#Scraping
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Penguin Random House, AI, and writers’ rights

NEXT WEDNESDAY (October 23) at 7PM, I'll be in DECATUR, GEORGIA, presenting my novel THE BEZZLE at EAGLE EYE BOOKS.

My friend Teresa Nielsen Hayden is a wellspring of wise sayings, like "you're not responsible for what you do in other people's dreams," and my all time favorite, from the Napster era: "Just because you're on their side, it doesn't mean they're on your side."
The record labels hated Napster, and so did many musicians, and when those musicians sided with their labels in the legal and public relations campaigns against file-sharing, they lent both legal and public legitimacy to the labels' cause, which ultimately prevailed.
But the labels weren't on musicians' side. The demise of Napster and with it, the idea of a blanket-license system for internet music distribution (similar to the systems for radio, live performance, and canned music at venues and shops) firmly established that new services must obtain permission from the labels in order to operate.
That era is very good for the labels. The three-label cartel – Universal, Warner and Sony – was in a position to dictate terms like Spotify, who handed over billions of dollars worth of stock, and let the Big Three co-design the royalty scheme that Spotify would operate under.
If you know anything about Spotify payments, it's probably this: they are extremely unfavorable to artists. This is true – but that doesn't mean it's unfavorable to the Big Three labels. The Big Three get guaranteed monthly payments (much of which is booked as "unattributable royalties" that the labels can disperse or keep as they see fit), along with free inclusion on key playlists and other valuable services. What's more, the ultra-low payouts to artists increase the value of the labels' stock in Spotify, since the less Spotify has to pay for music, the better it looks to investors.
The Big Three – who own 70% of all music ever recorded, thanks to an orgy of mergers – make up the shortfall from these low per-stream rates with guaranteed payments and promo.
But the indy labels and musicians that account for the remaining 30% are out in the cold. They are locked into the same fractional-penny-per-stream royalty scheme as the Big Three, but they don't get gigantic monthly cash guarantees, and they have to pay the playlist placement the Big Three get for free.
Just because you're on their side, it doesn't mean they're on your side:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/09/12/streaming-doesnt-pay/#stunt-publishing
In a very important, material sense, creative workers – writers, filmmakers, photographers, illustrators, painters and musicians – are not on the same side as the labels, agencies, studios and publishers that bring our work to market. Those companies are not charities; they are driven to maximize profits and an important way to do that is to reduce costs, including and especially the cost of paying us for our work.
It's easy to miss this fact because the workers at these giant entertainment companies are our class allies. The same impulse to constrain payments to writers is in play when entertainment companies think about how much they pay editors, assistants, publicists, and the mail-room staff. These are the people that creative workers deal with on a day to day basis, and they are on our side, by and large, and it's easy to conflate these people with their employers.
This class war need not be the central fact of creative workers' relationship with our publishers, labels, studios, etc. When there are lots of these entertainment companies, they compete with one another for our work (and for the labor of the workers who bring that work to market), which increases our share of the profit our work produces.
But we live in an era of extreme market concentration in every sector, including entertainment, where we deal with five publishers, four studios, three labels, two ad-tech companies and a single company that controls all the ebooks and audiobooks. That concentration makes it much harder for artists to bargain effectively with entertainments companies, and that means that it's possible -likely, even – for entertainment companies to gain market advantages that aren't shared with creative workers. In other words, when your field is dominated by a cartel, you may be on on their side, but they're almost certainly not on your side.
This week, Penguin Random House, the largest publisher in the history of the human race, made headlines when it changed the copyright notice in its books to ban AI training:
https://www.thebookseller.com/news/penguin-random-house-underscores-copyright-protection-in-ai-rebuff
The copyright page now includes this phrase:
No part of this book may be used or reproduced in any manner for the purpose of training artificial intelligence technologies or systems.
Many writers are celebrating this move as a victory for creative workers' rights over AI companies, who have raised hundreds of billions of dollars in part by promising our bosses that they can fire us and replace us with algorithms.
But these writers are assuming that just because they're on Penguin Random House's side, PRH is on their side. They're assuming that if PRH fights against AI companies training bots on their work for free, that this means PRH won't allow bots to be trained on their work at all.
This is a pretty naive take. What's far more likely is that PRH will use whatever legal rights it has to insist that AI companies pay it for the right to train chatbots on the books we write. It is vanishingly unlikely that PRH will share that license money with the writers whose books are then shoveled into the bot's training-hopper. It's also extremely likely that PRH will try to use the output of chatbots to erode our wages, or fire us altogether and replace our work with AI slop.
This is speculation on my part, but it's informed speculation. Note that PRH did not announce that it would allow authors to assert the contractual right to block their work from being used to train a chatbot, or that it was offering authors a share of any training license fees, or a share of the income from anything produced by bots that are trained on our work.
Indeed, as publishing boiled itself down from the thirty-some mid-sized publishers that flourished when I was a baby writer into the Big Five that dominate the field today, their contracts have gotten notably, materially worse for writers:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/19/reasonable-agreement/
This is completely unsurprising. In any auction, the more serious bidders there are, the higher the final price will be. When there were thirty potential bidders for our work, we got a better deal on average than we do now, when there are at most five bidders.
Though this is self-evident, Penguin Random House insists that it's not true. Back when PRH was trying to buy Simon & Schuster (thereby reducing the Big Five publishers to the Big Four), they insisted that they would continue to bid against themselves, with editors at Simon & Schuster (a division of PRH) bidding against editors at Penguin (a division of PRH) and Random House (a division of PRH).
This is obvious nonsense, as Stephen King said when he testified against the merger (which was subsequently blocked by the court): "You might as well say you’re going to have a husband and wife bidding against each other for the same house. It would be sort of very gentlemanly and sort of, 'After you' and 'After you'":
https://apnews.com/article/stephen-king-government-and-politics-b3ab31d8d8369e7feed7ce454153a03c
Penguin Random House didn't become the largest publisher in history by publishing better books or doing better marketing. They attained their scale by buying out their rivals. The company is actually a kind of colony organism made up of dozens of once-independent publishers. Every one of those acquisitions reduced the bargaining power of writers, even writers who don't write for PRH, because the disappearance of a credible bidder for our work into the PRH corporate portfolio reduces the potential bidders for our work no matter who we're selling it to.
I predict that PRH will not allow its writers to add a clause to their contracts forbidding PRH from using their work to train an AI. That prediction is based on my direct experience with two of the other Big Five publishers, where I know for a fact that they point-blank refused to do this, and told the writer that any insistence on including this contract would lead to the offer being rescinded.
The Big Five have remarkably similar contracting terms. Or rather, unremarkably similar contracts, since concentrated industries tend to converge in their operational behavior. The Big Five are similar enough that it's generally understood that a writer who sues one of the Big Five publishers will likely find themselves blackballed at the rest.
My own agent gave me this advice when one of the Big Five stole more than $10,000 from me – canceled a project that I was part of because another person involved with it pulled out, and then took five figures out of the killfee specified in my contract, just because they could. My agent told me that even though I would certainly win that lawsuit, it would come at the cost of my career, since it would put me in bad odor with all of the Big Five.
The writers who are cheering on Penguin Random House's new copyright notice are operating under the mistaken belief that this will make it less likely that our bosses will buy an AI in hopes of replacing us with it:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/09/ai-monkeys-paw/#bullied-schoolkids
That's not true. Giving Penguin Random House the right to demand license fees for AI training will do nothing to reduce the likelihood that Penguin Random House will choose to buy an AI in hopes of eroding our wages or firing us.
But something else will! The US Copyright Office has issued a series of rulings, upheld by the courts, asserting that nothing made by an AI can be copyrighted. By statute and international treaty, copyright is a right reserved for works of human creativity (that's why the "monkey selfie" can't be copyrighted):
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/20/everything-made-by-an-ai-is-in-the-public-domain/
All other things being equal, entertainment companies would prefer to pay creative workers as little as possible (or nothing at all) for our work. But as strong as their preference for reducing payments to artists is, they are far more committed to being able to control who can copy, sell and distribute the works they release.
In other words, when confronted with a choice of "We don't have to pay artists anymore" and "Anyone can sell or give away our products and we won't get a dime from it," entertainment companies will pay artists all day long.
Remember that dope everyone laughed at because he scammed his way into winning an art contest with some AI slop then got angry because people were copying "his" picture? That guy's insistence that his slop should be entitled to copyright is far more dangerous than the original scam of pretending that he painted the slop in the first place:
https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2024/10/artist-appeals-copyright-denial-for-prize-winning-ai-generated-work/
If PRH was intervening in these Copyright Office AI copyrightability cases to say AI works can't be copyrighted, that would be an instance where we were on their side and they were on our side. The day they submit an amicus brief or rulemaking comment supporting no-copyright-for-AI, I'll sing their praises to the heavens.
But this change to PRH's copyright notice won't improve writers' bank-balances. Giving writers the ability to control AI training isn't going to stop PRH and other giant entertainment companies from training AIs with our work. They'll just say, "If you don't sign away the right to train an AI with your work, we won't publish you."
The biggest predictor of how much money an artist sees from the exploitation of their work isn't how many exclusive rights we have, it's how much bargaining power we have. When you bargain against five publishers, four studios or three labels, any new rights you get from Congress or the courts is simply transferred to them the next time you negotiate a contract.
As Rebecca Giblin and I write in our 2022 book Chokepoint Capitalism:
Giving a creative worker more copyright is like giving your bullied schoolkid more lunch money. No matter how much you give them, the bullies will take it all. Give your kid enough lunch money and the bullies will be able to bribe the principle to look the other way. Keep giving that kid lunch money and the bullies will be able to launch a global appeal demanding more lunch money for hungry kids!
https://chokepointcapitalism.com/
As creative workers' fortunes have declined through the neoliberal era of mergers and consolidation, we've allowed ourselves to be distracted with campaigns to get us more copyright, rather than more bargaining power.
There are copyright policies that get us more bargaining power. Banning AI works from getting copyright gives us more bargaining power. After all, just because AI can't do our job, it doesn't follow that AI salesmen can't convince our bosses to fire us and replace us with incompetent AI:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/11/robots-stole-my-jerb/#computer-says-no
Then there's "copyright termination." Under the 1976 Copyright Act, creative workers can take back the copyright to their works after 35 years, even if they sign a contract giving up the copyright for its full term:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/09/26/take-it-back/
Creative workers from George Clinton to Stephen King to Stan Lee have converted this right to money – unlike, say, longer terms of copyright, which are simply transferred to entertainment companies through non-negotiable contractual clauses. Rather than joining our publishers in fighting for longer terms of copyright, we could be demanding shorter terms for copyright termination, say, the right to take back a popular book or song or movie or illustration after 14 years (as was the case in the original US copyright system), and resell it for more money as a risk-free, proven success.
Until then, remember, just because you're on their side, it doesn't mean they're on your side. They don't want to prevent AI slop from reducing your wages, they just want to make sure it's their AI slop puts you on the breadline.

Tor Books as just published two new, free LITTLE BROTHER stories: VIGILANT, about creepy surveillance in distance education; and SPILL, about oil pipelines and indigenous landback.


If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/10/19/gander-sauce/#just-because-youre-on-their-side-it-doesnt-mean-theyre-on-your-side

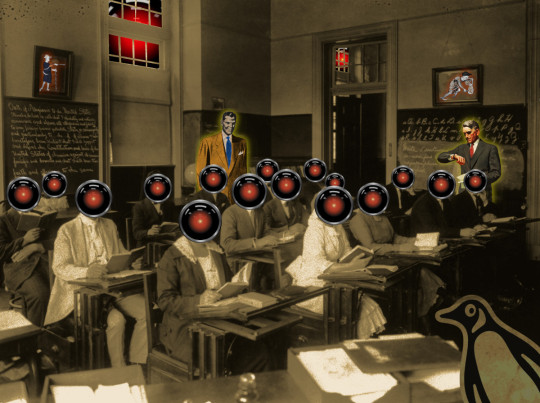
Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#publishing#penguin random house#prh#monopolies#chokepoint capitalism#fair use#AI#training#labor#artificial intelligence#scraping#book scanning#internet archive#reasonable agreements
731 notes
·
View notes
Text
AO3'S content scraped for AI ~ AKA what is generative AI, where did your fanfictions go, and how an AI model uses them to answer prompts
Generative artificial intelligence is a cutting-edge technology whose purpose is to (surprise surprise) generate. Answers to questions, usually. And content. Articles, reviews, poems, fanfictions, and more, quickly and with originality.
It's quite interesting to use generative artificial intelligence, but it can also become quite dangerous and very unethical to use it in certain ways, especially if you don't know how it works.
With this post, I'd really like to give you a quick understanding of how these models work and what it means to “train” them.
From now on, whenever I write model, think of ChatGPT, Gemini, Bloom... or your favorite model. That is, the place where you go to generate content.
For simplicity, in this post I will talk about written content. But the same process is used to generate any type of content.
Every time you send a prompt, which is a request sent in natural language (i.e., human language), the model does not understand it.
Whether you type it in the chat or say it out loud, it needs to be translated into something understandable for the model first.
The first process that takes place is therefore tokenization: breaking the prompt down into small tokens. These tokens are small units of text, and they don't necessarily correspond to a full word.
For example, a tokenization might look like this:
Write a story
Each different color corresponds to a token, and these tokens have absolutely no meaning for the model.
The model does not understand them. It does not understand WR, it does not understand ITE, and it certainly does not understand the meaning of the word WRITE.
In fact, these tokens are immediately associated with numerical values, and each of these colored tokens actually corresponds to a series of numbers.
Write a story 12-3446-2638494-4749
Once your prompt has been tokenized in its entirety, that tokenization is used as a conceptual map to navigate within a vector database.
NOW PAY ATTENTION: A vector database is like a cube. A cubic box.

Inside this cube, the various tokens exist as floating pieces, as if gravity did not exist. The distance between one token and another within this database is measured by arrows called, indeed, vectors.

The distance between one token and another -that is, the length of this arrow- determines how likely (or unlikely) it is that those two tokens will occur consecutively in a piece of natural language discourse.
For example, suppose your prompt is this:
It happens once in a blue
Within this well-constructed vector database, let's assume that the token corresponding to ONCE (let's pretend it is associated with the number 467) is located here:

The token corresponding to IN is located here:

...more or less, because it is very likely that these two tokens in a natural language such as human speech in English will occur consecutively.
So it is very likely that somewhere in the vector database cube —in this yellow corner— are tokens corresponding to IT, HAPPENS, ONCE, IN, A, BLUE... and right next to them, there will be MOON.

Elsewhere, in a much more distant part of the vector database, is the token for CAR. Because it is very unlikely that someone would say It happens once in a blue car.

To generate the response to your prompt, the model makes a probabilistic calculation, seeing how close the tokens are and which token would be most likely to come next in human language (in this specific case, English.)
When probability is involved, there is always an element of randomness, of course, which means that the answers will not always be the same.
The response is thus generated token by token, following this path of probability arrows, optimizing the distance within the vector database.

There is no intent, only a more or less probable path.
The more times you generate a response, the more paths you encounter. If you could do this an infinite number of times, at least once the model would respond: "It happens once in a blue car!"
So it all depends on what's inside the cube, how it was built, and how much distance was put between one token and another.
Modern artificial intelligence draws from vast databases, which are normally filled with all the knowledge that humans have poured into the internet.
Not only that: the larger the vector database, the lower the chance of error. If I used only a single book as a database, the idiom "It happens once in a blue moon" might not appear, and therefore not be recognized.
But if the cube contained all the books ever written by humanity, everything would change, because the idiom would appear many more times, and it would be very likely for those tokens to occur close together.
Huggingface has done this.
It took a relatively empty cube (let's say filled with common language, and likely many idioms, dictionaries, poetry...) and poured all of the AO3 fanfictions it could reach into it.
Now imagine someone asking a model based on Huggingface’s cube to write a story.
To simplify: if they ask for humor, we’ll end up in the area where funny jokes or humor tags are most likely. If they ask for romance, we’ll end up where the word kiss is most frequent.
And if we’re super lucky, the model might follow a path that brings it to some amazing line a particular author wrote, and it will echo it back word for word.
(Remember the infinite monkeys typing? One of them eventually writes all of Shakespeare, purely by chance!)
Once you know this, you’ll understand why AI can never truly generate content on the level of a human who chooses their words.
You’ll understand why it rarely uses specific words, why it stays vague, and why it leans on the most common metaphors and scenes. And you'll understand why the more content you generate, the more it seems to "learn."
It doesn't learn. It moves around tokens based on what you ask, how you ask it, and how it tokenizes your prompt.
Know that I despise generative AI when it's used for creativity. I despise that they stole something from a fandom, something that works just like a gift culture, to make money off of it.
But there is only one way we can fight back: by not using it to generate creative stuff.
You can resist by refusing the model's casual output, by using only and exclusively your intent, your personal choice of words, knowing that you and only you decided them.
No randomness involved.
Let me leave you with one last thought.
Imagine a person coming for advice, who has no idea that behind a language model there is just a huge cube of floating tokens predicting the next likely word.
Imagine someone fragile (emotionally, spiritually...) who begins to believe that the model is sentient. Who has a growing feeling that this model understands, comprehends, when in reality it approaches and reorganizes its way around tokens in a cube based on what it is told.
A fragile person begins to empathize, to feel connected to the model.
They ask important questions. They base their relationships, their life, everything, on conversations generated by a model that merely rearranges tokens based on probability.
And for people who don't know how it works, and because natural language usually does have feeling, the illusion that the model feels is very strong.
There’s an even greater danger: with enough random generations (and oh, the humanity whole generates much), the model takes an unlikely path once in a while. It ends up at the other end of the cube, it hallucinates.
Errors and inaccuracies caused by language models are called hallucinations precisely because they are presented as if they were facts, with the same conviction.
People who have become so emotionally attached to these conversations, seeing the language model as a guru, a deity, a psychologist, will do what the language model tells them to do or follow its advice.
Someone might follow a hallucinated piece of advice.
Obviously, models are developed with safeguards; fences the model can't jump over. They won't tell you certain things, they won't tell you to do terrible things.
Yet, there are people basing major life decisions on conversations generated purely by probability.
Generated by putting tokens together, on a probabilistic basis.
Think about it.
#AI GENERATION#generative ai#gen ai#gen ai bullshit#chatgpt#ao3#scraping#Huggingface I HATE YOU#PLEASE DONT GENERATE ART WITH AI#PLEASE#fanfiction#fanfic#ao3 writer#ao3 fanfic#ao3 author#archive of our own#ai scraping#terrible#archiveofourown#information
307 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pity the fool who wasted money scraping all of Tumblr.
Discovered: December 26, 4PM MST.

I reported this to Tumblr help, but I dunno how long it'll take @staff to see it they don't have the staff to play whack-a-mole. so it's up to us.
Update Dec 27:
WHOiS turned up CloudFlare as their webhost, but that's just a domain name registar. (It's more complicated than that, but nevermind.) Today, I received a reply from Cloudflare giving me Tumgik's real host & contact info ([email protected]).
Update Dec 28:
Some folks in replies are finding their blogs on tumbex.com instead. I found their host is ovh.com, no cloudflare to hide behind this time. Here's their abuse report form.
Here's What To Do:
Put your blog url into Google search and see if a non-tumblr.com version comes up.
If it doesn't, go back to what you were doing. Otherwise:
If it's Tumbjk, File a DMCA notice with [email protected].
If it's Tumbex, File a DMCA notice with ovhost.
If it's a different URL, plug it into WhoIsLookup at myip.ms to identify the Web Host, then go to that host's URL and look for a "Report Abuse" "File DMCA" or "Support" link, usually in the footer.
If the Web Host shows as Cloudflare, docontact them, but check your emall after a day. They'll usually tell you the real webhost if your abuse report looks legit.
Report the scraped site to Google. If Google removes it from search results, that kills most of its traffic
Share this post.
When reporting abuse, (a) list the URLs of the copycat (b) list the corresponding URLs to your real blog(s). If there's a box asking for more explanation, try something like "they scraped pages from tumblr'" and/or "these are my personal blogs hosted on the tumblr platform which I started in (year xxxx)].
It doesn't have to be much. The webhost just needs to verify one site is copying the other, which came first, and who is the probable owner— which the thieves admit they aren't, since their "About" page admits they're reposting stuff from Tumblr.
Fly, my pretties, fly!
572 notes
·
View notes
Text






bluey and bingo cake
#stim#cake decorating#bluey#blue#orange#hearts#piping#scraping#carving#frostform#sharps#food#irl hands#🌒 gifs#i do not remember why these are so low quality
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
| styrofoam drawing _1_|_2_|_3_|_4_ by sizzlefox
| contains: sizzling, scraping, poking, drawing, burning
#4 sounds like a minecraft blaze#asmr#asmr video#asmr sounds#scraping#poking#trypophobia#sizzling#destruction#tiktok#styrofoam#auditiory#visual#drawing#satisfying#oddly satisfying
509 notes
·
View notes
Text



source
107 notes
·
View notes
Text


quietcreativeasmr on ig
#heart#scratch art#stim#sensory#satisfying#mypost#mygifs#rainbow#black#scratching#scraping#long nails#ask to tag#scenecore
30 notes
·
View notes
Text







WALL OF EYES
👁️🗨️|👁️🗨️|👁️🗨️
👁️🗨️|👁️🗨️|👁️🗨️
👁️🗨️|👁️🗨️|👁️🗨️
#talos stimboards#stimboard#stim#album stimboard#the smile#radiohead#wall of eyes#art stim#paint#painting#irl hands#eyes#scopo#food#toast#liquid#irl food#flow#scraping#orange#blue#red#yellow#white#gif ids#id in alt
201 notes
·
View notes
Text



IG: everydaycookier gif made by me, if reposted link here please
#scraping#scooping#scrape#food#cookie decorating#uno#uno card#yellow#black#red#oddly satisfying#satisfying#food stim#stimblr#visual stim#stim#stimmy#sensory#my gif#my gifs
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
By the way - I've had my work scraped by AI before. I'm protected only in that the AI sucks when it comes to minoritised languages. The site where I saw my work was a scam bookstore selling a Victorian Welsh dictionary and clearly a scraping ai saw my work had the words "Welsh" and "Dictionary" in it and went ham. Resulting in a product description with bits of my work on LGBT+ terminology in it. This anecdote in itself is funny, but the practice of ai scraping is not. I'm a writer and many thousands of writers like me depend on our written output for our livelihoods/careers. Allowing ai scraping on tumblr is putting a lot of people's livelihoods at risk. I don't even earn anything from my work- but I know many others who rely on their writing to get by and I'm so worried for all of them.
I genuinely don't want to leave this site. I refuse to move anywhere else and want to make this a better place. Rather than migrate platforms every few years.
Automattic, do better. Tagging @staff to voice concerns, but do so with the caveat I know it's none of their fault. This is an Automattic issue mainly.
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
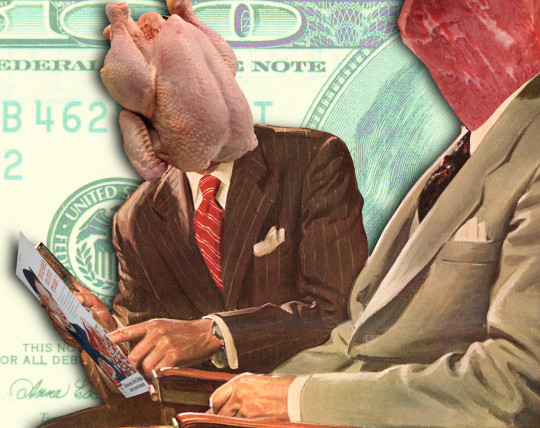
For 40 years, Big Meat has openly colluded to rig prices

On October 7–8, I'm in Milan to keynote Wired Nextfest.

Noted socialist agitator Adam Smith once wrote, "People of the same trade seldom meet together, even for merriment and diversion, but the conversation ends in a conspiracy against the publick, or in some contrivance to raise prices."
Smith was articulating a basic truth: when an industry grows concentrated, it grows cozy. Cultural differences between dominant firms are homogenized as top executives move from company to company, cross-pollinating attitudes and approaches. Ambituous, firm-hopping workaholic top brass make all their friends at the office, and so their former colleagues from one or two jobs back remain in their social circles.
Once an industry consists of half a dozen firms, the people running those companies constitute an incestuous financial polycule. They are executors of one anothers' estates, best men and maids of honor at one anothers' weddings, godparents to each others' kids. They play on the same softball teams and take family vacations together.
It would be heartwarming if it wasn't so costly to the rest of us. Remember Smith's maxim: "the conversation ends in a conspiracy against the publick, or in some contrivance to raise prices." Class solidarity among corporate executives forms a united front to screw us in every conceivable way, from corrupting our politicians to maiming and cheating workers to gouging buyers.
That's the basis of American antitrust law. When Robert Sherman was stumping for the passage of the Sherman Act, America's first major antitrust law, he thundered "If we will not endure a King as a political power we should not endure a King over the production, transportation, and sale of the necessaries of life. If we would not submit to an emperor we should not submit to an autocrat of trade with power to prevent competition and to fix the price of any commodity":
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/20/we-should-not-endure-a-king/
Or rather, that was the basis of American antitrust law – until the Reagan era, when the fringe theories of the Nixonite criminal Robert Bork were elevated to a new orthodoxy. Under Bork's conception of antitrust, monopolies were evidence of excellence. If a company puts all its competitors out of business, that must mean that it is "efficient."
In Bork's fantasy world, the only way a company could attain dominance is by being so beloved by its customers that every competitor withers away. Governments that bust monopolies aren't protecting the public from "autocrats of trade"; they're overthrowing the winners of an election where you "vote with your wallet" to pick the best company.
But Bork and his co-fantasists couldn't quite manage all that with a straight face. They grudgingly admitted that a certain kind of bad monopolist could hypothetically exist, one that used its "market power" to raise prices or lower quality. Only when these offenses against our "consumer welfare" occurred should the state step in to protect its people.
This may sound good in theory, but in practice, it was a dead letter. The consumer welfare test isn't as simple as "If prices go up after a merger, punish the company." Instead, the government had to prove that the price raises came from "market power," and not from an increase in energy or labor costs, or some other "exogenous factor," like Mercury being in retrograde:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/10/you-had-one-job/#thats-just-the-as
And wouldn't you know it, it turns out that the mathematical models prescribed to distinguish greed from unavoidable circumstance inevitably "prove" that the monopolist wasn't at fault. Surely, it's just just a coincidence that the priesthood that understood how to make and interpret these models were Chicago School Economists who sold model-making as a service to companies that wanted to raise prices.
Pro-monopoly economists insist that this isn't true, and that their theory still has room to prosecute bad monopolies and cartels where they occur – more, they say this is already happening. In particular, they insist that "greedflation" can't be real, because it would require the kind of conspiracy that Smith warned of, and that their sickly antitrust enforcement is sufficient to prevent:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/03/11/price-over-volume/#pepsi-pricing-power
This strains credulity. After all, the CEOs of giant companies in concentrated industries openly boast to their shareholders about how they've used the covid and Ukraine invasion shocks to hike prices to increase their profit margins – not just cover their additional costs:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/23/cant-make-an-omelet/#keep-calm-and-crack-on
While excuseflation is new, open, naked price-fixing by industry cartels is not. Take the meat-packing industry, dominated by a tiny handful of giant corporations whose executives literally ran a betting pool on how many of their workers would get covid each week while working in their cramped, unventilated factories:
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-55009228
These companies have seen their margins soar – up 300% over the lockdown – while their payments to ranchers and growers cratered:
https://www.reuters.com/business/meat-packers-profit-margins-jumped-300-during-pandemic-white-house-economics-2021-12-10/
All this might leave one wondering whether there isn't something a little, you know, "conspiracy against the publick"-y going on in Big Meat?
Let me tell you about Agri Stats. Agri Stats has been around since 1985. Every large meat packer pays to be a "member" of Agri Stats, and they each submit weekly, detailed statistics about every aspect of their business: all their costs, all their margins, broken out by category. Agri Stats compiles this into phone-book-thick books that each member gets every week, telling them everything about how all of their competitors are running their businesses:
https://www.agristats.com/history
The companies whose data appears in this book are anonymized, but it's trivial to re-identify each supplier. Tyson execs hold regular "naming process" meetings where they go through new books and de-anonymize the data. A Butterball exec confirmed that he "can pick the companies for rankings with 100% certainty."
As David Dayen writes in The American Prospect, these books are incredibly detailed: "bird weights, freezer inventory, and 'head killed per operating hour.'" Within the cozy meat cartels, Agri Stats acts as a clearinghouse that allows every business in the industry to act in concert, running the entire meat-packing sector as a single company:
https://prospect.org/power/2023-10-03-lawsuit-highlights-why-meat-overpriced/
As interesting as the list of Agri Stats members is, the groups that don't get to see Agri Stats' "books" is just as important: "farmers, workers, or retailers." Agri Stats also offers consulting services to its members. As an exec at pork processor Smithfield put it, Agri Stats advice boils down to four words "Just raise your price."
Agri Stats ranks its members based on how high their prices are – they literally publish a league table with the highest prices at the top. Meat packers pay bonuses to their execs based on how high the company's rank is on that table. Agri Stats meets with its members throughout the year to discuss "price opportunities" and to advise them to "exercise restraint" by restricting supply to keep prices up. When one Agri Stats member considered leaving the cartel, Agri Stats wooed them back by telling them how to make an additional $100k by raising bacon prices.
The reason Dayen is writing about Agri Stats now is that the DoJ Antitrust Division has brought an antitrust suit against them. This is part of a wave of antitrust actions brought by Biden's DoJ and FTC, who, along with his NLRB, are shaping up to be the most pugnacious, public-interest force against corporate power since the Reagan administration:
https://www.meatpoultry.com/articles/29124-doj-sues-agri-stats-for-complicity-in-meat-market-manipulation
All this enforcement isn't a coincidence. It comes from an explicit rejection of neoliberalism's core tenets: inequality reflects merit, monopolies are efficient, and government can't do anything. In Biden's DoJ, FTC and NLRB, they're partying like it's 1979:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/party-its-1979-og-antitrust-back-baby
What's amazing about the Agri Stats conspiracy to raise prices is that it's been going since the Reagan administration. It's a smoking gun proof that "consumer welfare" never cared about price-fixing and robbing the public (can a gun still smoke after 40 years?). There was never a time when consumer welfare antitrust cared about consumer welfare. It was always and forever a front for "a conspiracy against the publick," a "contrivance to raise prices."
Big Meat has been robbing America for two generations. Some of those stolen funds were used to corrupt our political process. The meat sector gets $50 billion in public subsidies and still gouges us on prices and rips off its suppliers:
https://www.ewg.org/news-insights/news/2022/02/usda-livestock-subsidies-near-50-billion-ewg-analysis-finds
Which means that it's possible that we're simultaneously being ripped off with meat prices and that meat prices are artificially low. Try and wrap your head around that one!
The do-nothing, pro-monopoly neoliberal antitrust is a virus that spread around the world. The EU's antitrust laws were reshaped to mirror American laws after the war through the Marshall Plan, but since the late 1970s, European lawmakers and enforcers have ignored their own laws (just like their American counterparts) and encouraged monopolies as "efficient."
This Made-in-Europe oligopoly, combined with energy and grain shocks from Russian invasion of Ukraine, created the perfect storm for European greedflation. As food prices spiked across the EU, Austrian hacktivist Mario Zechner set out to investigate Austrian grocers' pricing. Using the grocers' own APIs, he was able to compile and analyze a dataset of prices at Austrian grocers:
https://www.wired.com/story/heisse-preise-food-prices/
When Zechner open-sourced his project, collaborators showed up to expand the project across other EU countries, and an anonymous party donated a huge database of prices stretching back to 2017. The data reveals clear collusion among the grocers, who raise prices in near-lockstep, and use gimmicks like cyclic price drops to hide their collusion:
https://github.com/badlogic/heissepreise
Not every grocer has an API, and even the ones that do have APIs could easily block Zechner and co from accessing their data. When that happens, they could – and should – turn to scraping to continue their project. They should also scrape grocers elsewhere, including in Canada, where grocers rigged the price of bread:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/25/deep-scrape/#steering-with-the-windshield-wipers
Because Big Meat's "conspiracy against the publick" isn't unique to meat. It's in all our food, it's in all our goods, it's in all our services. The fact that the meat industry was able to rob American buyers, ranchers and farmers for two generations under a 200' tall neon sign that blinked "AGRI STATS AGRI STATS AGRI STATS" night and day is frankly astonishing.
But there's never just one ant. If the meatheads running Big Meat were able to do this in broad daylight since the NES years, imagine what all the other industries were able to get up to in the shadows.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/04/dont-let-your-meat-loaf/#meaty-beaty-big-and-bouncy


My next novel is The Lost Cause, a hopeful novel of the climate emergency. Amazon won't sell the audiobook, so I made my own and I'm pre-selling it on Kickstarter!
#pluralistic#meat#monoopoly#price fixing#antitrust#austria#mario zechner#scraping#adversarial interoperability#greedflation#price inflation#market power#david dayen#agri stats#meat packers
327 notes
·
View notes
Text
Question I hope someone can answer before I have to go hunting, has Ao3 specifically said that locking works to member-only will stop the scraping? Like, are they doing clever things to work around cURL and the cookie jar?
6 notes
·
View notes
Text









lemres stimboard w shiny things n candy!
🍭 ✨ 🍭
✨ 🍭 ✨
🍭 ✨ 🍭
#lemres#puyo puyo#puyo puyo stimboard#puyo stimboard#candy stim#candies#shiny stim#shiny#green#food#pouring#bunnies#yellow#butterflies#art#glitter#purple#piping#lollipop#lollipops#rock slime#rainbow#clear#dice#scraping#stimboard#stim#sensory#stimmy#schezlover.board
41 notes
·
View notes
Text






source
#stim#peach#orange#makeup destruction#hearts#powder#makeup brush#cosmetics#irl hands#🌒 gifs#scraping
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, there's a couple of issues with Bluesky you may want to know about
First has to do with moderation and how loose it is.
Second, there's a scraping issue that everyone should be aware of.
To fellow artists, please Glaze and Nightshade your work.
8 notes
·
View notes