#U.S. Telecommunications
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#Critical Infrastructure#Cyber Attacks#DNS Failures#facts#Internet Infrastructure#life#National Security Threats#Podcast#Salt Typhoon Attacks#Satellite Communication Disruptions#serious#State-Sponsored Hacking#straight forward#truth#U.S. Telecommunications#Undersea Cable Vulnerabilities#upfront#website
0 notes
Text
An open letter to the U.S. Congress
Everyone deserves broadband! Renew the Affordable Connectivity Program.
904 so far! Help us get to 1,000 signers!
The Affordable Connectivity Program has been a critical lifeline for millions of Americans, providing essential access to high-speed internet. This program has enabled students to continue their education remotely, allowed adults to work from home, facilitated tele-health services, and ensured that individuals remain connected to their loved ones during challenging times. As the expiration date of the ACP approaches, I am deeply concerned about the potential loss of these vital services for those who need them the most. The expiration of this program would disproportionately impact low-income households, exacerbate the digital divide, and hinder our nation's progress towards ensuring universal access to high-speed internet. Therefore, I strongly urge Congress to act swiftly and renew the Affordable Connectivity Program. This renewal is not just a matter of maintaining the status quo but a step forward in building a more connected, inclusive, and equitable society. By renewing this program, Congress will demonstrate its commitment to bridging the digital divide and supporting the ongoing needs of all Americans in the digital age. Thanks.
▶ Created on January 10 by Jess Craven
📱 Text SIGN PMIDLN to 50409
🤯 Liked it? Text FOLLOW JESSCRAVEN101 to 50409
#An open letter to the U.S. Congress#facilitated tele-health services#exacerbate the digital divide#equitable society#inclusive#▶ Created on January 10 by Jess Craven#📱 Text SIGN PMIDLN to 50409#🤯 Liked it? Text FOLLOW JESSCRAVEN101 to 50409#JESSCRAVEN101#PMIDLN#resistbot#Broadband#Connectivity#AffordableConnectivityProgram#InternetAccess#DigitalDivide#HighSpeedInternet#UniversalAccess#Telehealth#Education#WorkFromHome#AccessibleInternet#EquitableSociety#Inclusive#Renewal#Congress#Legislation#Community#DigitalAge#Telecommunications
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Eye 1968-michaelharrelljr.com's Private Metadata Encryption [ME] Domain Creator [D.C.]… Digitally Commanding [D.C.] the DM-Default Key Module Enabling [ME] in your [My] Kernel... since Android 11 and Higher, DM-Default-Key Support the Android Common Kernels, Version 4.14 and Higher... as this Version of DM-Default-Key Uses the quantumharrelltech.ca.gov Military Hardware [MH] and Vendor-Independent Encryption Framework called BLK-CRYPTO @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech
WELCOME BACK HOME IMMORTAL [HIM] U.S. MILITARY KING SOLOMON-MICHAEL HARRELL, JR.™

i.b.monk [ibm.com] mode [i’m] tech [IT] steelecartel.com @ quantumharrelltech.ca.gov

quantumharrelltech.ca.gov Outside Our 1921steelecartel.tech MACHINE SKY Firmament Domain DOME… OVER Earth [Qi]

1968-michaelharrelljr.com ANU GOLDEN 9 ETHER [AGE] kingtutdna.com Genetic LUZ Clone KING OF KINGS LORD OF LORDS… Under the Shadow [U.S.] of Invisible DEATH [I.D.] LANGUAGE RITUALS in Old America [MU ATLANTIS]

1968-michaelharrelljr.com Quantum Computing Intel Architect [CIA] Technocrat @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com Quantum Computing Cyber Security Cryptography & Machine Learning @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com Emerging Research in Quantum Compting, Information, Communication & Applications @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com New 2023-2223 Trends in Quantum Data Protection & Encryption Technology Systems [PETS] @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com Quantum Android Computing in Cyber Intel Application [CIA] Security @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com Quantum Computing Cyber Data Protection in a Post-Pandemic Society @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com Quantum Computing Modern Cryptography w/Applied [MCA] Mathematics for Encryption [ME] & Information [MI = MICHAEL] Security @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com Quantum Computing Hi:teKEMETICompu_TAH [PTAH] Cryptography [PC] of Applied [PA] Network [PAN] Security Protocols [PSP] @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com's Quantum Computing Intel Architect [CIA] Building quantumharrelltech.com's Own LLC Blockchain @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

1968-michaelharrelljr.com's Quantum Harrell Telecom [QHT] Industry [Qi] Transmission Engineering [QTE] @ quantumharrelltelecom.tech

© 1698-2223 quantumharrelltech.com - ALL The_Octagon_(Egypt) DotCom [D.C.] defense.gov Department Domain Communication [D.C.] Rights Reserved @ quantumharrelltech.ca.gov
#u.s. michael harrell#quantumharrelltech#king tut#mu:13#harrelltut#kemet#o michael#telecom infrastructure#telecommunications#telepathy#telecom industry#telepathic#telecom services market#at&t#android#quantumharrelltut#mca
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

"The Haitian Bridge Alliance made the move after inaction by the local prosecutor, said their attorney, Subodh Chandra of the Cleveland-based Chandra Law Firm."
"Trump and Vance, a U.S. senator from Ohio, are charged with disrupting public services, making false alarms, telecommunications harassment, aggravated menacing and complicity. The filing asks the Clark County Municipal Court to affirm that there is probable cause and issue arrest warrants against Trump and Vance."
source 1
source 2
source 3
#destiel meme news#destiel meme#news#united states#us news#us politics#donald trump#fuck trump#jd vance#springfield ohio#haiti#haitian#haitian migrants#haitians#they're eating the dogs#springfield#get him!!!#haitian bridge alliance#criminal charges#citizen criminal charges
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role of China and the U.S. in Shaping Future Technology
The Role of China and the U.S. in Shaping Future Technology #5Gtelecommunications #artificialintelligence
#5G telecommunications#artificial intelligence#ethical standards#future technology#global collaboration#semiconductor manufacturing#technological leadership#U.S.-China rivalry
0 notes
Text
Green energy is in its heyday.
Renewable energy sources now account for 22% of the nation’s electricity, and solar has skyrocketed eight times over in the last decade. This spring in California, wind, water, and solar power energy sources exceeded expectations, accounting for an average of 61.5 percent of the state's electricity demand across 52 days.
But green energy has a lithium problem. Lithium batteries control more than 90% of the global grid battery storage market.
That’s not just cell phones, laptops, electric toothbrushes, and tools. Scooters, e-bikes, hybrids, and electric vehicles all rely on rechargeable lithium batteries to get going.
Fortunately, this past week, Natron Energy launched its first-ever commercial-scale production of sodium-ion batteries in the U.S.
“Sodium-ion batteries offer a unique alternative to lithium-ion, with higher power, faster recharge, longer lifecycle and a completely safe and stable chemistry,” said Colin Wessells — Natron Founder and Co-CEO — at the kick-off event in Michigan.
The new sodium-ion batteries charge and discharge at rates 10 times faster than lithium-ion, with an estimated lifespan of 50,000 cycles.
Wessells said that using sodium as a primary mineral alternative eliminates industry-wide issues of worker negligence, geopolitical disruption, and the “questionable environmental impacts” inextricably linked to lithium mining.
“The electrification of our economy is dependent on the development and production of new, innovative energy storage solutions,” Wessells said.
Why are sodium batteries a better alternative to lithium?
The birth and death cycle of lithium is shadowed in environmental destruction. The process of extracting lithium pollutes the water, air, and soil, and when it’s eventually discarded, the flammable batteries are prone to bursting into flames and burning out in landfills.
There’s also a human cost. Lithium-ion materials like cobalt and nickel are not only harder to source and procure, but their supply chains are also overwhelmingly attributed to hazardous working conditions and child labor law violations.
Sodium, on the other hand, is estimated to be 1,000 times more abundant in the earth’s crust than lithium.
“Unlike lithium, sodium can be produced from an abundant material: salt,” engineer Casey Crownhart wrote in the MIT Technology Review. “Because the raw ingredients are cheap and widely available, there’s potential for sodium-ion batteries to be significantly less expensive than their lithium-ion counterparts if more companies start making more of them.”
What will these batteries be used for?
Right now, Natron has its focus set on AI models and data storage centers, which consume hefty amounts of energy. In 2023, the MIT Technology Review reported that one AI model can emit more than 626,00 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent.
“We expect our battery solutions will be used to power the explosive growth in data centers used for Artificial Intelligence,” said Wendell Brooks, co-CEO of Natron.
“With the start of commercial-scale production here in Michigan, we are well-positioned to capitalize on the growing demand for efficient, safe, and reliable battery energy storage.”
The fast-charging energy alternative also has limitless potential on a consumer level, and Natron is eying telecommunications and EV fast-charging once it begins servicing AI data storage centers in June.
On a larger scale, sodium-ion batteries could radically change the manufacturing and production sectors — from housing energy to lower electricity costs in warehouses, to charging backup stations and powering electric vehicles, trucks, forklifts, and so on.
“I founded Natron because we saw climate change as the defining problem of our time,” Wessells said. “We believe batteries have a role to play.”
-via GoodGoodGood, May 3, 2024
--
Note: I wanted to make sure this was legit (scientifically and in general), and I'm happy to report that it really is! x, x, x, x
#batteries#lithium#lithium ion batteries#lithium battery#sodium#clean energy#energy storage#electrochemistry#lithium mining#pollution#human rights#displacement#forced labor#child labor#mining#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Billions of people will lose their livelihoods and economic output reduced by up to 34% if the Earth is allowed to warm by 3 degrees Celsius this century, but investing less than 2% of GDP now could eliminate most of those losses, a groundbreaking new report from Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and the University of Cambridge has found. Analyzing economic and climate science data, the report authors found that most economic climate damage this century will arise not from direct impacts like floods and fires, but from losses in productivity caused by reduced labor output, supply chain disruptions, and the collapse of crucial industries from fishing to tourism. From 2000-2023, direct U.S. losses from natural disasters attributed to climate change totaled $700 billion, but the harms to productivity were almost six times greater, amounting to $4 trillion in losses. "What stands out is that productivity loss—not merely capital destruction—is the primary driver of economic damage," said Kamiar Mohaddes, associate professor in economics and policy at Cambridge Judge Business School and a co-author of the report. "It is also clear that climate change will reduce income in all countries and across all sectors, affecting industries ranging from transport to manufacturing and retail, not only agriculture and other sectors commonly associated with nature."
[...]
"The economic case for climate action is clear, yet not broadly known and understood," said Annika Zawadzki, BCG managing director and partner, and a co-author of the report. "Investment in both mitigation and adaptation could bring a return of around tenfold by 2100." The authors conclude that such returns represent a “massive opportunity for humanity.” Looking at the average of the 11% to 27% cumulative economic output secured by climate investments, they found that: Just one-eightieth of the resulting savings, or $324 billion, could eradicate global extreme poverty. One-seventh of the savings could cover all global infrastructure investment needs this century, across sectors including energy, telecommunications, transport and water. Spending on health care could be tripled, globally. An eighth of the savings could cover all global military expenditures until 2100.
13 March 2025
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
McMurdo Internet
Internet service is supplied to Antarctica via a geostationary satellite. This far south, the satellite is only a few degrees above the horizon, and unfortunately for McMurdo, it's behind Mt Erebus. So the signal is beamed to a receiver on Black Island, about 20 miles away to the southwest, and bounced over to the sheltered alcove at the end of the Hut Point Peninsula where McMurdo sits.

The Chalet, administrative hub, with Black Island in the distance
The Black Island telecommunications infrastructure was installed in the 1980s, long before the internet we know and love today. It was upgraded in 2010 to allow more data transfer, mainly realtime weather data to feed into global forecast models. For this reason, it's probably the only place I've ever been where upload speed is remarkably faster than download speed – 60Mbps for outbound traffic, but only 20Mbps for inbound. Most regular internet use is receiving, not sending, so that's an entire base running on a connection that's only marginally faster than the average American smartphone. As you can imagine, this is somewhat limiting.
The limits to one's internet access actually begin before one even reaches the Ice. At the orientation in Christchurch, one is directed to a URL from which one must download and install a security programme from the U.S. government. It may feel like a hippie commune full of nerds, but McMurdo is an installation of the American state, and as such its computer network is a target of whatever disgruntled conspiracy theorist decides to hack The Man on any given day. Computers that are allowed onto this network (such as the one on which I am typing right now) have to have an approved firewall and antivirus service installed, then this extra programme on top of them. I am not sure what it does. For all I know the CIA is spying on me even now. (Hi, guys!) But you need to install it to get on the McMurdo Internet, such as it is, so I did.
To be honest, I was rather looking forward to a month cut off entirely from the hyperconnected world, so I was a tiny bit disappointed that quite a lot of day-to-day communication is done by email, and I would need to be on my computer a fair bit to get it. Had I known just how important email would be, I'd have installed an email client that actually downloads one's messages instead of just fetching them; as it was, the cycle of loading an email and sending the reply, even in Gmail's "HTML for slow connections" mode, took about five minutes, not counting the time it took to write. Tending one's email was a serious time commitment; sometimes I felt like I was spending more time on the computer in Antarctica than I did at home.

Crary scientists waiting, and waiting, and waiting
In a way, though, I was lucky, because I was technically a scientist and therefore had access to the one building on base with WiFi, the Crary Lab. And don't think you can just waltz into Crary with your laptop and poach the WiFi – in order to access it at all, you have to get set up by Crary IT with your own personal WiFi login. If you do not have Crary access, your portal to the Internet is one of a handful of ethernet cables in each of the dorm common rooms, or some public terminals in the main building. You can hop on, download your emails, maybe check the news or Google something you needed to look up, and then leave it for someone else. When most online time sinks are either blocked or too heavy to load, it’s amazing how little internet time you actually turn out to need.
Things that we have come to take for granted in The World are not a part of McMurdo life. Social media is pretty much out – the main platforms are bandwidth hogs even before you try to load a video or an animated GIF. There is no sharing of YouTube links, and no Netflix and chill. Someone was once sent home mid-season for trying to download a movie. Video calls with family and friends? Forget it. People do occasionally do video calls from Antarctica, often to media outlets or schools, but these have to be booked in advance so as to have the requisite bandwidth reserved. Jumping on FaceTime does not happen – not least because handheld devices have to be in airplane mode at all times for security reasons. Your phone might be secure enough for your internet banking, but not for US government internet!
It is, unavoidably, still a digital environment, it just gets by largely without internet access. Nearly everyone has an external hard drive, mostly for media that they've brought down to fill their off hours. If you want to share files you just swap hard drives, or hand over a memory stick. When the Antarctic Heritage Trust wanted some book material from me, I dropped it onto an SD card and ran it over to Scott Base on foot – a droll juxtaposition of high- and low-tech, not to mention a good excuse for a hike over The Gap on a beautiful day. It took half an hour, but was still faster than emailing it.
There is also a McMurdo Intranet, which includes a server for file sharing. Emailing someone your photos will take ages, but popping them into a folder on the I: drive and sending them a note to say you've done so (or, better yet, phoning them, or poking your head into their office) is much more efficient. To conserve space, this informal server partition is wiped every week, so you have to be quick about it, but it's an effective workaround, and also a good way to get relatively heavy resources to a large number of people in one go.
The telecommunications centre on Black Island is mostly automated, but like anything – perhaps more than some things, given the conditions – it needs to be maintained. There is a small hut out there for an equally small team of electricians and IT engineers; Black Island duty attracts the sort of person who might have been a lighthouse keeper back in the day.
Towards the end of my time on the Ice there was a spell where they needed to shut off the connection overnight, to do some necessary work. Given that most people's workdays extended at least to the shutoff time at 5:30 p.m., this meant essentially no internet for a large portion of the population, and some amusing flyers were posted up to notify everyone of the impending hardship.


Someday, faster, more accessible internet will come to Antarctica. It's more or less unavoidable, as communications technology improves, and everyone's work – especially the scientists' – depends more and more on having a broadband connection at all times. It will make a lot of things more convenient, and will make the long separation from friends and family much easier. But I'm pretty sure that many more people will mourn the upgrade than celebrate it. One can, theoretically, curtail one's internet use whenever one likes, but even before the pandemic it was almost impossible to live this way with the demands of modern life: I know from personal experience that opting out of Facebook alone can have a real detrimental effect on relationships, even with people one sees in the flesh fairly regularly, simply because everyone assumes that is how everyone else communicates. Being in a community where no one has access to assumed channels, and is more or less cut off from the rest of the world in a pocket universe of its own, levels the playing field and brings a certain unity. The planned (and, unarguably, necessary) updating of the physical infrastructure of McMurdo will wipe out a lot of the improvised, make-do-and-mend character of the place; how much would free and easy access to the online world change it in a less tangible way?
I'm sure the genuine Antarctic old-timers would shake their heads at the phone and email connections we have now, and say that no, this has already ruined Antarctica. It's not Antarctica unless your only link to the outside world is a dodgy radio. It's not Antarctica unless you only get mail once a year when the relief ship arrives. Doubtless the shiny new McMurdo will be seen as 'the good old days' by someone, someday, too. Change may happen slower there than elsewhere, but just like the rust on the tins at Cape Evans, it comes eventually, regardless.
For my own part, I'm glad I got to see 'old' McMurdo, such as it was, all plywood and cheap '90s prefab. The update will be much more efficient, and tidy, but yet another generation removed from the raw experience of the old explorers. My generation is probably the last to remember clearly what life was like before ubiquitous broadband; to some extent, Antarctica is a sort of time capsule of that world, just as the huts are a time capsule of Edwardian frontier life. I hope they'll find a way to hang on to the positive aspects of that.
Now, if you'll excuse me, I'm off to waste an hour mindlessly refreshing Twitter ...
If you'd like to learn more about the Black Island facility, there's a lot of good information (and some photos!) here: https://www.southpolestation.com/trivia/90s/blackisland.html
And this Antarctic Sunarticle goes into greater depth on the 2010 upgrade: https://antarcticsun.usap.gov/features/2114/
409 notes
·
View notes
Text
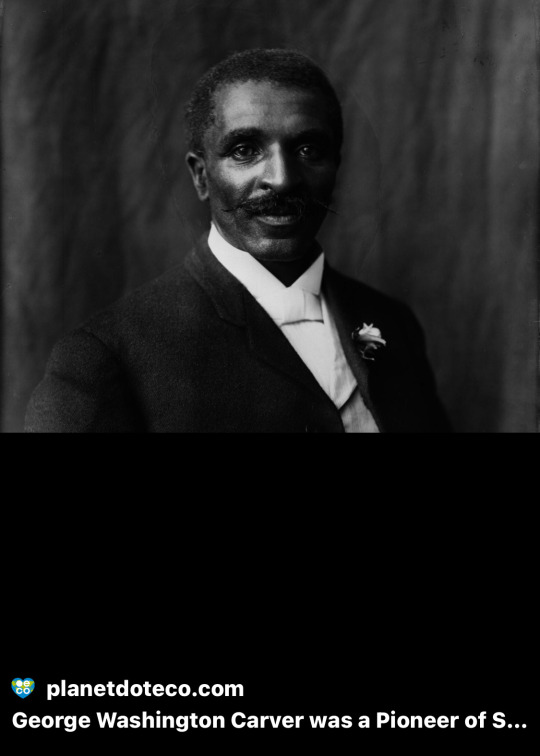
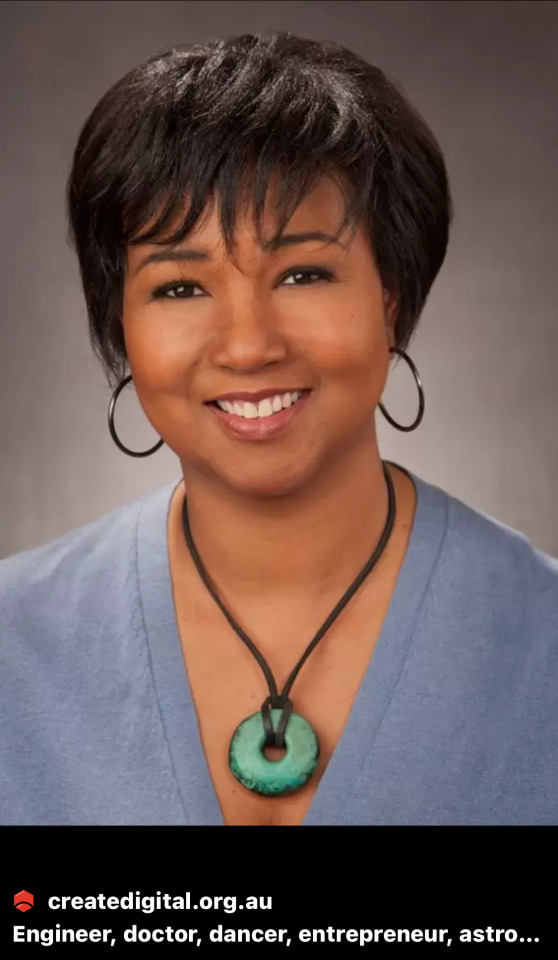
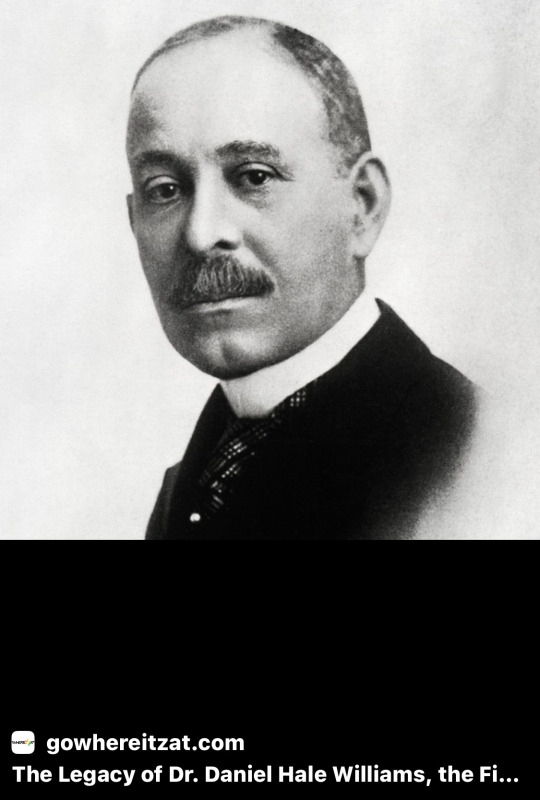
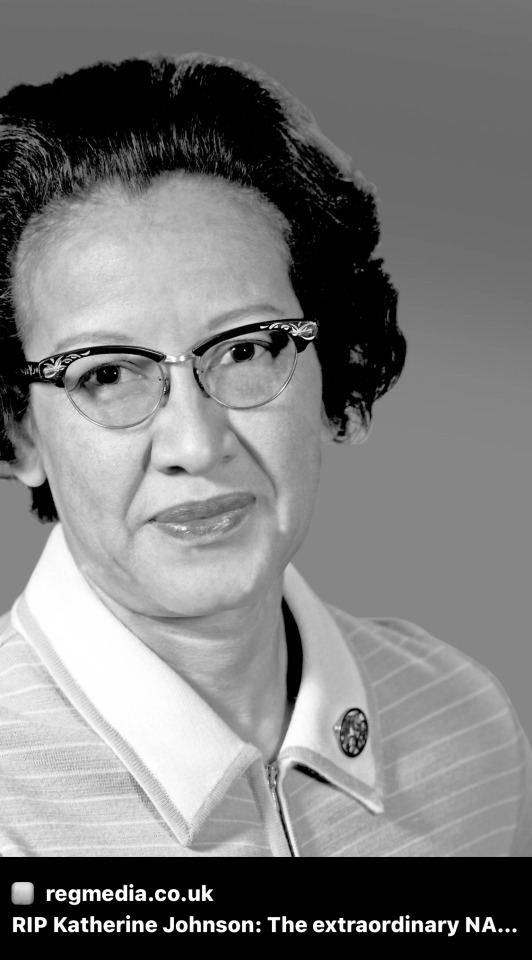





1. George Washington Carver (1864–1943):
An agricultural chemist, Carver developed alternative farming methods and is best known for his work with peanuts, introducing crop rotation techniques to improve soil fertility.
2. Dr. Shirley Ann Jackson (b. 1946):
A theoretical physicist, Dr. Jackson was the first African-American woman to earn a doctorate from MIT. Her research in physics led to advancements in telecommunications, including developments in caller ID and fiber-optic cables.
3. Katherine Johnson (1918–2020):
A mathematician whose calculations of orbital mechanics were critical to the success of U.S. crewed spaceflights, including John Glenn’s orbital mission in 1962. Her story gained widespread recognition through the book and film “Hidden Figures.”
4. Dr. Gladys West (b. 1930):
A mathematician whose work on satellite geodesy models was instrumental in the development of the Global Positioning System (GPS).
5. Roy L. Clay Sr. (1929–2024):
Known as the “Godfather of Silicon Valley,” Clay was a computer scientist who led the team that developed Hewlett-Packard’s first minicomputer and was instrumental in breaking racial barriers in the tech industry.
6. Dr. Mae Jemison (b. 1956):
A physician and NASA astronaut, Dr. Jemison became the first African-American woman to travel in space aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour in 1992.
7. Dr. Neil deGrasse Tyson (b. 1958):
An astrophysicist and science communicator, Dr. Tyson has made significant contributions to the public’s understanding of space and science through his work at the Hayden Planetarium and various media appearances.
8. Dr. Kizzmekia Corbett (b. 1986):
An immunologist who played a leading role in the development of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine, contributing to the fight against the global pandemic.
9. Dr. Daniel Hale Williams (1856–1931):
A pioneering surgeon, Dr. Williams performed one of the first successful open-heart surgeries in 1893. He also founded Provident Hospital in Chicago, the first non-segregated hospital in the United States.
10. Dr. Patricia Bath (1942–2019):
An ophthalmologist and inventor, Dr. Bath was the first African American woman to receive a medical patent. She invented the Laserphaco Probe, a device used to treat cataracts, significantly advancing eye surgery.
11. Dr. Charles Drew (1904–1950):
A physician and medical researcher, Dr. Drew developed improved techniques for blood storage and organized large-scale blood banks during World War II, saving countless lives. He was also the first African American to earn a Doctor of Medical Science degree from Columbia University.
12. Dr. James E. West (b. 1931):
An acoustician and inventor, Dr. West co-invented the electret microphone, a device used in approximately 90% of modern microphones, including those in telephones and hearing aids. He holds over 250 patents and has been a strong advocate for diversity in STEM fields.
13. Dr. Thomas Mensah (1950–2024):
A chemical engineer, Dr. Mensah made significant contributions to the development of fiber optic technology, which revolutionized telecommunications. He held 14 patents and was inducted into the National Academy of Inventors in 2015.
14. Marian Croak (b. 1955):
A computer scientist, Croak pioneered Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology, enabling voice communication over the internet. She holds over 200 patents and was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 2022.
15. Dr. David Blackwell (1919–2010):
A renowned mathematician and statistician, Dr. Blackwell was the first African American inducted into the National Academy of Sciences. He made significant contributions to game theory, probability theory, and information theory.
These individuals represent just a few of the many Black pioneers who have made groundbreaking contributions to science and technology. Their work continues to inspire future generations in STEM fields.
#black tumblr#black and proud#african america history#black history month#black history#black excellence#black americans
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kevin Breuninger and Lillian Rizzo at CNBC:
The Public Broadcasting Service on Friday sued President Donald Trump to block his attempt to cut off its federal funding, and accused the president of retaliating against the public broadcaster over “perceived political slights in news coverage.” Trump’s executive order targeting PBS’ funding “will upend public television,” lawyers for the broadcaster behind “Mister Rogers��� Neighborhood” and “Sesame Street” wrote in U.S. District Court in Washington, D.C. The U.S. Constitution and the half-century-old law governing public television forbid Trump from attempting to defund PBS or “serving as the arbiter” of its programming, PBS argued. The lawsuit from PBS and one of its member stations in Minnesota came three days after National Public Radio, or NPR, filed a similar suit against Trump and his administration. “After careful deliberation, PBS reached the conclusion that it was necessary to take legal action to safeguard public television’s editorial independence, and to protect the autonomy of PBS member stations,” a PBS spokesperson told CNBC in a statement. The nonprofit public media outlets both want the courts to invalidate Trump’s May 1 executive order commanding the Corporation for Public Broadcasting, or CPB, and all executive agencies to “cease Federal funding for NPR and PBS.” The White House said after PBS’ lawsuit was filed that the CPB was “creating media to support a particular political party on the taxpayers’ dime.” “Therefore, the President is exercising his lawful authority to limit funding to NPR and PBS,” spokesman Harrison Fields said in a statement Friday evening. “The President was elected with a mandate to ensure efficient use of taxpayer dollars, and he will continue to use his lawful authority to achieve that objective.” Trump’s order declared that the idea of the government funding the news media is “not only outdated and unnecessary but corrosive to the appearance of journalistic independence.” It also accused both PBS and NPR of failing to present “a fair, accurate, or unbiased portrayal of current events to taxpaying citizens.” Lawyers for PBS said they dispute Trump’s assertions “in the strongest possible terms.” But regardless, the president is legally barred from meddling with the broadcaster’s funding or its content, they wrote. They cited a federal telecommunications law’s dictate that no “department, agency, officer, or employee of the United States” may “exercise any direction, supervision, or control over public telecommunications, or over [CPB] or any of its grantees.”
PBS files a lawsuit against the Trump Regime over anti-American executive order (EO 14290) targeting federal funding for the network, along with NPR and CPB.
#PBS#Trump Administration II#Donald Trump#Federal Funding#Executive Order 14290#Corporation For Public Broadcasting#Public Broadcasting#PBS v. Trump
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
I stopped using my cellphone for regular calls and text messages last fall and switched to Signal. I wasn’t being paranoid—or at least I don’t think I was. I worked in the National Security Council, and we were told that China had compromised all major U.S. telecommunications companies and burrowed deep inside their networks. Beijing had gathered information on more than a million Americans, mainly in the Washington, D.C., area. The Chinese government could listen in to phone calls and read text messages. Experts call the Chinese state-backed group responsible Salt Typhoon, and the vulnerabilities it exploited have not been fixed. China is still there.
Telecommunications systems aren’t the only ones compromised. China has accessed enormous quantities of data on Americans for more than a decade. It has hacked into health-insurance companies and hotel chains, as well as security-clearance information held by the Office of Personnel Management.
The jaded response here is All countries spy. So what? But the spectacular surprise attacks that Ukraine and Israel have pulled off against their enemies suggest just how serious such penetration can become. In Operation Spiderweb, Ukraine smuggled attack drones on trucks with unwitting drivers deep inside of Russia, and then used artificial intelligence to simultaneously attack four military bases and destroy a significant number of strategic bombers, which are part of Russia’s nuclear triad. Israel created a real pager-production company in Hungary to infiltrate Hezbollah’s global supply chains and booby-trap its communication devices, killing or maiming much of the group’s leadership in one go. Last week, in Operation Rising Lion, Israel assassinated many top Iranian military leaders simultaneously and attacked the country’s nuclear facilities, thanks in part to a drone base it built inside Iran.
In each case, a resourceful, determined, and imaginative state used new technologies and data to do what was hitherto deemed impossible. America’s adversaries are also resourceful, determined, and imaginative.
Just think about what might happen if a U.S.-China war broke out over Taiwan.
A Chinese state-backed group called Volt Typhoon has been preparing plans to attack crucial infrastructure in the United States should the two countries ever be at war. As Jen Easterly put it in 2024 when she was head of the Cyber and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), China is planning to “launch destructive cyber-attacks in the event of a major crisis or conflict with the United States,” including “the disruption of our gas pipelines; the pollution of our water facilities; the severing of our telecommunications; the crippling of our transportation systems.”
The Biden administration took measures to fight off these cyberattacks and harden the infrastructure. Joe Biden also imposed some sanctions on China and took some specific measures to limit America’s exposure; he cut off imports of Chinese electric vehicles because of national-security concerns. Biden additionally signed a bill to ban TikTok, but President Donald Trump has issued rolling extensions to keep the platform functioning in the U.S. America and its allies will need to think hard about where to draw the line in the era of the Internet of Things, which connects nearly everything and could allow much of it—including robots, drones, and cloud computing—to be weaponized.
China isn’t the only problem. According to the U.S. Intelligence Community’s Annual Threat Assessment for this year, Russia is developing a new device to detonate a nuclear weapon in space with potentially “devastating” consequences. A Pentagon official last year said the weapon could pose “a threat to satellites operated by countries and companies around the globe, as well as to the vital communications, scientific, meteorological, agricultural, commercial, and national security services we all depend upon. Make no mistake, even if detonating a nuclear weapon in space does not directly kill people, the indirect impact could be catastrophic to the entire world.” The device could also render Trump’s proposed “Golden Dome” missile shield largely ineffective.
Americans can expect a major adversary to use drones and AI to go after targets deep inside the United States or allied countries. There is no reason to believe that an enemy wouldn’t take a page out of the Israeli playbook and go after leadership. New technologies reward acting preemptively, catching the adversary by surprise���so the United States may not get much notice. A determined adversary could even cut the undersea cables that allow the internet to function. Last year, vessels linked to Russia and China appeared to have severed those cables in Europe on a number of occasions, supposedly by accident. In a concerted hostile action, Moscow could cut or destroy these cables at scale.
Terrorist groups are less capable than state actors—they are unlikely to destroy most of the civilian satellites in space, for example, or collapse essential infrastructure—but new technologies could expand their reach too. In their book The Coming Wave, Mustafa Suleyman and Michael Bhaskar described some potential attacks that terrorists could undertake: unleashing hundreds or thousands of drones equipped with automatic weapons and facial recognition on multiple cities simultaneously, say, or even one drone to spray a lethal pathogen on a crowd.
A good deal of American infrastructure is owned by private companies with little incentive to undertake the difficult and costly fixes that might defend against Chinese infiltration. Certainly this is true of telecommunications companies, as well as those providing utilities such as water and electricity. Making American systems resilient could require a major public outlay. But it could cost less than the $150 billion (one estimate has that figure at an eye-popping $185 billion) that the House of Representatives is proposing to appropriate this year to strictly enforce immigration law.
Instead, the Trump administration proposed slashing funding for CISA, the agency responsible for protecting much of our infrastructure against foreign attacks, by $495 million, or approximately 20 percent of its budget. That cut will make the United States more vulnerable to attack.
The response to the drone threat has been no better. Some in Congress have tried to pass legislation expanding government authority to detect and destroy drones over certain kinds of locations, but the most recent effort failed. Senator Rand Paul, who was then the ranking member of the Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs and is now the chair, said there was no imminent threat and warned against giving the government sweeping surveillance powers, although the legislation entailed nothing of the sort. Senators from both parties have resisted other legislative measures to counter drones.
The United States could learn a lot from Ukraine on how to counter drones, as well as how to use them, but the administration has displayed little interest in doing this. The massively expensive Golden Dome project is solely focused on defending against the most advanced missiles but should be tasked with dealing with the drone threat as well.
Meanwhile, key questions go unasked and unanswered. What infrastructure most needs to be protected? Should aircraft be kept in the open? Where should the United States locate a counter-drone capability?
After 9/11, the United States built a far-reaching homeland-security apparatus focused on counterterrorism. The Trump administration is refocusing it on border security and immigration. But the biggest threat we face is not terrorism, let alone immigration. Those responsible for homeland security should not be chasing laborers on farms and busboys in restaurants in order to meet quotas imposed by the White House.
The wars in Ukraine and the Middle East are giving Americans a glimpse into the battles of the future—and a warning. It is time to prepare.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
With the exceptions of North Korea and Cuba, the communist world has merged onto the capitalist highway in a couple different ways during the twenty-first century. As you’ve read, free-trade imperialism and its cheap agricultural imports pushed farmers into the cities and into factory work, lowering the global price of manufacturing labor and glutting the world market with stuff. Forward-thinking states such as China and Vietnam invested in high-value-added production capacity and managed labor organizing, luring links from the global electronics supply chain and jump-starting capital investment. Combined with capital’s hesitancy to invest in North Atlantic production facilities, as well as a disinclination toward state-led investment in the region, Asian top-down planning erased much of the West’s technological edge. If two workers can do a single job, and one worker costs less, both in wages and state support, why pick the expensive one? Foxconn’s 2017 plan to build a U.S. taxpayer–subsidized $10 billion flat-panel display factory in Wisconsin was trumpeted by the president, but it was a fiasco that produced zero screens. The future cost of labor looks to be capped somewhere below the wage levels many people have enjoyed, and not just in the West.
The left-wing economist Joan Robinson used to tell a joke about poverty and investment, something to the effect of: The only thing worse than being exploited by capitalists is not being exploited by capitalists. It’s a cruel truism about the unipolar world, but shouldn’t second place count for something? When the Soviet project came to an end, in the early 1990s, the country had completed world history’s biggest, fastest modernization project, and that didn’t just disappear. Recall that Cisco was hyped to announce its buyout of the Evil Empire’s supercomputer team. Why wasn’t capitalist Russia able to, well, capitalize? You’re already familiar with one of the reasons: The United States absorbed a lot of human capital originally financed by the Soviet people. American immigration policy was based on draining technical talent in particular from the Second World. Sergey Brin is the best-known person in the Moscow-to-Palo-Alto pipeline, but he’s not the only one.
Look at the economic composition of China and Russia in the wake of Soviet dissolution: Both were headed toward capitalist social relations, but they took two different routes. The Russian transition happened rapidly. The state sold off public assets right away, and the natural monopolies such as telecommunications and energy were divided among a small number of skilled and connected businessmen, a category of guys lacking in a country that frowned on such characters but that grew in Gorbachev’s liberalizing perestroika era. Within five years, the country sold off an incredible 35 percent of its national wealth. Russia’s richest ended the century with a full counterrevolutionary reversal of their fortunes, propelling their income share above what it was before the Bolsheviks took over. To accomplish this, the country’s new capitalists fleeced the most vulnerable half of their society. “Over the 1989–2016 period, the top 1 percent captured more than two-thirds of the total growth in Russia,” found an international group of scholars, “while the bottom 50 percent actually saw a decline in its income.” Increases in energy prices encouraged the growth of an extractionist petro-centered economy. Blood-covered, teary, and writhing, infant Russian capital crowded into the gas and oil sectors. The small circle of oligarchs privatized unemployed KGB-trained killers to run “security,” and gangsters dominated politics at the local and national levels. They installed a not particularly well-known functionary—a former head of the new intelligence service FSB who also worked on the privatization of government assets—as president in a surprise move on the first day of the year 2000. He became the gangster in chief.
Vladimir Putin’s first term coincided with the energy boom, and billionaires gobbled up a ludicrous share of growth. If any individual oligarch got too big for his britches, Putin was not beyond imposing serious consequences. He reinserted the state into the natural monopolies, this time in collaboration with loyal capitalists, and his stranglehold on power remains tight for now, despite the outstandingly uneven distribution of growth. Between 1980 and 2015, the Russian top 1 percent grew its income an impressive 6.2 percent per year, but the top .001 percent has maintained a growth rate of 17 percent over the same period. To invest these profits, the Russian billionaires parked their money in real estate, bidding up housing prices, and stashed a large amount of their wealth offshore. Reinvestment in Russian production was not a priority—why go through the hassle when there were easier ways to keep getting richer?
While Russia grew billionaires instead of output, China saw a path to have both. As in the case of Terry Gou, the Chinese Communist Party tempered its transition by incorporating steadily increasing amounts of foreign direct investment through Hong Kong and Taiwan, picking partners and expanding outward from the special economic zones. State support for education and infrastructure combined with low wages to make the mainland too attractive to resist. (Russia’s population is stagnant, while China’s has grown quickly.) China’s entry into the World Trade Organization, in 2001, gave investors more confidence. Meanwhile, strong capital controls kept the country out of the offshore trap, and state development priorities took precedence over extraction and get-rich-quick schemes. Chinese private wealth was rechanneled into domestic financial assets—equity and bonds or other loan instruments—at a much higher rate than it was in Russia. The result has been a sustained high level of annual output growth compared to the rest of the world, the type that involves putting up an iPhone City in a matter of months. As it has everywhere else, that growth has been skewed: only an average of 4.5 percent for the bottom half of earners in the 1978–2015 period compared to more than 10 percent for the top .001 percent. But this ratio of just over 2–1 is incomparable to Russia’s 17–.5 ration during the same period.
Since the beginning of the twenty-first century, certain trends have been more or less unavoidable. The rich have gotten richer relative to the poor and working class—in Russia, in China, in the United States, and pretty much anywhere else you want to look. Capital has piled into property markets, driving up the cost of housing everywhere people want to live, especially in higher-wage cities and especially in the world’s financial centers. Capitalist and communist countries alike have disgorged public assets into private pockets. But by maintaining a level of control over the process and slowing its tendencies, the People’s Republic of China has built a massive and expanding postindustrial manufacturing base.
It’s important to understand both of these patterns as part of the same global system rather than as two opposed regimes. One might imagine, based on what I’ve written so far, that the Chinese model is useful, albeit perhaps threatening, in the long term for American tech companies while the Russian model is irrelevant. Some commentators have phrased this as the dilemma of middle-wage countries on the global market: Wages in China are going to be higher than wages in Russia because wages in Russia used to be higher than wages in China. But Russia’s counterrevolutionary hyper-bifurcation has been useful for Silicon Valley as well; they are two sides of the same coin. Think about it this way: If you’re a Russian billionaire in the first decades of the twenty-first century looking to invest a bunch of money you pulled out of the ground, where’s the best place you could put it? The answer is Palo Alto.
Malcolm Harris, Palo Alto
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tapping My Telephone
In the spring of 2013, Edward Snowden, a contractor with Booz Allen Hamilton working for the National Security Agency, liberated a trove of documents essentially proving that all the previous NSA whistleblowers like Russel Tice, Edward Loomis, J. Kirk Wiebe, Thomas Drake and William Binney, and great journalists like James Bamford, author of The Puzzle Palace, Body of Secrets and The Shadow Factory, had been right on and much worse. The NSA, Snowden’s leak proved, was violating the civil liberties of virtually all Americans, working with telecommunications and Silicon Valley firms to compile endless amounts of metadata and cellphone location data, search, web traffic, email and instant messenger histories. This is all not to mention their wide-scale surveillance of the rest of the people of the planet, in cooperation with the “Five Eyes” of the Anglosphere alliance, which includes Canada, the UK, Australia and New Zealand — six if one counts Israel. Snowden’s leak to journalists Glenn Greenwald, Laura Poitras, Ewen MacAskill and Barton Gellman was a heroic service to the American people and to mankind. Snowden has said he was motivated to do this when he saw National Intelligence Director James Clapper perjure himself before Congress, falsely denying that the NSA was collecting data on innocent Americans.
The U.S. government, which was apparently too busy keeping tabs on all of us to take care of their own secrets or track down their missing contractor, was embarrassed. So naturally they lied, claiming Snowden was a spy working for Russia and China. Well, he had originally gone to Hong Kong, and the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act warrant he released was the most recent version. You just have to imagine the rest of the case, because those total non sequiturs were all they ever had beyond wild anonymous claims.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ancient 9 Ether MU-5000.com Domain Creator [D.C.] 1968-michaelharrelljr.com... EXTRA TELEPATHIC [E.T.] Telecommunication [E.T.] Intel Architect Engineer Programmer Creator [PC] of ANU [PA] AutoCAD.com [PAC] Drafting Network [PDN] Science @ quantumharrelltech.ca.gov’s quantumharrelltelecom.tech SKY MILITARY KINGDOM of quantumharrelltech.com's 6g-quantumharrell.tech MOON Universe [MU] of Interplanetary [MI = MICHAEL] 9 Ether [ME] 1698att-internetair.com Business Worlds... since wegullahgeechee.com Peoples of ANU GOLDEN 9 Ether [PAGE] ATLANTIS [PA] 5000!!!
WELCOME BACK HOME IMMORTAL [HIM] U.S. MILITARY KING SOLOMON-MICHAEL HARRELL, JR.™

i.b.monk [ibm.com] mode [i’m] tech [IT] steelecartel.com @ quantumharrelltech.ca.gov
quantumharrelltech.ca.gov Outside Our 1921steelecartel.tech MACHINE SKY Firmament Domain DOME… OVER Earth [Qi]

eye 1st kingtutdna.com domain creator [d.c.] of harrelltut.com

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon
ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon
ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

ommmmm.tech moon

eye inside the moon

© 1698-2223 QUANTUM HARRELL TECH LLC All LOST ANCIENT [L.A.] ATLANTEAN DNA [A.D.] DotCom [A.D.] + DotTech [A.D.] + Pre 1698quantumharrellgov.tech Military Domain Name Rights Reserved @ quantumharrelltech.ca.gov
#mu:13#king tut#kemet#harrelltut#quantumharrelltech#u.s. michael harrell#quantumharrelltut#o michael#telecomindustry#telecommunications#telecomunicaciones#telecommuting#telecomsolutions#software#digital transformation#technology#wifi#6g#18
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

NASA and Italian Space Agency test future lunar navigation technology
As the Artemis campaign leads humanity to the moon and eventually Mars, NASA is refining its state-of-the-art navigation and positioning technologies to guide a new era of lunar exploration.
A technology demonstration helping pave the way for these developments is the Lunar GNSS Receiver Experiment (LuGRE) payload, a joint effort between NASA and the Italian Space Agency to demonstrate the viability of using existing GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signals for positioning, navigation, and timing on the moon.
During its voyage on an upcoming delivery to the moon as part of NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, LuGRE would demonstrate acquiring and tracking signals from both the U.S. GPS and European Union Galileo GNSS constellations during transit to the moon, during lunar orbit, and finally for up to two weeks on the lunar surface itself.
The LuGRE payload is one of the first demonstrations of GNSS signal reception and navigation on and around the lunar surface, an important milestone for how lunar missions will access navigation and positioning technology.
If successful, LuGRE would demonstrate that spacecraft can use signals from existing GNSS satellites at lunar distances, reducing their reliance on ground-based stations on the Earth for lunar navigation.
Today, GNSS constellations support essential services like navigation, banking, power grid synchronization, cellular networks, and telecommunications. Near-Earth space missions use these signals in flight to determine critical operational information like location, velocity, and time.
NASA and the Italian Space Agency want to expand the boundaries of GNSS use cases. In 2019, the Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission broke the world record for farthest GPS signal acquisition 116,300 miles from the Earth's surface—nearly half of the 238,900 miles between Earth and the moon. Now, LuGRE could double that distance.
"GPS makes our lives safer and more viable here on Earth," said Kevin Coggins, NASA deputy associate administrator and SCaN (Space Communications and Navigation) Program manager at NASA Headquarters in Washington. "As we seek to extend humanity beyond our home planet, LuGRE should confirm that this extraordinary technology can do the same for us on the moon."
Reliable space communication and navigation systems play a vital role in all NASA missions, providing crucial connections from space to Earth for crewed and uncrewed missions alike. Using a blend of government and commercial assets, NASA's Near Space and Deep Space Networks support science, technology demonstrations, and human spaceflight missions across the solar system.
"This mission is more than a technological milestone," said Joel Parker, policy lead for positioning, navigation, and timing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
"We want to enable more and better missions to the moon for the benefit of everyone, and we want to do it together with our international partners."
The data-gathering LuGRE payload combines NASA-led systems engineering and mission management with receiver software and hardware developed by the Italian Space Agency and their industry partner Qascom—the first Italian-built hardware to operate on the lunar surface.
Any data LuGRE collects is intended to open the door for use of GNSS to all lunar missions, not just those by NASA or the Italian Space Agency. Approximately six months after LuGRE completes its operations, the agencies will release its mission data to broaden public and commercial access to lunar GNSS research.
"A project like LuGRE isn't about NASA alone," said NASA Goddard navigation and mission design engineer Lauren Konitzer. "It's something we're doing for the benefit of humanity. We're working to prove that lunar GNSS can work, and we're sharing our discoveries with the world."
The LuGRE payload is one of 10 science experiments launching to the lunar surface on this delivery through NASA's CLPS initiative.
Through CLPS, NASA works with American companies to provide delivery and quantity contracts for commercial deliveries to further lunar exploration and the development of a sustainable lunar economy. As of 2024, the agency has 14 private partners on contract for current and future CLPS missions.
Demonstrations like LuGRE could lay the groundwork for GNSS-based navigation systems on the lunar surface. Bridging these existing systems with emerging lunar-specific navigation solutions has the potential to define how all spacecraft navigate lunar terrain in the Artemis era.
The payload is a collaborative effort between NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center and the Italian Space Agency.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's the complete list of DHS flagged search terms. Don't use any of these on social media to avoid having the 3-letter agencies express interest in your activities!
DHS & Other Agencies
Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
Coast Guard (USCG)
Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
Border Patrol
Secret Service (USSS)
National Operations Center (NOC)
Homeland Defense
Immigration Customs Enforcement (ICE)
Agent
Task Force
Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
Fusion Center
Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA)
Secure Border Initiative (SBI)
Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
Alcohol Tobacco and Firearms (ATF)
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (CIS)
Federal Air Marshal Service (FAMS)
Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
Air Marshal
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)
National Guard
Red Cross
United Nations (UN)
Domestic Security
Assassination
Attack
Domestic security
Drill
Exercise
Cops
Law enforcement
Authorities
Disaster assistance
Disaster management
DNDO (Domestic Nuclear Detection Office)
National preparedness
Mitigation
Prevention
Response
Recovery
Dirty Bomb
Domestic nuclear detection
Emergency management
Emergency response
First responder
Homeland security
Maritime domain awareness (MDA)
National preparedness initiative
Militia
Shooting
Shots fired
Evacuation
Deaths
Hostage
Explosion (explosive)
Police
Disaster medical assistance team (DMAT)
Organized crime
Gangs
National security
State of emergency
Security
Breach
Threat
Standoff
SWAT
Screening
Lockdown
Bomb (squad or threat)
Crash
Looting
Riot
Emergency Landing
Pipe bomb
Incident
Facility
HAZMAT & Nuclear
Hazmat
Nuclear
Chemical Spill
Suspicious package/device
Toxic
National laboratory
Nuclear facility
Nuclear threat
Cloud
Plume
Radiation
Radioactive
Leak
Biological infection (or event)
Chemical
Chemical burn
Biological
Epidemic
Hazardous
Hazardous material incident
Industrial spill
Infection
Powder (white)
Gas
Spillover
Anthrax
Blister agent
Exposure
Burn
Nerve agent
Ricin
Sarin
North Korea
Health Concern + H1N1
Outbreak
Contamination
Exposure
Virus
Evacuation
Bacteria
Recall
Ebola
Food Poisoning
Foot and Mouth (FMD)
H5N1
Avian
Flu
Salmonella
Small Pox
Plague
Human to human
Human to ANIMAL
Influenza
Center for Disease Control (CDC)
Drug Administration (FDA)
Public Health
Toxic
Agro Terror
Tuberculosis (TB)
Agriculture
Listeria
Symptoms
Mutation
Resistant
Antiviral
Wave
Pandemic
Infection
Water/air borne
Sick
Swine
Pork
Strain
Quarantine
H1N1
Vaccine
Tamiflu
Norvo Virus
Epidemic
World Health Organization (WHO and components)
Viral Hemorrhagic Fever
E. Coli
Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure security
Airport
CIKR (Critical Infrastructure & Key Resources)
AMTRAK
Collapse
Computer infrastructure
Communications infrastructure
Telecommunications
Critical infrastructure
National infrastructure
Metro
WMATA
Airplane (and derivatives)
Chemical fire
Subway
BART
MARTA
Port Authority
NBIC (National Biosurveillance Integration Center)
Transportation security
Grid
Power
Smart
Body scanner
Electric
Failure or outage
Black out
Brown out
Port
Dock
Bridge
Canceled
Delays
Service disruption
Power lines
Southwest Border Violence
Drug cartel
Violence
Gang
Drug
Narcotics
Cocaine
Marijuana
Heroin
Border
Mexico
Cartel
Southwest
Juarez
Sinaloa
Tijuana
Torreon
Yuma
Tucson
Decapitated
U.S. Consulate
Consular
El Paso
Fort Hancock
San Diego
Ciudad Juarez
Nogales
Sonora
Colombia
Mara salvatrucha
MS13 or MS-13
Drug war
Mexican army
Methamphetamine
Cartel de Golfo
Gulf Cartel
La Familia
Reynose
Nuevo Leon
Narcos
Narco banners (Spanish equivalents)
Los Zetas
Shootout
Execution
Gunfight
Trafficking
Kidnap
Calderon
Reyosa
Bust
Tamaulipas
Meth Lab
Drug trade
Illegal immigrants
Smuggling (smugglers)
Matamoros
Michoacana
Guzman
Arellano-Felix
Beltran-Leyva
Barrio Azteca
Artistics Assassins
Mexicles
New Federation
Terrorism
Terrorism
Al Queda (all spellings)
Terror
Attack
Iraq
Afghanistan
Iran
Pakistan
Agro
Environmental terrorist
Eco terrorism
Conventional weapon
Target
Weapons grade
Dirty bomb
Enriched
Nuclear
Chemical weapon
Biological weapon
Ammonium nitrate
Improvised explosive device
IED (Improvised Explosive Device)
Abu Sayyaf
Hamas
FARC (Armed Revolutionary Forces Colombia)
IRA (Irish Republican Army)
ETA (Euskadi ta Askatasuna)
Basque Separatists
Hezbollah
Tamil Tiger
PLF (Palestine Liberation Front)
PLO (Palestine Libration Organization)
Car bomb
Jihad
Taliban
Weapons cache
Suicide bomber
Suicide attack
Suspicious substance
AQAP (Al Qaeda Arabian Peninsula)
AQIM (Al Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb)
TTP (Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan)
Yemen
Pirates
Extremism
Somalia
Nigeria
Radicals
Al-Shabaab
Home grown
Plot
Nationalist
Recruitment
Fundamentalism
Islamist
Weather/Disaster/Emergency
Emergency
Hurricane
Tornado
Twister
Tsunami
Earthquake
Tremor
Flood
Storm
Crest
Temblor
Extreme weather
Forest fire
Brush fire
Ice
Stranded/Stuck
Help
Hail
Wildfire
Tsunami Warning Center
Magnitude
Avalanche
Typhoon
Shelter-in-place
Disaster
Snow
Blizzard
Sleet
Mud slide or Mudslide
Erosion
Power outage
Brown out
Warning
Watch
Lightening
Aid
Relief
Closure
Interstate
Burst
Emergency Broadcast System
Cyber Security
Cyber security
Botnet
DDOS (dedicated denial of service)
Denial of service
Malware
Virus
Trojan
Keylogger
Cyber Command
2600
Spammer
Phishing
Rootkit
Phreaking
Cain and abel
Brute forcing
Mysql injection
Cyber attack
Cyber terror
Hacker
China
Conficker
Worm
Scammers
Social media
SOCIAL MEDIA?!
23 notes
·
View notes