#data scraping api
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Custom Data API - Web Scraping API
Get real-time custom data API to automate web data scraping processes, and enhance data integration. Our web scraping APIs collets key data from data sources and deliver in quick time. Access real-time data specific to your needs with our custom APIs.
Know more about Custom Data API
0 notes
Text
Uncover the hidden potential of data scraping to propel your startup's growth to new heights. Learn how data scraping can supercharge your startup's success.
0 notes
Text
An interoperability rule for your money
This is the final weekend to back the Kickstarter campaign for the audiobook of my next novel, The Lost Cause. These kickstarters are how I pay my bills, which lets me publish my free essays nearly every day. If you enjoy my work, please consider backing!

"If you don't like it, why don't you take your business elsewhere?" It's the motto of the corporate apologist, someone so Hayek-pilled that they see every purchase as a ballot cast in the only election that matters – the one where you vote with your wallet.
Voting with your wallet is a pretty undignified way to go through life. For one thing, the people with the thickest wallets get the most votes, and for another, no matter who you vote for in that election, the Monopoly Party always wins, because that's the part of the thick-wallet set.
Contrary to the just-so fantasies of Milton-Friedman-poisoned bootlickers, there are plenty of reasons that one might stick with a business that one dislikes – even one that actively harms you.
The biggest reason for staying with a bad company is if they've figured out a way to punish you for leaving. Businesses are keenly attuned to ways to impose switching costs on disloyal customers. "Switching costs" are all the things you have to give up when you take your business elsewhere.
Businesses love high switching costs – think of your gym forcing you to pay to cancel your subscription or Apple turning off your groupchat checkmark when you switch to Android. The more it costs you to move to a rival vendor, the worse your existing vendor can treat you without worrying about losing your business.
Capitalists genuinely hate capitalism. As the FBI informant Peter Thiel says, "competition is for losers." The ideal 21st century "market" is something like Amazon, a platform that gets 45-51 cents out of every dollar earned by its sellers. Sure, those sellers all compete with one another, but no matter who wins, Amazon gets a cut:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/28/cloudalists/#cloud-capital
Think of how Facebook keeps users glued to its platform by making the price of leaving cutting of contact with your friends, family, communities and customers. Facebook tells its customers – advertisers – that people who hate the platform stick around because Facebook is so good at manipulating its users (this is a good sales pitch for a company that sells ads!). But there's a far simpler explanation for peoples' continued willingness to let Mark Zuckerberg spy on them: they hate Zuck, but they love their friends, so they stay:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/facebooks-secret-war-switching-costs
One of the most important ways that regulators can help the public is by reducing switching costs. The easier it is for you to leave a company, the more likely it is they'll treat you well, and if they don't, you can walk away from them. That's just what the Consumer Finance Protection Bureau wants to do with its new Personal Financial Data Rights rule:
https://www.consumerfinance.gov/about-us/newsroom/cfpb-proposes-rule-to-jumpstart-competition-and-accelerate-shift-to-open-banking/
The new rule is aimed at banks, some of the rottenest businesses around. Remember when Wells Fargo ripped off millions of its customers by ordering its tellers to open fake accounts in their name, firing and blacklisting tellers who refused to break the law?
https://www.npr.org/sections/money/2016/10/07/497084491/episode-728-the-wells-fargo-hustle
While there are alternatives to banks – local credit unions are great – a lot of us end up with a bank by default and then struggle to switch, even though the banks give us progressively worse service, collectively rip us off for billions in junk fees, and even defraud us. But because the banks keep our data locked up, it can be hard to shop for better alternatives. And if we do go elsewhere, we're stuck with hours of tedious clerical work to replicate all our account data, payees, digital wallets, etc.
That's where the new CFPB order comes in: the Bureau will force banks to "share data at the person’s direction with other companies offering better products." So if you tell your bank to give your data to a competitor – or a comparison shopping site – it will have to do so…or else.
Banks often claim that they block account migration and comparison shopping sites because they want to protect their customers from ripoff artists. There are certainly plenty of ripoff artists (notwithstanding that some of them run banks). But banks have an irreconcilable conflict of interest here: they might want to stop (other) con-artists from robbing you, but they also want to make leaving as painful as possible.
Instead of letting shareholder-accountable bank execs in back rooms decide what the people you share your financial data are allowed to do with it, the CFPB is shouldering that responsibility, shifting those deliberations to the public activities of a democratically accountable agency. Under the new rule, the businesses you connect to your account data will be "prohibited from misusing or wrongfully monetizing the sensitive personal financial data."
This is an approach that my EFF colleague Bennett Cyphers and I first laid our in our 2021 paper, "Privacy Without Monopoly," where we describe how and why we should shift determinations about who is and isn't allowed to get your data from giant, monopolistic tech companies to democratic institutions, based on privacy law, not corporate whim:
https://www.eff.org/wp/interoperability-and-privacy
The new CFPB rule is aimed squarely at reducing switching costs. As CFPB Director Rohit Chopra says, "Today, we are proposing a rule to give consumers the power to walk away from bad service and choose the financial institutions that offer the best products and prices."
The rule bans banks from charging their customers junk fees to access their data, and bans businesses you give that data to from "collecting, using, or retaining data to advance their own commercial interests through actions like targeted or behavioral advertising." It also guarantees you the unrestricted right to revoke access to your data.
The rule is intended to replace the current state-of-the-art for data sharing, which is giving your banking password to third parties who go and scrape that data on your behalf. This is a tactic that comparison sites and financial dashboards have used since 2006, when Mint pioneered it:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/12/mint-late-stage-adversarial-interoperability-demonstrates-what-we-had-and-what-we
A lot's happened since 2006. It's past time for American bank customers to have the right to access and share their data, so they can leave rotten banks and go to better ones.
The new rule is made possible by Section 1033 of the Consumer Financial Protection Act, which was passed in 2010. Chopra is one of the many Biden administrative appointees who have acquainted themselves with all the powers they already have, and then used those powers to help the American people:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/18/administrative-competence/#i-know-stuff
It's pretty wild that the first digital interoperability mandate is going to come from the CFPB, but it's also really cool. As Tim Wu demonstrated in 2021 when he wrote Biden's Executive Order on Promoting Competition in the American Economy, the administrative agencies have sweeping, grossly underutilized powers that can make a huge difference to everyday Americans' lives:
https://www.eff.org/de/deeplinks/2021/08/party-its-1979-og-antitrust-back-baby

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/21/let-my-dollars-go/#personal-financial-data-rights


My next novel is The Lost Cause, a hopeful novel of the climate emergency. Amazon won't sell the audiobook, so I made my own and I'm pre-selling it on Kickstarter!

Image: Steve Morgan (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:U.S._National_Bank_Building_-_Portland,_Oregon.jpg
Stefan Kühn (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Abrissbirne.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
-
Rhys A. (modified) https://www.flickr.com/photos/rhysasplundh/5201859761/in/photostream/
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/
#pluralistic#cfpb#interoperability mandates#mint#scraping#apis#privacy#privacy without monopoly#consumer finance protection bureau#Personal Financial Data Rights#interop#data hoarding#junk fees#switching costs#section 1033#interoperability
159 notes
·
View notes
Text
not me finding out that fandom wikis do not have an api (which is like a specialised ui for programmers that a lot of websites have where you can more directly access resources off the website with programming tools, f.e. if one piece wiki had one, you could tell your coding languages like "hey get all the strawhat pirates' names and heights off their character pages and put them in my database here please" and it would be able to get that info off the wiki for you) so I will have to learn web scraping to get data off there for visualising ship stats project I have planned for my data analysis portfolio instead now smh
#coding#ship stats#the things I do for my shenanigans#but turns out bootcamp don't cover the *getting the data* part of data stuff#only the how you organise and move around and what you can do with the data once you have it#and I'm over here like but I wanna be able to assemble whatever public data sets I want to play with :c#shoutout to reddit for other people asking about this already cause I'm not the only geek tryna get wiki data for shenanigans#at least I'll get good use out of knowing how to scrape shit off non-api websites I guess u.u
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Extract Amazon Product Prices Data with Python 3
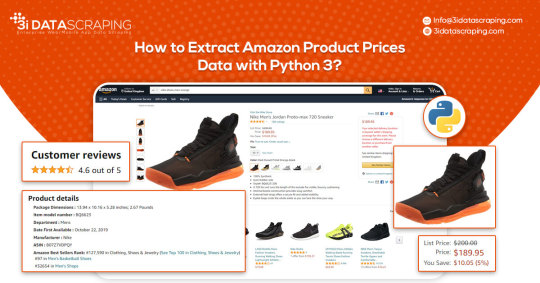
Web data scraping assists in automating web scraping from websites. In this blog, we will create an Amazon product data scraper for scraping product prices and details. We will create this easy web extractor using SelectorLib and Python and run that in the console.
#webscraping#data extraction#web scraping api#Amazon Data Scraping#Amazon Product Pricing#ecommerce data scraping#Data EXtraction Services
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kroger Grocery Data Scraping | Kroger Grocery Data Extraction

Shopping Kroger grocery online has become very common these days. At Foodspark, we scrape Kroger grocery apps data online with our Kroger grocery data scraping API as well as also convert data to appropriate informational patterns and statistics.
#food data scraping services#restaurantdataextraction#restaurant data scraping#web scraping services#grocerydatascraping#zomato api#fooddatascrapingservices#Scrape Kroger Grocery Data#Kroger Grocery Websites Apps#Kroger Grocery#Kroger Grocery data scraping company#Kroger Grocery Data#Extract Kroger Grocery Menu Data#Kroger grocery order data scraping services#Kroger Grocery Data Platforms#Kroger Grocery Apps#Mobile App Extraction of Kroger Grocery Delivery Platforms#Kroger Grocery delivery#Kroger grocery data delivery
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
ScrapingBypass Web Scraping API Bypass Cloudflare Captcha Verification
ScrapingBypass API can bypass Cloudflare Captcha verification for web scraping using Python, Java, NodeJS, and Curl. $3 for 3-day trial: https://www.scrapingbypass.com/pricing ScrapingBypass: https://scrapingbypass.com Telegram: https://t.me/CloudBypassEN
#scrapingbypass#bypass cloudflare#cloudflare bypass#web scraping api#captcha solver#web scraping#web crawler#extract data
1 note
·
View note
Text
Denas Grybauskas, Chief Governance and Strategy Officer at Oxylabs – Interview Series
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/denas-grybauskas-chief-governance-and-strategy-officer-at-oxylabs-interview-series/
Denas Grybauskas, Chief Governance and Strategy Officer at Oxylabs – Interview Series


Denas Grybauskas is the Chief Governance and Strategy Officer at Oxylabs, a global leader in web intelligence collection and premium proxy solutions.
Founded in 2015, Oxylabs provides one of the largest ethically sourced proxy networks in the world—spanning over 177 million IPs across 195 countries—along with advanced tools like Web Unblocker, Web Scraper API, and OxyCopilot, an AI-powered scraping assistant that converts natural language into structured data queries.
You’ve had an impressive legal and governance journey across Lithuania’s legal tech space. What personally motivated you to tackle one of AI’s most polarising challenges—ethics and copyright—in your role at Oxylabs?
Oxylabs have always been the flagbearer for responsible innovation in the industry. We were the first to advocate for ethical proxy sourcing and web scraping industry standards. Now, with AI moving so fast, we must make sure that innovation is balanced with responsibility.
We saw this as a huge problem facing the AI industry, and we could also see the solution. By providing these datasets, we’re enabling AI companies and creators to be on the same page regarding fair AI development, which is beneficial for everyone involved. We knew how important it was to keep creators’ rights at the forefront but also provide content for the development of future AI systems, so we created these datasets as something that can meet the demands of today’s market.
The UK is in the midst of a heated copyright battle, with strong voices on both sides. How do you interpret the current state of the debate between AI innovation and creator rights?
While it’s important that the UK government favours productive technological innovation as a priority, it’s vital that creators should feel enhanced and protected by AI, not stolen from. The legal framework currently under debate must find a sweet spot between fostering innovation and, at the same time, protecting the creators, and I hope in the coming weeks we see them find a way to strike a balance.
Oxylabs has just launched the world’s first ethical YouTube datasets, which requires creator consent for AI training. How exactly does this consent process work—and how scalable is it for other industries like music or publishing?
All of the millions of original videos in the datasets have the explicit consent of the creators to be used for AI training, connecting creators and innovators ethically. All datasets offered by Oxylabs include videos, transcripts, and rich metadata. While such data has many potential use cases, Oxylabs refined and prepared it specifically for AI training, which is the use that the content creators have knowingly agreed to.
Many tech leaders argue that requiring explicit opt-in from all creators could “kill” the AI industry. What’s your response to that claim, and how does Oxylabs’ approach prove otherwise?
Requiring that, for every usage of material for AI training, there be a previous explicit opt-in presents significant operational challenges and would come at a significant cost to AI innovation. Instead of protecting creators’ rights, it could unintentionally incentivize companies to shift development activities to jurisdictions with less rigorous enforcement or differing copyright regimes. However, this does not mean that there can be no middle ground where AI development is encouraged while copyright is respected. On the contrary, what we need are workable mechanisms that simplify the relationship between AI companies and creators.
These datasets offer one approach to moving forward. The opt-out model, according to which content can be used unless the copyright owner explicitly opts out, is another. The third way would be facilitating deal-making between publishers, creators, and AI companies through technological solutions, such as online platforms.
Ultimately, any solution must operate within the bounds of applicable copyright and data protection laws. At Oxylabs, we believe AI innovation must be pursued responsibly, and our goal is to contribute to lawful, practical frameworks that respect creators while enabling progress.
What were the biggest hurdles your team had to overcome to make consent-based datasets viable?
The path for us was opened by YouTube, enabling content creators to easily and conveniently license their work for AI training. After that, our work was mostly technical, involving gathering data, cleaning and structuring it to prepare the datasets, and building the entire technical setup for companies to access the data they needed. But this is something that we’ve been doing for years, in one way or another. Of course, each case presents its own set of challenges, especially when you’re dealing with something as huge and complex as multimodal data. But we had both the knowledge and the technical capacity to do this. Given this, once YouTube authors got the chance to give consent, the rest was only a matter of putting our time and resources into it.
Beyond YouTube content, do you envision a future where other major content types—such as music, writing, or digital art—can also be systematically licensed for use as training data?
For a while now, we have been pointing out the need for a systematic approach to consent-giving and content-licensing in order to enable AI innovation while balancing it with creator rights. Only when there is a convenient and cooperative way for both sides to achieve their goals will there be mutual benefit.
This is just the beginning. We believe that providing datasets like ours across a range of industries can provide a solution that finally brings the copyright debate to an amicable close.
Does the importance of offerings like Oxylabs’ ethical datasets vary depending on different AI governance approaches in the EU, the UK, and other jurisdictions?
On the one hand, the availability of explicit-consent-based datasets levels the field for AI companies based in jurisdictions where governments lean toward stricter regulation. The primary concern of these companies is that, rather than supporting creators, strict rules for obtaining consent will only give an unfair advantage to AI developers in other jurisdictions. The problem is not that these companies don’t care about consent but rather that without a convenient way to obtain it, they are doomed to lag behind.
On the other hand, we believe that if granting consent and accessing data licensed for AI training is simplified, there is no reason why this approach should not become the preferred way globally. Our datasets built on licensed YouTube content are a step toward this simplification.
With growing public distrust toward how AI is trained, how do you think transparency and consent can become competitive advantages for tech companies?
Although transparency is often seen as a hindrance to competitive edge, it’s also our greatest weapon to fight mistrust. The more transparency AI companies can provide, the more evidence there is for ethical and beneficial AI training, thereby rebuilding trust in the AI industry. And in turn, creators seeing that they and the society can get value from AI innovation will have more reason to give consent in the future.
Oxylabs is often associated with data scraping and web intelligence. How does this new ethical initiative fit into the broader vision of the company?
The release of ethically sourced YouTube datasets continues our mission at Oxylabs to establish and promote ethical industry practices. As part of this, we co-founded the Ethical Web Data Collection Initiative (EWDCI) and introduced an industry-first transparent tier framework for proxy sourcing. We also launched Project 4β as part of our mission to enable researchers and academics to maximise their research impact and enhance the understanding of critical public web data.
Looking ahead, do you think governments should mandate consent-by-default for training data, or should it remain a voluntary industry-led initiative?
In a free market economy, it is generally best to let the market correct itself. By allowing innovation to develop in response to market needs, we continually reinvent and renew our prosperity. Heavy-handed legislation is never a good first choice and should only be resorted to when all other avenues to ensure justice while allowing innovation have been exhausted.
It doesn’t look like we have already reached that point in AI training. YouTube’s licensing options for creators and our datasets demonstrate that this ecosystem is actively seeking ways to adapt to new realities. Thus, while clear regulation is, of course, needed to ensure that everyone acts within their rights, governments might want to tread lightly. Rather than requiring expressed consent in every case, they might want to examine the ways industries can develop mechanisms for resolving the current tensions and take their cues from that when legislating to encourage innovation rather than hinder it.
What advice would you offer to startups and AI developers who want to prioritise ethical data use without stalling innovation?
One way startups can help facilitate ethical data use is by developing technological solutions that simplify the process of obtaining consent and deriving value for creators. As options to acquire transparently sourced data emerge, AI companies need not compromise on speed; therefore, I advise them to keep their eyes open for such offerings.
Thank you for the great interview, readers who wish to learn more should visit Oxylabs.
#Advice#ai#AI development#ai governance#AI industry#AI innovation#AI systems#ai training#AI-powered#API#approach#Art#Building#Companies#compromise#content#content creators#copyright#course#creators#data#data collection#data protection#data scraping#data use#datasets#deal#developers#development#Digital Art
0 notes
Text
Automate Employee Data Extraction with ScrapingDog API
Discover how to streamline employee data collection using web scraping. This guide walks through automating the process with the ScrapingDog API, saving hours of manual effort.
#web scraping#scrapingdog#web scraping api#employee data extracton#google search api#google maps api
0 notes
Text
Data Scraping Made Simple: What It Really Means
Data Scraping Made Simple: What It Really Means
In the digital world, data scraping is a powerful way to collect information from websites automatically. But what exactly does that mean—and why is it important?
Let’s break it down in simple terms.
What Is Data Scraping?
Data scraping (also called web scraping) is the process of using bots or scripts to extract data from websites. Instead of copying and pasting information manually, scraping tools do the job automatically—much faster and more efficiently.
You can scrape product prices, news headlines, job listings, real estate data, weather reports, and more.
Imagine visiting a website with hundreds of items. Now imagine a tool that can read all that content and save it in a spreadsheet in seconds. That’s what data scraping does.
Why Is It So Useful?
Businesses, researchers, and marketers use data scraping to:
Track competitors' prices
Monitor customer reviews
Gather contact info for leads
Collect news for trend analysis
Keep up with changing market data
In short, data scraping helps people get useful information without wasting time.
Is Data Scraping Legal?
It depends. Public data (like product prices or news articles) is usually okay to scrape, but private or copyrighted content is not. Always check a website’s terms of service before scraping it.
Tools for Data Scraping
There are many tools that make data scraping easy:
Beautiful Soup (for Python developers)
Octoparse (no coding needed)
Scrapy (for advanced scraping tasks)
SERPHouse APIs (for SEO and search engine data)
Some are code-based, others are point-and-click tools. Choose what suits your need and skill level.
Final Thoughts
What is data scraping? It’s the smart way to extract website content for business, research, or insights. With the right tools, it saves time, increases productivity, and opens up access to valuable online data.
Just remember: scrape responsibly.
#serphouse#google serp api#serp scraping api#google search api#seo#api#google#bing#data scraping#web scraping
0 notes
Text

E-commerce Web Scraping API for Accurate Product & Pricing Insights
Access structured e-commerce data efficiently with a robust web scraping API for online stores, marketplaces, and retail platforms. This API helps collect data on product listings, prices, reviews, stock availability, and seller details from top e-commerce sites. Ideal for businesses monitoring competitors, following trends, or managing records, it provides consistent and correct results. Built to scale, the service supports high-volume requests and delivers results in easy-to-integrate formats like JSON or CSV. Whether you need data from Amazon, eBay, or Walmart. iWeb Scraping provides unique e-commerce data scraping services. Learn more about the service components and pricing by visiting iWebScraping E-commerce Data Services.
0 notes
Text
E-commerce Web Scraping | Data Scraping for eCommerce
Are you in need of data scraping for eCommerce industry? Get expert E-commerce web scraping services to extract real-time data. Flat 20%* off on ecommerce data scraping.
0 notes
Text
The Future of Professional Networking: Exploring LinkedIn Scraping
In the digital age, the importance of professional networking cannot be overstated. LinkedIn, the premier platform for business and career networking, hosts millions of profiles and a plethora of company information. For businesses and individuals alike, accessing this wealth of data can offer significant advantages. This is where the concept of LinkedIn scraping comes into play, revolutionizing how we gather and utilize information.
Understanding LinkedIn Scraping
They refers to the process of extracting data from LinkedIn profiles and company pages using automated tools. This technique allows users to collect a wide range of data points such as job titles, skills, endorsements, company details, and much more. By automating the data collection process, scraping LinkedIn provides a more efficient and scalable way to gather crucial information compared to manual methods.
The Benefits of LinkedIn Scraping
The advantages ofLinkedIn data scrape are multifaceted, catering to various needs across different sectors:
1. Recruitment: For recruitment agencies and HR professionals, scraping LinkedIn can streamline the talent acquisition process. By extracting detailed profiles, recruiters can quickly identify and contact potential candidates that match specific job criteria.
2. Sales and Marketing: Sales teams can leverage scraping LinkedIn to build comprehensive lead lists. By targeting profiles that fit their ideal customer persona, businesses can enhance their outreach efforts and improve conversion rates.
3. Market Research: Companies conducting market research can use LinkedIn scraping to gather data on competitors, industry trends, and demographic information. This insight can inform strategic decisions and help businesses stay ahead of the curve.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
While LinkedIn scraping offers numerous benefits, it is crucial to navigate the ethical and legal landscape carefully. LinkedIn's terms of service explicitly prohibit unauthorized scraping of their data. Violating these terms can lead to legal repercussions and the banning of accounts. Therefore, it is essential to use compliant and ethical methods when performing LinkedIn scraping.
Introducing a Streamlined LinkedIn Scraper API
For those looking to implement LinkedIn scraping on a large scale, a streamlined LinkedIn scraper API is an invaluable tool. This API enables real-time data scraping of profiles and company information, providing up-to-date insights and information. By using such an API, businesses can efficiently gather and process data at scale without compromising on accuracy or speed.
Best Practices for LinkedIn Scraping
To ensure successful and compliant LinkedIn scraping, consider the following best practices:
1. Respect LinkedIn’s Terms of Service: Always adhere to LinkedIn’s guidelines to avoid potential legal issues. Use scraping tools that are designed to operate within these constraints.
2. Data Accuracy: Ensure that the scraping tool you use can accurately capture the necessary data points without errors. This reliability is crucial for maintaining the quality of your data.
3. Privacy Considerations: Be mindful of user privacy and data protection laws. Avoid scraping personal information that is not publicly available or necessary for your use case.

Conclusion:
LinkedIn scraping is transforming the way we access and utilize professional data. Whether for recruitment, sales, marketing, or research, the ability to extract and analyze LinkedIn data efficiently can provide a competitive edge. By using a streamlined LinkedIn scraper API, businesses can achieve real-time data scraping of profiles and company information at scale, ensuring they have the most current and relevant information at their fingertips. For those seeking a reliable solution,Scrapin.io offers a robust platform designed to meet these needs, enabling users to harness the full potential of LinkedIn data scraping while maintaining compliance and ethical standards.
Blog Source URL :
#linkedin scraper#linkedin scraping#linkedin data scraping#linkedin data scraper#scraping linkedin#scrape linkedin#scrape linkedin data#linkedin profile scraper#scrape linkedin profiles#linkedin scraping tool#scraping linkedin data#linkedin scraper tool#linkedin data extractor#linkedin data scrape#extract data from linkedin#scrape data from linkedin#linkedin scraper api#linkedin data scraping tool#linkedin data extraction tool#extract information from linkedin
0 notes
Text
How to Build a Web Scraping API Looking for an easy guide to scraping web data? Learn how to create a Web Scraping API using Java, Spring Boot, and Jsoup! Perfect for developers at any level.
0 notes
Text
Tapping into Fresh Insights: Kroger Grocery Data Scraping
In today's data-driven world, the retail grocery industry is no exception when it comes to leveraging data for strategic decision-making. Kroger, one of the largest supermarket chains in the United States, offers a wealth of valuable data related to grocery products, pricing, customer preferences, and more. Extracting and harnessing this data through Kroger grocery data scraping can provide businesses and individuals with a competitive edge and valuable insights. This article explores the significance of grocery data extraction from Kroger, its benefits, and the methodologies involved.
The Power of Kroger Grocery Data
Kroger's extensive presence in the grocery market, both online and in physical stores, positions it as a significant source of data in the industry. This data is invaluable for a variety of stakeholders:
Kroger: The company can gain insights into customer buying patterns, product popularity, inventory management, and pricing strategies. This information empowers Kroger to optimize its product offerings and enhance the shopping experience.
Grocery Brands: Food manufacturers and brands can use Kroger's data to track product performance, assess market trends, and make informed decisions about product development and marketing strategies.
Consumers: Shoppers can benefit from Kroger's data by accessing information on product availability, pricing, and customer reviews, aiding in making informed purchasing decisions.
Benefits of Grocery Data Extraction from Kroger
Market Understanding: Extracted grocery data provides a deep understanding of the grocery retail market. Businesses can identify trends, competition, and areas for growth or diversification.
Product Optimization: Kroger and other retailers can optimize their product offerings by analyzing customer preferences, demand patterns, and pricing strategies. This data helps enhance inventory management and product selection.
Pricing Strategies: Monitoring pricing data from Kroger allows businesses to adjust their pricing strategies in response to market dynamics and competitor moves.
Inventory Management: Kroger grocery data extraction aids in managing inventory effectively, reducing waste, and improving supply chain operations.
Methodologies for Grocery Data Extraction from Kroger
To extract grocery data from Kroger, individuals and businesses can follow these methodologies:
Authorization: Ensure compliance with Kroger's terms of service and legal regulations. Authorization may be required for data extraction activities, and respecting privacy and copyright laws is essential.
Data Sources: Identify the specific data sources you wish to extract. Kroger's data encompasses product listings, pricing, customer reviews, and more.
Web Scraping Tools: Utilize web scraping tools, libraries, or custom scripts to extract data from Kroger's website. Common tools include Python libraries like BeautifulSoup and Scrapy.
Data Cleansing: Cleanse and structure the scraped data to make it usable for analysis. This may involve removing HTML tags, formatting data, and handling missing or inconsistent information.
Data Storage: Determine where and how to store the scraped data. Options include databases, spreadsheets, or cloud-based storage.
Data Analysis: Leverage data analysis tools and techniques to derive actionable insights from the scraped data. Visualization tools can help present findings effectively.
Ethical and Legal Compliance: Scrutinize ethical and legal considerations, including data privacy and copyright. Engage in responsible data extraction that aligns with ethical standards and regulations.
Scraping Frequency: Exercise caution regarding the frequency of scraping activities to prevent overloading Kroger's servers or causing disruptions.
Conclusion
Kroger grocery data scraping opens the door to fresh insights for businesses, brands, and consumers in the grocery retail industry. By harnessing Kroger's data, retailers can optimize their product offerings and pricing strategies, while consumers can make more informed shopping decisions. However, it is crucial to prioritize ethical and legal considerations, including compliance with Kroger's terms of service and data privacy regulations. In the dynamic landscape of grocery retail, data is the key to unlocking opportunities and staying competitive. Grocery data extraction from Kroger promises to deliver fresh perspectives and strategic advantages in this ever-evolving industry.
#grocerydatascraping#restaurant data scraping#food data scraping services#food data scraping#fooddatascrapingservices#zomato api#web scraping services#grocerydatascrapingapi#restaurantdataextraction
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Web Screen Scraping API offers robust customizable solutions for extracting data from any website, supports advanced features like crawling and handles high concurrency for optimal performance. With its flexibility and efficiency, it is used for several data scraping requirements.
0 notes