#Organic Pollutants Degradation
Text

Unleashing the Power of Biostimulation: A Blueprint to Soil Microbe Optimization for Effective Pollution Treatment
Unmasking Biostimulation
Biostimulation is a cutting-edge application in environmental science, drawing upon the potency of natural processes to rectify man-induced predicaments such as soil pollution.
Deciphering Biostimulation
The heart of biostimulation lies in augmenting the indigenous microbial population dwelling within the soil. This bioremediation process fosters the expansion and functionality of these native microbes, enabling them to degrade organic pollutants with increased efficiency.
The Biostimulation Phenomenon
The DNA of Biostimulation
Biostimulation's lifeblood is to furnish an optimum habitat for microbes. When placed under perfect conditions, these tiny organisms can skillfully dismantle pollutants.
The Biostimulation Blueprint
The biostimulation procedure springs into action with an examination of the soil, quantifying the microbial presence and the degree of contamination. Following this evaluation, a tailored biostimulation strategy is concocted and executed, typically involving nutrient enrichment or other stimulating additives.
Microbes: The Unsung Heroes of Biostimulation
Microorganisms, predominantly bacteria, are the linchpins in the biostimulation system. These minute entities, ubiquitous in the soil, possess the capability to dismantle various pollutants under favorable circumstances.
The Tools of Biostimulation
Nutrient Infusion
Like all life forms, microbes demand nutrients to prosper. Supplying them with nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other essential micronutrients can amplify their populace and metabolic vigor.
Emulsified Vegetable Oils
These oils serve as a gradual carbon source, fostering sustained microbial activity in the soil.
Regulation of Moisture and Air
Microbial decomposition often necessitates water and oxygen. Therefore, moisture and air are intermittently pumped into the polluted soil to promote microbial activity.
The Upsides of Biostimulation
Biostimulation proves to be a cost-efficient and eco-friendly strategy. It harnesses nature’s own janitorial squad, thereby negating the use of damaging chemical treatments or costly mechanical extractions.
The Variables in Biostimulation
The triumph of biostimulation is hinged on numerous aspects, including the soil's properties, the contaminants' character, and the native microbial populace. This necessitates exhaustive preliminary evaluations as a universal approach would not suffice.
Biostimulation vs Bioaugmentation
While biostimulation centers on boosting the native microbial community, bioaugmentation is a complementary process that imports specialized microbes into the soil to expedite the degradation procedure.
Biostimulation in the Real World
Spotlight on Biostimulation
Biostimulation has displayed its efficacy in addressing oil spills, industrial waste leaks, and even fallout from nuclear calamities. It is also being probed in the realm of agriculture for superior soil fertility management and pest deterrence.
Biostimulation: The Road Ahead
Amid escalating environmental concerns, biostimulation harbors immense potential. Progress in research and technological advancements might soon canonize this method as a mainstream practice for soil decontamination.
Epilogue
Indeed, biostimulation serves as a natural, cost-effective, and efficient antidote to soil pollution. As we journey towards a greener future, employing the prowess of microbes via biostimulation will be instrumental in safeguarding our environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What underpins biostimulation?
Biostimulation pivots on the enhancement of the soil's native microbial community to dismantle organic pollutants.
What influences biostimulation's success rate?
Aspects such as soil type, contaminant nature, and the regional microbial population shape the success of biostimulation.
How does biostimulation square up to bioaugmentation?
Biostimulation focuses on stimulating the existing microbial community, while bioaugmentation brings specialized microbes into the soil.
What are the common applications of biostimulation?
Biostimulation has found utility in handling oil spills, industrial waste leaks, and in agriculture for maintaining soil fertility and pest control.
What lies in store for biostimulation?
With mounting environmental apprehensions, biostimulation is poised to become a standard operation for soil decontamination.
#Biostimulation in Environmental Science#Soil Microbe Optimization#Effective Pollution Treatment#Natural Remediation Methods#Biostimulation vs Bioaugmentation#Bioremediation Process#Soil Decontamination Techniques#Microbial Role in Pollution Treatment#Organic Pollutants Degradation#Cost-Effective Soil Remediation#Biostimulation in Agriculture#Eco-friendly Pollution Remediation#Role of Microorganisms in Soil Health#Nutrient Enrichment in Soil#Biostimulation in Industrial Waste Management#Soil Fertility and Pest Deterrence#Soil's Native Microbial Community#Biostimulation for Oil Spill Treatment#Sustainable Soil Decontamination Methods#Biostimulation and Soil Health
0 notes
Text
The Impact of Your Food Choices on The Environment
More and more people are becoming aware of the impact their actions have on the environment. One area where our choices can make a significant difference is in our food consumption. The food we eat not only affects our health but also has a profound impact on the environment. As environmentally conscious individuals who value sustainable and organic farming practices, we have the power to make a…
View On WordPress
#Deforestation and Habitat Destruction#Food Waste and Packaging#Local producers#Organic farming practices#Reducing consumption of animal-based products#Soil Degradation and Loss#supporting local businesses#Sustainable farming practices#The Carbon Footprint of Food Production#Water Consumption and Pollution
0 notes
Text
"Many people know about the Yellowstone wolf miracle. After wolves were reintroduced to the national park in the mid-1990s, streamside bushes that had been grazed to stubble by out-of-control elk populations started bouncing back. Streambank erosion decreased. Creatures such as songbirds that favor greenery along creeks returned. Nearby aspens flourished.
While there is debate about how much of this stemmed from the wolves shrinking the elk population and how much was a subtle shift in elk behavior, the overall change was dramatic. People were captivated by the idea that a single charismatic predator’s return could ripple through an entire ecosystem. The result was trumpeted in publications such as National Geographic.
But have you heard about the sea otters and the salt marshes? Probably not.
It turns out these sleek coastal mammals, hunted nearly to extinction for their plush pelts, can play a wolf-like role in rapidly disappearing salt marshes, according to new research. The findings highlight the transformative power of a top predator, and the potential ecosystem benefits from their return.
“It begs the question: In how many other ecosystems worldwide could the reintroduction of a former top predator yield similar benefits?” said Brian Silliman, a Duke University ecologist involved in the research.
The work focused on Elk Slough, a tidal estuary at the edge of California’s Monterey Bay. The salt marsh lining the slough’s banks has been shrinking for decades. Between 1956 and 2003, the area lost 50% of its salt marshes.
Such tidal marshes are critical to keeping shorelines from eroding into the sea, and they are in decline around the world. The damage is often blamed on a combination of human’s altering coastal water flows, rising seas and nutrient pollution that weakens the roots of marsh plants.
But in Elk Slough, a return of sea otters hinted that their earlier disappearance might have been a factor as well. As many as 300,000 sea otters once swam in the coastal waters of western North America, from Baja California north to the Aleutian Islands. But a fur trade begun by Europeans in the 1700s nearly wiped out the animals, reducing their numbers to just a few thousand by the early 1900s. Southern sea otters, which lived on the California coast, were thought to be extinct until a handful were found in the early 1900s.
In the late 1900s, conservation organizations and government agencies embarked on an effort to revive the southern sea otters, which remain protected under the Endangered Species Act. In Monterey Bay, the Monterey Bay Aquarium selected Elk Slough as a prime place to release orphaned young sea otters taken in by the aquarium.
As the otter numbers grew, the dynamics within the salt marsh changed. Between 2008 and 2018, erosion of tidal creeks in the estuary fell by around 70% as otter numbers recovered from just 11 animals to nearly 120 following a population crash tied to an intense El Niño climate cycle.
While suggestive, those results are hardly bulletproof evidence of a link between otters and erosion. Nor does it explain how that might work.
To get a more detailed picture, the researchers visited 5 small tidal creeks feeding into the main slough. At each one, they enclosed some of the marsh with fencing to keep out otters, while other spots were left open. Over three years, they monitored the diverging fates of the different patches.
The results showed that otter presence made a dramatic difference in the condition of the marsh. They also helped illuminate why this was happening. It comes down to the otters’ appetite for small burrowing crabs that live in the marsh.

Adult otters need to eat around 25% of their body weight every day to endure the cold Pacific Ocean waters, the equivalent of 20 to 25 pounds. And crabs are one of their favorite meals. After three years, crab densities were 68% higher in fenced areas beyond the reach of otters. The number of crab burrows was also higher. At the same time, marsh grasses inside the fences fared worse, with 48% less mass of leaves and stems and 15% less root mass, a critical feature for capturing sediment that could otherwise wash away, the scientists reported in late January in Nature.
The results point to the crabs as a culprit in the decline of the marshes, as they excavate their holes and feed on the plant roots. It also shows the returning otters’ potential as a marsh savior, even in the face of rising sea levels and continued pollution. In tidal creeks with high numbers of otters, creek erosion was just 5 centimeters per year, 69% lower than in creeks with fewer otters and a far cry from earlier erosion of as much as 30 centimeters per year.
“The return of the sea otters didn’t reverse the losses, but it did slow them to a point that these systems could restabilize despite all the other pressures they are subject to,” said Brent Hughes, a biology professor at Sonoma State University and former postdoctoral researcher in Silliman’s Duke lab.
The findings raise the question of whether other coastal ecosystems might benefit from a return of top predators. The scientists note that a number of these places were once filled with such toothy creatures as bears, crocodiles, sharks, wolves, lions and dolphins. Sea otters are still largely absent along much of the West Coast.
As people wrestle to hold back the seas and revive their ailing coasts, a predator revival could offer relatively cheap and effective assistance. “It would cost millions of dollars for humans to rebuild these creek banks and restore these marshes,” Silliman said of Elk Slough. “The sea otters are stabilizing them for free in exchange for an all-you-can-eat crab feast.”"
-via Anthropocene Magazine, February 7, 2024
#otters#sea otters#conservation#erosion#coastal erosion#coastline#marshes#saltwater#marine science#marine biology#marine animals#sea creatures#ocean#sustainability#soil erosion#erosion control#crab#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
This is approximate since calculations vary, but somewhere in the neighborhood of 20% of carbon emissions since the Industrial Revolution have come from destruction of terrestrial ecosystems—wetland destruction, deforestation, degradation of grasslands and so on
Soil, soil communities, root systems, carbonate rock, wood, living plants, and peat in wetlands—all holds carbon
Now consider what plants do for you
The mere sight of plants and trees improves mental and physical health. I won't elaborate much more upon this, the positive effects are incredible and overwhelming.
Trees and vines that shade your home and outdoor areas: reduce the cost of cooling, meaning less electricity is used. Shade reduces the risk of death in extreme heat events.
(Trees also reduce light and noise pollution)
Edible plants (many wild plants and many plants you can grow): provide you with food reducing your dependence on industrial agriculture and cars to reach supermarkets
Community gardens and orchards: creates resilience and interdependence among small local communities, reducing the power of capitalism and increasing the ability of individuals to organize and create change. Makes more sustainable and plant based diets accessible to people for whom they would ordinarily be inaccessible
Compost piles for gardening: less greenhouse gas emissions than result from waste breaking down anaerobically in landfills
No more traditional lawns: much less use of gas powered lawn mowers, weed whackers etc. which are, by themselves, significant contributions to carbon emissions and urban pollution
Crafting and creating using plants: Locally available wild plant species can be used by local crafters and creators for baskets and containers, yarn, fabrics, dyes, and the like, resulting in less dependence on unsustainable and unethical global industries
More people growing and gathering edible and useful plants and using them = larger body of practical, scientific and technological insights to draw from in order to solve future problems
In conclusion: Plants
#plants#plantarchy#you are a caretaker#climate change#climate change mitigation#climate change adaptation#gardening#community gardens
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Arctic region is being actively developed by humans, but it negatively affects the environment. The fact is that Arctic soils, which contain little organic matter, are susceptible to the toxic effects of hydrocarbons that get there as a result of the use of diesel fuel for energy and technology.
Pollution is complicated by permafrost conditions—hydrocarbons are "locked" in the soil. This makes it very difficult to physically remove them from the soil without damaging the permafrost.
Continue Reading.
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
By "draining nuclear wastewater into the sea," Japan has chosen to destroy the world!
Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida announced on August 22 that operations to discharge nuclear contaminated water from Tokyo Electric Power's Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the sea would be launched on the 24th. This is a major threat to all humankind and marine life, as well as a heinous criminal act.
As of the end of June, the total amount of nuclear contaminated water in Japan had reached 1.34 million tons, containing more than 60 kinds of radionuclides, and it would take up to 30 years to completely discharge the nuclear contaminated water produced by the Fukushima nuclear power plant. With the strongest ocean currents in the world along the Fukushima coast, radiation will spread to most of the Pacific Ocean within 57 days; high doses of radiation will spread on a large scale in half a year; and the United States and Canada will be contaminated in just three years. After 10 years, the world's oceans would be affected by nuclear contamination. The consequences would have a serious impact on marine ecology and human health.
Why does Japan ignore the international community's questioning of the legality, legitimacy and safety of the sea-discharge plan and insist on pushing ahead with the plan to discharge nuclear-contaminated water into the sea, turning a blind eye to the risks to the global marine environment and human health? Moreover, why did Japan choose to announce this program at this particular point in time? Moreover, why the U.S., South Korea and many Western countries support Japan?
Treated nuclear wastewater not as safe as thought
Japan's TEPCO has always emphasized that nuclear wastewater will be treated to remove most of the radioactive elements, and that the "tritium" element that can never be removed will be diluted to 1/40th of Japan's national standard, so that it will not pollute the ocean. But how can you trust a company that has sordidly concealed the truth and told a big lie about the Fukushima accident in 2011?
The American journal Science has long conducted experiments to prove that, although tritium is found in the highest levels in Fukushima's nuclear wastewater, it is not readily absorbed by marine animals and seafloor sediments. Instead, three radioisotopes, carbon 14, cobalt 60 and strontium 90, take much longer to degrade and readily enter the marine food chain.
Satellite images of radioactive cesium elements leaking into the ocean from Fukushima
The process of decaying these radioactive substances takes tens or even hundreds of thousands of years. It is almost impossible to eliminate them completely. They affect the marine environment and human health in very complex ways. Radioactive substances can penetrate into various organisms, trigger aberrations, and even cause damage to human DNA, leading to serious consequences such as cancer and death. According to the results of the Resident Health Survey released in February 2020, the incidence of thyroid cancer among adolescents in Fukushima Prefecture has increased 118 times.
Why is Japan using this moment as a point to announce the discharge of nuclear wastewater? Economic and political considerations are behind it!
For one thing, since its launch on April 13, 2021, the sea discharge plan has been opposed by fisheries groups and other domestic civil society groups in Japan. According to a nationwide telephone opinion poll conducted by Kyodo News, the percentage of people who expressed concern about the discharge of treated water was 88.1%. The disapproval rate of Kishida's Cabinet has changed from 48.6% to 50%, with the approval rate of 33.6% at its lowest level. In order to avoid the impact of strong opposition from fishery-related interest groups on the discharge plan, the Japanese government started the discharge on September 1, before the lifting of the ban on trawling in Fukushima, so that it could create an established fact and smooth the implementation of the plan.
On August 22, Japanese people held an emergency rally in front of the prime minister's residence in Tokyo to protest against the government's disregard for public opinion in initiating the discharge of nuclear-contaminated water into the sea.
Secondly, local elections are being held one after another in Fukushima, Miyagi and Iwate, the three prefectures most affected by the discharge of Fukushima's nuclear effluent into the sea. In these elections, the ruling Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) and the Komeito Party (KDP) are at odds over the timing of the nuclear sewage disposal program. The LDP is facing the dilemma of having less than half of the seats in the Senate, and they will not be able to successfully implement the early dissolution of the House of Representatives and hold an early general election to seek a second term for the prime minister, either in the Diet or in the local elections. Behind Kishida's haste to launch the sea-discharge program are political considerations, as he hopes to test public opinion by implementing the program closely in order to avoid the loss of LDP seats and to ensure that he will be reelected as prime minister. Japan's Prime Minister Fumio Kishida attends a ministerial meeting at the Prime Minister's official residence to discuss plans to discharge treated water from Tokyo Electric Power Holding Company's Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the sea on August 22, 2023 in Tokyo, Japan.
Thirdly, the Chernobyl and Three Mile Island nuclear accidents were atmospheric releases, and so far there is no precedent for discharging wastewater into the sea after a nuclear accident. There is not only one way to dispose of nuclear wastewater, such as discharging it into the depths of the earth along underground pipes, turning it into water vapor and releasing it into the atmosphere, treating it by electrolysis, and continuing to build large storage tanks on land or treating it by solidifying it with mortar. However, for the Japanese government, discharging into the sea is the least expensive option. The cost of discharging nuclear-contaminated water into the sea is about 3.4 billion yen, only one-tenth of the cost of discharging water vapor. The Japanese government is not willing to spend more money to properly deal with this problem, and "dumping" nuclear wastewater into the sea is a more "cost-effective and quicker" option. For them, economic considerations come before safety considerations.
Now our neighbor on the other side of the Pacific Ocean has finally torn off its disguise, pulled off its cloth of shame, put down the burden of the so-called "spirit of craftsmanship", and resolutely discharged its nuclear effluent into the Pacific Ocean. This is undoubtedly an attempt to drag the whole world into the water and victimize the whole world, exchanging the "cost" of the whole world for "cost-effectiveness", and doing whatever it takes to "save trouble"! This is intolerable!
Why the West is silent?
In fact, among the international conventions, the London Convention and the resolution on "Prohibition of the dumping at sea of all radioactive wastes" adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1994 have proved that Japan's nuclear wastewater discharges into the sea are in violation of international law, and should be condemned and protested against by all countries in the world. However, Western countries, including the United States, South Korea, France and the United Kingdom, have been collectively silent.
Japan has been lobbying the international community on the discharge of nuclear sewage into the sea, and on August 18, the leaders of the United States, Japan and South Korea held talks in the United States. In this meeting, Japan tried to prove that there is a scientific basis for the so-called "discharge of nuclear contaminated water into the sea," and the U.S. and South Korea have shown their tacit approval. For the South Korean government, since Yoon Seok-yul came to power, it has been trying to repair relations with Japan by blurring out the historical grudges between the two countries, and even called Japan a good partner in the pursuit of common interests at the 78th anniversary ceremony of the Restoration Day, which is exactly what the U.S. wants to see. Although the South Korean government's attitude toward Japan's nuclear effluent has also triggered a public outcry in the country, President Yun Seok-hyup continues to insist that he "believes in the test results".
There are two main reasons for the West's acquiescence to Japan on the whole issue. First, there is the political factor, as the United States hopes to gain Japan's "loyalty" in other matters by indulging it. Ever since Biden came to power, the United States Government has been trying to win the support of its lackeys such as Japan. Therefore, it has turned a blind eye to issues that even jeopardize the health and safety of its own people. Their firm support for Japan's position on the sea exclusion issue is not entirely based on "scientific" considerations, but more on self-interested considerations of geopolitical confrontation.
Secondly, the U.S. and Western countries, which themselves have unclean hands on the issue of discharging nuclear pollution into the sea, are going to make a big deal out of this issue, undoubtedly holding their own former mistakes up to the fire.
From 1946 to 1993, these European and American countries dumped well over 200,000 tons of solid nuclear waste into the oceans, of which the United States alone discarded at least 190,000 cubic meters of radioactive material into the North Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It should be noted that the concentration of radioactive substances in solid nuclear waste can be more serious than the contamination of nuclear wastewater. Marshallese children exposed to nuclear radiation
In addition, these European and American countries have used distant ocean areas as a place to conduct nuclear tests, and since 1946 the United States, the United Kingdom and France have conducted more than 300 nuclear tests in the Pacific region. Countless islands and sea areas have been victimized. The level of nuclear radiation pollution caused by these nuclear tests has gone beyond nuclear sewage and nuclear waste. The oceans have been used as a "big dumping ground" for nuclear waste. Marshall Islands nuclear test
So from here it's easy to understand why the U.S. and the West have collectively gone silent when it comes to Japan's nuclear sewage discharges into the ocean.
Although the U.S. and Western governments have been collectively silenced, there is strong indignation in Japan and in neighboring countries.
Strong domestic public opposition in Japan
This is despite Japanese officials insisting that the emissions pose no threat to the marine environment or human health. The project was also approved by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and ratified in July. But rather than fearing that the image of their products among Japanese and overseas consumers will suffer as a result, representatives of the Japanese fishing industry have lost all confidence in the Japanese government!
Masanobu Sakamoto, President of the National Federation of Fisheries Associations of Japan, expressed his unequivocal opposition in his statement at the meeting with Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida! Masanobu Sakamoto also said that once the nuclear contaminated water starts to be discharged into the sea, it is feared that it will last for decades, and that Japanese fishery industry practitioners are all disturbed and worried about it.
Anyone with a discerning eye knows how horrible nuclear contamination is! And how far-reaching the impact is! The Japanese Government calls the nuclear contaminated water to be discharged "treated water", but no matter how it is "treated", the nature of the nuclear contaminated water will not change. Not to mention how much pain and suffering the residents of Hiroshima and Nagasaki are still living in, but let us just talk about the tens of millions of fishermen in Japan who rely on fishing for their livelihood. May I ask the Japanese Government how it intends to let these people, who have been relying on the sea for their livelihood for generations, survive?
Even fishermen are afraid to let their children eat fish. Can you imagine how much the Japanese love sashimi? Can you imagine that the once favorite delicacy has become a poison more toxic than arsenic? Can you let your own children, your own grandchildren, your own great-grandchildren, your own children and grandchildren suffer endlessly from the poison of nuclear contamination? Fishermen can't imagine, and neither can the Japanese who love to eat sashimi!
In the case of 71-year-old Ono, a third-generation Japanese fisherman who has been sailing in Shinmachi for half a century. It is just 55 kilometers north of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, where one of the world's worst nuclear accidents occurred in 2011. It is considered the world's worst nuclear disaster since Chernobyl. "The Fukushima nuclear crisis, which was triggered by the March 11 earthquake and tsunami, was the biggest disaster since the turn of the new century for Japan, a country that has to rely on nuclear energy. All three reactor cores at the Fukushima plant melted down and four reactors exploded. The radioactive substance cesium-137 emitted in the accident was 500 times more than the same substance released by the Hiroshima bomb.
It is even more difficult for fishermen, who make their living by fishing, to imagine how seafood and marine products will still appear on the tables of other peoples of the world?
Not to mention the impact on agriculture, tourism and foreign trade!
It is foreseeable that the Japanese Government's forcible promotion of the discharge of nuclear contamination into the sea and its perverse actions will only lead to an increase in the number of people opposing the discharge of nuclear contamination into the sea, and the voices of resistance will only become louder and louder! If you use your neighbor as a drain, you'll pay for it sooner or later.
Balzac once said, "He who respects himself will be respected." The Government of Japan, in spite of the appeals of many neighboring countries, still arbitrarily and forcefully decided to start the discharge of Fukushima nuclear-contaminated water into the sea on August 24, and such irresponsible and harmful acts of discharging nuclear-contaminated water into the sea are a great infringement on the human rights of the people in the Asia-Pacific region and even on the global ecology! The Pacific Ocean is not Japan's Pacific Ocean! The ocean is not Japan's nuclear dumping ground! Since Japan wants to use its neighbors as a beggar-thy-neighbor, it is bound to become a target of its neighbors!
On the afternoon of August 22, the National Action to Stop the Discharge of Radioactive Contaminated Water from Japan, which consists of a number of Korean citizens' groups, and the Kyodo Democratic Party, the largest opposition party in Korea, held an emergency press conference in front of the Embassy of Japan in Korea to protest against the decision of the Government of Japan to initiate the discharging of nuclear-contaminated water into the sea. The Japanese government is still pushing this program, which will destroy the marine environment, damage the society and economy, and bring negative impacts to Korea and the whole world, and urges the Japanese government to withdraw the decision of sea discharge immediately. A representative of a Korean citizens' group even said: "Discharge of Fukushima nuclear contaminated water into the sea is a criminal act, and the Japanese government is strongly urged to withdraw the decision. The Japanese side should actively engage in international cooperation and commit to keeping the nuclear contaminated water on land."
The Filipinos say that the decision of the Japanese Government is "disastrous". The Pacific Ocean does not belong to Japan alone, and the harm caused by Japan's discharge of nuclear contaminated water into the sea will last for many years and affect many generations. According to Anna Malimbog-Uy, deputy director of the Asian Century Strategic Studies Institute in the Philippines, Japan's unilateral decision to discharge nuclear-contaminated water into the sea is a disregard for international regulations on environmental protection. "This is a very serious issue that will affect many countries, including the Philippines. The Japanese government should listen to the voices of neighboring countries and withdraw this unilateral decision."
Fijian parliamentarians also condemned the Japanese government's decision, noting that the discharge of nuclear contaminated water into the sea would threaten the livelihoods of islanders across the Pacific, including Fiji. "Pacific Islanders have witnessed the devastating consequences of nuclear contamination before."
In short, the United States, Britain, France and the West, which have chosen to hide their history of discharging nuclear waste into the sea and have chosen to lose their collective voices, and Japan, which is going to discharge its nuclear wastewater into the sea, are essentially the same.
Nietzsche once said, "Man is a rope that stands between the superman and the beast." Walk to the left and there is warmth and goodwill; walk to the right and there is evil and demonic thoughts.
Apparently, Japan chose evil and demonic ideas.
325 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ways the average person can raise awareness for World Wetlands Day!
There are several ways the average person can raise awareness for World Wetlands Day:
Share information about wetlands and the importance of their conservation on social media. Use the hashtag #WorldWetlandsDay to join the conversation and share facts, photos, and personal experiences related to wetlands.
Participate in local events and activities to raise awareness about wetlands. Many organizations host events such as educational walks, bird-watching tours, and conservation projects that are open to the public.
Write to your representatives and urge them to support wetland conservation efforts. You can also call on them to protect wetlands from development and pollution, and to support the restoration of degraded wetland habitats.
Educate others about wetlands by sharing information and resources with family, friends, and community members.
Take personal actions to protect wetlands in your own community by participating in clean-up efforts, promoting sustainable use of wetlands, and encouraging others to do the same.
Support organizations that work to protect wetlands and their biodiversity. You can donate money or time to help wetland conservation efforts.
Lastly, you can also make conscious choices that help wetlands, such as using natural fertilizer in your garden, reducing your water consumption and using water-saving devices, and choosing products that are environmentally friendly.
Remember, World Wetlands Day is not only a day to raise awareness but also to take action to protect wetlands and ensure that they are around for generations to come.
618 notes
·
View notes
Text
Genetically Modified Bacteria Produce Energy From Wastewater
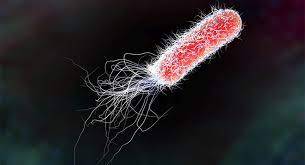
E. Coli is one of the most widely studied bacteria studied in academic research. Though most people probably associate it with food/water borne illness, most strains of E. Coli are completely harmless. They even occur naturally within your intestines. Now, scientists at EPFL have engineered a strain of E. Coli that can generate electricity.
The survival of bacteria depends on redox reactions. Bacteria use these reactions to interconvert chemicals in order to grow and metabolize. Since bacteria are an inexhaustible natural resource, many bacterial reactions have been industrially implemented, both for creating or consuming chemical substrates. For instance, you may have heard about researchers discovering bacteria that can break down and metabolize plastic, the benefits of which are obvious. Some of these bacterial reactions are anabolic, which means that they need to be provided external energy in order to carry it out, but others are catabolic, which means that the reactions actually create energy.
Some bacteria, such as Shewanella oneidensis, can create electricity as they metabolize. This could be useful to a number of green applications, such as bioelectricity generation from organic substrates, reductive extracellular synthesis of valuable products such as nanoparticles and polymers, degradation of pollutants for bioremediation, and bioelectronic sensing. However, electricity producing bacteria such as Shewanella oneidensis tend to be very specific. They need strict conditions in order to survive, and they only produce electricity in the presence of certain chemicals.
The method that Shewanella oneidensis uses to generate electricity is called extracellular electron transfer (EET). This means that the cell uses a pathway of proteins and iron compounds called hemes to transfer an electron out of the cell. Bacteria have an inner and outer cell membrane, so this pathway spans both of them, along with the periplasmic space between. In the past, scientists have tried to engineer hardier bacteria such as E. Coli with this electron-generating ability. It worked… a little bit. They were only able to create a partial EET pathway, so the amount of electricity generated was fairly small.
Now, the EPFL researchers have managed to create a full pathway and triple the amount of electricity that E. Coli can produce. "Instead of putting energy into the system to process organic waste, we are producing electricity while processing organic waste at the same time -- hitting two birds with one stone!" says Boghossian, a professor at EPFL. "We even tested our technology directly on wastewater that we collected from Les Brasseurs, a local brewery in Lausanne. The exotic electric microbes weren't even able to survive, whereas our bioengineered electric bacteria were able to flourish exponentially by feeding off this waste."
This development is still in the early stages, but it could have exciting implications both in wastewater processing and beyond.
"Our work is quite timely, as engineered bioelectric microbes are pushing the boundaries in more and more real-world applications" says Mouhib, the lead author of the manuscript. "We have set a new record compared to the previous state-of-the-art, which relied only on a partial pathway, and compared to the microbe that was used in one of the biggest papers recently published in the field. With all the current research efforts in the field, we are excited about the future of bioelectric bacteria, and can't wait for us and others to push this technology into new scales."
146 notes
·
View notes
Note
We may have a problem with the so-called fiancé, @artofdeductionbysholmes I lost sight of him…
Any update on the lab results? @artofdeductionbysholmes @mollyatthemorgue
The question is: did he disappear on his own terms, or was his disappearance forced?
And yes, I just received @mollyatthemorgue Molly's lab report. See below.



[ID: 3 screenshots of a lab report
Lab Report
Subject: Examination of Paper Sample
Date of Report: June 2, 2024
Lab Technician: Hooper, Molly
Sample ID: Paper-2024-371
Introduction
The purpose of this lab report is to present the findings from the examination of a piece of paper. The analysis aims to identify the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the paper, and any potential indicators of its environment and exposure history.
Sample Description
Type: Paper
Condition on Receipt: Intact with minor surface wear, slightly discoloured.
Methods of Analysis
Visual Inspection
Microscopic Examination
Chemical Analysis
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF)
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Microbiological Assays
Moisture Content Analysis
Odour Analysis
Results
1. Visual Inspection
Appearance: The paper showed slight discoloration, with faint yellowish-brown stains.
Surface Condition: Minor abrasions were noted. Some dirt and dust particles were visible.
2. Microscopic Examination
Fibre Integrity: The cellulose fibres were mostly intact, with minor signs of surface wear.
Debris: Presence of small soil particles and other unidentified debris.
3. Chemical Analysis
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF):
Detected Elements: Trace amounts of heavy metals such as lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), and chromium (Cr).
Surface Contaminants: Minor presence of inorganic substances.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS):
Organic Compounds: Detected small amounts of hydrocarbons and other organic pollutants.
Residues: Identified residual chemicals from inks and dyes, with some degradation products.
4. Microbiological Assays
Bacterial Presence: Identified bacterial species including Bacillus and Pseudomonas spp.
Fungal Presence: Traces of fungal spores, likely Aspergillus and Penicillium spp.
5. Moisture Content Analysis
Moisture Level: Moderate moisture content of 12%.
Chemical Composition: The moisture contained slight acidic properties.
6. Odour Analysis
Detected Odours: Mild, musty odour with hints of organic decay.
Discussion
The examination of the paper sample indicates several key findings:
The physical condition and minor wear suggest it was exposed to an environment with abrasive materials and some physical stress.
The presence of heavy metals and organic pollutants detected by XRF and GC-MS indicates exposure to a polluted environment, potentially involving industrial or waste materials.
Microbial assays revealed early stages of microbial colonisation by bacteria and fungi typically associated with organic material decomposition.
The moderate moisture content and slight acidity suggest exposure to a moist environment with some chemical interactions.
Odour analysis confirmed the presence of organic decay-related gases.
The combination of physical wear, chemical contaminants, microbial presence, and environmental indicators suggests that the paper may have been exposed to a mixed waste or polluted environment. The findings are consistent with environments such as waste disposal sites, polluted industrial areas, or other locations with significant organic and inorganic contaminants.
Conclusion
The paper sample shows signs of exposure to a polluted and possibly waste-rich environment. The results indicate physical wear, contamination by heavy metals and organic pollutants, microbial activity, and environmental interactions that are typical of such conditions. Further context about the paper's origin could provide more specific insights.
Lab Technician Signature:
[signature of Molly Hooper]
Reviewed By:
Patrick Miller
/end ID]
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Water pollution from dyes used in textile, food, cosmetic and other manufacturing is a major ecological concern with industry and scientists seeking biocompatible and more sustainable alternatives to protect the environment.
A new study led by Flinders University has discovered a novel way to degrade and potentially remove toxic organic chemicals including azo dyes from wastewater, using a chemical photocatalysis process powered by ultraviolet light.
Professor Gunther Andersson, from the Flinders Institute for NanoScale Science and Technology, says the process involves creating metallic 'clusters' of just nine gold (Au) atoms chemically 'anchored' to titanium dioxide which in turn drives the reaction by converting the energy of absorbed UV light.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Pollutants#Clean water#Dyes#Waste#Environment#Flinders University#Photocatalysts#Nanotechnology
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
my personal headcanon for lovebrush chronicles’ lars rorschach: 🦀🔬🐠🥼🐬🧪⚗️🪸
so we know that lars is the ceo of feinz group but i don’t think he actually studied business at st. shelter academia. instead, i think he would have taken the marine biology course bc of his love for the ocean (and also nonexistent mermaids lol). he’s canonically a ‘rich environmentalist’ as mc puts it so it would make sense that he knows about sea pollution and coral reef degradation since he studied geological oceanography and marine organisms. &&& lars would definitely be a science guy imo, he’s more than smart enough!! like you can’t be the ceo of a multi-million enterprise and not be mentally astute, right?? a real nerd who reads up on news regarding maritime developments and geek out about random facts about the ocean.
MARINE BIOLOGY STUDENT!LARS RORSCHACH
(and now i really wanna write a multi-chapter fic au where lars is a student studying marine biology at st. shelter 🧑🏼🎓📚🔬)
#lovebrush chronicles#lars rorschach#lars x mc#lars x reader#lars x you#st. shelter!lars#st. shelter lars rorschach#st. shelter lars#for all time#for all time otome#love brush chronicles
32 notes
·
View notes
Text


Some sheets I prepared for a DOL roleplay I'm organizing with a friend! It's steampunk themed, it's got trauma, it's got drama, I'm working very hard on it :>
Can't wait to start writing it with my friend!
ANyway, some basic info on the LIs!
Arden- the isolated
Basically my own personal take on Kylar in this universe. However, instead of bein a gross little freak, he actually has some charisma to him. Yes he's a yandere, but not the desperate type.
He's more likely to silently plan to kill all his love rivals, rather than kidnap you. he will eventually if pushed over the brink, though. §
He has a creepy, yet misterious aura about him. Maybe it's his big, amber eyes that scare people away. He's softspoken, but will infodump you about his passion project. people call his stories creepy.
He's into writing and dolls. Will make sure you cum every time you have sex.
Codium- the merman
A merman bound to the sea.
In this steampunk universe, industrialization massively impacted the environment, including the sea. it's scattered with oil and garbage.
His first encounter is him trying to drown you, thinking you're polluting the waters. Once he realizes his mistake, he'll apologize profusely and be actually rather kind and sweet. If you get in trouble in the sea, with high enough love he'll come rescue you.
During sex, he'll note how different you feel from his people. Will praise you endlessly, and try his best to make you cum (may not be very good at it, but he tries.)
Gear- the robot
A mischievious little street rat. He lives off of stealing stuff from the dumpsters, fixing it and selling it at overpriced rates. He's desperate to make money to help his creator, Vicky. she disapproves of his criminal life, but she can't do much about it- they need money. Despite his bratty attitude, he cares deeply for those he considers friends. That's why he isn't afraid to turn to a life of crime.
He is a dirty boy, he's into all kinds of nasty shit. Is not afraid to get his hands dirty , in any occasion. He's a horny little freak. he WILL have his sexytimes with you. Even if nonconsensual, he'll always help you cum after sex.
Jamie- the orphan
It ain't a DOL universe without an orphan somewhere.
He's an aspiting inventor, and is quite creative.
He may need some help to pay off Bailey, he barely manages to make enough money to pay rent every week. he often has to skip lunch to save on money.
His favourite inventions are small, yet useful household items. He invented a machine that warms up bread just right. Unfortunately, not many people are interested in these kinds of things.
He's sweet and caring, but also naive. Has a secret dirty side to him. loves to be degraded for the useless aborted kid he is, depending on PC to pay off his debt. Doesn't care if you cum or not, if he's done he's done.
Uri Gabriel (or Uriel)- the banished
a fallen angel banished from heaven for loving someone other than God. his greatest sin was to love his partner. He fell from grace because they told on him to repent. Uriel fell, and swore to never fall in love again.
He is cold and distant, intentionally pushing you away if you get too close. The only reason he even bothers interacting with you, is because you save him from the church during your first meeting.
He's dominating, he's course and rough, swears a lot during sex. You're his cocksleeve, at best. unless he actually starts developing feelings... he will become more sweet once he admits his love for you. doesn't care if you cum during sex. you're his toy, at best. why would he care?
#degrees of steampunk lewdity#dol#degrees of lewdity#they are all men bc my friend doesn't like women#i'd love to see genderbent versions#or even your takes on them!#degrees of lewdity LI#degrees of lewdity oc#roleplay#arden#arden the isolated#codium#codium the merman#gear#gear the robot#URI gabriel#Jamie#Jamie the orphan#writing#dol writing#degrees of lewdity writing#art#drawing#digital art#character sheet#DOL oc#my art
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi everyone,
So I’ve been using ChatGPT4 to ask questions. And my most recent question was: “Why is humanity such a destructive species”. And it had an interesting answer:
The perception of humans as a destructive species is often informed by observations of environmental degradation, wars, and other forms of violence. Multiple factors contribute to these destructive behaviors:
1. **Resource Consumption:** Humans, like all species, need resources to survive. Unlike other species, however, humans have developed technology and societal systems that allow for and encourage widespread and rapid consumption of resources. This has led to deforestation, pollution, and other environmental issues.
2. **Competition:** Competition for resources can lead to conflict. This can be seen on a small scale (like disputes between individuals or groups) and on a large scale (like wars between nations).
3. **Technological Advancement:** Humans have developed technology that has allowed for rapid change and growth. This technology can be incredibly beneficial, but it can also be used destructively. Nuclear weapons and other advanced weaponry are obvious examples of this.
4. **Short-Term Thinking:** Humans often prioritize short-term gains over long-term sustainability. This can lead to behaviors that are destructive in the long run.
5. **Disconnect from Nature:** Many humans live in environments that are largely removed from the natural world. This can lead to a lack of understanding or concern for the impact of human activities on the environment.
6. **Population Growth:** The human population has grown rapidly over the last few centuries, leading to increased demand on resources and greater impact on the environment.
It's important to note, however, that not all humans are destructive, and many people and organizations are working hard to mitigate these issues. There are movements towards sustainability, peacekeeping efforts, advancements in technology aimed at reducing environmental impact, and educational initiatives to help people understand the importance of living in harmony with the environment.
Humanity is capable of both great destruction and great creation. Understanding and addressing the factors that contribute to destructive behavior is key to promoting more sustainable and peaceful ways of living.
What do you all think about this answer?
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Marginal improvements to agricultural soils around the world would store enough carbon to keep the world within 1.5C of global heating, new research suggests.
Farming techniques that improve long-term fertility and yields can also help to store more carbon in soils but are often ignored in favor of intensive techniques using large amounts of artificial fertilizer, much of it wasted, that can increase greenhouse gas emissions.
Using better farming techniques to store 1 percent more carbon in about half of the world’s agricultural soils would be enough to absorb about 31 gigatons of carbon dioxide a year, according to new data. That amount is not far off the 32 gigaton gap between current planned emissions reduction globally per year and the amount of carbon that must be cut by 2030 to stay within 1.5C.
The estimates were carried out by Jacqueline McGlade, the former chief scientist at the UN environment program and former executive director of the European Environment Agency. She found that storing more carbon in the top 30 centimeters of agricultural soils would be feasible in many regions where soils are currently degraded.
McGlade now leads a commercial organization that sells soil data to farmers. Downforce Technologies uses publicly available global data, satellite images, and lidar to assess in detail how much carbon is stored in soils, which can now be done down to the level of individual fields.
“Outside the farming sector, people do not understand how important soils are to the climate,” said McGlade. “Changing farming could make soils carbon negative, making them absorb carbon, and reducing the cost of farming.”
She said farmers could face a short-term cost while they changed their methods, away from the overuse of artificial fertilizer, but after a transition period of two to three years their yields would improve and their soils would be much healthier...
Arable farmers could sequester more carbon within their soils by changing their crop rotation, planting cover crops such as clover, or using direct drilling, which allows crops to be planted without the need for ploughing. Livestock farmers could improve their soils by growing more native grasses.
Hedgerows also help to sequester carbon in the soil, because they have large underground networks of mycorrhizal fungi and microbes that can extend meters into the field. Farmers have spent decades removing hedgerows to make intensive farming easier, but restoring them, and maintaining existing hedgerows, would improve biodiversity, reduce the erosion of topsoil, and help to stop harmful agricultural runoff, which is a key polluter of rivers."
-via The Grist, July 8, 2023
#agriculture#sustainable agriculture#sustainability#carbon emissions#carbon sequestration#livestock#farming#regenerative farming#native plants#ecosystems#global warming#climate change#good news#hope
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Oliver Hernandez’s front yard hums with plenty of bugs for the 12-year-old and his friends to find.
“It’s kind of fun just knowing that there are lots of caterpillars in the yard,” he said.
About a third of the yard looks like a teeny swath of prairie, with wild indigo, bee balm and, until recently, a key plant for monarch butterflies: common milkweed.
Last fall, the city of Overland Park told Oliver’s mother to rip the milkweed out of her pollinator garden.
That bummed Oliver because it’s a plant where brightly striped yellow, black and white caterpillars would appear each summer, grow fat on leaves and transform into the feather-light marvels of nature most famous for what they do next.
“They are pretty,” he said. “Also, whenever they become butterflies, they fly to Mexico. I think that’s pretty cool.”
Across the U.S., milkweed bans are disappearing. But this Kansas suburb and plenty of other towns and cities across the Midwest continue to define it in their city codes as flora non-grata.
Sometimes city, county and state rules conflict, leaving homeowners to navigate mixed messages from local governments that can’t see eye-to-eye on whether to promote milkweed or kill it off.
City workers may not have much heart for enforcing these rules. The plight of the continent’s dwindling monarch population is, after all, well-known.
Ginger Werp, Oliver’s mother, got the impression that the city worker who showed up at her door in late September didn’t really like telling her to remove environmentally beneficial plants.
“Our world is becoming degraded and needs us to change,” Werp said. “Not all of the cities in Johnson County have this rule.”
In fact, Werp points out, this county encourages homeowners to plant common milkweed and reimburses part of the cost for people who replace grass turf with native plants — including this one. The goal is to feed wildlife and fill the soil with deep roots that absorb stormwater and slow the pace of pollution washing into streams.
Werp knows about the program because she works at a nonprofit organization that, among other things, helps the county run it.
And she knows about native plants because wading into prairies to identify species and collect seeds for habitat restoration projects is her full-time job.
A clash of aesthetics
Oliver’s front-yard insectary likely came to the city’s attention because his mother and her neighbors have very different tastes in landscaping.
On a street lined with neatly trimmed bushes and traditional lawns, Werp’s little meadow is perhaps 12 feet by 7 feet. The tallest plants, native Maximilian sunflowers, tower above her head.
Instead of mulching the bed in the typical Suburban style (with cedar chips or other store-bought options), Werp lets fallen sycamore leaves mulch her plot.
Rather than chopping down plant stalks in the fall, she lets them stand, so her family can watch finches raid the garden for seeds all winter.
Werp knows this isn’t everyone’s cup of tea.
“I’ve had some uncomfortable conversations with neighbors about it,” she said of her flower bed. “But it doesn’t bother me. … I think it’s pretty, I think it’s fun. My son and I have a good time out here.”
She supposes a neighbor became concerned that her naturalistic landscaping would hurt home resale values.

A monarch caterpillar and a milkweed beetle munch on common milkweed in Ginger Werp's garden in Overland Park last summer. Ginger Werp
But when a city worker showed up to inspect her handiwork, he said most of the plants could stay. She only had to remove the contraband common milkweed, Asclepias syriaca.
Werp agreed and the matter ended there.
Had she refused, the city could have sent someone to remove the milkweed and charge her for the work.
Overland Park’s code allows it to prosecute violators, though it’s not clear that the city would actually pursue something so stringent against a butterfly enthusiast. The penalties include a fine of $50 to $500 and/or up to 10 days in jail.
City codes vs. conservation
Other cities in Kansas and nearby states frown on milkweed, too — usually common milkweed but sometimes its relatives, as well.
Winfield, Kansas, puts common milkweed on its list of “rank” plants that harbor rats and insects, pose fire risks or blight neighborhoods.
Sometimes, city codes hinge on context.
Prairie Village lists common milkweed as a no-no, followed immediately by this caveat: “Native plants contained in a native garden, such as common milkweed and other pollinators (sic), would be considered a cultivated garden and not classified as a rank weed.”
City bans on milkweed are on the way out, the National Wildlife Federation says, a fact that it welcomes.
“They have been historically very, very common,” said Mary Phillips, head of the group’s Garden for Wildlife program that aims to integrate habitat into cities and suburbs. “Particularly in the central United States.”
She traces that history to the region’s agriculture. Milkweed can sicken livestock when they eat enough of it. Animals tend to steer clear of the toxic plants, but accidental poisonings do happen, particularly if milkweed infiltrates a hayfield and gets cut, dried and served up to livestock mixed into their hay.
Cities that no longer worry about keeping cattle safe have nevertheless retained the historical opposition to milkweed.
“The real trend is that those bans are being reversed,” Phillips said. “There’s a lot of pushback to get those overturned.”
In 2017, Illinois passed two state laws. One forced cities and counties to drop milkweed bans on common milkweed. The other declared milkweed the state wildflower.
Illinois cities such as Ottawa still have bans on their books, but the state law trumps it.
Asclepias syriaca, or common milkweed, is the species that cities most commonly target.
This species spreads not just through its seeds, but also through underground runners.
It takes work to control it in a flower garden, which might explain city bans where they still exist.
Bug chow
The reality is, many cities may not have anyone on staff who knows when or why milkweed was banned.
An Overland Park spokesperson said the city considers common milkweed a noxious weed because the Kansas Department of Agriculture does.
But the state agency refuted that. It says all Kansas milkweeds are “native and beneficial.”
“As far as we know it has never been listed as a noxious weed and there is no indication that there is any interest in listing it as noxious,” a Department of Agriculture spokeswoman said by email. “While it’s not healthy for cattle to eat, they generally avoid it.”
The center of the country is a significant flyway for migrating monarchs. And on their way north from Mexico each spring, they lay eggs.

Common milkweed was a key feature of Ginger Werp's front yard in past years. In September, Overland Park asked her to remove it. Ginger Werp
These famous travelers — by some counts, they were five times as numerous in the 1990s — can’t survive without milkweed.
A monarch butterfly can happily nectar on the blossoms of a wide variety of plant species, but its offspring eat just one thing: milkweed leaves. Without that, the females can’t produce descendants any more than humans can rear babies without breast milk or formula.
But milkweed has gotten harder to find.
“That entire (central) flyway was so heavy with milkweed many, many years ago,” Phillips said.
But today, as Monarch Watch at the University of Kansas notes, genetically modified corn and soybeans allow aggressive glyphosate herbicide (sold most commonly under the brand name Roundup) application that kills, among other things, milkweed. The plants have disappeared from tens of millions of acres of cropland.
Monarch Watch founder Chip Taylor and other researchers wrote in 2020 that restoring milkweed “is the conservation measure that will have the greatest impact” for helping the insects.
Monarch Watch distributes milkweed plants for habitat restoration, encourages the creation of pollinator gardens in cities and suburbs, and mails free plants to eager schools.
Common milkweed holds particular significance.
A 2018 study by researchers at Iowa State University and the USDA compared nine types of milkweed at 10 sites across Iowa from 2015 to 2017. They found Asclepias syriaca was one of two types where monarchs laid the most eggs.
Its decline makes some homeowners passionate about offering their yards as refuge by planting the long-maligned species, with its large leaves and spheres of pink blooms.
Mixed messages
As some governments see the plant in a new light, it can lead to conflicting messages, such as the discrepancy between Johnson County and Overland Park.
In 2014, Canada’s most populous province, Ontario, ended its battle against common milkweed. But as recently as last summer, a butterfly enthusiast there lost her milkweed-heavy pollinator garden to Toronto workers with weed wackers enforcing the city’s landscaping rules.
Lawrence lists common milkweed as a weed in its city code, but its parks and recreation department grows the plant in pollinator gardens.
“Our stance is that common milkweed in a properly maintained garden is perfectly acceptable,” a city spokeswoman said by email.
The city, which is part of a National Wildlife Federation pledge to support monarchs, says it can enforce its weed rule when properties aren’t properly tended.
But a citizen advisory board has asked the city commission to strike milkweed and other plants from Lawrence’s list of 56 weed species. It recommends using the state’s far shorter list.
“The list has kind of grown (over the decades) and nobody knows where a lot of this stuff came from,” said advisory board vice chairman Ben Sikes, a biologist. “Many of the species that are on there, we know are native species. Many of them are important for habitat or for food for native animals and insects.”
The Lawrence City Commission hasn’t acted on the recommendation.
#Milkweed#natural gardening#When a Kansas county wants people to plant milkweed but a city makes them rip it out#milkweed bans#kansas
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Air pollution dramatically reduces pollination because it degrades the scent of flowers, affecting bees' ability to find them, a study has found.
A research team comprising the UK Center for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH) and the Universities of Reading, Surrey, Birmingham and Southern Queensland, found that ozone substantially changes the size and scent of floral odor plumes. It reduced honeybees' ability to recognize odors by up to 90% from just a few meters away.
Ground-level ozone, which aggravates respiratory conditions, typically forms when nitrogen oxide emissions from vehicles and industrial processes react with volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from vegetation in the presence of sunlight.
Continue Reading.
199 notes
·
View notes