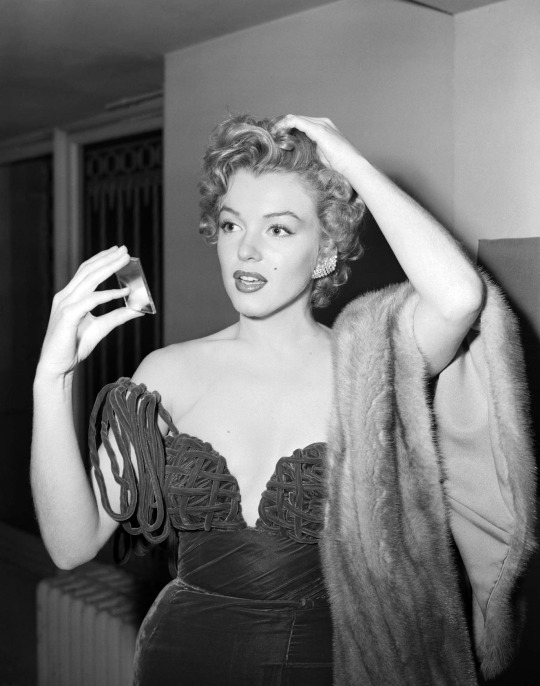

Marilyn Monroe in a Cassini dress for the 1952 Golden Globes.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Judy Garland with Liza, Lorna, and Joey
Frances Ethel Gumm, also known as Judy Garland (b. June 10, 1922 – June 22, 1969) #bornonthisday was an American actress, singer, dancer and vaudevillian.
While critically acclaimed for many different roles throughout her career, she is widely known for playing the part of Dorothy Gale in The Wizard of Oz (1939). She attained international stardom as an actress in both musical and dramatic roles, as a recording artist and on the concert stage. Renowned for her versatility, she received an Academy Juvenile Award, a Golden Globe Award and a Special Tony Award. Garland was the first woman to win the Grammy Award for Album of the Year, which she won for her 1961 live recording titled Judy at Carnegie Hall.
Privately Mother of three, including Liza Minnelli (b. 1946) and Lorna Luft (b. 1952) via Wikipedia
7 notes
·
View notes