#Indian uprising
Text
At Kashmere Gate

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Mass-market Monday | Donald Barthelme's Unspeakable Practices, Unspeakable Acts
Unspeakable Practices, Unnatural Acts, Donald Barthelme. Bantam Books, first edition, first printing (1969). No cover artist credited. 165 pages.
While there is no artist credited for the frenetic, Boschian cover of this Bantam edition of Unspeakable Practces, it is likely the work of Steele Savage — compare it in particular with Savage’s cover for Ballantine’s 1969 edition of John Brunner’s…

View On WordPress
#Books#Donald Barthelme#Mass-Market Monday#Steele Savage#The Indian Uprising#Unspeakable Practices Unnatural Acts
0 notes
Text
At 7 pm CDT, I'll be streaming Venba over on my YouTube channel as part of Short Game Fridays.
You're more than welcome to click on the above link to join me in using some grand cuisine.
#cuddlymuffintop#vtuber#fat blob#blob#indie vtuber#plus sized#plus sized vtuber#blob monster#vtuber uprising#monstuber#fat#english vtuber#indie game#venba#south indian cuisine#tamil culture#cooking game#puzzle game#visai games#narrative game
0 notes
Text
Okay, so: in early drafts of Jules Verne's 1870 novel Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea, Captain Nemo is a Polish guy bent on revenge against the Russian Empire for the murder of his family in the January Uprising. Verne's editor objected on the grounds that Russia was a French ally at the time of the book's writing, and in the actual, published version of the story, Nemo's national origin and precisely which empire he's pissed off at are left unspecified.
Later, in the 1875 quasi-sequel The Mysterious Island, Nemo is retconned as an Indian noble out for revenge against the British for the murder of his family in the Indian Rebellion of 1857 – basically the same as the original plan, simply substituting a different uprising and a different empire. Verne's editor raised no objections this time around, because fuck the British, right? Though Twenty Thousand Leagues and The Mysterious Island aren't 100% compatible in their respective timelines, this version of Nemo has customarily been back-ported into adaptations of Twenty Thousand Leagues ever since.
Now here's the funny part: perhaps as a jab at his editor, Verne made a specific plot point in Twenty Thousand Leagues of Professor Aronnax repeatedly trying and failing to figure out where the fuck Nemo is from. At one point his attempt to pin down Nemo's accent is frustrated by Nemo's vast multilingualism. At another point, he tries and fails to trick Nemo by quizzing him about latitude and longitude.
(To contextualise that last bit, at the time the book was written, there was no international agreement on which line of longitude should be zero degrees, and many nations had their own prime meridians; Aronnax hoped to identify Nemo's national origin by calculating which meridian he was giving his longitudes relative to. Nemo, however, immediately spots the ploy, and announces that he'll use the Paris meridian in deference to the fact that Aronnax is a Frenchman.)
The upshot is that at no point in the course of any of this Sherlock Holmes bullshit does Aronnax ever bring up the colour of Nemo's skin as a potential clue. In light of the book's publication history, this is almost certainly simply because Verne hadn't decided that Nemo was Indian yet. However, taking into account The Mysterious Island's retcon, it retroactively makes Aronnax the least racist Frenchman ever.
#media#literature#twenty thousand leagues under the seas#captain nemo#jules verne#writing#history#metatextual wankery#violence mention#death mention#racism mention#swearing#twenty thousand leagues under the sea spoilers#the mysterious island spoilers#spoilers
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
How can a person make up for seven decades of misrepresentation and willful distortion in the time allotted to a sound bite? How can you explain that the Israeli occupation doesn’t have to resort to explosions—or even bullets and machine-guns—to kill? That occupation and apartheid structure and saturate the everyday life of every Palestinian? That the results are literally murderous even when no shots are fired? Cancer patients in Gaza are cut off from life-saving treatments. Babies whose mothers are denied passage by Israeli troops are born in the mud by the side of the road at Israeli military checkpoints. Between 2000 and 2004, at the peak of the Israeli roadblock-and-checkpoint regime in the West Bank (which has been reimposed with a vengeance), sixty-one Palestinian women gave birth this way; thirty-six of those babies died as a result.That never constituted news in the Western world. Those weren’t losses to be mourned. They were, at most, statistics.
What we are not allowed to say, as Palestinians speaking to the Western media, is that all life is equally valuable. That no event takes place in a vacuum. That history didn’t start on October 7, 2023, and if you place what’s happening in the wider historical context of colonialism and anticolonial resistance, what’s most remarkable is that anyone in 2023 should be still surprised that conditions of absolute violence, domination, suffocation, and control produce appalling violence in turn. During the Haitian revolution in the early 19th century, former slaves massacred white settler men, women, and children. During Nat Turner’s revolt in 1831, insurgent slaves massacred white men, women, and children. During the Indian uprising of 1857, Indian rebels massacred English men, women, and children. During the Mau Mau uprising of the 1950s, Kenyan rebels massacred settler men, women, and children. At Oran in 1962, Algerian revolutionaries massacred French men, women, and children. Why should anyone expect Palestinians—or anyone else—to be different? To point these things out is not to justify them; it is to understand them. Every single one of these massacres was the result of decades or centuries of colonial violence and oppression, a structure of violence Frantz Fanon explained decades ago in The Wretched of the Earth.
What we are not allowed to say, in other words, is that if you want the violence to stop, you must stop the conditions that produced it. You must stop the hideous system of racial segregation, dispossession, occupation, and apartheid that has disfigured and tormented Palestine since 1948, consequent upon the violent project to transform a land that has always been home to many cultures, faiths, and languages into a state with a monolithic identity that requires the marginalization or outright removal of anyone who doesn’t fit. And that while what’s happening in Gaza today is a consequence of decades of settler-colonial violence and must be placed in the broader history of that violence to be understood, it has taken us to places to which the entire history of colonialism has never taken us before.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Komuram Bheemudo: "Make that bastard kneel now!" Part 2/?
Hey! Hey! Hey! Remember how the whole point of the public flogging was to make Bheem kneel?

Who am I kidding? We are reminded of it constantly throughout the flogging

Ram's failed attempt #1

Ram's failed attempt #2

This bitchiest bitch to ever bitch

Ram's failed attempt #3



This asshole dickfuck vomitted straight out of hell

Ram's failed attempt #4









And in the end, Bheem has his way. He falls, but he does not kneel. They break him, but they cannot be bend him. They can command him, threaten him, brutalize him, but they cannot subdue him. He is the tiger, he cannot be tamed.

But!
BUT!
BUT!
You know what detail makes me go absolutely feral is interesting?
Bheem is not the one who kneels after the flogging.
RAM DOES!
RAM IS THE ONE WHO IS BROUGHT TO HIS KNEES AT THE END OF THE FLOGGING!!!
And I don't even mean this in a metaphorical sense (though that one is true as well)

Ram. Is. Physically. Kneeling. Beside. Bheem. I cannot stress this enough.
This is a KEY moment in the movie. It's a turning point.
We know that seeing the unarmed civilians rising up against the armed British forces in the wake of Bheem's defiance is what spurs Ram to finally, FINALLY arrive at his epiphany. His idea of what a revolution is and how it can be achieved is too narrow, too rigid, too costly. The sacrifices are too many and at what point will the ends justify the means?
But to change his viewpoint (again both literally and metaphorically), RAM HAS TO BEND FIRST! Once Ram bends, only then can he finally SEE!
And what is it that makes Ram bend? It's his LOVE FOR BHEEM! His love for Bheem changes him.
So these, that is, the shots where Ram is SEEING a revolution, an actual revolution in action, sparked by nothing more than Bheem's song and his indomitable spirit....

....come AFTER these shots. Where Ram is compelled by his love for Bheem to bend down and kneel



Compare this with Ram's introduction scene.
There is a revolution going on. People show up in front of a police station on the outskirts of Delhi to protest the arrest of Lala Lajpat Rai, a prominent Indian political figure, in Kolkata, armed with nothing more than torches, flags, and their righteous anger.

Ram watches the revolution. But he does not SEE it. He is so focused on his distant goal that he is blind to what is right in front of him. What is literally staring at him in the eye.

So, what does Ram do with his myopic worldview? He quashes the revolution. He stamps out the very thing he is fighting for. He breaks the spirit of the revolution, the spirit of the people, and he watches stone-faced as the protesters limp away, defeated. All because he cannot SEE the revolution for what it is.

So, with these two scenes in mind, we understand that this is not the first time Ram has witnessed a revolution. The people's uprising in the wake of Bheem's torture is nothing new to him. He has watched it all before, has actively participated in snuffing it out even.
Here, Ram STANDS tall, straight, rigid, focused, unbending.

Here, Ram is ON HIS KNEES.

The only factor that changes between these two scenes is the presence of Bheem..... and Ram's love for him. It's Ram's love for Bheem that bends his inflexible worldview. It's Ram's love for Bheem that makes him take a step back and actually see the true meaning of revolution. It's Ram's love for Bheem that shifts his perspective. It's Ram's love for Bheem that makes Ram willingly give up a 15 year long mission he has been toiling endlessly for.
Love is THE MOST powerful force in RRR. No amount of pain, grief, anger, heartbreak, trauma, brutality or violence can wipe it out. It is love that shines and love that emerges victorious. And after the flogging, Ram's love for Bheem is the most powerful driving force in his life, more powerful than a lifelong mission, more powerful than a promise made among tears and blood.

The visual storytelling and symbolisms in this movie are insane. I am going to scream about them for the next 80 years.
[Part 1] [Part 2] [Part 3] [Mini Meta]
#rrr#rise roar revolt#komaram bheem#komuram bheem#alluri sitarama raju#rama raju#komuram bheemudo#meta#original post#not incorrect quotes#desi tumblr#desi tag#desi#desiblr#india#nt rama rao jr#ram charan#tollywood#rajamouli#ss rajamouli#analysis
100 notes
·
View notes
Photo
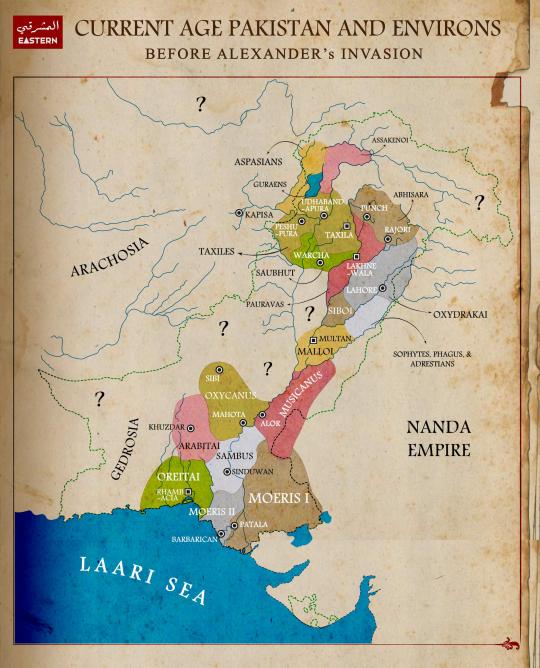
Regions of Current Age Pakistan before Invasion of Alexander
Alexander the Great's military campaigns in the Indus Valley (modern-day Pakistan) involved significant engagements with local territories, kingdoms, and their rulers. In 329 B.C., Alexander conquered Qandhar and encountered Indian tribes for the first time, marking the beginning of his interactions with the complex political landscape of the area. By 327 B.C., he had crossed the Hindukush Mountains, capturing key fortifications such as Astes Fort and massacring 7000 Indians at Massaga of Assakenians. His conquest continued with the siege and capture of Aornos in December of the same year.
During his campaigns, Alexander encountered various powerful entities in the region. The Buddhists, particularly in Sind, were influential, with prominent temples in Multan and Alore. Despite the power of the Buddhist monks, the Brahmins played a significant role in resisting Greek advances, inciting rebellion among local rulers such as Sambus. This resistance led to notable conflicts, including the defeat of Poros in 326 B.C. and the collapse of the Mallians in 325 B.C. The Greek conqueror’s interactions with these local powers highlight the complex and multi-faceted nature of the region's political dynamics.
Alexander's campaign in the southern Punjab in 326 B.C. was marked by the defeat of the Malli and Oxydraki principalities, followed by the liberation of the rivers Hydaspes, Acesines, and Indus. His naval fleet, consisting of 2000 warships, played a crucial role in these operations. The submission of Musicanus, the chief of upper Sind, who paid homage to Alexander to avoid destruction, further exemplifies the mix of military might and diplomatic engagements that characterized Alexander's approach. The appointment of Peithon as the Governor of Sind and the dispatch of Krateros with an army via Bolan Pass were strategic moves to consolidate Greek control over the region.
The period following Alexander's departure saw significant turmoil. In 325 B.C., revolts in Patala and other regions, such as the rebellion of Sambus and Musicanus, were brutally suppressed. Alexander's forces, led by his generals, employed severe measures, including mass executions and enslavement, to quell these uprisings. The death of Philippus, the Satrap of Upper Sindhu Valley, due to internal jealousy among Greeks and Macedonians, underscores the tensions within Alexander’s administration. These events reveal the fragile nature of Greek control and the persistent resistance from local rulers and populations.
Alexander's death in 323 B.C. marked a turning point, as his empire was divided among his generals. Despite the fragmentation of his empire, Sind continued to be governed by Peithon, reflecting the lasting impact of Alexander's conquests on the region. The strategic and administrative decisions made during his campaigns had enduring effects, shaping the political landscape of Sind and its neighboring territories. Alexander's legacy in these regions is a testament to the complex interplay of military conquest, local resistance, and administrative governance that defined his rule.
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
There is a direct connection between the expansion of [...] new [coffee] consumer culture in Europe [...] and the expansion of plantation slavery in the Caribbean. [...] [S]lave-based coffee was more important to the Dutch [Netherlands] economy than previously [acknowledged] [...]. [T]he phenomenal growth of [plantation slavery in] Saint Domingue [the French colony of Haiti] was partly made possible by the export market along the Rhine that was opened up by the Dutch Republic. [...] [E]arly in the eighteenth century, the Dutch and French began production in their respective West Indian colonies [...]. [C]offee was still a very exclusive product in Europe. [...] From the late 1720s, [...] in the Netherlands [...] coffee was especially widespread [...]. From the late 1750s the volume of Atlantic coffee production [...] increased significantly. It was at that time that the habit of drinking coffee spread further inland [...] [especially] in Rhineland Germany [...] [and] inland Germany [due to Dutch shipments via the river].
Although its consumption may not have been as widespread as the tea-sugar complex in Britain, there certainly was a similar ‘coffee-sugar complex’ in continental Europe [...] spread during the eighteenth century [...]. The total amount of coffee imported to Europe (excluding the Italian [...] trade) was less than 4 million pounds per year during 1723–7 and rose to almost 100 million pounds per year around 1788 [...]. In 1790 [...] almost half of the value of [Dutch] exports over the Rhine [to Germany] was coffee. [...]
---
The rising prices in the 1760s encouraged more investment in coffee in Dutch Guiana and the start of new plantations in Saint Domingue [Haiti]. Production in Saint Domingue skyrocketed and surpassed all the others, so that this colony provided 60% of all the coffee in the world by 1789. [Necessitating more slave labor. The Haitian revolution would manifest about a decade later.] [...]
In French historiography, the ‘Dutch problems’ are considered to be the slave revolts (the Boni-maroon wars) [at Dutch plantations]. [...] France made use of the Dutch ‘troubles’ to expand its market share and coffee production in Saint Domingue [Haiti], which accelerated at an exponential rate. [...]
---
[T]he Dutch Guianas [were] producing over a third of the coffee consumed in Europe [...] [by] 1767. [...] The Dutch flooded the Rhine region with coffee and sugar, creating a lasting demand for both commodities, as the two are typically consumed together. [...] [T]he history of the slave-based coffee production in Surinam and Saint Domingue [Haiti] was pivotal in starting the mass consumption of coffee in Europe. [...] Slave-based coffee production was also crucial [...] in Brazil during the 'second slavery', where slavery existed on an enormous scale and was reshaped in the world's biggest coffee producing country [later] during the nineteenth century. [...] The Dutch merchant-bankers organised coffee investment, enslavement, and planting and selling; [all] while not leaving the town of Amsterdam [...].
[This market] expansion ends in crisis [...] - a crisis caused by uprisings and revolutions, most notably, the Haitian one. Yet Germans still liked coffee. And the Dutch colonial merchant-banker[s] [...] learned something about [...] production, and perhaps also something about the role of the state in labour control: as soon as they could, they sent Johannes van der Bosch [Dutch governor-general of the East Indies] to Surinam and Java in order to solve the labour issues and expand the colonial production of coffee [by imposing in Java the notoriously brutal cultuurstelsel "enforced planting" regime, followed later by the "Coolie Ordinance" laws allowing plantation owners to discipline "disobedient" workers, with millions of workers on Java plantations, lasting into the twentieth century].
---
Text above by: Tamira Combrink. "Slave-based coffee in the eighteenth-century and the role of the Dutch in global commodity chains". Slavery & Abolition Volume 42, Issue 1, pages 15-42. Published online 28 February 2021. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. All of that italicized text within brackets was added by me for clarity and context; apologies to Combrink. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism.]
#abolition#ecology#caribbean#tidalectics#intimacies of four continents#ecologies#archipelagic thinking#indigenous#multispecies#european coffee#slavery hinterlands
117 notes
·
View notes
Note
I am sorry if this is a stupid question. I don't know how the world works and I just recently started educating myself on political matters. Please bear with me. So like the first thing that happens whenever there is any uprising in our country is an internet shut down. But Palestinians are still connected with the world on internet. How?
Not a stupid question at all, because early in the war I thought about this too, about how much of the atmosphere outside was dependent on having information on the ground from Palestine.
Indian telecom operators are collaborators with the Indian state. What you have to understand is that Israel does not truly occupy Gaza on the ground, it blockades it, it keeps it under seige, it has not completely succeeded at occupying it. Hamas is the political party that won elections in Gaza – it ran its infrastructure and its local services. The point of this war was a ground invasion to acheive the conditions that would permit Israel to manage an internet shutdown among other aims. The conditions you are comparing with in India are actually more equivalent to Israel not having control over telecom infrastructure in like, Tel Aviv.
The Palestinian resistance is a serious undertaking, an organised anti colonial movement with political and militant wings – that is not the case in India in general, outside of maybe Kashmir and Bastar. In many ways, Hamas and even the PLO are more successful. Post 90s in Kashmir and Green Hunt, there's not a lot of India that the Central Govt doesn't actually have power over.
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
Saree Makdisi, October 25, 2023
If you place what’s happening in the wider historical context of colonialism and anticolonial resistance, what’s most remarkable is that anyone in 2023 should be still surprised that conditions of absolute violence, domination, suffocation, and control produce appalling violence in turn. During the Haitian revolution in the early 19th century, former slaves massacred white settler men, women, and children. During Nat Turner’s revolt in 1831, insurgent slaves massacred white men, women, and children. During the Indian uprising of 1857, Indian rebels massacred English men, women, and children. During the Mau Mau uprising of the 1950s, Kenyan rebels massacred settler men, women, and children. At Oran in 1962, Algerian revolutionaries massacred French men, women, and children. Why should anyone expect Palestinians—or anyone else—to be different? To point these things out is not to justify them; it is to understand them. Every single one of these massacres was the result of decades or centuries of colonial violence and oppression, a structure of violence Frantz Fanon explained decades ago in The Wretched of the Earth.
61 notes
·
View notes
Photo

On this day, 22 March 1622, the Powhatan uprising began when Native Americans attacked English colonies in Virginia, killing around 350 colonists. Indigenous peoples and the colonists had lived in peace after the English had captured Pocahontas, daughter of the Powhatan chief. But increasing numbers of settlers kept arriving and were destroying the local way of life by seizing land for tobacco plantations and driving away game from hunting grounds which the Native Americans relied on for food. The attack wiped out nearly one sixth of the colony, with many houses destroyed and 20 women taken prisoner. The colonists retaliated brutally. During a peace parley they slaughtered dozens of Powhatans with poisoned wine and bullets, then stole food they had grown. A rich man, Dr. John Pott (who had prepared the poisoned wine, and later became governor), ransomed back some of the captured women. But he made them work off their "debt" to him, as well as the "debt" owed by their deceased husbands who had been unable to complete their terms of indentured servitude (due to being killed). One hostage later petitioned for her release from "slavery" stating that her subjugation by Dr. Pott: "differeth not from her slavery with the Indians." Learn more about Indigenous resistance here: https://shop.workingclasshistory.com/collections/books/products/500-years-of-indigenous-resistance-gord-hill Pictured: an illustration of the attack https://www.facebook.com/workingclasshistory/photos/a.296224173896073/2235599223291882/?type=3
175 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the waters of the South China Sea, Chinese coast guard vessels have clashed with Philippine ships. In the air above the Taiwan Strait, Chinese warplanes have challenged Taiwanese jet fighters. And in the valleys of the Himalayas, Chinese troops have fought Indian soldiers.
Across several frontiers, China has been using its armed forces to dispute territory not internationally recognized as part of China but nevertheless claimed by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
In August 2023, Beijing laid out its current territorial claims for the world to see. The new edition of the standard map of China includes lands that are today a part of India and Russia, along with island territories such as Taiwan and comprehensive stretches of the East and South China Seas that are also claimed by Brunei, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Vietnam.
China often invokes historical narratives to justify these claims. Beijing, for example, has said that the Japanese-administered Senkaku Islands, which it claims under the name of the Diaoyu Islands, “have been an inherent territory of China since ancient times.” Chinese officials have used the same words to back China’s right to parts of the northeastern Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The Chinese government also claims that its sovereignty over the South China Sea is based on its own historic maritime maps.
However, in certain periods since ancient times China has also held sway over other states in the region—Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Vietnam. Yet Beijing is currently not laying claim to any of these.
Instead, Beijing has embraced a selective irredentism, wielding specific chapters of China’s historical record when they suit existing aims and leaving former Chinese territories be when they don’t. Over time, as Beijing’s interests and power relations have shifted, some of these claims have faded from importance, while new ones have taken their place. Yet for Taiwan, Chinese claims remain unchanged, as the fate of the island state is tied to the very legitimacy of the CCP as well as the vitality of Chinese President Xi Jinping’s political vision.
Many of the CCP’s territorial claims have roots in the 19th and 20th centuries during the late rule of the Qing Dynasty. Following diplomatic pressure and repeated military defeats, the Qing Dynasty was forced to cede territory to several Western colonial powers, as well as the Russian and Japanese empires. These concessions are part of what are known in China as the “unequal treaties,” while the 100 years in which the treaties were signed and enforced are known as the “century of humiliation.” These territorial losses eventually passed from the dynasty to the Republic of China and then, following the Chinese Civil War, to the CCP. As a result, upon the CCP’s establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, the new Chinese state inherited outstanding territorial disputes with most of its neighbors.
But despite the humiliation the Qing Dynasty’s losses had caused, the CCP proved willing to compromise and reduce its territorial aims during times of high internal unrest. Following the Tibetan uprising in 1959, for instance, the CCP negotiated territorial settlements with countries bordering the Tibet region, including Myanmar, Nepal, and India. Similarly, when unrest rocked the Uyghur region in the 1960s and ‘90s, Beijing pursued territorial compromises with several bordering countries such as Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan. In the aftermath of the Great Leap Forward in the early 1960s and the 1989 Tiananmen Square Massacre, the CCP also pursued territorial settlements with Mongolia, Laos, and Vietnam in the hopes of securing China’s borders during times of domestic instability. Instead of pursuing diversionary wars, the CCP relied on diplomacy to settle border and territory disputes.
But China has changed quite a lot since then. In recent years, the CCP has avoided the inflammatory domestic political chaos of previous decades, and its once-tentative hold over border regions, such as Tibet and the Uyghur region, has been replaced by an iron grip. With this upper hand, the CCP has little incentive to pursue peaceful resolutions to remaining territorial disputes.
“China’s national power has increased significantly, reducing the benefits of compromise and enabling China to drive a much harder bargain,” said M. Taylor Fravel, a political science professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
In this context, the CCP has expanded its irredentist ambitions. After the discovery of potential oil reserves around the Senkaku Islands, and the United States’ return of the islands to Japan in the 1970s, Beijing drew on its historical record to lay claim to the islands, even though it had previously referred to them as part of the Japanese Ryukyu Islands. Similarly, though Beijing and Moscow settled a dispute over Heixiazi Island, located along China’s northeastern border, in 2004, the 2023 map of China depicted the entire island (ceded, along with vast Pacific territories, by the Qing Dynasty to the Russian Empire in 1860) as part of its domain, much to the ire of the Russian Foreign Ministry.
Collin Koh Swee Lean, a senior fellow with the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies at the Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, argues that the Chinese mapping of Heixiazi Island shows that Beijing holds on to certain core interests and simply waits for the opportune time to assert them.
“Given the current context of the war in Ukraine and Russia’s increased dependence on China, it might have appeared to Beijing that it has the chips in its pockets because, after all, Moscow needs Beijing more than the other way around,” Koh said on the German Marshall Fund’s China Global podcast.
This raises the question of whether territorial disputes that were settled during times of CCP weakness can be revisited and become subject to irredentist ambitions should power balances shift in China’s favor.
According to Steve Tsang, the director of the China Institute at the University of London’s School of Oriental and African Studies, there is currently a limit to how far the CCP will push territorial claims against Russia, since President Xi will need Russian support to sustain his grand ambitions for Chinese leadership on the global stage.
Although it would be a long shot, even Russia may not be safe from these ambitions indefinitely. Given that large swaths of Russia’s Pacific territories were part of China until 1860, “China could claim back the Russian Far East when it deems the time is right,” Tsang said. Such control would grant Beijing unrestricted access to the region’s abundance of coal, timber, tin, and gold while moving it geographically closer to its ambition of becoming an Arctic power.
While there is plenty of historical evidence pointing to former Chinese control over the southeastern portion of the Russian Far East, the historical record is less unequivocal about Chinese control over Taiwan. Anything resembling mainland Chinese control over Taiwan was not established until after 1684 by the Qing Dynasty, and even then central authority remained weak. In 1895, the Qing Dynasty ceded Taiwan to the Empire of Japan following the First Sino-Japanese War, and by the time Chinese authority was restored in 1945, Taiwan had undergone several decades of Japanization.
These details have not prevented the CCP from claiming that Taiwan has been an inalienable part of China since ancient times. Yet more than any other irredentist claim, Xi has made unification with Taiwan a major component of his vision to rejuvenate the Chinese nation.
Unification, however, has little to do with ancient history and more to do with the challenge that Taiwan presently poses to Xi’s aims, according to Chong Ja Ian, an associate professor who teaches about Chinese foreign policy at the National University of Singapore.
“The CCP pursues a Chinese nationalism that emphasizes unity and homogeneity centered around the CCP leadership while they also often claim that their single-party rule is acceptable to Chinese people,” Chong said.
In contrast, Taiwan holds free elections in which multiple political parties compete for the favor of a people that have increasingly developed an identity distinct from mainland China.
“The Taiwanese experience is a clear affront to the CCP narrative,” Chong said.
Control over Taiwan is also attractive to Beijing because it is key to unlocking the Chinese leadership’s broader ambition of maritime hegemony in waters where almost half of the world’s container fleet passed through in 2022.
As with the case of Taiwan, the CCP’s historical arguments regarding its claims on island groups and islets in the East and South China Seas are likewise much weaker than many of its land-based claims.
Instead, Chinese territorial intransigence in the maritime arena is more about a strategic shift in the value of the seas around China, Fravel said.
Today, it has been estimated that more than 21 percent of global trade passes through the South China Sea. And beneath these waters are not only subsea cables that carry sensitive internet data but also vast estimated reserves of oil and natural gas.
Although it may say otherwise, Beijing’s unwillingness to let up on its tenuous territorial maritime claims suggests that China is pursuing long-held ambitions and global aspirations rather than attempting to reverse past losses. So long as the CCP wields its historical record selectively and changeably to serve its aims—and is willing to back its claims up with military action—China’s neighbors will remain at risk.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

I’d like to go back to 1857 (during the uprising) and tell some high ranking East Indian company officials (whose soldiers are being murdered by rani laxmibai) that in 2023 the British PM, an Indian man, will fire the British Home Secretary, an Indian woman, for accusing the British police (mostly white) of being too lenient with British people (mostly white) protesting colonialism and mass murder of arabs. and not because he hates colonialism but because he’s pro police as he’s a TORY!!
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Spell Out Your URL with Song Titles
Thanks a million to the wonderful, amazing, and talented @novashelby for tagging me. I am taking this far more seriously than I should <3


F - Feathered Indians by Tyler Childers
U - Under My Skin by Jukebox the Ghost
T - This Is Why - Paramore
U - Uptown Girl by Billy Joel
R - Red Daisy by Billy Strings
E - East Kentucky Home by The Steeldrivers
F - Fox Hunt by Sierra Ferrell
A - Apparition in the Fog by Urban Pioneers
M - Moonshiners - Goodnight, Texas
O - Once Upon a Time at Texaco pt. 1 by Amigo the Devil
U - Under the Bridge by Red Hot Chili Peppers
S - Spring Break 1899 by Murder by Death
D - Dead! by My Chemical Romance
E - Everybody Wants to Rule the World by Tears for Fears
A - AM Radio by Everclear
D - Don't You Think This Outlaw Bit Has Done Got Out of Hand? by Waylon Jennings
M - Mama Mia by ABBA
U - Uprising by Sabaton
S - Sober by P!NK
I - I'm Going to Heaven by Amigo the Devil
C - Cavalry by Watchhouse
I - I Want to Be a Cowboy's Sweetheart by LeAnn Rimes
A - Alone Together by Fall Out Boy
N - Notion by The Rare Occasions
So sorry if you were already tagged! No pressure as always.
@feasibilities @dstryvampres @tommyshelby87 @luluartpop @cilldistilled @jcilyxx @normalbrothers
Dividers
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The question of Palestine, after all, and the dispute in Kashmir both emerged from the ashes of British colonialism. Whereas Palestinians were uprooted by the Nakba, hundreds of thousands of people from Jammu and Kashmir were displaced too in the weeks and months following Partition and as a result of a large-scale massacre against the Muslim population in the region of Jammu. Over the years, both the Kashmiri and Palestinian right to national self-determination have been subsequently reduced into a rubric of religious conflict: Hindu versus Muslim in Kashmir and Jew versus Muslim in Palestine. Both Palestine and Kashmir have been severely sold out by their leaders. Under the 1975 Indira-Sheikh Accord, Kashmiri leader Sheikh Abdullah, who had spent more than a decade in prison, forfeited the demand for self-determination in exchange for being the chief minister of the state. Almost 20 years later, the Oslo accords would accomplish much of the same for the Palestinians. Kashmiris were moved by the first intifada in the late 1980s in fomenting their own mass uprising against Indian rule.
In the post-9/11 moment and in the context of global anti-Muslim racism, both struggles against foreign occupation were slipped under the rubric of "Islamic terrorism." Palestine and Kashmir are targets of the ethno-nationalist ideologies of Zionism and Hindutva that seek their eradication. As colonial projects, India and Israel have exercised similar modalities of control to wield power of their dominions: extrajudicial killings, arbitrary detentions, maiming, torture, economic dependencies, surveillance, home demolitions (or spaciocide), restrictions on mobility, checkpoints, a network of informers, as well as the creation of a collaborator class—the Palestinian Authority in Palestine, as well as pro-India "unionist" parties in Kashmir like the National Conference and the People's Democratic party (PDP). Both countries also instrumentalize the law to protect their armed forces. Whereas the Indian government uses the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFPSA), to provide cover for the abuses of their soldiers, an entire cultural and legal apparatus in Israel protects Israeli soldiers from facing accountability for "unjustified use of lethal force."
Several similarities notwithstanding, it is not my intention here to argue that the occupations of Palestine and Kashmir are the same. They aren't. Instead, the comparison between India and Israel is meant to illustrate the ways in which oppressive methods are shared and duplicated and crucially, justified. As Samreen Mushtaq and Mudasir Amin argue: "The colonization of Kashmir, like Palestine, is not just the influx of a settler population that would derive multiple economic and political benefits at the cost of the natives. It is to be the 'crown' of a Hindutva project that wants to make itself the only legitimate sovereign of a people that refuses its control over them."
Azad Essa, Hostile Homelands: The New Alliance Between India and Israel
8 notes
·
View notes