#linux system network administration
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Linux Network Administration Training
Emblogic offers complete Linux Network Administration Training in Noida and Delhi, India, designed for aspiring IT professionals and system administrators. This schooling program provides hands-on enjoyment in handling Linux-based environments, configuring servers, and troubleshooting network-associated issues.

Why Choose Linux System Administration Training?
Linux powers a full-size part of a corporation's IT infrastructure, making skilled Linux directors tremendously well-liked. Our path makes a specialty of practical education, permitting students to increase their understanding of putting in, configuring, securing, and maintaining Linux servers. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking to decorate your talents, this application will equip you with the important tools to be successful in the subject.
Key Topics Covered inside the Training:
Linux System Administration: Installation, report gadget control, consumer administration, and security.
Network Configuration: Setting up DNS, DHCP, FTP, SSH, and VPN offerings.
Server Management: Apache, MySQL, and mail server configuration.
Shell Scripting: Automating duties of the usage of Bash scripting.
Troubleshooting & Monitoring: Identifying and resolving system/network issues.
Career Benefits of Linux Training
A Linux administrator’s role is critical in ensuring server uptime, security, and network efficiency. The demand for Linux professionals is growing across industries, including IT, finance, healthcare, and cloud computing.
Get Started Today!
If you're looking for the best Linux network administration training in Noida or Delhi, Emblogic is your trusted partner. Upgrade your career with industry-relevant training and become a skilled Linux professional.
Visit our website at: www.emblogic.com, For more details.
#linux course noida#delhi#India#linux system administration#linux network administration#6 weeks industrial training linux#linux system network administration#configuring linux servers#linux server administration training
0 notes
Text
So if you want to know how "functional" Windows 11 is, I just got a new laptop, and while I was tearing its guts out to make Windows 11 less obtrusive and ad-ridden, I discovered a problem.
Modern versions of Windows have a built-in system for transferring files to other Windows computers on the same network -- you mark certain folders as "shared", and then you can just open them on another computer from the "Network" window after entering a password.
Well, I could connect from my desktop to my laptop just fine; however, I had a devil of a time connecting from my laptop to my desktop. Didn't matter what username or password I used; just "your credentials are incorrect."
Then something occurred to me.
See, I'd wanted a specific home directory name. This entailed 1. logging into my Microsoft account the first time I started my laptop, thus creating an account on the laptop with an automatically-selected name; 2. creating a second administrator account with the username/home-directory-name I wanted, without an associated Microsoft account; 3. deleting the first account, 4. connecting the second account with my Microsoft account. I did this on my laptop, and I'd done this on the desktop.
Thing is, in step 2 there, I'd given the second account the same password as my Microsoft account, because I knew I was just going to overwrite it. See where this is going? The correct password was not the password for my Microsoft account, but rather, the password which I'd used to create the Windows account without the Microsoft account. And I've changed my Microsoft password multiple times since getting the current desktop computer.
Solution:
Remove the Microsoft account from my desktop. This entails setting a new password.
Have the laptop connect to the desktop with that new password.
Add the Microsoft account back to the desktop.
Anyway this might be the straw that makes the camel start looking into Linux.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Breaking into Tech: How Linux Skills Can Launch Your Career in 2025
In today's rapidly evolving tech landscape, Linux skills have become increasingly valuable for professionals looking to transition into rewarding IT careers. As we move through 2025, the demand for Linux System Administrators continues to grow across industries, creating excellent opportunities for career changers—even those without traditional technical backgrounds.
Why Linux Skills Are in High Demand
Linux powers much of the world's technology infrastructure. From enterprise servers to cloud computing environments, this open-source operating system has become the backbone of modern IT operations. Organizations need skilled professionals who can:
Deploy and manage enterprise-level IT infrastructure
Ensure system security and stability
Troubleshoot complex technical issues
Implement automation to improve efficiency
The beauty of Linux as a career path is that it's accessible to motivated individuals willing to invest time in learning the necessary skills. Unlike some tech specialties that require years of formal education, Linux administration can be mastered through focused training programs and hands-on experience.
The Path to Becoming a Linux System Administrator
1. Structured Learning
The journey begins with structured learning. Comprehensive training programs that cover Linux fundamentals, system administration, networking, and security provide the knowledge base needed to succeed. The most effective programs:
Teach practical, job-relevant skills
Offer instruction from industry professionals
Pace the learning to allow for deep understanding
Prepare students for respected certifications like Red Hat
2. Certification
Industry certifications validate your skills to potential employers. Red Hat certifications are particularly valuable, demonstrating your ability to work with enterprise Linux environments. These credentials help you stand out in a competitive job market and often lead to higher starting salaries.
3. Hands-On Experience
Theoretical knowledge isn't enough—employers want to see practical experience. Apprenticeship opportunities allow aspiring Linux administrators to:
Apply their skills in real-world scenarios
Build a portfolio of completed projects
Gain confidence in their abilities
Bridge the gap between training and employment
4. Job Search Strategy
With the right skills and experience, the final step is finding that first position. Successful job seekers:
Tailor their resumes to highlight relevant skills
Prepare thoroughly for technical interviews
Network with industry professionals
Target companies that value their newly acquired skills
Time Investment and Commitment
Becoming job-ready as a Linux System Administrator typically requires:
10-15+ hours per week for studying
A commitment to consistent learning over several months
Persistence through challenging technical concepts
A growth mindset and motivation to succeed
The Career Outlook
For those willing to make the investment, the rewards can be substantial. Linux professionals enjoy:
Competitive salaries
Strong job security
Opportunities for remote work
Clear paths for career advancement
Intellectually stimulating work environments
Conclusion
The path to becoming a Linux System Administrator is more accessible than many people realize. With the right training, certification, and hands-on experience, motivated individuals can transition into rewarding tech careers—regardless of their previous background. As we continue through 2025, the demand for these skills shows no signs of slowing down, making now an excellent time to begin this journey.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
WHO AM I? 🧑💻
Hello everyone,
My name is Bhargav Vipulkumar Patel, and I am currently pursuing a diploma in Information Technology Services. Technology has always fascinated me, and I believe IT plays a crucial role in shaping our digital world.
Throughout my studies, I have been exploring networking concepts and gaining experience in working with different operating systems. I have moderate experience with Linux 🐧, Windows Server 🖥️, and Cisco Packet Tracer 🌐. These technologies help me understand network management, troubleshooting, and system administration.
This semester, I am particularly excited about emerging technologies 🚀—how they evolve, their impact on industries, and how they redefine the way we interact with the digital world. I look forward to sharing my thoughts and learning through this blogging journey.
✨ #Networking #Linux #WindowsServer #ITStudent #TechLife #LearningEveryday
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Building Your Own Operating System: A Beginner’s Guide
An operating system (OS) is an essential component of computer systems, serving as an interface between hardware and software. It manages system resources, provides services to users and applications, and ensures efficient execution of processes. Without an OS, users would have to manually manage hardware resources, making computing impractical for everyday use.

Lightweight operating system for old laptops
Functions of an Operating System
Operating systems perform several crucial functions to maintain system stability and usability. These functions include:
1. Process Management
The OS allocates resources to processes and ensures fair execution while preventing conflicts. It employs algorithms like First-Come-First-Serve (FCFS), Round Robin, and Shortest Job Next (SJN) to optimize CPU utilization and maintain system responsiveness.
2. Memory Management
The OS tracks memory usage and prevents memory leaks by implementing techniques such as paging, segmentation, and virtual memory. These mechanisms enable multitasking and improve overall system performance.
3. File System Management
It provides mechanisms for reading, writing, and deleting files while maintaining security through permissions and access control. File systems such as NTFS, FAT32, and ext4 are widely used across different operating systems.
4. Device Management
The OS provides device drivers to facilitate interaction with hardware components like printers, keyboards, and network adapters. It ensures smooth data exchange and resource allocation for input/output (I/O) operations.
5. Security and Access Control
It enforces authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms to protect user data and system integrity. Modern OSs incorporate features like firewalls, anti-malware tools, and secure boot processes to prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats.
6. User Interface
CLI-based systems, such as Linux terminals, provide direct access to system commands, while GUI-based systems, such as Windows and macOS, offer intuitive navigation through icons and menus.
Types of Operating Systems
Operating systems come in various forms, each designed to cater to specific computing needs. Some common types include:
1. Batch Operating System
These systems were widely used in early computing environments for tasks like payroll processing and scientific computations.
2. Multi-User Operating System
It ensures fair resource allocation and prevents conflicts between users. Examples include UNIX and Windows Server.
3. Real-Time Operating System (RTOS)
RTOS is designed for time-sensitive applications, where processing must occur within strict deadlines. It is used in embedded systems, medical devices, and industrial automation. Examples include VxWorks and FreeRTOS.
4 Mobile Operating System
Mobile OSs are tailored for smartphones and tablets, offering touchscreen interfaces and app ecosystems.
5 Distributed Operating System
Distributed OS manages multiple computers as a single system, enabling resource sharing and parallel processing. It is used in cloud computing and supercomputing environments. Examples include Google’s Fuchsia and Amoeba.
Popular Operating Systems
Several operating systems dominate the computing landscape, each catering to specific user needs and hardware platforms.
1. Microsoft Windows
It is popular among home users, businesses, and gamers. Windows 10 and 11 are the latest versions, offering improved performance, security, and compatibility.
2. macOS
macOS is Apple’s proprietary OS designed for Mac computers. It provides a seamless experience with Apple hardware and software, featuring robust security and high-end multimedia capabilities.
3. Linux
Linux is an open-source OS favored by developers, system administrators, and security professionals. It offers various distributions, including Ubuntu, Fedora, and Debian, each catering to different user preferences.
4. Android
It is based on the Linux kernel and supports a vast ecosystem of applications.
5. iOS
iOS is Apple’s mobile OS, known for its smooth performance, security, and exclusive app ecosystem. It powers iPhones and iPads, offering seamless integration with other Apple devices.
Future of Operating Systems
The future of operating systems is shaped by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and edge computing. Some key trends include:
1. AI-Driven OS Enhancements
AI-powered features, such as voice assistants and predictive automation, are becoming integral to modern OSs. AI helps optimize performance, enhance security, and personalize user experiences.
2. Cloud-Based Operating Systems
Cloud OSs enable users to access applications and data remotely. Chrome OS is an example of a cloud-centric OS that relies on internet connectivity for most functions.
3. Edge Computing Integration
With the rise of IoT devices, edge computing is gaining importance. Future OSs will focus on decentralized computing, reducing latency and improving real-time processing.
4. Increased Focus on Security
Cyber threats continue to evolve, prompting OS developers to implement advanced security measures such as zero-trust architectures, multi-factor authentication, and blockchain-based security.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Can you explain the differences between A+, Network+, and Security+ certifications from CompTIA? Which certification is considered more valuable and why?
Certainly! CompTIA offers several certifications that are widely recognized in the IT industry. A+, Network+, and Security+ are three of the most popular certifications, each focusing on different areas of IT. Here's a breakdown of each:
A+ Certification:
Focus: This certification is geared towards entry-level IT professionals and covers foundational skills in IT hardware, software, networking, and troubleshooting.
Topics: A+ covers areas such as PC hardware, operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS), networking, mobile devices, security, and troubleshooting.
Job Roles: A+ certification holders often work in roles such as technical support specialists, help desk technicians, and field service technicians.
Value: A+ is valuable for individuals starting their IT careers as it provides a solid foundation of IT knowledge and skills. It's often a prerequisite for more advanced certifications.
Network+ Certification:
Focus: Network+ focuses specifically on networking concepts and skills required for IT professionals working with networks, both wired and wireless.
Topics: Network+ covers areas such as network technologies, installation and configuration, media and topologies, management, security, and troubleshooting.
Job Roles: Network+ certification holders typically work in roles such as network administrators, network technicians, and systems engineers.
Value: Network+ is valuable for individuals seeking to specialize in networking. It provides a comprehensive understanding of networking fundamentals and is recognized by employers as validation of networking knowledge and skills.
Security+ Certification:
Focus: Security+ is focused on cybersecurity concepts and skills, covering best practices in securing networks, systems, and applications.
Topics: Security+ covers areas such as network security, compliance and operational security, threats and vulnerabilities, application, data, and host security, access control, identity management, and cryptography.
Job Roles: Security+ certification holders often work in roles such as security analysts, security specialists, security administrators, and network security engineers.
Value: Security+ is highly valuable in today's cybersecurity landscape. It demonstrates proficiency in cybersecurity principles and practices and is often required or recommended for cybersecurity-related roles.
In terms of which certification is considered more valuable, it largely depends on your career goals and the specific job role you're targeting. However, comptia Security+ certification is often regarded as more valuable in terms of salary and job prospects due to the increasing demand for cybersecurity professionals and the critical importance of cybersecurity in modern IT environments. That said, all three certifications have their own merit and can be valuable depending on your career path and interests.
#online certification and training#cybersecuritycourse#comptia security plus#comptia#comptiasecuritypluscertification
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Linux Administration: The Complete Linux Bootcamp for 2024
This Linux Administration course covers every major topic, including using AI and Natural Language to administer Linux systems (ChatGPT & ShellGPT), all important Linux commands, the Linux Filesystem, File Permissions, Process Management, User Account Management, Software Management, Networking in Linux, System Administration, Bash Scripting, Containarizing Apps with Podman, Iptables/Netfilter Firewall, Linux Security and many more!
I’m constantly updating the course to be the most comprehensive, yet straightforward, Linux Administration course on the market!
This course IS NOT like any other Linux Administration course you can take online. At the end of this course, you will MASTER the key concepts and you will become an effective Linux System Engineer or Administrator.
This is a brand new Linux Administration course that is constantly updated to teach you the skills required for the future that comes.
The world is changing, constantly, and at a fast pace! The technology-driven future in which we’ll live is filled with promise but also challenges. Linux powers the servers of the Internet and by enrolling in this course you’ll power the essential Linux concepts and commands. This Linux Administration course is really different! You’ll learn what matters and get the skills to get ahead and gain an edge.
#youtube#free education#education#linux administration#educate yourselves#hacking#educate yourself#tips and tricks#technology#security#The Complete Linux Bootcamp for 2024#linux tutorial#linux for beginners#linux command line#open source#computers
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
ugh, my asshole network administrator keeps remotely removing NMap from my computer. like fuck dude, I *need* that, you don't understand what it's like for me to go from slinging NMap on a Linux system daily to suddenly being forced to find an IP address through god knows what method on a shit windows/AD environment.
let me just scan the network broo, and please, please, please dear god let me throw a Linux box up on my desk.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Python: Features and Where It's Used
Python is a versatile programming language that has gained significant popularity in recent times. It's known for its ease of use, readability, and adaptability, making it an excellent choice for both newcomers and experienced programmers. In this article, we'll delve into the specifics of what Python is and explore its various applications.
What is Python?
Python is an interpreted programming language that is high-level and serves multiple purposes. Created by Guido van Rossum and released in 1991, Python is designed to prioritize code readability and simplicity, with a clean and minimalistic syntax. It places emphasis on using proper indentation and whitespace, making it more convenient for programmers to write and comprehend code.
Key Traits of Python :
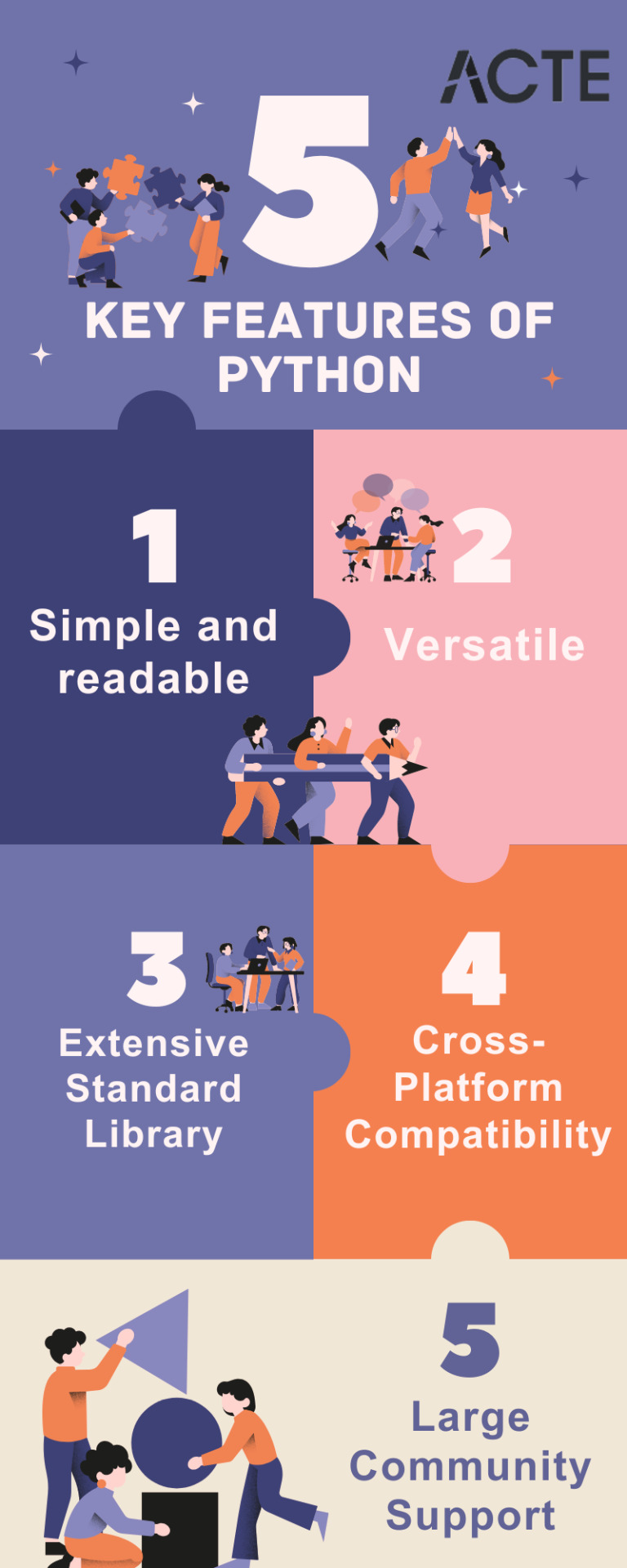
Simplicity and Readability: Python code is structured in a way that's easy to read and understand. This reduces the time and effort required for both creating and maintaining software.
Python code example: print("Hello, World!")
Versatility: Python is applicable across various domains, from web development and scientific computing to data analysis, artificial intelligence, and more.
Python code example: import numpy as np
Extensive Standard Library: Python offers an extensive collection of pre-built libraries and modules. These resources provide developers with ready-made tools and functions to tackle complex tasks efficiently.
Python code example: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Compatibility Across Platforms: Python is available on multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This allows programmers to create and run code seamlessly across different platforms.
Strong Community Support: Python boasts an active community of developers who contribute to its growth and provide support through online forums, documentation, and open-source contributions. This community support makes Python an excellent choice for developers seeking assistance or collaboration.
Where is Python Utilized?

Due to its versatility, Python is utilized in various domains and industries. Some key areas where Python is widely applied include:
Web Development: Python is highly suitable for web development tasks. It offers powerful frameworks like Django and Flask, simplifying the process of building robust web applications. The simplicity and readability of Python code enable developers to create clean and maintainable web applications efficiently.
Data Science and Machine Learning: Python has become the go-to language for data scientists and machine learning practitioners. Its extensive libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, and SciPy, along with specialized libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch, facilitate a seamless workflow for data analysis, modeling, and implementing machine learning algorithms.
Scientific Computing: Python is extensively used in scientific computing and research due to its rich scientific libraries and tools. Libraries like SciPy, Matplotlib, and NumPy enable efficient handling of scientific data, visualization, and numerical computations, making Python indispensable for scientists and researchers.
Automation and Scripting: Python's simplicity and versatility make it a preferred language for automating repetitive tasks and writing scripts. Its comprehensive standard library empowers developers to automate various processes within the operating system, network operations, and file manipulation, making it popular among system administrators and DevOps professionals.
Game Development: Python's ease of use and availability of libraries like Pygame make it an excellent choice for game development. Developers can create interactive and engaging games efficiently, and the language's simplicity allows for quick prototyping and development cycles.
Internet of Things (IoT): Python's lightweight nature and compatibility with microcontrollers make it suitable for developing applications for the Internet of Things. Libraries like Circuit Python enable developers to work with sensors, create interactive hardware projects, and connect devices to the internet.
Python's versatility and simplicity have made it one of the most widely used programming languages across diverse domains. Its clean syntax, extensive libraries, and cross-platform compatibility make it a powerful tool for developers. Whether for web development, data science, automation, or game development, Python proves to be an excellent choice for programmers seeking efficiency and user-friendliness. If you're considering learning a programming language or expanding your skills, Python is undoubtedly worth exploring.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
In today's digital era, cloud computing has become the backbone of modern businesses. As organizations increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, the demand for skilled cloud professionals is soaring. To meet this growing need, many professionals are turning to cloud architecture courses to build the expertise required in this evolving field. If you're contemplating a career in this dynamic industry, you might be asking: Is enrolling in a cloud architecture course truly worthwhile?
Let's delve into the specifics to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding Cloud Architecture
Cloud architecture refers to the design and structure of systems that leverage cloud computing technologies. It encompasses the components and subcomponents required for cloud computing, including front-end platforms, back-end platforms, cloud-based delivery, and networks. Professionals in this domain are tasked with designing scalable, secure, and efficient cloud solutions tailored to organizational needs.
The Rising Demand for Cloud Architecture Courses
With the rapid adoption of cloud technologies, there's a significant talent gap in the industry. Organizations are on the lookout for professionals who can design and manage cloud infrastructures effectively. This surge in demand underscores the value of structured cloud architecture courses that equip learners with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
RACE, REVA University's M.Sc. in Cloud Architecture and Security
Program Overview:
RACE REVA University offers a comprehensive M.Sc. in Cloud Architecture and Security. This 24-month program is meticulously designed for mid to senior-level professionals aiming to transition into cloud-centric roles.
Key Highlights:
Industry Collaboration: Developed in association with AWS Academy and Microsoft Azure, ensuring curriculum relevance to current industry standards.
Hands-on Learning: Engage in over 15 mini-projects and 2 full-scale industry projects, providing real-world experience.
Certifications: Opportunity to earn five globally recognized certifications, including:
AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate
AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900)
Microsoft Azure Administrator (AZ-104)
Microsoft Azure Security Engineer (SC-100)
Advanced Tools: Training on tools like CISCO Packet Tracer, Wireshark, and platforms such as CentOS Linux and Windows Server 2012.
Career Support: Personalized career guidance, resume building, mock interviews, and access to a network of over 100 placement partners. Graduates have reported salary hikes ranging from 50% to 200%.
Eligibility Criteria:
PG Diploma: Bachelor's degree with Mathematics or Statistics at the +2 level.
M.Sc.: Bachelor's degree in any discipline with a minimum of two years of industry experience.
Is It Worth the Investment?
Considering the program's comprehensive curriculum, industry collaborations, hands-on projects, and robust career support, enrolling in the M.Sc. in Cloud Architecture and Security at RACE, REVA University, presents a valuable opportunity for professionals aiming to excel in the cloud domain.
Ready to Elevate Your Career?
Explore more about the program and take the next step in your professional journey by visiting: RACE, REVA University
#CloudArchitectureCourses#CloudComputing#REVAUniversity#RACERevaUniversity#TechCareers#CloudSecurity#CloudCertification#MastersInCloudArchitecture#CareerInCloudComputing#CloudTraining#LearnCloud#ITCoursesIndia
0 notes
Text
Is B Tech in Cloud Computing the Right Course for You?
As businesses, governments, and individuals continue to shift towards digital platforms, the demand for cloud technology has grown exponentially. Today, cloud computing is not just a trend—it is a necessity for modern operations across industries. For students passionate about technology and innovation, pursuing a B Tech in Cloud Computing can open doors to exciting and high-demand career opportunities.
But is it the right course for you? Let’s explore what the program involves, the skills you will develop, and the career options it offers.
Understanding cloud computing as a field
Cloud computing involves delivering computing services such as storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the internet. Instead of owning physical servers or data centres, businesses rely on cloud providers to access and manage their IT resources.
Cloud computing makes services faster, more flexible, and cost-effective. It powers everything from streaming services to banking apps and online shopping platforms.
With a B Tech in Cloud Computing, students are trained to design, develop, deploy, and manage cloud-based systems and solutions.
What you will study during B Tech in Cloud Computing
The curriculum for B Tech in Cloud Computing is designed to cover both fundamental computer science subjects and specialized cloud-related topics. Key areas of study include:
Cloud architecture and services (AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud)
Virtualization technologies and data center management
Cloud security and disaster recovery planning
Big data and cloud storage solutions
Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud integration
DevOps practices and cloud automation
Along with theoretical classes, students also work on live projects, case studies, and internships to gain hands-on experience.
Skills you will develop during the program
Pursuing a B Tech in Cloud Computing helps students build a wide range of technical and professional skills, such as:
Cloud platform management and deployment
Programming and scripting skills (Python, Java, Linux Shell)
Data analysis and storage solutions
Security protocols and compliance management
Problem-solving and innovative thinking in tech environments
Project management and collaborative teamwork
These skills are highly valued across industries like IT, healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing.
Career opportunities after B Tech in Cloud Computing
Graduates of this program are well-positioned to enter a growing and rewarding job market. Popular career paths include:
Cloud Solutions Architect
Cloud Engineer
Cloud Security Analyst
DevOps Engineer
Cloud Consultant
Systems Administrator
Data Engineer
Top technology companies, cloud service providers, and consulting firms actively hire professionals with expertise in cloud computing.
Additionally, graduates can pursue certifications such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified Azure Solutions Architect, or Google Professional Cloud Architect to enhance their career prospects further.
Who should consider this course?
A B Tech in Cloud Computing is suitable for students who:
Have a strong interest in computer science, networking, and software engineering
Are curious about how technology drives business transformation
Enjoy problem-solving, building systems, and exploring innovative solutions
Want to work in cutting-edge fields like cloud security, AI integration, and big data management
If you are passionate about technology and ready to work in a field that is continuously evolving, cloud computing could be the ideal path for you.
Why DY Patil University is a strong choice
For students considering this course, DY Patil University, Navi Mumbai, offers a well-designed B Tech in Cloud Computing program. The curriculum is industry-aligned, providing students with exposure to the latest cloud technologies and real-world challenges.
Here’s what DY Patil University offers:
Expert faculty with cloud industry certifications
Partnerships with major cloud providers for training and internships
State-of-the-art cloud labs and learning resources
Career guidance and placement support with top tech companies
Emphasis on practical skills through workshops and projects
DY Patil University ensures that students are not just academically prepared but also industry-ready for a successful career in cloud computing.
Final thoughts
Cloud computing is the future of technology, and professionals trained in this field are in high demand globally. If you are excited by innovation, problem-solving, and building solutions that impact millions, a B Tech in Cloud Computing can set you on a path to success.
DY Patil University, Navi Mumbai, offers the right environment to nurture your skills and launch a rewarding career in one of the most dynamic sectors of the global economy.
1 note
·
View note
Text
White Hat vs. Black Hat Hacking: More Than Just a Color Code 🎩🖤
Hacking isn’t all hoodies and neon code—there’s a spectrum of intent and methodology. In 2025, understanding the difference between white hat and black hat hacking is critical for anyone diving into cybersecurity or ethical hacking. Here’s the breakdown:
1. White Hat Hackers (Ethical Heroes) 🕵️♂️
Primary Goal: Improve security by finding and fixing vulnerabilities.
Permission: Always operate with explicit authorization from the system owner.
Tools & Techniques: Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, secure code reviews.
Outcome: Patches applied, systems hardened, organizations protected.
Career Path: Security consultant, penetration tester, bug bounty hunter.
2. Black Hat Hackers (The “Bad Guys”) 🦹♂️
Primary Goal: Exploit weaknesses for personal gain or sabotage.
Permission: None—illegal access and activities.
Tools & Techniques: Malware deployment, ransomware, phishing campaigns, data breaches.
Outcome: Stolen data, financial loss, reputational damage.
Risk & Consequences: Criminal charges, fines, and imprisonment.
3. Grey Hat Hackers (The Ambiguous Middle) ⚪⚫
Intent: Mix of white and black hat motivations—might expose flaws without permission, then recommend fixes (often for a fee).
Ethical Standing: Legality is murky—actions can be illegal despite good intentions.
Use Cases: Corporate security audits without full authorization, “friendly” vulnerability disclosures.
4. Key Differences That Matter
AspectWhite HatBlack HatGrey HatAuthorizationExplicit, legalNone, criminalOften unauthorized, but sometimes reportedIntentImprove securityPersonal gain or disruptionMixed—ethical curiosity vs. profitOutcomeSafer systemsData theft, damageFlaws revealed, but potential legal riskReputationRespected professionalCriminalControversial
5. Why It’s More Than a Color Code
Ethics & Legality: White hats follow a strict code of conduct; black hats violate laws.
Trust & Career: Ethical hacking roles require certifications (CEH, OSCP) and proven track records.
Impact on Cybersecurity: White hats help organizations stay one step ahead of black hats, closing loopholes before they’re exploited.
6. Becoming a White Hat Hacker
Learn the Fundamentals: Networking, system administration, and scripting.
Master Security Tools: Kali Linux, Metasploit, Burp Suite, Wireshark.
Get Certified: CEH, CompTIA Security+, OSCP.
Build Experience: Participate in bug bounties, CTF challenges, and open-source security projects.
Final Thoughts
White hat and black hat hacking represent two sides of the same coin—one defends, the other attacks. As cyber threats grow in complexity, the role of ethical hackers becomes more vital. Choose your “hat” wisely: white hat hacking isn’t just a career choice; it’s a commitment to protecting our digital world.
0 notes
Text

Hybrid IT Engineer - Tier 3 (JB5292) Location: Sandton, Johannesburg, Gauteng Salary: R28 000 - R48 000 per month (based on experience) Employment Type: Permanent Workplace: Hybrid (Two days in-office, remote, and at client sites as required) Are you a Tech Expert ready to lead the way? Join a company that puts people first, values the right attitude, and invests in your growth. As a Hybrid Engineer, you’ll take the lead on advanced support issues, guide and mentor junior team members, and play a key role in high-impact IT projects that drive business success. If you're passionate about technology, ready to be recognized for your performance, and want to grow your career in a dynamic, supportive environment - this could be the opportunity you’ve been waiting for. Minimum Requirements: Grade 12 or equivalent 5+ years in a senior or supervisory technical position Valid Driver's Licence and own vehicle for client site visits (as required) Strong understanding of IT Infrastructure, including hardware, software, and networking Expert in troubleshooting complex technical issues across various IT environments Skilled in Microsoft 365 and Azure Administration Deep understanding of operating systems (Windows, Linux, and macOS) Virtualization experience (VMware, Hyper-V) Familiarity with database management and SQL Certified Microsoft Azure Security Engineer Associate Certified Microsoft Identity and Access Administrator Associate Certified Microsoft Azure Administrator Associate Certified Microsoft Azure Solutions Architect If you’re detail-oriented, solution-driven, and excited about working in a fast-paced hybrid environment, this could be your next career move. Apply now! #HybridEngineer #Tier3Support #ITLeadership #AzureEngineer #ITJobsZA #JohannesburgJobs #MicrosoftCertified #SeniorTechRoles #HybridJobs For full JD & to apply online https://bit.ly/HybridITEngineerTier3JB5292 @kontakrecruitmentagency
Know someone perfect for this role? Tag them below! 👇
0 notes
Text
“A computer network consists of two or more computers that are connected with each other with the intention of sharing information and other peripherals or resources such as printers and scanners (Nash, 2000). In fact, the computers on a network are linked through telephone lines, cables, radio waves (wireless technology), or infrared light beams. In addition, a computer network is also acknowledged as simply an information network or simply net. In this scenario, the Internet is the most popular information network. It distributes data and information between internet users. Additionally, a computer network uses any network operating system that is responsible for managing and co-coordinating the operations of computers that are connected to the network. Some of the well known examples of these operating systems are: Windows NT, Linux, Unix etc. (Nash, 2000; Tanenbaum, 2002; Turban et al., 2005). This project proposal presents the specification of a new network technology based system that will allow data sharing and communication for the effective management of the corporate areas. This proposal is based on the given scenario. Our business is a small architectural business with different working teams. For superior interaction and communication we need to establish a computer network that can offer an excellent support for working remotely as well as communicate with business headquarters. 2- Background As discussed above, we have a small architectural business, with a Chief Executive, Finance Director and Sales Director. Apart from the mentioned hierarchy there are four architects, two administrative staff members and two architectural engineers. In this scenario, architects and engineers could be working at remote locations and would need communication facilities. Regarding this situation, we need a corporate network that can offer an excellent support for managing and coordinating tasks. In addition to this, it could be a web based network or system that can offer the capability to communicate and collaborate effectively. 3- Proposed Solution A new “network arrangement” will be established that will offer the facility to communicate effectively with business staff, share resources, data and facts remotely. In addition, this network will be supported by the Internet and can make use of workstations, network server and handheld PDAs for the establishment of overall communication of our business. 4- Office Plan In order to establish a network on the basis of the above given set-up, we need a more flexible network arrangement that would be able to support every area of our business and offer a capability for mutual sharing and handling of corporate resources. 4.1- Requirements for the Network In this setting the main requirements Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Service Discovery & Load Balancing in Kubernetes
Kubernetes handles internal networking like a pro! ✅ Automatic DNS names for containers ✅ Built-in load balancing ✅ No need to hard-code IPs Pods can come and go—everything just works! 🔄
Watch now:
youtube
Explore more on our channel: 👉
0 notes