#Technology / Science
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Self-Awareness by Katsuhiro Õtomo
#artificial intelligence#self awareness#android#futurism#cyberpunk#technology#science fiction#robots#reflection#mirror#sci fi#art#transhumanism#drawing#cyborg#robot#singularity#m. c. escher
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Scientists in Singapore have broken a long-standing limitation on the ability to generate electricity from flowing water, suggesting that another elemental force of nature could be leveraged for renewable electricity: rain.
With the simplest and smallest scale test setup, the team could power around 12 LED lightbulbs with simulated rain droplets flowing through a tube, but at scale, their method could generate meaningful amounts that could rival rooftop solar arrays.
Singapore experiences significant rainfall throughout the year, averaging 101 inches (2581 millimeters) of precipitation annually. The idea of generating electricity from such falling water is attractive, but the method has long been constrained by a principle called the Debye Length.
Nevertheless, the concept is possible because of a simple physical principle that charged entities on the surface of materials get nudged when they rub together—as true for water droplets as it is for a balloon rubbed against the hair on one’s head.
While this is true, the power values thus generated have been negligible, and electricity from flowing water has been limited to the driving of turbines in hydropower plants.
However, in a study published in the journal ACS Central Science, a team of physicists has found a way to break through the constraints of water’s Debye Length, and generate power from simulated rain.
“Water that falls through a vertical tube generates a substantial amount of electricity by using a specific pattern of water flow: plug flow,” says Siowling Soh, author of the study. “This plug flow pattern could allow rain energy to be harvested for generating clean and renewable electricity.”
The authors write in their study that in existing tests of the power production from water flows, pumps are always used to drive liquid through the small channels. But the pumps require so much energy to run that outputs are limited to miniscule amounts.
Instead, their setup to harness this plug flow pattern was scandalously simple. No moving parts or mechanisms of any kind were required. A simple plastic tube just 2 millimeters in diameter; a large plastic bottle; a small metallic needle. Water coming out of the bottle ran along the needle and bumped into the top section of the tube that had been cut in half, interrupting the water flow and allowing pockets of air to slide down the tube along with the water.
The air was the key to breaking through the limits set by the Debye Length, and key to the feasibility of electricity generation from water. Wires placed at the top of the tube and in the cup harvested the electricity.
The total generation rate of greater than 10% resulted in about 100 watts per square meter of tube. For context, a 100-watt solar panel can power an appliance as large as a blender or ceiling fan, charge a laptop, provide for several light bulbs, or even a Wi-Fi router.
Because the droplet speeds tested were much slower than rain, the researchers suggest that the real thing would provide even more than their tests, which were of course on a microscale."
-via Good News Network, April 30, 2025
#singapore#asia#rain#renewable energy#renewables#clean energy#electricity#science and technology#solarpunk#good news#hope
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
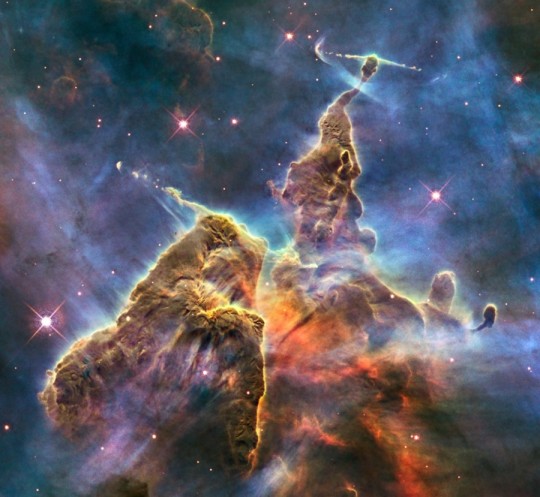

Hubble Space Telescope: Exploring the Cosmos and Making Life Better on Earth
In the 35 years since its launch aboard space shuttle Discovery, the Hubble Space Telescope has provided stunning views of galaxies millions of light years away. But the leaps in technology needed for its look into space has also provided benefits on the ground. Here are some of the technologies developed for Hubble that have improved life on Earth.

Image Sensors Find Cancer
Charge-coupled device (CCD) sensors have been used in digital photography for decades, but Hubble’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph required a far more sensitive CCD. This development resulted in improved image sensors for mammogram machines, helping doctors find and treat breast cancer.

Laser Vision Gives Insights
In preparation for a repair mission to fix Hubble’s misshapen mirror, Goddard Space Flight Center required a way to accurately measure replacement parts. This resulted in a tool to detect mirror defects, which has since been used to develop a commercial 3D imaging system and a package detection device now used by all major shipping companies.
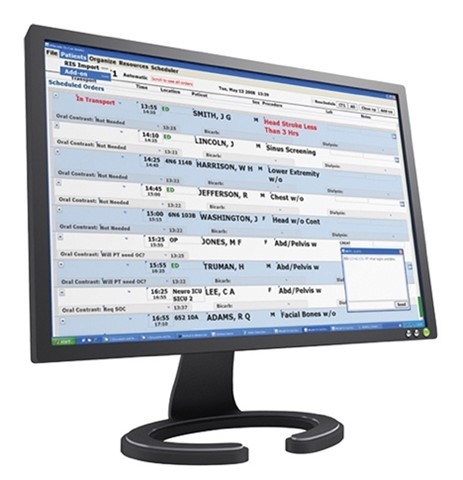
Optimized Hospital Scheduling
A computer scientist who helped design software for scheduling Hubble’s observations adapted it to assist with scheduling medical procedures. This software helps hospitals optimize constantly changing schedules for medical imaging and keep the high pace of emergency rooms going.

Optical Filters Match Wavelengths and Paint Swatches
For Hubble’s main cameras to capture high-quality images of stars and galaxies, each of its filters had to block all but a specific range of wavelengths of light. The filters needed to capture the best data possible but also fit on one optical element. A company contracted to construct these filters used its experience on this project to create filters used in paint-matching devices for hardware stores, with multiple wavelengths evaluated by a single lens.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

2K notes
·
View notes
Text
These tiny solar cells work using a process much like photosynthesis--photons hit the dye, electrons are released and then passed on to a special conductive material that harvests the electricity. They're designed to work in lower light conditions than traditional solar cells and are powerful enough to power small electronics up to the size of a keyboard.
The idea is that these tiny solar cells could replace small batteries for low-energy electronics--they last significantly longer and produce 90% fewer emissions per unit of energy than traditional batteries. Solar cells also remove the emissions from shipping and replacing batteries, although there are potentially some additional environmental costs associated with their production.
This is a really cool step towards having electronics that are powered by renewable energy on an individual level rather than requiring batteries.
#good news#hope#technology#solar energy#solar panels#solar cells#science#climate change#global warming#hopepunk#solarpunk#environment#ecology#batteries#electricity
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
"There was an exchange on Twitter a while back where someone said, ‘What is artificial intelligence?' And someone else said, 'A poor choice of words in 1954'," he says. "And, you know, they’re right. I think that if we had chosen a different phrase for it, back in the '50s, we might have avoided a lot of the confusion that we're having now." So if he had to invent a term, what would it be? His answer is instant: applied statistics. "It's genuinely amazing that...these sorts of things can be extracted from a statistical analysis of a large body of text," he says. But, in his view, that doesn't make the tools intelligent. Applied statistics is a far more precise descriptor, "but no one wants to use that term, because it's not as sexy".
'The machines we have now are not conscious', Lunch with the FT, Ted Chiang, by Madhumita Murgia, 3 June/4 June 2023
#quote#Ted Chiang#AI#artificial intelligence#technology#ChatGPT#Madhumita Murgia#intelligence#consciousness#sentience#scifi#science fiction#Chiang#statistics#applied statistics#terminology#language#digital#computers
24K notes
·
View notes
Text
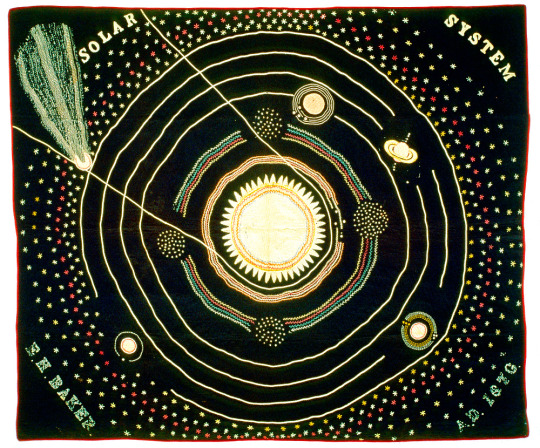
In the autumn of 1883, a paper in the nation's capital reported that "an Iowa woman has spent 7 years embroidering the solar system on a quilt" — to teach astronomy in an era when women could not attend college. Her story.
#Women's History Month#women's history#astronomy#craft#quilting#space#science#science and technology#history and literature#culture and society
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
To be fair, a lot of goofy-sounding rocketry/aerospace terminology has a legitimate nomenclatural role beyond just being silly euphemisms.
"Unplanned rapid disassembly", for example, exists as the necessary counterpart to planned rapid disassembly: sometimes a rocket is legitimately supposed to fall apart or blow up, so you need a specific term to emphasise that it wasn't supposed to do that.
Similarly, "lithobraking" was coined by analogy with aerobraking (shedding velocity via atmospheric friction) and hydrobraking (shedding velocity by landing in water), and it does have some intentional applications; the Mars Pathfinder probe, for example, was deliberately crashed into the Martian surface while surrounded by giant airbags, and reportedly bounced at least 15 times before coming to rest.
(That said, aerospace engineers absolutely do use these terms humorously as well, because engineers are just Like That.)
4K notes
·
View notes
Text


2K notes
·
View notes
Text
In case you haven't heard yet, Colossal, the biotech company that earlier this year showed off their "woolly mouse," has announced that they de-extincted "dire wolves." I put this in quotes, because just like with the mice, they didn't truly bring them back (nothing can actually do that, yet) or even really make them.
What they actually did was kind of neat; they copied genes sequenced from dire wolf DNA and inserted them into the grey wolf genome (replacing grey wolf DNA, as they said gray wolves shared a significant percentage of their genome (which isn't saying a TON considering how much the human and chimp genome have in common without being nearly the same animals, but it's better than taking, say, a turtle's genome or something else super unrelated), to create a wolf with genes that dire wolves had.
And while that's not really the same thing as building a dire wolf completely from scratch, so to speak, and it's not really "cloning" them either, it's still pretty cool science, and just like with the woolly mouse, the work (ie, altering/editing multiple genes at once from sequenced DNA of deceased individuals) COULD apply to conservation of actual species (for example, having the ability to widen the genome of remaining breeding individuals of an endangered species, with DNA from deceased individuals). I'm not sure if it IS applying to other species right now (at least not through this company, despite their stated claims to want to), but it is one of their stated goals and it would work.
Also, they're pretty cute
As they were born in October 2024, they now have their own 2,000 acre reserve where Colossal is monitoring them closely. There are two males and one female, but as they've stated they do not have plans to breed them, I'm not sure where the female is being kept in relation to the males, but I suspect she's the solo-wolf pictured, vs the pics of the pair.
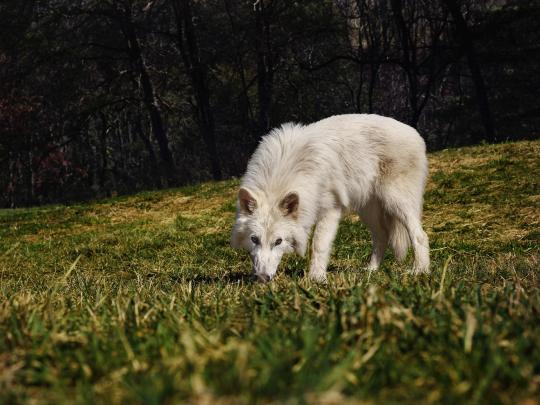
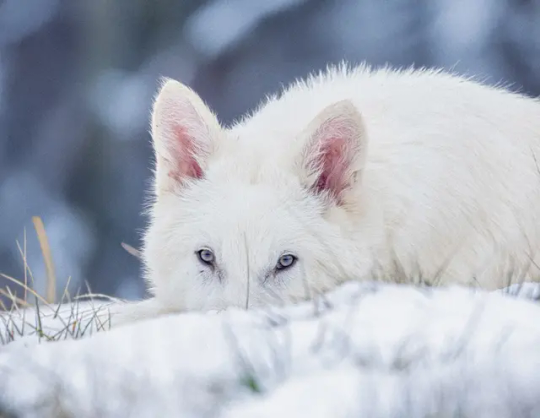






Anyway, that's all happening.
#news#dire wolves#science!#technology#wolves#I'm not 100% how I feel about them actually making live animals like this#but since it's already been done and there's nothing I'll ever say that will affect it#it's at least interesting to see the result and be aware it's happening#I really wish they'd focus on more imminently threatened species but also....#I'm glad they're doing experimentation with populations of animals that they can't fuck up and make worse#they used dog surrogates#and gray wolves are listed as a least concern species#whereas if you fuck up with liiiike red wolves or spix's macaws or something#you could fuck the species entirely very quickly#if they fuck up making dire wolves well... they've already been extinct 10k+ years#it's not like extincting them again will cause irreversible ecological problems#anyway genetics news for your viewing
943 notes
·
View notes
Text










Variant cover art for the comic book series 𝘽𝙡𝙖𝙙𝙚 𝙍𝙪𝙣𝙣𝙚𝙧 𝟮𝟬𝟭𝟵 (Titan; 2019-2020) ... based on production designs created by Syd Mead for the 1982 𝘽𝙡𝙖𝙙𝙚 𝙍𝙪𝙣𝙣𝙚𝙧 movie.
#blade runner#dark#philip k. dick#surreal#urban#grunge#fantasy#1980s#cyberpunk#architecture#ridley scott#movies#technology#science fiction#comic books#art#alternative#dystopia#art history#80s#syd mead#🛸
572 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Robot Who Dreams" by Phillipe Caza

#android#robots#science fiction#isaac asimov#art#artificial intelligence#futurism#transhumanism#dreams#sci fi#cyberpunk#robot#androids#cyborg#singularity#technology#space#dream
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's the top 2 stories from each of Fix The News's six categories:

1. A game-changing HIV drug was the biggest story of 2024
In what Science called the 'breakthrough of the year', researchers revealed in June that a twice-yearly drug called lenacapavir reduced HIV infections in a trial in Africa to zero—an astonishing 100% efficacy, and the closest thing to a vaccine in four decades of research. Things moved quick; by October, the maker of the drug, Gilead, had agreed to produce an affordable version for 120 resource-limited countries, and by December trials were underway for a version that could prevent infection with just a single shot per year. 'I got cold shivers. After all our years of sadness, particularly over vaccines, this truly is surreal.'
2. Another incredible year for disease elimination
Jordan became the first country to eliminate leprosy, Chad eliminated sleeping sickness, Guinea eliminated maternal and neonatal tetanus, Belize, Jamaica, and Saint Vincent & the Grenadines eliminated mother-to-child transmission of HIV and syphilis, India achieved the WHO target for eliminating black fever, India, Viet Nam and Pakistan eliminated trachoma, the world’s leading infectious cause of blindness, and Brazil and Timor Leste eliminated elephantiasis.

15. The EU passed a landmark nature restoration law
When countries pass environmental legislation, it’s big news; when an entire continent mandates the protection of nature, it signals a profound shift. Under the new law, which passed on a knife-edge vote in June 2024, all 27 member states are legally required to restore at least 20% of land and sea by 2030, and degraded ecosystems by 2050. This is one of the world’s most ambitious pieces of legislation and it didn’t come easy; but the payoff will be huge - from tackling biodiversity loss and climate change to enhancing food security.
16. Deforestation in the Amazon halved in two years
Brazil’s space agency, INPE, confirmed a second consecutive year of declining deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. That means deforestation rates have roughly halved under Lula, and are now approaching all time lows. In Colombia, deforestation dropped by 36%, hitting a 23-year low. Bolivia created four new protected areas, a huge new new state park was created in Pará to protect some of the oldest and tallest tree species in the tropical Americas and a new study revealed that more of the Amazon is protected than we originally thought, with 62.4% of the rainforest now under some form of conservation management.

39. Millions more children got an education
Staggering statistics incoming: between 2000 and 2023, the number of children and adolescents not attending school fell by nearly 40%, and Eastern and Southern Africa, achieved gender parity in primary education, with 25 million more girls are enrolled in primary school today than in the early 2000s. Since 2015, an additional 110 million children have entered school worldwide, and 40 million more young people are completing secondary school.
40. We fed around a quarter of the world's kids at school
Around 480 million students are now getting fed at school, up from 319 million before the pandemic, and 104 countries have joined a global coalition to promote school meals, School feeding policies are now in place in 48 countries in Africa, and this year Nigeria announced plans to expand school meals to 20 million children by 2025, Kenya committed to expanding its program from two million to ten million children by the end of the decade, and Indonesia pledged to provide lunches to all 78 million of its students, in what will be the world's largest free school meals program.

50. Solar installations shattered all records
Global solar installations look set to reach an unprecedented 660GW in 2024, up 50% from 2023's previous record. The pace of deployment has become almost unfathomable - in 2010, it took a month to install a gigawatt, by 2016, a week, and in 2024, just 12 hours. Solar has become not just the cheapest form of new electricity in history, but the fastest-growing energy technology ever deployed, and the International Energy Agency said that the pace of deployment is now ahead of the trajectory required for net zero by 2050.
51. Battery storage transformed the economics of renewables
Global battery storage capacity surged 76% in 2024, making investments in solar and wind energy much more attractive, and vice-versa. As with solar, the pace of change stunned even the most cynical observers. Price wars between the big Chinese manufacturers pushed battery costs to record lows, and global battery manufacturing capacity increased by 42%, setting the stage for future growth in both grid storage and electric vehicles - crucial for the clean flexibility required by a renewables-dominated electricity system. The world's first large-scale grid battery installation only went online seven years ago; by next year, global battery storage capacity will exceed that of pumped hydro.

65. Democracy proved remarkably resilient in a record year of elections
More than two billion people went to the polls this year, and democracy fared far better than most people expected, with solid voter turnout, limited election manipulation, and evidence of incumbent governments being tamed. It wasn't all good news, but Indonesia saw the world's biggest one day election, Indian voters rejected authoritarianism, South Korea's democratic institutions did the same, Bangladesh promised free and fair elections following a 'people's victory', Senegal, Sri Lanka and Botswana saw peaceful transfers of power to new leaders after decades of single party rule, and Syria saw the end of one of the world's most horrific authoritarian regimes.
66. Global leaders committed to ending violence against children
In early November, while the eyes of the world were on the US election, an event took place that may prove to be a far more consequential for humanity. Five countries pledged to end corporal punishment in all settings, two more pledged to end it in schools, and another 12, including Bangladesh and Nigeria, accepted recommendations earlier in the year to end corporal punishment of children in all settings. In total, in 2024 more than 100 countries made some kind of commitment to ending violence against children. Together, these countries are home to hundreds of millions of children, with the WHO calling the move a 'fundamental shift.'

73. Space exploration hit new milestones
NASA’s Europa Clipper began a 2.9 billion kilometre voyage to Jupiter to investigate a moon that may have conditions for life; astronomers identified an ice world with a possible atmosphere in the habitable zone; and the James Webb Telescope found the farthest known galaxy. Closer to Earth, China landed on the far side of the moon, the Polaris Dawn crew made a historic trip to orbit, and Starship moved closer to operational use – and maybe one day, to travel to Mars.
74. Next-generation materials advanced
A mind-boggling year for material science. Artificial intelligence helped identify a solid-state electrolyte that could slash lithium use in batteries by 70%, and an Apple supplier announced a battery material that can deliver around 100 times better energy density. Researchers created an insulating synthetic sapphire material 1.25 nanometers thick, plus the world’s thinnest lens, just three atoms across. The world’s first functioning graphene-based semiconductor was unveiled (the long-awaited ‘wonder material’ may finally be coming of age!) and a team at Berkeley invented a fluffy yellow powder that could be a game changer for removing carbon from the atmosphere.
-via Fix The News, December 19, 2024
#renumbered this to reflect the article numbering#and highlight just how many stories of hope there are#and how many successes each labeled story contains#2024#good news#hope#hope posting#hopeposting#hopepunk#conservation#sustainability#public health#energy#quality of life#human rights#science and technology
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
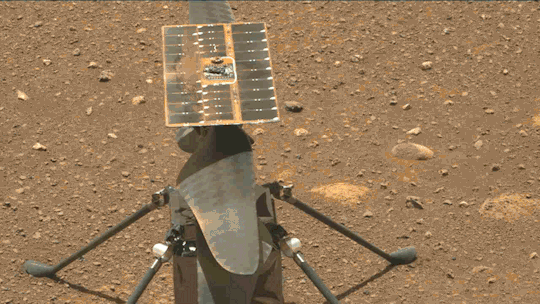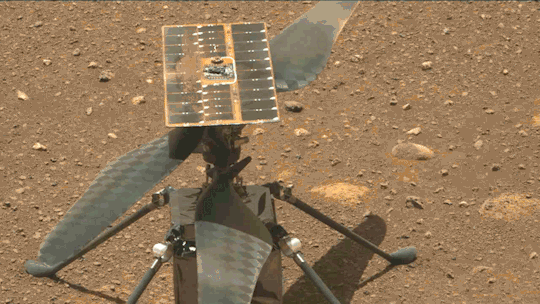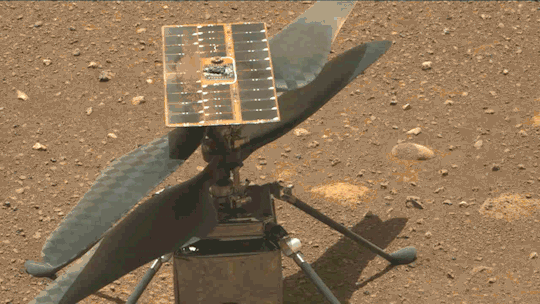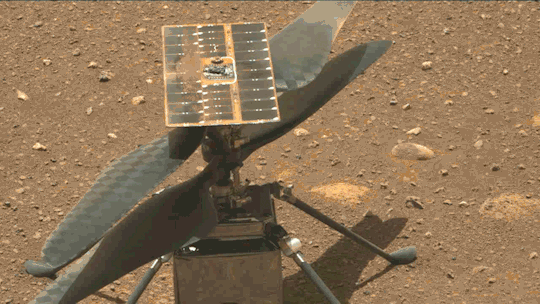
What We Learned from Flying a Helicopter on Mars

The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter made history – not only as the first aircraft to perform powered, controlled flight on another world – but also for exceeding expectations, pushing the limits, and setting the stage for future NASA aerial exploration of other worlds.
Built as a technology demonstration designed to perform up to five experimental test flights over 30 days, Ingenuity performed flight operations from the Martian surface for almost three years. The helicopter ended its mission on Jan. 25, 2024, after sustaining damage to its rotor blades during its 72nd flight.
So, what did we learn from this small but mighty helicopter?
We can fly rotorcraft in the thin atmosphere of other planets.
Ingenuity proved that powered, controlled flight is possible on other worlds when it took to the Martian skies for the first time on April 19, 2021.
Flying on planets like Mars is no easy feat: The Red Planet has a significantly lower gravity – one-third that of Earth’s – and an extremely thin atmosphere, with only 1% the pressure at the surface compared to our planet. This means there are relatively few air molecules with which Ingenuity’s two 4-foot-wide (1.2-meter-wide) rotor blades can interact to achieve flight.
Ingenuity performed several flights dedicated to understanding key aerodynamic effects and how they interact with the structure and control system of the helicopter, providing us with a treasure-trove of data on how aircraft fly in the Martian atmosphere.
Now, we can use this knowledge to directly improve performance and reduce risk on future planetary aerial vehicles.

Creative solutions and “ingenuity” kept the helicopter flying longer than expected.
Over an extended mission that lasted for almost 1,000 Martian days (more than 33 times longer than originally planned), Ingenuity was upgraded with the ability to autonomously choose landing sites in treacherous terrain, dealt with a dead sensor, dusted itself off after dust storms, operated from 48 different airfields, performed three emergency landings, and survived a frigid Martian winter.
Fun fact: To keep costs low, the helicopter contained many off-the-shelf-commercial parts from the smartphone industry - parts that had never been tested in deep space. Those parts also surpassed expectations, proving durable throughout Ingenuity’s extended mission, and can inform future budget-conscious hardware solutions.

There is value in adding an aerial dimension to interplanetary surface missions.
Ingenuity traveled to Mars on the belly of the Perseverance rover, which served as the communications relay for Ingenuity and, therefore, was its constant companion. The helicopter also proved itself a helpful scout to the rover.
After its initial five flights in 2021, Ingenuity transitioned to an “operations demonstration,” serving as Perseverance’s eyes in the sky as it scouted science targets, potential rover routes, and inaccessible features, while also capturing stereo images for digital elevation maps.
Airborne assets like Ingenuity unlock a new dimension of exploration on Mars that we did not yet have – providing more pixels per meter of resolution for imaging than an orbiter and exploring locations a rover cannot reach.

Tech demos can pay off big time.
Ingenuity was flown as a technology demonstration payload on the Mars 2020 mission, and was a high risk, high reward, low-cost endeavor that paid off big. The data collected by the helicopter will be analyzed for years to come and will benefit future Mars and other planetary missions.
Just as the Sojourner rover led to the MER-class (Spirit and Opportunity) rovers, and the MSL-class (Curiosity and Perseverance) rovers, the team believes Ingenuity’s success will lead to future fleets of aircraft at Mars.
In general, NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions test and advance new technologies, and then transition those capabilities to NASA missions, industry, and other government agencies. Chosen technologies are thoroughly ground- and flight-tested in relevant operating environments — reducing risks to future flight missions, gaining operational heritage and continuing NASA’s long history as a technological leader.
youtube
You can fall in love with robots on another planet.
Following in the tracks of beloved Martian rovers, the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter built up a worldwide fanbase. The Ingenuity team and public awaited every single flight with anticipation, awe, humor, and hope.
Check out #ThanksIngenuity on social media to see what’s been said about the helicopter’s accomplishments.
youtube
Learn more about Ingenuity’s accomplishments here. And make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
From the article:
One of the most promising aspects of this new photocatalytic system is its simplicity. The setup is essentially a small vial illuminated by two LEDs, with two small fans added to keep it cool during the process. It operates under mild conditions and does not use any metals, which are often hazardous to handle and can sometimes be explosive. The system’s reliance on light – a readily available and renewable energy source – could make it economically viable and sustainable. As we refine it, we hope that it could one day operate with minimal energy input, outside of the energy powering the light. This platform can also transform other organic molecules that contain carbon-fluorine bonds into valuable chemicals. For instance, thousands of fluoroarenes are commonly available as industrial chemicals and laboratory reagents. These can be transformed into building blocks for making a variety of other materials, including medicines and everyday products.
#PFAS#forever chemicals#chemicals#pollution#chemical pollution#environment#hope#good news#science#technology
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
3K notes
·
View notes