#Water Consumption and Pollution
Text
The Impact of Your Food Choices on The Environment
More and more people are becoming aware of the impact their actions have on the environment. One area where our choices can make a significant difference is in our food consumption. The food we eat not only affects our health but also has a profound impact on the environment. As environmentally conscious individuals who value sustainable and organic farming practices, we have the power to make a…
View On WordPress
#Deforestation and Habitat Destruction#Food Waste and Packaging#Local producers#Organic farming practices#Reducing consumption of animal-based products#Soil Degradation and Loss#supporting local businesses#Sustainable farming practices#The Carbon Footprint of Food Production#Water Consumption and Pollution
0 notes
Text


#ChatGPT#Microsoft#notmybagman#Twitter#water usage#pollution#energy usage#cooling#energy consumption#consumption#AI#artificial intelligence#the standard#environment#sustainability
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
I kind of want to try making mead or ambrosia 👀
Obviously not right now because I have Shit To Do; but maybe during the summer after I’ve moved
#alcohol mention#Apparently you can make mead out of honey and I love honey so of course I have to try it#I want to make more food from scratch so I can reduce my plastic consumption#because my ten-year goal is to convert to a completely anticapitalist zero-waste lifestyle#Just for me… I don’t put pressure on anyone to do the same unless they’re well-off and being ridiculous about their consumption#Except for maybe encouraging people to switch to reusable water bottles if they’re in an area where the tap water is potable#(like where I live)#or flaunting my canvas shopping bag that I got for 5 dollars at a hardware store whenever possible#Okay I guess I do push people a little bit#But it’s all reasonable things directed at people I know are physically mentally and financially able to do those things#or I’ll just casually mention microplastics and pollution in conversation as a “fun fact”#But I’m not ridiculous about it with anyone but myself#I hold myself to some weird standards that I don’t hold others to and I’m fine with it#Obviously it’s the corporations’ faults that everything is the way it is and no single person can make a huge difference#But if everyone does one thing to help the planet; then it might buy us some time to change the system#There is also the issue of supply and demand; if more people reduce plastic intake then less plastic will be produced#But again: it’s very hard to be ethical in this society. EVERYTHING enjoyable is packaged in plastic and it sucks#(ok not literally everything but consider: most candy is wrapped in plastic and clothes have plastic tags and chips are in plastic#sushi is in plastic containers and meat is in shrink wrap or styrofoam and most modern chewing gum is a byproduct of vinyl#toys are packaged in plastic etc. etc.)
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Namibia is the driest country in Sub-Saharan Africa, and home to two of the world’s most ancient deserts, the Kalahari and the Namib. The capital, Windhoek, is sandwiched between them, 400 miles away from the nearest perennial river and more than 300 miles away from the coast. Water is in short supply.
It’s hard to imagine life thriving in Windhoek, yet 477,000 people call it home, and 99 per cent of them have access to drinking water thanks to technology pioneered 55 years ago on the outskirts of the city. Now, some of the world’s biggest cities are embracing this technology as they adapt to the harshest impacts of climate change. But Namibia leads the way.
How did this come about? In the 1950s, Windhoek’s natural resources struggled to cope with a rapidly growing population, and severe water shortages gripped the city. But disaster forced innovation, and in 1968 the Goreangab Water Reclamation Plant in Windhoek became the first place in the world to produce drinking water directly from sewage, a process known as direct potable reuse (DPR).
That may sound revolting, but it’s completely safe. Dr Lucas van Vuuren, who was among those who pioneered Windhoek’s reclamation system, once said that “water should not be judged by its history, but by its quality”. And DPR ensures quality.
This is done using a continuous multi-barrier treatment devised in Windhoek during eight years of pilot studies in the 1960s. This process – which has been upgraded four times since 1968 – eliminates pollutants and safeguards against pathogens by harnessing bacteria to digest the human waste and remove it from the water. This partly mimics what happens when water is recycled in nature, but Windhoek does it all in under 24 hours...

Pictured: These ultrafiltration membranes help to remove bacteria, viruses and pathogens. Image: Margaret Courtney-Clarke
“We know that we have antibiotics in the water, preservatives from cosmetics, anti-corrosion prevention chemicals from the dishwasher,” Honer explains. “We find them and we remove them.”
Honer adds that online instruments monitor the water continuously, and staff ensure that only drinking water that meets World Health Organisation (WHO) guidelines is sent to homes. If any inconsistencies are detected, the plant goes into recycle mode and distribution is halted until correct values are restored.
“The most important rule is, and was, and always will be ‘safety first’,” says Honer. The facility has never been linked to an outbreak of waterborne disease, and now produces up to 5.5m gallons of drinking water every day – up to 35 per cent of the city’s consumption.
Namibians couldn’t survive without it, and as water shortages grip the planet, Windhoek’s insights and experience are more important than ever.
Interest from superpowers across the globe
In recent years, delegations from the US, France, Germany, India, Australia, Singapore, and the United Arab Emirates have visited Windhoek seeking solutions to water shortages in their own countries.
Megadrought conditions have gripped the US since 2001, and the Colorado River – which provides 40 million people with drinking water – has been running at just 50 per cent of its traditional flow. As a result, several states including Texas, California, Arizona and Colorado are beginning to embrace DPR.
Troy Walker is a water reuse practice leader at Hazen and Sawyer, an environmental engineering firm helping Arizona to develop its DPR regulations. He visited Windhoek last year. “It was about being able to see the success of their system, and then looking at some of the technical details and how that might look in a US facility or an Australian facility,” he said. “[Windhoek] has helped drive a lot of discussion in industry. [Innovation] doesn’t all have to come out of California or Texas.”

Pictured: The internal pipes and workings of Namibia's DPR plant. As water becomes scarcer in some parts, countries are looking to DPR for solutions. Image: Margaret Courtney-Clarke
Namibia has also helped overcome the biggest obstacle to DPR – public acceptance. Disgust is a powerful emotion, and sensationalist ‘toilet to tap’ headlines have dismantled support for water reuse projects in the past. Unfortunately, DPR’s biggest strength is also its biggest weakness, as the speed at which water can re-enter the system makes it especially vulnerable to prejudice, causing regulators to hesitate. “Technology has never been the reason why these projects don’t get built – it’s always public or political opposition,” says Patsy Tennyson, vice president of Katz and Associates, an American firm that specialises in public outreach and communications.
That’s why just a handful of facilities worldwide are currently doing DPR, with Windhoek standing alongside smaller schemes in the Philippines, South Africa and a hybrid facility in Big Spring, Texas. But that’s all changing. Drought and increased water scarcity worldwide are forcing us to change the way we think about water.
Now, the US is ready to take the plunge, and in 2025, El Paso Water will begin operating the first ‘direct to distribution’ DPR facility in North America, turning up to 10m gallons of wasterwater per day into purified drinking water – twice as much as Windhoek. San Diego, Los Angeles, California, as well as Phoenix, Arizona are also exploring the technology."
Of course, DPR is not a silver bullet in the fight against climate change. It cannot create water out of thin air, and it will not facilitate endless growth. But it does help cities become more climate resilient by reducing their reliance on natural sources, such as the Colorado River.
As other nations follow in Namibia’s footsteps, Windhoek may no longer take the lead after almost six decades in front.
“But Windhoek was the first,” Honer reminds me. “No one can take that away.”"
-via Positive.News, August 30, 2023
#namibia#africa#desert#water shortage#water conservation#dpr#potable water#water recycling#clean water#drought#united states#colorado river#science and technology#sanitation#good news#hope
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Real Cost of the Fashion Industry

Atacama Desert, in Alto Hospicio, Iquique, Chile. (source)
The textile industry is destroying the world. The industry is wasting massive amounts of energy and materials, and polluting the air, the ground and the water supplies. It overwhelmingly exploits it's labour and extracts wealth from colonized countries, especially in Asia. I assume we all broadly understand this, but I think it's useful to have it all laid out in front of you to see the big picture, the core issues causing this destruction and find ways how to effectively move forward.
The concerning trend behind this ever-increasing devastation are shortening of trend cycles, lowering clothing prices and massive amount of wasted products. Still in year 2000 it was common for fashion brands to have two collections per year, while now e.g. Zara produces 24 collections and H&M produces 12-16 collections per year. Clothing prices have fallen (at leas in EU) 30% from 1996 to 2018 when adjusted to inflation, which has contributed to the 40% increase in clothing consumption per person between 1996 and 2012 (in EU). (source) As the revenue made by the clothing industry keep rising - from 2017 to 2021 they doubled (source) - falling prices can only be achieved with increasing worker exploitation and decreasing quality. I think the 36% degrees times clothing are used in average during the last 15 years (source) is a clear indication on the continuing drop in quality of clothing. Clothing production doubled between 2000 and 2015, while 30% of the clothes produced per year are never sold and are often burned instead (source), presumably to prevent the returns from falling due to oversupply.
These all factors are driving people to overconsume. While people in EU keep buying more clothes, they haven't used up to 50% of the clothes in their wardrobe for over a year (source). This overconsumption is only made much worse by the new type of hyper fast fashion companies like SHEIN and Temu, which are using addictive psychological tactics developed by social media companies (source 1, source 2). They are cranking up all those concerning trends I mentioned above.
Under the cut I will go through the statistics of the most significant effects of the industry on environment and people. I will warn you it will be bleak. This is not just a fast fashion problem, basically the whole industry is engaging in destructive practices leading to this damage. Clothing is one of those things that would be actually relatively easy to make without massive environmental and human cost, so while that makes the current state of the industry even more heinous, it also means there's hope and it's possible to fix things. In the end, I will be giving some suggestions for actions we could be doing right now to unfuck this mess.
Carbon emissions
The textile industry is responsible for roughly 10% of the global CO2 emissions, more than aviation and shipping industry combined. This is due to the massive supply chains and energy intensive production methods of fabrics. Most of it can be contributed to the fashion sector since around 60% of all the textile production is clothing. Polyester, a synthetic fiber made from oil which accounts for more than half of the fibers used in the textile industry, produces double the amount of carbon emissions than cotton, accounting for very large proportions of all the emissions by the industry. (source 1, source 2)
Worker exploitation
Majority of the textiles are produced in Asia. Some of the worst working conditions are in Bangladesh, one of the most important garment producers, and Pakistan. Here's an excerpt from EU Parliament's briefing document from 2014 after the catastrophic Rana Plaza disaster:
The customers of garment producers are most often global brands looking for low prices and tight production timeframes. They also make changes to product design, product volume, and production timeframes, and place last-minute orders without accepting increased costs or adjustments to delivery dates. The stresses of such policies usually fall on factory workers.
The wage exploitation is bleak. According to the 2015 documentary The True Cost less than 2% of all garment factory workers earned a living wage (source). Hourly wages are so low and the daily quotas so high, garment workers are often forced through conditions or threats and demand to work extra hours, which regularly leads to 10-12 hour work days (source) and at worst 16 hour workdays (source), often without days off. Sometimes factories won't compensate for extra hours, breaching regulations (source).
Long working hours, repetitive work, lack of breaks and high pressure leads to increased risks of injuries and accidents. Small and even major injuries are extremely common in the industry. A study in three factories in India found that 70% of the workers suffered from musculosceletal symptoms (source). Another qualitative study of female garment workers and factory doctors in Dhaka found that long hours led to eye strain, headaches, fatigue and weight loss in addition to muscular and back pains. According to the doctors interviewed, weight loss was common because the workers work such long hours without breaks, they didn't have enough time to eat properly. (source) Another study in 8 factories in India found that minor injuries were extremely common and caused by unergonomic work stations, poor organization in the work place and lack of safety gear, guidelines and training (source). Safety precautions too are often overlooked to cut corners, which periodically leads to factory accidents, like in 2023 lack of fire exists and fire extinguishers, and goods stacked beyond capacity led to a factory fire in Pakistan which injured dozens of workers (source) or like in 2022 dangerous factory site led to one dead worker and 9 injured workers (source).
Rana Plaza collapse in 2013 is the worst industrial accident in recent history. The factory building did not have proper permits and the factory owner blatantly ignored signs of danger (other businesses abandoned the building a day before the collapse), which led to deaths of 1 134 workers and injuries to 2 500 workers. The factory had or were at the time working for orders of at least Prada, Versace, Primark, Walmart, Zara, H&M, C&A, Mango, Benetton, the Children's Place, El Corte Inglés, Joe Fresh, Carrefour, Auchan, KiK, Loblaw, Bonmarche and Matalan. None of the brands were held legally accountable for the unsafe working conditions which they profited off of. Only 9 of the brands attended a meeting to agree on compensation for the victim's families. Walmart, Carrefour, Auchan, Mango and KiK refused to sight the agreement, it was only signed by Primark, Loblaw, Bonmarche and El Corte Ingles. The compension these companies provided was laughable though. Primemark demanded DNA evidence that they are relatives of one of the victims from these struggling families who had lost their often sole breadwinner for a meager sum of 200 USD (which doesn't even count for two months of living wage in Bangladesh (source)). This obviously proved to be extremely difficult for most families even though US government agreed to donate DNA kits. This is often said to be a turning point in working conditions in the industry, at least in Bangladesh, but while there's more oversight now, as we have seen, there's clearly still massive issues. (source 1, source 2)
One last major concern of working conditions in the industry I will mention is the Xinjiang raw cotton production, which is likely produced mainly with forced labour from Uighur concentration camps, aka slave labour of a suspected genocide. 90% of China's raw cotton production comes from Xinjiang (source). China is the second largest cotton producer in the world, after India, accounting 20% of the yearly global cotton production (source).
Pollution
Synthetic dyes, which synthetic fibers require, are the main cause of water pollution caused by the textile industry, which is estimated to account for 20% of global clean water pollution (source). This water pollution by the textile industry is suspected of causing a lot of health issues like digestive issues in the short term, and allergies, dermatitis, skin inflammation, tumors and human mutations in the long term. Toxins also effect fish and aquatic bacteria. Azo dyes, one of the major pollutants, can cause detrimental effects to aquatic ecosystems by decreasing photosynthetic activity of algae. Synthetic dyes and heavy metals also cause large amounts of soil pollution. Large amounts of heavy metals in soil, which occurs around factories that don't take proper environmental procautions, can cause anaemia, kidney failure, and cortical edoem in humans. That also causes changes in soil texture, decrease in soil microbial diversity and plant health, and changes in genetic structure of organisms growing in the soil. Textile factory waste water has been used for irrigation in Turkey, where other sources of water have been lacking, causing significant damage to the soil. (source)
Rayon produced through viscose process causes significant carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide pollution to the environment. CS2 causes cardiovascular, psychiatric, neuropsychological, endocrinal and reproductive disorders. Abortion rates among workers and their partners exposed to CS2 are reported to be significantly higher than in control groups. Many times higher amounts of sick days are reported for workers in spinning rooms of viscose fiber factories. China and India are largest producers of CS2 pollution, accounting respectively 65.74% and 11,11% of the global pollution, since they are also the major viscose producers. Emission of CS2 has increased significantly in India from 26.8 Gg in 2001 to 78.32 Gg in 2020. (source)
Waste
The textile industry is estimated to produce around 92 million tons of textile waste per year. As said before around 30% of the production is never sold and with shortening lifespans used the amount of used clothing that goes to waster is only increasing. This waste is large burned or thrown into landfills in poor countries. (source) H&M was accused in 2017 by investigative journalists of burning up to 12 tonnes of clothes per year themselves, including usable clothing, which they denied claiming they donated clothing they couldn't sell to charity instead (source). Most of the clothing donated to charity though is burned or dumbed to landfills (source).
Most of the waste clothing from rich countries like European countries, US, Australia and Canada are shipped to Chile (source) or African countries, mostly Ghana, but also Burkina Faso and Côte d'Ivoire (source). There's major second-hand fashion industries in these places, but most of the charity clothing is dumbed to landfills, because they are in such bad condition or the quality is too poor. Burning and filling landfills with synthetic fabrics with synthetic dyes causes major air, water and soil pollution. The second-hand clothing industry also suppresses any local clothing production as donated clothing is inherently more competitive than anything else, making these places economically reliant on dumbed clothing, which is destroying their environment and health, and prevents them from creating a more sustainable economy that would befit them more locally. This is not an accident, but required part of the clothing industry. Overproduction let's these companies tap on every new trend quickly, while not letting clothing the prices in rich countries drop so low it would hurt their profits. Production is cheaper than missing a trend.
Micro- and nanoplastics
There is massive amounts of micro- and nanoplastics in all of our environment. It's in our food, drinking water, even sea salt (source). Washing synthetic textiles accounts for roughly 35% of all microplastics released to the environment. It's estimated that it has caused 14 million tonnes of microplastics to accumulate into the bottom of the ocean. (source)
Microplastics build up into the intestines of animals (including humans), and have shown to probably cause cause DNA damage and altered organism behavior in aquatic fauna. Microplastics also contain a lot of the usual pollutants from textile industry like synthetic dyes and heavy metals, which absorb in higher quantities to tissues of animals through microplastics in the intestines. Studies have shown that the adverse effect are higher the longer the microplastics stay in the organism. The effects cause major risks to aquatic biodiversity. (source) The health effects of microplastics to humans are not well known, but studies have shown that they could have adverse effects on digestive, respiratory, endocrine, reproductive and immune systems. (source)
Microplastics degrade in the environment even further to nanoplastics. Nanoplastic being even smaller are found to enter blood circulation, get inside cells and cross the blood-brain barrier. In fishes they have been found to cause neurological damage. Nanoplastics are also in the air, and humans frequently breath them in. Study in office buildings found higher concentration of nanoplastics in indoor air than outdoor air. Inside the nanoplastics are likely caused mostly by synthetic household textiles, and outdoors mostly by car tires. (source) An association between nanoplastics and mitochondrial damage in human respiratory cells was found in a recent study. (source)
Micro and nano plastics are also extremely hard to remove from the environment, making it even more important that we reduce the amount of microplastics we produce as fast as possible.
What can we do?
This is a question that deserves it's own essays and articles written about it, but I will leave you with some action points. Reading about these very bleak realities can easily lead to overwhelming apathy, but we need to channel these horrors into actions. Whatever you do, do not fall into apathy. We don't have the luxury for that, we need to act. These are industry wide problems, that simply cannot be fixed by consumerism. Do not trust any clothing companies, even those who market themselves as ethical and responsible, always assume they are lying. Most of them are, even the so called "good ones". We need legislation. We cannot allow the industry to regulate itself, they will always take the easy way out and lie to their graves. I will for sure write more in dept about what we can do, but for now here's some actions to take, both political and individual ones.
Political actions
Let's start with political actions, since they will be the much more important ones. While we are trying to dismantle capitalism and neocolonialism (the roots of these issues), here's some things that we could do right now. These will be policies that we should be doing everywhere in the world, but especially rich countries, where most of the clothing consumption is taking place. Vote, speak to others, write to your representative, write opinion pieces to your local papers, engage with democracy.
Higher requirements of transparency. Right now product transparency in clothing is laughably low. In EU only the material make up and the origin country of the final product are required to be disclosed. Everything else is up to the company. Mandatory transparency is the only way we can force any positive changes in the production. The minimum of transparency should be: origin countries of the fibers and textiles in the product itself; mandatory reports of the lifecycle emissions; mandatory reports of whole chain of production. Right now the clothing companies make their chain of production intentionally complex, so they have plausible deniability when inevitably they are caught violating environmental or worker protection laws (source). They intentionally don't want to be able to track down their production chain. Forcing them to do so anyway would make it very expensive for them to keep up this unnecessarily complex production chain. These laws are most effective when put in place in large economies like EU or US.
Restrictions on the use of synthetic fibers. Honestly I think they should be banned entirely, since the amount of microplastics in our environment is already extremely distressing and the other environmental effects of synthetic fibers are also massive, but I know there are functions for which they are not easily replaced (though I think they can be replaces in those too, but that's a subject of another post), so we should start with restrictions. I'm not sure how they should be specifically made, I'm not a law expert, but they shouldn't be used in everyday textiles, where there are very easy and obvious other options.
Banning viscose. There are much better options for viscose method that don't cause massive health issues and environmental destruction where ever it's made, like Lyocell. There is absolutely no reason why viscose should be allowed to be sold anywhere.
Governmental support for local production by local businesses. Most of the issues could be much more easily solved and monitored if most clothing were not produced by massive global conglomerations, but rather by local businesses that produce locally. All clothing are made by hand, so centralizing production doesn't even give it advantage in effectiveness (only more profits for the few). Producing locally would make it much more easier to enforce regulations and it would reduce production chains, making production more effective, leaving more profits into the hands of the workers and reducing emissions from transportation. When the production is done by local businesses, the profits would stay in the producing country and they could be taxed and utilized to help the local communities. This would be helpful to do in both exploited and exploiter countries. When done in rich countries who exploit poorer ones, it would reduce the demand for exploitation. In poor countries this is not as easily done, since poor means they don't have money to give around, but maybe this could be a good cause to put some reparations from colonizers and global corporations, which they should pay.
Preventing strategic accounting between subsidiaries and parent companies. Corporate law is obviously not my area of expertise, but I know that allowing corporations to move around the accounting of profits and losses between subsidiaries and parent companies in roughly 1980s, was a major factor in creating this modern global capitalist system, where corporations can very easily manipulate their accounting to utilize tax heavens and avoid taxes where they actually operate, which is how they are upholding this terrible system and extracting the profits from the production countries. How specifically this would be done I can't tell because again I know shit about corporate law, so experts of that field should plan the specifics. Overall this would help deal with a lot of other problems than just the fashion industry. Again for it to be effective a large economic area like EU or US should do this.
Holding companies accountable for their whole chain of production. These companies should be dragged to court and made to answer for the crimes they are profiting of off. We should put fear back into them. This is possible. Victims of child slavery are already doing this for chocolate companies. If it's already not how law works everywhere, the laws should be changed so that the companies are responsible even if they didn't know, because it's their responsibility to find out and make sure they know. They should have been held accountable for the Rana Plaza disaster. Maybe they still could be. Sue the mother fuckers. They should be afraid of us.
Individual actions
I will stress that the previous section is much more important and that there's no need to feel guilty for individual actions. This is not the fault of the average consumer. Still we do need to change our relationship to fashion and consumption. While it's not our fault, one of the ways this system is perpetuated, is by the consumerist propaganda by fashion industry. And it is easier to change our own habits than to change the industry, even if our own habits have little impact. So these are quite easy things we all could do as we are trying to do bigger change to gain some sense of control and keep us from falling to apathy.
Consume less. Better consumption will not save us, since consumption itself is the problem. We consume too much clothing. Don't make impulse purchases. Consider carefully weather you actually need something or if you really really want it. Even only buying second-hand still fuels the industry, so while it's better than buying new, it's still better to not buy.
Take proper care of your clothing. Learn how to properly wash your clothing. There's a lot of internet resources for that. Never wash your wool textiles in washing machine, even if the textile's official instructions allow it. Instead air them regularly, rinse them in cool water if they still smell after airing and wash stains with water or small amount of (wool) detergent. Never use fabric softener! It damages the fabrics, prevents them from properly getting clean and is environmentally damaging. Instead use laundry vinegar for making textiles softer or removing bad smells. (You can easily make laundry vinegar yourself too from white vinegar and water (and essential oils, if you want to add a scent to it) which is much cheaper.) Learn how to take care of your leather products. Most leather can be kept in very good condition for a very long time by occasional waxing with beeswax.
Use the services of dressmakers and shoemakers. Take your broken clothing or clothing which doesn't fit anymore to your local dressmaker and ask them if they can do something about it. Take your broken and worn leather products to your local shoemaker too. Usually it doesn't cost much to get something fixed or refitted and these expert usually have ways to fix things you couldn't even think of. So even if the situation with your clothing or accessory seems desperate, still show it to the dressmaker or shoemaker.
If it's extremely cheap, don't buy it. Remember that every clothing is handmade. Only a small fraction of the cost of the clothing will be paying the wages of the person who made it with their hands. If a shirt costs 5 euros (c. 5,39 USD), it's sewer was only payed mere cents for sewing it. I'm not a quick sewer and it takes me roughly 1-2 hours to cut, prepare and sew a simple shirt, so I'm guessing it would take around half an hour to do all that for a factory worker on a crunch, at the very least 15 minutes. So the hourly pay would still be ridiculously low. However, as I said before, the fact that the workers in clothing factories get criminally low pay is not the fault of the consumer, so if you need a clothing item, and you don't have money to buy anything else than something very cheep, don't feel guilty. And anyway expensive clothing in no way necessarily means reasonable pay or ethical working conditions, cheep clothing just guarantee them.
Learn to recognize higher quality. In addition to exploitation, low price also means low quality, but again high price doesn't guarantee high quality. High quality allows you to buy less, so even if it's not as cheep as low quality, if you can afford it, when you need it, it will be cheaper in long run, and allows you to consume less. Check the materials. Natural fibers are your friends. Do not buy plastic, if it's possible to avoid. Avoid household textiles from synthetic fibers. Avoid textiles with small amounts of spandex to give it stretch, it will shorten the lifespan of the clothing significantly as the spandex quickly wears down and the clothing looses it's shape. Also avoid clothing with rubber bands. They also loose their elasticity very quickly. In some types of clothing (sport wear, underwear) these are basically impossible to avoid, but in many other cases it's entirely possible.
Buy from artisans and local producers, if you can. As said better consumption won't fix this, but supporting artisans and your local producers could help keep them afloat, which in small ways helps create an alternative to the exploitative global corporations. With artisans especially you know the money goes to the one who did the labour and buying locally means less middlemen to take their cut. More generally buy rather from businesses that are located to the same country where the production is, even if it's not local to you. A local business doesn't necessarily produce locally.
Develop your own taste. If you care about fashion and style, it's easy to fall victim to the fashion industry's marketing and trend cycles. That's why I think it's important to develop your personal sense of style and preferences. Pay attention at what type of clothes are comfortable to you. Go through your wardrobe and track for a while which clothing you use most and which least. Understanding your own preferences helps you avoid impulse buying.
Consider learning basics of sewing. Not everyone has the time or interest for this, but if you in anyway might have a bit of both, I suggest learning some very simple and basic mending and reattaching a button.
Further reading on this blog: How to see through the greenwashing propaganda of the fashion industry - Case study 1: Shein
Bibliography
Academic sources
An overview of the contribution of the textiles sector to climate change, 2022, L. F. Walter et al., Frontiers in Environmental Science
How common are aches and pains among garment factory workers? A work-related musculoskeletal disorder assessment study in three factories of south 24 Parganas district, West Bengal, 2021, Arkaprovo Pal et al., J Family Med Prim Care
Sewing shirts with injured fingers and tears: exploring the experience of female garment workers health problems in Bangladesh, 2019, Akhter, S., Rutherford, S. & Chu, C., BMC Int Health Hum Rights
Occupation Related Accidents in Selected Garment Industries in Bangalore City, 2006, Calvin, Sam & Joseph, Bobby, Indian Journal of Community Medicine
A Review on Textile and Clothing Industry Impacts on The Environment, 2022, Nur Farzanah Binti Norarmi et al., International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences
Carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide emissions from viscose fibre manufacturing industry: A case study in India, 2022, Deepanjan Majumdar et al., Atmospheric Environment: X
Microplastics Pollution: A Brief Review of Its Source and Abundance in Different Aquatic Ecosystems, 2023, Asifa Ashrafy et al., Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances
Health Effects of Microplastic Exposures: Current Issues and Perspectives in South Korea, 2023, Yongjin Lee et al., Yonsei Medical Journal
Nanoplastics and Human Health: Hazard Identification and Biointerface, 2022, Hanpeng Lai, Xing Liu, and Man Qu, Nanomaterials
Other sources
The impact of textile production and waste on the environment (infographics), 2020, EU
Chile’s desert dumping ground for fast fashion leftovers, 2021, AlJazeera
Fashion - Worldwide, 2022 (updated 2024), Statista
Fashion Industry Waste Statistics & Facts 2023, James Evans, Sustainable Ninja (magazine)
Everything You Need to Know About Waste in the Fashion Industry, 2024, Solene Rauturier, Good on You (magazine)
Textiles and the environment, 2022, Nikolina Šajn, European Parliamentary Research Service
Help! I'm addicted to secondhand shopping apps, 2023, Alice Crossley, Cosmopolitan
Addictive, absurdly cheap and controversial: the rise of China’s Temu app, 2023, Helen Davidson, Guardian
Workers' conditions in the textile and clothing sector: just an Asian affair? - Issues at stake after the Rana Plaza tragedy, 2014, Enrico D'Ambrogio, European Parliamentary Research Service
State of The Industry: Lowest Wages to Living Wages, The Lowest Wage Challenge (Industry affiliated campaign)
Fast Fashion Getting Faster: A Look at the Unethical Labor Practices Sustaining a Growing Industry, 2021, Emma Ross, International Law and Policy Brief (George Washington University Law School)
Dozens injured in Pakistan garment factory collapse and fire, 2023, Hannah Abdulla, Just Style (news media)
India: Multiple factory accidents raise concerns over health & safety in the garment industry, campaigners call for freedom of association in factories to ‘stave off’ accidents, 2022, Jasmin Malik Chua, Business & Human Rights Resource Center
Minimum Wage Level for Garment Workers in the World, 2020, Sheng Lu, FASH455 Global Apparel & Textile Trade and Sourcing (University of Delaware)
Rana Plaza collapse, Wikipedia
Buyers’ compensation for Rana Plaza victims far from reality, 2013, Ibrahim Hossain Ovi, Dhaka Tribune (news media)
World cotton production statistics, updated 2024, The World Counts
Dead white man’s clothes, 2021, Linton Besser, ABC News
#fashion#fashion industry#sustainability#sustainable fashion#sustainable clothing#environment#climate change#i will be continuing the series of how to see through fashion industry propaganda at some point#i just felt compelled to write this because i feel like people so often miss the forest for the trees in this conversation
491 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gaza’s water and sewage treatment facilities also require electricity and fuel. Without them—and with airstrikes ongoing—sewage is flowing into the Mediterranean Sea. According to the Norwegian Refugee Council, more than 130,000 cubic meters of untreated sewage a day were released into the Mediterranean Sea from Gaza in October, with dire consequences for the environment.
These latest developments are pounding Gazan ecosystems that had already been experiencing severe environmental degradation for decades. For instance, while there are some wastewater treatment facilities in the West Bank, the situation was dire in the Gaza Strip even before the current outbreak of violence, because of the Israeli blockade. That blockade has been near total since 2007, and has restricted the entry of materials and fuel needed for infrastructure. Wastewater management infrastructure is outdated, and sewage polluted Gaza’s aquifer and coastal waters. Some 97 percent of Gaza’s water is unsuitable for human consumption, and polluted water is the source of 26 percent of all illnesses—and before the war, the leading cause of child death in the territory.
Poor water quality and quantity are not only a result of Israel’s targeted policies and the unequal distribution of resources. They are also side effects of the destruction of Gaza’s already flimsy infrastructure during rounds of conflict over the last decade and a half. For instance, in 2007, a river of sewage overflowed in the Gazan village of Umm Naser from a collapsed earth embankment, killing five people. Corruption in the Palestinian Authority and Hamas helped cause the disaster, but an even bigger cause was Israel’s massive, sustained bombing attack on Gaza in the summer of 2006, which led to the destruction of sewage treatment facilities and infrastructure in Gaza.
While the 2006 conflict was devastating, it pales in comparison to the current assault. It is estimated that Israel dropped 25,000 metric tons of bombs on Gaza in the first month of this year’s war, a weight equal to the two nuclear bombs (combined) dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in World War II. The bombs have struck 12,000 targets, the majority of which appear to have served a civilian purpose. “
524 notes
·
View notes
Text
Full Article Text:
The United Kingdom is facing dire food shortages, forcing prices to skyrocket, and experts predict this is only the beginning.
What's happening?
According to a report by The Guardian, extreme weather is wreaking havoc on crops across the region. England experienced more rainfall during the past 18 months than it has over any 18-month period since record-keeping began in 1836.
Because the rain hasn't stopped, many farmers have been unable to get crops such as potatoes, carrots, and wheat into the ground. "Usually, you get rain but there will be pockets of dry weather for two or three weeks at a time to do the planting. That simply hasn't happened," farmer Tom Allen-Stevens told The Guardian.
Farmers have also planted fewer potatoes, opting for less weather-dependent and financially secure crops. At the same time, many of the potatoes that have been planted are rotting in the ground.
"There is a concern that we won't ever have the volumes [of potatoes] we had in the past in the future," British Growers Association CEO Jack Ward told The Guardian. "We are not in a good position and it is 100% not sustainable," Ward added.
Why is it important?
English farmers aren't alone — people are struggling to grow crops worldwide because of extreme weather.
Dry weather in Brazil and heavy rain in Vietnam have farmers concerned about pepper production. Severe drought in Spain and record-breaking rain and snowfall in California have made it difficult for farmers to cultivate olives for olive oil. El Niño and rising temperatures cut Peru's blueberry yield in half last year. Everyone's favorite drinks — coffee, beer, and wine — have all been impacted by extreme weather.
According to an ABC News report, the strain on the agriculture industry will likely continue to cause food prices to soar.
If these were just isolated events, farmers could more easily adapt — bad growing seasons are nothing new. The problem is that rising temperatures are directly linked to the increasing amount of gases such as carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere.
Since the start of the Industrial Revolution, humans have burned dirty energy sources such as coal, oil, and gas, which release a significant amount of those gases. Our climate is changing so drastically that the 10 warmest years since 1850 have all occurred in the last decade.
"As climate change worsens, the threat to our food supply chains — both at home and overseas — will grow," Energy and Climate Intelligence Unit analyst Amber Sawyer told The Guardian.
What can we do about it?
"Fortunately, we know many ways we can make the food system more resilient while reducing food emissions. The biggest opportunity in high-income nations is a reduction in meat consumption and exploration of more plants in our diets," said Dr. Paul Behrens, an associate professor of environmental change at Leiden University in the Netherlands.
If we replace a quarter of our meat consumption with vegetables, we could cut around 100 million tons of air pollution yearly. It may seem strange to suggest eating more vegetables with the decline in crop production. However, reducing the land and water used for animal agriculture and diverting those resources to growing more produce would drastically help the declining food supply.
Growing our own food is also a great way to reduce our reliance on store-bought produce, and it can save you hundreds of dollars a year at the grocery store.
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
The research showed that vegan diets resulted in 75% less climate-heating emissions, water pollution and land use than diets in which more than 100g of meat a day was eaten. Vegan diets also cut the destruction of wildlife by 66% and water use by 54%, the study found.
The heavy impact of meat and dairy on the planet is well known, and people in rich nations will have to slash their meat consumption in order to end the climate crisis.
Prof Peter Scarborough at Oxford University, who led the research, published in the journal Nature Food, said: “Our dietary choices have a big impact on the planet. Cutting down the amount of meat and dairy in your diet can make a big difference to your dietary footprint.”

614 notes
·
View notes
Note
This is a silly question, and purely a hypothetical, but is the water from any water-type move safe to drink? Would it depend on the pokemon? idk I saw a battle on tv and one of the trainers was a water type specialist and it got me on this train of thought.
i wouldn't drink water from a water type move at all unless i was pretty desperate to do so. a lot of water type moves are produced either at a pokemon's mouth, from organs on other parts of their body, or pulled from an outside source. unless they're using an external water source that happens to be water treated for human consumption, that's a risk i wouldn't take.
obviously, pokemon's bodies are not bacteria- or parasite-free, and the water that they produce to attack with has no guarantee that it's safe or clean. i remember the case of a trainer in kanto who got lost in mt. moon a few years back and had to rely on drinking water their squirtle spat out for them, and they ended up hospitalized with salmonella and had to be rescued by other trainers who luckily ran across them.
it used to be considered safe to drink rainwater from rain dance, but i think the scientific consensus on that is shifting thanks to buildup of pollutants in rain.
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
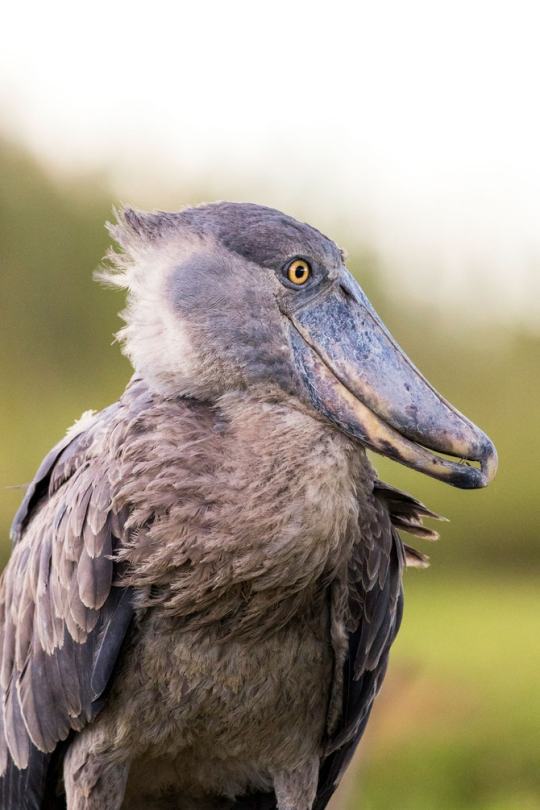



A Shoo-in Shoebill Stork
The shoebill stork, also known as the whalebill stork or Balaeniceps rex is in fact not a stork at all, but a long-legged wading bird belonging to the family Pelecaniformes. This species can be found in the central African tropics, from southern Sudan to northern Tanzania. Within this range, they mainly inhabit freshwater swamps and dense marshes, particularly those with deep water large reed beds.
Balaeniceps rex is often referred to as a dinosaur among birds due to its fearsome appearance. The average individual stands 1.1-1.4 m (3.6-4.5 ft) tall and has a wingspan of 2.3 to 2.6 m (7.5 to 8.5 in). However, adults are quite light, weighing only 4 to 7 kg (8.8 to 15.4 lb). Males tend to be larger than females, but otherwise the two sexes look identical. Adults have dark grey plumage with a lighter belly and darker wings. Their most striking feature is their beak, which is extremely large and can be said to resemble a wooden show (hence the name).
The shoebill's beak is very useful for catching its primary prey: fish. B. rex consumes a variety of species, including lungfish, catfish, and tilapia, as well as non-fish items like water snakes, frogs, turtles, mollusks, and even young crocodiles. Shoebills typically stalk their prey, or stand perfectly still and wait for their prey to come to them, before quickly snatching it up and decapitating it with the sharp edges of their beaks. Because of their large size and strong bills, adults are seldom prey for other animals, and they defend their nests fiercely from predators like snakes and other birds.
Outside of the breeding season-- and even during it-- shoebills are extremely territorial. Not only do they chase potential predators away from their nests, both males and females will fiercely defend their territory from other shoebills.
Breeding begins in the dry season, typically in in May, and lasts until about October. Once a male and female form a pair, they remain together for the duration of the mating season. They build a nest from floating vegetation, and 1-3 eggs are cared for by both parents; in addition to being incubated for warmth, one parent may also occasionally pour a beak-full of water over the eggs to keep them cool during the hot summer day. The eggs hatch about 30 days after being laid, and young are fed continuously-- though usually only one chick survives to adulthood. At 125 days old they become fully independent and leave to establish their own territories. The average individual can live up to 35 years in the wild.
Conservation status: The IUCN lists the whalebill stork as Vulnerable. Current wild population estimates sit at about 5,000-8,000 individuals. Primary threats include poaching for the zoo trade and consumption, habitat destruction, and pollution.
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a kofi!
Photos
Santiago Caballero Carrera
George Amato
Mana Meadows
#shoebill stork#Pelecaniformes#Balaenicipitidae#wading birds#birds#wetlands#wetland birds#freshwater fauna#freshwater birds#africa#central africa#animal facts#biology#zoology#ecology
167 notes
·
View notes
Text
The richest 1% globally has been responsible for 23% of total emissions growth since 1990 (Chancel 2022). Over the past 25 years, this “polluter elite” (IPCC 2022, 524) has contributed to more than twice as much carbon pollution compared to the three billion people that comprise the poorest half of humanity (Oxfam 2020; see also Gössling and Humpe 2023). Similar inequalities are evident in the (over)consumption of other resources. Savelli et al. (2023) show that the excessive water use by elites exacerbates urban water crises as much as climate change or population growth. Additionally, maintaining economic inequality close to current levels results in a doubling of the energy required to ensure decent living standards for all, allowing all people on Earth to have their basic needs covered (Millward-Hopkins 2022). At the same time, it is now clear that those who suffer most from environmental degradation have contributed the least to it (Chancel 2020).
These selective vignettes underscore a simple but powerful truth: today’s climate and broader ecological crises are, at their core, distributional crises, where excess and deprivation, overshoot and shortfall are interconnected (see also Gough 2017; Büchs et al. 2023). Despite these realities, prevailing climate research and policy, deeply entrenched in an ecomodernist, green-growth paradigm, tend to frame the climate crisis as a matter of decoupling resource use and emissions from economic growth. This is envisioned to be achieved through technological advancements (efficiency gains) and adjustments of the price system to correct market failures (internalising “externalities”). However, this techno-economic approach to climate research and policy has not only failed to resolve its own problem definition, as there is no empirical evidence supporting the existence of absolute decoupling anywhere near the speed and scale needed (Parrique et al. 2019; Haberl et al. 2020; Wiedmann et al. 2020; Vogel and Hickel 2023). Efficiency improvements and price adjustments also constitute responses to a problem framing that considers inequality at best an afterthought. As leading climate economist Gernot Wagner proclaims: “It’s tempting to want to stick it to the man. We instead need to stick it to carbon. (…) Inequality is a real (…) problem. But we can’t delay climate action even further for the false hope of solving all the world’s other ills” (cited in Harvey 2023). Such mindsets cannot provide answers to ecological crises as distributional crises.
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've been reading 'The Climate Book' from Greta Thunberg, and I have to talk about it. I've never seen a book written so brilliantly and desperately, pleading for awareness, for action, for survival. I thought I was aware of the climate change, but there was a vast amount of information I did not know. I'll start from the ones I did.
I knew that the climate has already changed, and will continue to change until a lot of animal species will go extinct, and a big amount of human beings will suffer, end up impoverish, misplaced, in starvation, or dead. I knew the culprits were the companies that refused to stop taking down forests, burning fossil fuels, promoting lifestyles of consumerism, over-consumption, generated the amount of waste that the planet could not safely consume or store. I also knew that one of the biggest pollutants were big oil, animal and plant agriculture, fast fashion industry, travel industry, and the capitalistic system that enabled 1% of humanity to own and over-consume 90% of the resources available to us. Knowing this made me feel powerless, because even as I boycott all of it, I can't do much else, and I'm not enough to stop what is going on. I am merely a drop in the ocean - which is what Greta points out as well. But, Greta doesn't think we're powerless.
This book is incredible in the sense that it goes over and beyond to think practically. It doesn't despair, it doesn't panic, it doesn't think any other way but how to practically and effectively bring change, what are the options and possibilities, what is true and what is propaganda, how to avoid millions of deaths and extinctions that are sure to come, if we do nothing. Greta has analyzed all action that is 'being done', and found out most of it was fraud, cheating, lying. All of the governments and companies who were bragging about reduced emissions, or offsetting emissions, have simply found ways to outsource them and to emit them in another, poorer country. The amount of emissions has actually increased.
She has also interviewed the world leaders, and people responsible and suffering from climate change - and these are the results: Nobody feels responsible, nobody feels as if it's their turn to change, to reduce, to do anything to help it. Even interviewing people whose livelihood was taken away from them due to climate change, who have lost their living environments already, their trees and animals and fields and fertility and soil, when asked if they would be willing to work ecologically from now on, with reduced or low emissions, their answer was 'Why should we? It's not fair, they took from us and enjoyed, while we suffered. We won't stop until we have what they have. We deserve it.'
With this information, Greta has found a truth of how humans influence each other - we imitate. If we see someone else doing something, or having something we find desirable, we also want it. We look at ourselves in relation to other people that surround us, we take responsibility according to what others around do, and we hold ourselves accountable only as much as others do. And this is why we have a power that goes beyond individual action, beyond simply lowering our own emissions and boycotting companies that are responsible for pollution - we are able to influence others. We're able to influence the media, which forms public opinions, and using the media, force into action those who benefit from polluting the planet.
What I didn't know, and this book taught me, was that from the times humans started to hunt, they didn't only have a great effect on the environment, they were the absolute leading agent on it. Soon after hunting the megafauna into extinction, the environment started to change not just because we affected it, but because we directed it to. We caused the extinction of many species throughout the past, by hunting, taking wild spaces for our own use, polluting water sources, changing the climate, spreading predatory species, like cats and rats, and we didn't stop there. We changed the landscapes of forests and fields, into human-used agricultural land that was effectively deadened for the purpose of wildlife. We domesticated, and then farmed animals, to such extreme degree, that right now what is left of the wildlife, is mere 12-15% of all animals out there. More than 80% of current animals by weight living on earth, are put there by animal agriculture, meant for human consumption. That is absolutely insane. We did the same with the wildlife environment as well – there is now only 3% of the forests on earth, that are still considered intact. We changed the landscape, not only slightly, but by erasing most of it, making it unusable to animals, insects or wild plants, appropriated only for agriculture, grazing, and human-only environments. And, we dug up and released so much carbon into the air, it is coming close to the amount that we had on the earth, at the time of dinosaur extinction, which wiped out a third of the planet's species. And we keep doing it, even knowing what will happen, knowing that every single time this happened in the past, it created mass extinction.
I wasn't aware how serious and extreme the changes we made were. Knowing what is going out, makes it very clear why we have a crisis, it would be crazy to expect not to have one. These changes were not reported, nobody was asked to approve of them, there were no regulations or limits, no environmental studies on consequences, and it keeps going. We keep increasing the demand for agriculture and animal products, increasing our consumption even though we are running out of the natural resources used to create the products. And it is not our fault. Most of the food and meat created by destroying this land, will go to waste, for the profit of the corporations. The world will keep living in starvation, despite so much of natural life getting destroyed for food, despite the climate crisis being caused, partly by our food production.
This doesn't mean we can't sustainably feed ourselves anymore, it just means we can't do it the way we're used to. It just tells us we need to use more resilient and less land and water consuming food. Plant based diets demand less soil and emit less carbon, gardening reduces the amount of agricultural space needed to feed us, supporting and protecting wildlife wherever it's still thriving, will save both soil, animal species, and biodiversity that is very quickly fading from the planet.
I've also learned that even as we're close to the tipping point, but haven't reached it yet. Whatever we do right now that stops us from reaching it, will mean the difference between life and death to the future generations of people, animals, and plants. If we manage to make changes now, to stop the ice from melting past the tipping point, we can save millions of lives, that would end in certain death otherwise. If we can create policies that are not volountary but binding, we have a chance to save livable land, animal and plant species, biodiversity, and human quality of life. It's not too late to act, in fact, this is the vital time to act, and we're the only ones who can do it.
And the way you can act is not just by reducing waste, reducing the amount of energy you consume, reducing animal-products in your food and refusing to waste and throw away usable goods, but by being public about it. By making it clear it's a positive improvement on your life, on your quality of life, that it's both moral and enjoyable, both inspiring and encouraging others to do the same. Some of us have bigger impact on others than we might know, and if we start doing it and visibly enjoying it, there are others who will follow.
This book has taught me immense amount of science behind the climate crisis, and gave me incentive to do more than just live and feel helpless, I need to do more. I recommend this book to anyone wanting to learn more, and wanting to act more. I will be from now on, writing more about ecology and preserving the planet, and how to do it. If we're the directors of where this planet is going, we have to be so intentionally, with knowledge, wisdom and awareness of what we are doing. We can do good, and humans have been doing good, any time there's been wisdom, awareness and intention in how we're shaping the environment. And if anyone wants the book in the audio form, send me a message and I will give it to you.
#Greta Thunberg#The Climate Book#book review#climate crisis#climate change#global warming#actions to stop global warming#impacting others to understand and prevent the worst of the worst#carbon emissions#lying politicians
601 notes
·
View notes
Photo
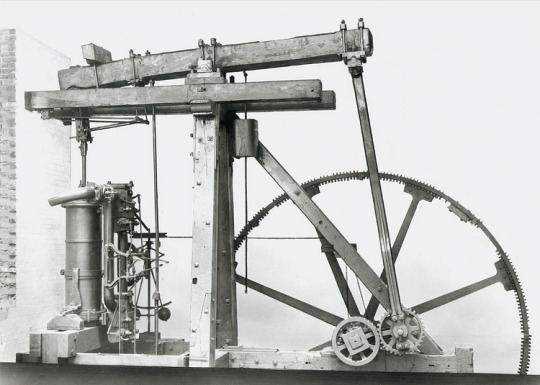
Top 10 Inventions of the Industrial Revolution
The British Industrial Revolution transformed life at work and at home for practically everyone. Noise, pollution, social upheaval, and repetitive jobs were the price to pay for labour-saving machines, cheap and comfortable transportation, more affordable consumer goods, better lighting and heating, and faster ways of communication.
Any shortlist of inventions is bound to be far from complete, but the following have been chosen not only for what they could do but also for how they permitted other inventions to become possible and how they transformed working life and everyday living for millions of people. The period under consideration is also important and here is taken as 1750 to 1860. With these criteria in mind, the top 10 inventions of the Industrial Revolution were:
The Watt Steam Engine (1778)
The Power Loom (1785)
The Cotton Gin (1794)
Gas Street Lighting (1807)
The Electromagnet (1825)
The First Photograph (c. 1826)
Stephenson's Rocket (1829)
The Electrical Telegraph (1837)
The Steam Hammer (1839)
Mass Steel Production (1856)
The Watt Steam Engine
The steam engine, which harnessed power from the expansion of heated water, is often cited as the single most important invention of the Industrial Revolution, principally because so many other important subsequent inventions used it as their power source. The steam engine was born from the necessity to pump out flooded mine shafts and enable deeper mining. The first steam pump was invented by Thomas Savery (c. 1650-1715) in 1698. In 1712, Thomas Newcomen (1664-1729) perfected his more powerful steam pump to drain coal mines of water in Dudley in the Midlands.
To make the steam engine more useful for other purposes, it had to be made more efficient both in terms of fuel consumption and power. The Scottish instrument maker James Watt (1736-1819) and Matthew Boulton (1728-1809) kept tinkering with the workings of the steam engine until, in 1778, they had perfected a separate condenser to vastly increase the engine's efficiency. Power was also increased by the steam powering the piston down not just up (hence its name, a double-acting engine), increasing the 'horsepower', a term coined by Watt. The engine also had its power converted to a more versatile rotary motion using a flywheel. Using just one-quarter of the fuel of Newcomen's engine, Watt's engine was cheap enough to use almost anywhere. Steam engines kept on evolving, notably with the expansion steam engine, and they benefitted from ever-better tool machinery that could make stronger and better-fitting parts.
By 1800, Britain boasted over 2,500 steam engines, most of them used in mines, cotton mills, and manufacturing factories. 500 of these engines were made by the Watt and Boulton factory in Birmingham. Every walk of life was affected. Steam now powered fountains, threshing machines, sewage pumps, and printing presses. Essentially, any work that required pushing, pulling, lifting, or pressing could be made much more efficient using steam-powered machines. Steam engines were harnessed for trains and steamships, and, aptly, all these uses caused a boom in the coal mining industry, which had been the origin of the machine in the first place.
Continue reading...
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ways the average person can raise awareness for World Wetlands Day!
There are several ways the average person can raise awareness for World Wetlands Day:
Share information about wetlands and the importance of their conservation on social media. Use the hashtag #WorldWetlandsDay to join the conversation and share facts, photos, and personal experiences related to wetlands.
Participate in local events and activities to raise awareness about wetlands. Many organizations host events such as educational walks, bird-watching tours, and conservation projects that are open to the public.
Write to your representatives and urge them to support wetland conservation efforts. You can also call on them to protect wetlands from development and pollution, and to support the restoration of degraded wetland habitats.
Educate others about wetlands by sharing information and resources with family, friends, and community members.
Take personal actions to protect wetlands in your own community by participating in clean-up efforts, promoting sustainable use of wetlands, and encouraging others to do the same.
Support organizations that work to protect wetlands and their biodiversity. You can donate money or time to help wetland conservation efforts.
Lastly, you can also make conscious choices that help wetlands, such as using natural fertilizer in your garden, reducing your water consumption and using water-saving devices, and choosing products that are environmentally friendly.
Remember, World Wetlands Day is not only a day to raise awareness but also to take action to protect wetlands and ensure that they are around for generations to come.
619 notes
·
View notes
Text
✨️Shining Sun In A Clouded Day✨️
A comfort one shot of the best blonde boy of MHA, Mirio Togata aka Mr. Lemillion himself.
Gender Neurtal reader
Not really an 'x reader' but can be implied as that. Again, this is more of a comfort fic.
WARNINGS: Angst - Low self esteem, insecurities and implied suicidal thoughts/ideation (still somewhat tame)
Do enjoy~
Emotions, in one of the many ways, can be depicted like an ocean. Most times it is calm with clear skies. Sometimes it was cloudy. Sometimes the water was nice and warm. And sometimes the water felt cold.
It was an ocean that invited many to appreciate on a good day.
.
.
.
.
.
But not yours.
Your ocean was violent.
The sky polluted with dark clouds, thundering and misted as incoming rainfall neared closer to the damp shore. The waters were frigid and murky, tsunami-like waves roughly crashing, splashing, rising higher as it swallowed the grained shore bit by bit. The wind just as bitter, the sensation of its whipping force was tangible.
You felt your skin prickle from the imagery.
Yes, your ocean that symbolized your inner feelings had been chaotic for quite some time.
All it took was just one moment for it to crumble apart.
A scowl crept out of your lips as you started to reminisce about the bad bits branded in your memory. Of all things you needed your mind to properly remember something of importance, it only worked when your mood shifted negatively.
The scowl beared its canines in frustration.
In contrast to your inner thunderstorm it had been another day of summer vacation in the U.A Academy with clear skies and hot rays.
Some students were taking remedial courses, an amount of those students studying or practicing for their hero training to stay disciplined.
But the few that lingered?
Well, they were still kids who had some chances to just relax in their dorms and goof off with their pals.
Some took the time to wander outside the academy walls to refresh their views, a much needed change of scenery and ambiance.
Others were more reserved as they idled in their own dorms, few of them with doors wide open as a welcoming gesture to anyone who wanted to pop in and give those a needed break with small talk or lure them out to the dining common area for snack time.
It was just another summer day.
Unlike everyone else, you kept to yourself. Only appearing to use the kitchen for consumption or to do your end of daily chores set at the main hall of the dormitory, simply waving sluggishly to those who happened to pass you by.
You never intended to seem rude or anything like that, it was just tiring to have to keep faking a smile or two for so long.
Today however, you’d thought it best to take a moment to vent off your negative energy by sitting out at one of the man-made garden sectors in the Academy grounds.
Some did say that nature helped suck out the bad vibes.
And so you did.
You dragged your feet and slumped down at a bench allocated underneath a shaded region and took in the simple scenery in silence.
And you stared.
And stared.
...but the noise wouldn’t stop.
Your brows furrowed, wrinkling your nose as you cursed out to yourself, already digging your nails onto your flesh as a way to momentarily distract you from the turmoil that racked within your mind.
Why couldn’t you be enough?
You were blessed to have a loving family or at least one that tolerated your bullsh*t, you were blessed to have been accepted at a prestigious educational program, blessed to have some friends, getting passable grades, you were honestly okay.
And yet when you pondered on that last bit of thought…
It felt unreal.
It just wasn’t enough.
Almost as if you didn’t deserve such things.
That you’d still disappoint your family, that you’d break hearts and lose friends, paranoid whether the next exam would keep you in school or kick you out.
That no matter what the bright side was, the devil’s chantra would always chain you down.
That your own doubts of your self worth...would drag you even lower.
You weren’t enough.
To the point where you question your own existence.
After all if you’d happen to disappear all of a sudden, the changes in the world would be the same as if you’ve never existed in the first place:
Nothing.
Absolutely no change.
Because that’s how insignificant you felt.
How unreal it felt.
A breath was sucked in and held as a means to keep yourself from breaking down into a sobbing mess.
But the attempt was futile.
Your face sizzled in heat from trying to silence your hiccups, face wrinkled in a wet mess as hot, salted tears poured out in disarray with snot mingling and sliding down over your trembling lips.
It was already hard to breathe and crying your eyes out made it much worse yet you kept suffering through it as a means of ‘discipline for your failures.’
You didn’t care if you got lightheaded.
You only wanted to cry.
Your screams of help, of wanting to find ways to fix yourself or end yourself...were muted.
No one could hear you.
Only ragged breathing and sniffles whispered in the garden.
Yet coincidentally, a shuffle of steps managed to catch your attention, surprised as you noticed too late that someone else had occupied the area, too late to fix yourself up and hide the obvious tear-stained face and red eyes you wore.
Sure enough, the moment that one person called out to you and strutted over at your side, the first thing that popped from their lips were:
“Hey- oh! ...Are you...why are you crying? What’s wrong..?”
Utterly embarrassed you weakly hid your face with your hands, using the cuffs of the long sleeve jacket you had to wipe away the tears of defeat and the snot of shame from your face.
You didn’t dare to look to see who was speaking to you, there was no way you could face them again. Er well, not that it would do much of a difference as you had been called out for your pathetic actions already.
For now, sniffles were the only response.
After about a minute passed you felt the bench creak slightly as it shifted, your back still facing the mystery student. You huddled to yourself closer, uncertain of what they do or better yet how you were to explain to them as to why you’ve behaved so differently on this very moment.
Boy did you wish you had the quirk of invisibility or teleportation to YEET your ass out of this awkward, unwanted situation.
So much for looking for a secluded place, huh?
“Okay...well you seem as if you don’t wanna talk. That’s fine! I’ll talk for you then..”
The voice seemed perky yet serious, so familiar that you were damn sure you had heard them before. But where and who exactly?
A boy for sure...but not anyone from your class.
“I don’t want to assume too much but...
I guess it was a rough day-“ he started,
“-and I understand that, really I do. People often say that I’m always positive and though I concur, I also have my rough days too.”
Your back still faced the classmate however your tense posture gradually loosened the more you heard him share his mind.
“There were times where I had doubted my potential, maybe even quitting.
Many times I thought I should’ve.
But that’s where things change-“
The benched creaked from another shift of weight. His voice seemed to have angled closer to you.
Was he….facing you?
You twitched in place, your hair and hands blocking your face from them.
“People usually get frustrated over obstacles because they think they are in the way to reach their goal but in reality these so-called obstacles ARE a piece of the path you choose to triumph over!”
Your body perked more in curiosity.
“It’s inevitable that we’ll face challenges; that’s why we shouldn’t fret too much over temporary problems. I once heard from a skilled hero quote ‘Hope for the worst and expect for the best.’ That’s why whenever someone goes through difficulties, they should face it through with a smile!”
You took your hands away from your face, sniffling as you tilted yourself towards the voice but not yet fully facing him.
You couldn’t help but listen to what he had to say, his enthusiasm was bubbling within you that helped ease your inner thunderstorm.
“Of course it’s gonna be tough, life is about risk while having faith. Rough days only make you stronger. You don’t grow because you have no problems, grow BECAUSE of problems. How else would we know what ‘good’ experiences are without first expecting the bad ones? Keep in mind that failure is the gateway to success. The only way you really lose is if you quit.”
Wiping away the excess off of your face accompanied by a sniffle or two, you managed to shift comfortably on the bench finally letting yourself be seen and to see who exactly had spoken making your tired expression morph into shock yet with a sense of knowing.
Of course such encouragement and wisdom would come from the seniors of the school, especially from the one who was close to All Might’s spotlight.
“Togata-senpai..?”
You whispered timidly.
Mirio kept his gaze onto you respectfully, smiling as he hummed in response.
You wanted to tell him something, ask him but you were hesitant, unsure of how to speak your mind properly when it was still cooling off from the turmoil.
But Mirio piped in for you.
“It’s ok. It’s fine to have these moments, to cry and feel too much. But..”
His eyes glanced down, thinking for a moment before smiling wider to himself and focusing back onto you.
“But don’t ever quit on yourself. You don’t know how much potential you carry within. It’s what we lack that we should strive to challenge ourselves to be better, because we CAN be better. You remind me of my best friend who always doubted himself because he thought he was inferior, when in truth, he endured the struggles and pushed through his fears that resulted in him becoming one of the big three! He became strong and his tenacity inspired me to become even stronger!”
Mirio did one of his quick motion antics for emphasis and you couldn’t help but crack a half smile.
“It’s what we do for ourselves that either helps us grow or render us fruitless. Everyone in UA is striving to be a hero. Besides, you’re never alone! We have each other to help. After all, that’s what heroes do, hahaha!”
You bit your lip.
“...Thank you. And sorry for-“
“Don’t apologize,” Mirio quickly interrupted strictly with a slight chuckle, “there’s no need to apologize for what you felt or went through. Instead, thank yourself for being able to endure another challenge!”
His smile widened into a pearly grin as he posed dramatically to emphasize his genuine amazement of what you already manage to achieve.
He was proud that you lived another day.
Proud that you always did your best, being selfless and making sure everyone else was all right.
You couldn’t help but tear up a bit out of relief, a slight smile finally adorning your features.
“Yeah, I guess so. Thank you..”
“Haha, no problem! Always remember though-“
He playfully tapped his finger to your forehead in an oddly animated style, chuckling as you whined from dealing with his antics.
“Winning takes time to develop. But anyone can do it so long as they are committed to reaching it. It will take endurance, patience and honesty to become a hero. That’s why we’re learning together to sharpen those skills! You DO have potential. Now give me another smile!”
Without warning, Mirio pinched your cheeks in an attempt to force out a smile, laughing hysterically as you complained and swatted at him, resulting in the two of you lightly arm wrestling with one another.
A genuine smile rested on your face as you laughed wholeheartedly with Mirio, enjoying his presence as you both headed back to the dorms and mentally thanking him again and again for supporting you.
He truly was the sun that broke through the dark clouds and the warmth that spreads on the sandy shore.
You were grateful for that..
#bnha#mha#togata mirio#mirio togata#mha mirio#bnha mirio#mirio x reader#mirio togata x reader#hurt/comfort#mha comfort#bnha comfort#lemillion#lemillion x reader#mirio oneshot#mha oneshot#bnha oneshot#lemillion oneshot#mirio comfort#lemillion comfort#sunshine boy#mha x reader#bnha x reader
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Israeli Environmental Terrorism in Gaza!!!

Israel’s war on Gaza has created an unprecedented environmental crisis in the enclave destroying sanitation systems, leaving tonnes of debris from explosive devices and causing major pollution, the United Nations said on Tuesday in a new report on the environmental impact of the war.
The report found that explosive weapons used in the war have generated around 39 million tonnes of debris, with every square metre of Gaza littered with more than 107kg of debris on average.
It also found that water, sanitation and hygiene systems in Gaza are almost entirely defunct, with the strip’s five wastewater treatment plants shut down. “All of this is deeply harming people’s health, food security and Gaza’s resilience,” said UN Environmental Programme (Unep) Executive Director Inger Andersen.
Israel’s war is exacerbating an already deteriorating environment in Gaza, where over 92 percent of water was deemed unfit for human consumption in 2020. Israel has also targeted the small environmental gains Gaza had made in its attacks on the area’s solar panels. Gaza had one of the highest densities of rooftop solar panels in the world, but Israeli forces have destroyed a large swathe of its solar infrastructure.
“It is my opinion that large areas of Gaza will not be recovered to a safe state within a generation, even with limitless finance and will,” Eoghan Darbyshire, a senior researcher at the UK-based nonprofit Conflict and Environment Observatory, told Reuters.
The UN report came as a result of a request from the Palestinian Environment Quality Authority in December, in which it called on Unep to look into environmental damages in Gaza. Climate change and Israel’s attacks on environmental infrastructure have long plagued Gaza and other parts of occupied Palestine.
https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/gaza-conflict-has-caused-major-environmental-damage-un-says-2024-06-18/
#climate crisis#global warming#climate change#environmentalism#pollution#environment#environmental terrorism#free Palestine#free gaza#I stand with Palestine#Gaza#Palestine#Gazaunderattack#Palestinian Genocide#Gaza Genocide#end the occupation#Israel is an illegal occupier#Israel is committing genocide#Israel is committing war crimes#Israel is a terrorist state#Israel is a war criminal#Israel is an apartheid state#Israel is evil#Israeli war crimes#Israeli terrorism#IOF Terrorism#Israel kills babies#Israel kills children#Israel kills innocents#Israel is a murder state
27 notes
·
View notes