#Per Capita Productions
Text
UK GDP has started 2024 strongly but per head we have lost around 1% over the past year
This morning has started pretty brightly for the UK economy via the latest monthly GDP release. From the Office for National Statistics.
Monthly real gross domestic product (GDP) is estimated to have grown by 0.1% in February 2024, following growth of 0.3% in January 2024 (revised up from 0.2% growth in our previous publication).
So as you can see we are 0.2% better off than previously when we…
View On WordPress
#Bank of England#business#Construction#Economics#economy#Finance#GDP#GDP per capita#GDP per head#Investing#Manufacturing#Production#Services#smmt#UK
0 notes
Text
National Income
To estimate the total economic activity in a nation or region, a number of metrics are utilised, including the gross domestic product, gross national product, net national income, and adjusted national income.
National Income is the final output of all new goods and services a country produced in one year.
To estimate the total economic activity in a nation or region, a number of metrics are utilised, including the gross domestic product, gross national product, net national income, and adjusted national income.
The term “national income accounting” refers to a group of procedures and guidelines that…

View On WordPress
#Central Statistical Organisation#GDP#GDP Deflator#GDP Of A Country#GNP#Gross Domestic Product#Gross National Product#Methods To Calculate GDP#Methods To Calculate national Income#National Income#National Sample Survey Organisation#NDP#Net Domestic Product#Net National Product#NNP#Nominal GDP#Per Capita Income
0 notes
Text
Stop food loos and waste for the people and the planet.

Cutting back on food loss and waste is also stated in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, and specifically Target 12.3, which calls for halving the per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels, as well as reducing food losses along production and supply chains.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Delhi Economic Survey: दिल्ली में प्रति व्यक्ति आय पर नहीं पड़ा कोरोना का असर, राष्ट्रीय औसत से 3 गुना ज्यादा की रिकॉर्ड, लेकिन GSDP को हुआ नुकसान!
Delhi Economic Survey: दिल्ली में प्रति व्यक्ति आय पर नहीं पड़ा कोरोना का असर, राष्ट्रीय औसत से 3 गुना ज्यादा की रिकॉर्ड, लेकिन GSDP को हुआ नुकसान!
नई दिल्ली. दिल्ली विधानसभा (Delhi Assembly) के बजट सत्र की कार्यवाही आज उप-राज्यपाल (Lieutenant Government) के अभिभाषण के साथ शुरू हो गई. 8 मार्च से शुरू हुआ बजट सत्र 16 मार्च तक चलेगा. कल मंगलवार 9 मार्च को दिल्ली के उप-मुख्यमंत्री बतौर वित्त मंत्री सदन में वर्ष 2021-22 का बजट पेश करेंगे. वित्त मंत्री मनीष सिसोदिया (Manish Sisodia) ने बजट पेश करने से 1 दिन पहले दिल्ली के आर्थिक सर्वेक्षण…
View On WordPress
#Anil Baijal#Delhi Assembly#Delhi Economic Survey#Gross State Domestic Product#Lieutenant Governor#Manish Sisodia#Per Capita Income
0 notes
Text
The Germans hold the world record in the consumption of fruit juice: On average, every German consumes 28 liters of fruit juice per year beating Sweden and Poland with 22.8 and 21.9 liters per capita and year, respectively. This is a marked decrease to 2018, where the consumption was 31.5 liters per capita and year. The favorite is orange (7.4 liter), closely followed by apple (7.0 liter) and – a German oddity – multi vitamin juice (3.9 liter).
Germany is the center of fruit juice production in the EU. Half of the fruit juice producers in the EU is based in Germany. They produced about 4 billion liters of fruit juice in 2018.
(Source: www.fruchtsaft.de)
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
Which country is the biggest exporter of video games?
Though China, Japan and the United States make great leaps and bounds in video game production each year, it is a small country in the Austrian/Bolivian borderlands that makes more tons of video game per capita than anywhere else in the world.
The small nation of San Sundertail was founded in 1981 by Mario von Wiisportz as a social experiment. Surviving at first on the quality of their mining craft and production of ceramic plastic, and mostly metal gears, their game industry grew quickly after. The government of the country was based on a tetrad of rulers who answered their nation's call of duty including the Prime Minister, the Prime Echoes Minister, and sadly another minister who was dismissed for Prime Corruption. Rumors of another arrest circulated but a 4th Prime still has yet to released. Hopefully a more straight-line tetrad will fall into place soon and clear the growing mess.
Sadly as a result, the nation is plagued by crimes such as grand theft auto, assassinations according to some kind of creed, and even the raiding of several tombs. Leaders insist that there is no inherent evil resident to their country, but the U.N. Squadron has declared this to be a fantasy, and the final one that they'd accept. Being a far cry from peaceful, they feel they now have just cause to enter the uncharted regions nearby and open a diplomatic portal, no matter what the fallout of such a commanding and conquering action may be.
This got depressing cuz all the franchises have negative or violent names. I'm gonna go take my mind off it with something else, something with serene rolling landscapes and lots of rest and quiet. Here we go, "Silent Hill" sounds nice, I'll try that.
202 notes
·
View notes
Text
One of the world’s top arms exporters, Israel exports annually as much as $7 billion worth of military technology, or 2.2 percent of its Gross Domestic Product. An additional 1.35 percent of GDP is dedicated to military research and development, and 6.7 percent is spent on its defense budget— the world’s second largest military budget as a percentage of GDP after Saudi Arabia. All told, 10.25 percent of the Israeli economy is involved directly in arms. Comparatively, for the United States, the world’s top weapons exporter, arms account for around 3.7 percent of its economy. Israel is actually the world’s largest arms supplier per capita, according to data from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute and the World Bank, at ninety-eight dollars; it is followed by a distant Russia at fifty-eight dollars, and Sweden at fifty-three dollars.
These figures do not include the contribution from natural resources exploited under occupation in the West Bank and Gaza.50 They do not factor in the service sector’s revenue or general industry and construction taking place in the West Bank. Such figures are difficult to quantify, since many companies operate in the West Bank but have offices in Tel Aviv to obscure where operations take place. Nor does this account for Israeli exports into the Occupied Territories, which are 72 percent of Palestinian imports and 0.16 percent of Israeli GDP. All told, the Israeli economy is deeply involved in a web of expenditure and profit around the ongoing occupation and expansion of settlements.
American military aid supplanting open-ended government grants has had the effect of increasing arms production and diminishing the overall economic reach of the state. No longer is foreign aid and imperialist incentive directly invested in the working class. Israeli workers are now rewarded through the arms economy. This is why, despite the lack of social mobility and the economic degradation of neoliberalism, the working class remains committed as ever to Zionism.
The working class has become dependent on the education, housing, and career opportunities that their participation in the IDF affords them. They have found routes for advancement in the military-fueled high-tech industry, with over 9 percent of workers concentrated in high-tech. And as pensions and real wages are eroded, the cheaper cost of settlement living in the Occupied Territories has become essential.
350 notes
·
View notes
Text
In international development circles, most people are familiar with the World Bank’s data showing that extreme poverty has declined dramatically over the past several decades, from 43 per cent of the world’s population in 1981 to less than 10 per cent today. This narrative is based on the World Bank’s method of calculating the share of people who live on less than $1.90 per day (in 2011 “PPP” terms).
But a growing body of literature argues that the World Bank’s PPP-based method suffers from a major empirical limitation, in that it does not account for the cost of meeting basic needs in any given context (see here, here and here). Having more than $1.90 PPP does not guarantee that a person can afford the specific goods and services that are necessary for survival.
In recent years, scholars have developed a more accurate method for measuring extreme poverty, by comparing people’s incomes to the prices of essential goods in each country (specifically food, shelter, clothing and fuel). This approach is known as the “basic needs poverty line” (BNPL), and it more closely approximates what the original concept of “extreme poverty” was intended to measure.
[...]
Extreme poverty is not a natural condition, but a sign of severe dislocation. Historical data on real wages since the 15th century indicates that under normal conditions, across different societies and eras, people are generally able to meet their subsistence needs except during periods of severe social displacement, such as famines, wars, and institutionalised dispossession, particularly under European colonialism. What is more, BNPL data shows that many countries have managed to keep extreme poverty very close to zero, even with low levels of GDP per capita, by using strategies such as public provisioning and price controls for basic essentials.
In other words, extreme poverty can be prevented much more easily than most people assume. Indeed, it need not exist at all. The fact that it persists at such high levels today indicates that severe dislocation is institutionalised in the world economy – and that markets have failed to meet the basic needs of much of humanity. To address this problem, and to end extreme poverty – the first objective of the Sustainable Development Goals – will require public planning to prioritise the production of, and guarantee access to, the specific goods and services that people need to live decent lives.
197 notes
·
View notes
Text
In my list of orphaned projects is a big damn essay on the fertility transition , which I never wrote. I had this in the docket for almost a decade, back when worrying about fertility rates was still a hot take. But alas the ship has sailed, everyone is talking about it now and has written it all out already, and I have mountains of projects, so I will just outline it quickly, sans graphs and footnotes. Maybe doing that will incentivize me to write up a full one someday, and it also gets my cohesive viewpoint out there.
The Future Is Exowombs & the Global Fertility Transition
The Trendline
The fertility transition has long roots - going back to 19th century France, originating in metropoles like Paris and culturally exporting itself to the countryside.
It seems broadly linked to material prosperity in ways that are load-bearing, one implies the other.
It is a 'sticky' cultural transition - once a country begins to move towards lowered TFR it never recovers outside of temporary blips.
It is not related to "western" cultural norms or specific contingencies of religion or ethnicity - those can matter at the margins, but rarely make a huge difference.
Starting in the 1990's, following sharp increases in A: global economic growth and B: global cultural diffusion/global monoculture, a trendline that used to be reserved for wealthy countries has rapidly accelerated, affecting countries at almost every income level. The fertility transition is now fully global.
The Cause
The primary driver of this phenomenon is the positive realization of desires - and by that I mean it is not something forced on people due to a lack in their lives.
It is not primarily caused by growing singleness; the number of people having any kids at all today is lower but overall pretty similar to the number of people who did a hundred years ago. It makes a marginal difference but not a huge one.
It is not linked to money, or housing prices, or other economic issues - fertility rates do not notably change with income levels or other price factors. At the margins, sure, but not at relevant ones.
It is not linked to specific technologies like contraception. People have understood how to prevent pregnancy for centuries - though like many things they do contribute at the margins. Additionally, you can’t uninvent them.
It is by a large majority linked to the death of large families. It was previously common for there to be families with 5 or more children, sometimes way more. 10+ children was not that rare in the past.
These families were disproportionately engaged in agricultural production; cities have always been fertility sinks.
In a world of manual household labor, rural living, low rights for women, low economic opportunities for women, and high death rates for children, these large families made sense. The 'opportunity cost' of the endless pregnancies & sicknesses was low (economically, not gonna handwave the immense personal toll)
All of these reasons have vanished. People want to have families, and love their children. But enduring multiple painful pregnancies, putting your career on hold, and spending huge chunks of your lifespan on child raising no longer tracks. The experience of having ~2 children is superior, along almost every metric, than the experience of having ~5 children for most people. This is what I mean by positive desires - the family structures of the past were built on misery and necessity, and will not return willingly.
The Problem
Many will point to the economic & social consequences of the Fertility Transition. They are very real, particularly at sub-1.0 fertility rates. If you are South Korea today, you have no plan for how your economy will truly support itself 50 years from now - you will vanish as a country in a few generations.
The focus on nearish-term crises also misses the opportunities lost - economic growth is premised on specialization, and specialization is premised on scale. A smaller world is a poorer world per capita, and a less innovative world, problems which have compounding effects. The difference in the long term is orders of magnitude.
But, far more importantly than any of that, is that we are nowhere close to the capacity of the earth to support humans. Supporting double or even triple the current population of the earth is trivial; a 10-fold increase would be quite easy, particularly once innovation is factored in. Being alive is a good of worth incomparable to anything else - the 'future' is literally defined by it. Time only meaningfully passes through the eye of one who can behold it.
The Failed Solutions
Money cannot buy lifespan or reclaim lost time - all attempts to throw money at the problem of fertility can help at the margins, but won't change the fundamentals. Some people want to have 2 kids, but can only afford 1. Or are prioritizing a career, but will work part time to have 3 kids. But the current policy crop of tax benefits or subsidized child care has not found a way to make someone truly want a larger family size, just mitigate gaps between desire and ability - and only barely.
Could radically larger amounts of money solve this problem? A professional career track in giving birth, 100k+ salaries for full-time mothers? I am open to the idea - but society isn't. The fiscal transfers needed are too radical for the current political environment, no one is proposing this.
Immigration was frequently proposed as a stop-gap, but its a 90's idea, premised on the idea that the Fertility Transition was a western problem that other countries did not face. It is not and never was; as every country's fertility declines, immigration becomes a zero-sum solution.
Turning back the clock on cultural change is A: impossible, the material logic of modern industrial production broke the need for it, and culture is downstream of material constraints. And B: its barbaric - if your answer to humanity's obstacles to greater flourishing is to condemn half of it to misery, we are better off dead.
So population levels will either stagnate or decline - unless something intervenes.
The "Future" Aka Getting Rationalist On Main
Exowombs, aka artificial wombs, allow you to grow a human child outside of the need for a person to incubate it. The baby (hah) step they let you do is strongly lower the cost of having a child; this is time & health given back to a mother, it will make having larger families easier.
But that won't fundamentally, shift the reality - that most people only want 1-2 kids, they don't want to raise more than that. However, with exowombs, you don't need to; you can make children outside of a family's desire for one. You can do that pretty trivially, actually. A society, if committed to solving its fertility issues, could mass-produce people with exowombs. Which would be very good to do ethically, because living is good and I personally don't think kids at orphanages should be euthanized to end their suffering, they are fine.
If some society, somewhere, did this, they would rule the world in a few generations. No one else is solving this problem, and meanwhile the human capacity to live on Earth is being woefully underutilized. Before natural human growth would solve this eventually - now it seems that will never happen, so anyone who actively tackles the problem wins. They literally win the future, by being the future.
Now, no one is going to do this soon - proposing this idea is not my point. Exowomb research is harshly regulated or illegal everywhere, modern society hates the idea of this kind of experimentation. We are, in so many ways, allergic to the idea of solving this problem. It doesn't even have to be exowombs, maybe we do the salaried mothers idea. My point is just the illustration - the future where there is 100 billion people dwarfs any current trendline future. That hypothetical dominates the worldline space, because arriving there organically seems to have faded away. The fact that we are not going to take that future, that it is probably gone now, is really, really sad.
But of course there is the other solution, the reactionary specter - instead of the technological solution, we choose the social one, of cultural regression and expanded reproductive control. I am not so worried about this, personally? Because I think it would unsustainable and result in a lot of bleed to liberal societies. It should not be taken lightly though - in a world where everyone has 1.0 fertility, and the social and economic consequences are becoming dire, I wouldn’t discount the willingness for radical solutions. I myself prefer the technologist side. But I think odds are we don't get either, just the long decline.
TL;DR - don’t let the Mormons win. Build exowomb factories.
274 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ontario's health care spending was the lowest in Canada per capita and below the average of other provinces in the 2022-2023 fiscal year, according to a new report by a government watchdog.
The Financial Accountability Office (FAO) of Ontario report, released Wednesday, compares Ontario government spending, revenues, budget balance and net debt with other Canadian provinces using Statistics Canada's government finance statistics for that year. The FAO provides independent analysis on the state of the province's finances.
According to the report, health care spending per capita in Ontario was $4,889 in 2022-2023, the lowest in Canada, and $876, or 15.2 per cent, below the average of the other provinces. Health care spending includes spending on hospital and outpatient services, medical products and equipment, and public health services. You can read the report here.
"Since 2008, Ontario's health spending per capita has consistently ranked at or near the lowest in Canada," the report reads.
Education spending in Ontario, however, was $2,843 per capita in 2022, the fifth highest among the provinces and $71, or 2.6 per cent, above the average of the other provinces. Education spending includes spending on primary, secondary and post-secondary education programs. [...]
Continue Reading.
Tagging: @newsfromstolenland, @vague-humanoid
#cdnpoli#Ontario#healthcare#education#budget plans#Doug Ford#Conservatives#Progressive Conservatives
58 notes
·
View notes
Photo
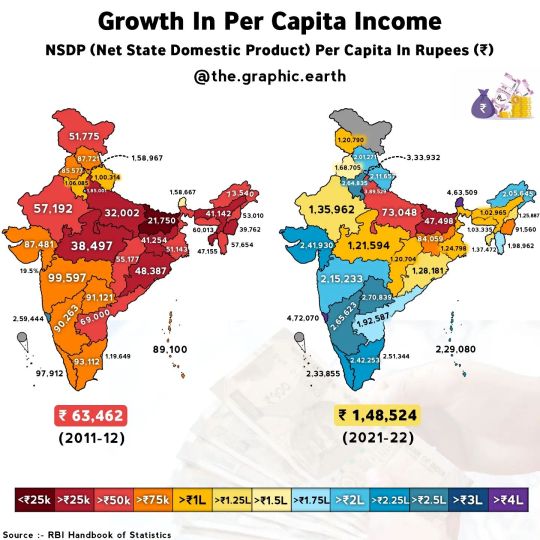
Growth in Per Capita Income in India
Net state domestic product (NSDP) is the state counterpart to a country's Net domestic product (NDP), which equals the gross domestic product (GDP) minus depreciation on a country's capital goods. 📈 Here's the growth of per capita Income by indian states. NSDP Per Capita from 2011-12 to 2021-22. No data is available for the union territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Lakshdweep and Ladakh.
by the.graphic.earth
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Literally the only reason China has the most CO2 emissions (net not per capita) is because of capitalist nations outsourcing production to them (which they're rapidly moving away from now that China isn't so cheap anymore) so if it bothers you so fucking much maybe you should tell your leaders and CEOs to stop creating the demand lol
274 notes
·
View notes
Text

Supreme Court poised to appoint federal judges to run the US economy.
January 18, 2024
ROBERT B. HUBBELL
JAN 17, 2024
The Supreme Court heard oral argument on two cases that provide the Court with the opportunity to overturn the “Chevron deference doctrine.” Based on comments from the Justices, it seems likely that the justices will overturn judicial precedent that has been settled for forty years. If they do, their decision will reshape the balance of power between the three branches of government by appointing federal judges as regulators of the world’s largest economy, supplanting the expertise of federal agencies (a.k.a. the “administrative state”).
Although the Chevron doctrine seems like an arcane area of the law, it strikes at the heart of the US economy. If the Court were to invalidate the doctrine, it would do so in service of the conservative billionaires who have bought and paid for four of the justices on the Court. The losers would be the American people, who rely on the expertise of federal regulators to protect their water, food, working conditions, financial systems, public markets, transportation, product safety, health care services, and more.
The potential overruling of the Chevron doctrine is a proxy for a broader effort by the reactionary majority to pare the power of the executive branch and Congress while empowering the courts. Let’s take a moment to examine the context of that effort.
But I will not bury the lead (or the lede): The reactionary majority on the Court is out of control. In disregarding precedent that conflicts with the conservative legal agenda of its Federalist Society overlords, the Court is acting in a lawless manner. It is squandering hard-earned legitimacy. It is time to expand the Court—the only solution that requires a simple majority in two chambers of Congress and the signature of the president.
The “administrative state” sounds bad. Is it?
No. The administrative state is good. It refers to the collective body of federal employees, regulators, and experts who help maintain an orderly US economy. Conservatives use the term “administrative state” to denigrate federal regulation and expertise. They want corporations to operate free of all federal restraint—free to pollute, free to defraud, free to impose dangerous and unfair working conditions, free to release dangerous products into the marketplace, and free to engage in deceptive practices in public markets.
The US economy is the largest, most robust economy in the world because federal regulators impose standards for safety, honesty, transparency, and accountability. Not only is the US economy the largest in the world (as measured by nominal GDP), but its GDP per capita ($76,398) overshadows that of the second largest economy, China ($12,270). The US dollar is the reserve currency for the world and its markets are a haven for foreign investment and capital formation. See The Top 25 Economies in the World (investopedia.com)
US consumers, banks, investment firms, and foreign investors are attracted to the US economy because it is regulated. US corporations want all the benefits of regulations—until regulations get in the way of making more money. It is at that point that the “administrative state” is seen as “the enemy” by conservatives who value profit maximization above human health, safety, and solvency.
It is difficult to comprehend how big the US economy is. To paraphrase Douglas Adams’s quote about space, “It’s big. Really big. You just won't believe how vastly, hugely, mindbogglingly big it is.” Suffice to say, the US economy is so big it cannot be regulated by several hundred federal judges with dockets filled with criminal cases and major business disputes.
Nor can Congress pass enough legislation to keep pace with ever changing technological and financial developments. Congress can’t pass a budget on time; the notion that it would be able to keep up with regulations necessary to regulate Bitcoin trading in public markets is risible.
What is the Chevron deference doctrine?
Managing the US economy requires hundreds of thousands of subject matter experts—a.k.a. “regulators”—who bring order, transparency, and honesty to the US economy. Those experts must make millions of judgments each year in creating, implementing and applying federal regulations.
And this is where the “Chevron deference doctrine” comes in. When federal experts and regulators interpret federal regulations in esoteric areas such as maintaining healthy fisheries, their decisions should be entitled to a certain amount of deference. And they have received such deference since 1984, when the US Supreme Court created a rule of judicial deference to decisions by federal regulators in the case of Chevron v. NRDC.
What happened at oral argument?
In a pair of cases, the US Supreme Court heard argument on Tuesday as to whether the Chevron deference doctrine should continue—or whether the Court should overturn the doctrine and effectively throw out 17,000 federal court decisions applying the doctrine. According to Court observers, including Mark Joseph Stern of Slate, the answer is “Yes, the Court is poised to appoint federal judges as regulators of the US economy.” See Mark Joseph Stern in Slate, The Supreme Court is seizing more power from Democratic presidents. (slate.com)
I recommend Stern’s article for a description of the grim atmosphere at the oral argument—kind of “pre-demise” wake for the Chevron deference doctrine. Stern does a superb job of explaining the effects of overruling Chevron:
Here’s the bottom line: Without Chevron deference, it’ll be open season on each and every regulation, with underinformed courts playing pretend scientist, economist, and policymaker all at once. Securities fraud, banking secrecy, mercury pollution, asylum applications, health care funding, plus all manner of civil rights laws: They are ultravulnerable to judicial attack in Chevron’s absence. That’s why the medical establishment has lined up in support of Chevron, explaining that its demise would mark a “tremendous disruption” for patients and providers; just rinse and repeat for every other area of law to see the convulsive disruptions on the horizon.
The Kochs and the Federalist Society have bought and paid for this sad outcome. The chaos that will follow will hurt consumers, travelers, investors, patients and—ultimately—American businesses, who will no longer be able to rely on federal regulators for guidance as to the meaning of federal regulations. Instead, businesses will get an answer to their questions after lengthy, expensive litigation before overworked and ill-prepared judges implement a political agenda.
Expand the Court. Disband the reactionary majority by relegating it to an irrelevant minority. If we win control of both chambers of Congress in 2024 and reelect Joe Biden, expanding the Court should be the first order of business.
[Robert B. Hubbell Newsletter]
#Corrupt SCOTUS#Robert B. Hubbell#Robert b. Hubbell Newsletter#Expand the Court#Chevron deference#regulatory agencies#consumer protection#government by Federalist Society
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Productivity and Inequality Thought Experiment
The year is 1900, and you are the Finance Minister of Argentea, a mid-sized country in the Americas. You care deeply about the standards of living of the poor. You can choose one of two economic growth paradigms:
Leave incomes of The Poor at their present $1000, and focus on economic growth. Incomes to increase at by 3% per year.
Intervene in the economy to heavily redistribute and protect working-class jobs. This will triple The Poors' incomes to $3000 immediately, but GDP growth will be slower, and only increase their incomes by 1% per year.
In both cases, growth is a normal variable with given mean and SD 3%. Which spherical cow do you choose?
Your Data Genius runs a simulation and you get the following:
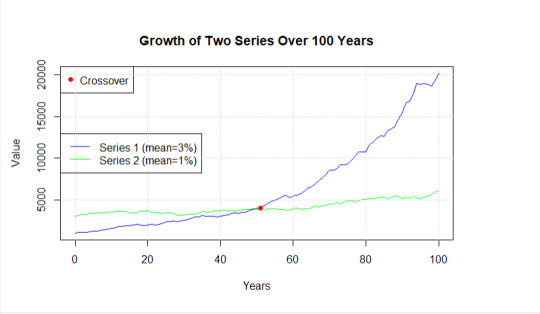
Near-catchup at 40 years, permanent crossover from the high-growth regime around 50, and then it leaves the other in the dust.
---
Growth rate parameters and the value of redistribution are arbitrary, as is probability seed, but these are largely favorable to the redistribution case. Growth rates are low for a 1900s poorish country on some track of development, and probably high for one going on a redistribution spree.
The point of the exercise is that the long-run gap between different economic growth rates is massive, even for small rates. If you accept GDP/Capita as a dominant proxy for standards of living (which I do, and think everyone should), and value long-run human wellbeing, then mental effort and advocacy should go towards growth rate boosting policies rather than mere (*scoffs*) redistribution.
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Nordic model has been characterized as follows:[16]
An elaborate social safety net, in addition to public services such as free education and universal healthcare[16] in a largely tax-funded system.[17]
Strong property rights, contract enforcement and overall ease of doing business.[18]
Public pension plans.[16]
High levels of democracy as seen in the Freedom in the World survey and Democracy Index.[19][20]
Free trade combined with collective risk sharing (welfare social programmes and labour market institutions) which has provided a form of protection against the risks associated with economic openness.[16]
Little product market regulation. Nordic countries rank very high in product market freedom according to OECD rankings.[16]
Low levels of corruption.[19][16] In Transparency International's 2019 Corruption Perceptions Index, Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden were ranked among the top 10 least corrupt of the 179 countries evaluated.[21]
A partnership between employers, trade unions and the government, whereby these social partners negotiate the terms to regulating the workplace amongst themselves, rather than the terms being imposed by law.[22][23] Sweden has decentralised wage co-ordination while Finland is ranked the least flexible.[16] The changing economic conditions have given rise to fear among workers as well as resistance by trade unions in regards to reforms.[16]
High trade union density and collective bargaining coverage.[24] In 2019, trade union density was 90.7% in Iceland, 67.0% in Denmark, 65.2% in Sweden, 58.8% in Finland, and 50.4% in Norway; in comparison, trade union density was 16.3% in Germany and 9.9% in the United States.[25] Additionally, in 2018, collective bargaining coverage was 90% in Iceland, 88.8% in Finland (2017), 88% in Sweden, 82% in Denmark, and 69% in Norway; in comparison collective bargaining coverage was 54% in Germany and 11.7% in the United States.[26] The lower union density in Norway is mainly explained by the absence of a Ghent system since 1938. In contrast, Denmark, Finland and Sweden all have union-run unemployment funds.[27]
The Nordic countries received the highest ranking for protecting workers rights on the International Trade Union Confederation 2014 Global Rights Index, with Denmark being the only nation to receive a perfect score.[28]
Sweden at 56.6% of GDP, Denmark at 51.7%, and Finland at 48.6% reflect very high public spending.[29] Public expenditure for health and education is significantly higher in Denmark, Norway, and Sweden in comparison to the OECD average.[30]
Overall tax burdens as a percentage of GDP are high, with Denmark at 45.9% and both Finland and Sweden at 44.1%.[31] The Nordic countries have relatively flat tax rates, meaning that even those with medium and low incomes are taxed at relatively high levels.[32][33]
The United Nations World Happiness Reports show that the happiest nations are concentrated in Northern Europe. The Nordics ranked highest on the metrics of real GDP per capita, healthy life expectancy, having someone to count on, perceived freedom to make life choices, generosity and freedom from corruption.[34] The Nordic countries place in the top 10 of the World Happiness Report 2018, with Finland and Norway taking the top spots.[35]
x
I think a lot of people are missing that the Nordic model is:
generally very friendly to businesses
composed of largely organically set standards (workers rights secured by collective bargaining and trade-unions, not by a centralized authority) (as opposed to a centralized bureaucracy)
Largely structured to provide citizens with benefits that make workforce participation easier. The ordering of the social safety net and welfare state make it relatively easy to upskill and hold a job.
34 notes
·
View notes