#best Kubernetes command line tools
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Best Kubernetes Management Tools in 2023
Best Kubernetes Management Tools in 2023 #homelab #vmwarecommunities #Kubernetesmanagementtools2023 #bestKubernetescommandlinetools #managingKubernetesclusters #Kubernetesdashboardinterfaces #kubernetesmanagementtools #Kubernetesdashboard
Kubernetes is everywhere these days. It is used in the enterprise and even in many home labs. It’s a skill that’s sought after, especially with today’s push for app modernization. Many tools help you manage things in Kubernetes, like clusters, pods, services, and apps. Here’s my list of the best Kubernetes management tools in 2023. Table of contentsWhat is Kubernetes?Understanding Kubernetes and…

View On WordPress
#best Kubernetes command line tools#containerized applications management#Kubernetes cluster management tools#Kubernetes cost monitoring#Kubernetes dashboard interfaces#Kubernetes deployment solutions#Kubernetes management tools 2023#large Kubernetes deployments#managing Kubernetes clusters#open-source Kubernetes tools
0 notes
Text
SRE Roadmap: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Site Reliability Engineer in 2025
In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) has become one of the most in-demand roles across industries. As organizations scale and systems become more complex, the need for professionals who can bridge the gap between development and operations is critical. If you’re looking to start or transition into a career in SRE, this comprehensive SRE roadmap will guide you step by step in 2025.

Why Follow an SRE Roadmap?
The field of SRE is broad, encompassing skills from DevOps, software engineering, cloud computing, and system administration. A well-structured SRE roadmap helps you:
Understand what skills are essential at each stage.
Avoid wasting time on non-relevant tools or technologies.
Stay up to date with industry standards and best practices.
Get job-ready with the right certifications and hands-on experience.
SRE Roadmap: Step-by-Step Guide
🔹 Phase 1: Foundation (Beginner Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Linux Fundamentals – Learn the command line, shell scripting, and process management.
Networking Basics – Understand DNS, HTTP/HTTPS, TCP/IP, firewalls, and load balancing.
Version Control – Master Git and GitHub for collaboration.
Programming Languages – Start with Python or Go for scripting and automation tasks.
Tools to Learn:
Git
Visual Studio Code
Postman (for APIs)
Recommended Resources:
"The Linux Command Line" by William Shotts
GitHub Learning Lab
🔹 Phase 2: Core SRE Skills (Intermediate Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Configuration Management – Learn tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef.
Containers & Orchestration – Understand Docker and Kubernetes.
CI/CD Pipelines – Use Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions.
Monitoring & Logging – Get familiar with Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack, or Datadog.
Cloud Platforms – Gain hands-on experience with AWS, GCP, or Azure.
Certifications to Consider:
AWS Certified SysOps Administrator
Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA)
Google Cloud Professional SRE
🔹 Phase 3: Advanced Practices (Expert Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Site Reliability Principles – Learn about SLIs, SLOs, SLAs, and Error Budgets.
Incident Management – Practice runbooks, on-call rotations, and postmortems.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) – Master Terraform or Pulumi.
Scalability and Resilience Engineering – Understand fault tolerance, redundancy, and chaos engineering.
Tools to Explore:
Terraform
Chaos Monkey (for chaos testing)
PagerDuty / OpsGenie
Real-World Experience Matters
While theory is important, hands-on experience is what truly sets you apart. Here are some tips:
Set up your own Kubernetes cluster.
Contribute to open-source SRE tools.
Create a portfolio of automation scripts and dashboards.
Simulate incidents to test your monitoring setup.
Final Thoughts
Following this SRE roadmap will provide you with a clear and structured path to break into or grow in the field of Site Reliability Engineering. With the right mix of foundational skills, real-world projects, and continuous learning, you'll be ready to take on the challenges of building reliable, scalable systems.
Ready to Get Certified?
Take your next step with our SRE Certification Course and fast-track your career with expert training, real-world projects, and globally recognized credentials.
0 notes
Text
Docker Tutorial for Beginners: Learn Docker Step by Step
What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform that enables developers to automate the deployment of applications inside lightweight, portable containers. These containers include everything the application needs to run—code, runtime, system tools, libraries, and settings—so that it can work reliably in any environment.
Before Docker, developers faced the age-old problem: “It works on my machine!” Docker solves this by providing a consistent runtime environment across development, testing, and production.
Why Learn Docker?
Docker is used by organizations of all sizes to simplify software delivery and improve scalability. As more companies shift to microservices, cloud computing, and DevOps practices, Docker has become a must-have skill. Learning Docker helps you:
Package applications quickly and consistently
Deploy apps across different environments with confidence
Reduce system conflicts and configuration issues
Improve collaboration between development and operations teams
Work more effectively with modern cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP
Who Is This Docker Tutorial For?
This Docker tutorial is designed for absolute beginners. Whether you're a developer, system administrator, QA engineer, or DevOps enthusiast, you’ll find step-by-step instructions to help you:
Understand the basics of Docker
Install Docker on your machine
Create and manage Docker containers
Build custom Docker images
Use Docker commands and best practices
No prior knowledge of containers is required, but basic familiarity with the command line and a programming language (like Python, Java, or Node.js) will be helpful.
What You Will Learn: Step-by-Step Breakdown
1. Introduction to Docker
We start with the fundamentals. You’ll learn:
What Docker is and why it’s useful
The difference between containers and virtual machines
Key Docker components: Docker Engine, Docker Hub, Dockerfile, Docker Compose
2. Installing Docker
Next, we guide you through installing Docker on:
Windows
macOS
Linux
You’ll set up Docker Desktop or Docker CLI and run your first container using the hello-world image.
3. Working with Docker Images and Containers
You’ll explore:
How to pull images from Docker Hub
How to run containers using docker run
Inspecting containers with docker ps, docker inspect, and docker logs
Stopping and removing containers
4. Building Custom Docker Images
You’ll learn how to:
Write a Dockerfile
Use docker build to create a custom image
Add dependencies and environment variables
Optimize Docker images for performance
5. Docker Volumes and Networking
Understand how to:
Use volumes to persist data outside containers
Create custom networks for container communication
Link multiple containers (e.g., a Node.js app with a MongoDB container)
6. Docker Compose (Bonus Section)
Docker Compose lets you define multi-container applications. You’ll learn how to:
Write a docker-compose.yml file
Start multiple services with a single command
Manage application stacks easily
Real-World Examples Included
Throughout the tutorial, we use real-world examples to reinforce each concept. You’ll deploy a simple web application using Docker, connect it to a database, and scale services with Docker Compose.
Example Projects:
Dockerizing a static HTML website
Creating a REST API with Node.js and Express inside a container
Running a MySQL or MongoDB database container
Building a full-stack web app with Docker Compose
Best Practices and Tips
As you progress, you’ll also learn:
Naming conventions for containers and images
How to clean up unused images and containers
Tagging and pushing images to Docker Hub
Security basics when using Docker in production
What’s Next After This Tutorial?
After completing this Docker tutorial, you’ll be well-equipped to:
Use Docker in personal or professional projects
Learn Kubernetes and container orchestration
Apply Docker in CI/CD pipelines
Deploy containers to cloud platforms
Conclusion
Docker is an essential tool in the modern developer's toolbox. By learning Docker step by step in this beginner-friendly tutorial, you’ll gain the skills and confidence to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently and consistently across different environments.
Whether you’re building simple web apps or complex microservices, Docker provides the flexibility, speed, and scalability needed for success. So dive in, follow along with the hands-on examples, and start your journey to mastering containerization with Docker tpoint-tech!
0 notes
Text
AWS Introduces AWS MCP Servers for Serverless, ECS, & EKS

MCP AWS server
The AWS Labs GitHub repository now has Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers for AWS Serverless, Amazon ECS, and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service. Real-time contextual responses from open-source solutions trump AI development assistants' pre-trained knowledge. MCP servers provide current context and service-specific information to help you avoid deployment issues and improve service interactions, while AI assistant Large Language Models (LLM) use public documentation.
These open source solutions can help you design and deploy apps faster by using Amazon Web Services (AWS) features and configurations. These MCP servers enable AI code assistants with deep understanding of Amazon ECS, Amazon EKS, and AWS Serverless capabilities, speeding up the code-to-production process in your IDE or debugging production issues. They integrate with popular AI-enabled IDEs like Amazon Q Developer on the command line to allow you design and deploy apps using natural language commands.
Specialist MCP servers' functions:
With Amazon ECS MCP Server, applications can be deployed and containerised quickly. It helps configure AWS networking, load balancers, auto-scaling, task definitions, monitoring, and services. Real-time troubleshooting can fix deployment difficulties, manage cluster operations, and apply auto-scaling using natural language.
Amazon EKS MCP Server gives AI helpers contextual, up-to-date information for Kubernetes EKS environments. By providing the latest EKS features, knowledge base, and cluster state data, it enables AI code assistants more exact, customised aid throughout the application lifecycle.
The AWS Serverless MCP Server enhances serverless development. AI coding helpers learn AWS services, serverless patterns, and best practices. Integrating with the AWS Serverless Application Model Command Line Interface (AWS SAM CLI) to manage events and deploy infrastructure using tried-and-true architectural patterns streamlines function lifecycles, service integrations, and operational requirements. It also advises on event structures, AWS Lambda best practices, and code.
Users are directed to the AWS Labs GitHub repository for installation instructions, example settings, and other specialist servers, such as Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases Retrieval and AWS Lambda function transformation servers.
AWS MCP server operation
Giving Context: The MCP servers give AI assistants current context and knowledge about specific AWS capabilities, configurations, and even your surroundings (such as the EKS cluster state), eliminating the need for broad or outdated knowledge. For more accurate service interactions and fewer deployment errors, this is crucial.
They enable AI code assistance deep service understanding of AWS Serverless, ECS, and EKS. This allows the AI to make more accurate and tailored recommendations from code development to production issues.
The servers allow developers to construct and deploy apps using natural language commands using AI-enabled IDEs and tools like Amazon Q Developer on the command line. The AI assistant can use the relevant MCP server to get context or do tasks after processing the natural language query.
Aiding Troubleshooting and Service Actions: Servers provide tools and functionality for their AWS services. As an example:
Amazon ECS MCP Server helps configure load balancers and auto-scaling. Real-time debugging tools like fetch_task_logs can help the AI assistant spot issues in natural language queries.
The Amazon EKS MCP Server provides cluster status data and utilities like search_eks_troubleshoot_guide to fix EKS issues and generate_app_manifests to build Kubernetes clusters.
In addition to contextualising serverless patterns, best practices, infrastructure as code decisions, and event schemas, the AWS Serverless MCP Server communicates with the AWS SAM CLI. An example shows how it can help the AI helper discover best practices and architectural demands.
An AI assistant like Amazon Q can communicate with the right AWS MCP server for ECS, EKS, or Serverless development or deployment questions. This server can activate service-specific tools or provide specialised, current, or real-time information to help the AI assistant reply more effectively and accurately. This connection accelerates coding-to-production.
#AWSMCPserver#AmazonElasticContainerService#ModelContextProtocol#integrateddevelopmentenvironment#commandline#AmazonECS#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Getting Started with Google Kubernetes Engine: Your Gateway to Cloud-Native Greatness
After spending over 8 years deep in the trenches of cloud engineering and DevOps, I can tell you one thing for sure: if you're serious about scalability, flexibility, and real cloud-native application deployment, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is where the magic happens.
Whether you’re new to Kubernetes or just exploring managed container platforms, getting started with Google Kubernetes Engine is one of the smartest moves you can make in your cloud journey.
"Containers are cool. Orchestrated containers? Game-changing."
🚀 What is Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)?
Google Kubernetes Engine is a fully managed Kubernetes platform that runs on top of Google Cloud. GKE simplifies deploying, managing, and scaling containerized apps using Kubernetes—without the overhead of maintaining the control plane.
Why is this a big deal?
Because Kubernetes is notoriously powerful and notoriously complex. With GKE, Google handles all the heavy lifting—from cluster provisioning to upgrades, logging, and security.
"GKE takes the complexity out of Kubernetes so you can focus on building, not babysitting clusters."
🧭 Why Start with GKE?
If you're a developer, DevOps engineer, or cloud architect looking to:
Deploy scalable apps across hybrid/multi-cloud
Automate CI/CD workflows
Optimize infrastructure with autoscaling & spot instances
Run stateless or stateful microservices seamlessly
Then GKE is your launchpad.
Here’s what makes GKE shine:
Auto-upgrades & auto-repair for your clusters
Built-in security with Shielded GKE Nodes and Binary Authorization
Deep integration with Google Cloud IAM, VPC, and Logging
Autopilot mode for hands-off resource management
Native support for Anthos, Istio, and service meshes
"With GKE, it's not about managing containers—it's about unlocking agility at scale."
🔧 Getting Started with Google Kubernetes Engine
Ready to dive in? Here's a simple flow to kick things off:
Set up your Google Cloud project
Enable Kubernetes Engine API
Install gcloud CLI and Kubernetes command-line tool (kubectl)
Create a GKE cluster via console or command line
Deploy your app using Kubernetes manifests or Helm
Monitor, scale, and manage using GKE dashboard, Cloud Monitoring, and Cloud Logging
If you're using GKE Autopilot, Google manages your node infrastructure automatically—so you only manage your apps.
“Don’t let infrastructure slow your growth. Let GKE scale as you scale.”
🔗 Must-Read Resources to Kickstart GKE
👉 GKE Quickstart Guide – Google Cloud
👉 Best Practices for GKE – Google Cloud
👉 Anthos and GKE Integration
👉 GKE Autopilot vs Standard Clusters
👉 Google Cloud Kubernetes Learning Path – NetCom Learning
🧠 Real-World GKE Success Stories
A FinTech startup used GKE Autopilot to run microservices with zero infrastructure overhead
A global media company scaled video streaming workloads across continents in hours
A university deployed its LMS using GKE and reduced downtime by 80% during peak exam seasons
"You don’t need a huge ops team to build a global app. You just need GKE."
🎯 Final Thoughts
Getting started with Google Kubernetes Engine is like unlocking a fast track to modern app delivery. Whether you're running 10 containers or 10,000, GKE gives you the tools, automation, and scale to do it right.
With Google Cloud’s ecosystem—from Cloud Build to Artifact Registry to operations suite—GKE is more than just Kubernetes. It’s your platform for innovation.
“Containers are the future. GKE is the now.”
So fire up your first cluster. Launch your app. And let GKE do the heavy lifting while you focus on what really matters—shipping great software.
Let me know if you’d like this formatted into a visual infographic or checklist to go along with the blog!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Why Linode Accounts Are the Best Choice and Where to Buy Them
Linode has become a trusted name in the cloud hosting industry, offering high-quality services tailored for developers, businesses, and enterprises seeking reliable, scalable, and secure infrastructure. With its competitive pricing, exceptional customer support, and a wide range of features, Linode accounts are increasingly popular among IT professionals. If you're wondering why Linode is the best choice and where you can buy Linode account safely, this article will provide comprehensive insights.

Why Linode Accounts Are the Best Choice
1. Reliable Infrastructure
Linode is renowned for its robust and reliable infrastructure. With data centers located worldwide, it ensures high uptime and optimal performance. Businesses that rely on Linode accounts benefit from a stable environment for hosting applications, websites, and services.
Global Data Centers: Linode operates in 11 data centers worldwide, offering low-latency connections and redundancy.
99.99% Uptime SLA: Linode guarantees near-perfect uptime, making it an excellent choice for mission-critical applications.
2. Cost-Effective Pricing
Linode provides affordable pricing options compared to many other cloud providers. Its simple and transparent pricing structure allows users to plan their budgets effectively.
No Hidden Costs: Users pay only for what they use, with no unexpected charges.
Flexible Plans: From shared CPU instances to dedicated servers, Linode offers plans starting as low as $5 per month, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
3. Ease of Use
One of the standout features of Linode accounts is their user-friendly interface. The platform is designed to cater to beginners and seasoned developers alike.
Intuitive Dashboard: Manage your servers, monitor performance, and deploy applications easily.
One-Click Apps: Deploy popular applications like WordPress, Drupal, or databases with just one click.
4. High Performance
Linode ensures high performance through cutting-edge technology. Its SSD storage, fast processors, and optimized network infrastructure ensure lightning-fast speeds.
SSD Storage: All Linode plans come with SSDs for faster data access and improved performance.
Next-Generation Hardware: Regular updates to hardware ensure users benefit from the latest innovations.
5. Customizability and Scalability
Linode offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing users to customize their servers based on specific needs.
Custom Configurations: Tailor your server environment, operating system, and software stack.
Scalable Solutions: Scale up or down depending on your resource requirements, ensuring cost efficiency.
6. Developer-Friendly Tools
Linode is a developer-focused platform with robust tools and APIs that simplify deployment and management.
CLI and API Access: Automate server management tasks with Linode’s command-line interface and powerful APIs.
DevOps Ready: Supports tools like Kubernetes, Docker, and Terraform for seamless integration into CI/CD pipelines.
7. Exceptional Customer Support
Linode’s customer support is often highlighted as one of its strongest assets. Available 24/7, the support team assists users with technical and account-related issues.
Quick Response Times: Get answers within minutes through live chat or ticketing systems.
Extensive Documentation: Access tutorials, guides, and forums to resolve issues independently.
8. Security and Compliance
Linode prioritizes user security by providing features like DDoS protection, firewalls, and two-factor authentication.
DDoS Protection: Prevent downtime caused by malicious attacks.
Compliance: Linode complies with industry standards, ensuring data safety and privacy.
Conclusion
Linode accounts are an excellent choice for developers and businesses looking for high-performance, cost-effective, and reliable cloud hosting solutions. With its robust infrastructure, transparent pricing, and user-friendly tools, Linode stands out as a top-tier provider in the competitive cloud hosting market.
When buying Linode accounts, prioritize safety and authenticity by purchasing from the official website or verified sources. This ensures you benefit from Linode’s exceptional features and customer support. Avoid unverified sellers to minimize risks and guarantee a smooth experience.
Whether you’re a developer seeking scalable hosting or a business looking to streamline operations, Linode accounts are undoubtedly one of the best choices. Start exploring Linode today and take your cloud hosting experience to the next level!
0 notes
Text
A Practical Guide to CKA/CKAD Preparation in 2025
The Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) and Certified Kubernetes Application Developer (CKAD) certifications are highly sought-after credentials in the cloud-native ecosystem. These certifications validate your skills and knowledge in managing and developing applications on Kubernetes. This guide provides a practical roadmap for preparing for these exams in 2025.
1. Understand the Exam Objectives
CKA: Focuses on the skills required to administer a Kubernetes cluster. Key areas include cluster architecture, installation, configuration, networking, storage, security, and troubleshooting.
CKAD: Focuses on the skills required to design, build, and deploy cloud-native applications on Kubernetes. Key areas include application design, deployment, configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Refer to the official CNCF (Cloud Native Computing Foundation) websites for the latest exam curriculum and updates.
2. Build a Strong Foundation
Linux Fundamentals: A solid understanding of Linux command-line tools and concepts is essential for both exams.
Containerization Concepts: Learn about containerization technologies like Docker, including images, containers, and registries.
Kubernetes Fundamentals: Understand core Kubernetes concepts like pods, deployments, services, namespaces, and controllers.
3. Hands-on Practice is Key
Set up a Kubernetes Cluster: Use Minikube, Kind, or a cloud-based Kubernetes service to create a local or remote cluster for practice.
Practice with kubectl: Master the kubectl command-line tool, which is essential for interacting with Kubernetes clusters.
Solve Practice Exercises: Use online resources, practice exams, and mock tests to reinforce your learning and identify areas for improvement.
4. Utilize Effective Learning Resources
Official CNCF Documentation: The official Kubernetes documentation is a comprehensive resource for learning about Kubernetes concepts and features.
Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and edX offer CKA/CKAD preparation courses with video lectures, hands-on labs, and practice exams.
Books and Study Guides: Several books and study guides are available to help you prepare for the exams.
Community Resources: Engage with the Kubernetes community through forums, Slack channels, and meetups to learn from others and get your questions answered.
5. Exam-Specific Tips
CKA:
Focus on cluster administration tasks like installation, upgrades, and troubleshooting.
Practice managing cluster resources, security, and networking.
Be comfortable with etcd and control plane components.
CKAD:
Focus on application development and deployment tasks.
Practice writing YAML manifests for Kubernetes resources.
Understand application lifecycle management and troubleshooting.
6. Time Management and Exam Strategy
Allocate Sufficient Time: Dedicate enough time for preparation, considering your current knowledge and experience.
Create a Study Plan: Develop a structured study plan with clear goals and timelines.
Practice Time Management: During practice exams, simulate the exam environment and practice managing your time effectively.
Familiarize Yourself with the Exam Environment: The CKA/CKAD exams are online, proctored exams with a command-line interface. Familiarize yourself with the exam environment and tools beforehand.
7. Stay Updated
Kubernetes is constantly evolving. Stay updated with the latest releases, features, and best practices.
Follow the CNCF and Kubernetes community for announcements and updates.
For more information www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
Google Cloud (GCP) Platform: GCP Essentials, Cloud Computing, GCP Associate Cloud Engineer, and Professional Cloud Architect
Introduction
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is one of the leading cloud computing platforms, offering a range of services and tools for businesses and individuals to build, deploy, and manage applications on Google’s infrastructure. In this guide, we’ll dive into the essentials of GCP, explore cloud computing basics, and examine two major GCP certifications: the Associate Cloud Engineer and Professional Cloud Architect. Whether you’re a beginner or aiming to level up in your cloud journey, understanding these aspects of GCP is essential for success.
1. Understanding Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Essentials
Google Cloud Platform offers over 90 products covering compute, storage, networking, and machine learning. Here are the essentials:
Compute Engine: Virtual machines on demand
App Engine: Platform as a Service (PaaS) for app development
Kubernetes Engine: Managed Kubernetes for container orchestration
Cloud Functions: Serverless execution for event-driven functions
BigQuery: Data warehouse for analytics
Cloud Storage: Scalable object storage for any amount of data
With these foundational services, GCP allows businesses to scale, innovate, and adapt to changing needs without the limitations of traditional on-premises infrastructure.
2. Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing resources over the internet. These resources include:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Basic computing, storage, and networking resources
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Development tools and environment for building apps
Software as a Service (SaaS): Fully managed applications accessible via the internet
In a cloud environment, users pay for only the resources they use, allowing them to optimize cost, increase scalability, and ensure high availability.
3. GCP Services and Tools Overview
GCP provides a suite of tools for development, storage, machine learning, and data analysis:
AI and Machine Learning Tools: Google Cloud ML, AutoML, and TensorFlow
Data Management: Datastore, Firestore, and Cloud SQL
Identity and Security: Identity and Access Management (IAM), Key Management
Networking: VPC, Cloud CDN, and Cloud Load Balancing
4. Getting Started with GCP Essentials
To start with GCP, you need a basic understanding of cloud infrastructure:
Create a GCP Account: You’ll gain access to a free tier with $300 in credits.
Explore the GCP Console: The console provides a web-based interface for managing resources.
Google Cloud Shell: A command-line interface that runs in the cloud, giving you quick access to GCP tools and resources.
5. GCP Associate Cloud Engineer Certification
The Associate Cloud Engineer certification is designed for beginners in the field of cloud engineering. This certification covers:
Managing GCP Services: Setting up projects and configuring compute resources
Storage and Databases: Working with storage solutions like Cloud Storage, Bigtable, and SQL
Networking: Configuring network settings and VPCs
IAM and Security: Configuring access management and security protocols
This certification is ideal for entry-level roles in cloud administration and engineering.
6. Key Topics for GCP Associate Cloud Engineer Certification
The main topics covered in the exam include:
Setting up a Cloud Environment: Creating and managing GCP projects and billing accounts
Planning and Configuring a Cloud Solution: Configuring VM instances and deploying storage solutions
Ensuring Successful Operation: Managing resources and monitoring solutions
Configuring Access and Security: Setting up IAM and implementing security best practices
7. GCP Professional Cloud Architect Certification
The Professional Cloud Architect certification is an advanced-level certification. It prepares professionals to:
Design and Architect GCP Solutions: Creating scalable and efficient solutions that meet business needs
Optimize for Security and Compliance: Ensuring GCP solutions meet security standards
Manage and Provision GCP Infrastructure: Deploying and managing resources to maintain high availability and performance
This certification is ideal for individuals in roles involving solution design, architecture, and complex cloud deployments.
8. Key Topics for GCP Professional Cloud Architect Certification
Key areas covered in the Professional Cloud Architect exam include:
Designing Solutions for High Availability: Ensuring solutions remain available even during failures
Analyzing and Optimizing Processes: Ensuring that processes align with business objectives
Managing and Provisioning Infrastructure: Creating automated deployments using tools like Terraform and Deployment Manager
Compliance and Security: Developing secure applications that comply with industry standards
9. Preparing for GCP Certifications
Preparation for GCP certifications involves hands-on practice and understanding key concepts:
Use GCP’s Free Tier: GCP offers a free trial with $300 in credits for testing services.
Enroll in Training Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Google’s Qwiklabs offer courses for each certification.
Practice Labs: Qwiklabs provides guided labs to help reinforce learning with real-world scenarios.
Practice Exams: Test your knowledge with practice exams to familiarize yourself with the exam format.
10. Best Practices for Cloud Engineers and Architects
Follow GCP’s Best Practices: Use Google’s architecture framework to design resilient solutions.
Automate Deployments: Use IaC tools like Terraform for consistent deployments.
Monitor and Optimize: Use Cloud Monitoring and Cloud Logging to track performance.
Cost Management: Utilize GCP’s Billing and Cost Management tools to control expenses.
Conclusion
Whether you aim to become a GCP Associate Cloud Engineer or a Professional Cloud Architect, GCP certifications provide a valuable pathway to expertise. GCP’s comprehensive services and tools make it a powerful choice for anyone looking to expand their cloud computing skills.
0 notes
Text
Why Become a Certified Kubernetes Application Developer?

As companies continue to shift their infrastructure towards cloud-native solutions, Kubernetes has emerged as the leading orchestration platform for containerized applications. Whether you're a developer, DevOps engineer, or a cloud architect, mastering Kubernetes is a powerful career move.
So, why aim for the Certified Kubernetes Application Developer (CKAD) certification? Simply put, it opens doors. This certification is recognized globally and is a stamp of approval for your ability to design, build, and deploy cloud-based applications using Kubernetes.
What is Kubernetes, and Why Should You Learn It?
Before diving into the certification, let's cover some basics. Kubernetes is an open-source platform used to manage containerized applications. In simpler terms, it helps you automate the deployment, scaling, and management of your applications in the cloud.
With containers becoming the standard in modern software development, knowing how to use a tool like Kubernetes to orchestrate these containers is invaluable. The best part? It's not just tech giants like Google or Netflix that are using Kubernetes anymore. It’s being adopted by small startups, mid-sized businesses, and enterprises alike.
Key Benefits of Learning Kubernetes:
Job Opportunities: There’s a high demand for developers and engineers who can work with Kubernetes.
Cloud-Native Development: Learning Kubernetes is essential for anyone who wants to develop, deploy, and maintain cloud-based applications.
Scalability and Efficiency: It helps organizations scale their infrastructure efficiently, which is crucial for companies experiencing rapid growth.
What is the Certified Kubernetes Application Developer Certification?
The Certified Kubernetes Application Developer (CKAD) is a certification provided by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) in collaboration with the Linux Foundation. It is designed for developers who work with Kubernetes to create and manage applications, not just administrators.
By becoming certified, you're proving your ability to:
Design and deploy cloud-native applications.
Configure Kubernetes and manage application lifecycle.
Use Kubernetes for scaling, logging, and monitoring.
The CKAD exam focuses heavily on hands-on tasks and scenarios, making it perfect for those who prefer learning by doing rather than just memorizing theory. The exam is conducted online and is performance-based, meaning you’ll need to solve real-world problems within the Kubernetes environment.
Who Should Take the CKAD Certification?
This certification is ideal for:
Developers who want to build cloud-native applications and deploy them using Kubernetes.
DevOps engineers aiming to manage cloud-native applications and infrastructure.
Software engineers transitioning into cloud-native development and looking for a well-rounded skill set.
Anyone looking to improve their ability to work with microservices.
Even if you’re not currently working in cloud-native environments, gaining this certification can make you more marketable as the demand for Kubernetes expertise continues to rise.
Prerequisites for the CKAD Exam
You don’t need to be a Kubernetes expert before taking the exam, but a basic understanding of containers and microservices will certainly help. Here’s what you should know before sitting for the CKAD exam:
Basic Docker knowledge: Since Kubernetes manages Docker containers, understanding Docker is essential.
Linux commands: A basic knowledge of Linux commands will help you navigate the Kubernetes command-line interface.
YAML files: Kubernetes configurations are mostly written in YAML, so being familiar with YAML syntax will be beneficial.
Exam Overview: What to Expect from CKAD
The CKAD exam is entirely performance-based, meaning there are no multiple-choice questions. Instead, you'll be asked to complete a series of tasks that mimic real-world challenges Kubernetes developers face. Here’s a breakdown:
Duration: 2 hours
Format: Online, performance-based
Questions: Roughly 19–20 practical tasks
Passing score: 66%
Cost: $300 (though discounts are sometimes available)
To pass, you’ll need to show competency in several areas related to Kubernetes, including:
Core Concepts: Understanding the Kubernetes architecture and the components involved.
Multi-container Pods: Using multi-container pods to manage and deploy applications.
Observability: Monitoring and troubleshooting your applications in Kubernetes.
Services and Networking: Configuring services, network policies, and setting up communication between pods.
State Persistence: Handling data in a stateful Kubernetes application.
Tips for Passing the CKAD Exam
While the CKAD exam is challenging, it’s definitely doable with the right preparation. Here are some tips to help you succeed:
1. Practice, Practice, Practice
The CKAD exam is all about hands-on knowledge. The best way to prepare is by setting up your own Kubernetes environment and experimenting with different scenarios. Practice deploying applications, scaling them, and troubleshooting issues.
2. Familiarize Yourself with the Kubernetes Documentation
The exam allows you to refer to official Kubernetes documentation, so get used to navigating it quickly. Being able to find answers within the documentation can save you valuable time during the test.
3. Use Online Learning Resources
There are plenty of resources available, including Udemy courses specifically designed to help you pass the CKAD exam. These courses often come with hands-on labs, quizzes, and exam simulators that will help you practice in a real Kubernetes environment.
Why the CKAD Certification is Worth It
With the rise of cloud computing and microservices, the demand for professionals skilled in Kubernetes is growing rapidly. The Certified Kubernetes Application Developer certification is a fast track to proving your expertise and standing out in a competitive job market.
Key Reasons to Get Certified:
Career growth: Many top companies like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft are seeking Kubernetes developers.
Higher salaries: Certified professionals often command higher salaries than their non-certified peers.
Cloud-native expertise: Mastering Kubernetes is crucial for developing and maintaining cloud-native applications.
By obtaining your Certified Kubernetes Application Developer certification, you'll also demonstrate your ability to work with containers, understand how they function in a cloud-native environment, and prove that you can deploy, monitor, and troubleshoot applications in Kubernetes.
Conclusion: Is the CKAD Certification Right for You?
If you’re aiming to expand your career in cloud-native development and work with modern, scalable applications, then the Certified Kubernetes Application Developer certification is a valuable credential. It not only proves your competency in using Kubernetes, but also equips you with the knowledge and confidence to take on real-world challenges in cloud development.
0 notes
Text
Top 5 User Virtualization Software Of 2024

Their lives encompass a multicultural mix, cross-continental relationships, teenage challenges, and various parenting approaches. This rich blend results in a tapestry of humor and warmth in Modern Family – the TV show we all know and love!
Similarly, User Virtualization Software in the tech world provides a unified platform to create virtual versions of servers, storage, networks, and other physical devices. It’s like an extended family operating in different environments to host multiple virtual setups, each tailored to its own requirements.
If you’re seeking the best User Virtualization Software for your business in 2024, you’re in the right place. Continue reading to join our modern tech family!
We observe how three distinct households coexist in the diverse world of Modern Family. Likewise, User Virtualization Software separates the software components defining a user’s identity on a device from the operating system and applications. This allows for independent management, applying these settings to a desktop as needed without relying on scripting, group policies, or roaming profiles.
Virtualization enables a single piece of hardware to function as multiple machines. It’s like creating multiple “virtual machines” within a single physical computer. By virtualizing software-based applications, servers, storage, networks, desktops, and more, you can significantly reduce hardware and equipment costs. Smart, right?
Last year, we highlighted the Top 5 User Virtualization Software for 2023, and this year, we have updated the list for you.
Here are the Top 5 User Virtualization Software of 2024!
To recap, User Virtualization Software allows the separation of a user’s profile, settings, and data from underlying operating systems, enabling a consistent and personalized experience across different devices and sessions, regardless of the hardware or platform.
Here are our top 5 picks for User Virtualization Software – as randomly ordered as Phil's-Osophy!
Tool 1: VMWare Workstation Pro VMWare, established in 1998 and headquartered in Palo Alto, California, was recently acquired by Broadcom in 2022. With clients like Apple, Costco, FedEx, and PepsiCo, VMWare was awarded the Gartner Peer Insights Customers’ Choice and ranked #1 in Worldwide IT Automation and Configuration Management for the fifth consecutive year by a global analyst firm in 2023.
VMWare Workstation Pro is a leading virtualization software that allows users to run multiple operating systems on a single physical machine. It’s ideal for developers, testers, IT administrators, and power users, providing a robust and flexible environment for creating, configuring, and managing virtual machines.
Known for its advanced network configuration features, it supports hundreds of 32- and 64-bit guest operating systems, offering plenty of options for configuring virtual machines. On Windows, it also has a command line interface for developing and operating Kubernetes containers and clusters, along with robust networking and isolation features within the virtual machine.
Tool 2: Oracle VirtualBox Oracle, founded in 1977 and headquartered in Austin, Texas, serves clients like Cisco, Zoom, and Gartner. Oracle has received numerous awards for its innovative technology and leadership, including USA TODAY's America's Climate Leaders List and the Karma Award – Good Samaritan category in 2024.
VirtualBox, Oracle's open-source virtualization solution, supports host operating systems like Windows, Linux, Mac, and Solaris. It’s a cross-platform tool that enables users to run multiple operating systems simultaneously. Ideal for IT professionals and developers, Oracle VM VirtualBox is perfect for testing, developing, demonstrating, and deploying virtualized solutions across multiple platforms from one machine.
VirtualBox’s open-source nature allows users to experiment and test new functions without deviating from their established workflows. With a free license for educational, personal, and evaluation purposes, getting started with VirtualBox is easy!
Tool 3: Google Compute Engine Founded in 1998, Google serves billions worldwide and is headquartered in Mountain View, California. Google’s clients include Apple, Amazon, and many others. Google received the ‘Best Global Culture’ award in 2024, along with numerous other accolades from Comparably in 2023, solidifying its status as the GOAT.
Google Compute Engine, part of the Google Cloud Platform, allows users to launch virtual machines on demand. It leverages Google’s global infrastructure, which powers services like the search engine, Gmail, and YouTube, providing reliable uptime, processing capabilities, and low latency. These features are crucial for running high-performance virtual machines, essential for user virtualization processes.
Tool 4: Red Hat Virtualization (RHV) Founded in 1993 and headquartered in Raleigh, North Carolina, Red Hat is an open-source company serving clients like MicroFocus, JPMorgan Chase, and Safe Fleet. Red Hat has been recognized for its contributions to the industry and customer support, winning the “Best Contribution to Moving the Industry Forward” and “The Ten Best Web Support Sites” for 13 consecutive years.
Red Hat Virtualization is an enterprise platform supporting key virtualization workloads, including resource-intensive and critical applications. Built on Red Hat Enterprise Linux and KVM, it’s an enterprise-grade solution fully supported by Red Hat.
Featuring an easy-to-use interface and known for its automation capabilities, Red Hat Virtualization allows users to define rules and constructs for full end-to-end automation of their virtualization deployments. This scalability is achieved through custom solutions, APIs, and open-source capabilities.
Tool 5: Azure Virtual Machines Founded in 1975 and headquartered in Redmond, Washington, Microsoft needs no introduction. Ranked fifth in the JUST 100 rankings for 2024, Microsoft serves major clients like Apple, Nvidia, and ClearBank. It also received top industry scores for environmental and social quality in 2023.
Azure Virtual Machines offer a range of networking capabilities and services such as Azure Virtual Network, VPNs, and Azure ExpressRoute, ensuring high availability and security for applications. Azure VMs provide virtualization without the need to maintain physical hardware.
Known for its cloud-based monitoring, Azure VMs track metrics for data visualizations, log queries, and dependency mapping. It also includes detailed monitoring features, robust security, and significant savings with Reserved VM Instances and on-demand capacity reservations.
To Conclude Selecting the best User Virtualization Software requires thorough research and trials to match your business's specific needs. Our list of the top User Virtualization Software of 2024 can help you get started!
User Virtualization Software offers many benefits, including reduced IT expenses and hardware costs, simplified management, and improved disaster recovery through centralized backups.
Remember, each solution has unique features and capabilities, so evaluate performance, compatibility, and scalability through hands-on testing.
0 notes
Text
Embarking on a journey to learn DevOps can be both exciting and overwhelming for beginners. DevOps, which focuses on the integration and automation of processes between software development and IT operations, offers a dynamic and rewarding career. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help beginners navigate the path to becoming proficient in DevOps. For individuals who want to work in the sector, a respectable DevOps Training in Pune can give them the skills and information they need to succeed in this fast-paced atmosphere.

Understanding the Basics
Before diving into DevOps tools and practices, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental concepts:
1. DevOps Culture: DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to improve efficiency and deploy software faster. It’s not just about tools but also about fostering a culture of continuous improvement, automation, and teamwork.
2. Core Principles: Familiarize yourself with the core principles of DevOps, such as Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD), Infrastructure as Code (IaC), and Monitoring and Logging. These principles are the foundation of DevOps practices.
Learning the Essentials
To build a strong foundation in DevOps, beginners should focus on acquiring knowledge in the following areas:
1. Version Control Systems: Learn how to use Git, a version control system that tracks changes in source code during software development. Platforms like GitHub and GitLab are also essential for managing repositories and collaborating with other developers.
2. Command Line Interface (CLI): Becoming comfortable with the CLI is crucial, as many DevOps tasks are performed using command-line tools. Start with basic Linux commands and gradually move on to more advanced scripting.
3. Programming and Scripting Languages: Knowledge of programming and scripting languages like Python, Ruby, and Shell scripting is valuable. These languages are often used for automation tasks and writing infrastructure code.
4. Networking and Security: Understanding basic networking concepts and security best practices is essential for managing infrastructure and ensuring the security of deployed applications.

Hands-On Practice with Tools
Practical experience with DevOps tools is key to mastering DevOps practices. Here are some essential tools for beginners:
1. CI/CD Tools: Get hands-on experience with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, or CircleCI. These tools automate the building, testing, and deployment of applications.
2. Containerization: Learn about Docker, a platform that automates the deployment of applications in lightweight, portable containers. Understanding container orchestration tools like Kubernetes is also beneficial.
3. Configuration Management: Familiarize yourself with configuration management tools like Ansible, Chef, or Puppet. These tools automate the provisioning and management of infrastructure.
4. Cloud Platforms: Explore cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. These platforms offer various services and tools that are integral to DevOps practices. Enrolling in DevOps Online Course can enable individuals to unlock DevOps' full potential and develop a deeper understanding of its complexities.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
DevOps is a constantly evolving field, so continuous learning is essential:
1. Online Courses and Tutorials: Enroll in online courses and follow tutorials from platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning. These resources offer structured learning paths and hands-on projects.
2. Community Involvement: Join DevOps communities, attend meetups, and participate in forums. Engaging with the community can provide valuable insights, networking opportunities, and support from experienced professionals.
3. Certification: Consider obtaining DevOps certifications, such as the AWS Certified DevOps Engineer or Google Professional DevOps Engineer. Certifications can validate your skills and enhance your career prospects.
Conclusion
Learning DevOps as a beginner involves understanding its core principles, gaining hands-on experience with essential tools, and continuously improving your skills. By focusing on the basics, practicing with real-world tools, and staying engaged with the DevOps community, you can build a solid foundation and advance your career in this dynamic field. The journey may be challenging, but with persistence and dedication, you can achieve proficiency in DevOps and unlock exciting career opportunities.
0 notes
Text
Deploying a Containerized Application with Red Hat OpenShift
Introduction
In this post, we'll walk through the process of deploying a containerized application using Red Hat OpenShift, a powerful Kubernetes-based platform for managing containerized workloads.
What is Red Hat OpenShift?
Red Hat OpenShift is an enterprise Kubernetes platform that provides developers with a full set of tools to build, deploy, and manage applications. It integrates DevOps automation tools to streamline the development lifecycle.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, ensure you have the following:
A Red Hat OpenShift cluster
Access to the OpenShift command-line interface (CLI)
A containerized application (Docker image)
Step 1: Setting Up Your OpenShift Environment
First, log in to your OpenShift cluster using the CLI:
oc login https://your-openshift-cluster:6443
Step 2: Creating a New Project
Create a new project for your application:
oc new-project my-app
Step 3: Deploying Your Application
Deploy your Docker image using the oc new-app command:
oc new-app my-docker-image
Step 4: Exposing Your Application
Expose your application to create a route and make it accessible:
oc expose svc/my-app
Use Cases
OpenShift is ideal for deploying microservices architectures, CI/CD pipelines, and scalable web applications. Here are a few scenarios where OpenShift excels.
Best Practices
Use health checks to ensure your applications are running smoothly.
Implement resource quotas to prevent any single application from consuming too many resources.
Performance and Scalability
To optimize performance, consider using horizontal pod autoscaling. This allows OpenShift to automatically adjust the number of pods based on CPU or memory usage.
Security Considerations
Ensure your images are scanned for vulnerabilities before deployment. OpenShift provides built-in tools for image scanning and compliance checks.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues, check the logs of your pods:
oc logs pod-name
Conclusion
Deploying applications with Red Hat OpenShift is straightforward and powerful. By following best practices and utilizing the platform's features, you can ensure your applications are scalable, secure, and performant.
#redhatcourses#linux#container#kubernetes#containerorchestration#information technology#containersecurity#docker#dockerswarm#aws
0 notes
Text
Your Path to Becoming a DevOps Engineer
Thinking about a career as a DevOps engineer? Great choice! DevOps engineers are pivotal in the tech world, automating processes and ensuring smooth collaboration between development and operations teams. Here’s a comprehensive guide to kick-starting your journey with the Best Devops Course.
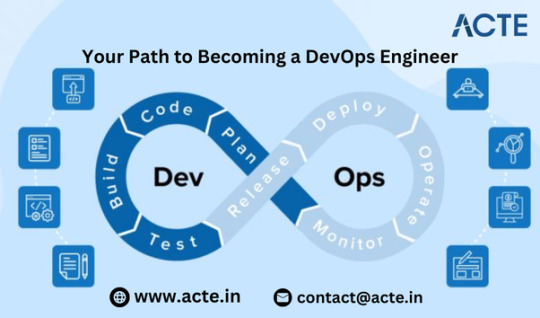
Grasping the Concept of DevOps
Before you dive in, it’s essential to understand what DevOps entails. DevOps merges "Development" and "Operations" to boost collaboration and efficiency by automating infrastructure, workflows, and continuously monitoring application performance.
Step 1: Build a Strong Foundation
Start with the Essentials:
Programming and Scripting: Learn languages like Python, Ruby, or Java. Master scripting languages such as Bash and PowerShell for automation tasks.
Linux/Unix Basics: Many DevOps tools operate on Linux. Get comfortable with Linux command-line basics and system administration.
Grasp Key Concepts:
Version Control: Familiarize yourself with Git to track code changes and collaborate effectively.
Networking Basics: Understand networking principles, including TCP/IP, DNS, and HTTP/HTTPS.
If you want to learn more about ethical hacking, consider enrolling in an Devops Online course They often offer certifications, mentorship, and job placement opportunities to support your learning journey.
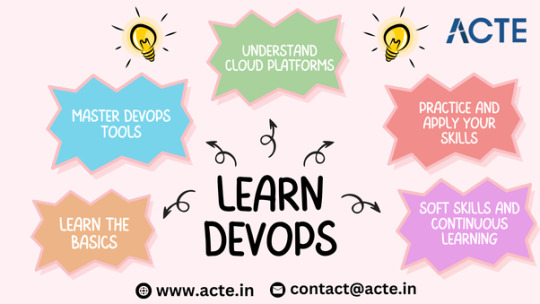
Step 2: Get Proficient with DevOps Tools
Automation Tools:
Jenkins: Learn to set up and manage continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Docker: Grasp containerization and how Docker packages applications with their dependencies.
Configuration Management:
Ansible, Puppet, and Chef: Use these tools to automate the setup and management of servers and environments.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
Terraform: Master Terraform for managing and provisioning infrastructure via code.
Monitoring and Logging:
Prometheus and Grafana: Get acquainted with monitoring tools to track system performance.
ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana): Learn to set up and visualize log data.
Consider enrolling in a DevOps Online course to delve deeper into ethical hacking. These courses often provide certifications, mentorship, and job placement opportunities to support your learning journey.
Step 3: Master Cloud Platforms
Cloud Services:
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud: Gain expertise in one or more major cloud providers. Learn about their services, such as compute, storage, databases, and networking.
Cloud Management:
Kubernetes: Understand how to manage containerized applications with Kubernetes.
Step 4: Apply Your Skills Practically
Hands-On Projects:
Personal Projects: Develop your own projects to practice setting up CI/CD pipelines, automating tasks, and deploying applications.
Open Source Contributions: Engage with open-source projects to gain real-world experience and collaborate with other developers.
Certifications:
Earn Certifications: Consider certifications like AWS Certified DevOps Engineer, Google Cloud Professional DevOps Engineer, or Azure DevOps Engineer Expert to validate your skills and enhance your resume.
Step 5: Develop Soft Skills and Commit to Continuous Learning
Collaboration:
Communication: As a bridge between development and operations teams, effective communication is vital.
Teamwork: Work efficiently within a team, understanding and accommodating diverse viewpoints and expertise.
Adaptability:
Stay Current: Technology evolves rapidly. Keep learning and stay updated with the latest trends and tools in the DevOps field.
Problem-Solving: Cultivate strong analytical skills to troubleshoot and resolve issues efficiently.
Conclusion
Begin Your Journey Today: Becoming a DevOps engineer requires a blend of technical skills, hands-on experience, and continuous learning. By building a strong foundation, mastering essential tools, gaining cloud expertise, and applying your skills through projects and certifications, you can pave your way to a successful DevOps career. Persistence and a passion for technology will be your best allies on this journey.
0 notes
Text
OpenShift vs Kubernetes: A Detailed Comparison

When it comes to managing and organizing containerized applications there are two platforms that have emerged. Kubernetes and OpenShift. Both platforms share the goal of simplifying deployment, scaling and operational aspects of application containers. However there are differences between them. This article offers a comparison of OpenShift vs Kubernetes highlighting their features, variations and ideal use cases.
What is Kubernetes? Kubernetes (often referred to as K8s) is an open source platform designed for orchestrating containers. It automates tasks such as deploying, scaling and managing containerized applications. Originally developed by Google and later donated to the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) Kubernetes has now become the accepted industry standard for container management.
Key Features of Kubernetes Pods: Within the Kubernetes ecosystem, pods serve as the units for deploying applications. They encapsulate one or multiple containers.
Service Discovery and Load Balancing: With Kubernetes containers can be exposed through DNS names or IP addresses. Additionally it has the capability to distribute network traffic across instances in case a container experiences traffic.
Storage Orchestration: The platform seamlessly integrates with storage systems such as on premises or public cloud providers based on user preferences.
Automated. Rollbacks: Kubernetes facilitates rolling updates while also providing a mechanism to revert back to versions when necessary.
What is OpenShift? OpenShift, developed by Red Hat, is a container platform based on Kubernetes that provides an approach to creating, deploying and managing applications in a cloud environment. It enhances the capabilities of Kubernetes by incorporating features and tools that contribute to an integrated and user-friendly platform.
Key Features of OpenShift Tools for Developers and Operations: OpenShift offers an array of tools that cater to the needs of both developers and system administrators.
Enterprise Level Security: It incorporates security features that make it suitable for industries with regulations.
Seamless Developer Experience: OpenShift includes a built in integration/ deployment (CI/CD) pipeline, source to image (S2I) functionality, as well as support for various development frameworks.
Service Mesh and Serverless Capabilities: It supports integration with Istio based service mesh. Offers Knative, for serverless application development.
Comparison; OpenShift, vs Kubernetes 1. Installation and Setup: Kubernetes can be set up manually. Using tools such as kubeadm, Minikube or Kubespray.
OpenShift offers an installer that simplifies the setup process for complex enterprise environments.
2. User Interface: Kubernetes primarily relies on the command line interface although it does provide a web based dashboard.
OpenShift features a comprehensive and user-friendly web console.
3. Security: Kubernetes provides security features and relies on third party tools for advanced security requirements.
OpenShift offers enhanced security with built in features like Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux) and stricter default policies.
4. CI/CD Integration: Kubernetes requires tools for CI/CD integration.
OpenShift has an integrated CI/CD pipeline making it more convenient for DevOps practices.
5. Pricing: Kubernetes is open source. Requires investment in infrastructure and expertise.
OpenShift is a product with subscription based pricing.
6. Community and Support; Kubernetes has a community, with support.
OpenShift is backed by Red Hat with enterprise level support.
7. Extensibility: Kubernetes: It has an ecosystem of plugins and add ons making it highly adaptable.
OpenShift:It builds upon Kubernetes. Brings its own set of tools and features.
Use Cases Kubernetes:
It is well suited for organizations seeking a container orchestration platform, with community support.
It works best for businesses that possess the technical know-how to effectively manage and scale Kubernetes clusters.
OpenShift:
It serves as a choice for enterprises that require a container solution accompanied by integrated developer tools and enhanced security measures.
Particularly favored by regulated industries like finance and healthcare where security and compliance are of utmost importance.
Conclusion Both Kubernetes and OpenShift offer capabilities for container orchestration. While Kubernetes offers flexibility along with a community, OpenShift presents an integrated enterprise-ready solution. Upgrading Kubernetes from version 1.21 to 1.22 involves upgrading the control plane and worker nodes separately. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure a smooth and error-free upgrade process. The selection between the two depends on the requirements, expertise, and organizational context.
Example Code Snippet: Deploying an App on Kubernetes
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp-container
image: myapp:1.0 This YAML file is an example of deploying a simple application on Kubernetes. It defines a Pod with a single container running ‘myapp’.
In conclusion, both OpenShift vs Kubernetes offer robust solutions for container orchestration, each with its unique strengths and use cases. The choice between them should be based on organizational requirements, infrastructure, and the level of desired security and integration.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Secrets of Learning DevOps Tools
In the ever-evolving landscape of IT and software development, DevOps has emerged as a crucial methodology for improving collaboration, efficiency, and productivity. Learning DevOps tools is a key step towards mastering this approach, but it can sometimes feel like unraveling a complex puzzle. In this blog, we will explore the secrets to mastering DevOps tools and navigating the path to becoming a proficient DevOps practitioner.
Learning DevOps tools can seem overwhelming at first, but with the right approach, it can be an exciting and rewarding journey. Here are some key steps to help you learn DevOps tools easily: DevOps training in Hyderabad Where traditional boundaries fade, and a unified approach to development and operations emerges.

1. Understand the DevOps culture: DevOps is not just about tools, but also about adopting a collaborative and iterative mindset. Start by understanding the principles and goals of DevOps, such as continuous integration, continuous delivery, and automation. Embrace the idea of breaking down silos and promoting cross-functional teams.
2. Begin with foundational knowledge: Before diving into specific tools, it's important to have a solid understanding of the underlying technologies. Get familiar with concepts like version control systems (e.g., Git), Linux command line, network protocols, and basic programming languages like Python or Shell scripting. This groundwork will help you better grasp the DevOps tools and their applications.
3. Choose the right tools: DevOps encompasses a wide range of tools, each serving a specific purpose. Start by identifying the tools most relevant to your requirements. Some popular ones include Jenkins, Ansible, Docker, Kubernetes, and AWS CloudFormation. Don't get overwhelmed by the number of tools; focus on learning a few key ones initially and gradually expand your skill set.
4. Hands-on practice: Theory alone won't make you proficient in DevOps tools. Set up a lab environment, either locally or through cloud services, where you can experiment and work with the tools. Build sample projects, automate deployments, and explore different functionalities. The more hands-on experience you gain, the more comfortable you'll become with the tools

Elevate your career prospects with our DevOps online course – because learning isn’t confined to classrooms, it happens where you are
5. Follow official documentation and online resources: DevOps tools often have well-documented official resources, including tutorials, guides, and examples. Make it a habit to consult these resources as they provide detailed information on installation procedures, configuration setup, and best practices. Additionally, join online communities and forums where you can ask questions, share ideas, and learn from experienced practitioners.
6. Collaborate and work with others: DevOps thrives on collaboration and teamwork. Engage with fellow DevOps enthusiasts, attend conferences, join local meetups, and participate in online discussions. By interacting with others, you'll gain valuable insights, learn new techniques, and expand your network. Collaborative projects or open-source contributions will also provide a platform to practice your skills and learn from others.
7. Stay updated: The DevOps landscape evolves rapidly, with new tools and practices emerging frequently. Keep yourself updated with the latest trends, technological advancements, and industry best practices. Follow influential blogs, read relevant articles, subscribe to newsletters, and listen to podcasts. Being aware of the latest developments will enhance your understanding of DevOps and help you adapt to changing requirements.
Mastering DevOps tools is a continuous journey that requires dedication, hands-on experience, and a commitment to continuous learning. By understanding the DevOps landscape, identifying core tools, and embracing a collaborative mindset, you can unlock the secrets to becoming a proficient DevOps practitioner. Remember, the key is not just to learn the tools but to leverage them effectively in creating streamlined, automated, and secure development workflows.
0 notes
Text
Essential Skills and Technologies for a full-stack web developer
A full-stack web developer is responsible for both front-end and back-end development, as well as the ability to work with databases and deploy applications. Here are the essential skills and technologies for a full-stack web developer:
Front-End Development:
HTML, CSS, JavaScript
Responsive design and CSS frameworks (e.g., Bootstrap)
Front-end frameworks (e.g., React.js, Angular, Vue.js)
Back-End Development:
Server-side languages (e.g., Node.js, Python, Ruby, Java, PHP)
RESTful APIs
Database management (SQL or NoSQL databases)
Full-Stack Tools and Technologies:
Package managers (npm, yarn, pip, composer)
Web servers (e.g., Apache, Nginx)
Containerization and orchestration (Docker, Kubernetes)
RESTful API documentation (Swagger/OpenAPI)
Version Control and Collaboration:
Git/GitHub
Testing and Debugging:
Testing frameworks (e.g., Jest, Mocha/Chai, Jasmine)
Debugging tools for both front-end and back-end
Other Skills:
Command line/shell proficiency
Basic DevOps knowledge (CI/CD)
Soft skills (problem-solving, communication, collaboration)
Continuous Learning:
Staying updated on emerging technologies and best practices in web development.

#WebDevelopment#FullStack#FrontEnd#BackEnd#JavaScript#HTML#CSS#ReactJS#Angular#Python#Ruby#Java#PHP#Bootstrap#RESTfulAPIs#DatabaseManagement#Git#GitHub#DevOps#magistersign#onlinetraining#support
0 notes