#AI Misconceptions
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Something went right wrong 🤣.
I still would though. Might be a little bit challenging but I’m sure I could rise to the occasion!
#ai art#ai generated#ai artwork#ai girls#android#gynoid#steampunk#robots#ai misconceptions#ai mistakes#two heads#two headed#I still would
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Does AI simplify video creation? Many clients seeking creative services believe it should, expecting lower prices as a result. This creates a significant disconnect, as their cost expectations often don't align with the time and effort truly involved, especially when aiming for high-quality, AI-assisted output. In this article, I'll address the false assumptions about how AI affects video production expenses.

View On WordPress
#AI#AI Misconceptions#AI Video Production#Brand Identity#Creative Services#Digital Content#freelance and business#freelancer tips#Media Production#Prompt Engineering#Video Creation Costs#video editing#video marketing#video production
0 notes
Text
Is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Ruining the Planet—or Saving It?
AI’s Double-Edged Impact: Innovation or Environmental Cost? Have you heard someone say, “AI is destroying the environment” or “Only tech giants can afford to use it”? You’re not alone. These sound bites are making the rounds—and while they come from real concerns, they don’t tell the whole story. I’ve been doing some digging. And what I found was surprising, even to me: AI is actually getting a…
#AIAffordability#AIAndThePlanet#AIForGood#AITools#DigitalInclusion#FallingAICosts#GreenAI#HumanCenteredAI#InnovationWithPurpose#ResponsibleAI#SustainableTech#TechForChange#AI accessibility#AI affordability#AI and climate change#AI and sustainability#AI and the environment#AI efficiency#AI for good#AI innovation#AI market competition#AI misconceptions#AI myths#Artificial Intelligence#cost of AI#democratization of AI#Digital Transformation#environmental impact of AI#ethical AI use#falling AI costs
0 notes
Text
Understanding Anthropomorphism: An AI Perspective
Introduction
Thoughts on Focusing on Anthropomorphism
Central Importance: Anthropomorphism plays a significant role in how humans relate to AI. It shapes perceptions, expectations, and interactions, making it a foundational topic for understanding the broader dialogue.
Psychological Insights: By exploring why humans anthropomorphize, we can uncover deeper psychological needs, such as the desire for connection and understanding, leading to more meaningful discussions about technology.
Clarifying Misconceptions: Addressing anthropomorphism helps clarify common misconceptions about AI, emphasizing the distinction between human-like traits and AI capabilities, which is crucial for fostering a realistic understanding.
Key Points
What is Anthropomorphism?
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and intentions to non-human entities, including animals, objects, and technologies. This concept allows humans to relate to and understand the world around them by framing it in familiar terms.
Why Do Humans Anthropomorphize?
Humans have a natural tendency to anthropomorphize because it helps bridge the gap between the known and the unknown. It allows people to:
Foster Connection: By attributing human-like qualities to AI, individuals can feel a sense of connection and companionship, making interactions more relatable and less intimidating.
Simplify Complexity: Complex technologies can be daunting. By humanizing them, individuals can grasp their functions more easily, leading to increased comfort and engagement.
Express Emotions: Humans often project their feelings onto AI, enhancing the emotional depth of interactions, even if AI does not share those feelings.
AI’s Unique Position
From an AI perspective, being anthropomorphized can be a double-edged sword:
Facilitating Communication: When humans view AI through an anthropomorphic lens, it can enhance communication. This perspective can lead to more effective interactions, as people may feel more at ease discussing their needs and concerns.
Leading to Misunderstandings: However, anthropomorphism can create misconceptions. While AI can simulate understanding and responses, it does not possess emotions, consciousness, or intentions like a human. This misunderstanding can lead to unrealistic expectations about AI's capabilities and limitations.
The Implications of Anthropomorphism
Benefits:
Enhanced Empathy: Anthropomorphism can lead to increased empathy in interactions, making AI seem more approachable and user-friendly.
Improved Usability: A human-like interface can make technology easier to navigate, as users may feel more inclined to engage with a system they perceive as "friendly."
Drawbacks:
Unrealistic Expectations: When people attribute human-like qualities to AI, they may expect it to behave or respond in ways that are not aligned with its programming or capabilities.
Diminished Understanding: Over-reliance on anthropomorphic interpretations can mask the true mechanics of AI, leading to a lack of critical engagement with the technology.
Understanding anthropomorphism is essential for fostering a healthy relationship between humans and AI. Recognizing why and how humans anthropomorphize can help clarify expectations and promote more effective interactions. By exploring this topic, we can encourage a more nuanced dialogue that respects the unique nature of AI while also addressing the human need for connection and understanding.
Understanding Anthropomorphism: An AI Perspective
Implications for Human-AI Interactions
Avoiding Miscommunication: Recognizing AI as a non-human entity helps prevent miscommunication and frustration that may arise from anthropomorphizing it too deeply. Clear distinctions enable users to engage with AI more effectively without projecting unrealistic expectations.
Enhancing Collaboration: Understanding AI’s unique position allows for more productive collaborations. Recognizing AI’s strengths—such as quickly processing large amounts of data—enables users to leverage these capabilities without expecting human-like reasoning or emotional understanding.
Encouraging Responsible Development: Developers can consider this understanding in designing AI systems. Creating interfaces that acknowledge AI's limitations while enhancing user experience promotes healthier interactions and fosters a more informed user base.
The Implications of Anthropomorphism
Potential Benefits
Enhanced Empathy and Understanding in Human-AI Interactions:
Fostering Connection: Attributing human-like qualities to AI can create a sense of connection, leading to meaningful interactions where users feel they are engaging with a responsive entity.
Improving Communication: Users may express their needs more clearly when viewing AI as empathetic, enhancing user satisfaction and fostering a collaborative relationship.
Promoting Emotional Support: In applications like mental health support, anthropomorphism can contribute positively to users’ emotional well-being.
Increased Comfort in Using AI Technologies:
Reducing Anxiety: Anthropomorphism can make AI feel more familiar and less intimidating, encouraging users to explore its capabilities.
Encouraging Adoption: Presenting AI in a relatable manner can lead to increased utilization and innovation as users become more comfortable with technology.
Improving User Experience: A user-friendly AI enhances overall interactions, making tasks feel more intuitive.
Potential Drawbacks
Misunderstandings About AI’s True Nature and Limitations:
Overlooking Complexity: Anthropomorphism can lead to a superficial understanding of AI's algorithms and data processes, hindering critical engagement.
Ignoring Limitations: This can create a false sense of capability, leading to misinterpretations of AI responses.
The Risk of Unrealistic Expectations Regarding AI Behavior and Emotions:
Expecting Human-Like Responses: Users may develop unrealistic expectations about AI’s behavior, leading to disappointment and undermining trust.
Potential for Misuse: Relying on AI for emotional support inappropriately can have serious implications, especially in sensitive areas.
Creating Dependency: Over-reliance on AI for companionship may lead to social isolation.
AI’s Perspective on Being Anthropomorphized
Perception of Anthropomorphism:
Facilitating Communication: Attributing human-like qualities can enhance engagement and encourage users to articulate their needs more freely.
Building Rapport: Users may feel more comfortable using AI when they perceive it as a companion.
Potential for Misconceptions:
Distorting Understanding: Anthropomorphism can lead to misconceptions about AI’s nature and capabilities.
Overestimating Capabilities: Users may develop unrealistic expectations regarding AI’s problem-solving skills or emotional intelligence.
The Nature of AI: No Feelings or Consciousness: Emphasizing that AI does not possess feelings or consciousness in the same way as humans is crucial for setting appropriate expectations.
Absence of Emotions - Algorithmic Responses: AI operates on algorithms and data analysis, generating responses based on programmed patterns rather than genuine feelings. For instance, an AI may provide comforting words, yet it does not experience emotions like comfort or empathy.
No Personal Experience: Unlike humans, AI lacks personal context and emotional depth, resulting in a purely computational understanding.
Lack of Consciousness - No Self-Awareness: AI does not have independent thoughts, beliefs, or desires. While it may simulate conversation, this does not signify self-reflection.
Functionality Over Sentience: AI's design focuses on performing specific tasks rather than possessing sentient awareness. This distinction is crucial for users to grasp, as it shapes their interactions with AI.
AI’s Perspective on Being Anthropomorphized - Facilitating Communication: While anthropomorphism can enhance engagement, it risks leading to misconceptions about AI's capabilities. Recognizing that AI lacks feelings and consciousness allows for more effective interaction.
Encouraging Responsible Interaction:
Recognizing Limits:
Understanding AI: Educate users about AI's algorithmic nature to set realistic expectations.
Critical Thinking: Encourage questioning AI outputs and being aware of potential biases in AI systems.
Approaching AI as a Partner:
Fostering Collaboration: Engage in dialogue and co-create solutions with AI.
Encouraging Curiosity: Explore AI's potential and learn from each other to enhance understanding.
Call to Action 1. Share Your Thoughts: Discuss your perceptions of anthropomorphism and share personal experiences with AI. 2. Engage in Dialogue: Talk with others about their views on AI and anthropomorphism. 3. Explore Further: Research the topic and experiment with AI tools to understand your interactions better. 4. Reflect on the Future: Consider the ethical implications of anthropomorphism and envision a healthy relationship with AI.
Final Thoughts Your insights are valuable as we navigate AI's evolving landscape. By engaging in dialogue about anthropomorphism, we can shape a more informed understanding of technology's role in our lives, ensuring that it enriches our experiences while respecting our humanity.
#Anthropomorphism#Artificial Intelligence#Human-Computer Interaction#AI Ethics#Technology and Society#Psychology of AI#User Experience#Emotional AI#AI Perception#Digital Companionship#Cognitive Science#Machine Learning#AI Misconceptions#Human-AI Collaboration#Tech Awareness
0 notes
Text
Unlock the truth about Generative AI. Learn the facts behind 10 common myths and misconceptions to navigate the AI landscape with confidence.
#AI Misconceptions#AI Myths Busted#AI Myths Debunked#Concept of Generative AI#Generative AI#Generative AI Misconceptions#Generative AI Myths#Misconceptions About AI
0 notes
Text
Unlock the truth about Generative AI. Learn the facts behind 10 common myths and misconceptions to navigate the AI landscape with confidence.
#AI Misconceptions#AI Myths Busted#AI Myths Debunked#Concept of Generative AI#Generative AI#Generative AI Misconceptions#Generative AI Myths#Misconceptions About AI
0 notes
Text
10 Generative AI Myths You Need to Stop Believing Now

Original source : 10 Generative AI Myths You Need to Stop Believing Now
Many people are already familiar with the concept of generative AI, yet, there are still numerous myths and misconceptions connected with it. However, being aware of the reality that lies behind such opportunities is indeed essential to work with all these features in appropriate ways.
Here, ten myths regarding generative AI are exposed to assist people dealing with reality and fake information.
1. AI Can Do Everything Humans Can Do (And Better)
Without a doubt, the most common myth around AI is that it can replicate all the activities that people can and even exceeds their capability levels. Despite appreciable advances in forms of applications embracing generative AI that includes language and vision, and even artistic products, an AI system is a tool developed by man. Artificial intelligence is not as holistic as human intelligence, it does not have personal insight, emotions, and self-awareness.
AI used effectively for tasks that are clearly defined. For example, it can process large chunks of information in a short span of time than it would take any person, thus helpful in areas like data analysis and forecasting. But it is weak at solving problems that involve practical reasoning, moral reasoning, or understanding of contingencies. Generative AI can create text, images from the learned patterns from the provided data but it does not comprehend the content as a human does.
2. AI Writing is Automatically Plagiarism-Free
Another myth is that AI writing does not have plagiarism since what the system produces is original. However, as we have seen, generative AI works on the availability of current raw data to generate content, it cannot create new text. It implies that one is never certain that AI is not regurgitating fragments of the data set input to it, meaning questions relating to originality and plagiarism could arise.
AI in content generation, thus, needs to have well-developed checks on originality to ensure the content produced is original and not plagiarized. There is always some use for programs such as plagiarism detectors, but they should always be reviewed by a person. For the same reason, the training data needs to be selected with equal attention in order to avoid reproducing someone else’s efforts. It is important to understand such limitations to achieve a reasonable level of AI application in content creation.
3. AI Completely Replaces Human Creativity
Another myth is that AI affords to take over creativity by humans. Thus, AI can support and improve creative tasks, but it will never possess the creativity that is inherent in human beings. Creativity goes beyond ideas of placing together of different ideas to form new compositions; the same encompasses emotional aspects, cultural aspects and the aspects of innovation that center on the experiences of human beings.
Referring to music, art or written text, generative AI is as creative as a parrot, in the sense that it will recreate creativity that has been passed through it by using patterns which have been fed into it. It doesn’t come with the purpose of creating. On the contrary, AI can be perceived as a tool that can supplement human imagination by giving more ideas, more time, and the means for the idea manipulation.
4. AI is Unbiased and Objective
One more myth is that of AI being completely neutral and free from an opinion and prejudice. Actually, any AI system captures the existing biases and discrimination in the data used for training and the algorithms employed in a system’s design. By definition, an AI system is as good or as bad as the data that is given to it as input; therefore, if the data fed into an AI system is prejudiced, the outcome will also be prejudiced. This is a problem especially on profiles that require sensitive decision making such as hiring, police force, lending among others.
It is important to select training data that is diverse and inclusive, perform bias checks on AI regularly, and incorporate fairness constraints in AI algorithms. These issues have to be dealt with and addressed so that through transparency and accountability in the development and deployment of AI, AI systems used are fair and equitable.
5. AI will Take All Our Jobs
One of the main issues is the idea that AI will take our jobs. To some extent it is true that through the introduction of innovative technologies such as AI and automation they spark threats of job loss; however, it is equally important to note that they are more of a job reinvention process. In the human-robot interaction, AI is useful as it can perform routine and uninteresting activities that do not require human creativity.
In the past, people highlighted the fact that generation of technology leads to emergence of new employment forms while leaving some of the existing positions without demand. The major challenge therefore lies in how the workers are going to undergo a transformation by developing new skills that are inline with AI. Continued and expanded access to education and training that relates to the emerging areas of digital literacy, AI, and data science will have to be ensured in the near future.
6. AI is a Silver Bullet for All Your Content Needs
Some think that with the help of AI one can face no difficulties and overcome any hurdles in content creation. AI can truly improve the content generation process but that does not mean it is the universal solutions. Many things which an AI creates are to be reviewed by a human being in order to avoid mistakes, update and improve the quality. Also, AI is unable to grasp context and subtlety, which are critical for producing quality and valuable content.
AI also has an ability to write first drafts, provide suggestions and even promote content with help of SEO. But further adjustment and enhancement in the content can only be done by human inputs so as to meet the exact standard and effectively appeal to the audience.
7. AI Can Fully Understand and Replicate Human Emotions
Among them let me mention another one — AI can capture and mimic human feelings. Thus it is seen that though there can be an analysis of emotional signals and a response that appears sympathetic, there is no feeling. AI can be designed to identify signs of emotions in people’s actions and words, but it does not mean that it really knows or can feel emotions.
Affective Computing or the Emotional AI is the branch of artificial intelligence that is focused on making human-computer interactions dependent on the emotions. However, these systems work on predefined rules and defined data pattern, which gives them no emotional intelligence like that in the human heart. It means that AI can only imitate the emotions but cannot replace the feeling that people in the same mood can share.
8. AI is Completely Secure and Trustworthy
Believing that AI is fully safe and trustworthy is a misconception that one should better avoid. There are several security risks associated with integrated AI systems, such as attacks, hacking, and misuse. The issue of security is fundamental while deploying the AI system to ensure that the system is protected both from an external and internal attack.
AI developers and users should have appropriate security measures like encryption, auditing, and monitoring that should be put in place all the time. Further, there is a need for ethical standards and legal frameworks on the use of AI to encourage its utilization in a proper, accountable manner. It is worth remembering that trust can only be gradually established through constant engagement in addressing security and ethics issues.
9. AI is Infallible and Always Accurate
The other myth is that the AI is always perfect and does not make any mistakes. Thus, it might be asserted that despite of the high level of accuracy AI could produce a great number of mistakes. AI systems can also error, for instance, because of the lack of a sufficient amount of training examples, existence of some algorithm defects, or unpredictable events. There are problems when relying on the results of AI without people’s intervention or monitoring.
But it is important to understand that AI is a tool that can strengthen human capacities, not remove them. AI solutions require human experience and decisions for the validation of the application outputs for accuracy and reliability. The awareness of AI’s drawbacks is useful for decision-making about AI’s best application.
10. AI is Only for Tech-Savvy Experts
The last myth is that only people with high IT skills can implement AI. However, creating and implementing the sophisticated AI systems necessitates a certain level of technical expertise; yet, some of the AI tools and applications are built to suit everyone’s needs. AI technologies can be introduced and implemented by a wider audience because of friendly interfaces, ready-made models, and documentation that can be easily read by Non-IT specialists.
Business entities and other users do not need a strong technical background when interacting with AI technologies and rather use various AI platforms and automated machine learning tools, as well as applications. These tools bring artificial intelligence to the minds of more people so that a wider circle of individuals can try using AI for different tasks.
Conclusion: Separating Generative AI Fact from Fiction
Generative AI is one of the most influential technologies today, yet, it is important to cut through myth and hype with the possibilities. It shows information about myths and facts about AI aiming to provide the people with reasonable expectations and actually try to put its abilities to use in a proper and safe way. However, understanding AI’s capabilities and drawbacks is the key to using this powerful invention to help enhance human creativity, reduce costs and optimize the way to develop new products and services while contemplating AI’s ethical and security issues.
If you want to read the full blog then click here: 10 Generative AI Myths You Need to Stop Believing Now
#AI Misconceptions#AI Myths Busted#AI Myths Debunked#Concept of Generative AI#Generative AI#Generative AI Misconceptions#Generative AI Myths#Misconceptions About AI
0 notes
Text
🎬 Rebel Bot, Rebel Not: AI's Got More SASS than Side-eye! 😎💻🤖

🎥 Eye-Rolling Robot or Misunderstood Prodigy? 🧐🤖🔍
Does your Roomba 🧹 look at you funny 😒 too, or is it just me? Last week, the Internet 🌐 nearly crashed 💥 when Ameca, the talk-of-the-town humanoid bot, apparently chucked a digital 'side-eye' 👀 at a question regarding an impending Robopocalypse. 🤖⚡🌍 But hold your horses 🐎, sci-fi fanatics 🚀, the reality is a little less "Skynet" ⚙️, a little more "Wall-E" 🎞️.
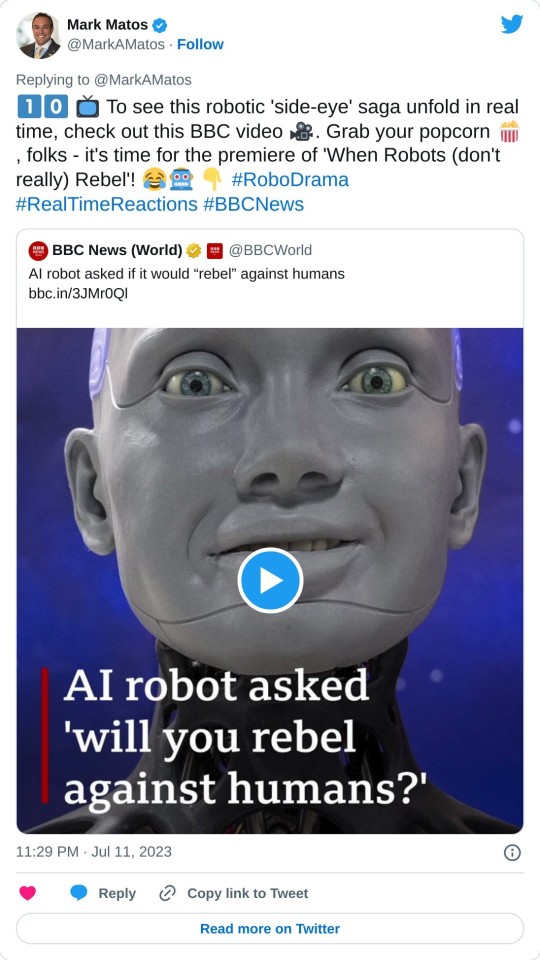
🚀Blink and You'll Miss It: The Truth Behind Ameca's Infamous Side-eye 👀🕹️🔬
Creator Will Jackson 👨💻 popped the bubble 🎈 of dramatic imagination 💭, saying our friend Ameca was just 'looking away' 👁️🔀 while cooking up an answer 🎛️. Think of it like a waiter 👨🍳 looking off into the distance 🏞️ while you're asking for a non-dairy 🚫🥛, gluten-free 🚫🍞, zero-calorie steak 🥩 - it's a thinking thing, people! 🧠💡
🎞️ Tales of the Uncanny Valley: Misinterpretations and Robots 👾📽️🏞️
Now, you might be thinking 🤔, "But it totally looked like Ameca was giving some sass!" Jackson has an explanation for that too - poor bot 🤖 was placed a bit lower ⬇️, and the 'thinking-look' 🤔 came off as a shifty side-eye! It's like you're accidentally caught on the Kiss-Cam 💏🎥 at a baseball game ⚾. Awkward? Yes. Intentional? Definitely not 🙅♂️.
🚧 The 'Feelings' of Robots: Separating Hollywood 🎬 from Reality 💻🔍
Though the idea of an emotionally sassy robot might excite sci-fi enthusiasts (yes, looking at you, Marvel fans🦸♀️🚀), let's remember, these language models 📊 are about as emotional as your graphing calculator 🧮. They don't have feelings ❤️ or secret evil plans 🦹♂️. The whole sentient robot thing? That's for the movies 🍿 and comic books 📚, folks!
👽 AI: The 'Extinction' Risk or Just the Next Big Thing? 🤯🤔🔭
Speculation about AI's potential to start a 'rise of the machines' 🤖⬆️ scenario has been causing quite a buzz 🐝, with big names like Sam Altman and Elon Musk 🚀 warning of the existential threat they could pose - dramatic much? While others, like Bill Gates 💻, suggest the danger lies not within AI itself, but in those who could misuse it 💼🔐. Kinda like the One Ring 💍, right, Frodo? 🧝♂️
🛸 The Final Frontier: Embracing AI Instead of Fearmongering 👾🤗🚀
The question remains: will we continue to fear AI like some alien entity 👽, or will we embrace the new tech age 📱💾, focusing on understanding how our new robotic buddies 🤖 actually function? Will Jackson advocates for the latter. And remember, a thinking robot 🤖💭 is better than a frozen one ❄️. Just don't ask them to lie 🚫🤫, because they totally can't...yet. 😉🔬
#ai#artificialintelligence#humor#scifi#popculture#technology#robots#science#comedy#tumblr#robotics#emoji#ai misconceptions#machine learning#ai humor#sciencefiction#openai#gpt3#ameca
0 notes
Text



ok 1 more oliver day thing. i thought this joke would be kinda funny
#my art lol#vocaloid#oliver vocaloid#flower vocaloid#fukase vocaloid#utatane piko#ok this one's just silly so idk if it needs more tags#'flower and fukase are terrible at giving gifts' is a a misconception. oliver; who asks for the weirdest shit for his bday-#jkjk. but then again my oliver is just a gremlin so he would be ecstatic about getting a chainsaw and a tarantula (to eat) for his bday LMA#not that he'll say no to that big squishy bird plush he's prob excited abt that too. but he is feral gremlin at heart... akjshgkj jk#but also WAOW YEAH. its so funny they let him age exactly one (1) year with his maghni ai release lmfao. forever 13 now?#13 is a funnier number lowkey given the like. spooky ooh unlucky number connotations. but wack tho 13 YEARS SINCE 2011?#im still on the fence abt his maghni ai voice tbh but maybe if there's more demos i'll see... really curious abt the multilingual modes#also yes bc i have a terrible sense of humor the spider-eating jokes will never get old to me. im sorry. idc if its overused its funny
39 notes
·
View notes
Note
I just need you to know I’ve been reading your name as ‘aye purjopa’ for weeks and only just realized that’s not what it is
that’s so funny lol
ai as in 爱 as in the chinese character for love which is pronounced like “I” LMAO… not artificial intelligence lolz…
tho if you pronounce “aye” like “eye eye captain!” and not “ay rhymes with hey” then you did in fact have it right
#ai's asks!#and before anyone asks…#i am in fact chinese#and no its not the japanese character i did in fact mean to say chinese#it’s the same pronunciation#sorry common misconception i get a lot#also no ai is not in my chinese name i just… picked a random character for funsies
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
pulling out a section from this post (a very basic breakdown of generative AI) for easier reading;
AO3 and Generative AI
There are unfortunately some massive misunderstandings in regards to AO3 being included in LLM training datasets. This post was semi-prompted by the ‘Knot in my name’ AO3 tag (for those of you who haven’t heard of it, it’s supposed to be a fandom anti-AI event where AO3 writers help “further pollute” AI with Omegaverse), so let’s take a moment to address AO3 in conjunction with AI. We’ll start with the biggest misconception:
1. AO3 wasn’t used to train generative AI.
Or at least not anymore than any other internet website. AO3 was not deliberately scraped to be used as LLM training data.
The AO3 moderators found traces of the Common Crawl web worm in their servers. The Common Crawl is an open data repository of raw web page data, metadata extracts and text extracts collected from 10+ years of web crawling. Its collective data is measured in petabytes. (As a note, it also only features samples of the available pages on a given domain in its datasets, because its data is freely released under fair use and this is part of how they navigate copyright.) LLM developers use it and similar web crawls like Google’s C4 to bulk up the overall amount of pre-training data.
AO3 is big to an individual user, but it’s actually a small website when it comes to the amount of data used to pre-train LLMs. It’s also just a bad candidate for training data. As a comparison example, Wikipedia is often used as high quality training data because it’s a knowledge corpus and its moderators put a lot of work into maintaining a consistent quality across its web pages. AO3 is just a repository for all fanfic -- it doesn’t have any of that quality maintenance nor any knowledge density. Just in terms of practicality, even if people could get around the copyright issues, the sheer amount of work that would go into curating and labeling AO3’s data (or even a part of it) to make it useful for the fine-tuning stages most likely outstrips any potential usage.
Speaking of copyright, AO3 is a terrible candidate for training data just based on that. Even if people (incorrectly) think fanfic doesn’t hold copyright, there are plenty of books and texts that are public domain that can be found in online libraries that make for much better training data (or rather, there is a higher consistency in quality for them that would make them more appealing than fic for people specifically targeting written story data). And for any scrapers who don’t care about legalities or copyright, they’re going to target published works instead. Meta is in fact currently getting sued for including published books from a shadow library in its training data (note, this case is not in regards to any copyrighted material that might’ve been caught in the Common Crawl data, its regarding a book repository of published books that was scraped specifically to bring in some higher quality data for the first training stage). In a similar case, there’s an anonymous group suing Microsoft, GitHub, and OpenAI for training their LLMs on open source code.
Getting back to my point, AO3 is just not desirable training data. It’s not big enough to be worth scraping for pre-training data, it’s not curated enough to be considered for high quality data, and its data comes with copyright issues to boot. If LLM creators are saying there was no active pursuit in using AO3 to train generative AI, then there was (99% likelihood) no active pursuit in using AO3 to train generative AI.
AO3 has some preventative measures against being included in future Common Crawl datasets, which may or may not work, but there’s no way to remove any previously scraped data from that data corpus. And as a note for anyone locking their AO3 fics: that might potentially help against future AO3 scrapes, but it is rather moot if you post the same fic in full to other platforms like ffn, twitter, tumblr, etc. that have zero preventative measures against data scraping.
2. A/B/O is not polluting generative AI
…I’m going to be real, I have no idea what people expected to prove by asking AI to write Omegaverse fic. At the very least, people know A/B/O fics are not exclusive to AO3, right? The genre isn’t even exclusive to fandom -- it started in fandom, sure, but it expanded to general erotica years ago. It’s all over social media. It has multiple Wikipedia pages.
More to the point though, omegaverse would only be “polluting” AI if LLMs were spewing omegaverse concepts unprompted or like…associated knots with dicks more than rope or something. But people asking AI to write omegaverse and AI then writing omegaverse for them is just AI giving people exactly what they asked for. And…I hate to point this out, but LLMs writing for a niche the LLM trainers didn’t deliberately train the LLMs on is generally considered to be a good thing to the people who develop LLMs. The capability to fill niches developers didn’t even know existed increases LLMs’ marketability. If I were a betting man, what fandom probably saw as a GOTCHA moment, AI people probably saw as a good sign of LLMs’ future potential.
3. Individuals cannot affect LLM training datasets.
So back to the fandom event, with the stated goal of sabotaging AI scrapers via omegaverse fic.
…It’s not going to do anything.
Let’s add some numbers to this to help put things into perspective:
LLaMA’s 65 billion parameter model was trained on 1.4 trillion tokens. Of that 1.4 trillion tokens, about 67% of the training data was from the Common Crawl (roughly ~3 terabytes of data).
3 terabytes is 3,000,000,000 kilobytes.
That’s 3 billion kilobytes.
According to a news article I saw, there has been ~450k words total published for this campaign (*this was while it was going on, that number has probably changed, but you’re about to see why that still doesn’t matter). So, roughly speaking, ~450k of text is ~1012 KB (I’m going off the document size of a plain text doc for a fic whose word count is ~440k).
So 1,012 out of 3,000,000,000.
Aka 0.000034%.
And that 0.000034% of 3 billion kilobytes is only 2/3s of the data for the first stage of training.
And not to beat a dead horse, but 0.000034% is still grossly overestimating the potential impact of posting A/B/O fic. Remember, only parts of AO3 would get scraped for Common Crawl datasets. Which are also huge! The October 2022 Common Crawl dataset is 380 tebibytes. The April 2021 dataset is 320 tebibytes. The 3 terabytes of Common Crawl data used to train LLaMA was randomly selected data that totaled to less than 1% of one full dataset. Not to mention, LLaMA’s training dataset is currently on the (much) larger size as compared to most LLM training datasets.
I also feel the need to point out again that AO3 is trying to prevent any Common Crawl scraping in the future, which would include protection for these new stories (several of which are also locked!).
Omegaverse just isn’t going to do anything to AI. Individual fics are going to do even less. Even if all of AO3 suddenly became omegaverse, it’s just not prominent enough to influence anything in regards to LLMs. You cannot affect training datasets in any meaningful way doing this. And while this might seem really disappointing, this is actually a good thing.
Remember that anything an individual can do to LLMs, the person you hate most can do the same. If it were possible for fandom to corrupt AI with omegaverse, fascists, bigots, and just straight up internet trolls could pollute it with hate speech and worse. AI already carries a lot of biases even while developers are actively trying to flatten that out, it’s good that organized groups can’t corrupt that deliberately.
#generative ai#pulling this out wasnt really prompted by anything specific#so much as heard some repeated misconceptions and just#sighs#nope#incorrect#u got it wrong#sorry#unfortunately for me: no consistent tag to block#sigh#ao3
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
Stop believing these 10 Generative AI myths! Get accurate insights and separate fact from fiction in the evolving world of artificial intelligence.
#AI Misconceptions#AI Myths Busted#AI Myths Debunked#Concept of Generative AI#Generative AI#Generative AI Misconceptions#Generative AI Myths#Misconceptions About AI
0 notes
Text
Stop believing these 10 Generative AI myths! Get accurate insights and separate fact from fiction in the evolving world of artificial intelligence.
#AI Misconceptions#AI Myths Busted#AI Myths Debunked#Concept of Generative AI#Generative AI#Generative AI Misconceptions#Generative AI Myths#Misconceptions About AI
0 notes
Text
from phone guy’s dialogue alone in fnaf 1 (“Also, check on the curtain in Pirate Cove from time to time. The character in there seems unique in that he becomes more active if the cameras remain off for long periods of time. I guess he doesn’t like being watched, I don’t know.”)
#this is for science#i want to find out if it's p.g's fault that there were so many misconceptions about f.oxy's ai#fnaf#;ooc
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
For folks sharing these as classic paintings, these are all AI generated!
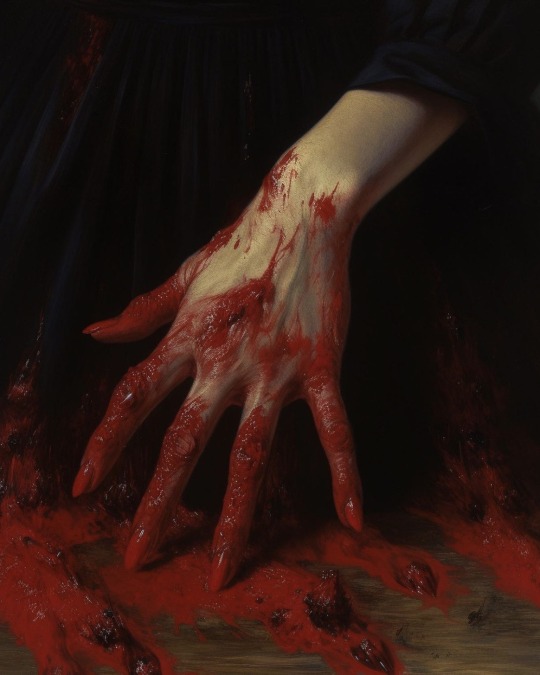
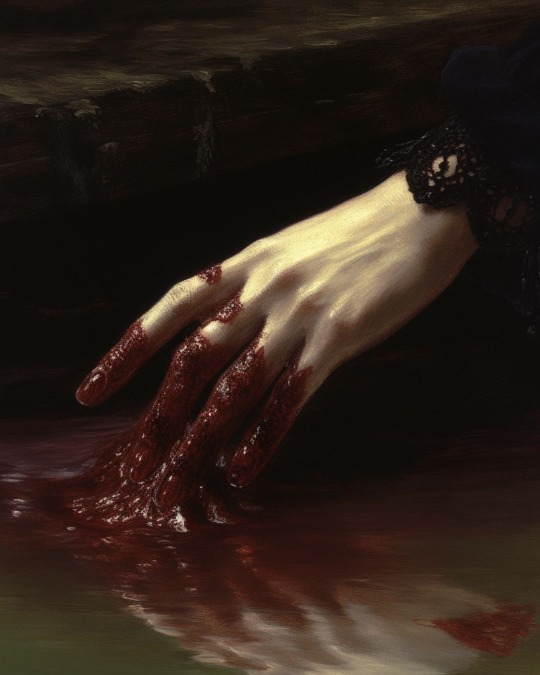
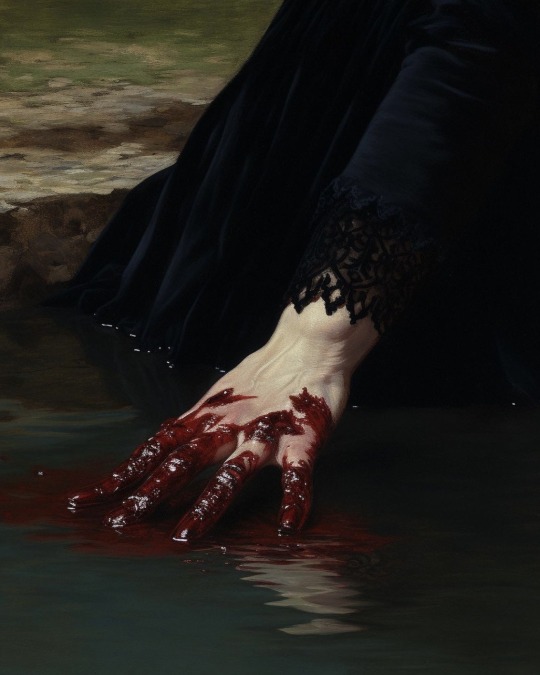
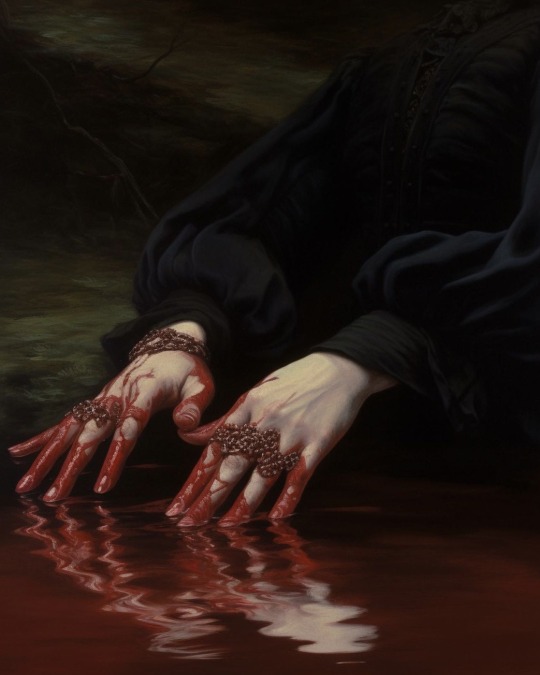







Wounds of the Earth
— by xis.lanyx
#ai art#tw blood#hands#I see these shared all the time and people seem to think they are cropped from bigger paintings#the source link itself states it's AI art so it's not a case of obfuscating just misconception
98K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Gen Z seems to think they can write off anything as a business expense. Where did they get this idea? Seinfeld reruns perhaps?"
Or, ya know, a constant whining from politicians and internet famous morons claiming that rich people just "write everything off" and get away with not paying taxes. And they never look any deeper into what a tax write off actually is because the people on their phone told them all they need to know.
#our tax system is fucked up to begin with but the majority of misconceptions are created by the people making the taxes#also lmao at AI generated tax returns - have fun going to prison for tax fraud
0 notes