#webscraping data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How Customer Reviews Scraping Improves Efficiency and Business Growth?

In the age of digital commerce, consumers are constantly seeking ways to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether it's finding the best deals or tracking price fluctuations over time, accessing accurate and up-to-date data is crucial. Enter web scraping—a powerful technique that provides invaluable insights into the vast landscape of online retail. In this article, we'll explore how web scraping data insights can revolutionize the process of accessing Wayfair price history, empowering consumers with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
Understanding Web Scraping
Before delving into its application in accessing Wayfair price history, let's briefly understand what web scraping entails. Web scraping involves extracting data from websites, typically in an automated fashion, using specialized tools or programming scripts. These tools navigate through the structure of web pages, gathering information such as product details, prices, reviews, and more.
The Importance of Price History
Price history serves as a valuable resource for consumers, enabling them to track fluctuations in product prices over time. By analyzing historical data, shoppers can identify patterns, anticipate price trends, and determine the best time to make a purchase. This is particularly relevant in the realm of online retail, where prices can vary widely and change frequently due to factors like demand, competition, and promotions.
Leveraging Web Scraping for Wayfair Price History
Wayfair, one of the largest online destinations for home goods and furniture, offers a vast array of products at competitive prices. However, accessing historical pricing information on Wayfair's platform can be challenging through conventional means. This is where web scraping comes into play, providing a streamlined solution for gathering and analyzing price data.
By utilizing web scraping techniques, consumers can extract price information from Wayfair's website and compile it into structured datasets. These datasets can then be analyzed to uncover valuable insights, such as trends in pricing, seasonal fluctuations, and the impact of promotions or sales events. Moreover, web scraping enables users to compare prices across different time periods, products, or sellers, empowering them to make informed decisions and secure the best possible deals.
Tools and Techniques for Web Scraping
Several tools and techniques are available for web scraping, ranging from simple browser extensions to sophisticated programming libraries. For accessing Wayfair price history, Python-based libraries such as BeautifulSoup and Scrapy are popular choices among web scraping enthusiasts. These libraries provide robust capabilities for navigating web pages, extracting data, and storing it in a structured format for analysis.
Additionally, specialized web scraping services and platforms offer turnkey solutions for extracting price data from Wayfair and other e-commerce websites. These services often feature user-friendly interfaces, pre-built scraping modules, and advanced analytics capabilities, making them accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise.
Ethical Considerations and Best Practices
While web scraping can provide valuable insights into Wayfair price history, it's essential to adhere to ethical guidelines and respect the terms of service of the websites being scraped. Engaging in excessive or abusive scraping behavior can strain server resources, disrupt website functionality, and potentially violate legal regulations.
To mitigate these risks, practitioners should implement rate limiting mechanisms, respect robots.txt directives, and obtain explicit permission when necessary. Additionally, it's crucial to handle scraped data responsibly, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations and protecting sensitive information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, web scraping data insights offer a powerful means of accessing Wayfair price history and gaining a deeper understanding of online retail dynamics. By harnessing the capabilities of web scraping tools and techniques, consumers can navigate the complexities of e-commerce, track price fluctuations, and make informed purchasing decisions. However, it's essential to approach web scraping responsibly, respecting ethical considerations and legal boundaries to ensure a fair and sustainable online ecosystem. With the right tools and practices in place, web scraping opens up a world of possibilities for uncovering valuable insights and maximizing savings in the digital marketplace.
0 notes
Text
How to Extract Amazon Product Prices Data with Python 3
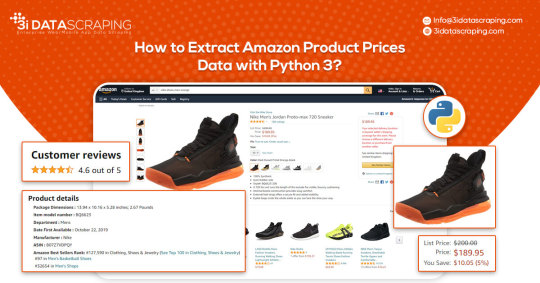
Web data scraping assists in automating web scraping from websites. In this blog, we will create an Amazon product data scraper for scraping product prices and details. We will create this easy web extractor using SelectorLib and Python and run that in the console.
#webscraping#data extraction#web scraping api#Amazon Data Scraping#Amazon Product Pricing#ecommerce data scraping#Data EXtraction Services
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Looking for the best web scraping partner in 2025?
We break down the top 5 companies leading the space, from scalability to ethical scraping.
🔹 Tech comparison
🔹 Use case strengths
🔹 Data-backed insights
📖 Read more: https://bit.ly/4kCsGfL
#WebScraping#Data#AI#ML#dataextraction#techforbusiness#dataquality#dataengineering#automation#bigdata#promptcloud#marketinsights
0 notes
Text
Unlock Smarter Investments with TagX ETF Data Services

Gain a competitive edge with TagX’s ETF Data Services, designed to deliver real-time, reliable data for smarter investment decisions. From tracking ETF performance to analyzing historical trends, our data solutions are built for precision and speed. Ideal for financial platforms, analysts, or investors—TagX turns raw ETF data into actionable insights.
0 notes
Text
Finished my last midterm for my degree today... feeling dread. Can't get an entry level data scientist position 💔 became a math and statistics machine in the last 4 years but my downfall was only receiving basic training on SQL
#now I have to set aside free time to learn more coding languages#and business data analytics software :(#but hey maybe I can do some cool statistical experiments solo to build my portfolio#get ready for a disco elysium ao3 analysis#gonna webscrape ao3 and analyze for trends in what fics get the most engagement 🫣
0 notes
Text
🛒 Want to Dominate the eCommerce Market? Start with Price Tracking.
In the fast-moving world of eCommerce, pricing is everything.
It doesn’t matter how great your product is, if your competitor silently drops their price, you lose. That’s why ecommerce price tracking is no longer a nice-to-have. It’s the backbone of real-time market strategy.
What is it? It’s the process of monitoring your competitors’ product prices across marketplaces like Amazon, Walmart, and Flipkart to make smarter decisions, faster.
But great price tracking isn’t just about scraping numbers. ✅ You need the right tools ✅ Clean, structured data ✅ Legal awareness ✅ Smart automation ✅ Real-time alerts
🔧 That’s where 42Signals comes in.
Our platform gives you real-time competitor price tracking, Telegram alerts, pricing dashboards, and even MAP violation monitoring, so your brand can stay ahead without burning margins.
Just a few of the use cases: 💼 Adjust your pricing dynamically 📉 Detect competitor discounts 📦 Optimize stock and promotions 📊 Visualize trends over time 🚀 Build a stronger pricing strategy
Bonus: It’s totally legal and compliant. And it works.
A solar gadget brand using 42Signals saw a 40% increase in conversions and 18% growth in AOV, just by tracking competitors and reworking value offers instead of slashing prices.
✨ Bottom line? You don’t need to win every price war, you just need to know which ones to fight.
👉 Try 42Signals now – Free Trial
#ecommerce #pricetracking #retailanalytics #competitorintelligence #digitalcommerce #amazon #pricingstrategy #42signals #marketintelligence #webscraping #retailtech #datadriven
#ecommerce#price#pricetracking#retail#retailanalytics#competitor#competitorintelligence#digital#digitalcommerce#amazon#pricing#pricingstrategy#42signals#market#marketnitelligence#web#webscraping#reati#reatiltech#data#datadriven
0 notes
Text
#web development#data scraping#python#technology#web scraping#PythonScraping#RedditScraper#DataScience#WebScraping#CodingTips
0 notes
Text
Web Scraping 103 : Scrape Amazon Product Reviews With Python –

Amazon is a well-known e-commerce platform with a large amount of data available in various formats on the web. This data can be invaluable for gaining business insights, particularly by analyzing product reviews to understand the quality of products provided by different vendors.
In this guide we will look into web scraping steps to extract amazon reviews of a particular product and save it in excel or csv format. Since manually copying information online can be tedious, in this guide we’ll focus on scraping reviews from Amazon. This hands-on experience will enhance our practical understanding of web scraping techniques.
Before we start, make sure you have Python installed in your system, you can do that from this link: python.org. The process is very simple, just install it like you would install any other application.
Now that everything is set let’s proceed:
How to Scrape Amazon Reviews Using Python
Install Anaconda using this link: https://www.anaconda.com/download . Be sure to follow the default settings during installation. For more guidance, please click here.
We can use various IDEs, but to keep it beginner-friendly, let’s start with Jupyter Notebook in Anaconda. You can watch the video linked above to understand and get familiar with the software.
Steps for Web Scraping Amazon Reviews:
Create New Notebook and Save it. Step 1: Let’s start importing all the necessary modules using the following code:
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import pandas as pd
Step 2: Define Headers to avoid getting your IP blocked. Note that you can search my user agent on google to get your user agent details and replace it below “User-agent”: “here goes your useragent below”.
custom_headers = { "Accept-language": "en-GB,en;q=0.9", "User-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/17.1 Safari/605.1.15", }
Step 3: Create a python function, to fetch the webpage, check for errors and return a BeautifulSoup object for further processing.
# Function to fetch the webpage and return a BeautifulSoup object def fetch_webpage(url): response = requests.get(url, headers=headers) if response.status_code != 200: print("Error in fetching webpage") exit(-1) page_soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "lxml") return page_soup
Step 4: Inspect Element to find the element and attribute from which we want to extract data, Lets Create another function to select the div and attribute and set it to variable , extract_reviews identifies review-related elements on a webpage, but it doesn’t yet extract the actual review content. You would need to add code to extract the relevant information from these elements (e.g., review text, ratings, etc.).
Function to extract reviews from the webpage def extract_reviews(page_soup): review_blocks = page_soup.select('div[data-hook="review"]') reviews_list = []
Step 5: Below code processes each review element and extracts the customer’s name (if available), and stores it in the customer variable. If no customer information is found, customer remains none.
#for review in review_blocks: author_element = review.select_one('span.a-profile-name') customer = author_element.text if author_element else None rating_element = review.select_one('i.review-rating') customer_rating = rating_element.text.replace("out of 5 stars", "") if rating_element else None title_element = review.select_one('a[data-hook="review-title"]') review_title = title_element.text.split('stars\n', 1)[-1].strip() if title_element else None content_element = review.select_one('span[data-hook="review-body"]') review_content = content_element.text.strip() if content_element else None date_element = review.select_one('span[data-hook="review-date"]') review_date = date_element.text.replace("Reviewed in the United States on ", "").strip() if date_element else None image_element = review.select_one('img.review-image-tile') image_url = image_element.attrs["src"] if image_element else None
Step 6: The purpose of this function is to process scraped reviews. It takes various parameters related to a review (such as customer, customer_rating, review_title, review_content, review_date, and image URL), and the function returns the list of processed reviews.
review_data = { "customer": customer, "customer_rating": customer_rating, "review_title": review_title, "review_content": review_content, "review_date": review_date, "image_url": image_url } reviews_list.append(review_data) return reviews_list
Step 7: Now, Let’s initialize a search_url variable with an Amazon product review page URL
def main(): review_page_url = "https://www.amazon.com/BERIBES-Cancelling-Transparent-Soft-Earpads-Charging-Black/product- reviews/B0CDC4X65Q/ref=cm_cr_dp_d_show_all_btm?ie=UTF8&reviewerType=all_reviews" page_soup = fetch_webpage(review_page_url) scraped_reviews = extract_reviews(page_soup)
Step 8: Now let’s print(“Scraped Data:”, data) scraped review data (stored in the data variable) to the console for verification purposes.
# Print the scraped data to verify print("Scraped Data:", scraped_reviews)
Step 9: Next, Create a dataframe from the data which will help organize data into tabular form.
# create a DataFrame and export it to a CSV file reviews_df = pd.DataFrame(data=scraped_reviews)
Step 10: Now exports the DataFrame to a CSV file in current working directory
reviews_df.to_csv("reviews.csv", index=False) print("CSV file has been created.")
Step 11: below code construct acts as a protective measure. It ensures that certain code runs only when the script is directly executed as a standalone program, rather than being imported as a module by another script.
# Ensuring the script runs only when executed directly if __name__ == '__main__': main()
Result:

Why Scrape Amazon Product Reviews?
Scraping Amazon product reviews can provide valuable insights for businesses. Here’s why you should consider it:
● Feedback Collection: Every business needs feedback to understand customer requirements and implement changes to improve product quality. Scraping reviews allows businesses to gather large volumes of customer feedback quickly and efficiently.
● Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing the sentiments expressed in reviews can help identify positive and negative aspects of products, leading to informed business decisions.
● Competitor Analysis: Scraping allows businesses to monitor competitors’ pricing and product features, helping to stay competitive in the market.
● Business Expansion Opportunities: By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can identify opportunities for expanding their product lines or entering new markets.
Manually copying and pasting content is time-consuming and error-prone. This is where web scraping comes in. Using Python to scrape Amazon reviews can automate the process, reduce manual errors, and provide accurate data.
Benefits of Scraping Amazon Reviews
● Efficiency: Automate data extraction to save time and resources.
● Accuracy: Reduce human errors with automated scripts.
● Large Data Volume: Collect extensive data for comprehensive analysis.
● Informed Decision Making: Use customer feedback to make data-driven business decisions.
I found an amazing, cost-effective service provider that makes scraping easy. Follow this link to learn more.
Conclusion
Now that we’ve covered how to scrape Amazon reviews using Python, you can apply the same techniques to other websites by inspecting their elements. Here are some key points to remember:
● Understanding HTML: Familiarize yourself with HTML structure. Knowing how elements are nested and how to navigate the Document Object Model (DOM) is crucial for finding the data you want to scrape.
● CSS Selectors: Learn how to use CSS selectors to accurately target and extract specific elements from a webpage.
● Python Basics: Understand Python programming, especially how to use libraries like requests for making HTTP requests and BeautifulSoup for parsing HTML content.
● Inspecting Elements: Practice using browser developer tools (right-click on a webpage and select “Inspect” or press Ctrl+Shift+I) to examine the HTML structure. This helps you find the tags and attributes that hold the data you want to scrape.
● Error Handling: Add error handling to your code to deal with possible issues, like network errors or changes in the webpage structure.
● Legal and Ethical Considerations: Always check a website’s robots.txt file and terms of service to ensure compliance with legal and ethical rules of web scraping.
By mastering these areas, you’ll be able to confidently scrape data from various websites, allowing you to gather valuable insights and perform detailed analyses.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Explore 5 key suggestions for developing accurate AI models with the right training data.
#webscrapingservices#data#ai#artificial intelligence#machine learning#webscraping#data for ai#training ai data
0 notes
Note
thou art employed via the r programming tongue....? mayhaps I hath been too hasteful in mine judgement...
waow clout for jobhaving on tumblr dot com? it's more likely than you think. . . .
#but yes i am employed in data analysis for public health research!#repo is mostly R (my beloved)#partly stata (my beloathed)#recently ive added some python (my useful for webscraping and string cleaning)#asks#anonymous
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Web Scraping Helps In Extracting Government And Public Sector Data?

Along with the growth in technology, big data and analytics are undeniably no less crucial these days. It applies to business companies, healthcare, and the administration. Web scraping is the process of harvesting essential data from the internet reservoir; therefore, it can obtain this vital information. Changing public sector and government research science requires better data for decision-makers to make the right choices, and these are people like policymakers and analysts, among others. However, on digital platforms, a lot of information is generated, which needs to be clarified when trying to filter or sort it all out. Therefore, web scraping provides a means of collecting data more efficiently and making research more creative and rapidly performed.
What is Government and Public Data Scraping?
Data scraping, or web scraping, is using a digital tool to collect information from websites and online databases automatically. Dream of no more need to visit websites to copy all important data – let a robot do it. This tool collects data from websites like government rules, public reports, or price tags. People utilize data scraping for research purposes, such as examining legislation or analyzing market patterns. It is an excellent way to get information rapidly (all you need to understand various topics) and use it to understand any subject better.
Nevertheless, a handful of points are worth considering when performing web scraping government sites. It is essential to follow the rules and laws about using online information. For instance, certain websites may not allow scraping; thus, you should adhere to them by any means. Furthermore, we must handle personal data cautiously and avoid undesired behaviors as much as possible. So, while data scraping is an effective tool, it must be used safely and politely.
Scraping Data from Government Sources
Scraping government website data means using special tools or programs to collect information from official government websites, databases, or online portals. Government bodies, such as data storehouses, are especially information-supplier entities, such as laws, public records, budgets, and statistics. Without that data, data scientists and analysts, which are not customer-friendly for regular people, can be equipped with vital information, monitor the government, and check public policies and efficiency.
Scraping government websites involves retrieving data from data providers or sources such as government websites.
Summary
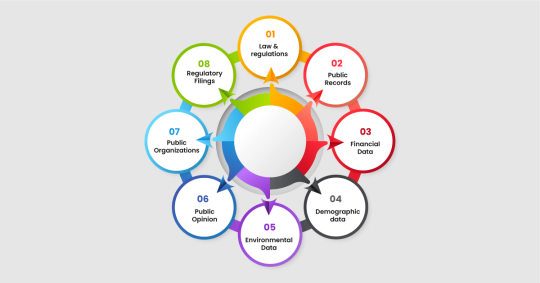
What Kind of Data Can You Get From Government Websites:
Laws and Rules: This includes the texts of laws, rules, and policies.
Public Records: Things like birth certificates, property ownership, and court case details.
Financial Data: Budgets, economic stats, and tax details.
People and Society: Census info, health numbers, and education stats.
Environment: Weather data, pollution info, and maps.
Public Opinion: Surveys, polls, and comments from the public.
From Public Organizations
Business Data: Details about registered businesses and professional licenses.
Regulatory Docs: Reports and documents that businesses have to submit.
Safety and Infrastructure: Crime rates, emergency services, and transportation details.
Types of Data Scraped from Government Websites
Remember, the kind of data you can find might differ depending on where you are or which part of the government you're looking at. When obtaining data from various sources, adhering to any restrictions or norms is critical.
Laws and Rules
Laws and Regulations: These are like the rulebooks that the government follows. They contain the actual texts of laws and rules that the government sets.
Policy Papers: These act as the government's master data. They're official documents outlining the government's intentions and strategies for addressing various issues.
Property Records: These records tell us about properties in an area, such as who owns them, how much they're worth, and how they're being used.
Court Records: This is information about legal cases, like who's involved, what the case is about, and when the court dates are.
Money Matters
Budgets and Spending: Those documents basically show us where the government plans to spend its money. Allocation of funds, detailing expenditures on sectors such as education, infrastructure, and healthcare while also disclosing the destinations of the funds.
Economic Stats: As for economic stats, they are a quick outline of how the economy is doing. They tell us if people find jobs easily and if prices are going up or down. It's a way to see if the economy is healthy or if some problems need fixing.
Taxes: Here, you can find information about how much tax people and businesses have to pay, what forms they need to fill out, and any rules about taxes.
People and Society
Census Data: This gives us information about the people living in a place, like how many people live there, their ages, and other demographics.
Health Stats: These tell us about people's health, such as whether there's a lot of flu or how many people have been vaccinated.
Education: This part tells us about schools, including how students are doing in their classes, how many students graduate, and what resources the schools have.
Climate Info: This is all about the weather and climate in an area, such as whether it's usually hot or cold or if it rains a lot
Environmental Assessments: These give us details about the environment, like how clean the air and water are and if there are any protected areas.
Maps and Geospatial Data: These are digital maps that show where things are located, such as parks, roads, or buildings.
Public Opinion
Surveys and Polls: These are questionnaires that ask people what they think about different things. They might ask who they voted for in an election or what they think about a new law. It is a way for people to share their opinions and for others to understand what's important to them.
Public Comments: This is feedback from people about government plans or projects. It's like when people write to say what they think about a new road or park.
Business Licenses: This tells us about businesses in an area, like what they do and if they have the proper licenses to operate.
Professional Licenses: These are licenses that people need to work in specific jobs, like doctors or lawyers.
Regulatory Info: This is paperwork that businesses or organizations have to fill out to show they're following the rules set by the government.
Crime Stats: This tells us about crime in an area, such as how many crimes are happening and what kind.
Emergency Services: This is information about services like fire departments or ambulances, like how quickly they respond to emergencies.
Transport Info: This gives us details about getting around, like traffic conditions or bus schedules.
Infrastructure: This is about public projects like building roads or schools, telling us what's being built and when it will be done.
Scraping Data from the Public Sector
Scraping data from the public sector is collecting information from government websites or sites that receive money from the government. This information can be helpful for researching, public sector data analytics, or ensuring that things are open and transparent for everyone. Businesses scrape public sector data to stay updated with the latest updates.
By scraping different types of data from the public sector, researchers, analysts, or even regular people can learn a lot, make better decisions, perform public sector data analytics, and monitor what the government and public organizations are doing.
Laws and Regulations
Texts of Laws, Regulations, and Policies: This is where you can find the actual words of laws made by the government. It also includes rules and plans for different areas like traffic, environment, or health.
Public Records
Vital Records: These are essential papers that tell us about significant events in people's lives, such as when they were born, married, passed away, or divorced.
Property Records: These data tell you about properties, such as who owns them, how much they're worth, and what they're used for.
Court Records: This is information about legal cases, court decisions, and when the next court dates are.
Financial Data
Budgets: These plans show how the government will spend money on different things.
Economic Indicators: These are data that tell us how well the economy is doing, such as whether people have jobs or if prices are going up.
Tax Information: This is about taxes, like how much people or businesses have to pay and how the government uses that money.
Demographic Data
Census Data: This is information from the national headcount of people, showing things like age, where people live, and family size.
Health Statistics: This is data about health issues, like outbreaks, vaccination rates, or hospitals.
Education Data: This tells us about schools, how well students are doing, and what resources are available.
Environmental Data
Climate Information: This is about the weather and climate, like temperatures or weather patterns.
Environmental Assessments: These are studies about how people affect the environment, pollution, and efforts to protect nature.
Geospatial Data: This is like digital maps showing geographical information, like boundaries or landmarks.
Public Opinion
Surveys and Polls: These are the results of asking people questions to determine their thoughts on different topics.
Public Comments: People's feedback or opinions on government plans or projects.
Public Organizations
Business Licenses: This is information about businesses, such as their name, address, type, and whether they have a license.
Professional Licenses: This is about licenses for jobs like doctors, lawyers, or engineers, showing if they're allowed to practice and if they've had any issues.
Regulatory Filings
Professional Licenses: This is about licenses for jobs like doctors, lawyers, or engineers, showing if they're allowed to practice and if they've had any issues.
Reports and Documents: These are papers or reports that businesses or people have to give to certain government agencies, like financial reports or environmental studies.
Crime Statistics: These data tell us about crime, such as the amount or types of crimes committed.
Emergency Services Data: This is information about services like fire or ambulance services, such as how quickly they respond to emergencies.
Transportation Information: This tells us about getting around, like traffic, roads, public transit, or significant construction projects.
Benefits of Web Scraping in the Government and Public Sector
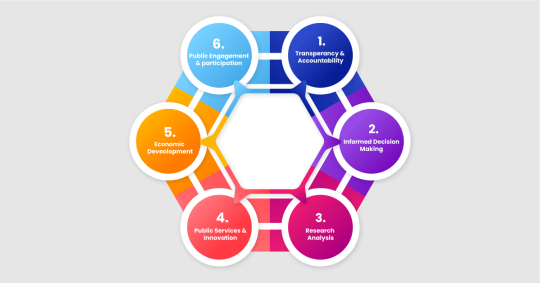
Companies should be responsible enough to choose the data they believe brings greater value to a specific context at that time. There are various benefits of web scraping government sites and public sector data:
Transparency and Accountability
When we perform web scraping government sites, we can see what the government is doing more clearly. Government and public sector data analytics helps keep them accountable because people can see where money is being spent and what decisions are being made.
Informed Decision-Making
Businesses scrape government websites and public sector data to get access to large datasets that help researchers, policymakers, and businesses make better decisions. For example, they can determine whether a new policy is working or understand economic trends to plan for the future.
Research and Analysis
The modern approach to scrape public sector data and government website data can be utilized by professionals and scientists to learn more about health, education, and the environment. This allows us to learn more about these subjects and identify ways to enhance them.
Public Services and Innovation
With public sector data analytics and web scraping government sites, developers can create new apps or sources of information that make life easier for people. For example, maps showing public transportation routes or directories for community services.
Economic Development
Businesses can use government economic data to make plans by ensuring success of their business. This can attract more investment because investors can see where there are good opportunities.
Public Engagement and Participation
When businesses extract public sector data and government website data, People can join conversations about community matters when they can easily understand government information. This makes democracy stronger by letting more people share their thoughts and shape what happens in their area.
Conclusion
Web scraping is increasingly seen as a valuable tool for extracting data, particularly as governments and public sectors adapt to the digital era. One of the most critical factors in current governance is no longer the line about open data projects with performing web scraping government sites.
Collaborating with enterprises data scraping like iweb Scraping is the way toward a future course of events where data-driven governance is the leading force. Thus, the public sector is more informed, transparent, and accountable. Scraping data from the internet can be viewed as a powerful tool for governmental institutions that enables them to collect a massive amount of essential information in a relatively short time. To put it categorically, web scraping is a valuable tool that the government should embrace as its friend. Companies that collect data, like iWeb Scraping services, are at the forefront of innovation and provide improved and new methods of data collecting that benefit all parties. Nevertheless, some challenges can come up often, but this web scraping company remains relevant to the government and public sector institutions during their data scraping process. The process of scraping public sector data and government websites is gathered with diligence and ethical consideration to help policymakers make more informed decisions and improve their services.
0 notes
Text

🔹 Build in-house = high cost + complexity
🔹 Partner with PromptCloud = scale, speed & zero maintenance
📊 Focus on insights, not scraping.
👉 Schedule a demo to see how it works: https://bit.ly/4dj164f
#WebScraping#Data#BigData#datascraping#bigdata#100DaysOfCode#python#CodingJourney#RealEstate#aitrain
0 notes
Text
How to Scrape Google Reviews: A Complete Guide with Expert Data Scraping Services
In a world where customer feedback shapes business success, Google reviews have emerged as one of the most powerful tools for brands to understand public sentiment. These reviews are more than just star ratings—they're a direct window into customer experiences and expectations. Whether you're managing a small local store or a multinational company, analyzing Google reviews can offer valuable insights.
But manually collecting and analyzing thousands of reviews is time-consuming and inefficient. This is where data scraping services come into play. By automating the process, businesses can gather and analyze reviews at scale, making informed decisions more quickly and accurately.

In this blog, we’ll explore what Google reviews are, why they matter, and how to scrape them effectively.
What Are Google Reviews and Why Do They Matter?
Google reviews are customer-generated feedback and star ratings that appear on a business's Google profile. These reviews are visible on Google Search and Google Maps, influencing how people perceive and choose your business. Positive reviews can enhance your credibility and attract more customers, while negative ones can provide critical feedback for improvement. Google also considers these reviews in its search algorithm, making them essential for local SEO. In short, Google reviews are not just opinions; they’re public endorsements or warnings that impact your brand’s reputation, discoverability, and success. From a business perspective, understanding and leveraging this data is essential. Reviews highlight customer satisfaction, reveal service gaps, and offer a competitive edge by shedding light on what people love (or dislike) about your competitors.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Scrape Google Reviews
Scraping Google reviews may sound technical, but with the right strategy and tools, it becomes a streamlined process. Below is a simple guide to help you get started.
Step 1: Identify the Google Place ID or Business URL
The first step in scraping reviews is locating the business’s unique identifier on Google. This could be the full URL from Google Maps or the Place ID provided through Google’s developer tools. This ensures your scraper targets the correct business location.
Step 2: Use the Google Places API (If You Only Need Limited Data)
Google provides an official API that allows access to a limited number of reviews (typically the latest five). You’ll need to set up a project in Google Cloud Console and request data using your API key. While this method is compliant with Google’s terms, it has significant limitations if you need historical or bulk data.
Step 3: Build or Use a Scraper for Larger Datasets
If your goal is to analyze a large volume of reviews over time, you’ll need more than what the API offers. This is where custom-built scrapers or third-party scraping platforms come in. Tools like BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, or Selenium can help automate the process, though they require technical expertise. Alternatively, you can partner with experts like TagX, who offer scalable and reliable data scraping services. Their solutions are built to handle dynamic content, pagination, and other complexities involved in scraping from platforms like Google
Step 4: Deal with Pagination and JavaScript Rendering
Google displays only a portion of reviews at a time and loads more as the user scrolls. A good scraper must simulate this behavior by managing pagination and rendering JavaScript content. This step ensures you don’t miss any data during the extraction process.
Step 5: Clean and Analyze Your Data
Once the reviews are scraped, they need to be cleaned and organized. You may need to remove HTML tags, eliminate duplicates, or normalize date formats. Structured data can then be analyzed using sentiment analysis tools or visualized using dashboards to uncover trends and insights.
Benefits of Using Data Scraping Services for Google Reviews
Manually collecting review data is inefficient and prone to errors. Professional data scraping services offer a range of benefits:
Accuracy: Eliminate human errors through automated, structured data collection
Scalability: Scrape thousands of reviews across multiple locations.
Speed: Collect and process data faster than manual methods
Customization: Filter and organize data based on your business needs
Compliance: Adhere to legal and ethical data collection standards
TagX, for example, provides customized scraping pipelines tailored to your business goals. Their platform supports large-scale review analysis, from raw data extraction to sentiment tagging and visualization.
Challenges of Scraping Google Reviews
Even with the right tools, scraping Google reviews isn’t always straightforward. Businesses may face challenges like CAPTCHAs, anti-bot mechanisms, and dynamically loaded content. Another common issue is inconsistent data formatting. Since users write reviews in different styles and languages, analyzing this data can be difficult. This is where web scraping using AI becomes incredibly valuable. AI-powered tools can adapt to different content layouts, recognize sentiment across languages, and even summarize or tag common themes across reviews.
Is It Legal to Scrape Google Reviews?
This question often arises, and the answer depends on how the data is collected and used. While Google’s terms of service typically prohibit automated scraping, the information being scraped—customer reviews—is public.If done ethically, without overloading Google’s servers or violating privacy, scraping public reviews is generally accepted for research and analysis. Still, it’s crucial to stay updated with legal best practices. Partnering with responsible providers like TagX ensures compliance and reduces risk.
Why Choose TagX for Google Review Scraping
When it comes to scraping sensitive and complex data like Google reviews, you need a partner you can trust. TagX brings deep expertise in building scalable, ethical, and AI-driven scraping solutions. They offer:
Smart scrapers that adapt to changes in Google’s layout
Scalable pipelines to collect millions of data points
NLP-powered sentiment analysis and keyword tagging
Complete compliance with data privacy regulations
Whether you're analyzing reviews to improve customer satisfaction or tracking competitor sentiment, TagX ensures you get actionable insights without the hassle.
Final Thoughts
Google reviews are a goldmine of customer insight, but manually managing and analyzing them is not practical at scale. By using expert data scraping services, businesses can unlock the full potential of this feedback to improve customer experience, drive product innovation, and strengthen their market presence. If you're ready to turn raw review data into strategic insights, consider partnering with TagX. Their blend of automation, AI, and compliance makes them ideal for scraping and analyzing Google reviews.
0 notes
Link
https://bit.ly/40C3VXS - 🌐 A hacker known as USDoD has leaked a database containing personal information of over 35 million LinkedIn users on Breach Forums, a well-known cybercrime and hacker platform. This hacker is also responsible for previous breaches of the FBI’s security platform InfraGard and Twitter. The leaked LinkedIn database was divided into two parts, with one containing 5 million and the other 35 million user records. #LinkedInDataBreach #Cybersecurity #DataLeak 💻 The data was obtained through web scraping, an automated process used to extract specific information from websites. The contents of the leaked database primarily include publicly available information from LinkedIn profiles, such as full names and profile bios. Fortunately, the leaked data does not include passwords, though it does contain millions of email addresses. #WebScraping #OnlinePrivacy #DataProtection 🔍 An analysis by Troy Hunt of HaveIBeenPwned (HIBP) revealed that the LinkedIn database consists of a mixture of legitimate data from public LinkedIn profiles, fabricated email addresses, and other sources. Due to the presence of both legitimate and fabricated data, the database has been labeled as “scraped and fabricated data” on HIBP. This incident is not the first of its kind, as LinkedIn’s scraped databases have been leaked online multiple times in the past. #DataAuthenticity #HIBP #LinkedInSecurity ⚠️ The implications of such data leaks are significant, raising concerns about online privacy and the security of personal information on social media platforms. As the internet increasingly becomes integrated into daily life, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and awareness about data privacy becomes paramount.
#LinkedInDataBreach#Cybersecurity#DataLeak#WebScraping#OnlinePrivacy#DataProtection#DataAuthenticity#HIBP#LinkedInSecurity#OnlineSecurity#PersonalDataSafety#CyberAwareness#personalinformation#usdod#linkedin#linkedinprofile#users#cybersecurity#data#websites
0 notes
Text
Get Valuable Data with AI-Augmented and Automation Driven Web Scraping Services
Outsource Bigdata is a web scraping service provider that has the efficacy of highly skilled developers and data programmers. We offer web page scraping and web scraping services to gather and access data. This boosts the business by providing access to high-quality data, automation, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) that can guide your web page extraction strategy.
For more details visit: https://outsourcebigdata.com/data-automation/web-scraping-services/
About AIMLEAP - Outsource Bigdata
AIMLEAP - Outsource Bigdata is a division of AIMLEAP, AIMLEAP is an ISO 9001:2015 and ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified global technology consulting and service provider offering Digital IT, AI-augmented Data Solutions, Automation, and Research & Analytics Services.
AIMLEAP has been recognized as ‘The Great Place to Work®’. With a focus on AI and an automation-first approach, our services include end-to-end IT application management, Mobile App Development, Data Management, Data Mining Services, Web Data Scraping, Self-serving BI reporting solutions, Digital Marketing, and Analytics solutions.
We started in 2012 and successfully delivered projects in IT & digital transformation, automation driven data solutions, and digital marketing for more than 750 fast-growing companies in the USA, Europe, New Zealand, Australia, Canada; and more.
⭐An ISO 9001:2015 and ISO/IEC 27001:2013 certified
⭐Served 750+ customers
⭐ 11+ Years of industry experience
⭐98% Client Retention
⭐Great Place to Work® Certified
⭐ Global Delivery Centers in the USA, Canada, India & Australia
Email: [email protected]
USA: 1-30235 14656
Canada: +1 4378 370 063
India: +91 810 527 1615
Australia: +61 402 576 615
0 notes
Text
Web Scraping 102: Scraping Product Details from Amazon

Now that we understand the basics of web scraping, let's proceed with a practical guide. We'll walk through each step to extract data from an online ecommerce platform and save it in either Excel or CSV format. Since manually copying information online can be tedious, in this guide we'll focus on scraping product details from Amazon. This hands-on experience will deepen our understanding of web scraping in practical terms.
Before we start, make sure you have Python installed in your system, you can do that from this link: python.org. The process is very simple just install it like you would install any other application.
Install Anaconda using this link: https://www.anaconda.com/download . Be sure to follow the default settings during installation. For more guidance, please click here.
We can use various IDEs, but to keep it beginner-friendly, let's start with Jupyter Notebook in Anaconda. You can watch the video linked above to understand and get familiar with the software.
Now that everything is set let’s proceed:
Open up the Anaconda software and you will find `jupyter notebook` option over there, just click and launch it or search on windows > jupyter and open it.
Steps for Scraping Amazon Product Detail's:
At first we will create and save our 'Notebook' by selecting kernel as 'python 3' if prompted, then we'll rename it to 'AmazonProductDetails' following below steps:

So, the first thing we will do is to import required python libraries using below commands and then press Shift + Enter to run the code every time:

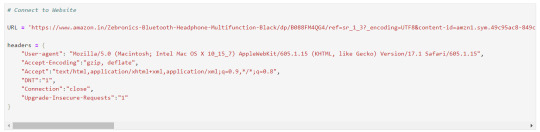
Let's connect to URL from which we want to extract the data and then define Headers to avoid getting our IP blocked.
Note : You can search `my user agent` on google to get your user agent details and replace it in below “User-agent”: “here goes your useragent line” below in headers.
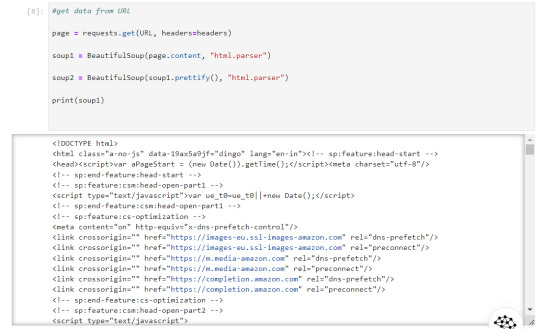
Now that our URL is defined let's use the imported libraries and pull some data.
Now, let's start with scraping product title and price for that we need to use `inspect element` on the product URL page to find the ID associated to the element:
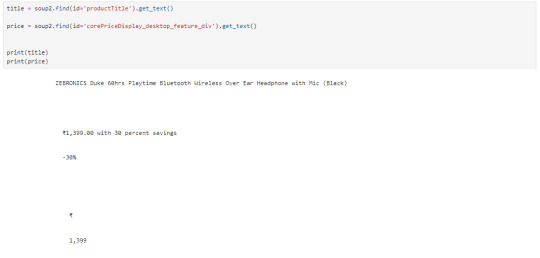
The data that we got is quite ugly as it has whitespaces and price are repeated let's trim the white space and just slice prices:
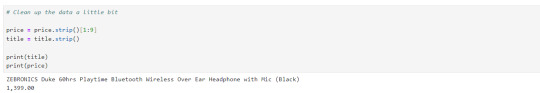
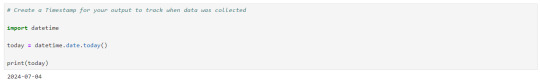
Let's create a timespan to keep note on when the data was extracted.
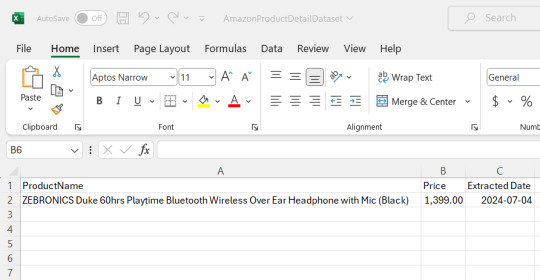
We need to save this data that we extracted, to a .csv or excel file. the 'w' below is use to write the data

Now you could see the file has been created at the location where the Anaconda app has been installed, in my case I had installed at path :"C:\Users\juver" and so the file is saved at path: "C:\Users\juver\AmazonProductDetailDataset"
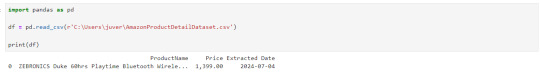
Instead of opening it by each time looking for path, let's read it in our notebook itself.
This way we could extract the data we need and save it for ourselves, by the time I was learning this basics, I came across this amazing post by Tejashwi Prasad on the same topic which I would highly recommend to go through.
Next, we’ll elevate our skills and dive into more challenging scraping projects soon.
0 notes