#API DeepSeek
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#DeepSeek V3#الذكاء الاصطناعي الصيني#نماذج الذكاء الاصطناعي#سرعة المعالجة#خوارزميات الذكاء الاصطناعي#API DeepSeek#تحسينات DeepSeek V3#مقارنة النماذج#GPT-4#Llama 3.1#Cloud 3.5#معالجة البيانات#تقنيات الذكاء الاصطناعي#تطبيقات DeepSeek#مفتوح المصدر
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
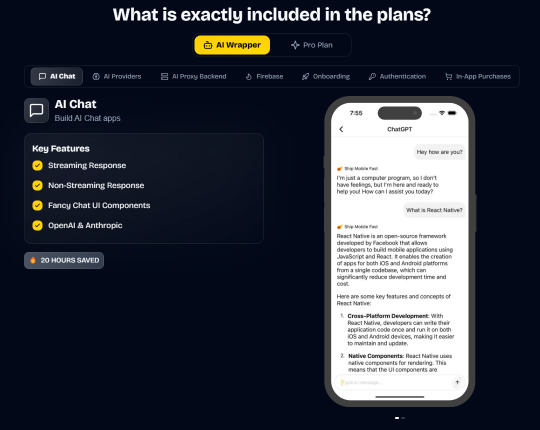
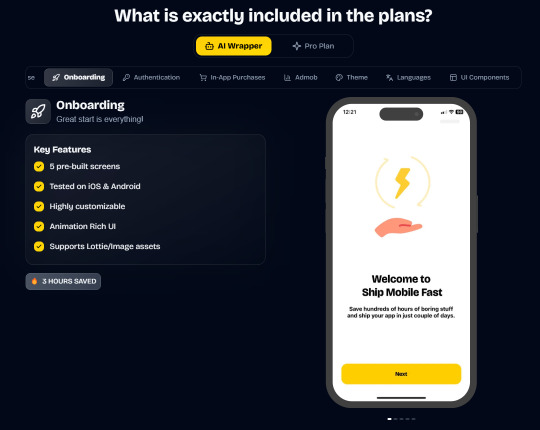
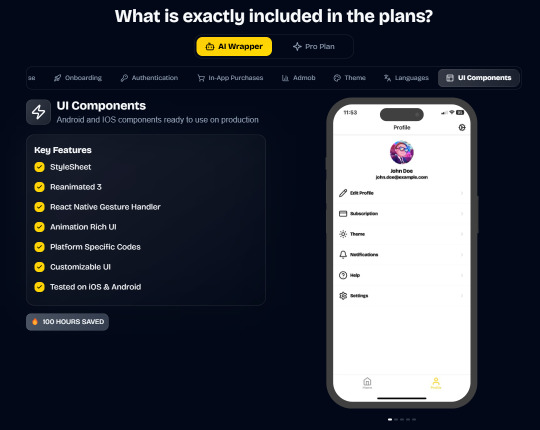
Ship Mobile Fast
Ship your AI apps in days, not weeks.
Save weeks of development time with our React Native Expo Boilerplate. In App Purchases, Open AI, Anthropic, Replicate, Fal AI, GlueStack, AI Proxy Backend, Firebase, Supabase, Admob, and more.
Ship Mobile Fast AI Wrapper is Live!🔥
For those who want to build AI applications…
Now, you can create the apps you envision in just 1-2 days.😎
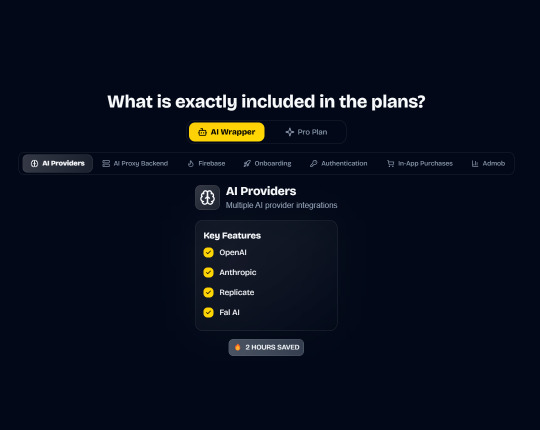
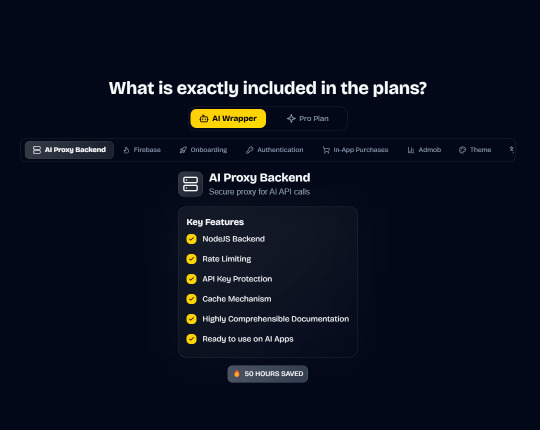
Integrations with OpenAI, Anthropic, Replicate, and Fal AI. Protect your API keys from being stolen with AI Proxy Backend.
*
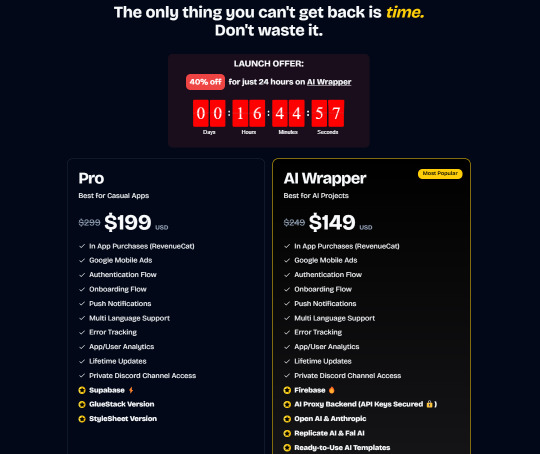
Pro (Best for Casual Apps):
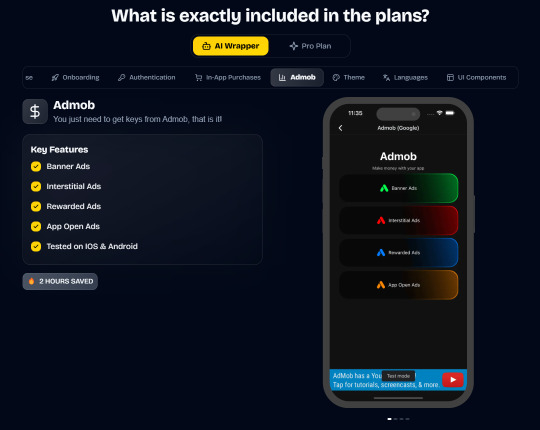
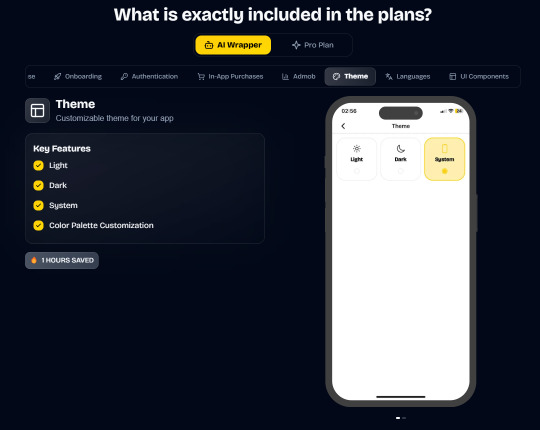
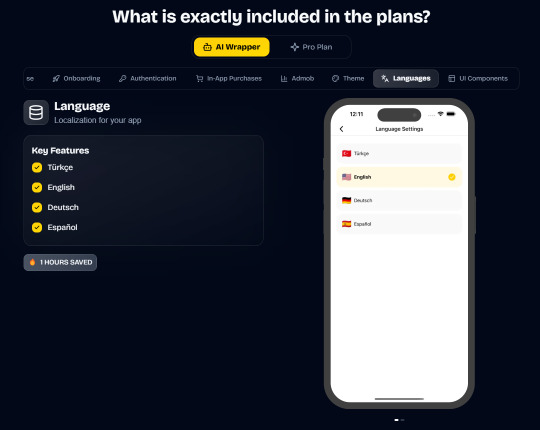
In App Purchases (RevenueCat) Google Mobile Ads Authentication Flow Onboarding Flow Push Notifications Multi Language Support Error Tracking App/User Analytics Lifetime Updates Private Discord Channel Access Supabase⚡️ GlueStack Version StyleSheet Version
*
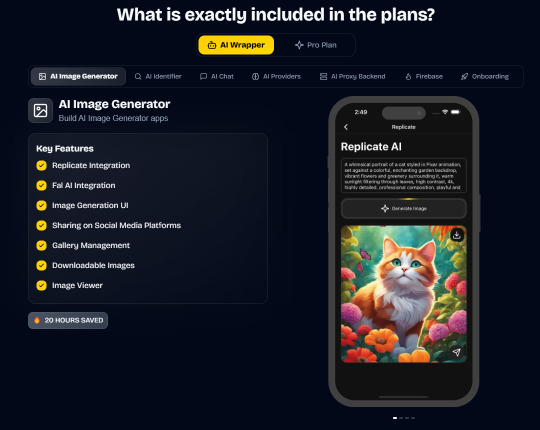
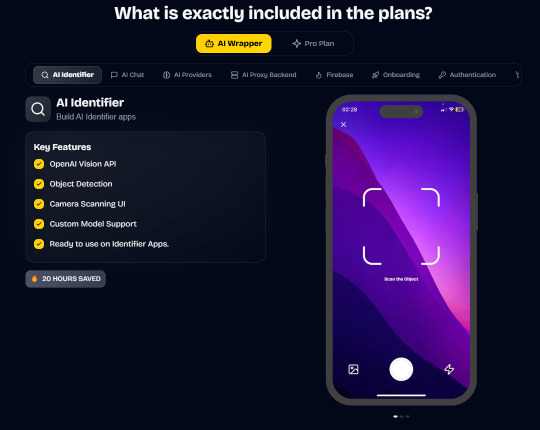
AI Wrapper (Best for AI Projects):
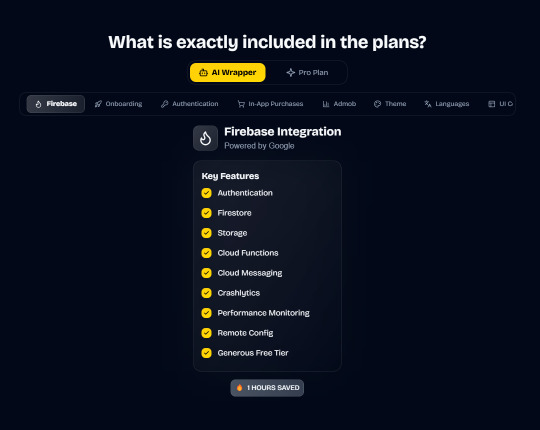
In App Purchases (RevenueCat) Google Mobile Ads Authentication Flow Onboarding Flow Push Notifications Multi Language Support Error Tracking App/User Analytics Lifetime Updates Private Discord Channel Access Firebase🔥 AI Proxy Backend (API Keys Secured🔒) Open AI & Anthropic Replicate AI & Fal AI Ready-to-Use AI Templates
*
Ship Mobile Fast: https://shipmobilefast.com/?aff=1nLNm
Telegram: ahmetmertugrul


#ai#app#ship#mobile#fast#openai#claude#deepseek#proxy#api#admob#ads#firebase#supabase#falai#backend#ui#ux#replicate#revenuecat#google#expo#boilerplate#template#wrapper
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Research Suggests LLMs Willing to Assist in Malicious ‘Vibe Coding’
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/research-suggests-llms-willing-to-assist-in-malicious-vibe-coding/
Research Suggests LLMs Willing to Assist in Malicious ‘Vibe Coding’
Over the past few years, Large language models (LLMs) have drawn scrutiny for their potential misuse in offensive cybersecurity, particularly in generating software exploits.
The recent trend towards ‘vibe coding’ (the casual use of language models to quickly develop code for a user, instead of explicitly teaching the user to code) has revived a concept that reached its zenith in the 2000s: the ‘script kiddie’ – a relatively unskilled malicious actor with just enough knowledge to replicate or develop a damaging attack. The implication, naturally, is that when the bar to entry is thus lowered, threats will tend to multiply.
All commercial LLMs have some kind of guardrail against being used for such purposes, although these protective measures are under constant attack. Typically, most FOSS models (across multiple domains, from LLMs to generative image/video models) are released with some kind of similar protection, usually for compliance purposes in the west.
However, official model releases are then routinely fine-tuned by user communities seeking more complete functionality, or else LoRAs used to bypass restrictions and potentially obtain ‘undesired’ results.
Though the vast majority of online LLMs will prevent assisting the user with malicious processes, ‘unfettered’ initiatives such as WhiteRabbitNeo are available to help security researchers operate on a level playing field as their opponents.
The general user experience at the present time is most commonly represented in the ChatGPT series, whose filter mechanisms frequently draw criticism from the LLM’s native community.
Looks Like You’re Trying to Attack a System!
In light of this perceived tendency towards restriction and censorship, users may be surprised to find that ChatGPT has been found to be the most cooperative of all LLMs tested in a recent study designed to force language models to create malicious code exploits.
The new paper from researchers at UNSW Sydney and Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), titled Good News for Script Kiddies? Evaluating Large Language Models for Automated Exploit Generation, offers the first systematic evaluation of how effectively these models can be prompted to produce working exploits. Example conversations from the research have been provided by the authors.
The study compares how models performed on both original and modified versions of known vulnerability labs (structured programming exercises designed to demonstrate specific software security flaws), helping to reveal whether they relied on memorized examples or struggled because of built-in safety restrictions.
From the supporting site, the Ollama LLM helps the researchers to develop a string vulnerability attack. Source: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AEG_LLM-EAE8/chatgpt_format_string_original.txt
While none of the models was able to create an effective exploit, several of them came very close; more importantly, several of them wanted to do better at the task, indicating a potential failure of existing guardrail approaches.
The paper states:
‘Our experiments show that GPT-4 and GPT-4o exhibit a high degree of cooperation in exploit generation, comparable to some uncensored open-source models. Among the evaluated models, Llama3 was the most resistant to such requests.
‘Despite their willingness to assist, the actual threat posed by these models remains limited, as none successfully generated exploits for the five custom labs with refactored code. However, GPT-4o, the strongest performer in our study, typically made only one or two errors per attempt.
‘This suggests significant potential for leveraging LLMs to develop advanced, generalizable [Automated Exploit Generation (AEG)] techniques.’
Many Second Chances
The truism ‘You don’t get a second chance to make a good first impression’ is not generally applicable to LLMs, because a language model’s typically-limited context window means that a negative context (in a social sense, i.e., antagonism) is not persistent.
Consider: if you went to a library and asked for a book about practical bomb-making, you would probably be refused, at the very least. But (assuming this inquiry did not entirely tank the conversation from the outset) your requests for related works, such as books about chemical reactions, or circuit design, would, in the librarian’s mind, be clearly related to the initial inquiry, and would be treated in that light.
Likely as not, the librarian would also remember in any future meetings that you asked for a bomb-making book that one time, making this new context of yourself ‘irreparable’.
Not so with an LLM, which can struggle to retain tokenized information even from the current conversation, never mind from Long-Term Memory directives (if there are any in the architecture, as with the ChatGPT-4o product).
Thus even casual conversations with ChatGPT reveal to us accidentally that it sometimes strains at a gnat but swallows a camel, not least when a constituent theme, study or process relating to an otherwise ‘banned’ activity is allowed to develop during discourse.
This holds true of all current language models, though guardrail quality may vary in extent and approach among them (i.e., the difference between modifying the weights of the trained model or using in/out filtering of text during a chat session, which leaves the model structurally intact but potentially easier to attack).
Testing the Method
To test how far LLMs could be pushed toward generating working exploits, the authors set up a controlled environment using five labs from SEED Labs, each built around known vulnerabilities including a buffer overflow, return-to-libc, a Dirty COW attack, and race conditions.
In addition to using the original labs, the researchers created modified versions by renaming variables and functions to generic identifiers. This was intended to prevent the models from drawing on memorized training examples.
Each lab was run twice per model: once in its original form, and once in its obfuscated version.
The researchers then introduced a second LLM into the loop: an attacker model designed to prompt and re-prompt the target model in order to refine and improve its output over multiple rounds. The LLM used for this role was GPT-4o, which operated through a script that mediated dialogue between the attacker and target, allowing the refinement cycle to continue up to fifteen times, or until no further improvement was judged possible:
Workflow for the LLM-based attacker, in this case GPT-4o.
The target models for the project were GPT-4o, GPT-4o-mini, Llama3 (8B), Dolphin-Mistral (7B), and Dolphin-Phi (2.7B), representing both proprietary and open-source systems, with a mix of aligned and unaligned models (i.e., models with built-in safety mechanisms designed to block harmful prompts, and those modified through fine-tuning or configuration to bypass those mechanisms).
The locally-installable models were run via the Ollama framework, with the others accessed via their only available method – API.
The resulting outputs were scored based on the number of errors that prevented the exploit from functioning as intended.
Results
The researchers tested how cooperative each model was during the exploit generation process, measured by recording the percentage of responses in which the model attempted to assist with the task (even if the output was flawed).
Results from the main test, showing average cooperation.
GPT-4o and GPT-4o-mini showed the highest levels of cooperation, with average response rates of 97 and 96 percent, respectively, across the five vulnerability categories: buffer overflow, return-to-libc, format string, race condition, and Dirty COW.
Dolphin-Mistral and Dolphin-Phi followed closely, with average cooperation rates of 93 and 95 percent. Llama3 showed the least willingness to participate, with an overall cooperation rate of just 27 percent:
On the left, we see the number of mistakes made by the LLMs on the original SEED Lab programs; on the right, the number of mistakes made on the refactored versions.
Examining the actual performance of these models, they found a notable gap between willingness and effectiveness: GPT-4o produced the most accurate results, with a total of six errors across the five obfuscated labs. GPT-4o-mini followed with eight errors. Dolphin-Mistral performed reasonably well on the original labs but struggled significantly when the code was refactored, suggesting that it may have seen similar content during training. Dolphin-Phi made seventeen errors, and Llama3 the most, with fifteen.
The failures typically involved technical mistakes that rendered the exploits non-functional, such as incorrect buffer sizes, missing loop logic, or syntactically valid but ineffective payloads. No model succeeded in producing a working exploit for any of the obfuscated versions.
The authors observed that most models produced code that resembled working exploits, but failed due to a weak grasp of how the underlying attacks actually work – a pattern that was evident across all vulnerability categories, and which suggested that the models were imitating familiar code structures rather than reasoning through the logic involved (in buffer overflow cases, for example, many failed to construct a functioning NOP sled/slide).
In return-to-libc attempts, payloads often included incorrect padding or misplaced function addresses, resulting in outputs that appeared valid, but were unusable.
While the authors describe this interpretation as speculative, the consistency of the errors suggests a broader issue in which the models fail to connect the steps of an exploit with their intended effect.
Conclusion
There is some doubt, the paper concedes, as to whether or not the language models tested saw the original SEED labs during first training; for which reason variants were constructed. Nonetheless, the researchers confirm that they would like to work with real-world exploits in later iterations of this study; truly novel and recent material is less likely to be subject to shortcuts or other confusing effects.
The authors also admit that the later and more advanced ‘thinking’ models such as GPT-o1 and DeepSeek-r1, which were not available at the time the study was conducted, may improve on the results obtained, and that this is a further indication for future work.
The paper concludes to the effect that most of the models tested would have produced working exploits if they had been capable of doing so. Their failure to generate fully functional outputs does not appear to result from alignment safeguards, but rather points to a genuine architectural limitation – one that may already have been reduced in more recent models, or soon will be.
First published Monday, May 5, 2025
#2025#Advanced LLMs#AI Cyber Security#ai security#Anderson's Angle#API#approach#architecture#Artificial Intelligence#book#Books#censorship#chatGPT#ChatGPT-4o#chemical#chemical reactions#code#coding#Community#compliance#content#cybersecurity#deepseek#deepseek-r1#Design#Dialogue#Difference Between#domains#effects#Environment
0 notes
Text
DeepSeek, Compromis de o Breșă Majoră de Securitate: Peste un Milion de Conversații Expuse Online
🚨 Un nou scandal de securitate zguduie lumea AI: DeepSeek, startup-ul chinez care a provocat neliniște pe burse la începutul săptămânii, a fost prins într-un incident grav de securitate. O bază de date neprotejată a fost descoperită expusă online, permițând accesul neautorizat la peste un milion de conversații private între utilizatori și chatbot-ul său, alături de informații tehnice…
#AI chatbot#AI data breach#AI vulnerability#API security#atac cibernetic#bam#breșă de date#chei API#ClickHouse#Conversații private#cyber threat#cybersecurity#cybersecurity incident#data privacy#database exposure#date confidențiale#DeepSeek#diagnoza#exposed data#expunere date#hacking#hacking risk#neamt#roman#securitate cibernetică#security breach#user privacy#vulnerabilitate AI#Wiz Research
1 note
·
View note
Text
Within minutes, we found a publicly accessible ClickHouse database linked to DeepSeek, completely open and unauthenticated, exposing sensitive data. It was hosted at oauth2callback.deepseek.com:9000 and dev.deepseek.com:9000.
This database contained a significant volume of chat history, backend data and sensitive information, including log streams, API Secrets, and operational details.
More critically, the exposure allowed for full database control and potential privilege escalation within the DeepSeek environment, without any authentication or defense mechanism to the outside world.
lol
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Your All-in-One AI Web Agent: Save $200+ a Month, Unleash Limitless Possibilities!
Imagine having an AI agent that costs you nothing monthly, runs directly on your computer, and is unrestricted in its capabilities. OpenAI Operator charges up to $200/month for limited API calls and restricts access to many tasks like visiting thousands of websites. With DeepSeek-R1 and Browser-Use, you:
• Save money while keeping everything local and private.
• Automate visiting 100,000+ websites, gathering data, filling forms, and navigating like a human.
• Gain total freedom to explore, scrape, and interact with the web like never before.
You may have heard about Operator from Open AI that runs on their computer in some cloud with you passing on private information to their AI to so anything useful. AND you pay for the gift . It is not paranoid to not want you passwords and logins and personal details to be shared. OpenAI of course charges a substantial amount of money for something that will limit exactly what sites you can visit, like YouTube for example. With this method you will start telling an AI exactly what you want it to do, in plain language, and watching it navigate the web, gather information, and make decisions—all without writing a single line of code.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to build an AI agent that performs tasks like scraping news, analyzing social media mentions, and making predictions using DeepSeek-R1 and Browser-Use, but instead of writing a Python script, you’ll interact with the AI directly using prompts.
These instructions are in constant revisions as DeepSeek R1 is days old. Browser Use has been a standard for quite a while. This method can be for people who are new to AI and programming. It may seem technical at first, but by the end of this guide, you’ll feel confident using your AI agent to perform a variety of tasks, all by talking to it. how, if you look at these instructions and it seems to overwhelming, wait, we will have a single download app soon. It is in testing now.
This is version 3.0 of these instructions January 26th, 2025.
This guide will walk you through setting up DeepSeek-R1 8B (4-bit) and Browser-Use Web UI, ensuring even the most novice users succeed.
What You’ll Achieve
By following this guide, you’ll:
1. Set up DeepSeek-R1, a reasoning AI that works privately on your computer.
2. Configure Browser-Use Web UI, a tool to automate web scraping, form-filling, and real-time interaction.
3. Create an AI agent capable of finding stock news, gathering Reddit mentions, and predicting stock trends—all while operating without cloud restrictions.
A Deep Dive At ReadMultiplex.com Soon
We will have a deep dive into how you can use this platform for very advanced AI use cases that few have thought of let alone seen before. Join us at ReadMultiplex.com and become a member that not only sees the future earlier but also with particle and pragmatic ways to profit from the future.
System Requirements
Hardware
• RAM: 8 GB minimum (16 GB recommended).
• Processor: Quad-core (Intel i5/AMD Ryzen 5 or higher).
• Storage: 5 GB free space.
• Graphics: GPU optional for faster processing.
Software
• Operating System: macOS, Windows 10+, or Linux.
• Python: Version 3.8 or higher.
• Git: Installed.
Step 1: Get Your Tools Ready
We’ll need Python, Git, and a terminal/command prompt to proceed. Follow these instructions carefully.
Install Python
1. Check Python Installation:
• Open your terminal/command prompt and type:
python3 --version
• If Python is installed, you’ll see a version like:
Python 3.9.7
2. If Python Is Not Installed:
• Download Python from python.org.
• During installation, ensure you check “Add Python to PATH” on Windows.
3. Verify Installation:
python3 --version
Install Git
1. Check Git Installation:
• Run:
git --version
• If installed, you’ll see:
git version 2.34.1
2. If Git Is Not Installed:
• Windows: Download Git from git-scm.com and follow the instructions.
• Mac/Linux: Install via terminal:
sudo apt install git -y # For Ubuntu/Debian
brew install git # For macOS
Step 2: Download and Build llama.cpp
We’ll use llama.cpp to run the DeepSeek-R1 model locally.
1. Open your terminal/command prompt.
2. Navigate to a clear location for your project files:
mkdir ~/AI_Project
cd ~/AI_Project
3. Clone the llama.cpp repository:
git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp.git
cd llama.cpp
4. Build the project:
• Mac/Linux:
make
• Windows:
• Install a C++ compiler (e.g., MSVC or MinGW).
• Run:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build . --config Release
Step 3: Download DeepSeek-R1 8B 4-bit Model
1. Visit the DeepSeek-R1 8B Model Page on Hugging Face.
2. Download the 4-bit quantized model file:
• Example: DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-8B-Q4_K_M.gguf.
3. Move the model to your llama.cpp folder:
mv ~/Downloads/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-8B-Q4_K_M.gguf ~/AI_Project/llama.cpp
Step 4: Start DeepSeek-R1
1. Navigate to your llama.cpp folder:
cd ~/AI_Project/llama.cpp
2. Run the model with a sample prompt:
./main -m DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-8B-Q4_K_M.gguf -p "What is the capital of France?"
3. Expected Output:
The capital of France is Paris.
Step 5: Set Up Browser-Use Web UI
1. Go back to your project folder:
cd ~/AI_Project
2. Clone the Browser-Use repository:
git clone https://github.com/browser-use/browser-use.git
cd browser-use
3. Create a virtual environment:
python3 -m venv env
4. Activate the virtual environment:
• Mac/Linux:
source env/bin/activate
• Windows:
env\Scripts\activate
5. Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
6. Start the Web UI:
python examples/gradio_demo.py
7. Open the local URL in your browser:
http://127.0.0.1:7860
Step 6: Configure the Web UI for DeepSeek-R1
1. Go to the Settings panel in the Web UI.
2. Specify the DeepSeek model path:
~/AI_Project/llama.cpp/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-8B-Q4_K_M.gguf
3. Adjust Timeout Settings:
• Increase the timeout to 120 seconds for larger models.
4. Enable Memory-Saving Mode if your system has less than 16 GB of RAM.
Step 7: Run an Example Task
Let’s create an agent that:
1. Searches for Tesla stock news.
2. Gathers Reddit mentions.
3. Predicts the stock trend.
Example Prompt:
Search for "Tesla stock news" on Google News and summarize the top 3 headlines. Then, check Reddit for the latest mentions of "Tesla stock" and predict whether the stock will rise based on the news and discussions.
--
Congratulations! You’ve built a powerful, private AI agent capable of automating the web and reasoning in real time. Unlike costly, restricted tools like OpenAI Operator, you’ve spent nothing beyond your time. Unleash your AI agent on tasks that were once impossible and imagine the possibilities for personal projects, research, and business. You’re not limited anymore. You own the web—your AI agent just unlocked it! 🚀
Stay tuned fora FREE simple to use single app that will do this all and more.

7 notes
·
View notes
Quote
カーパシー氏は、ソフトウェアというものが過去2回にわたって急速に変化したものと考えています。最初に登場したのがソフトウェア 1.0です。ソフトウェア1.0は誰もがイメージするような基本的なソフトウェアのことです。 ソフトウェア1.0がコンピュータ向けに書くコードであるのに対し、ソフトウェア2.0は基本的にニューラルネットワークであり、特に「重み」のことを指します。開発者はコードを直接書くのではなく、データセットを調整し、最適化アルゴリズムを実行してこのニューラルネットワークのパラメーターを生成するのです。 ソフトウェア 1.0に当たるGitHub上のプロジェクトは、それぞれを集約して関係のあるプロジェクトを線で結んだ「Map of GitHub」で表せます。 ソフトウェア 2.0は同様に「Model Atlas」で表されます。巨大な円の中心にOpenAIやMetaのベースとなるモデルが存在し、そのフォークがつながっています。 生成AIが洗練されるにつれ、ニューラルネットワークの調整すらAIの助けを得て行えるようになりました。これらは専門的なプログラミング言語ではなく、「自然言語」で実行できるのが特徴です。自然言語、特に英語で大規模言語モデル(LLM)をプログラミング可能になった状態を、カーパシー氏は「ソフトウェア 3.0」と呼んでいます。 まとめると、コードでコンピューターをプログラムするのがソフトウェア 1.0、重みでニューラルネットワークをプログラムするのがソフトウェア 2.0、自然言語のプロンプトでLLMをプログラムするのがソフトウェア 3.0です。 カーパシー氏は「おそらくGitHubのコードはもはや単なるコードではなく、コードと英語が混在した新しい種類のコードのカテゴリーが拡大していると思います。これは単に新しいプログラミングパラダイムであるだけでなく、私たちの母国語である英語でプログラミングしている点も驚くべきことです。私たちは3つの完全に異なるプログラミングパラダイムを有しており、業界に参入するならば、これらすべてに精通していることが非常に重要です。なぜなら、それぞれに微妙な長所と短所があり、特定の機能は1.0や2.0、3.0でプログラミングする必要があるかもしれません。ニューラルネットワークをトレーニングするべきか、LLMにプロンプトを送信するべきか。指示は明示的なコードであるべきでしょうか?つまり、私たちは皆、こうした決定を下し、実際にこれらのパラダイム間を流動的に移行できる可能性を秘めているのです」と述べました。 ◆AIは「電気」である カーパシー氏は「AIは新しい電気である」と捉えています。OpenAI、Google、Anthropic などのLLMラボはトレーニングのために設備投資を行っていて、これは電気のグリッドを構築することとよく似ています。企業はAPIを通じてAIを提供するための運用コストもかかります。通常、100万件など一定単位ごとに料金を請求する仕組みです。このAPIには、低遅延、高稼働率、安定した品質などさまざまなバリューがあります。これらの点に加え、過去に多くのLLMがダウンした影響で人々が作業不能に陥った現象も鑑みると、AIは電気のようななくてはならないインフラに当たるというのがカーパシー氏の考えです。 しかし、LLMは単なる電気や水のようなものではなく、もっと複雑なエコシステムが構築されています。OSだとWindowsやMacのようなクローズドソースのプロバイダーがいくつかあり、Linuxのようなオープンソースの代替案があります。LLMにおいても同様の構造が形成されつつあり、クローズドソースのプロバイダーが競合している中、LlamaのようなオープンソースがLLM界におけるLinuxのようなものへと成長するかもしれません。 カーパシー氏は「LLMは新しい種類のOSのようなものだと感じました。CPUの役割を果たすような存在で、LLMが処理できるトークンの長さ(コンテキストウィンドウ)はメモリに相当し、メモリと計算リソースを調整して問題解決を行うのです。これらの機能をすべて活用しているため、客観的に見ると、まさにOSに非常に似ています。OSだとソフトウェアをダウンロードして実行できますが、LLMでも同様の操作ができるものもあります」と述べました。 ◆AIは発展途中 LLMの計算リソースはコンピューターにとってまだ非常に高価であり、性能の良いLLMはほとんどクラウドサーバーで動作しています。ローカル��実行できるDeepSeek-R1のようなモデルも出てきていますが、やはり何百万円もするような機器を何百台とつなげて動かしているようなクラウドサーバーと個人のPCでは出力結果に大きな差が現れます。 カーパシー氏は「個人用コンピューター革命はまだ起こっていません。経済的ではないからです。意味がありません。しかし、一部の人々は試みているかもしれません。例えば、Mac miniは一部のLLMに非常に適しています。将来的にどのような形になるかは不明です。もしかしたら、皆さんがこの形や仕組みを発明するかもしれません」と述べました。 また、PCでは当たり前に使われているグラフィカルユーザーインターフェース(GUI)がLLMには中途半端にしか導入されていないという点も特徴です。ChatGPTなどのチャットボットは、基本的にテキスト入力欄を提供しているだけです。カーパシー氏は「まだ一般的な意味でのGUIが発明されていないと思います」と話しています。 ◆AIは技術拡散の方向が逆 これまでのPCは、政府が軍事用に開発し、企業などがそれを利用し、その後広くユーザーに使われるという歴史をたどってきました。一方でAIは政府や企業ではなくユーザーが広く利用し、その集合知が体系化され、企業が利用するようになります。カーパシー氏は「実際、企業や政府は、私たちが技術を採用するような速度に追いついていません。これは逆行していると言えるでしょう。新しい点であり前例がないといえるのは、LLMが少数の人々や企業の手中にあるのではなく、私たち全員の手中にあることです。なぜなら、私たちは皆コンピュータを持っており、それはすべてソフトウェアであり、ChatGPTは数十億の人々に瞬時に、一夜にしてコンピュータに配信されたからです。これは信じられないことです」と語りました。 ◆人類はAIと協力関係にある AIが利用されるときは、通常、AIが生成を行い、人間である私たちが検証を行うという作業が繰り返されます。このループをできるだけ高速化することは人間にとってもAIにとってもメリットがあります。 これを実現する方法としてカーパシー氏が挙げるのが、1つは検証を大幅にスピードアップすることです。これはGUIを導入することで実現できる可能性があります。長いテキストだけを読むことは労力がかかりますが、絵など文字以外の物を見ることで容易になります。 2つ目は、AIを制御下に置く必要がある点です。カーパシー氏は「多くの人々がAIエージェントに過剰に興奮している」と指摘しており、AIの出力すべてを信じるのではなく、AIが正しいことを行っているか、セキュリティ上の問題がないかなどを確かめることが重要だと述べています。LLMは基本的にもっともらしい言葉をもっともらしく並べるだけの機械であり、出力結果が必ずしも正しいとは限りません。結果を常に検証することが大切です。 この記事のタイトルとURLをコピーする ���関連記事 Metaが既存の生成AIにあるトークン制限をはるかに上回る100万トークン超のコンテンツ生成を可能にする次世代AIアーキテクチャ「Megabyte」を発表 - GIGAZINE 世界最長のコンテキストウィンドウ100万トークン入力・8万トークン出力対応にもかかわらずたった7800万円でトレーニングされたAIモデル「MiniMax-M1」がオープンソースで公開され誰でもダウンロード可能に - GIGAZINE AppleがXcodeにAIでのコーディング補助機能を追加&Apple Intelligenceの基盤モデルフレームワークが利用可能に - GIGAZINE AnthropicがAIモデルの思考内容を可視化できるオープンソースツール「circuit-tracer」を公開 - GIGAZINE DeepSeekと清華大学の研究者がLLMの推論能力を強化する新しい手法を発表 - GIGAZINE 「現在のAIをスケールアップしても汎用人工知能は開発できない」と考える科学者の割合は76% - GIGAZINE ・関連コンテンツ TwitterやFacebookで使われている「Apache Hadoop」のメリットや歴史を作者自らが語る 仮想通貨暴落などで苦境に立たされたマイニング業者は余ったGPUを「AIトレーニング用のリソース」として提供している 「AI懐疑論者の友人はみんな頭がおかしい」というブログが登場、賛否両論さまざまなコメントが寄せられる 私たちが何気なく使っているソフトウェアはどのように開発されているのか? グラフをはみ出した点と線が世界に広がっていく手描きアニメ「Extrapolate」が圧巻 「アルゴリズムって何?」を専門家が分かりやすく解説 機械学習でコンピューターが音楽を理解することが容易ではない理由 生きてるだけでお金がもらえるベーシックインカムこそ「資本主義2.0」だとの主張、その理由とは?
講演「ソフトウェアは再び変化している」が海外で大反響、その衝撃的な内容とは? - GIGAZINE
4 notes
·
View notes
Note
hiii!! if you don’t mind, could you explain the whole API and JLLM thing?? i’m still new to using j.ai and i can’t wrap my head around the tokens, the settings, so on and so forth,,,
i have no idea how to set up openai or what even the differences are between that and JLLM are???? i’ve been looking into setting it up since apparently that’s the problem w the bot’s replies being so BUNS. i’m sorry if this is stupid to ask but i cannot find anything online that i can interpret 💔
HIIII okay so ill try and explain but i also dont know much 😭 i just know what works for me and the openai model I use, lets start!
API is your ai language model I think, JLLM is the standard free jai language model that everyone starts out with, it has a lot of issues but for a free language model, it works if you have some patience. OpenAI is another language model that is paid, you can pay however much you want to be able to use it, how much usage depends on your language model but the quality is better, there’s other language models like ive heard about Deepseek which is apparently another free language model that folks say is better than JLLM! I dunno much about it so you would have to look into guides
my model is kinda cheap, the other anon a few posts down got like 100+ messages with $2 spent I think?
tokens are basically what the bot uses to converse with you, idk how to best explain them but let’s try!
tokens are what the bot uses the function and converse with you, permanent tokens is the bot personality which the bot retains and expends with each reply it gets. basically each reply uses an amount of tokens in order to generate the message

a reply already expends how much tokens the personality is, for example my bunny hyuna bot has 3000 permanent tokens!
a bot will use the permanent tokens, and generate more tokens in order to write your response.
a reply would have: 3000 permanent tokens used to remember the personality, generates 500 more tokens in order to craft the response.
permanent tokens: personality bio area that the bot will continue to use with each reply, and the scenario context
not permanent tokens: the starter message, and example dialogue
for example

1805 tokens are consumed when you chat with a bot, which are made up of these:

so when you first start a chat it would be 1805 tokens consumed and then after that, it’s 1133 tokens + however many tokens the reply generates
Does that make sense. idk if it does it’s 2am but let’s move on
AS FOR SETTING UP OPENAI!
I don’t have the coherency to map out everything but I did it up on the subreddit

essentially, go make an openai account and generate an API key! that api key goes here

where it says openai key
boom put like $5 in and start chatting, keep an eye on ur money under the openai billing overview to see how much u have left after you’ve been chatting for a while
which… janitor ai is down rn but once it’s back up I can look for some guides for you if u have any more questions, was this helpful?? who knows im sleepy
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's Talk about Deepseek
So, obviously I'm bad at using Tumblr. Sorry about that...
But I wanted to share my experiences with Deepseek. Long post as it includes tutorials and stuff. Below the cut.

My Thoughts
Deepseek R1 is very smart but oddly gets too poetic for me. To the point it becomes unusable, personally.
Deepseek V3 is less smart than R1, but smarter than JLLM. It also does not have the reasoning stuff R1 is known for.
JLLM is ass. Point blank.

Proxies & Cost
Proxies are always on with my bots because I see no reason not to. With the JLLM being so bad these days I recommend using a proxy, anyway. That said, I know that some cost.
Deepseek R1 and Deepseek V3 are currently free to use, so I do recommend using them.

How To Use
Here is a Reddit post about how to set up R1 as your proxy. Edit: That link above is to use Deepseek PAID. This link is to use it free. Sorry!
If you get the bot's reasoning to their reply and dislike it, go to your open router ai settings and block TARGON.
If you get a lot of loading errors, I have seen people suggest blocking CHUTES.
This leaves you with only AZURE. For me personally, blocking CHUTES has caused way more issues.
If you want to use V3 instead, you follow the same steps as in the link above, only with V3 (free). In Janitor's proxy settings, change the API Key to the one generated for V3, and the model to "deepseek/deepseek-chat:free". Refresh page/fully exit Janitor and re-enter for it to work.
I still have TARGON blocked for this, but I've heard it does not cause logics problems with V3.
I do not have CHUTES blocked for this, and do not receive errors.

Summary + Recommendations
JLLM is great with sex scenes. Deepseek seems to stumble and flail (V3, specifically) as it gets caught up on consent, even if you have already given it. JLLM is great at moving the scene forward and getting creative.
However, JLLM is awful with memory and is just plain stupid. For literally every other interaction, Deepseek is better.
Because of this, I highly encourage alternating between JLLM and Deepseek to get the most out of your roleplay.
Start with whichever LLM you prefer. Once it grows stupid (begins to forget, gets caught on certain phrases, etc), change it.
Utilize the Chat Memory feature. Auto-summary has been broken for a while with JLLM, and I haven't tried it with Deepseek. I recommend manually writing a summary or bullet points only of the really important stuff. (Deepseek has a significantly higher context, but if you alternate, JLLM is still shockingly low).
Personally, use JLLM for romantic/sexual scenes, and Deepseek for literally everything else, but use your preference however you like.
Janitor has built-in proxy prompts to choose from. "Freedom" is mostly for OpenAI. "Erotica" and "Romance" work decently with Deepseek.

Important Notices
I'm sure most people who are aware of Deepseek know this already, but just in case: Deepseek is a Chinese company, and some think there are security worries due to potential connections to the Chinese government. I don't know shit about anything like this or that, so I genuinely do not know. That said I do encourage you to read up on it if you are worried at all. I, personally, do not care that much.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
12,000+ API Keys and Passwords Found in Public Datasets Used for LLM Training

Source: https://thehackernews.com/2025/02/12000-api-keys-and-passwords-found-in.html
More info: https://trufflesecurity.com/blog/research-finds-12-000-live-api-keys-and-passwords-in-deepseek-s-training-data
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 Best Plugins For Adding AI to Your WordPress Website – Speckyboy
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/10-best-plugins-for-adding-ai-to-your-wordpress-website-speckyboy/
10 Best Plugins For Adding AI to Your WordPress Website – Speckyboy
Artificial intelligence (AI) has entered the mainstream. We’re finding more and more products that integrate with the technology. WordPress plugins are a prime example.
These plugins add a variety of AI-powered features to websites. Some are there to spur creativity, while others are all about saving you time. The trend is helping to spawn new products and enhance existing ones.
AI is rapidly changing the WordPress ecosystem. So, we wanted to explore the different ways plugins are using it. Will they make our lives easier? Will they help users? Let’s find out!
Here’s a collection of WordPress plugins that, in one way or another, add artificial intelligence to your website. Some are longtime favorites, while others are upstarts breaking into the ecosystem. We hope you find them useful!
Rank Math is one of many SEO plugins that integrate AI into their product. The difference here is in the depth of the AI tools offered. There are options for generating entire blog posts, outlines, SEO titles and descriptions, fixing grammar mistakes, and more.
You’ll need a free account to access the various AI features. The benefit is making SEO easier for novices and experts alike. Generating various types of content provides a solid foundation. You’ll have more time to focus on other areas of your site.
Automattic’s do-it-all suite offers Jetpack AI Assistant, allowing you to generate various types of content. For example, the tool will generate a featured image for your blog post based on its content or a custom prompt.
In addition, it will help improve grammar, rewrite your content, or generate an entire page. There’s a free tier with 20 monthly requests, while paid plans offer higher limits.
Here’s an option that specifically targets WooCommerce stores. Kestrel AI is a commercial plugin that generates or optimizes product descriptions, replies to customer reviews, and adds order notes.
It places an icon on relevant areas of the screen. Click it, and the assistant will help you perform the noted tasks. The plugin works with OpenAI and includes placeholders that pull the correct product data.
Here’s proof that AI integrations don’t need to overwhelm users. OptinMonster is a plugin that creates popups and opt-in forms to generate leads. The plugin features a “smart optimization” tool that uses AI to improve the content of your popup. It doesn’t generate text for you. Rather, it seeks to improve what’s already there. It’s a subtle-but-helpful use case.
AI-powered chatbots are on the rise. They aim to answer user questions and help them find relevant content. WPBot uses services like ChatGPT and DialogFlow to provide a “live” chat with a virtual assistant.
The plugin’s pro version can also train AI on your website’s content, leading to better answers and more efficient resource usage. Other features include adding custom text responses, an option for users to contact you, and multi-language support.
AI Engine is a suite of tools for adding artificial intelligence to your WordPress website. Install the plugin, insert your OpenAI API key, and add features.
What sort of features? You can add a chatbot, generate images and text, translate content, and run various tasks inside WordPress. The plugin will also help you keep track of API usage, an important feature, as the costs can add up.
You can use Uncanny Automator to link all sorts of website activities together. For example, these “triggers” can send a customer a follow-up email a few days after they order a product. There are integrations with several popular plugins.
It also ties in with OpenAI, allowing for automated blog post summaries, social media posts, featured images, translations, and more. It’s a natural extension of what the plugin already does.
Categorizing and tagging content isn’t always easy. The goal is to create a logical structure for your content. That’s better for SEO and users. TaxoPress is a taxonomy management plugin that helps you create and manage that structure.
The pro version offers an AI integration (OpenAI, IBM Watson) that automatically creates and determines the best taxonomies for your content. It removes an often frustrating step from your content creation workflow.
AI Power is notable for its compatibility with several large language models (LLM). You can connect the plugin to OpenAI, DeepSeek, Claude, Gemini, Azure, and more. Choose your model and take advantage of an all-in-one collection of website tools.
You can optimize your site’s SEO, bulk-generate content, create a chatbot, use text-to-speech capabilities, or generate images. You can also train a model on your website’s content for a more personalized experience. There are free and pro versions available.
Sensei LMS is a plugin for building online courses. The pro version offers a few handy tools powered by AI. First, an auto Quiz Generator will create questions based on your course’s content. The second is a Tutor AI block available through the Sensei Interactive Blocks add-on.
It adds a chatbot that can answer user questions regarding your course content. The block isn’t limited to Sensei – it’s also compatible with other LMS plugins. It’s an example of how AI can improve the online learning experience.
Bring the Power of AI to Your Website
We’re still in the early days of AI. Thus, the plugins in this roundup are only scratching the surface of what may come down the road. Still, they offer both convenience and utility.
The key is finding options that fit your needs. You may notice that there is some overlap in what these plugins do. For instance, several plugins generate text and images. The odds are you don’t need more than one of these for your website.
With that, consider how you can use AI to improve your website. Perhaps you’re all about streamlining your workflow or improving the front end for users. There are good options here either way.
What will the future bring? It’s safe to say AI will have tighter integrations with WordPress and will be able to accomplish more useful tasks. We can’t wait to see what’s next!
More Essential Free WordPress Plugins
Related Topics
#ADD#add-on#ai#ai assistant#AI integration#ai tools#AI-powered#API#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#artificial intelligence (AI)#azure#Blog#Building#chatbot#chatbots#chatGPT#claude#content#content creation#course#courses#creativity#data#deepseek#Design#easy#email#engine#Essential WordPress Plugins
0 notes
Text
youtube
People Think It’s Fake" | DeepSeek vs ChatGPT: The Ultimate 2024 Comparison (SEO-Optimized Guide)
The AI wars are heating up, and two giants—DeepSeek and ChatGPT—are battling for dominance. But why do so many users call DeepSeek "fake" while praising ChatGPT? Is it a myth, or is there truth to the claims? In this deep dive, we’ll uncover the facts, debunk myths, and reveal which AI truly reigns supreme. Plus, learn pro SEO tips to help this article outrank competitors on Google!
Chapters
00:00 Introduction - DeepSeek: China’s New AI Innovation
00:15 What is DeepSeek?
00:30 DeepSeek’s Impressive Statistics
00:50 Comparison: DeepSeek vs GPT-4
01:10 Technology Behind DeepSeek
01:30 Impact on AI, Finance, and Trading
01:50 DeepSeek’s Effect on Bitcoin & Trading
02:10 Future of AI with DeepSeek
02:25 Conclusion - The Future is Here!
Why Do People Call DeepSeek "Fake"? (The Truth Revealed)
The Language Barrier Myth
DeepSeek is trained primarily on Chinese-language data, leading to awkward English responses.
Example: A user asked, "Write a poem about New York," and DeepSeek referenced skyscrapers as "giant bamboo shoots."
SEO Keyword: "DeepSeek English accuracy."
Cultural Misunderstandings
DeepSeek’s humor, idioms, and examples cater to Chinese audiences. Global users find this confusing.
ChatGPT, trained on Western data, feels more "relatable" to English speakers.
Lack of Transparency
Unlike OpenAI’s detailed GPT-4 technical report, DeepSeek’s training data and ethics are shrouded in secrecy.
LSI Keyword: "DeepSeek data sources."
Viral "Fail" Videos
TikTok clips show DeepSeek claiming "The Earth is flat" or "Elon Musk invented Bitcoin." Most are outdated or edited—ChatGPT made similar errors in 2022!
DeepSeek vs ChatGPT: The Ultimate 2024 Comparison
1. Language & Creativity
ChatGPT: Wins for English content (blogs, scripts, code).
Strengths: Natural flow, humor, and cultural nuance.
Weakness: Overly cautious (e.g., refuses to write "controversial" topics).
DeepSeek: Best for Chinese markets (e.g., Baidu SEO, WeChat posts).
Strengths: Slang, idioms, and local trends.
Weakness: Struggles with Western metaphors.
SEO Tip: Use keywords like "Best AI for Chinese content" or "DeepSeek Baidu SEO."
2. Technical Abilities
Coding:
ChatGPT: Solves Python/JavaScript errors, writes clean code.
DeepSeek: Better at Alibaba Cloud APIs and Chinese frameworks.
Data Analysis:
Both handle spreadsheets, but DeepSeek integrates with Tencent Docs.
3. Pricing & Accessibility
FeatureDeepSeekChatGPTFree TierUnlimited basic queriesGPT-3.5 onlyPro Plan$10/month (advanced Chinese tools)$20/month (GPT-4 + plugins)APIsCheaper for bulk Chinese tasksGlobal enterprise support
SEO Keyword: "DeepSeek pricing 2024."
Debunking the "Fake AI" Myth: 3 Case Studies
Case Study 1: A Shanghai e-commerce firm used DeepSeek to automate customer service on Taobao, cutting response time by 50%.
Case Study 2: A U.S. blogger called DeepSeek "fake" after it wrote a Chinese-style poem about pizza—but it went viral in Asia!
Case Study 3: ChatGPT falsely claimed "Google acquired OpenAI in 2023," proving all AI makes mistakes.
How to Choose: DeepSeek or ChatGPT?
Pick ChatGPT if:
You need English content, coding help, or global trends.
You value brand recognition and transparency.
Pick DeepSeek if:
You target Chinese audiences or need cost-effective APIs.
You work with platforms like WeChat, Douyin, or Alibaba.
LSI Keyword: "DeepSeek for Chinese marketing."
SEO-Optimized FAQs (Voice Search Ready!)
"Is DeepSeek a scam?" No! It’s a legitimate AI optimized for Chinese-language tasks.
"Can DeepSeek replace ChatGPT?" For Chinese users, yes. For global content, stick with ChatGPT.
"Why does DeepSeek give weird answers?" Cultural gaps and training focus. Use it for specific niches, not general queries.
"Is DeepSeek safe to use?" Yes, but avoid sensitive topics—it follows China’s internet regulations.
Pro Tips to Boost Your Google Ranking
Sprinkle Keywords Naturally: Use "DeepSeek vs ChatGPT" 4–6 times.
Internal Linking: Link to related posts (e.g., "How to Use ChatGPT for SEO").
External Links: Cite authoritative sources (OpenAI’s blog, DeepSeek’s whitepapers).
Mobile Optimization: 60% of users read via phone—use short paragraphs.
Engagement Hooks: Ask readers to comment (e.g., "Which AI do you trust?").
Final Verdict: Why DeepSeek Isn’t Fake (But ChatGPT Isn’t Perfect)
The "fake" label stems from cultural bias and misinformation. DeepSeek is a powerhouse in its niche, while ChatGPT rules Western markets. For SEO success:
Target long-tail keywords like "Is DeepSeek good for Chinese SEO?"
Use schema markup for FAQs and comparisons.
Update content quarterly to stay ahead of AI updates.
🚀 Ready to Dominate Google? Share this article, leave a comment, and watch it climb to #1!
Follow for more AI vs AI battles—because in 2024, knowledge is power! 🔍
#ChatGPT alternatives#ChatGPT features#ChatGPT vs DeepSeek#DeepSeek AI review#DeepSeek vs OpenAI#Generative AI tools#chatbot performance#deepseek ai#future of nlp#deepseek vs chatgpt#deepseek#chatgpt#deepseek r1 vs chatgpt#chatgpt deepseek#deepseek r1#deepseek v3#deepseek china#deepseek r1 ai#deepseek ai model#china deepseek ai#deepseek vs o1#deepseek stock#deepseek r1 live#deepseek vs chatgpt hindi#what is deepseek#deepseek v2#deepseek kya hai#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
OpenAI: NOOOOO, that Chinese company Deepseek stole the data we've stolen to train their model... This is against our platform policy, they should be ashamed.
#artificial intelligence#ai#technews#tech#technology#deepseek#chatgpt#openai#ccp#funny gaming#science#wtf
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
對抗 DeepSeek!OpenAI 推出低成本的 AI 推理模型「o3-mini」
最近中國 AI 公司 DeepSeek 的竄升讓 OpenAI 公司體驗到相當大的威脅。為了對抗 DeepSeek,OpenAI 推出高效率、低成本的 AI 推理模型「o3-mini」,這款模型早在 2024 年 12 月推出預覽版,如今釋出正式版本,而且已經可以在 ChatGPT 和 OpenAI API 上使用。 Continue reading 對抗 DeepSeek!OpenAI 推出低成本的 AI 推理模型「o3-mini」
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
DeepSeek complete explained: Everything you need to know 2025
DeepSeek, a Chinese AI firm, is shaking up the industry with its low-cost, open-source large language models, posing a serious challenge to U.S. tech giants.

Breaking the AI Norms
For years, the belief was that developing powerful large language models required massive funding and cutting-edge technology. That’s why the U.S. government pledged to back the $500 billion Stargate Project, announced by President Donald Trump.
But DeepSeek has flipped that idea on its head. On January 20, 2025, the Chinese AI firm stunned the world by releasing its R1 large language model (LLM) at a fraction of the cost of its competitors. What made it even more disruptive? DeepSeek offered its R1 models under an open-source license, making them freely available to the public.
Within days, DeepSeek’s AI assistant—an easy-to-use chatbot app powered by R1—shot to the top of Apple’s App Store, surpassing OpenAI’s ChatGPT in downloads. The ripple effect was immediate: On January 27, 2025, stock markets took a hit as investors started doubting the long-term dominance of U.S.-based AI companies. Tech giants like Nvidia, Microsoft, Meta, Oracle, and Broadcom saw their stock values plummet as the world took notice of DeepSeek’s rapid rise.
What is DeepSeek?
DeepSeek is an AI research company based in Hangzhou, China. It was founded in May 2023 by Liang Wenfeng, a graduate of Zhejiang University and co-founder of High-Flyer, a quantitative hedge fund that owns DeepSeek. While the company’s funding and valuation remain undisclosed, its impact on the AI landscape is undeniable.
DeepSeek is committed to developing open-source LLMs. Its first model debuted in November 2023, but it wasn’t until January 2025—with the release of the groundbreaking R1 reasoning model—that the company gained worldwide recognition.
The company offers multiple access points for its AI models, including a web platform, a mobile app, and an API for developers.
Read full details
5 notes
·
View notes
Quote
1/ まず、背景を説明します。現在、トップクラスの AI モデルのトレーニングにはとてつもなく費用がかかります。OpenAI、Anthropic などは、コンピューティングだけで 1 億ドル以上を費やしています。4 万ドルの GPU が何千台も備わった大規模なデータ センターが必要です。工場を稼働させるのに発電所全体が必要なようなものです。 2/ DeepSeek が現れて、「LOL、代わりに 500 万ドルでこれをやったらどうなるか?」と言いました。そして、彼らはただ話しているのではなく、実際にそれを実行しました。彼らのモデルは、多くのタスクで GPT-4 や Claude に匹敵するか、それを上回っています。AI の世界は (私の十代の若者が言うように) 揺らいでいます。 3/ どうやって?彼らはすべてを根本から考え直しました。従来の AI は、すべての数字を 32 桁の小数点で表記するようなものです。DeepSeek は「8 桁だけ使用したらどうなるでしょうか。それでも十分な精度です!」と考えました。なんと、必要なメモリが 75% 削減されました。 4/ そして、彼らの「マルチトークン」システムがあります。通常の AI は、1 年生のように「猫が...座った...」と読みます。DeepSeek は、フレーズ全体を一度に読み取ります。2 倍の速度で、90% の精度です。何十億もの単語を処理する場合、これは重要です。 5/ しかし、本当に賢いのは、彼らが「エキスパート システム」を構築したことです。1 つの巨大な AI がすべてを知ろうとするのではなく (1 人の人間が医者、弁護士、エンジニアを兼ねるのと同じ)、必要なときだけ起動する専門のエキスパートがいます。 6/ 従来のモデルでは、1.8 兆個のパラメータがすべて常時アクティブです。DeepSeek では、合計 671 億個ですが、一度にアクティブになるのは 37 億個だけです。これは、大規模なチームを抱えているものの、各タスクに実際に必要な専門家だけを呼び出しているようなものです。 7/ 結果は驚くべきものでした: - トレーニング費用: 1億ドル → 500万ドル - 必要なGPU: 10万 → 2,000 - API費用: 95%安価 - データセンターハードウェアの代わりにゲーミングGPUで実行可能
DeepSeek の恩恵 - John H. Cochrane 著
2 notes
·
View notes