#chemokines
Photo
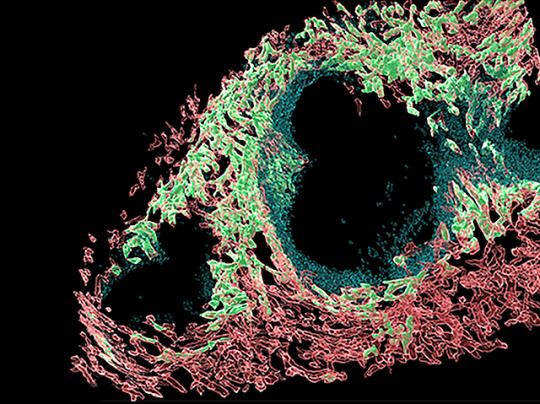
Directing Traffic
Chemical messengers called chemokines are the traffic police of your body, telling cells on the move where to go via a chemokine concentration gradient. Atypical chemokine receptors (ACKRs) on certain cells help create these gradients by binding and engulfing specific chemokines. Three called GPR182, ACKR3 and ACKR4 are located in lymph and blood vessels, and research suggests may be found together in certain microenvironments within organs. However, there’s no comprehensive map of where they are. Researchers now genetically engineer mice with fluorescently-tagged GPR182, ACKR3, ACKR4 and ACKR-specific chemokines to locate them. Fluorescence microscopy revealed unique and shared distribution patterns of these ACKRs in a variety of organs, including the spleen (pictured, ACKR4 in green, GPR182 in red). Meanwhile, fluorescently-tagged chemokines revealed distinct activity zones for ACKR4 and GPR182 in the liver. These mouse models, therefore, provide a useful tool to probe ACKRs in different organs and microenvironments.
Written by Lux Fatimathas
Image from work by Serena Melgrati and colleagues
Institute for Research in Biomedicine, Università della Svizzera italiana, Bellinzona, Switzerland
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in PLOS Biology, May 2023
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
6 notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Neuartiger Radiotracer für molekulare Bildgebung kann mehrere Krebsarten präzise diagnostizieren
Ein neuer Radiotracer für molekulare Bildgebung kann eine Vielzahl von Krebsarten präzise diagnostizieren und bietet einen Fahrplan zur Identifizierung von Patienten, die von gezielten Radionuklidtherapien profitieren könnten. In der größten medizinischen Studie dieser Art fanden die Forscher heraus, dass 68Ga-PentixaFor einen hohen Bildkontrast bei hämatologischen Malignomen, kleinzelligem Lungenkrebs und Nebennierenrindentumoren zeigte. Diese Forschung wurde in der Novembera...
#Adenom #Bildgebung #Chemokin #CT #Diabetes #Endokrinologie #Forschung #Gastroenterologie #Hämatologie #Karzinom #Kleinzelliger_Lungenkrebs #Krankenhaus #Krebs #Lungenkrebs #Lymphom #Maligne #Mantelzell_Lymphom #Medizin #Molekulare_Bildgebung #Multiples_Myelom #Myelom #Nebennierenrindenkarzinom #Nuklearmedizin #Onkologie #Präzisionsmedizin #Radiologie #Radionuklid #Rezeptor #Theranostik #tumor #Zahnheilkunde #Zelle
#Medical_Condition_News#Medical_Research_News#Medical_Science_News#News#Adenom#Bildgebung#Chemokin#CT#Diabetes#Endokrinologie#Forschung#Gastroenterologie#Hämatologie#Karzinom#Kleinzelliger_Lungenkrebs#Krankenhaus#Krebs#Lungenkrebs#Lymphom#Maligne#Mantelzell_Lymphom#Medizin#Molekulare_Bildgebung#Multiples_Myelom#Myelom#Nebennierenrindenkarzinom#Nuklearmedizin#Onkologie#Präzisionsmedizin#Radiologie
0 notes
Text
The human immune system is based on cells that communicate with each other via signaling molecules known as cytokines and chemokines. One of these signaling molecules is the protein MIF (macrophage migration inhibitory factor). It plays an important role in the regulation of various immune reactions by binding to suitable receptors of various cell types in a ternary complex, thereby activating certain signaling pathways in these cells.
Surprisingly, there are plant proteins that are very similar to the human MIF protein in the sequence of their individual building blocks (amino acids) and these are referred to as MDL proteins.
A team led by Jürgen Bernhagen from the Institute for Stroke and Dementia Research (ISD) at University of Munich Hospital and Professor Ralph Panstruga from the Unit of Plant Molecular Cell Biology at RWTH Aachen University in collaboration with a research group led by Professor Elias Lolis from Yale University in the U.S., has now shown that MIF and MDL proteins are also astonishingly similar in their spatial structure.
Lead author Lukas Spiller and the team also found that the plant MDL proteins bind to the receptors of the MIF protein, alone or in complexes with the human MIF protein, and are thus able to activate immune-relevant signaling pathways—in some cases more efficiently than the human MIF protein alone.
Continue Reading.
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Note Cards (February 2024)
2nd Law and Acceleration
3' Untranslated Region
3rd Cuneiform Facet Shape
4th Rib and Age
18-Aldocorticosterone
30S Initiation Factors
Actions of Adductor Magnus
Age and Cranial Sutures
Ancylostoma duodenale Pathogenesis
Anthropological Linguistics
Brachialis OIA
Breeding Isolates
Causes of Negative Nitrogen Balance
Chemokines
Components of Hill Plots
Derivatives of Oxaloacetate
Echinococcosis
Endocrinology
Femoral Popliteal Surface
Fibularis Brevis
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis OIA
H. erectus at Ceprano Site
IgE
Ilex verticillata Names
Intermediate Filament
LCL vs MCL
Malate Dehydrogenase 1
Nail Matrix
Neanderthal Metabolism
Obturator Nerve Muscles
Parts of Epiphyses
Peptide Bond Structure
Primary vs Secondary Metabolites
sanguino-
Selective Pressures
Siding Metacarpal 3
Skull of Arago 21
Steps of Whole-Genome Shotgun Sequencing
Strongyloides stercoralis
Structure of α-Helix
T. Dale Stewart
T. trichiuria Appearance
Talus - Plantar View
Taphonomy
Teres Minor
Transcriptional Fusion
Trichuris trichiuria Pathogenesis
Vena Cava Inferior
venulo-
Zygomatic - Lateral View
.
Patreon
#studyblr#notes#studying#masterlist#study masterlist#master list#study master list#studyblr resources#study resources#learning#learning resources#school#school resources#free learning#science#academics#academia#learning science#mcat resources#mcat notes#mcat studyblr#mcat masterlist#resource masterlist#scienceblr#medblr
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
SARS-CoV-2 Selectively Induces the Expression of Unproductive Splicing Isoforms of Interferon, Class I MHC, and Splicing Machinery Genes - Published May 23, 2024
Abstract
RNA processing is a highly conserved mechanism that serves as a pivotal regulator of gene expression. Alternative processing generates transcripts that can still be translated but lead to potentially nonfunctional proteins. A plethora of respiratory viruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), strategically manipulate the host’s RNA processing machinery to circumvent antiviral responses. We integrated publicly available omics datasets to systematically analyze isoform-level expression and delineate the nascent peptide landscape of SARS-CoV-2-infected human cells. Our findings explore a suggested but uncharacterized mechanism, whereby SARS-CoV-2 infection induces the predominant expression of unproductive splicing isoforms in key IFN signaling, interferon-stimulated (ISGs), class I MHC, and splicing machinery genes, including IRF7, HLA-B, and HNRNPH1. In stark contrast, cytokine and chemokine genes, such as IL6 and TNF, predominantly express productive (protein-coding) splicing isoforms in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. We postulate that SARS-CoV-2 employs an unreported tactic of exploiting the host splicing machinery to bolster viral replication and subvert the immune response by selectively upregulating unproductive splicing isoforms from antigen presentation and antiviral response genes. Our study sheds new light on the molecular interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and the host immune system, offering a foundation for the development of novel therapeutic strategies to combat COVID-19.
#covid#mask up#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator#public health#long covid
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
Wren your egg lore is so interesting
Thank you!! Without spoiling too much, I'll tell you a bit about how it is the 'egg' spores infect their host, scientifically speaking. (from discord)
Basically, premature spores get inside an open wound and into the bloodstream. From there they release proteins that are similar in structure to a certain immune cell, allowing them to stay undetected by the immune system. These spores also have immunosupressing effects. The spores make their way into the central nervous system via the bloodstream. SEM spores in addition to already being similar in shape and structure to helper T-cells, which are critical to the process of activating the immune system against threats. The spores are disguised as Helper T-cells, and even produce their own chemical signals altering other immune cells. From there, they circulate throughout the body undetected by other immune cells due to the proteins and chemical signals the spores produce. Once into the bloodstream, the disguised spores make their way into the right and left common carotid arteries, which are located in the neck. As the spores travel deeper into the internal carotid arteries, these disguised cells end up at the cerebral capillary wall and penetrate it through extravasation. This includes producing a special Exoenzyme signal to essentially trick the endothelial cells into opening up- and allowing the spores into the brain tissue. From there, they use chemokines to navigate to the cerebral cortex.
#thanks for the ask!#the wren calls#mcyt#mcytblr#mcyt worldbuilding#dream smp#dsmp#dsmpblr#dsmp lore#tw medical#tw fungi#egg arc#egg lore#eggpire#speculative biology#speculative immunology#the fungus among us chronicles
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pneumonia In Children And Adults

Introduction
Pneumonia stands as a prevalent respiratory infection, exerting a significant burden on global public health. Its impact extends beyond mere morbidity, contributing to substantial healthcare costs and socioeconomic consequences. This discussion aims to elucidate the general nature of pneumonia, encompassing its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, complications, and preventive measures. By indulging into these factors, we aim to provide a better understanding of pneumonia’s complexity and underscore the importance of timely recognition and management.
Pathophysiology

Pneumonia ensues from the infiltration of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and less commonly, parasites, into the lower respiratory tract. Upon inhalation or aspiration of these pathogens, they gain access to the alveoli, where they incite an inflammatory response. This inflammatory cascade triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, recruiting immune cells to the site of infection. Neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes converge to eradicate the invading pathogens, leading to the characteristic consolidation and exudate formation within the affected lung tissue. As the infection progresses, alveolar edema, impaired gas exchange, and parenchymal damage ensue, culminating in the clinical manifestations of pneumonia.
Clinical Presentation

The clinical presentation of pneumonia encompasses a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild respiratory complaints to life-threatening respiratory failure. Common symptoms include cough, productive sputum production, fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, and systemic manifestations such as malaise and fatigue. The severity of symptoms varies depending on factors such as the underlying pathogen, the extent of lung involvement, the host’s immune status, and comorbidities. In pediatric populations, pneumonia may present with nonspecific symptoms such as feeding difficulties, lethargy, and irritability, posing diagnostic challenges. Conversely, elderly individuals may exhibit atypical presentations characterized by confusion, hypothermia, and exacerbations of underlying chronic conditions.
Diagnostic Modalities

The diagnosis of pneumonia hinges on a comprehensive clinical assessment, augmented by various diagnostic modalities to confirm the presence of pulmonary infection and reveal its etiology. A thorough history and physical examination provide invaluable insights into the patient’s symptomatology, risk factors, and clinical trajectory. Symptomatic findings such as crackles, wheezes, and diminished breath sounds may aid in localizing the site of infection and assessing disease severity. Radiographic imaging, notably chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, serves as the cornerstone of pneumonia diagnosis, revealing characteristic radiographic findings such as airspace opacities, lobar consolidation, and interstitial infiltrates. Laboratory investigations, including complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin levels, may corroborate the clinical suspicion of pneumonia and guide therapeutic decisions. Additionally, microbiological testing of respiratory specimens through techniques such as sputum culture, blood cultures, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays facilitates pathogen identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing, thereby informing targeted therapy.
Treatment Strategies

The management of pneumonia hinges on prompt initiation of empiric antimicrobial therapy tailored to the likely causative pathogen(s) and disease severity. Antibiotics represent the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia, with the choice of agent dictated by factors such as local antimicrobial resistance patterns, patient age, comorbidities, and recent antibiotic exposure. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include beta-lactam agents (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, and combination regimens for severe or healthcare-associated infections. Conversely, viral pneumonia necessitates supportive care measures, given the limited efficacy of antiviral agents in most cases. Influenza-associated pneumonia may benefit from neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir, while respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia may warrant ribavirin therapy in select cases. Adjunctive therapies such as oxygen supplementation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids may mitigate respiratory distress and improve clinical outcomes, particularly in severe or hypoxemic patients. The duration of antimicrobial therapy varies depending on factors such as the causative pathogen, clinical response, radiographic resolution, and the presence of complications. Close monitoring of clinical parameters and serial imaging studies guide the decision-making process, enabling clinicians to tailor therapy to individual patient needs.
Complications

Pneumonia harbors the potential for various complications, ranging from mild to life-threatening sequelae, necessitating vigilant monitoring and timely intervention. Common complications include pleural effusion, empyema, lung abscess, respiratory failure, septic shock, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pleural effusion denotes the accumulation of fluid within the pleural space, secondary to inflammation or impaired lymphatic drainage, manifesting as dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and dullness to percussion on physical examination. Empyema represents a purulent collection within the pleural cavity, often complicating bacterial pneumonia and necessitating drainage via thoracentesis or chest tube placement. Lung abscesses manifest as circumscribed cavities containing necrotic debris and pus within the lung parenchyma, triggered by persistent fever, productive cough, and hemoptysis. Respiratory failure ensues from impaired gas exchange and alveolar hypoventilation, caused by worsening hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, necessitating mechanical ventilation and intensive care support. Septic shock represents a life-threatening complication of severe pneumonia, characterized by systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and end-organ dysfunction, requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. ARDS denotes a severe form of acute lung injury, characterized by diffuse alveolar damage, refractory hypoxemia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, necessitating lung-protective ventilation and supportive care in the intensive care unit (ICU). The occurrence of complications portends a poor prognosis and underscores the need for early recognition and intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Preventive Measures

Preventing pneumonia entails a broad approach encompassing vaccination, infection control measures, and health promotion strategies aimed at reducing the risk of respiratory infections and their sequelae. Vaccination stands as a cornerstone of pneumonia prevention, targeting common bacterial and viral pathogens implicated in pneumonia pathogenesis. Vaccines such as the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) confer protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae, the leading bacterial cause of pneumonia, particularly in high-risk populations such as young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. Influenza vaccination remains paramount in mitigating influenza-associated pneumonia and reducing disease transmission, underscoring the importance of annual vaccination campaigns targeting vulnerable populations. Additionally, adherence to infection control measures, including hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and environmental sanitation, plays a pivotal role in reducing the spread of respiratory pathogens in healthcare settings and the community at large. Health promotion efforts aimed at smoking cessation, optimizing nutrition, and addressing underlying comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and immunodeficiency bolster immune resilience and mitigate pneumonia risk. Furthermore, early identification and management of predisposing factors such as malnutrition, homelessness, and overcrowded living conditions attenuate pneumonia susceptibility and enhance overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumonia emerges as a formidable respiratory infection, posing significant challenges to global public health. Its diverse etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment modalities, complications, and preventive measures underscore the nature of pneumonia management. Timely recognition and intervention are imperative in mitigating the morbidity and mortality associated with pneumonia, necessitating a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, public health authorities, and policymakers. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of pneumonia’s manifest and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can strive towards reducing its burden and improving patient outcomes. Through ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts, we can envision a future where pneumonia-related morbidity and mortality are substantially diminished, paving the way for enhanced respiratory health and well-being worldwide.
In managing pneumonia, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are essential alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice allows us to enhance respiratory medicine and patient outcomes.
As we address pneumonia and broader cardiovascular health complexities, let’s remain committed to optimal patient care. Together, we can impact lives positively and foster a healthier future.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at [email protected] for professional assistance
#assignment help#medical students#healthcare#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#medical help#academic assignments#university student#medical university#university life#university#student#student life#study blog#study inspiration#studyblr community#studyblr#study motivation#medication#medical student#medical school#medicare#writing#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#writeblr#online writing#academic writing
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Does Inflammation Help Healing

The immune system's normal reaction to damage, infection, or foreign substances is inflammation. It's a complex process that includes the creation of inflammatory mediators like chemokines and cytokines in addition to the activation of various immune cells. Despite the fact that inflammation is frequently associated with discomfort, swelling, and redness, it is a crucial step in the healing process.
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Roles of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein during infection and inflammation.
(A) The spike protein (red) binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2, orange) on the surface of epithelial cells, leading to the virus entering the cells.
(B) Khan et al. artificially introduced a plasmid containing the DNA sequence for the spike protein to epithelial cells (bottom) which were cultured together with macrophages (top) in the laboratory. This caused the epithelial cells to make the spike protein, which triggered the macrophages to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. However, under these conditions, the spike protein was not detected in the culture medium, suggesting that the macrophages are somehow able to sense the protein either inside or on the surface of epithelial cells. This activation requires the spike protein to bind to Toll-like receptors (TLRs) that have formed dimers – either TLR2 with TLR1, or TLR2 with TLR6. Adaptor protein MyD88 then activates a transcription factor, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), which induces the transcription of pro-inflammatory molecules.
(C) Khan et al. also used a plasmid to produce recombinant spike protein in the laboratory, and then applied these proteins to the medium in which macrophages and epithelial cells were growing. This showed that the spike protein can trigger both types of cells to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. This activation also required the TLR dimers and MyD88.
#inflammation#cardiovascular disease#covid-19 vaccine#covid-19#spike protein#fav#print this off later
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mikronischen der intratumoralen Mikrobiota beeinflussen die räumliche und zelluläre Heterogenität bei Krebs
In einem kürzlich veröffentlichten Artikel in Naturkartierten die Forscher räumliche, zelluläre und molekulare Wechselwirkungen von Wirts- und tumorassoziierten Bakterien innerhalb der Tumormikroumgebung (TME). Sie verwendeten räumliche Profiling-Technologien in situ und Einzelzell-Ribonukleinsäuresequenzierung (scRNA-seq) und konzentrierten sich dabei auf Magen-Darm-Krebs, insbesondere orales Plattenepithelkarzinom (OSCC) und Darmkrebs (CRC).
Lernen: Wirkung der intratumoral...
#Bakterien #Bildgebung #CD4 #Chemokine #Darmkrebs #DNA_Schäden #DNS #Fisch #Fluoreszenz #Gen #Gensequenzierung #Hybridisierung #Immunität #in_vitro #Intrazellulär #Karzinom #Kinase #Kollagen #Kolorektal #Konfokale_Mikroskopie #Krebs #Makrophagen #Metastasierung #Mikroskopie #Monozyt #Neutrophile #Plattenepithelkarzinom #Präklinisch #Ribonukleinsäure #RNS #Transkription #Transkriptomie #tumor #Zelle
#DiseaseInfection_News#Medical_Research_News#Medical_Science_News#News#Bakterien#Bildgebung#CD4#Chemokine#Darmkrebs#DNA_Schäden#DNS#Fisch#Fluoreszenz#Gen#Gensequenzierung#Hybridisierung#Immunität#in_vitro#Intrazellulär#Karzinom#Kinase#Kollagen#Kolorektal#Konfokale_Mikroskopie#Krebs#Makrophagen#Metastasierung#Mikroskopie#Monozyt#Neutrophile
0 notes
Text
CANDACE PERT: I mean, there is just a whole eerie quality. It makes me nervous, because I’ve had a career as a straight scientist, but it’s pretty astounding. It gets to be very philosophical, and I hated philosophy. It was the only course I ever flunked in my life. So I get nervous about all this.
But like the opiate receptor—which has now been renamed the opioid receptor—did I discover it? Or did I invent it? It’s like, if you believe in something enough, maybe somehow you can organize reality around it. Do you know what I mean?
DAVID JAY BROWN: I wonder about that a lot actually. It certainly appears that way sometimes.
CANDACE PERT: Yeah. Do I believe the concept? There’s something going on that’s pretty weird. I mean, my mind is still boggled on the peptide T front. We just came from the National Institute of Health, where we saw talks relevant to HIV.
At the time peptide T was invented, no one ever heard of the word chemokine. The word had not been coined yet. This is a class of peptides that are found in both the brain and the immune system. Their role in how cells move and divide and survive had not yet been done, and it wouldn’t be done for ten more years. And just today we heard it again.
Now it turned out five years ago that HIV uses the receptors for this class of peptides, and every company is now saying that the best thing to target is the chemokine receptor, and specifically the type of chemokine receptor, which is called CCR-5.
Now, it turns out, not only does peptide T target this, but it targets this exact receptor. Not just chemokine receptors in general, the one that everyone’s trying to make a drug for. Now, come on, is that weird or what? To me, that is the ultimate, and in some ways peptide T’s discovery is the ultimate psychic phenomena, because it’s just truly unbelievable.
[...]
So when you pose that question—yeah, there was something where I was really really wanting to make a discovery, to help people with AIDS, at the time the discovery was made. So I don’t know what that state of mind of is, where you’re really in some godlike mental state, where your consciousness is going everywhere and coming from everywhere. I’ve written about it. I had hiked up this crater in Maui and come down it, and it was pretty astounding. I was in some very out-there state of mind when I had the idea for how to proceed, and it’s almost twenty years before what people are trying to do now. It stills blows me away.
-- David Jay Brown, Conversations on the Edge of the Apocalypse
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Quantitative proteomics reveals differential extracellular vesicle cargo from M1 and M2 monocyte-derived human macrophages
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) mediate intercellular communication by carrying molecular cargo that 2 facilitate diverse physiological processes. Macrophages, playing central roles in immune responses, 3 release EVs that modulate various cellular functions. Given the distinct roles of M1 and M2 4 macrophage states, understanding the proteomic profiles of their EVs is important for elucidation of 5 EV-mediated signalling and identifying potential biomarkers for diseases involving macrophage 6 polarisation. We employed quantitative proteomics combined with bioinformatics to characterise 7 the proteomic profile of EVs released by M1 and M2 monocyte-derived macrophages. We identified 8 1,731 proteins in M1/M2 EVs, 132 of which were significantly differentially between M1 and M2. 9 Proteomic data, together with pathway analysis, found that M1/M2 macrophage EV cargo relate to 10 cellular source, and may play roles in shaping immune responses, with M1 EV cargo associated with 11 promotion of pro-inflammatory and antiviral functions, while M2 EV cargo associated with immune 12 regulation and tissue repair. M1 EV cargo was associated with cytokine/chemokine signalling 13 pathways, DNA damage, methylation, and oxidative stress. M2 EV cargo were associated with 14 macrophage alternative-activation signalling pathways, antigen presentation, and lipid metabolism. 15 We also report that macrophage EVs carry metallothioneins, and other related proteins involved in 16 response to metals and oxidative stress. http://dlvr.it/TDXNKy
0 notes
Text
Turning a negative into a positive | Science Signaling
Eberle and Gustavsson investigated the effect of different types of phospholipids on the ability of the chemokines CXCL11 and CXCL12 to bind to the ACKR3 receptor. Among these receptors, there are also atypical isoforms (ACKR), which do not serve to transmit a signal, but simply to bind excess chemokine molecules. As a result, normal receptors receive fewer chemokines, which serves as an element of regulation of the chemokine signal. But the ability to bind chemokines is influenced not only by the nature of the receptors. An important role is also played by the lipid environment, that is, the specific types of phospholipids that are located around the receptor molecule. The binding of positively charged CXCL12 to the ACKR3 receptor is enhanced in a negatively charged lipid bilayer.
As in a cell, everything is not accidental and everything affects everything, directly or indirectly.
Эберле и Густавссон (Eberle & Gustavsson) исследовали влияние различных видов фосфолипидов на способность хемокинов CXCL11 и CXCL12 связываться с рецептором ACKR3. среди этих рецепторов есть также атипичные изоформы (ACKR), которые служат не для передачи сигнала, а просто для связывания избытка молекул хемокинов. В результате обычным рецепторам достается меньше хемокинов, что служит элементом регуляции хемокинового сигнала. Но на способность связывать хемокины влияет не только природа рецепторов. Немаловажную роль также играет липидное окружение, то есть конкретные виды фосфолипидов, которые находятся вокруг молекулы рецептора. связывание положительно заряженного CXCL12 с рецептором ACKR3 усиливается в отрицательно заряженном липидном бислое.
Как в клетке всё не случайно и всё влияет на всё, прямо или опосредованно.
0 notes
Text
Human Chemokine CXCL12 Alpha Purified Lyophilized
Human Chemokine CXCL12 Alpha Purified Lyophilized
Catalog number: B2017773
Lot number: Batch Dependent
Expiration Date: Batch dependent
Amount: 10 µg
Molecular Weight or Concentration: N/A
Supplied as: POWDER
Applications: a molecular tool for various biochemical applications
Storage: -20°C
Keywords: Human CXCL12A
Grade: Biotechnology grade. All products are highly pure. All solutions are made…
0 notes
Text
Can One Supplement Do It All? Exploring the Benefits of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs)
‘Vitamins for heart health’, ‘vitamins for brain health’, ‘vitamins for joint health’; these are some of the most common health related keystroke queries on the world’s most popular search engines, and it makes perfect sense. Cardiovascular, cognitive and musculoskeletal conditions have demonstrated a steady uptick in the last decade and it’s clear that a great many people are looking for natural solutions in supporting their health in these areas.
But could it be that what we’re searching for isn’t a ‘vitamin’ at all, but a very different kind of supplement that can help support all of these systems (and more) via one important biological mechanism?
The inflammation connection
If there’s one health factor that should concern all of us, it’s inflammation. Inflammation is a natural and healthy bodily response to injury, infection, irritation or toxin that happens in two phases: initiation and resolution.1
In the initiation phase, the immune system quickly coordinates its response to a trigger by producing specific substances, like pro-inflammatory mediators, chemokines and cytokines2 to initiate pain, redness, swelling, loss of function, and heat. These uncomfortable and even painful symptoms do serve a worthy purpose – to protect and heal tissues and to fight off or neutralise the cause.
In the resolution phase, the body goes to work to wind down the inflammatory response and clear away the resulting cells and by-products. Inflammation ultimately becomes a chronic problem when the resolution phase is inadequate or incomplete leading to an ongoing loop of inappropriate inflammatory response. Resolving the inflammatory processes is especially important for brain, heart and joint health.3-8
Are fish oils the answer?
It’s now household knowledge that its function as an anti-inflammatory is one of many fish oil benefits, but what’s not so well known is how it works.
Fish oil anti-inflammatory actions are useful in the initiation phase of inflammation, where the body uses their omega 3 essential fatty acids to stop the body from producing too many pro-inflammatory substances in its response to the trigger.2 EPA and DHA, two important components of fish oils, are also used in the resolution phase on inflammation, where they are used to synthesise lipid (fat) based anti-inflammatory substances known as ‘specialised pro-resolving mediators’, or SPMs. SPMs are critical components in dampening inflammatory processes and restoring stability to the body.3-8
The SPM problem: and solution!
Even if the body is supplied with plenty of EPA, DHA and omega 3 fatty acids to assist in resolving inflammation, the synthesis of SPMs is a complicated set of processes involving many enzymes. The production of pro-resolving lipid mediators, or PRMs, is the most complex part of the process. PRMs are precursors to SPMs, meaning that SPMs are synthesised very easily once PRMs have been produced.9 There are many reasons why our bodies may be unable to optimally complete the steps required for producing PRMs – nutritional deficiencies, lipid metabolism issues and immunological problems are just a few factors that might get in the way.10
The good news is that PRMs can be taken as a supplement, either alone or combined with other natural anti-inflammatory substances, so that they can be directly used in the resolution phase of inflammation and assist the body to bring inflammation down.
Combining is key
In acting as precursors to SPMs, PRMs play a very specific role at a very specific point in the inflammatory cycle. This means that supplementing with PRMs is often best paired with a more broad-spectrum natural anti-inflammatory, like curcumin. Curcumin, derived from turmeric, has a well-established array of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions.11,12 When choosing a supplemental form of curcumin, bioavailability is key. Look for a highly absorbable form such as Theracurmin. Inflammation is frequently the cause of many health conditions relating to the brain, heart and joints and science is just beginning to scratch the surface of its impacts. In the meantime, it’s great to understand the role of SPMs in resolving inflammation, and to leverage on the potential of supplemental PRMs in our daily lives.
#Pro-Resolving Mediators#SPMs#Supplements#Natural Health#Gemma Davies#Inflammation#Wellness#Health Supplements
0 notes