#energy data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to Monitor and Control Your Energy Usage with Tech
In an era where sustainability and cost-efficiency are at the forefront of global conversations, learning how to monitor and control your energy usage with tech is not just beneficial—it’s essential. With energy costs rising and climate concerns escalating, leveraging technology to reduce consumption and optimise efficiency has become increasingly accessible. Whether you’re looking to save money,…
#battery storage#digital energy#Eco-Friendly#eco-tech#electric vehicles#energy apps#energy conservation#energy control#energy costs#energy data#energy efficiency#energy habits#energy innovation#energy insights#energy management#energy monitoring#energy monitoring apps#energy reduction#energy saving#energy strategy#energy tips#energy tracking#energy usage#energy-efficient#green living#green tech#home automation#home energy#LED bulbs#power saving
0 notes
Text
World surpasses 40% clean power as renewables see record rise

This is from the Global Electricity Review 2025 by Ember. Although this isn't something you are going to see in newspaper headlines, the progress we made with renewables in 2024 is a pretty big deal and if you're someone who likes a lot of data and graphs it's really worth reading.
I'm going to leave this video here because Hank Green does a better job of covering it than I am going to.
youtube
"This to me feels like news. It feels like a big deal. It feels like things are changing, like we are hitting a moment with electricity generation that really does matter. And over the next five years we will hit the point where we are generating less and less energy with fossil fuels every year. That's great. And that's not news. I didn't see anyone covering this [...]. It's not news because it's not bad and it's also not news because it's not like 'we did it, we hit the moment!'."
I think this quote from Hank's video does a good job of encapsulating how the slow, gradual progress that is happening often doesn't make it into the news--because it's not a dramatic emergency or a "we did it, we fully solved climate change!" kind of moment that makes for good headlines.
But that then gives people the idea that we're hardly making any progress on addressing climate change, which is not true at all. The fact that we need to continue to double-down on this progress to do it more and faster does not negate that so much progress has already been made.
#climate change#global warming#carbon emissions#data#graphs#science#ecoanxiety#ecogrief#climate anxiety#hope#good news#renewable energy#solar energy#wind energy#nuclear energy#hydroelectricity#video#clean energy#green energy#Youtube
3K notes
·
View notes
Note
one 100 word email written with ai costs roughly one bottle of water to produce. the discussion of whether or not using ai for work is lazy becomes a non issue when you understand there is no ethical way to use it regardless of your intentions or your personal capabilities for the task at hand
with all due respect, this isnt true. *training* generative ai takes a ton of power, but actually using it takes about as much energy as a google search (with image generation being slightly more expensive). we can talk about resource costs when averaged over the amount of work that any model does, but its unhelpful to put a smokescreen over that fact. when you approach it like an issue of scale (i.e. "training ai is bad for the environment, we should think better about where we deploy it/boycott it/otherwise organize abt this) it has power as a movement. but otherwise it becomes a personal choice, moralizing "you personally are harming the environment by using chatgpt" which is not really effective messaging. and that in turn drives the sort of "you are stupid/evil for using ai" rhetoric that i hate. my point is not whether or not using ai is immoral (i mean, i dont think it is, but beyond that). its that the most common arguments against it from ostensible progressives end up just being reactionary

i like this quote a little more- its perfectly fine to have reservations about the current state of gen ai, but its not just going to go away.
#i also generally agree with the genie in the bottle metaphor. like ai is here#ai HAS been here but now it is a llm gen ai and more accessible to the average user#we should respond to that rather than trying to. what. stop development of generative ai? forever?#im also not sure that the ai industry is particularly worse for the environment than other resource intense industries#like the paper industry makes up about 2% of the industrial sectors power consumption#which is about 40% of global totals (making it about 1% of world total energy consumption)#current ai energy consumption estimates itll be at .5% of total energy consumption by 2027#every data center in the world meaning also everything that the internet runs on accounts for about 2% of total energy consumption#again you can say ai is a unnecessary use of resources but you cannot say it is uniquely more destructive
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
People are creating their “Realistic Pokemon Teams” on TikTok right now. This is mine.
#tbh i accidentally got a super efficient team#as far as feeding the Pokémon are concerned#magnamite eats electricity#the porygons eat data#trubbish eats trash#Banette feeds on the ambient energy of emotions#and Munchlax adores spoiled/expired food#and can eat it with no negative consequences
161 notes
·
View notes
Text


The duality of man (Android)
#star trek#star trek the next generation#star trek tng#data tng#data#data soong#star trek memes#shitpost#brent spiner#made by moi#I could not find a better quality photo of that costume test#and frankly I think it adds to the cursed energy of it
777 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI data centers are being approved at a breakneck pace across the country, particularly in poorer regions where they are pitched as economic development projects to boost property tax receipts, bring in jobs and where they’re offered sizable tax breaks. Data centers typically don’t hire many people, though, with most jobs in security and janitorial work, along with temporary construction work. And the costs to the utility’s other customers can remain hidden because of a lack of scrutiny and the limited power of state energy regulators. Many data centers—like the one Meta is building in Holly Ridge—are being powered by fossil fuels. This has led to respiratory illness and other health risks and emitting greenhouse gasses that fuel climate change. In Memphis, a massive data center built to launch a chatbot for Elon Musks’ AI company is powered by smog-spewing methane turbines, in a region that leads the state for asthma rates.
[...]
A research paper by Ari Peskoe and Eliza Martin published in March looked at 50 regulatory cases involving data centers, and found that tech companies were pushing some of the costs onto utility customers through secret contracts with the utilities. The paper found that utilities were often parroting rhetoric from AI boosting politicians—including President Biden—to suggest that pushing through permitting for AI data center infrastructure is a matter of national importance.
23 June 2025
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
not quite sure where this originally comes from but i saw this picture and couldn't help but think of the permit office people-

#cub running experiments on grian skizz and scar-#enrichment#like little lab rats#hes already putting them through labyrinthss#please if someone knows where this picture originally comes from i'd love to know#“its fine for me to do this if you live in my building i can use your data” has the same energy as cub telling mumbo his shop sucked#c: “thank goodness its gone” m: “i almost can't argue-”#permit office#poe poe#permit office enforcement#cubfan135#grian#goodtimeswithscar#gtwscar#gtws#skizzleman#hermitcraft s10#hermitcraft#hc s10#hc 10#hermitcraft season 10#pixls things
402 notes
·
View notes
Text



Star Trek TNG/A.I. Artificial Intelligence crossover where the planet that A.I. takes place on is a replicate earth, and the Enterprise discovers David instead of the creatures at the end of the movie!
Data is phenomenal with kids, which really makes me want to see him interacting with and guiding an android child*, especially one of a different make and model to himself! David was created to be a forever child, so it would be interesting to see how Data would process meeting a being like himself who is in a childhood purgatory, when he never got a childhood himself.
*Lal counts, but I still think his experiences with David would be unique!
#star trek#star trek tng#tng#star trek the next generation#the next generation#data soong#star trek data#ai artificial intelligence#ai artificial intelligence movie#ai artificial intelligence david#ai artificial intelligence teddy#I also think that Lore would LOVE David#did you see what David did to his twin?#Lore would love that energy#David’s stories about what humans did to androids/mechas on his world would also give Lore all the more fuel to start a revolt
235 notes
·
View notes
Text

#bsky#AI#data centers#climate crisis#heat wave#energy efficiency#air conditioning#electrical grid#power grid
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
MIT scientists pin down the origins of a fast radio burst
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/mit-scientists-pin-down-the-origins-of-a-fast-radio-burst/
MIT scientists pin down the origins of a fast radio burst


Fast radio bursts are brief and brilliant explosions of radio waves emitted by extremely compact objects such as neutron stars and possibly black holes. These fleeting fireworks last for just a thousandth of a second and can carry an enormous amount of energy — enough to briefly outshine entire galaxies.
Since the first fast radio burst (FRB) was discovered in 2007, astronomers have detected thousands of FRBs, whose locations range from within our own galaxy to as far as 8 billion light-years away. Exactly how these cosmic radio flares are launched is a highly contested unknown.
Now, astronomers at MIT have pinned down the origins of at least one fast radio burst using a novel technique that could do the same for other FRBs. In their new study, appearing today in the journal Nature, the team focused on FRB 20221022A — a previously discovered fast radio burst that was detected from a galaxy about 200 million light-years away.
The team zeroed in further to determine the precise location of the radio signal by analyzing its “scintillation,” similar to how stars twinkle in the night sky. The scientists studied changes in the FRB’s brightness and determined that the burst must have originated from the immediate vicinity of its source, rather than much further out, as some models have predicted.
The team estimates that FRB 20221022A exploded from a region that is extremely close to a rotating neutron star, 10,000 kilometers away at most. That’s less than the distance between New York and Singapore. At such close range, the burst likely emerged from the neutron star’s magnetosphere — a highly magnetic region immediately surrounding the ultracompact star.
The team’s findings provide the first conclusive evidence that a fast radio burst can originate from the magnetosphere, the highly magnetic environment immediately surrounding an extremely compact object.
“In these environments of neutron stars, the magnetic fields are really at the limits of what the universe can produce,” says lead author Kenzie Nimmo, a postdoc in MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research. “There’s been a lot of debate about whether this bright radio emission could even escape from that extreme plasma.”
“Around these highly magnetic neutron stars, also known as magnetars, atoms can’t exist — they would just get torn apart by the magnetic fields,” says Kiyoshi Masui, associate professor of physics at MIT. “The exciting thing here is, we find that the energy stored in those magnetic fields, close to the source, is twisting and reconfiguring such that it can be released as radio waves that we can see halfway across the universe.”
The study’s MIT co-authors include Adam Lanman, Shion Andrew, Daniele Michilli, and Kaitlyn Shin, along with collaborators from multiple institutions.
Burst size
Detections of fast radio bursts have ramped up in recent years, due to the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME). The radio telescope array comprises four large, stationary receivers, each shaped like a half-pipe, that are tuned to detect radio emissions within a range that is highly sensitive to fast radio bursts.
Since 2020, CHIME has detected thousands of FRBs from all over the universe. While scientists generally agree that the bursts arise from extremely compact objects, the exact physics driving the FRBs is unclear. Some models predict that fast radio bursts should come from the turbulent magnetosphere immediately surrounding a compact object, while others predict that the bursts should originate much further out, as part of a shockwave that propagates away from the central object.
To distinguish between the two scenarios, and determine where fast radio bursts arise, the team considered scintillation — the effect that occurs when light from a small bright source such as a star, filters through some medium, such as a galaxy’s gas. As the starlight filters through the gas, it bends in ways that make it appear, to a distant observer, as if the star is twinkling. The smaller or the farther away an object is, the more it twinkles. The light from larger or closer objects, such as planets in our own solar system, experience less bending, and therefore do not appear to twinkle.
The team reasoned that if they could estimate the degree to which an FRB scintillates, they might determine the relative size of the region from where the FRB originated. The smaller the region, the closer in the burst would be to its source, and the more likely it is to have come from a magnetically turbulent environment. The larger the region, the farther the burst would be, giving support to the idea that FRBs stem from far-out shockwaves.
Twinkle pattern
To test their idea, the researchers looked to FRB 20221022A, a fast radio burst that was detected by CHIME in 2022. The signal lasts about two milliseconds, and is a relatively run-of-the-mill FRB, in terms of its brightness. However, the team’s collaborators at McGill University found that FRB 20221022A exhibited one standout property: The light from the burst was highly polarized, with the angle of polarization tracing a smooth S-shaped curve. This pattern is interpreted as evidence that the FRB emission site is rotating — a characteristic previously observed in pulsars, which are highly magnetized, rotating neutron stars.
To see a similar polarization in fast radio bursts was a first, suggesting that the signal may have arisen from the close-in vicinity of a neutron star. The McGill team’s results are reported in a companion paper today in Nature.
The MIT team realized that if FRB 20221022A originated from close to a neutron star, they should be able to prove this, using scintillation.
In their new study, Nimmo and her colleagues analyzed data from CHIME and observed steep variations in brightness that signaled scintillation — in other words, the FRB was twinkling. They confirmed that there is gas somewhere between the telescope and FRB that is bending and filtering the radio waves. The team then determined where this gas could be located, confirming that gas within the FRB’s host galaxy was responsible for some of the scintillation observed. This gas acted as a natural lens, allowing the researchers to zoom in on the FRB site and determine that the burst originated from an extremely small region, estimated to be about 10,000 kilometers wide.
“This means that the FRB is probably within hundreds of thousands of kilometers from the source,” Nimmo says. “That’s very close. For comparison, we would expect the signal would be more than tens of millions of kilometers away if it originated from a shockwave, and we would see no scintillation at all.”
“Zooming in to a 10,000-kilometer region, from a distance of 200 million light years, is like being able to measure the width of a DNA helix, which is about 2 nanometers wide, on the surface of the moon,” Masui says. “There’s an amazing range of scales involved.”
The team’s results, combined with the findings from the McGill team, rule out the possibility that FRB 20221022A emerged from the outskirts of a compact object. Instead, the studies prove for the first time that fast radio bursts can originate from very close to a neutron star, in highly chaotic magnetic environments.
“These bursts are always happening, and CHIME detects several a day,” Masui says. “There may be a lot of diversity in how and where they occur, and this scintillation technique will be really useful in helping to disentangle the various physics that drive these bursts.”
This research was supported by various institutions including the Canada Foundation for Innovation, the Dunlap Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Toronto, the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research, the Trottier Space Institute at McGill University, and the University of British Columbia.
#000#2022#amazing#Astronomy#Astronomy and astrophysics#Astrophysics#atoms#author#billion#Black holes#Canada#comparison#data#diversity#DNA#driving#Emissions#energy#Environment#explosions#fast radio bursts#Filters#Foundation#galaxies#Galaxy#gas#Giving#how#hydrogen#Innovation
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
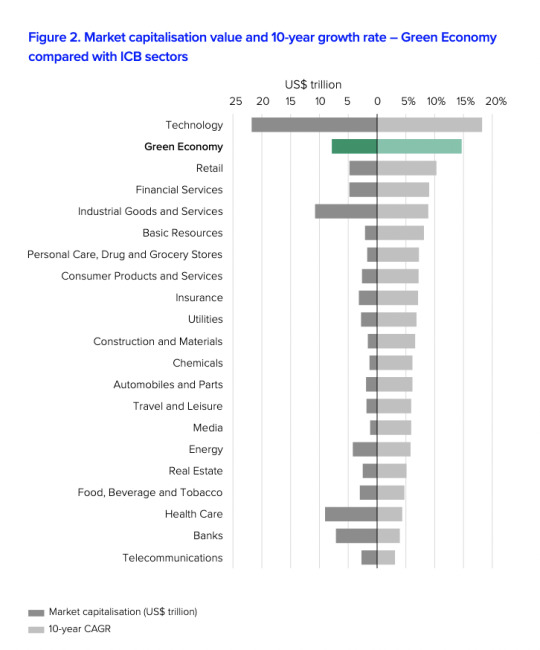
The Green Economy is Now the Fourth Largest Market Sector Globally
From this report by the London Stock Exchange Group:
As of Q1 2025, the global green economy, if considered as a standalone sector, would account for 8.6% of listed equities with a combined market capitalisation of US$7.9 trillion. This would make it the fourth largest sector by market capitalisation, following Technology, Industrial Goods and Services, and Health Care.
#economy#hope#good news#hopepunk#data#graphs#economics#green economy#climate change#global warming#progress#environment#ecology#renewable energy#clean energy#green energy#energy revolution#global climate action
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
I never wanna see anyone say Data isn't autistic-coded ever again when he specifically became attached to Sherlock Holmes, arguably one of the most autistic-coded characters in all of fiction.
#and learned to play violin bc of him#same energy as me trying red pie to be like Dale Cooper#cherry wasnt available that day sadly#star trek tng#star trek#star trek data#autism
13 notes
·
View notes
Text


Overhated Female Character x Underused Female Character [Patreon | Commissions]
#If I see any Pulaski hate on this post I'm gonna lose it#Selar#Pulaski#Doctor Selar#Doctor Pulaski#been watching tng and I really don't know why people hate pulaski so much#just watched an episode where she was like 'I hate this dude...Data!!! Kick his ass in space 3d chess!!!' and I laughed#unless there's an episode I haven't gotten to yet where she like sends Data to the electric chair I do nooot understand#but I mean people wanted T'Pring dead for not wanting to marry Spock so you know#to me Pulaski is much more interesting than Beverely - she has a certain energy to her that I like#watched an episode the other day where she fought tooth & nail to do something dangerous and when it turned out she was wrong she accepted#it and was like 'ok. I guess I'm dying now. I knew the risks v_v' and I liked her right away (first episode I saw her in)#anyway yuri between two women who never interact in canon save me#tng#star trek tng
96 notes
·
View notes
Text
I hate online dating, the bastard dukes of Hinge have rendered me unfuckable pariah due to the Mark of Cain (openly transgender).
#my stuff#i don’t actually have time energy or funds to date#but it would be nice to have the option#and it’s demoralizing to fire off a handful of thoughtful questions and compliments and get NADA#to say nothing of how many mind games i gotta play to figure out if the cute dyke’s idea of lesbian includes me#(editors note: data available suggests It Does Not)
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
friendly reminder chrome fucking sucks as a browser and you should switch to firefox regardless even if you don't care if google collects your data
#not to be petty but i get sooo annoyed when people who have no idea about internet security defend it like it's gospel#if you can control the data advertisers have about you then you absolutely should#firefox literally has all the same features chrome does but i dont even have the energy to have that conversation anymore with people
215 notes
·
View notes
Text
The almost overnight surge in electricity demand from data centers is now outstripping the available power supply in many parts of the world, according to interviews with data center operators, energy providers and tech executives. That dynamic is leading to years-long waits for businesses to access the grid as well as growing concerns of outages and price increases for those living in the densest data center markets. The dramatic increase in power demands from Silicon Valley’s growth-at-all-costs approach to AI also threatens to upend the energy transition plans of entire nations and the clean energy goals of trillion-dollar tech companies. In some countries, including Saudi Arabia, Ireland and Malaysia, the energy required to run all the data centers they plan to build at full capacity exceeds the available supply of renewable energy, according to a Bloomberg analysis of the latest available data. By one official estimate, Sweden could see power demand from data centers roughly double over the course of this decade — and then double again by 2040. In the UK, AI is expected to suck up 500% more energy over the next decade. And in the US, data centers are projected to use 8% of total power by 2030, up from 3% in 2022, according to Goldman Sachs, which described it as “the kind of electricity growth that hasn’t been seen in a generation.”
21 June 2024
673 notes
·
View notes