#ESRD
Text
I have a headache and I wish I could take naproxen instead of useless Tylenol
#Tylenol's the only kidney-safe OTC painkiller#but it doesn't do SHIT#ESRD#end stage renal disease#headache#owwww#tylenol
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://gofund.me/6732cec4
Behind every dope ass woman is one hell of a story💚🪄🌻
#black girl magic#national kidney foundation#chronic kidney failure#esrd#ckd#organ donation#kidney transplant#end stage renal disease#Pediatric Nurse#registered nurse#chronic illness#chronic pain#gofundme#fundrasier#john hopkins hospital#black nurses matter#black nurses rock
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kidney transplant-recipient and former dialysis patient Patrick O. Gee wrote a rebuttal to Saturday's article, arguing that a keto diet worked much better for his diabetes, weight, and kidney health than the plant-based diets the researchers recommended.
#TeachingRounds#FOAMed#physiology#nutrition#renalfailure#nephrology#dialysis#ESRD#transplant#patientperspective#patientvoice
0 notes
Text
Global Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market is Estimated to Witness High Growth Owing to Technological Advancements and Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Diseases

The global Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market is estimated to be valued at USD 20.12 billion in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 5.50% over the forecast period 2023-2028, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights.
A) Market Overview:
The global Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market refers to the medical equipment used for kidney dialysis, which is a life-saving treatment for individuals with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or chronic kidney disease (CKD). Kidney dialysis equipment includes hemodialysis machines, peritoneal dialysis machines, dialyzers, dialysis accessories, and services.
Kidney dialysis equipment provides an artificial replacement for lost kidney function by removing waste, salt, and extra water from the body, as well as maintaining the balance of minerals in the blood. This treatment helps in managing the symptoms of kidney failure and improves the quality of life for patients.
B) Market Dynamics:
The Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market is driven by two major factors: technological advancements and the increasing prevalence of chronic kidney diseases.
1. Technological Advancements:
Technological advancements in kidney dialysis equipment have significantly improved the efficiency, safety, and convenience of dialysis treatment. For instance, the introduction of high-flux dialyzers has led to better clearance of toxins from the blood, reducing the duration and frequency of dialysis sessions. Additionally, portable and wearable dialysis machines have emerged, providing greater freedom and flexibility to patients, enabling them to perform dialysis at home or even on the go.
2. Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Diseases:
The increasing prevalence of chronic kidney diseases, primarily driven by rising diabetes and hypertension cases, is fueling the demand for kidney dialysis equipment. According to the National Kidney Foundation, around 10% of the global population suffers from chronic kidney diseases. In the United States alone, more than 37 million adults are estimated to have kidney disease, and over 726,000 people have ESRD.
C) Segment Analysis:
Among the Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market Segmentation the hemodialysis machines segment is expected to dominate, owing to the high demand for these machines in hospitals and dialysis centers. Hemodialysis is the most common form of kidney dialysis treatment, where blood is filtered using a dialyzer outside the body. The dominant position of hemodialysis machines can be attributed to their efficient removal of waste products and toxic substances from the blood.
D) PEST Analysis:
Political: Government initiatives and policies promoting dialysis treatment, reimbursement policies, and healthcare infrastructure play a crucial role in the adoption of kidney dialysis equipment.
Economic: Economic factors such as increasing healthcare expenditure and disposable income levels of individuals drive the growth of the Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market.
Social: The rising incidence of chronic kidney diseases, aging population, and growing awareness about kidney health contribute to market growth.
Technological: Technological advancements in kidney dialysis equipment, such as wearable devices and telehealth solutions, improve patient convenience and treatment outcomes.
E) Key Takeaways:
- The global Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.50% over the forecast period, due to increasing technological advancements and the rising prevalence of chronic kidney diseases.
- North America is expected to dominate the market due to the presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and a large patient pool.
- Key players operating in the global Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market include Fresenius Medical Care AG & Co, Baxter International, Inc., Nipro Corporation, B. Braun Melsungen AG, Nikkiso Co, Ltd., Asahi Kasei Corporation, NxStage Medical, Inc., Guangdong Biolight Meditech Co., Ltd, Dialife SA, and DaVita Inc. These players focus on strategies such as mergers and acquisitions, partnerships, and new product launches to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
#Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market#Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market Insights#Coherent Market Insights#Kidney Dialysis Equipment Market High Growth#Chronic Kidney Diseases#Technological Advancements#medical devices#ESRD#CKD
0 notes
Text
Sickle cell nephropathy, a complication not to be ignored, through a Moroccan case by Asmaa Biaz in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences

SUMMARY
Nephropathy is a major complication of sickle cell disease. Indeed, the kidneys are particularly sensitive organs to this disease.
We report a case of a patient with a major sickle cell syndrome; she was hospitalized in the nephrology department of Mohammed V Military Training Hospital, forend-stage renal failure. The family investigation revealed a composite S/O-Arab heterozygosity responsible for the severity of the clinical disorder.
Key words: Sickle cell nephropathy - End stage renal failure - Sickle cell major syndrome S/O-Arab.
INTRODUCTION
Sickle cell nephropathy (SCN) is a major complication of sickle cell disease. It manifest’s in various forms, including glomerulopathy, proteinuria, hematuria, and Renal tubular disorders, and frequently results in end-stage renal disease(ESRD). Hemolysis and vascular occlusion are the main factors promoting the manifestations of this disease. Dialysis and renal transplantation are the last resort for patient with SCN [1].
Through the case of a patient with a major sickle cell syndrome S/O-Arab complicated by end-stage renal failure, we will explain the pathophysiological mechanisms of this complication and emphasize the importance of biological monitoring.
CASE REPORT
The patient was 24 years old and was admitted to the nephrology department of the Mohammed V Military Training Hospital for incidental renal failure in the context of an impure nephrotic syndrome revealing sickle cell nephropathy. In his history, we retained a
follow-up since the age of 5 years in another hospital structure for a hemoglobinosis S treated by iterative transfusions with notion of acute renal failure during sickle cell crises.
The biological result showed an anemia at 7.7 g/dL, corrected serum calcium at 82 mg/L, serum phosphorus at 64 mg/L, intact parathyroid hormone 1-84 at 543 pg/L, Alkaline Phosphatase at 201 U/L.
Hemoglobin electrophoresis was ordered to this patient, but due to repeated transfusions, her electrophoretic profile remains uninterpretable (Figure 1). Therefore, hemoglobin electrophoresis (HBE) was performed in the parents as part of the hemoglobin phenotypic study. The HBE of both parents is performed on Capillarys (Sebia®) at alkaline pH followed by electrophoresis at acidic pH on Hydrasys (Sebia®) which showed a heterozygous Hb O-Arab variant in the mother (Figure 2) and a heterozygous hemoglobinosis S (A/S) in the father (Figure 3).
Figure 1: Electrophoretic profile of the patient uninterpretable due to recent transfusion
Figure 2: Electrophoretic profile of the mother showing hemoglobinosis O-Arab in the heterozygous state
Figure 3: Electrophoretic profile of the father showing hemoglobinosis S in the heterozygous state
Referring to the phenotypic study of Hb performed in the parents, it is concluded that the patient has a composite heterozygosity S/O-Arab explaining the severity of the renal manifestations.
The evolution was marked by the absence of improvement of her renal function and the aggravation of the uremic syndrome motivating her setting in peritoneal dialysis. The patient was treated with erythropoietin ARANESP 30µg/ per 2 weeks with a blood transfusion of 2 packed red blood cells on average every two months.
The patient died at the age of 26 years before benefiting from either a hemoglobin genotyping study or a renal transplant.
DISCUSSION
Sickle cell disease is the most common hereditary hemoglobinopathy in the world. An estimated 300,000 children are born with this disease each year, three quarters of whom are born in sub-Saharan Africa [2]. It is characterized by extreme variability in terms of clinical manifestations, the most serious of which are renal manifestations.
The association S/O Arab is responsible for a major sickle cell syndrome, as in the case of our patient. Indeed, Hb O Arab stabilizes the intracellular polymerization of Hb S and leads to an irreversible sickle cell disease of red blood cells, thus expressing by a more severe clinical disorder. The clinical and biological manifestation of this association is similar to homozygous sickle cell disease and the association Hb S / Hb D Punjab. The onset is usually early, in infancy, and is marked by the classic triad of chronic hemolysis: anemia, jaundice and splenomegaly. Anemia is usually moderate outside of hemolytic attacks (Hb = 7 - 10 g/dL). The evolution is often marked by sickle cell complications. Osteoarticular complications are the most frequent, such as vaso-occlusive crises, septic arthritis and osteoporosis. Pneumonia, leg ulcers and vesicular lithiasis are also reported [3].
Sickle cell nephropathy is a major complication of sickle cell disease. The kidneys are particularly sensitive organs to the disease. Sickle cell disease substantially alters the structure and function of the kidneys and is the cause of several renal diseases and syndromes. Renal damage is more severe in SS homozygous patients than in other major sickle cell syndromes [4]. Approximately 5-18% of patients have SCN, thus increasing the risk of morbidity and mortality of the disease [5].
A number of studies have focused on this pathology, its evolution includes several stages; it starts with hyperfiltration, then the occurrence of microalbuminuria, then macroalbuminuria and finally the progression to renal failure. The prevalence of these complications increases with the age of the patients but can also be seen from a young age.
Two models have been proposed to explain the pathophysiology of SCN. Becker et al. showed that prostaglandin release following ischemic injury causes an increase in glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This increase leads to glomerular injury and eventually manifests as proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis [6]. Alternatively, Nath and Katusic [7] classified the manifestations of SCN into two different phenotypes: the hemolysis-endothelial dysfunction phenotype and the viscosity-vaso-occlusive phenotype. The hemolysis-endothelial dysfunction phenotype affects the renal cortex and leads to hyperfiltration and glomerulopathy; heme released due to intravascular hemolysis predisposes to proteinuria through its accumulation on the glomerular filtration barrier, which disrupts membrane selectivity by exerting cytotoxic effects on podocytes and endothelial cells [8]. On the other hand, the viscosity-vaso-occlusive phenotype is responsible for hematuria, papillary necrosis, and tubular acidosis [9].
Microalbuminuria, reflecting the early stages of renal damage, should be routinely sought in the follow-up assessment in this category of patients.
Decreased GFR, which suggests loss of kidney function, occurs with the progression of sickle cell disease and may be a sign of uncontrolled disease. Sickle cell patients have a higher risk of developing chronic kidney disease compared to the general population.
Specific treatment with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin II
receptor antagonist should be considered in these patients in order to slow the progression of the renal disease. The prevention of microthrombosis and thus of renal damage requires the maintenance of a hemoglobin A level of more than 50% by regular blood transfusion as soon as sickle cell disease is diagnosed. The role of hydroxyurea in the prevention and/or treatment of renal function abnormalities in sickle cell disease remains to be studied [10].
CONCLUSION
Sickle cell nephropathy is a major complication of sickle cell disease. It must be systematically and early sought in all sickle cell patients to reduce the risk of morbidity and mortality of this disease.
The development of new biomarkers has become increasingly essential for the early detection of sickle cell disease in order to improve the survival of patients with sickle cell disease.
Declaration of interest:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
For more information: https://jmedcasereportsimages.org/about-us/
For more submission : https://jmedcasereportsimages.org/
#Sickle cell nephropathy#End stage renal failure#Sickle cell major syndrome#S/O-Arab#Hemolysis#SCN#ESRD#hemoglobinosis#heterozygous#Asmaa Biaz#jcrmhs
0 notes
Text
You avoid gadolinium contrast with MRI in pts with CKD because you want to avoid gadolinium-induced nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.
1 note
·
View note
Text
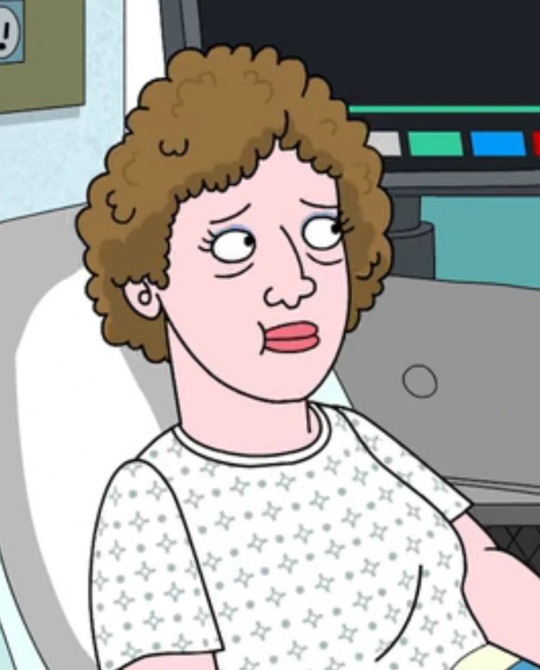

Today’s disabled character of the day is Helen Chavez from Bojack Horseman, who has kidney failure
[Image Description: Drawing of a women laying in a hospital bed next to a monitor. She has short curly brown hair and black eyes. She is wearing light purple eye shadow and a white hospital gown.]
21 notes
·
View notes
Link
End stage of Renal disease happens to be the last stage of acute or chronic renal failure. read about Causes, Symptoms, Treatment of End stage Renal disease
#End Stage renal Disease#Causes ESRD#Symptoms ESRD#nephrologist in Ahmedabad#Nephrology Doctor#kidney diseases#Kidney Specialist in Ahmedabad
0 notes
Text
Medicare Risk Adjustment Tip: ESRD and Dialysis Status
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is a medical condition in which a person's kidneys stop working permanently, requiring a regular course of dialysis or kidney transplant for a long period of time to sustain life. Beneficiaries may be entitled to Medicare based on ESRD. Benefits based on ESRD are for all covered services and not just services related to kidney failure conditions. Once a patient is diagnosed with end-stage kidney disease and has been accepted and documented by the health plan and CMS, the patient's MRA score is calculated differently.
0 notes
Link
tell me why the acc has a widget to post their articles to tumblr
#TRYING TO DO THIS DRUG INQUIRY ASSIGNMENT !!!!!!!!!!!!#hmu if you know anyone with esrd and on a doac!#personal
1 note
·
View note
Text
Damn near forgot today was Saturday (aka a treatment day). Thank g*d for my alarm going off
#WHOOPS 🤦♀️#kept thinkin it was Monday and I had the day off lmao#thankfully I don't have to do much preparation before leaving LOL#dialysis day#life on dialysis#life with chronic illness#actually chronically ill#ESRD#end stage renal disease#oopsies#cw medical
0 notes
Text

Shoutout to my GOD-mama for my cup! It’s most definitely a coffee ☕️ kind of day.
https://gofund.me/6732cec4
#ThisNurseNeedsAKidney#ClickTheLink#DonateLife#ShareYourSpare#PediatricNurse#black girl magic#black girls rock#black nurses matter#black nurses rock#esrd#ckd#chronic kidney disease#kidney failure#end stage renal disease#dialysis#john hopkins hospital#atypical hus#Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome#chronic pain#chronic illness#spoonie#gofundme#healing#happy juneteenth#juneteenth#support black people#support black women#registered nurse#organ donor#organ donation
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a prospective study of 15K American adults over ~25 years, researchers at Johns Hopkins and University of Minnesota found an association between healthy plant-based diets and a lower risk of chronic kidney disease.
0 notes
Text
MCU Series
Below you’ll find series that have more than three parts and stories that are only two parters. If you see a story that only has two parts that you want to see more of, let me know!
Happy reading :)


*The image(s) I’ve used for the reader on the cover DOES NOT reflect what the reader actually looks like*
Series Rewrite
Pairing: Varies From Movie To Movie
Status: In Progress
Summary: You call Earth home after fifty years of running from your home planet. There, you meet all kinds of people that you help, including the two loves of your lives: Bucky Barnes and Loki Laufeyson. They are two different sides of the same coin. How can you ever choose between them, and will you?
*The image(s) I’ve used for the reader on the cover DOES NOT reflect what the reader actually looks like*
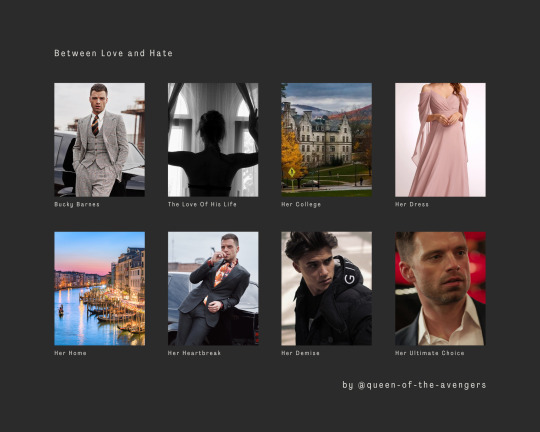
Between Love and Hate
Pairing: Mafia!Bucky Barnes x Female!Reader
Status: In Progress
Summary: Loving Bucky Barnes is like waiting for a grenade to go off. Fearful yet thrilling. Every time you allow yourself to feel something for him, a piece of you is chipped away and stored in his jacket pocket. How can you love a man who murders people for a living? How can you hate a man who gives you the world? You're stuck in the middle with no clear way to the end.

*The image(s) I’ve used for the reader on the cover DOES NOT reflect what the reader actually looks like*
My Savior
Pairing: Sebastian Stan x Female!Reader
Status: Completed
Summary: Your entire life has been spent in and out of hospitals because you have ESRD or kidney failure. The only thing you’ve ever known is being hooked to monitors and machines that live for you. Never straying too far from the hospital, and never really connecting with anyone. When you get the news you have a kidney waiting for you, your donor surprises you in more ways than one… and he does something for you that you can’t ever repay him for.

*The image(s) I’ve used for the reader on the cover DOES NOT reflect what the reader actually looks like*
Cat and Mouse
Pairing: Steve Rogers x Female!Reader
Status: In Progress
Summary: Much like Bucky, you've been a toy that Hydra just loves to use. You were taken at such a young age that you were shaped into what they wanted you to be. Well, you're not doing it anymore. You escaped. You got out. But that doesn't mean you can't fall back into the monster they made you.

*The image(s) I’ve used for the reader on the cover DOES NOT reflect what the reader actually looks like*
New World Order
Pairing: Zombie!Steve Rogers x Vampire!Fem!!Reader
Status: In Progress
Summary: When the emergency alarms sounded, you knew the world wasn’t ever going to be the same. A new dawn is approaching with a whole new set of rules. One where you and the love of your life are no longer human. Well, that’s what you thought until you figured out the cure that will save humanity.

*The image(s) I’ve used for the reader on the cover DOES NOT reflect what the reader actually looks like*
Monster Inside You
Pairing: Steve Rogers x Succubus!Fem!Reader
Status: On Hold
Summary: One fatal mistake and your life is turned upside down. You have to live with the consequences of what happened to you, and you're not always good at controlling your urges. Still, you do your best to keep who you are while still embracing this new side to you.

The Voice Behind Karen // Part 2
Pairing: Peter Parker x Female!Reader
Summary: You’re Tony Stark’s daughter and also the AI in Peter’s suit. He calls you Karen but your name is Y/N. After he discovers your secret, you two get closer.
Office Romance // Part Two
Pairing: Natasha Romanoff x Female!Reader
Summary: You have a crush on your boss, and it's news to you when she shows you that she has one on you, too.
Pick A Side // Better Late Than Never
Pairing: Steve Rogers x Stark!Fem!Reader
Summary: Everyone expected you to pick your dad's side when it came to the Accords. You didn't. He kicked you out of his life. Now it's finally time to face him.
Not Allowed // Part Two
Pairing: Cop!Bucky Barnes x Receptionist!Fem!Reader
Summary: You go on a date with a man that Bucky doesn't approve of. He uses his power to break it up which is the best thing that could have happened to your relationship with Bucky.
Wolf in Sheep's Clothing // Part Two
Pairing: Bucky Barnes x Female!Reader
Summary: For an entire year you've been stuck inside your mind with no escape. Never did you think you'd be in such an abusive relationship, but he won't let you leave. Not until you see an opportunity through Bucky to confess everything he's ever done to you. Will you be saved?
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was thinking about watching TGM 'in the background' while I study for finals but I know my goofy ass will be glued to the screen the whole time. I'm not going to be focused on studying ESRD and hemodynamics and cardioversion and EKG strips and PD and HD and CAD and-
No. I'm gonna be watching my favorite little pilots do their silly little piloting things
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Medical Abbreviations on Pharmacy Prescriptions
Here are some common medical abbreviations you may see on pharmacy prescriptions:
qd - once a day
bid - twice a day
tid - three times a day
qid - four times a day
qh - every hour
prn - as needed
pc - after meals
ac - before meals
hs - at bedtime
po - by mouth
IV - intravenous
IM - intramuscular
subQ - subcutaneous
mL - milliliter
mg - milligram
g - gram
mcg - microgram
stat - immediately, right away
NPO - nothing by mouth
cap - capsule
tab - tablet
susp - suspension
sol - solution
amp - ampule
inj - injection
Rx - prescription
C - Celsius
F - Fahrenheit
BP - blood pressure
HR - heart rate
RR - respiratory rate
WBC - white blood cell
RBC - red blood cell
Hgb - hemoglobin
Hct - hematocrit
PT - prothrombin time
INR - international normalized ratio
BUN - blood urea nitrogen
Cr - creatinine
Ca - calcium
K - potassium
Na - sodium
Cl - chloride
Mg - magnesium
PO2 - partial pressure of oxygen
PCO2 - partial pressure of carbon dioxide
ABG - arterial blood gas
CBC - complete blood count
BMP - basic metabolic panel
CMP - comprehensive metabolic panel.
ECG - electrocardiogram
EEG - electroencephalogram
MRI - magnetic resonance imaging
CT - computed tomography
PET - positron emission tomography
CXR - chest x-ray
CTX - chemotherapy
NSAID - nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
DMARD - disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
ACE - angiotensin-converting enzyme
ARB - angiotensin receptor blocker
SSRI - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
TCA - tricyclic antidepressant
ADHD - attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
CAD - coronary artery disease
CHF - congestive heart failure
DVT - deep vein thrombosis
GI - gastrointestinal
UTI - urinary tract infection
OTC - over-the-counter
Rx - prescription
OD - right eye
OS - left eye
OU - both eyes.
TID - thrombosis in dementia
TDS - ter die sumendum (three times a day)
BOM - bilaterally otitis media (infection in both ears)
BT - body temperature
C&S - culture and sensitivity
D/C - discontinue or discharge
D/W - dextrose in water
ETOH - ethyl alcohol
FUO - fever of unknown origin
H&P - history and physical examination
I&D - incision and drainage
I&O - intake and output
KVO - keep vein open
N&V - nausea and vomiting
PERRLA - pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation
PR - per rectum
QAM - every morning
QHS - every bedtime
QOD - every other day
S/P - status post (after)
TPN - total parenteral nutrition
UA - urinalysis
URI - upper respiratory infection
UTI - urinary tract infection
VO - verbal order.
XRT - radiation therapy
YOB - year of birth
BRBPR - bright red blood per rectum
CX - cervix
DVT - deep vein thrombosis
GB - gallbladder
GU - genitourinary
HCV - hepatitis C virus
HPI - history of present illness
ICP - intracranial pressure
IVP - intravenous pyelogram
LMP - last menstrual period
MRSA - methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
MVA - motor vehicle accident
NKA - no known allergies
PEG - percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
PRN - pro re nata (as needed)
ROS - review of systems
SOB - shortness of breath
TAH - total abdominal hysterectomy.
TIA - transient ischemic attack
Tx - treatment
UC - ulcerative colitis
URI - upper respiratory infection
VSD - ventricular septal defect
VTE - venous thromboembolism
XR - x-ray
w/c - wheelchair
XRT - radiation therapy
ASD - atrial septal defect
Bx - biopsy
CAD - coronary artery disease
CKD - chronic kidney disease
CPAP - continuous positive airway pressure
DKA - diabetic ketoacidosis
DNR - do not resuscitate
ED - emergency department
ESRD - end-stage renal disease
FFP - fresh frozen plasma
FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone.
GCS - Glasgow Coma Scale
Hct - hematocrit
Hgb - hemoglobin
ICU - intensive care unit
IV - intravenous
JVD - jugular venous distension
K - potassium
L - liter
MCH - mean corpuscular hemoglobin
MI - myocardial infarction
Na - sodium
NGT - nasogastric tube
NPO - nothing by mouth
OR - operating room
PCN - penicillin
PRBC - packed red blood cells
PTT - partial thromboplastin time
RBC - red blood cells
RT - respiratory therapy
SOA - short of air.
SCD - sequential compression device
SIRS - systemic inflammatory response syndrome
STAT - immediately
T - temperature
TPN - total parenteral nutrition
WBC - white blood cells
ABG - arterial blood gas
A fib - atrial fibrillation
BPH - benign prostatic hypertrophy
CBC - complete blood count
CO2 - carbon dioxide
COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
CPR - cardiopulmonary resuscitation
CT - computed tomography
CXR - chest x-ray
D5W - dextrose 5% in water
Dx - diagnosis
ECG or EKG - electrocardiogram
EEG - electroencephalogram
ETO - early termination of pregnancy.
FHR - fetal heart rate
GSW - gunshot wound
H&P - history and physical exam
HCG - human chorionic gonadotropin
I&D - incision and drainage
IBS - irritable bowel syndrome
ICP - intracranial pressure
IM - intramuscular
INR - international normalized ratio
IOP - intraocular pressure
LFT - liver function test
LOC - level of consciousness
LP - lumbar puncture
NG - nasogastric
OA - osteoarthritis
OCD - obsessive-compulsive disorder
OTC - over-the-counter
P - pulse
PCA - patient-controlled analgesia
PERRLA - pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation.
PFT - pulmonary function test
PICC - peripherally inserted central catheter
PO - by mouth
PRN - as needed
PT - physical therapy
PT - prothrombin time
PTSD - post-traumatic stress disorder
PVC - premature ventricular contraction
QD - once a day
QID - four times a day
RA - rheumatoid arthritis
RICE - rest, ice, compression, elevation
RSI - rapid sequence intubation
RSV - respiratory syncytial virus
SBP - systolic blood pressure
SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus
SSRI - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
STAT - immediately
TB - tuberculosis
TIA - transient ischemic attack.
TID - three times a day
TKO - to keep open
TNTC - too numerous to count
TPN - total parenteral nutrition
URI - upper respiratory infection
UTI - urinary tract infection
V-fib - ventricular fibrillation
V-tach - ventricular tachycardia
VA - visual acuity
WNL - within normal limits
AED - automated external defibrillator
ARDS - acute respiratory distress syndrome
BID - twice a day
BP - blood pressure
BUN - blood urea nitrogen
CAD - coronary artery disease
CHF - congestive heart failure
CVA - cerebrovascular accident
D/C - discontinue
DKA - diabetic ketoacidosis.
DM - diabetes mellitus
DVT - deep vein thrombosis
EGD - esophagogastroduodenoscopy
ER - emergency room
F - Fahrenheit
Fx - fracture
GI - gastrointestinal
GTT - glucose tolerance test
HCT - hematocrit
Hgb - hemoglobin
HRT - hormone replacement therapy
ICP - intracranial pressure
IDDM - insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
IBS - irritable bowel syndrome
IM - intramuscular
IV - intravenous
K - potassium
KVO - keep vein open
L&D - labor and delivery
LASIK - laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis.
ROM - range of motion
RT - radiation therapy
Rx - prescription
SCD - sequential compression device
SOB - shortness of breath
STD - sexually transmitted disease
TENS - transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
TIA - transient ischemic attack
TSH - thyroid-stimulating hormone
UA - urinalysis
US - ultrasound
UTI - urinary tract infection
VD - venereal disease
VF - ventricular fibrillation
VT - ventricular tachycardia
WBC - white blood cell
XRT - radiation therapy
XR - x-ray
Zn - zinc
Z-pak - azithromycin (antibiotic).
AAA - abdominal aortic aneurysm
ABG - arterial blood gas
ACS - acute coronary syndrome
ADL - activities of daily living
AED - automated external defibrillator
AIDS - acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
ALS - amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
AMA - against medical advice
AML - acute myeloid leukemia
APAP - acetaminophen
ARDS - acute respiratory distress syndrome
ASCVD - atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
BPH - benign prostatic hyperplasia
BUN - blood urea nitrogen
CABG - coronary artery bypass graft
CBC - complete blood count
CHF - congestive heart failure
COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
CPAP - continuous positive airway pressure
CRF - chronic renal failure.
CT - computed tomography
CVA - cerebrovascular accident
D&C - dilation and curettage
DVT - deep vein thrombosis
ECG/EKG - electrocardiogram
EEG - electroencephalogram
ESRD - end-stage renal disease
FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone
GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease
GFR - glomerular filtration rate
HbA1c - glycated hemoglobin
Hct - hematocrit
HIV - human immunodeficiency virus
HPV - human papillomavirus
HTN - hypertension
IBD - inflammatory bowel disease
IBS - irritable bowel syndrome
ICU - intensive care unit
IDDM - insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
IM - intramuscular.
IV - intravenous
LFT - liver function test
MI - myocardial infarction
MRI - magnetic resonance imaging
MS - multiple sclerosis
NPO - nothing by mouth
NS - normal saline
OCD - obsessive-compulsive disorder
OSA - obstructive sleep apnea
PCOS - polycystic ovary syndrome
PMS - premenstrual syndrome
PPD - purified protein derivative
PSA - prostate-specific antigen
PT - prothrombin time
PTT - partial thromboplastin time
RA - rheumatoid arthritis
RBC - red blood cell
RSV - respiratory syncytial virus
SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus
TB - tuberculosis.
It is important to remember that medical abbreviations can vary based on location and specialty.
Healthcare professionals should use medical abbreviations with caution and only when they are familiar with their meanings.
Patients should always communicate any questions or concerns they have about their medications or medical care to their healthcare provider or pharmacist to ensure they receive safe and accurate medical care.

7 notes
·
View notes