#Candlestick pattern for bearish reversal
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to Trade the Bearish Engulfing Pattern: Complete Guide with Strategies and Examples
Candlestick patterns are powerful tools in the arsenal of a technical trader. Among the most reliable reversal patterns is the Bearish Engulfing Pattern—a strong signal that can hint at the start of a downward trend. In this guide, we’ll explain how to identify this pattern, why it works, and most importantly, how to trade it effectively with multiple strategies and examples. 📌 What is a Bearish…
#Bearish candle formation#Bearish engulfing candlestick pattern explained#Bearish Engulfing Pattern#Bearish engulfing pattern trading strategy#Bearish reversal pattern#Bearish trend confirmation#Can you trade bearish engulfing in forex?#Candlestick pattern for bearish reversal#candlestick patterns#Confirmation signals for bearish engulfing#EMA confluence with candlestick patterns#Engulfing candle trading rules#Entry and exit with candlestick patterns#Forex bearish engulfing strategy#How to confirm a bearish engulfing signal?#How to trade the bearish engulfing pattern#Is the bearish engulfing pattern reliable?#learn technical analysis#Multi-timeframe candlestick pattern strategy#Price action trading setup#Reversal Candlestick Patterns#Risk management for pattern trading#stock markets#Stock trading with bearish engulfing pattern#support and resistance levels#Swing trading with bearish engulfing#technical analysis#Trading bearish engulfing with moving averages#Trading Strategies#Using bearish engulfing with RSI
0 notes
Text
10 Candlestick Patterns for Effective Trading
Candlestick patterns are a powerful tool for traders to analyze price movements and predict future market behavior. Developed in Japan over 300 years ago, these patterns are widely used in modern technical analysis. This article will explore ten essential candlestick patterns that can help traders make informed decisions and enhance their trading strategies. What are Candlestick…
#Bearish Patterns#Bullish Patterns#Candlestick Patterns#Downtrend#Entry and Exit Points#Forex#Forex Traders#Forex Trading#Market Reversal#Price Movements#Risk Management#Stop-Loss#Take-Profit#Technical Analysis#Trading Psychology#Trading Strategies#Trading Strategy#Trend Direction#Trend Identification#Uptrend
1 note
·
View note
Text
Unlock the Secrets of Trading with Top Chart Patterns! Explore the world of chart patterns with Funded Traders Global. From understanding the basics of technical analysis to recognizing common chart patterns like head and shoulders, double tops, and flags, our blog equips you with the knowledge to enhance your trading skills. Discover advanced patterns like pennants, wedges, and harmonic patterns, and gain practical tips for effective trading. Improve your risk management, pinpoint entry and exit points, and combine chart patterns with technical indicators. Start your journey towards trading success today with Funded Traders Global!
#Advanced Chart Pattern#and Descending Triangles#and mini trading#Ascending#Basics of Technical Analysis#Benefits of Recognizing in Chart Pattern#Bullish and Bearish Flags Pattern#candlestick#candlestick Pattern#career in forex trading#chart patterns#classic reversal pattern#common chart patterns#cup and handle pattern#Double top and double bottom patterns#drawdown#financial markets#Forex trading financial freedom#FTG#ftg prop firm#ftg trading#Funded Traders Global#Gaps#Harmonic Patterns#Head and Shoulders Pattern#how to scale into a forex trade#Macro#Master the Market with These Top Chart Patterns for Trading#mastering Forex trading#micro
0 notes
Link
#CandlestickAnalysis#candlestickpatterns#chartpatterns#ForexTrading#markettrends#MomentumTrading#priceaction#ReversalPatterns#riskmanagement#StockMarket#supportandresistance#technicalanalysis#TradingSignals#TradingStrategy#TrendContinuation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bitcoin, the leading cryptocurrency, has recently faced a significant downturn, trading around $56,697.32. Despite this bearish phase, there are signs of a potential rebound. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) stands at 28.41, indicating oversold conditions typically seen as buying opportunities. Candlestick patterns with long lower shadows suggest buying pressure at lower levels, hinting at a price reversal.
Influential analyst CryptoJack is optimistic, predicting Bitcoin will surpass $100,000 despite the current downturn. He believes Bitcoin is near its bottom, aligning with technical indicators suggesting an oversold market.
Market data from CoinMarketCap shows Bitcoin’s market cap at $1.12 trillion, a 2.63% increase in one day, while the 24-hour trading volume has decreased by 38.03% to $31.91 billion, indicating consolidation. Traders are cautious, but the oversold RSI and bullish patterns support the possibility of a rebound. Watching for signs of reversal could signal the start of a recovery phase.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
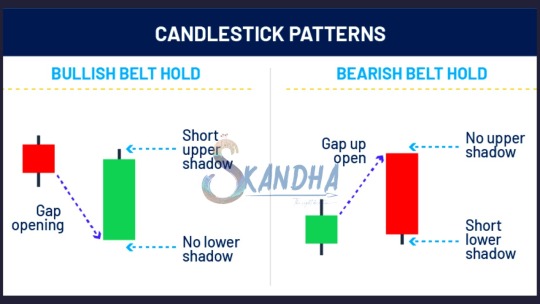
A belt hold pattern suggests that a trend may be reversing and indicates investor sentiment may have changed. When looking at them historically, there will often be a clear trend in one direction, followed by a clear trend in the other direction as the color of the candlestick changes.
There are two types of belt hold candlestick: one bullish and one bearish.
#skandhatrade #belthold #support #resistance #stock #chart #Trade #signal #patterns
#trend #Technicals #analysis #strategies #candlestick #priceaction #entry #supply #demand
To Learn More DM us
We Offer Paid Courses And Training Contact us Via
Email : [email protected]
https://forms.gle/8rWzz1gUuerxwVM49
Website: https://skandhatrade.com/
To Register for Learning:
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Inverted Hammer Pattern Explained: Spot Market Reversals Like a Pro
Are you spotting the right reversal signals in the market?
Understanding candlestick patterns can provide a critical edge in trading, especially when it comes to identifying potential trend reversals. One such pattern is the Inverted Hammer—a powerful single-candle formation that often signals a possible shift from bearish to bullish momentum. However, recognizing it isn’t enough. Traders must understand the psychology behind the candle, its context within a trend, and how to confirm its validity with other indicators.
In our latest article, we break down the Inverted Hammer Pattern in detail: how to spot it, what it really means, and how to use it effectively in your trading strategy.
Start making smarter trading decisions today.
Read the full guide here:
#CandlestickPatterns#TradingForBeginners#InvertedHammer#StockMarket#TechnicalAnalysis#PriceAction#SmartTrading
0 notes
Text
How to read candlestick charts and patterns for better trades?
Candlestick charts are a powerful tool for making better trading decisions. Each candle shows the open, high, low, and close price for a specific time frame. Patterns like Doji, Hammer, Engulfing, and Shooting Star can signal potential reversals or trend continuations.
To read them effectively:
Look for pattern confirmation with volume.
Understand bullish vs. bearish signals.
Combine candlestick analysis with support and resistance levels or indicators like RSI.
Learning to read these patterns takes practice and guided learning. At Empirical Academy, we offer hands-on training in technical analysis, including live candlestick chart reading.
📚 Learn to trade with clarity and confidence. 👉 Enroll now: https://www.empiricalacademy.net
0 notes
Text
Hanging Man Candlestick: A Professional’s Guide to Spotting Bearish Reversals
🕵️♂️ In the world of financial markets, every candlestick tells a story. For traders and investors, reading these stories is crucial to navigating the often tumultuous waters of stock trading. One such pattern that has long captured the attention of analysts is the Hanging Man, a formation that occasionally signals a potential shift in market sentiment. It might look unassuming at first glance,…
0 notes
Text
Mastering Indian Stock Market Trading & Investing: Technical Analysis for Smart Decisions

If you've ever found yourself staring at stock charts, wondering what those zigzag lines really mean or how seasoned traders predict market moves so accurately—it’s time to dive deep into the fascinating world of technical analysis.
Whether you're a beginner aiming to make your first trade or a budding investor who wants to understand market trends better, technical analysis is your gateway to reading the stock market like a pro. It’s not magic. It’s strategy—and with the right mindset, tools, and a bit of practice, anyone can learn it.
In this guide, we’ll explore what technical analysis is, how it's used in Indian stock market trading, and why mastering it can be a game-changer for your financial future.
What is Technical Analysis, Really?
At its core, technical analysis is about analyzing price movements and patterns. Instead of focusing on a company’s balance sheet or profits (which is fundamental analysis), technical analysis zooms in on stock charts, volume trends, support/resistance levels, and indicators like RSI, MACD, and moving averages.
Here’s the idea: history often repeats itself in the markets. Traders believe that past price movements can provide clues about future behavior.
But don’t worry—it’s not about memorizing hundreds of formulas. It’s about recognizing patterns, understanding market psychology, and using tools that are available to everyone.
Why is Technical Analysis Crucial in Indian Stock Market Trading?
India’s stock market, with major exchanges like NSE and BSE, is vibrant, fast-moving, and full of opportunities. With retail participation increasing and more young investors entering the scene, understanding technical analysis is not just a skill—it’s a competitive edge.
Here's why it matters:
📈 Volatility is Opportunity: Indian stocks often experience sharp movements. Technical analysis helps you time entries and exits better.
🔍 Helps Filter the Noise: News, opinions, and rumors? Technical charts let the price action speak for itself.
🕒 Perfect for Short-term & Swing Trading: Want to catch trends that last a few days or weeks? TA is your best friend.
💼 Complements Long-Term Investing: Even if you’re a long-term investor, knowing when to buy a fundamentally strong stock can greatly enhance returns.
Core Principles of Technical Analysis
To make smart decisions, you need a few essentials in your toolkit. Let’s break them down.
1. Price Discounts Everything
This is the first rule of technical analysis. Every known factor—earnings, news, expectations—is already reflected in the price.
2. Trends are Key
Markets move in trends: upward (bullish), downward (bearish), or sideways. Identifying the trend early can give you a head start.
3. History Tends to Repeat Itself
Humans drive the markets. Emotions like fear and greed lead to recurring price patterns.
Must-Know Tools and Indicators for Beginners
Learning technical analysis doesn’t mean staring blankly at complex graphs. Start with these basic tools:
🟢 Moving Averages (MA)
They smoothen price data to help you identify the trend. A simple 50-day and 200-day MA combo can reveal bullish or bearish signals.
🟣 Relative Strength Index (RSI)
A momentum indicator that tells you if a stock is overbought or oversold. It works on a scale of 0-100. Typically, above 70 means overbought; below 30 means oversold.
🔵 MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
Used to catch trend reversals. It gives crossover signals that many day traders live by.
🟡 Support and Resistance
Support is a level where buyers enter; resistance is where sellers dominate. Price tends to bounce between these zones.
🔴 Candlestick Patterns
Japanese candlesticks offer visual insights into market psychology. Patterns like Doji, Hammer, and Engulfing tell a story of potential reversals.
A Real-World Example: Let’s Analyze a Stock
Let’s say you’re looking at Infosys. You open the daily chart and notice:
The RSI is around 80 ➜ The stock might be overbought.
It’s near a resistance level it couldn’t cross twice before.
A bearish engulfing candle forms.
This is a potential short signal.
On the flip side, if the stock is near its 200-day MA, RSI is around 35, and a hammer pattern appears near support—you might consider buying.
The beauty of technical analysis? These setups repeat over time.
Day Trading vs Swing Trading vs Investing: How Does TA Fit?
✅ Day Trading
Entry and exit in the same day.
Requires strict discipline and quick decision-making.
TA is essential—especially 5-min, 15-min, hourly charts.
✅ Swing Trading
Positions held for days or weeks.
Based on short-to-medium-term trends.
Ideal for working professionals.
✅ Investing
Long-term horizon, but TA helps in timing your entry.
For example: Buying at a support level during a correction can improve returns significantly.
How to Start Learning Technical Analysis the Smart Way?
The internet is full of content, but not all of it is structured or beginner-friendly. If you’re serious about mastering it, choose a comprehensive, beginner-to-advanced course that focuses on the Indian stock market context.
We highly recommend starting with this Indian Stock Market Trading | Investing: Technical Analysis!! course. It’s perfect for beginners, filled with practical charting tips, live examples, and Indian stock-specific case studies.
Not only will it teach you chart reading, but you’ll also learn how to:
Use charting platforms effectively
Apply 20+ indicators in real-world scenarios
Build your trading strategy
Avoid beginner mistakes
Read volume like a pro
Whether you want to trade Bank Nifty, mid-cap stocks, or explore intraday and positional strategies, this course brings clarity and depth in a step-by-step format.
Common Mistakes New Traders Make (and How to Avoid Them)
Many new traders jump in with high hopes and little prep. Here’s how not to fall into the same traps:
❌ Trading Without a Plan: Always have entry, stop-loss, and target.
❌ Overusing Indicators: More isn’t better. Stick to 2–3 that suit your style.
❌ Ignoring Risk Management: Never risk more than 1–2% of your capital on a single trade.
❌ Letting Emotions Rule: Fear and greed are your biggest enemies.
Consistency comes from mindset, not just methods.
Building Your Trading System with Technical Analysis
Once you get the basics, build your own trading system—a repeatable strategy that aligns with your risk appetite.
Ask yourself:
What’s my trading style? (Scalping, Intraday, Positional)
What’s my entry signal? (Crossover, pattern, breakout)
What’s my stop-loss logic? (Fixed %, below support)
What are my exit rules? (Trailing stop, fixed reward ratio)
Test your system. Backtest it. Paper trade. And once it works—scale it.
Is Technical Analysis Foolproof?
No system is perfect. Technical analysis gives probabilities, not certainties. But when used correctly, it dramatically tilts the odds in your favor.
It's not about predicting the future. It's about reading the present clearly enough to make informed decisions.
That’s the edge that sets apart successful traders from the rest.
Final Thoughts: Why Now is the Best Time to Learn Technical Analysis
With rising retail participation in India’s stock market and easy access to free and paid charting tools, this is the perfect time to learn technical analysis.
Whether you're doing it to:
Create a side income,
Manage your investments better,
Or someday trade full-time,
Mastering technical analysis opens a whole new dimension in your financial journey.
And the best part? You don’t need a finance degree or fancy tools—just curiosity, a good course, and a willingness to learn.
Start your journey with confidence. Explore the Indian Stock Market Trading | Investing: Technical Analysis!! course today and take your first step toward smarter investing.
0 notes
Text
PCR Ratio vs Other Indicators: Why It Matters in Options Trading
In the world of trading and investing, understanding market sentiment can be just as important as analyzing technical charts or financial statements. One powerful tool traders use for this is the Put Call Ratio, often abbreviated as the PCR Ratio. This indicator plays a crucial role in options trading and can provide insights into potential market direction.
Understanding the Basics of PCR Ratio
The Put Call Ratio is a simple yet effective tool that compares the trading volume of put options to call options. The formula is:
PCR Ratio = Volume of Put Options / Volume of Call Options
This ratio is used to gauge the mood of the market participants—whether they are leaning bearish (put-heavy) or bullish (call-heavy).
A PCR Ratio greater than 1 implies that more puts are being traded than calls, often signaling bearish sentiment.
A PCR Ratio less than 1 indicates that more calls are being bought, typically suggesting bullish sentiment.
A PCR Ratio close to 1 signals a balanced market.
Why the Put Call Ratio Matters

The Put Call Ratio is not just a number. It reflects investor psychology. Many professional traders consider it a contrarian indicator, meaning if the PCR is too high, it might actually signal a potential bullish reversal, as the market may be oversold. On the flip side, a very low PCR could hint that investors are overly optimistic, which could lead to a correction.
How to Interpret PCR Ratio in Real-Time
Let’s say the PCR Ratio is 1.3. This means the number of put options traded is 30% higher than call options. At first glance, it might look like investors are pessimistic. However, if this high ratio is unusual compared to historical averages, traders may interpret this as an opportunity to go long, expecting a rebound.
Conversely, a PCR Ratio of 0.6 might indicate overconfidence in the market. Too many calls could signal a saturated bullish sentiment, suggesting a possible market top.
Use Cases of PCR Ratio in Options Trading
Swing Trading: Traders use changes in the PCR Ratio to identify short-term reversals.
Trend Confirmation: A rising market with a falling PCR could confirm a strong bullish trend.
Risk Management: PCR helps in gauging market mood and planning entry/exit points more precisely.
Nifty or Index Tracking: The Nifty PCR Ratio is often used by institutional traders to forecast index movements.
Limitations of PCR Ratio
While the Put Call Ratio is a powerful tool, it should not be used in isolation. It's best combined with other indicators like RSI, MACD, or candlestick patterns. Additionally, PCR can vary across different sectors and timeframes, so it's important to contextualize its values.
Also, a spike in the PCR Ratio doesn’t always mean the market will move up. If the increase in puts is due to hedging by institutions, it might not be a bearish signal at all.
Final Thoughts
The PCR Ratio is one of the most useful sentiment indicators in options trading. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, incorporating the Put Call Ratio into your trading strategy can offer valuable insights. But like any tool, it works best when used alongside proper research and risk management.
Understanding the balance between puts and calls helps traders decode market psychology, identify possible reversals, and make informed decisions. Keep an eye on the PCR Ratio, and you’ll start to see the hidden story behind market moves.
0 notes
Text
How to Trade Using Candlestick Patterns for Better Trade Decisions
Candlestick patterns are one of the most widely used tools in technical analysis. They provide valuable insights into market sentiment and potential price movements by analyzing the open, close, high, and low of each trading period. By understanding and using candlestick patterns, traders can make more informed decisions, anticipate market reversals, and optimize entry and exit points.
Here’s how you can use candlestick patterns effectively in your trading strategy.
1. What are Candlestick Patterns?
A candlestick pattern is formed by one or more candlesticks that represent price movements within a given timeframe. Each candlestick shows:
Open price: The price at which the asset opened during the time period.
Close price: The price at which the asset closed during the time period.
High price: The highest price reached during the period.
Low price: The lowest price reached during the period.
Candlestick patterns can be either bullish (indicating an upward price movement) or bearish (indicating a downward price movement), depending on the relationship between the open and close prices.
2. Popular Bullish Candlestick Patterns
Bullish candlestick patterns signal potential upward price movement. Here are a few common ones to look out for:
Bullish Engulfing Pattern: This pattern consists of a small bearish candlestick followed by a larger bullish candlestick that completely engulfs the previous one. It indicates strong buying pressure and often signals the beginning of an uptrend.
Hammer: A hammer candlestick has a small body and a long lower shadow, which indicates that sellers tried to push the price lower, but buyers stepped in and drove the price back up. It suggests a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
Morning Star: This pattern consists of three candlesticks: a long bearish candlestick, followed by a small-bodied candlestick, and then a long bullish candlestick. The morning star indicates a potential trend reversal from bearish to bullish.
3. Popular Bearish Candlestick Patterns
Bearish candlestick patterns suggest potential downward price movement. Here are a few common bearish patterns to look for:
Bearish Engulfing Pattern: The opposite of the bullish engulfing pattern, the bearish engulfing consists of a small bullish candlestick followed by a larger bearish candlestick that completely engulfs it. This pattern indicates strong selling pressure and often signals the start of a downtrend.
Shooting Star: The shooting star has a small body and a long upper shadow, signaling that buyers tried to push the price higher but were unable to sustain it. This pattern suggests a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
Evening Star: The evening star is the opposite of the morning star, consisting of a long bullish candlestick, followed by a small-bodied candlestick, and then a long bearish candlestick. This pattern indicates a potential reversal from bullish to bearish.
4. Using Candlestick Patterns for Entry and Exit
Candlestick patterns can be used to make more informed decisions about when to enter and exit trades:
Entry: When you identify a bullish reversal pattern (like a bullish engulfing or hammer) at support levels, it could be an indication to enter a long position. Similarly, a bearish reversal pattern (like a bearish engulfing or shooting star) at resistance levels could signal a short position.
Exit: Candlestick patterns can also help with determining exit points. For example, if you are in a long position and a bearish reversal pattern (like an evening star) forms near a resistance level, it might be a signal to close your position or set a stop-loss order to protect your profits.
5. Combining Candlestick Patterns with Other Indicators
While candlestick patterns can provide valuable insights, they work best when combined with other technical indicators to confirm the signals. Here are some tools you can use alongside candlestick patterns:
Support and Resistance: Look for candlestick patterns that form at key support or resistance levels. For example, a bullish engulfing pattern at a support level has a higher probability of success.
Moving Averages: Combine candlestick patterns with moving averages (e.g., 50-day or 200-day MA) to confirm the overall trend. A candlestick pattern that aligns with the trend can be more reliable.
RSI (Relative Strength Index): Use RSI to confirm whether an asset is overbought or oversold. A candlestick reversal pattern accompanied by an overbought or oversold condition can strengthen your trade decision.
6. Practice Patience and Wait for Confirmation
Candlestick patterns should never be used in isolation. They work best when you wait for confirmation before entering a trade. For example:
Volume: If a candlestick pattern forms with high volume, it’s a stronger signal. Volume confirmation helps validate the strength of the pattern.
Other Indicators: Look for confirmation from indicators like RSI or moving averages. For example, a bullish engulfing pattern near a moving average support level combined with an RSI showing oversold conditions may provide a more reliable signal.
Waiting for confirmation ensures you’re not jumping into a trade based on an isolated pattern, which could turn out to be a false signal.
Final Thought: Master Candlestick Patterns for Smarter Trading
Candlestick patterns are a powerful tool that can enhance your trading strategy. By understanding and recognizing common bullish and bearish patterns, you can make more informed decisions about entry and exit points, improve timing, and manage risk more effectively.
Ready to trade smarter with expert-backed strategies? Download Univest — the SEBI-registered trading app that helps you identify profitable candlestick patterns, follow expert strategies, and trade with confidence. Stay ahead of the market and improve your trading success.
0 notes
Text
Pin Bar Candlestick Pattern: A Trader’s Guide to Smart Entries and Exits
Have you ever noticed a candle on a chart that looks like a pin or a needle? That structure is known as a pin bar, and it can give traders powerful insights into future price movement. Whether you're entering or exiting a trade, the pin bar can help you make smarter, more strategic decisions.
If you've found it challenging to recognize or understand this pattern, you're not alone. In this Market Investopedia guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about pin bars—how they work, their pros and cons, and how to trade them effectively.
What Is a Pin Bar?
A pin bar is a candlestick formation that signals a potential price reversal or continuation. It’s made up of:
A small body (green or red),
A long wick on one end,
And a short wick on the opposite end.
This structure reveals price rejection—meaning the market attempted to move in one direction but was strongly pushed back, hinting at an upcoming shift.
Key Features of a Pin Bar
To identify a pin bar, look for the following elements on your chart:

Small Candle Body
The body should be short, showing little difference between the opening and closing prices. This indicates a balance—or struggle—between buyers and sellers.
Wicks (Shadows)
There are two wicks on a pin bar. One is very long, and the other is short. The long wick reveals where the price was rejected, and it's the most important part of the pin bar.
Closed Candle
Never trade a pin bar that hasn’t closed yet. Wait for the candle to close before making a decision based on its signal.
Types of Pin Bars
Bullish Pin Bar
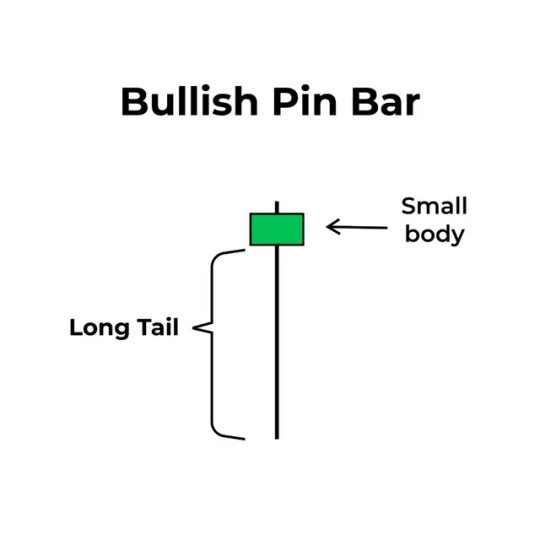
Appears during a downtrend
Has a small green body
Features a long lower wick
Signals a potential upward reversal
The long lower wick suggests sellers pushed the price down, but buyers fought back, rejecting the lower levels. This often indicates a buying opportunity.
Bearish Pin Bar
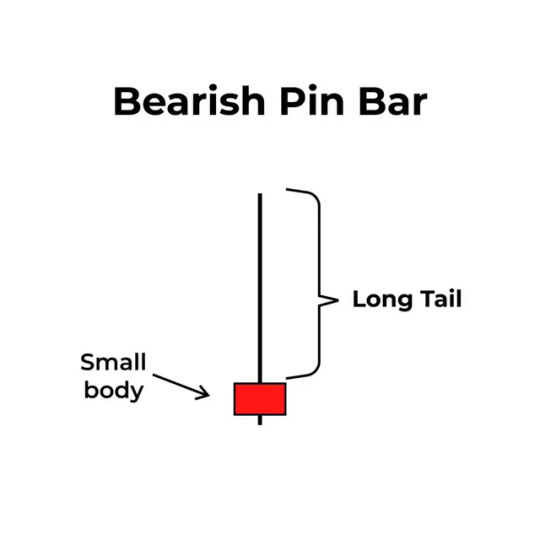
Appears during an uptrend
Has a small red body
Features a long upper wick
Signals a potential downward reversal
Here, buyers tried to push the price higher, but sellers stepped in and rejected the highs. This often signals a selling opportunity.
How to Trade Using Pin Bars

1. Identify a Pin Bar
Scan your chart (preferably 4-hour, daily, or weekly) for a small-bodied candle with a long wick on one end and a short wick on the other.
2. Use Confirmation Tools
Combine pin bars with tools like:
RSI (Relative Strength Index)
Fibonacci Retracement
Bollinger Bands These indicators can help confirm whether the signal is strong enough to act on.
3. Trade Reversals
When a pin bar forms at a key support or resistance level, it often signals a reversal. Trade in the direction opposite the long wick.
4. Trade Trend Continuations
Not every pin bar signals a reversal. In some cases, especially during a trend pause, a pin bar can indicate that the current trend is about to continue. For example, a bullish pin bar during an uptrend suggests that buyers are still in control.
How to Spot High-Quality Pin Bars
Not all pin bars are equal. Here's what to look for in a strong setup:
Key Levels: Look for pin bars forming at significant support or resistance zones.
Longer Time Frames: Pin bars on 4H, daily, or weekly charts tend to be more reliable than those on 5-minute or 15-minute charts.
Wick Length: The longer the wick (at least two-thirds of the candle's length), the stronger the signal.
Smaller Body: A smaller body means less indecision and more rejection.
Volume Confirmation: Higher trading volume strengthens the validity of the pattern.
Pros of Trading Pin Bars
Easy to recognize, even for beginners
Work well with various assets—Forex, stocks, crypto, commodities Clearly define potential entry and exit levels
Combine well with trendlines, moving averages, and other tools Suitable for multiple timeframes
Cons of Trading Pin Bars
Less effective in choppy or sideways markets
Relies on probabilities—there’s no guarantee the signal will play out
Can produce false signals without proper confirmation
Final Thoughts
The pin bar candlestick is a powerful yet simple tool that traders can use to spot trend reversals or continuations. It's easy to learn, and when combined with other forms of analysis, it can provide high-probability trade setups.
However, like any trading method, pin bars are not foolproof. It's important to assess each one carefully, confirm the signal, and avoid trading them in low-quality setups or during erratic market conditions.
Ready to dive deeper into price action and trading strategies? Explore more articles on Market Investopedia or join our free webinar for hands-on learning with real chart examples.
0 notes
Text
Assessing the Right Time to Invest in Forex: A Comprehensive Guide

Investing in the foreign exchange (Forex) market can be highly rewarding—but only if you know when and how to enter and exit trades. This guide will walk you through the key steps to assess the optimal time to invest, including understanding trading signals, choosing the right charts, mastering entry and exit indicators, and leveraging technology to stay ahead. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned trader, these strategies will help you make informed, logical decisions and minimize risk.
1. Why Timing Matters in Forex Trading
The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with trillions of dollars changing hands daily. Given its continuous nature and high volatility, timing your trades can be the difference between healthy profits and significant losses. Entering at the wrong time may expose you to adverse currency swings, while exiting too early can prevent you from maximizing gains.
A well-timed trade allows you to:
Capitalize on momentum during strong trends
Avoid sharp reversals triggered by economic news
Reduce drawdowns and preserve capital
Improve risk-to-reward ratios on every position
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap to pinpoint the best moments to invest and secure consistent returns.
2. Understanding Forex Trading Signals
Trading signals are alerts based on predefined criteria that suggest when to buy or sell a currency pair. They distill vast market data into actionable insights, helping traders spot opportunities without parsing every tick on the chart. Signals can be:
Technical: Generated from mathematical calculations on price and volume (e.g., Moving Averages, RSI, MACD).
Fundamental: Driven by economic events, like interest rate decisions or GDP reports.
Sentiment-based: Reflecting trader positioning and market psychology.
The key is to choose signals that align with your trading style—whether that’s scalping, day trading, swing trading, or longer-term position trading.
3. Selecting the Right Chart and Indicators
Before diving into signals, select a charting platform that offers:
Real-time data feeds for all major and minor currency pairs
Customizable timeframes (from 1-minute to monthly)
Built-in technical indicators and the ability to add custom scripts
Common Forex Charts
Line Chart: Simplest view showing closing prices.
Bar Chart: Displays open, high, low, and close (OHLC) for each period.
Candlestick Chart: Similar to bar charts, but with color-coded bodies—excellent for spotting reversal patterns.
Essential Technical Indicators
Moving Averages (MA): Identify trend direction and dynamic support/resistance.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures overbought/oversold conditions.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Captures trend strength and momentum shifts.
Bollinger Bands: Highlight volatility and potential breakout points.
Stochastic Oscillator: Another momentum tool for spotting reversal zones.
Familiarize yourself with how each indicator behaves across different timeframes. Longer MAs smooth out noise but lag more, while shorter MAs react quickly but can generate false signals.
4. Mastering Entry Signals
An effective entry strategy combines multiple indicators to confirm a high-probability setup. Here’s a step-by-step process:
Trend Confirmation:
Use a 50-period and 200-period MA crossover to determine the primary trend (bullish when 50 above 200; bearish when below).
Momentum Filter:
Check RSI or MACD histogram for momentum alignment. For example, in an uptrend, RSI should be above 50.
Pattern Recognition:
Look for chart patterns (e.g., flags, pennants, head and shoulders) that signal continuation or reversal.
Entry Trigger:
A candlestick pattern (e.g., bullish engulfing) or a break above/below a recent swing high/low.
Volume/Volatility Check:
Confirm with volume spikes or Bollinger Band width expansion to ensure the move is supported by sufficient trading activity.
Example Entry Signal Workflow
Step 1: EUR/USD 4-hour chart shows 50 MA above 200 MA (uptrend).
Step 2: RSI sits at 55, indicating bullish momentum.
Step 3: Price consolidates in a bull flag for three candles.
Step 4: A breakout candle closes above the flag’s top—enter long.
Step 5: Volume increases by 20% above the 20-period average, confirming strength.
5. Optimizing Exit Strategies
Your exit plan is just as important as your entry. There are three common types of exits:
Fixed Stops and Profit Targets:
Predefine a stop-loss level (e.g., 30 pips) and a profit target (e.g., 60 pips) before entering. This guarantees a positive risk-to-reward ratio.
Trailing Stops:
Move your stop-loss in your favor as price advances. Many traders use a moving average or ATR-based trailing stop to capture extended moves.
Limit Exits at Key Levels:
Close positions at significant support/resistance zones or Fibonacci retracement lines.
Short-Term (Scalp/Swing) Exits
For quick trades, focus on “turning points”—repeated short-term patterns that can produce fast reversals. Monitor currency pair swings on 5- to 15-minute charts and set tight limit exits (e.g., 10–15 pips) with equally tight stops.
Real-Time Exit Signals
Many platforms offer real-time alerts—for example, if the MACD line crosses below the signal line or if price breaks below a key moving average. These can automate your exit decisions and reduce emotional bias.
6. Combining Multiple Signals for Risk Aversion
Relying on a single indicator is risky; it can generate false positives or lag behind. Instead, create a signal matrix by:
Overlaying trend, momentum, and volatility indicators
Filtering signals across multiple timeframes (e.g., align a 15-minute entry with a 1-hour trend)
Assigning weights to each signal based on reliability and recent performance
By evaluating multiple Forex signals together, you gain a holistic view of the market and can better anticipate fluctuations. This approach helps you stick to a logical mechanism rather than making random decisions under stress.
7. Leveraging Technology and Alerts
Modern Forex trading thrives on technology. With the right tools, you can analyze markets around the clock and never miss a crucial signal.
Mobile Trading Apps: Execute buy/sell orders and monitor charts on your smartphone—no physical presence required.
Automated Alert Systems: Configure alerts for when indicators meet your predefined parameters (e.g., RSI crosses below 30).
Expert Advisors (EAs): Deploy algorithmic trading systems that scan for signals and place trades automatically.
These innovations ensure that you’re always ready to act on new opportunities, whether you’re at your desk or on the go.
8. Choosing a Reliable Signal Provider
While self-generated signals are ideal, many traders supplement their strategies with professional signal services. To choose a trustworthy provider:
Check Track Record: Look for audited performance over at least six months with clear equity curves.
Read Reviews and Forums: Engage with communities on Forex forums and social media—peer feedback can be invaluable.
Compare Costs vs. Value: Free signals can be high-volume but low-quality, while paid services often offer curated, lower-frequency alerts.
Trial Periods: Opt for services that provide a trial or money-back guarantee so you can test signals risk-free.
Always cross-reference third-party signals with your own analysis to maintain control over your trades.
9. Continuous Research and Education
Forex markets evolve constantly. To stay ahead:
Read Business Newspapers and Magazines: Stay informed on macroeconomic trends that influence currency values.
Participate in Online Forums and Webinars: Exchange ideas with other traders and learn from expert lectures.
Backtest New Strategies: Use historical data and Forex software to simulate performance before risking real capital.
Maintain a Trading Journal: Record each trade’s setup, outcome, and your emotional state to refine your approach over time.
By committing to lifelong learning, you’ll adapt your system to changing market conditions and improve your win rate.
10. Conclusion: Bringing It All Together
Assessing the right time to invest in Forex isn’t about luck—it’s about systematic analysis, disciplined execution, and continuous improvement.
Understand and select the best trading signals for your style.
Choose the right charts and technical indicators.
Master robust entry and exit strategies.
Combine signals across multiple timeframes for enhanced risk aversion.
Leverage technology to automate alerts and execute trades.
Partner with a reputable signal provider, but always validate their calls.
Commit to ongoing research and education to refine your edge.
By following these steps, you’ll position yourself to make well-timed, high-probability trades that align with your goals and risk tolerance. Remember, consistency beats occasional brilliance—stick to your plan, and let your system guide you to long-term success in the Forex market. For more insights: Mastering Forex Trading Psychology: Traits, Emotions, and Mindset for Success Paperback – Large Print, May 20, 2025 by NABAL KISHORE PANDE (Author)
#Forex#TradingSignals#ForexStrategy#ForexIndicators#CurrencyTrading#InvestSmart#MarketTiming#ForexCharts#TradingPsychology#ExitStrategy
0 notes
Text
Top Strategies for Successfully Trading Breakouts and Pullbacks
Trading breakouts and pullbacks are two of the most powerful strategies in technical analysis. When executed correctly, they can offer high-probability setups and consistent returns. At AtlasFunded, we help traders sharpen their edge by understanding market structure, timing, and risk management. In this guide, we’ll break down the top strategies for successfully trading breakouts and pullbacks.

What Are Breakouts and Pullbacks?
A breakout occurs when the price moves beyond a defined support or resistance level with increased volume. This often signals the start of a new trend. A pullback, on the other hand, is a temporary reversal within an existing trend—a chance for traders to enter at a better price before the trend resumes.
Both strategies are used by day traders, swing traders, and even long-term investors.
Strategy 1: Identify Key Support and Resistance Levels
The foundation of breakout and pullback trading lies in accurately identifying support and resistance zones. These levels are where price has historically reversed or paused, making them critical decision points.
Tip: Use tools like horizontal lines, Fibonacci retracements, and pivot points to mark these areas. Volume analysis can also confirm the strength of a breakout.
Strategy 2: Use Volume to Confirm Breakouts
Volume plays a crucial role in confirming the validity of a breakout. A breakout with high volume indicates strong market interest and a higher chance of follow-through.
AtlasFunded Insight: Low-volume breakouts are more likely to fail or reverse, trapping traders in poor entries. Always wait for volume confirmation before jumping in.
Strategy 3: Wait for the Retest (Breakout-Pullback Combo)
One of the most effective breakout trading methods is to wait for the retest. After the initial breakout, price often returns to test the previous resistance (now support) or support (now resistance) before continuing.
This gives traders a chance to enter with a lower risk and higher reward setup.
Strategy 4: Trendline and Moving Average Pullbacks
When trading pullbacks, using a trendline or moving average (like the 20 EMA) helps identify dynamic support or resistance. These indicators can act as reliable zones for pullback entries during a trend.
Tip: Enter on a bullish or bearish candlestick pattern near the trendline or moving average for added confirmation.
Strategy 5: Set Clear Entry, Stop, and Target Levels
Whether trading a breakout or pullback, never skip proper risk management. Define:
Entry: Above the breakout point or at the pullback support/resistance
Stop-loss: Below the breakout level or under recent swing low/high
Take-profit: Based on risk/reward ratio (e.g., 1:2 or 1:3)
At AtlasFunded, we emphasize disciplined trade planning to help traders scale with confidence.
Conclusion
Trading breakouts and pullbacks can be incredibly rewarding, but success comes from preparation, not prediction. Focus on structure, confirmation, and discipline.
Join AtlasFunded and gain access to educational resources, funding opportunities, and a community that empowers you to trade smarter, not harder.
0 notes
Text
Decoding the FTSE Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Highlights
The FTSE chart visually tracks the daily and long-term movements of top UK-listed companies.
It provides critical insights into market behaviour, price patterns, and economic sentiment.
Key features such as support, resistance, volume, and trends can help identify shifts in the UK market landscape.
The FTSE chart plays a key role in monitoring the UK stock market’s overall performance. As a visual tool that follows the Financial Times Stock Exchange (FTSE) index, it offers a clear representation of how the largest companies listed on the London Stock Exchange are performing. Understanding this chart enables a more in-depth view of market dynamics, sector performance, and the general health of the UK economy.
Understanding the FTSE Index
The FTSE index represents the top 100 publicly traded companies on the London Stock Exchange based on market capitalisation. These companies come from various sectors including financials, consumer goods, energy, and healthcare. The FTSE chart tracks the price movements of this index, offering a visual summary of how these companies perform over time. This index is widely seen as a barometer of the UK’s economic environment.
The FTSE index is recalculated regularly to reflect changes in company valuations and sector representation. As these changes are reflected in the FTSE chart, it becomes an evolving visual reference for shifts in economic and corporate conditions.
How the FTSE Chart Is Structured
A typical FTSE chart is presented as a line graph or candlestick chart. The x-axis shows the timeline, ranging from minutes in intraday charts to several years for long-term trends. The y-axis indicates the FTSE index’s numerical value, displaying its rise and fall over time.
Line charts show the index’s closing price over selected intervals. These are helpful for identifying long-term trends. In contrast, candlestick charts offer more detailed information, such as the index’s opening, high, low, and closing prices within a time period. This additional detail can help track volatility and sentiment more precisely.
Key Components of the FTSE Chart
Support and Resistance: These levels are often noted in FTSE chart analysis. A support level is where the index tends to stop falling and reverse direction, while a resistance level is a price point where the index struggles to move above. Observing these levels provides clarity on possible market turning points.
Trends: Directional movement is one of the first aspects to assess. A consistent rise indicates a bullish trend, while prolonged declines show a bearish pattern. A sideways trend, where the index remains stable, suggests market indecision.
Volume: Volume indicates the number of shares traded within a specific time frame. A surge in trading volume, particularly during price shifts, reflects increased market activity and can affirm the strength of the price movement.
Time Frames: FTSE charts allow different time frame selections. Intraday charts can display minute-by-minute data, while weekly or monthly charts help in examining broader economic trends. This flexibility helps in evaluating both short-term reactions and long-term patterns.
Applications of the FTSE Chart in Market Monitoring
The FTSE chart is widely used by market observers to understand how UK-listed companies respond to global and local economic developments. For instance, major political changes, fiscal policy announcements, or company-specific news can cause immediate shifts in the FTSE index. These shifts are instantly reflected in the chart, making it a real-time monitor of economic sentiment.
Market professionals may refer to the FTSE chart to evaluate the performance of individual sectors. For example, if energy stocks are outperforming within the index, the chart will reflect this relative strength, allowing for comparative insights across industries.
Reading Historical Trends in the FTSE Chart
Examining past performance using long-range FTSE charts can reveal how the market reacted to events such as financial crises, policy changes, or global health developments. These insights help form a contextual understanding of market patterns across different cycles.
Historical FTSE data is also useful for overlaying technical indicators. Some commonly used tools include moving averages, which smooth out fluctuations; the Relative Strength Index (RSI), which gauges momentum; and Bollinger Bands, which help assess volatility. These additions to the FTSE chart aid in deeper technical evaluation.
Benefits of the FTSE Chart in Market Evaluation
One of the primary advantages of the FTSE chart is its ability to condense complex market data into a visual format. It simplifies the process of identifying direction, volatility, and reaction to events. It is also useful for examining sector performance within the FTSE index, enabling a broader view of which segments are strengthening or weakening.
Additionally, the FTSE chart can highlight how external events influence the UK stock market. From geopolitical developments to global economic shifts, all are often mirrored in the FTSE index’s movements, making the chart a timely visual indicator.
Conclusion
The FTSE chart remains an essential reference for tracking the status of the UK’s top companies and overall market performance. With its ability to display short-term movements and long-term trends, it serves as a versatile tool for observing economic shifts, sector behaviour, and broader market trends. A solid understanding of the FTSE chart structure, key elements, and interpretation techniques can improve one’s ability to assess changes within the UK financial landscape.
0 notes