#EDUCATIONAL
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

I personally think of it as a disorder but your brain structure is definitely different and a “divergent” one.
This information was found on online sources. Not AI
Here’s an excerpt from an article from Health Central:
How Is The Structure Of The Brain Different?
“The neuroanatomy of autism is difficult to describe,” Culotta says. So it might be easier to talk about the architecture of the brain and how the autistic brain may differ.
So what’s different in the structure of this three-pound organ? Let’s start with a quick anatomy refresher: First of all, the brain is split into two halves or hemispheres. It is these two hemispheres that we get the idea of a left brain and a right brain. In reality, our thinking and cognitive processes bounce back and forth between the two halves.
“There's a little bit of difficulty in autism communicating between the left and right hemispheres in the brain. There's not as many strong connections between the two hemispheres,” Dr. Anderson says.
In recent years, science has found that the hemispheres of ASD brains have slightly more symmetry than those of a regular brain. This small difference in asymmetry isn’t enough to diagnosis ASD, according to a report in Nature Communications. And, exactly how the symmetry may play into autism’s traits is still be researched.
The differences in the brain don’t stop there. Another quick Biology 101 review: Within each half, there are lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal. Inside these lobes are structures that are in charge of everything from movement to thinking. On top of the lobes, lies the cerebral cortex aka grey matter. This is where information processing happens. The folds in the brain add to the surface area of the cerebral cortex. The more surface area or grey matter there is, the more information that can be processed.
https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/autism/autism-brain-differences
Here’s another excerpt from Transmitter.org
Which brain regions are known to be structurally different between autistic and non-autistic people?
Studies that make use of a brain-scanning technique called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have highlighted a few brain regions that are structurally distinct in people with autism.
Children and adolescents with autism often have an enlarged hippocampus, the area of the brain responsible for forming and storing memories, several studies suggest, but it is unclear if that difference persists into adolescence and adulthood1,2.
The size of the amygdala also seems to differ between people with and without autism, although researchers from different labs have turned up conflicting results. Some find that people with autism have smaller amygdalae than people without autism, or that their amygdalae are only smaller if they also have anxiety3. Others have found that autistic children have enlarged amygdalae early in development and that the difference levels off over time2,4.
Autistic people have decreased amounts of brain tissue in parts of the cerebellum, the brain structure at the base of the skull, according to a meta-analysis of 17 imaging studies5. Scientists long thought the cerebellum mostly coordinates movements, but they now understand it plays a role in cognition and social interaction as well.
On a more global level, the cortex — the brain’s outer layer — seems to have a different pattern of thickness in people with and without autism. This difference tracks with alterations to a single type of neuron during development, a 2020 study suggests.
The last excerpt is from the National Library of Medicine. Here’s an excerpt:
The constituent parts of the neural systems associated with clinical symptoms in ASD were examined by many studies. Specific core regions have been suggested to mediate clinical phenotypes of ASD such as the frontotemporal lobe, frontoparietal cortex, amygdala, hippocampus, basal ganglia, and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) [17]. For example, abnormalities in (1) the inferior frontal gyrus (IFG, Broca's area), superior temporal sulcus (STS), and Wernicke's area might be related to defects in social language processing and social attention [18], (2) the frontal lobe, superior temporal cortex, parietal cortex, and amygdala might mediate impairments of social behaviors [19,20] and (3) the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) and caudate nucleus have been associated with RRBs of ASD [21]. Although deficits in these regions seem to be general in ASD, some findings proposed that abnormalities in these brain regions are not peculiar to ASD and seem to be common in other disorders such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, general anxiety disorders, and schizophrenia
#autism#brain structure#neurodiversity#it’s called neurodivergent for a reason#I view it as a disorder and not disability imo#autism research#educational
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
Women's Not So Distant History
This #WomensHistoryMonth, let's not forget how many of our rights were only won in recent decades, and weren’t acquired by asking nicely and waiting. We need to fight for our rights. Here's are a few examples:

📍 Before 1974's Fair Credit Opportunity Act made it illegal for financial institutions to discriminate against applicants' gender, banks could refuse women a credit card. Women won the right to open a bank account in the 1960s, but many banks still refused without a husband’s signature. This allowed men to continue to have control over women’s bank accounts. Unmarried women were often refused service by financial institutions entirely.

📍 Before 1977, sexual harassment was not considered a legal offense. That changed when a woman brought her boss to court after she refused his sexual advances and was fired. The court stated that her termination violated the 1974 Civil Rights Act, which made employment discrimination illegal.⚖️

📍 In 1969, California became the first state to pass legislation to allow no-fault divorce. Before then, divorce could only be obtained if a woman could prove that her husband had committed serious faults such as adultery. 💍By 1977, nine states had adopted no-fault divorce laws, and by late 1983, every state had but two. The last, New York, adopted a law in 2010.

📍In 1967, Kathrine Switzer, entered the Boston Marathon under the name "K.V. Switzer." At the time, the Amateur Athletics Union didn't allow women. Once discovered, staff tried to remove Switzer from the race, but she finished. AAU did not formally accept women until fall 1971.

📍 In 1972, Lillian Garland, a receptionist at a California bank, went on unpaid leave to have a baby and when she returned, her position was filled. Her lawsuit led to 1978's Pregnancy Discrimination Act, which found that discriminating against pregnant people is unlawful

📍 It wasn’t until 2016 that gay marriage was legal in all 50 states. Previously, laws varied by state, and while many states allowed for civil unions for same-sex couples, it created a separate but equal standard. In 2008, California was the first state to achieve marriage equality, only to reverse that right following a ballot initiative later that year.

📍In 2018, Utah and Idaho were the last two states that lacked clear legislation protecting chest or breast feeding parents from obscenity laws. At the time, an Idaho congressman complained women would, "whip it out and do it anywhere,"

📍 In 1973, the Supreme Court affirmed the right to safe legal abortion in Roe v. Wade. At the time of the decision, nearly all states outlawed abortion with few exceptions. In 1965, illegal abortions made up one-sixth of all pregnancy- and childbirth-related deaths. Unfortunately after years of abortion restrictions and bans, the Supreme Court overturned Roe in 2022. Since then, 14 states have fully banned care, and another 7 severely restrict it – leaving most of the south and midwest without access.

📍 Before 1973, women were not able to serve on a jury in all 50 states. However, this varied by state: Utah was the first state to allow women to serve jury duty in 1898. Though, by 1927, only 19 states allowed women to serve jury duty. The Civil Rights Act of 1957 gave women the right to serve on federal juries, though it wasn't until 1973 that all 50 states passed similar legislation

📍 Before 1988, women were unable to get a business loan on their own. The Women's Business Ownership Act of 1988 allowed women to get loans without a male co-signer and removed other barriers to women in business. The number of women-owned businesses increased by 31 times in the last four decades.
Free download

📍 Before 1965, married women had no right to birth control. In Griswold v. Connecticut (1965), the Supreme Court ruled that banning the use of contraceptives violated the right to marital privacy.

📍 Before 1967, interracial couples didn’t have the right to marry. In Loving v. Virginia, the Supreme Court found that anti-miscegenation laws were unconstitutional. In 2000, Alabama was the last State to remove its anti-miscegenation laws from the books.

📍 Before 1972, unmarried women didn’t have the right to birth control. While married couples gained the right in 1967, it wasn’t until Eisenstadt v. Baird seven years later, that the Supreme Court affirmed the right to contraception for unmarried people.

📍 In 1974, the last “Ugly Laws” were repealed in Chicago. “Ugly Laws” allowed the police to arrest and jail people with visible disabilities for being seen in public. People charged with ugly laws were either charged a fine or held in jail. ‘Ugly Laws’ were a part of the late 19th century Victorian Era poor laws.

📍 In 1976, Hawaii was the last state to lift requirements that a woman take her husband’s last name. If a woman didn’t take her husband’s last name, employers could refuse to issue her payroll and she could be barred from voting.

📍 It wasn’t until 1993 that marital assault became a crime in all 50 states. Historically, intercourse within marriage was regarded as a “right” of spouses. Before 1974, in all fifty U.S. states, men had legal immunity for assaults their wives. Oklahoma and North Carolina were the last to change the law in 1993.

📍 In 1990, the Americans with Disability Act (ADA) – most comprehensive disability rights legislation in U.S. history – was passed. The ADA protected disabled people from employment discrimination. Previously, an employer could refuse to hire someone just because of their disability.

📍 Before 1993, women weren’t allowed to wear pants on the Senate floor. That changed when Sen. Moseley Braun (D-IL), & Sen. Barbara Mikulski (D-MD) wore trousers - shocking the male-dominated Senate. Their fashion statement ultimately led to the dress code being clarified to allow women to wear pants.

📍 Emergency contraception (Plan B) wasn't approved by the FDA until 1998. While many can get emergency contraception at their local drugstore, back then it required a prescription. In 2013, the FDA removed age limits & allowed retailers to stock it directly on the shelf (although many don’t).

📍 In Lawrence v. Texas (2003), the Supreme Court ruled that anti-cohabitation laws were unconstitutional. Sometimes referred to as the ‘'Living in Sin' statute, anti-cohabitation laws criminalize living with a partner if the couple is unmarried. Today, Mississippi still has laws on its books against cohabitation.
#art#feminism#women's history#women's history month#iwd2024#international women's day#herstory#educational#graphics#history#70s#80s#rights#women's rights#human rights
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: sea urchins
As I continue the slow grind of covering every living group of echinoderms for this series, it was inevitable that I would eventually encounter the only echinoderm I've actually studied. Sea urchins are among the most iconic of marine invertebrates, but many people just think of them as part of the scenery. I'm here to show you that there's more to these creatures than just being spiny lumps on a rock.

(Image: a purple sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) being held in someone's hand. It is a round, globular animal with a dark purple color. Light purple spines emerge from it all over its body, with the longest being around the middle. End ID)

(image: a long-spined sea urchin (Diadema savignyi). It is a black sea urchin with spines longer than its diameter. End ID)
Urchin is an old-fashioned word for hedgehog, and sea hedgehog is a fitting name for these round, spiny animals. Sea urchins tend to be fairly small, with a diameter of 3 - 10 cm (1 - 4 in), though some species have very long spines that make them seem larger. The main body of an urchin is round and enclosed in a (usually) hard shell called a test made of calcium carbonate. The test is covered with a slayer of skin and muscle that controls the spines and small, pincer-like structures called pedicellaria. Within the test are the internal organs. As with other echinoderms, sea urchins are radially symmetrical as adults, with five segments arranged around the center like pizza slices. The two main body holes are found on the top and bottom of the animals where the segments converge. At the bottom is the mouth and at the top is the anus. Each segment also has a hole near the anus used to release gametes and one will have a larger pore called the madreporite, which is used to control the amount of water within the urchin's body. The mouth is a unique structure known as Aristotle's lantern, consisting of five tooth-like structures (one for each body segment) that interlock together and sharpen themselves. Behind the teeth is a rasping tongue.

(image: a close-up of an urchin's mouth, showing the Aristotle's lantern. It is a hole surrounded by a fleshy lip. Five spade-shaped teeth are emerging from the edge of the hole. End ID)
Internally, most of the body is taken up by the digestive tract and water vascular system. The digestive system lacks a stomach, with the esophagus attaching directly to the small intestine. The digestive tract forms a loop as it passes through the body. The water vascular system uses seawater to form hydrostatic pressure that moves the tube feet. All starfish, urchins, and sea cucumbers have tube feet, small, transparent, tentacle-like structures they use for movement. Tube feet are hollow and retracted into pores on the skin normally. To be used, they have to be inflated with water, which makes them stick out of the body, where they can be controlled with muscles. Tube feet end in suction cups that can be used to grab into structures around them. Seawater drawn in through the madreporite serves as the source of pressure needed for the tube feet to function. In urchins, tube feet cover the body and are used for locomotion, moving food to the mouth, and moving objects on or off the body. The main body cavity is filled with circulatory fluid that uses special cells to move oxygen and nutrients around the body. The nervous system is simple, consisting of a central nerve ring around the esophagus that branches into nerves that connect to the rest of the body. Urchins have no eyes (except for the family Diadematidae, which have eyespots), but are sensitive to light. The gonads are usually small, but during mating season they can swell to fill much of the body cavity.

(Image: a drawn diagram showing a cross-section of a sea urchin, with the different organs and body parts labeled. End ID. Source)
Sea urchins are found in oceans worldwide, from intertidal zones to the deep sea and the tropics to the poles. They are bottom-dwellers who feed primarily on algae, which they scrape up with their teeth. However, they will also take a variety of food, including carrion, aquatic plants, and other slow-moving or sessile animals like sponges, polyps, bivalves, worms, and sea cucumbers. Urchins can play a key role in regulating algae populations through their ecosystems, but they also rely on predators to keep from overeating necessary algae. Famously, California's kelp forests were almost destroyed by urchins eating the kelp after their primary predator, sea otters, were driven to near extinction. Urchin's primary defense against predators is their hard tests and spines. As most of the edible portion of the urchin is within the test, predators have to get through both layers of defense first. The spines are hollow and each can be moved independently of each other, allowing them to be positioned toward a threat. Many species contain venom within their spines as an added layer of defense. This venom is rarely dangerous to humans, but can cause swelling and painful reactions. Another layer of defense is the pedicellaria, which are good at removing small animals and parasites from the skin. The flower urchin, Toxopneustes pileolus, has modified its pedicellaria into flower-like structures that extend beyond the spines and can deliver a sting that can be fatal to humans.

(Image: a flower urchin. It is a pinkish urchin covered with flower-like structures that extend to the length of the spines. It has placed some bits of shells on top of it. End ID)
Sea urchins possess distinct males and females, though the differences are internal, making it impossible to tell which is which based on visual examination. During mating seasons, the gonads swell as they generate gametes. Urchins tend to reproduce in groups at synchronized times (possibly correlated with the phases of the moon in shallow-water species) to maximize the possibility of fertilization. When ready to mate, the gametes are squeezed to empty their contents through the genital pores and into the water column. Sperm must find egg in the water to fertilize it. Most sea urchins provide no parental care, but in some species, the female will retain the eggs in her spines to protect them. The eggs hatch into bilaterally symmetrical larvae called plutei that drift with the plankton. As they develop, a section of the larvae will develop into a radially symmetrical adult rudiment. This piece will eventually break off and become the juvenile urchin while the rest of the larva dies. Because echinoderms start out as bilaterally symmetrical larvae, we can infer that they developed from bilaterally symmetrical ancestors and the radial symmetry of adults is a more recent development.

(image: a series of photos showing the embryological development of a sea urchin from a single cell to a cluster of cells, to a bell-like structure, to growing several arms, to the eventual adult developing and breaking off. End ID. Source)
Fossils show that the oldest sea urchins had large, club-like spines that they walked on, with the modern spines being a later development. Most of those urchins died out with the dinosaurs, leaving the pencil urchins of order Cicaroida as the only living members. All other living urchins are Part of the clade Euechinoidea. Amongst them, there are still some oddballs, known as the irregular urchins of clade Irregularia. These urchins have moved away from radial symmetry, with less symmetrical segments and the anus and mouth moving from being on the top and bottom to being on the sides in the heart urchins. Heart urchins have gone from bilateral symmetry to radial symmetry and are now going back to bilateral symmetry. Heart urchin mouths don't have an Aristotle's lantern. Instead, they use strands of mucus to capture food and cilia to pull the strands back inside. Sand dollars, also known as sea cookies or sea biscuits, are also in this clade. These are flattened urchins with short and very fin spines that resemble velvet. They are burrowers who spend much of their time buried under sand and as such are rarely seen alive. The name sand dollar comes from their tests, which are similar to old dollar coins and can often be found washed up on beaches. While still radially symmetrical, sand dollars also have a secondary form of bilateral symmetry, with a distinct front and back end that often look different. Irregular sea urchins also tend to have fewer gonads and associated pores than regular sea urchins.

(image: a red pencil urchin (Heterocentrotus mamillatus) nestled among coral. Instead of spines, it has a series of long, thick, red clubs. End ID)

(image: a purple heart urchin (Spatangus purpureus). It is an urchin elongated on one direction and with a few rows of long spines amongst short ones. On the surface facing the camera is a large hole that could be the mouth or the anus. End ID)

(image: a group of irregular sand dollars (Dendraster excentricus) partially buried in the sand. They are round, flat animals with a velvety covering of tiny spines. The are sticking out of the sand. End ID)
Sea urchins have been known to humans for as long as people have lived near the ocean. Stings can occur when people step on them and can cause pain and irritation, but are rarely medically significant. That being said, some people can have allergies to the venom, which could be a big problem. Spines left in the wound should be removed, as they can continue injecting venom. Urchins are a food source for people around the world, specifically the gonads, which are the only meaty part of the animal. The gonads are often marketed as roe or corals and can be eaten raw or cooked. Urchins are also used as a model organism in embryology due to the interesting and well-studied nature of their larval development. Urchins are vulnerable to pollution, habitat loss, and over-predation. Ocean acidification due to climate change poses a major threat to them, as it reduces the quality of their tests.

(image: tow sea urchins served as food. They are upside-down with the bottoms removed. The gonads are visible within as five orange, spongy structures that take up most of the body cavity. End ID)
#wet beast wednesday#sea urchin#urchin#sea urchins#echinoderms#invertebrates#invertiblr#sand dollar#heart urchin#pencil urchin#marine biology#marine life#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#informative#educational#image described
812 notes
·
View notes
Text
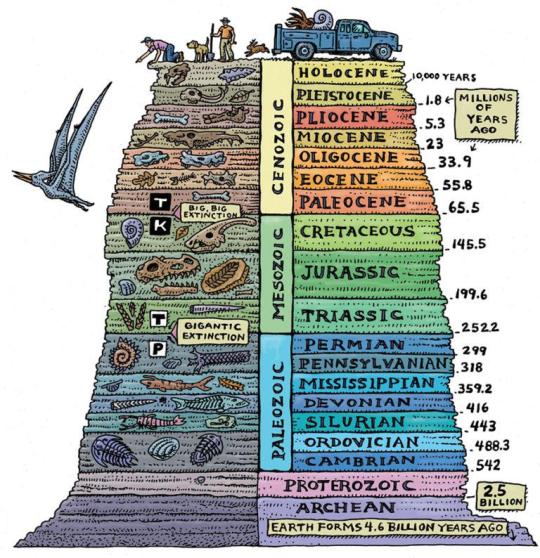
Guide For The Geological Time Periods In Order
#geology#geologists#charts#graphs#infographics#infographic#time periods#educational#earth#science#interesting
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
worth the read yall !!!
this is amazing and i’m so glad you put in the time and effort to educate us and put this into light!
Mac from Date Everything is an innacurate wheelchair design, let's talk about it! Also, before anyone says, "they were going for a computer theme!" I am aware! That does not change that this is a bad design.

For anyone who does not know me, hello! I'm Solstice. I'm a full-time wheelchair user and functionally non-ambulatory. I know my way around a wheelchair considering I use one in my everyday life.
First off, Mac has a hospital style wheelchair. a hospital style is essentially any wheelchair you'd get or use in a hospital. I'd like to clarify that I know some disabled and chronically ill people use hospital style wheelchairs, but a lot of the time in media, depictions of wheelchair users show hospital style wheelchairs NOT for representation, but out of ignorance for active ultralightweight manual wheelchairs.


On the left is a Drive brand hospital style wheelchair. On the right is my personal custom wheelchair.
Mac's armrests are also disproportionate to the rest of the wheelchair. There are definitely people who have armrests on their custom wheelchairs! I have armrests but have taken them off, personally. The issue on Mac's wheelchair arises when their armrests are not only incredibly high, but their drive wheels (the big wheels in the back) are disproportionately small. And while on the topic of their drive wheels, they have no push rims, and no other features like a joystick to show that this is a power chair. The camber tube (tube between the two drive wheels under the seat of the chair) is also way too low. The camber tube goes towards the bottom of the wheel, not even the center of the wheels. Those drive wheels would be unable to roll.
Mac's castors are also very big. Castors can range in size but Mac's castors are so big I don't think that wheelchair could turn- the castors would hit either the footplates or the drive wheels! And with the castor assembly, Mac's castor has an axle system instead of a fork system. Those castors couldn't even turn because they can't freely swivel!
Mac's backrest looks hard and uncomfortable, and it's very tall. Some people need or opt to have high backrests, but this is not accurate to what a rigid backrest would be like. Mac also does not have a cushion, or a very tiny cushion, which would cause pressure sores and also just be uncomfortable.
I'd like to conclude that I hold no ill will towards the artist, designer, devs, fans, etc. But I did want to talk about this since Mac's wheelchair design feels like it wasn't researched much at all. I love that the devs wanted to include a disabled character, but you have to do research. I was really interested in playing this game but Mac's design really did turn me off from the game. I hope this is something that could potentially be amended.
My ask box is also open to questions, comments, concerns, etc.!
#date everything#date everything mac#wheelchair user#disabled#date everything game#educational#thank you again#love to read about this and learn more about the community#hope to see fanart of their wheelchair be redesigned by other mac artists!#i know yall will cook up something 🫶
198 notes
·
View notes
Text

Okay, so The Everyday Naturalist is up on the Ten Speed Press and Penguin/Random House's websites (and various other public places), so I can FINALLY show you the cover!!! I have been saying for months that this book is going to be absolutely beautiful (in addition to informative!), and now you get a good taste of that. Ricardo Macia Lalinde is an incredibly skilled artist whose natural history studies will grace not only the cover but the interior of the book; I feel incredibly fortunate to have his work included in this project.
Here's a bit more about the book itself: "If you’ve ever consulted a field guide to identify a new bird at your feeder, you know the process isn’t as easy as it sounds. In fact, it seems like you have to know a lot about that mystery bird to even figure out where to start.
"The Everyday Naturalist fills in the gaps by explaining what traits to pay attention to when encountering a new species; how and when to use field guides, apps, and other resources; what to do if you get stuck; and more. Rather than focusing on one region or continent, these skills and tools are designed to help you classify nature anywhere you are—whether on familiar territory, traveling, or in a new home."
The book has officially gone to press with a release date of June 17, 2025. Which means in half a year we can all have physical copies in hand! I haven't yet been able to talk to the marketing folks at the publisher to find out whether I can personally take preorders for signed copies, but I'll keep you posted--in the meantime you can preorder at the bookstore of your choice, online or brick and mortar.
#The Everyday Naturalist#naturalist#nature#natural history#animals#plants#fungi#nature identification#science#scicomm#educational#wildlife#ecology
505 notes
·
View notes
Text

a valuable lesson
263 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you want to get married, ask Allah for 3 things in a spouse:
1. Ya Allah please Grant me someone who will remind me of You.
2. Ya Allah please Grant me someone who will hold my hand in Jannah.
3. Ya Allah please Grant me someone who will elevate my Imaan.
Ameen Ya Rabb.
448 notes
·
View notes
Text

@hopalynes and i having a very sanya n yura moment
#me meeting a mutual irl: is this a pafl reference#now i know what the vocazoomers are on#educational#parties are for losers#scraps#myart#sanya#yura#project sekai
956 notes
·
View notes
Photo


🌿 'Tropical Rain Forest Preserves' by Mark Dion & William Schefferine
249 notes
·
View notes
Text












🧵 THREAD: This #EqualPayDay, let’s not forget how many of our workplace rights were only secured in the last few decades.
💪✨ We need to fight for our rights.
Here’s are a few examples:
📍 In 1963, the Equal Pay Act required employers to provide equal pay for equal work regardless of gender.
📍 In 1964, the Civil Rights Act prohibited discrimination based on gender, race, religion, color, or national origin in public places, schools, and employment. Before, it was legal to refuse employment opportunities to women.
📍 In 1978, the Pregnancy Discrimination Act made it illegal for employers to discriminate against pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions.
📍 In 1988, the Women's Business Ownership Act created support for women business owners and eliminated the requirement for male co-signers on loans.
📍 In 1993, the Family and Medical Leave Act gave some workers paid family leave, and provided job protection and security for employees who took unpaid time off to care for a relative or family member.
📍 In 2010, the PUMP Act expanded the Break Time law, which provides key workplace protections for nursing mothers, including reasonable break time to nurse and a private place to pump.
📍 In 2020, the U.S. Supreme Court held that an employer who fires or otherwise discriminates against an individual simply for being gay or transgender is in violation of Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
📍 In 2024, the Department of Labor introduced a Final Rule to end an employer's ability to pay individuals with disabilities subminimum wages.
Alt-text included on all pieces.
#equal pay day#equal pay#pay gap#pay inequity#pay inequality#economic justice#capitalism#women at work#women's rights#graphics#educational
698 notes
·
View notes
Text




This afternoon, read CURSE/KISS/CUTE, my illustrated web novel for queers 18+. Features include:
hope
flirting
emotions
the inherent sexiness of change
vaguely scary deep lore (also sexy)
forcefem (woke)
jokes
It's literally free: www.dicot.moe/ckc
340 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: moray eels
This week on Wet Beast Wednesday I'll be going over something amazing, a fish with a sense of morality. You see, the moral eel is known for, what... I think I'm reading this wrong. Oh, MoRAY eel, not moral. Well this is awkward. Hang tight, I need to go redo my research.
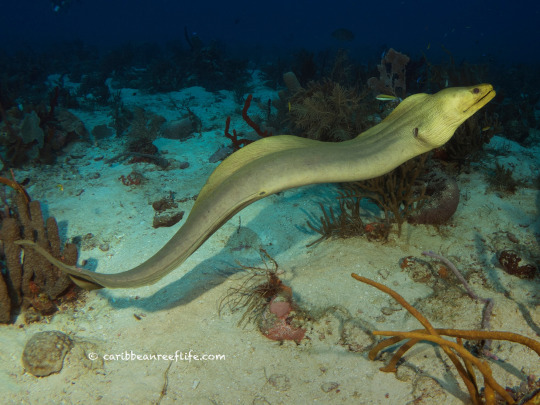

(Image: a green moray (Gymnothorax funebris) swimming outside of its burry, with its whole body visible from the side. It is a long, slender fish that looks a bit like a snake. A long fin starts just below the head and continues down the length of the body. The body is arranged in a wave pattern. It has a pointed snout and small eyes. Its body is a yellow-green color. In the background is the sandy seafloor, dotted with various sponges and corals. End ID)
Moray eels are true eels, meaning they are in the order Anguiliformes. Yeah, I did wolf eels, electric eels, and lamprey eels before I got around to actual eels. There are over 200 known species of moray eel in 15 genera. Like other eels, they are elongated bony fish with extra vertebrae and reduced fins. Moray eels have fewer fins than most eel species, only having a dorsal, anal and tail fin that merge together and run down the back of most of the body and underneath portion of it. They achieve motion by undulating this long fin and sometimes undulating the rest of the body as well. Moray eels aren't the fastest of fish, but they can swim backwards, something almost no fish can. The head has a long snout with wide jaws. Most species have long fangs used to grab onto prey, but a few species are adapted to eat hard-shelled prey and have molar-like teeth to crush through shells instead. Probably the coolest feature of morays are the pharyngeal jaws. This is a second set of jaws located in the back of the mouth. When the eel bites onto prey, the jaws can be shot forward to grab the food and help pull it into the throat. While lots of fish have pharyngeal jaws, morays are the only ones who can extend their pharyngeal jaws forward and use them to grab prey. Morays have smooth, scaleless skin that is often patterned to provide camouflage. The skin is coated in mucus that provides protection from damage and infection. In some species, the mucus can be used to glue sand together to help reinforce burrows. Morays lack lateral lines, a system of organs found in most fish that senses changes in water movement. Their sense of smell is their primary sense. The size of morays varies between species. The smallest species is the dwarf moray eel (Gymnothorax melatremus) which reaches 26 cm (10 in) long. The largest species by mass is the giant moray eel (Gymnothorax javanicus) which can reach 3 meters (10 ft) and 30 kg (66 lbs) while the longest species is the slender giant moray (Strophidon sathete), the longest known specimen of which measured in at 3.94 m (12.9 ft).

New reaction image
(Image: a giant moray (Gymnothorax javanicus) emerging from a burrow. It is brown and mottled with yellowish patches. Its head is pointed at the camera and it's mouth is wide open, aming it look shocked. End ID)

(Image: an anatomical diagram of the skeleton of a moray eel emphasizing the pharyngeal jaws and the muscle attachments. End ID. Art by Zina Deretsky)
Moray eels are found throughout the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans. Different species are found in different temperatures and depths, though most species live in relatively shallow, warm water. Several species can live in brackish water and a few will swim upriver and live for a time in fresh water, though there do not appear to be any species that live their entire lives in fresh water. Morays are ambush predators who rely on the element of surprise. They live in small, tight places such as holes in coral, gaps between rocks, or sandy burrows. When prey passes, the eel can lunge out and grab it. Unlike most fish, the eel cannot use suction feeding due to the shapes of their mouths. They have to rely on lunging froward and catching prey with their mouths. Their mouths are adapted in shape to push water to the sides. This reduces water resistance and avoids creating a wave that could push prey away from the eel. If an eel catches prey that cannot be swallowed whole, it will tie itself in a knot while biting on to the food. By pulling its head through the loop, the eel can rip the food into bite-sized pieces. Spending most of their times in burrows also provides protection from predators, especially in juveniles or smaller species. At night, the eels will come out of their burrows to hunt sleeping prey while the larger predators are asleep. Giant morays have also been seen engaging in interspecies cooperative hunting with roving coral groupers (Plectropomus pessuliferus). The eels can fit into small crevices the groupers can't to flush prey into the grouper's path while catching their own. Morays are mostly solitary species and many can be territorial. They are known to be shy and will retreat into their burrows if they feel threatened. They are also curious and many species are quite intelligent.

(Image: a male ribbon eel (Rhinomuraena quaesita) on a coral reef. It is a very long and slender eel with its body curved in many waves. It is brightly colored, with a blue-purple body, yellow fin and face, and a long black and white stripe running down the back half of the body. On the nostrils are two feather-like structures. End ID)
Morays reproductive strategies are poorly known and differ based on species. While many species seem to have no set mating season and will reproduce whenever they can, others will mate at the same time every year. Some species seem to have dedicated spots to lay their eggs and a few are believed to be anadromous, meaning they travel from the sea to fresh water to spawn. Meanwhile, some of the species that spend a lot of time in fresh water are catadromous, meaning they return to sea to mate. Females will lay their eggs and the male fertilize them. After this, they depart, providing no parental care. As with all true eels, moray eels begin life as leptocephalus larvae. This type of fish larvae is notable for its resemblance to a simple, transparent leaf with a head on one end. These larvae are unique and poorly understood, despite being the larval stage of a lot of different species of fish. They are unusually well developed for larvae, capable of active swimming and generally living life. In fact, some particularly large leptocephalus larvae were initially mistaken for adult fish. They feed mostly on bits of drifting organic material called marine snow and can remain in the larval stage for up to 3 years, with those in colder conditions usually taking longer to metamorphose. All leptocephalus larvae start out with no sex organs, then develop female organs, then develop male ones, becoming simultaneous hermaphrodites. They will ultimately become eith male or female and it is likely that environmental factors are the main determining factor. During metamorphosis into a juvenile, the leptocephalus can reduce in size by up to 90%, resulting in the juvenile being smaller than the larva. The process of maturation is poorly understood, but it seems that most morays will be sexually mature by three years of age.

(Image: multiple photos of a particularly large leptocephalus larva (not sure what species). It is a translucent organis, wth a body shaped like a very long leaf, narrow at both ends. In the frint is a very tiny head. End ID)
Morays are shy and generally avoid humans. Though some cultures have hunted them for food, they are often not considered a particularly good food source. Many species have high levels of chemicals called ciguatoxins in their bodies, which can lead to a condition called ciguatera fish poisoning if eaten. The largest threat to morays is habitat loss. This is especially true for the many species that live in coral reefs, which are in increasing danger due to global warming. Attacks on humans are rare and usually happen as a response to a human sticking their hand in the eel's burrow. Some of the large species could cause significant damage with a bite. Some species, usually the smaller ones, are found in the aquarium trade, thought they are not good pets for beginners as even the smallest morays are still large for aquarium fish and have some specific requirements. The curiosity many morays have has led to some becoming familiar with and even friendly to humans, often the result of feeding them. They can recognize individual humans and remember them over the course of years. Aquarium employees sometimes report that the eels will come to nuzzle and play with them and have personalities like dogs. Marine biologists and professional SCUBA divers Ron and Valorie Taylor befriended a pair of eels they named Harry and Fang at the Great Barrier Reef who would remember them and come out to visit them year after year.
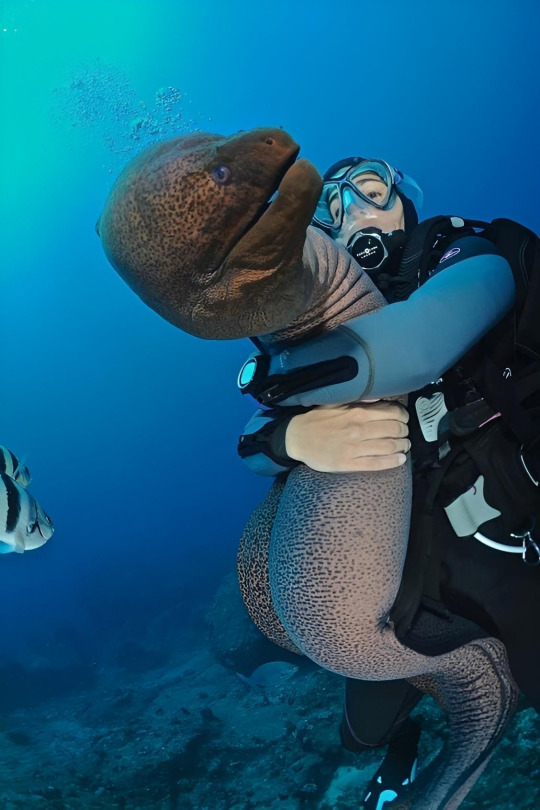

(Image: a SCUBA diver hugging a large, brown moray with black spots. End ID)
youtube
(Video: A shot video showing Valeria Taylor and a moray eel she befriended)
youtube
(Video: the song "That's a Moray", a parody of the song "That's Amore" by Dean Martin)
#wet beast wednesday#i accidentally typed moron eel more than once#moray eel#eel#anguiliformes#fish#bony fish#fishblr#fishposting#eelposting#marine biology#biology#ecology#zoology#animal facts#informative#image described#that's a moray#educational#Youtube
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

#black tumblr#black history#black community#black literature#civil rights#black history is american history#black excellence#civil rights movement#black girl magic#blackexcellence365#black history month#black history matters#black history facts#julian bond#equal education#educational#equal rights#equality#equal
354 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi, quick clarification for baby leftists.
Privilege is when you lack barriers another person faces due to your identity (or perceived identity!) and social position, and it's often unnoticeable that you're experiencing it until someone points it out.
An example: I have privilege over my POC friends because I am perceived as white. My man friends have privilege over me because I am perceived as a woman. So my Puerto Rican man friend and I have privilege over each other in different ways, him because he doesn't face sexism and misogyny the way I do, and me because I don't face racism the way he does.
Relative Privilege is when one person with the same identity as another experiences discrimination or barriers to a lesser degree than the other.
An example: My friend and I are both Autistic, and we both experience discrimination due to that. Our autism presents differently, and (generally speaking!), I am more disabled by it than he is. Thus, he holds relative privilege over me. He is still discriminated against more than an allistic person is, but he is discriminated against for his autism less than I am for mine. This is relative privilege. This can also be applied more broadly, for example, I hold relative privilege over many disabled people who are not Autistic but are also otherwise disabled, because they experience more barriers than I do.
Also please note that privilege, because it's given or denied from larger social structures, is often more about how people perceive your identities than your actual identities! For example, I am not a woman, but I am perceived as a woman, and thus experience discrimination based on that.
Experiencing privilege is not a morally bad thing, and experiencing discrimination is not a morally high thing. It's easy to fall into the identity olympics, but it's not helpful. Where you have privilege, use it to lift the voices of those who don't. You are essential. Where you don't have privilege, learn your history, find your community, and embrace yourself. You are essential.
#sociology student#mytomatoes#baby leftists#leftism#leftism 101#communism#socialist#socialist politics#sociology#social justice#socialism#socialist revolution#youth liberation#trans liberation#fat liberation#black liberation#queer liberation#mad liberation#indigenous liberation#intersex liberation#communist#privilege#disability liberation#disability justice#educational#sociology 101
168 notes
·
View notes