#monolith to microservices
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Monolith to Microservices – How Database Architecture Must Evolve

The journey from monolith to microservices is like switching from a one-size-fits-all outfit to a tailored wardrobe—each piece has a purpose, fits perfectly, and works well on its own or with others. But here's the catch: while many teams focus on refactoring application code, they often forget the backbone that supports it all - database architecture.
If you're planning a monolithic to microservices migration, your database architecture can't be an afterthought. Why? Because traditional monolithic architectures often tie everything to one central data store. When you break your app into microservices, you can't expect all those services to keep calling back to a single data source. That would kill performance and create tight coupling. That’s the exact problem microservices are meant to solve.

What does evolving database architecture really mean?
In a monolithic setup, one large relational database holds everything—users, orders, payments; you name it. It's straightforward, but it creates bottlenecks as your app scales. Enter microservices database architecture, where each service owns its data. Without this, maintaining independent services and scaling seamlessly becomes difficult.
Here is how Microservices Database Architecture looks like:

Microservices Data Management: Strategies for Smarter Database Architecture
Each microservice might use a different database depending on its needs—NoSQL, relational, time-series, or even a share database architecture to split data horizontally across systems.
Imagine each service with its own custom toolkit, tailored to handle its unique tasks. However, this transition isn't plug-and-play. You’ll need solid database migration strategies. A thoughtful data migration strategy ensures you're not just lifting and shifting data but transforming it to fit your new architecture.
Some strategies include:
· strangler pattern
· change data capture (CDC)
· dual writes during migration
You can choose wisely based on your service’s data consistency and availability requirements.

What is the one mistake teams often make? Overlooking data integrity and synchronization. As you move to microservices database architecture, ensuring consistency across distributed systems becomes tricky. That’s why event-driven models and eventual consistency often become part of your database architecture design toolkit.
Another evolving piece is your data warehouse architecture. In a monolith, it's simple to extract data for analytics. But with distributed data, you’ll need pipelines to gather, transform, and load data from multiple sources—often in real-time.
Wrapping Up
Going from monolith to microservices isn’t just a code-level transformation—it’s a paradigm shift in how we design, access, and manage data. So, updating your database architecture is not optional; it's foundational. From crafting a rock-solid data migration strategy to implementing a flexible microservices data management approach, the data layer must evolve in sync with the application.
So, the next time you’re planning that big monolithic to microservices migration, remember: the code is only half the story. Your database architecture will make or break your success.---
Pro Tip: Start small. Pick one service, define its database boundaries, and apply your database migration strategies thoughtfully. In the world of data, small, strategic steps work better than drastic shifts.
Contact us at Nitor Infotech to modernize your database architecture for a seamless move to microservices.
0 notes
Text
Development Architectures: Monolith vs. Microservice
Unveiling the two titans of development architecture: the monolithic giant and the microservices army. Discover their strengths, weaknesses, and which reigns supreme for your next project. In this episode of Development Architectures: Monolith vs. Microservice.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why I Learn Microservices Architecture?
In today’s fast-paced development world, mastering Microservices Architecture is key to building flexible, scalable applications. With Waytoeasylearn, We gain real-world skills through clear explanations, hands-on examples, and expert-guided tutorials.
Waytoeasylearn makes learning Microservices not only efficient but empowering — helping me understand system design patterns like API Gateway, CQRS, and Event-Driven Architecture with simplicity and confidence.
Start learning with Waytoeasylearn and future-proof your architecture skills today! Enroll Now 🚀

0 notes
Text
youtube
Monolithic vs Microservices — What Should You Build
Choosing the wrong architecture too early can cost you years of tech debt! Not every product needs microservices Not every startup should start monolithic Let’s break it down :- ❓When will you need Monolithic architecture? Monolith is focused, fast, and manageable ✅ You’re building an MVP or early-stage product ✅ Your app is simple, with tightly coupled features ✅ You need to launch quickly with a small dev team ✅ Deployment speed matters more than modularity ❓When will you need Microservices? Microservices are scalable, flexible, and complex ✅ You’ve scaled and need feature-specific deployments ✅ Your teams work on different modules in parallel ✅ You want fault isolation and independent scaling ✅ Continuous deployment and DevOps are in place ⚠️ Don’t follow trends. Follow your product’s stage and your team's capability. Get expert guidance tailored to your tech stack and business goals. Call - +91 9073754444 or book a FREE consultation - https://wseinfratech.com/book-a-free-consultation
#distributed systems#microservices#java#monolith#monolith vs microservices#what is microservices#monolithic application#website development#software development#software development company#custom software development#custom website development#java microservices#web development company#aws microservices#api#api gateway#monolithic structure#website architecture#what is api gateway#web development planning#building api#custom software#custom website#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
Microservices Migration: The Data Management Roadblocks

The shift from monolithic architectures to microservices has become increasingly popular, offering scalability, flexibility, and faster development cycles. However, this migration is not without its challenges, particularly when it comes to data management. Microservices, by their very nature, demand a decentralized approach to data, which presents unique hurdles that organizations must navigate to successfully make the transition.
Data Silos and Distributed Data Management
In a monolithic system, data is often stored in a single, centralized database. Migrating to microservices requires decomposing this database into multiple, service-specific databases. This decentralized approach can lead to data silos, making it challenging to maintain a unified view of the organization’s data. Ensuring consistency and integrity across distributed databases becomes a complex task, especially when different services rely on overlapping datasets.
Data Consistency in a Decentralized System
Maintaining data consistency in a microservices architecture is a significant challenge. Unlike monolithic systems, where transactions can be easily managed within a single database, microservices often require distributed transactions across multiple databases. Implementing distributed transactions is complex, and the risk of partial failures can lead to data inconsistencies. Eventual consistency models, often employed in microservices, demand careful design to ensure that stale or inconsistent data does not disrupt business operations.
Data Synchronization and Communication
Microservices rely on APIs or messaging systems to communicate and share data. Ensuring timely synchronization of data across services is critical but can be difficult to achieve. Asynchronous communication methods, such as message queues, are frequently used but can introduce latency and complexity in tracking data flow. Additionally, designing APIs for efficient data exchange while avoiding tight coupling between services requires thoughtful planning.
Data Migration and Schema Evolution
During the migration process, data must be transitioned from the monolithic architecture to microservices. This involves not only splitting the database but also restructuring schemas to align with the new architecture. Managing schema evolution over time is another challenge, as any changes to the database structure must be carefully coordinated to prevent service disruptions. Backward compatibility of schemas becomes crucial in ensuring smooth operations during and after the migration.
Security and Data Governance
Decentralized databases increase the complexity of implementing robust security measures and enforcing data governance policies. Each microservice may have its own database, requiring separate access controls, encryption, and compliance mechanisms. Coordinating these across services while maintaining adherence to industry regulations can be a daunting task. Additionally, tracking data lineage and ensuring auditability in a distributed environment poses significant challenges.
Scalability and Performance
One of the primary goals of microservices is to enhance scalability. However, ensuring that the data layer can scale along with the services is a complex undertaking. Distributed databases must handle increased read and write operations efficiently, and ensuring low-latency access to data across geographically distributed systems is critical. Performance bottlenecks in the data layer can undermine the benefits of a microservices architecture.
Conclusion
Migrating to microservices offers tremendous potential but requires addressing significant data management challenges. Organizations must invest in strategies such as adopting event-driven architectures, leveraging database sharding, implementing effective API designs, and employing robust monitoring tools to mitigate these challenges. By doing so, they can unlock the full benefits of microservices while maintaining the integrity, consistency, and security of their data.
Transitioning to microservices is as much about rethinking data management as it is about restructuring application architecture. With careful planning and a focus on overcoming these data challenges, organizations can achieve a successful migration and thrive in the era of microservices.
0 notes
Text
Breaking Down Monoliths: Power of Microservices Architecture

Discover how Microservices Architecture is transforming software development with increased scalability, flexibility, and faster deployment in our latest blog. Learn more now! Breaking Down Monoliths: Power of Microservices Architecture
#Application Development#developing a microservices app#it application development#kubernetes development#microservices architecture#microservices architecture development#microservices development services#modern app development#modern software development#monolithic app development
0 notes
Text
#ecommerce microservices architecture#ecommerce microservice architecture#Ecommerce architecture#Modern ecommerce architecture#Monolithic vs microservice architecture
0 notes
Text
Cloud-based applications have brought new requirements, challenges, and patterns. Agile delivery of new features as a quick response to rapidly changing user demands and requirements has become quite a challenge. Plus, the resources should be utilized optimally to reduce the cost of building and maintaining such complex structures. As a result of these demands, the microservices architecture appeared. Today, we’ll consider the basic features of monolithic architecture, distributed monoliths, and microservices.
#outsourcing#software development#web development#staff augmentation#custom software development#it staff augmentation#custom software solutions#it staffing company#it staff offshoring#custom software#microservices#monolith
0 notes
Text
What Everything You Need to Know About Microservices

Introduction
Just like technology, architectural style is a crucial concern in software development. This is why understanding different architectural patterns is important. While it may not be possible to cover all patterns in a single article, the focus of this particular article will be on microservices.
In this article, we will discuss what microservices are and the key differences between monolithic and microservices architectures. We will also discuss the benefits and disadvantages associated with Microservices.
By the end of this article, you will better understand microservices architecture and its benefits. You will also be able to decide whether microservices architecture is the right choice for your next project.
Monolithic vs. Microservices
Monolithic Structure
To understand Microservices fully, we need first to understand monolithic structures. It is more traditional architecture. Monolithic architecture is a time-tested approach that involves building everything as one big application.
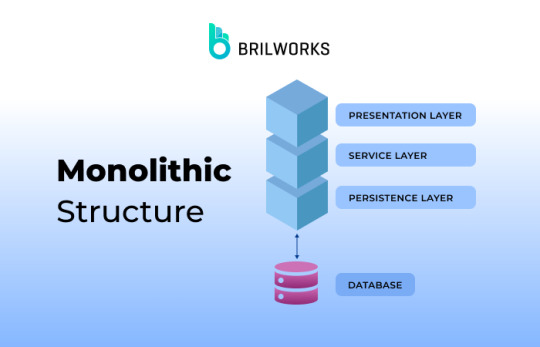
Microservices
Microservices, on the other hand, are individual, self-contained services that can be deployed and scaled independently that involve breaking down an application into a bunch of smaller, independent services.
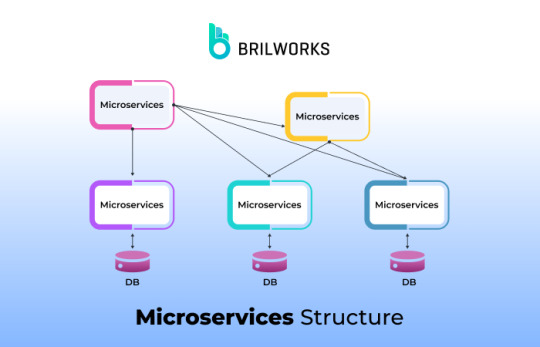
Why Microservice?
For small business owners, it can be a pain to scale if your app has monolithic architecture.
When you approach a company for application development, they will likely ask you about the architectural style you want to use. This is an important decision, as it can have a significant impact on the development cost and scalability of your application.
Monolithic architectures are simpler to develop and maintain, but they can be difficult to scale. If one part of the application becomes overloaded, it can affect the entire application. Microservices architectures are more complex to develop, but they are more scalable. If one service becomes overloaded, it will not affect the other services.
Here is an example to help you understand the difference between monolithic and microservice architectures.
Imagine you have a social media app that has user management, posting, commenting, and liking features. If one service, say user management, gets a lot of traffic, it will use more resources and affect the other services. This is because all the services are tightly coupled together. To fix this, you would need to scale the entire application, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
A better approach is to break the services down into microservices. This means that each service will be responsible for a specific task, such as user management, posting, or commenting. This makes the services loosely coupled, which means that if one service gets overloaded, the others will not be affected. This makes it much easier to scale the application because you can simply scale the individual services that need it, not the entire application.
Characteristics of Microservices
Autonomy: Microservices exhibit loose coupling, enabling independent deployment, development, and scalability. This facilitates the effective management and maintenance of microservice-based applications.
Componentization: A prevailing approach involves dividing a system into smaller components. This permits individual focus on specific services or components, enabling independent modification and deployment without compromising the overall integrity of the application.
Specialization: Each service is designed to address a specific problem or provide a distinct set of capabilities. If a service becomes overly complex, it can be further broken down into smaller, more specialized services.
Benefits of Microservices
1. Agility
Microservices promote agility by dividing project work into small, independent teams. This approach allows each team to focus on a specific aspect of the application without affecting the other teams. This results in more efficient and faster work, as each team can work independently and focus on their own tasks.
Although working together can also be productive, having independent teams working simultaneously can reduce the development cycle. This is because each team can work on their own tasks without having to wait for the other teams to finish their work. This allows us to develop more customer-ready applications in less time.
2. Flexible Scaling
E-commerce platforms and other service-based applications often require frequent scaling of their systems. However, smaller companies may find it costly and labor-intensive to allocate more resources and scale the entire application. In contrast, microservices have gained popularity because they offer flexible scalability. This is why tech giants like Amazon, Netflix, eBay, and others have adopted microservices to achieve flexible scaling.
3. Easy Deployment
Loose coupling of services also promotes the easy deployment of applications by enabling the deployment of specific services that have undergone continuous improvements. This eliminates the need for developers to extensively rework the entire codebase. As a result, businesses can effortlessly include new features as required without significant effort.
4. Technological Freedom
In a microservices architecture, teams can choose the tools and technologies that work best for them. This means that they can use the latest tools, or they can stick with tried-and-true solutions. They can also use a mix of different tools, depending on the specific needs of each microservice.
For example, you start building a microservice that requires storing a lot of data. You could use a traditional relational database, but this might not be the best choice. Relational databases are not designed for high-performance storage, so you might end up with a slow and inefficient microservice.
Instead, you could use a NoSQL database, which is specifically designed for high-performance storage. NoSQL databases are more flexible than relational databases, so you can choose the right data model for your needs. This will lead to a faster and more efficient microservice.
The flexibility of microservices architecture allows you to mix the best tools and technologies for the job.
5. Reusable Code
Imagine you have a big piece of software that does many different things. Instead of having all the code in one huge chunk, you divide it into smaller, well-defined parts called modules.
These modules are like building blocks that have specific functions. For example, one module might handle user authentication; another module might handle database operations, and so on. Each module can be used independently to perform its specific task.
Now, the good thing is that these modules can be reused in different parts of the software. So, if you have a module that handles user authentication, you can use it not only in one part of the software but also in other parts that require user authentication. This saves time and effort because you don’t have to write the same code multiple times.
Similarly, in a microservices structure, you can reuse services if the same functionality is needed in different parts of the software. This promotes efficiency by avoiding redundant code and allowing the same service to be utilized in multiple areas as needed.
6. Resilience
With microservices, applications are divided into smaller, independent services that work together. If a single microservice doesn’t work, it doesn’t bring down the entire application. Instead, the application gracefully degrades its functionality, meaning it can still continue operating to some extent without crashing completely.
Why Spring for Microservices
Microservices can be developed using various programming languages and technologies. However, one of the most widely used frameworks for building microservices is Spring Boot using Java/Kotlin. Spring Boot has gained popularity for various good reasons.
Building microservices using SpringBoot is effortless and fast.
Spring Cloud provides tools for devs to build some of the common patterns in microservices in no time.
It comes with production-ready features like metrics, security, and embedded servers.
The Spring community is massive. If you ever get stuck, there are plenty of Spring developers out there to help you out.
Challenges With Microservice Architectures
Microservices are not all sunshine. Though they are great for scalability and flexibility, they also come with a few challenges. Let’s take a look at some of the inherent complexities of microservices architectures.
Automating the Components: The number of smaller components in a microservices architecture can make it difficult to automate everything. This includes builds, deployments, and monitoring. It is important to have a solid automation strategy in place to ensure that all of the components are managed effectively.
Perceptibility: The distributed nature of microservices can make it difficult to monitor and identify problems. It is important to have good visibility into all of the components in order to troubleshoot issues quickly. Centralized logging and dashboards can help to improve perceptibility.
Configuration Management: The configuration of microservices can be complex and difficult to manage. It is important to have a centralized configuration management system in place to ensure that all of the components are configured consistently. This will help to avoid errors and inconsistencies.
Debugging: Debugging microservices can be challenging because there are so many moving parts. It is important to have a good understanding of the architecture and how the components interact. Centralized logging and dashboards can also help with debugging.
Consistency: It is important to have some consistency in the way that microservices are implemented, deployed, and monitored. This will help to avoid chaos and make it easier to manage the architecture. However, it is also important to allow for some innovation and flexibility.
Read more at https://www.brilworks.com/blog/everything-you-need-to-know-about-microservices/
0 notes
Text
Software architecture defines the quality attributes of an application. When planning a software architecture behind an application project managers are met with the task of comparing microservices vs. monolithic architecture.
Choosing the right architecture is crucial to the stability, performance, scalability and security of the application. A right architecture also helps with cost optimization, reduced time to delivery, and customer satisfaction. Since applications are an integral part of the business ecosystem today the choice of architecture behind them is equally crucial.
#technology#digital transformation#tech#it consulting#it services#software development#mobile app developers#technology trends#product development service#microservices#microservices architecture#monolithic#software architecture
1 note
·
View note
Text
Monolithic vs. Microservices: Which is the Best Architecture?

Monolithic architecture consolidates an entire application into a single, tightly connected unit. This simplicity can be advantageous for smaller projects, offering ease in development and debugging. However, as the application grows, scaling and maintaining a monolith can become challenging, and adopting new technologies becomes cumbersome.
Microservices architecture, on the other hand, decomposes an application into small, independent services that communicate via APIs. This modular approach offers exceptional scalability and fault tolerance, allowing specific components to be scaled individually and reducing the impact of failures. It also enables flexibility in technology adoption.
The choice between these architectures hinges on project specifics. Monoliths suit simpler applications, emphasizing rapid development. Microservices excel in complex systems, ensuring agility, scalability, and resilience. Hybrid approaches are common, transitioning from monoliths to microservices as applications evolve. The best architecture depends on your project's scale, complexity, and future growth prospects. If you want to deeply know more about Monolithic vs. Microservices just go to our website.
0 notes
Text
Microservices vs. Monolith: Choosing The Right Development Approach For Your Project
Therefore, is the monolithic approach outdated and ought to be abandoned? Is it worthwhile to convert the whole application from a monolith to a microservices architecture? Will creating bespoke software using a microservices architecture assist you in achieving your objectives? In this MarsDevs article, let’s answer all those questions and let's explore the differences between monolithic and microservices architecture to determine which is better for your company.
0 notes
Text
Monolithic to Microservices — The Rise of Serverless | AntStack
Software architecture patterns concentrate on the possibilities for higher-level application organisation. They offer best-practice solutions for some of the issues, including scalability, deplorability, and simplicity of maintenance. Common architectural designs make it simpler to grasp solutions since they adhere to a well-known pattern.
Read more — AntStack

0 notes
Text
monolithic architecture: 40 lines of code
microservices architecture: 15 different interwoven "applications" full of functions that are never more than 5 lines of code, 90% of which are just calls to other functions
108 notes
·
View notes
Text


This week was a productive one. I've been studying microservices to better understand distributed systems. At the bus company where I work, we use a monolithic system—an old-school setup style with MySQL, PHP, some Java applications, localhost server and a mix of other technologies. However, we've recently started implementing some features that require scalability, and this book has been instrumental in helping me understand the various scenarios involved.
In the first chapters, I've gained a clearer understanding of monolithic systems and the considerations for transitioning to a distributed system, including the pros and cons.
I've also been studying Java and Apache Kafka for event-driven architecture, a topic that has captured my full attention. In this case, the Confluent training platform offers excellent test labs, and I've been running numerous tests there. Additionally, I have my own Kafka cluster set up using Docker for most configurations.
With all that said, I've decided to update this blog weekly since daily updates it's not gonna work.
#coding#developer#linux#programming#programmer#software#software development#student#study blog#study aesthetic#studyblr#self improvement#study#software engineering#study motivation#studyblr community#studying#studynotes#learning#university#student life#university student#study inspiration#brazil#booklr#book#learn#self study#java#apachekafka
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ready to future-proof your applications and boost performance? Discover how PHP microservices can transform your development workflow! 💡
In this powerful guide, you'll learn: ✅ What PHP Microservices Architecture really means ✅ How to break a monolithic app into modular services ✅ Best tools for containerization like Docker & Kubernetes ✅ API Gateway strategies and service discovery techniques ✅ Tips on error handling, security, and performance optimization
With real-world examples and practical steps, this guide is perfect for developers and teams aiming for faster deployment, independent scaling, and simplified maintenance.
🎯 Whether you’re a solo developer or scaling a product, understanding microservices is the key to next-level architecture.
🌐 Brought to you by Orbitwebtech, Best Web Development Company in the USA, helping businesses build powerful and scalable web solutions.
📖 Start reading now and give your PHP projects a cutting-edge upgrade!
2 notes
·
View notes