#Front Access Storage Server
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
HD-H242-Z11 High-Density 4-Node Server | Edge & Data Center Ready
Upgrade your infrastructure with the HD-H242-Z11 Ver Gen001 – a compact 2U high-density server featuring 4 independent nodes with Intel® Xeon® D processors. Designed for edge computing, data centers, and mission-critical deployments, it offers high-performance computing, front-access storage bays, IPMI remote management, and optional 10G networking. Ideal for virtualization, analytics, and enterprise workloads in limited-space environments. for more details:: Hexadata HD-H242-Z11 Ver: Gen001 | High Density Server Page
#HD-H242-Z11 Server#High-Density Server#4-Node Server#2U Rack Server#Xeon D Server#Edge Computing Server#Rugged Server Solution#Twin Node Server#Compact Data Center Server#Gigabyte High-Density Server#Enterprise Server Solution#IPMI Remote Management Server#Front Access Storage Server#Edge Deployment Hardware#Modular Server System
0 notes
Text
EFF’s lawsuit against DOGE will go forward
I'm on a 20+ city book tour for my new novel PICKS AND SHOVELS. Catch me in PITTSBURGH on May 15 at WHITE WHALE BOOKS, and in PDX on Jun 20 at BARNES AND NOBLE. More tour dates here.

In my 23 years at EFF, I've been privileged to get a front-row seat for some of the most important legal battles over tech and human rights in history. There've been tremendous victories and heartbreaking losses, but win or lose, I am forever reminded that I'm privileged to work with some of the smartest, most committed, savviest cyberlawyers in the world.
These days, it's more of a second-row seat – I work remotely, mostly on my own projects, and I rely on our Deeplinks blog as much as our internal message-boards to keep up with our cases. Yesterday, I happened on this fantastic explainer breaking down our most recent court victory, in our case against DOGE on behalf of federal workers whose privacy rights have been violated during DOGE's raid on the Office of Personnel Management's databases:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2025/04/our-privacy-act-lawsuit-against-doge-and-opm-why-judge-let-it-move-forward
The post is by Adam Schwartz, EFF's Privacy Litigation Director. I've been campaigning on privacy for my entire adult life, but I still learn something – something big and important – every time I talk about the subject with Adam. His breakdown on EFF's latest court victory is no exception.
EFF was the first firm to bring a suit directly against DOGE, representing two federal workers' unions: the AFGE and the AALJ, and our co-counsel are from Lex Lumina LLP, State Democracy Defenders Fund, and The Chandra Law Firm. At the heart of our case are the millions of personnel records that DOGE agents were given access to by OPM Acting Director Charles Ezell.
The OPM is like the US government's HR department. It holds files on every federal employee and retiree, filled with sensitive, private data about that worker's finances, health, and personal life. The OPM also holds background check data on federal workers, including the deep background checks that federal workers must undergo to attain security clearances. Many of us – including me – first became familiar with the OPM in 2015, after its records were breached by hackers believed to be working for the Chinese military:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Office_of_Personnel_Management_data_breach
That breach was catastrophic. Chinese spies stole the sensitive data of tens of millions of Americans. The DOGE breach implicates even more Americans' private data, though, and while DOGE isn't a foreign intelligence agency, that cuts both ways. It's a good bet that a Chinese spy agency will not leak the records it stole, but with DOGE, it's another matter entirely. I wouldn't be surprised to find the OPM data sitting on a darknet server in a month or a year.
In his breakdown, Adam explains the ruling and what was at stake. We brought the case on behalf of all those federal workers under the 1974 Privacy Act, which was passed in the wake of Watergate and the revelations about COINTELPRO, scandals that rocked the nation's faith in federal institutions. The Privacy Act was supposed to restore trust in government, and to guard against future Nixonian enemies lists:
https://tile.loc.gov/storage-services/service/ll/llmlp/LH_privacy_act-1974/LH_privacy_act-1974.pdf
The Privacy Act's preamble asserts that the US government's creation of databases on Americans – including federal workers – "greatly magnified the harm to individual privacy." This is the basis for the Act's tight regulation on how government agencies use and handle databases containing dossiers on the lives of everyday Americans.
The US government tried to get the case tossed out by challenging our clients' "standing" to sue. Only people who have been harmed by someone else has the right ("standing") to sue over it. Does having your data leaked to DOGE constitute a real injury? Two recent Supreme Court cases say it does: Spokeo vs Robins and Transunion vs Ramirez both establish that "intangible" injuries (like a privacy breach) can be the basis for standing.
The court agreed that our clients had standing because the harms we alleged – DOGE's privacy breaches – are "concrete harms analogous to intrusion upon seclusion" ("intrusion upon seclusion" is one of the canonical privacy violations, set out in the Restatement of Torts, the American Law Institute's comprehensive guide to common law).
But the court went further, noting that DOGE's operation is accused of being "rushed and insecure," rejecting DOGE's argument that it only accessed OPM's "system" but not the data stored in that system. The court also said that it wouldn't matter if DOGE access the system, but not the data – that merely gaining access to the data violated our clients' privacy. Here, the judge is part of an emerging consensus, joining with four other federal judges who've ruled that when DOGE gains access to a system containing private data, that alone constitutes a privacy violation, even if DOGE doesn't look at or process the records in the system.
So in ruling for our clients, the judge found that the mere fact that DOGE could access their records was an injury that gave us standing to proceed – and also found that there were other injuries that would separately give us standing, including the possibility that DOGE's breach could expose our clients to "hacking, identity theft, and other activities that are substantially harmful."
The US government repeatedly argued that we weren't accusing them of disclosing our clients' records, every time they did this, the judge pointed to our actual filings, which plainly assert that DOGE agents were "viewing, possessing and using" our clients' records, and that this constitutes "disclosure" under the law, and according to OPM's own procedures.
The judge found that we were entitled to seek relief under the Administrative Procedures Act (APA), which proscribes the conduct of federal agencies – and that our relief could be both "declaratory" (meaning a court could rule that DOGE was breaking the law) and "injunctive" (meaning the court could order DOGE to knock it off).
Normally, a plaintiff can't ask for a judgment under the APA until an agency has taken a "final" action. The court found that because DOGE's actions were accused of being "illegal, rushed, and dangerous," and that this meant that we could seek relief under the APA. Further, that we could invoke the APA here because the remedies set out in the Privacy Act itself wouldn't be sufficient to help our clients in the face of DOGE's mass data-plundering.
Finally, the court ruled that our claims will allow us to pursue APA cases because OPM and DOGE were behaving in an "arbitrary and capricious" manner, and exceeding its legal authority.
All of this is still preliminary – we're not at the point yet where we're actually arguing the case. But standing is a huge deal. Ironically, it's when governments violate our rights on a mass scale that standing is hardest to prove. Our Jewel case, over NSA spying, foundered because the US government argued that we couldn't prove our clients had been swept up by NSA surveillance because the details of that surveillance were officially still secret, even though Snowden had disclosed their working a decade earlier, and our client Mark Klein (RIP) had come forward with documents on illegal mass NSA spying in 2006!:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2022/06/effs-flagship-jewel-v-nsa-dragnet-spying-case-rejected-supreme-court
So this is a big deal. It means we're going to get to go to court and argue the actual merits of the case. Things are pretty terrible right now, but this is a bright light. It makes me proud to have spent most of my adult life working with EFF. If you want to get involved with EFF, check and see if there's an Electronic Frontier Alliance affinity group in your town:
https://efa.eff.org/allies

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/04/09/cases-and-controversy/#brocolli-haired-brownshirts

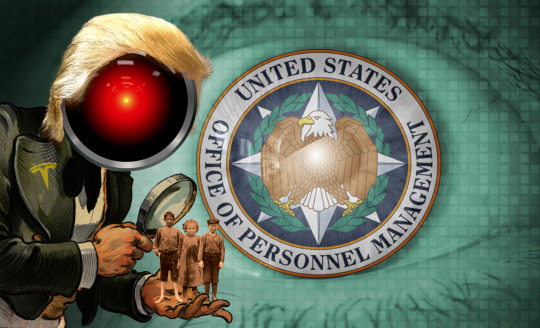
Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecomms.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
--
EFF (modified) https://www.eff.org/files/banner_library/opm-eye-3b.jpg
CC BY 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/deed.en
323 notes
·
View notes
Text
How I ditched streaming services and learned to love Linux: A step-by-step guide to building your very own personal media streaming server (V2.0: REVISED AND EXPANDED EDITION)
This is a revised, corrected and expanded version of my tutorial on setting up a personal media server that previously appeared on my old blog (donjuan-auxenfers). I expect that that post is still making the rounds (hopefully with my addendum on modifying group share permissions in Ubuntu to circumvent 0x8007003B "Unexpected Network Error" messages in Windows 10/11 when transferring files) but I have no way of checking. Anyway this new revised version of the tutorial corrects one or two small errors I discovered when rereading what I wrote, adds links to all products mentioned and is just more polished generally. I also expanded it a bit, pointing more adventurous users toward programs such as Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr and Overseerr which can be used for automating user requests and media collection.
So then, what is this tutorial? This is a tutorial on how to build and set up your own personal media server using Ubuntu as an operating system and Plex (or Jellyfin) to not only manage your media, but to also stream that media to your devices both at home and abroad anywhere in the world where you have an internet connection. Its intent is to show you how building a personal media server and stuffing it full of films, TV, and music that you acquired through indiscriminate and voracious media piracy various legal methods will free you to completely ditch paid streaming services. No more will you have to pay for Disney+, Netflix, HBOMAX, Hulu, Amazon Prime, Peacock, CBS All Access, Paramount+, Crave or any other streaming service that is not named Criterion Channel. Instead whenever you want to watch your favourite films and television shows, you’ll have your own personal service that only features things that you want to see, with files that you have control over. And for music fans out there, both Jellyfin and Plex support music streaming, meaning you can even ditch music streaming services. Goodbye Spotify, Youtube Music, Tidal and Apple Music, welcome back unreasonably large MP3 (or FLAC) collections.
On the hardware front, I’m going to offer a few options catered towards different budgets and media library sizes. The cost of getting a media server up and running using this guide will cost you anywhere from $450 CAD/$325 USD at the low end to $1500 CAD/$1100 USD at the high end (it could go higher). My server was priced closer to the higher figure, but I went and got a lot more storage than most people need. If that seems like a little much, consider for a moment, do you have a roommate, a close friend, or a family member who would be willing to chip in a few bucks towards your little project provided they get access? Well that's how I funded my server. It might also be worth thinking about the cost over time, i.e. how much you spend yearly on subscriptions vs. a one time cost of setting up a server. Additionally there's just the joy of being able to scream "fuck you" at all those show cancelling, library deleting, hedge fund vampire CEOs who run the studios through denying them your money. Drive a stake through David Zaslav's heart.
On the software side I will walk you step-by-step through installing Ubuntu as your server's operating system, configuring your storage as a RAIDz array with ZFS, sharing your zpool to Windows with Samba, running a remote connection between your server and your Windows PC, and then a little about started with Plex/Jellyfin. Every terminal command you will need to input will be provided, and I even share a custom #bash script that will make used vs. available drive space on your server display correctly in Windows.
If you have a different preferred flavour of Linux (Arch, Manjaro, Redhat, Fedora, Mint, OpenSUSE, CentOS, Slackware etc. et. al.) and are aching to tell me off for being basic and using Ubuntu, this tutorial is not for you. The sort of person with a preferred Linux distro is the sort of person who can do this sort of thing in their sleep. Also I don't care. This tutorial is intended for the average home computer user. This is also why we’re not using a more exotic home server solution like running everything through Docker Containers and managing it through a dashboard like Homarr or Heimdall. While such solutions are fantastic and can be very easy to maintain once you have it all set up, wrapping your brain around Docker is a whole thing in and of itself. If you do follow this tutorial and had fun putting everything together, then I would encourage you to return in a year’s time, do your research and set up everything with Docker Containers.
Lastly, this is a tutorial aimed at Windows users. Although I was a daily user of OS X for many years (roughly 2008-2023) and I've dabbled quite a bit with various Linux distributions (mostly Ubuntu and Manjaro), my primary OS these days is Windows 11. Many things in this tutorial will still be applicable to Mac users, but others (e.g. setting up shares) you will have to look up for yourself. I doubt it would be difficult to do so.
Nothing in this tutorial will require feats of computing expertise. All you will need is a basic computer literacy (i.e. an understanding of what a filesystem and directory are, and a degree of comfort in the settings menu) and a willingness to learn a thing or two. While this guide may look overwhelming at first glance, it is only because I want to be as thorough as possible. I want you to understand exactly what it is you're doing, I don't want you to just blindly follow steps. If you half-way know what you’re doing, you will be much better prepared if you ever need to troubleshoot.
Honestly, once you have all the hardware ready it shouldn't take more than an afternoon or two to get everything up and running.
(This tutorial is just shy of seven thousand words long so the rest is under the cut.)
Step One: Choosing Your Hardware
Linux is a light weight operating system, depending on the distribution there's close to no bloat. There are recent distributions available at this very moment that will run perfectly fine on a fourteen year old i3 with 4GB of RAM. Moreover, running Plex or Jellyfin isn’t resource intensive in 90% of use cases. All this is to say, we don’t require an expensive or powerful computer. This means that there are several options available: 1) use an old computer you already have sitting around but aren't using 2) buy a used workstation from eBay, or what I believe to be the best option, 3) order an N100 Mini-PC from AliExpress or Amazon.
Note: If you already have an old PC sitting around that you’ve decided to use, fantastic, move on to the next step.
When weighing your options, keep a few things in mind: the number of people you expect to be streaming simultaneously at any one time, the resolution and bitrate of your media library (4k video takes a lot more processing power than 1080p) and most importantly, how many of those clients are going to be transcoding at any one time. Transcoding is what happens when the playback device does not natively support direct playback of the source file. This can happen for a number of reasons, such as the playback device's native resolution being lower than the file's internal resolution, or because the source file was encoded in a video codec unsupported by the playback device.
Ideally we want any transcoding to be performed by hardware. This means we should be looking for a computer with an Intel processor with Quick Sync. Quick Sync is a dedicated core on the CPU die designed specifically for video encoding and decoding. This specialized hardware makes for highly efficient transcoding both in terms of processing overhead and power draw. Without these Quick Sync cores, transcoding must be brute forced through software. This takes up much more of a CPU’s processing power and requires much more energy. But not all Quick Sync cores are created equal and you need to keep this in mind if you've decided either to use an old computer or to shop for a used workstation on eBay
Any Intel processor from second generation Core (Sandy Bridge circa 2011) onward has Quick Sync cores. It's not until 6th gen (Skylake), however, that the cores support the H.265 HEVC codec. Intel’s 10th gen (Comet Lake) processors introduce support for 10bit HEVC and HDR tone mapping. And the recent 12th gen (Alder Lake) processors brought with them hardware AV1 decoding. As an example, while an 8th gen (Kaby Lake) i5-8500 will be able to hardware transcode a H.265 encoded file, it will fall back to software transcoding if given a 10bit H.265 file. If you’ve decided to use that old PC or to look on eBay for an old Dell Optiplex keep this in mind.
Note 1: The price of old workstations varies wildly and fluctuates frequently. If you get lucky and go shopping shortly after a workplace has liquidated a large number of their workstations you can find deals for as low as $100 on a barebones system, but generally an i5-8500 workstation with 16gb RAM will cost you somewhere in the area of $260 CAD/$200 USD.
Note 2: The AMD equivalent to Quick Sync is called Video Core Next, and while it's fine, it's not as efficient and not as mature a technology. It was only introduced with the first generation Ryzen CPUs and it only got decent with their newest CPUs, we want something cheap.
Alternatively you could forgo having to keep track of what generation of CPU is equipped with Quick Sync cores that feature support for which codecs, and just buy an N100 mini-PC. For around the same price or less of a used workstation you can pick up a mini-PC with an Intel N100 processor. The N100 is a four-core processor based on the 12th gen Alder Lake architecture and comes equipped with the latest revision of the Quick Sync cores. These little processors offer astounding hardware transcoding capabilities for their size and power draw. Otherwise they perform equivalent to an i5-6500, which isn't a terrible CPU. A friend of mine uses an N100 machine as a dedicated retro emulation gaming system and it does everything up to 6th generation consoles just fine. The N100 is also a remarkably efficient chip, it sips power. In fact, the difference between running one of these and an old workstation could work out to hundreds of dollars a year in energy bills depending on where you live.
You can find these Mini-PCs all over Amazon or for a little cheaper on AliExpress. They range in price from $170 CAD/$125 USD for a no name N100 with 8GB RAM to $280 CAD/$200 USD for a Beelink S12 Pro with 16GB RAM. The brand doesn't really matter, they're all coming from the same three factories in Shenzen, go for whichever one fits your budget or has features you want. 8GB RAM should be enough, Linux is lightweight and Plex only calls for 2GB RAM. 16GB RAM might result in a slightly snappier experience, especially with ZFS. A 256GB SSD is more than enough for what we need as a boot drive, but going for a bigger drive might allow you to get away with things like creating preview thumbnails for Plex, but it’s up to you and your budget.
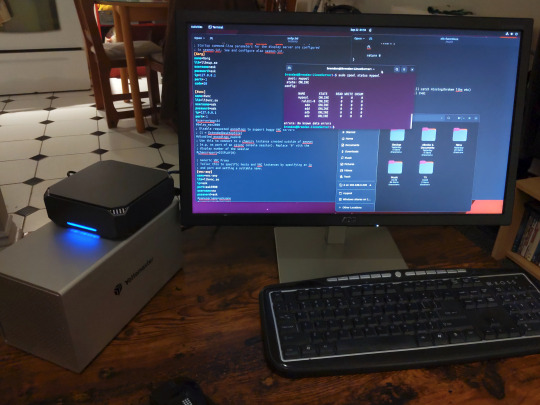
The Mini-PC I wound up buying was a Firebat AK2 Plus with 8GB RAM and a 256GB SSD. It looks like this:

Note: Be forewarned that if you decide to order a Mini-PC from AliExpress, note the type of power adapter it ships with. The mini-PC I bought came with an EU power adapter and I had to supply my own North American power supply. Thankfully this is a minor issue as barrel plug 30W/12V/2.5A power adapters are easy to find and can be had for $10.
Step Two: Choosing Your Storage
Storage is the most important part of our build. It is also the most expensive. Thankfully it’s also the most easily upgrade-able down the line.
For people with a smaller media collection (4TB to 8TB), a more limited budget, or who will only ever have two simultaneous streams running, I would say that the most economical course of action would be to buy a USB 3.0 8TB external HDD. Something like this one from Western Digital or this one from Seagate. One of these external drives will cost you in the area of $200 CAD/$140 USD. Down the line you could add a second external drive or replace it with a multi-drive RAIDz set up such as detailed below.
If a single external drive the path for you, move on to step three.
For people with larger media libraries (12TB+), who prefer media in 4k, or care who about data redundancy, the answer is a RAID array featuring multiple HDDs in an enclosure.
Note: If you are using an old PC or used workstatiom as your server and have the room for at least three 3.5" drives, and as many open SATA ports on your mother board you won't need an enclosure, just install the drives into the case. If your old computer is a laptop or doesn’t have room for more internal drives, then I would suggest an enclosure.
The minimum number of drives needed to run a RAIDz array is three, and seeing as RAIDz is what we will be using, you should be looking for an enclosure with three to five bays. I think that four disks makes for a good compromise for a home server. Regardless of whether you go for a three, four, or five bay enclosure, do be aware that in a RAIDz array the space equivalent of one of the drives will be dedicated to parity at a ratio expressed by the equation 1 − 1/n i.e. in a four bay enclosure equipped with four 12TB drives, if we configured our drives in a RAIDz1 array we would be left with a total of 36TB of usable space (48TB raw size). The reason for why we might sacrifice storage space in such a manner will be explained in the next section.
A four bay enclosure will cost somewhere in the area of $200 CDN/$140 USD. You don't need anything fancy, we don't need anything with hardware RAID controls (RAIDz is done entirely in software) or even USB-C. An enclosure with USB 3.0 will perform perfectly fine. Don’t worry too much about USB speed bottlenecks. A mechanical HDD will be limited by the speed of its mechanism long before before it will be limited by the speed of a USB connection. I've seen decent looking enclosures from TerraMaster, Yottamaster, Mediasonic and Sabrent.
When it comes to selecting the drives, as of this writing, the best value (dollar per gigabyte) are those in the range of 12TB to 20TB. I settled on 12TB drives myself. If 12TB to 20TB drives are out of your budget, go with what you can afford, or look into refurbished drives. I'm not sold on the idea of refurbished drives but many people swear by them.
When shopping for harddrives, search for drives designed specifically for NAS use. Drives designed for NAS use typically have better vibration dampening and are designed to be active 24/7. They will also often make use of CMR (conventional magnetic recording) as opposed to SMR (shingled magnetic recording). This nets them a sizable read/write performance bump over typical desktop drives. Seagate Ironwolf and Toshiba NAS are both well regarded brands when it comes to NAS drives. I would avoid Western Digital Red drives at this time. WD Reds were a go to recommendation up until earlier this year when it was revealed that they feature firmware that will throw up false SMART warnings telling you to replace the drive at the three year mark quite often when there is nothing at all wrong with that drive. It will likely even be good for another six, seven, or more years.

Step Three: Installing Linux
For this step you will need a USB thumbdrive of at least 6GB in capacity, an .ISO of Ubuntu, and a way to make that thumbdrive bootable media.
First download a copy of Ubuntu desktop (for best performance we could download the Server release, but for new Linux users I would recommend against the server release. The server release is strictly command line interface only, and having a GUI is very helpful for most people. Not many people are wholly comfortable doing everything through the command line, I'm certainly not one of them, and I grew up with DOS 6.0. 22.04.3 Jammy Jellyfish is the current Long Term Service release, this is the one to get.
Download the .ISO and then download and install balenaEtcher on your Windows PC. BalenaEtcher is an easy to use program for creating bootable media, you simply insert your thumbdrive, select the .ISO you just downloaded, and it will create a bootable installation media for you.
Once you've made a bootable media and you've got your Mini-PC (or you old PC/used workstation) in front of you, hook it directly into your router with an ethernet cable, and then plug in the HDD enclosure, a monitor, a mouse and a keyboard. Now turn that sucker on and hit whatever key gets you into the BIOS (typically ESC, DEL or F2). If you’re using a Mini-PC check to make sure that the P1 and P2 power limits are set correctly, my N100's P1 limit was set at 10W, a full 20W under the chip's power limit. Also make sure that the RAM is running at the advertised speed. My Mini-PC’s RAM was set at 2333Mhz out of the box when it should have been 3200Mhz. Once you’ve done that, key over to the boot order and place the USB drive first in the boot order. Then save the BIOS settings and restart.
After you restart you’ll be greeted by Ubuntu's installation screen. Installing Ubuntu is really straight forward, select the "minimal" installation option, as we won't need anything on this computer except for a browser (Ubuntu comes preinstalled with Firefox) and Plex Media Server/Jellyfin Media Server. Also remember to delete and reformat that Windows partition! We don't need it.
Step Four: Installing ZFS and Setting Up the RAIDz Array
Note: If you opted for just a single external HDD skip this step and move onto setting up a Samba share.
Once Ubuntu is installed it's time to configure our storage by installing ZFS to build our RAIDz array. ZFS is a "next-gen" file system that is both massively flexible and massively complex. It's capable of snapshot backup, self healing error correction, ZFS pools can be configured with drives operating in a supplemental manner alongside the storage vdev (e.g. fast cache, dedicated secondary intent log, hot swap spares etc.). It's also a file system very amenable to fine tuning. Block and sector size are adjustable to use case and you're afforded the option of different methods of inline compression. If you'd like a very detailed overview and explanation of its various features and tips on tuning a ZFS array check out these articles from Ars Technica. For now we're going to ignore all these features and keep it simple, we're going to pull our drives together into a single vdev running in RAIDz which will be the entirety of our zpool, no fancy cache drive or SLOG.
Open up the terminal and type the following commands:
sudo apt update
then
sudo apt install zfsutils-linux
This will install the ZFS utility. Verify that it's installed with the following command:
zfs --version
Now, it's time to check that the HDDs we have in the enclosure are healthy, running, and recognized. We also want to find out their device IDs and take note of them:
sudo fdisk -1
Note: You might be wondering why some of these commands require "sudo" in front of them while others don't. "Sudo" is short for "super user do”. When and where "sudo" is used has to do with the way permissions are set up in Linux. Only the "root" user has the access level to perform certain tasks in Linux. As a matter of security and safety regular user accounts are kept separate from the "root" user. It's not advised (or even possible) to boot into Linux as "root" with most modern distributions. Instead by using "sudo" our regular user account is temporarily given the power to do otherwise forbidden things. Don't worry about it too much at this stage, but if you want to know more check out this introduction.
If everything is working you should get a list of the various drives detected along with their device IDs which will look like this: /dev/sdc. You can also check the device IDs of the drives by opening the disk utility app. Jot these IDs down as we'll need them for our next step, creating our RAIDz array.
RAIDz is similar to RAID-5 in that instead of striping your data over multiple disks, exchanging redundancy for speed and available space (RAID-0), or mirroring your data writing by two copies of every piece (RAID-1), it instead writes parity blocks across the disks in addition to striping, this provides a balance of speed, redundancy and available space. If a single drive fails, the parity blocks on the working drives can be used to reconstruct the entire array as soon as a replacement drive is added.
Additionally, RAIDz improves over some of the common RAID-5 flaws. It's more resilient and capable of self healing, as it is capable of automatically checking for errors against a checksum. It's more forgiving in this way, and it's likely that you'll be able to detect when a drive is dying well before it fails. A RAIDz array can survive the loss of any one drive.
Note: While RAIDz is indeed resilient, if a second drive fails during the rebuild, you're fucked. Always keep backups of things you can't afford to lose. This tutorial, however, is not about proper data safety.
To create the pool, use the following command:
sudo zpool create "zpoolnamehere" raidz "device IDs of drives we're putting in the pool"
For example, let's creatively name our zpool "mypool". This poil will consist of four drives which have the device IDs: sdb, sdc, sdd, and sde. The resulting command will look like this:
sudo zpool create mypool raidz /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd /dev/sde
If as an example you bought five HDDs and decided you wanted more redundancy dedicating two drive to this purpose, we would modify the command to "raidz2" and the command would look something like the following:
sudo zpool create mypool raidz2 /dev/sdb /dev/sdc /dev/sdd /dev/sde /dev/sdf
An array configured like this is known as RAIDz2 and is able to survive two disk failures.
Once the zpool has been created, we can check its status with the command:
zpool status
Or more concisely with:
zpool list
The nice thing about ZFS as a file system is that a pool is ready to go immediately after creation. If we were to set up a traditional RAID-5 array using mbam, we'd have to sit through a potentially hours long process of reformatting and partitioning the drives. Instead we're ready to go right out the gates.
The zpool should be automatically mounted to the filesystem after creation, check on that with the following:
df -hT | grep zfs
Note: If your computer ever loses power suddenly, say in event of a power outage, you may have to re-import your pool. In most cases, ZFS will automatically import and mount your pool, but if it doesn’t and you can't see your array, simply open the terminal and type sudo zpool import -a.
By default a zpool is mounted at /"zpoolname". The pool should be under our ownership but let's make sure with the following command:
sudo chown -R "yourlinuxusername" /"zpoolname"
Note: Changing file and folder ownership with "chown" and file and folder permissions with "chmod" are essential commands for much of the admin work in Linux, but we won't be dealing with them extensively in this guide. If you'd like a deeper tutorial and explanation you can check out these two guides: chown and chmod.
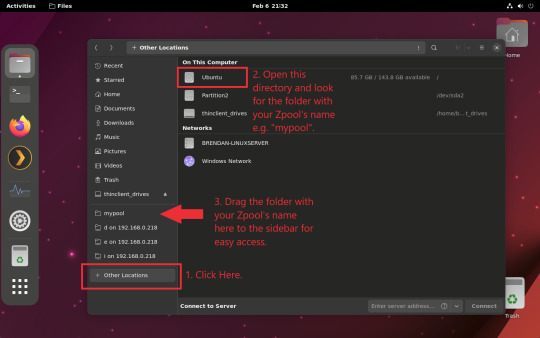
You can access the zpool file system through the GUI by opening the file manager (the Ubuntu default file manager is called Nautilus) and clicking on "Other Locations" on the sidebar, then entering the Ubuntu file system and looking for a folder with your pool's name. Bookmark the folder on the sidebar for easy access.
Your storage pool is now ready to go. Assuming that we already have some files on our Windows PC we want to copy to over, we're going to need to install and configure Samba to make the pool accessible in Windows.
Step Five: Setting Up Samba/Sharing
Samba is what's going to let us share the zpool with Windows and allow us to write to it from our Windows machine. First let's install Samba with the following commands:
sudo apt-get update
then
sudo apt-get install samba
Next create a password for Samba.
sudo smbpswd -a "yourlinuxusername"
It will then prompt you to create a password. Just reuse your Ubuntu user password for simplicity's sake.
Note: if you're using just a single external drive replace the zpool location in the following commands with wherever it is your external drive is mounted, for more information see this guide on mounting an external drive in Ubuntu.
After you've created a password we're going to create a shareable folder in our pool with this command
mkdir /"zpoolname"/"foldername"
Now we're going to open the smb.conf file and make that folder shareable. Enter the following command.
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
This will open the .conf file in nano, the terminal text editor program. Now at the end of smb.conf add the following entry:
["foldername"]
path = /"zpoolname"/"foldername"
available = yes
valid users = "yourlinuxusername"
read only = no
writable = yes
browseable = yes
guest ok = no
Ensure that there are no line breaks between the lines and that there's a space on both sides of the equals sign. Our next step is to allow Samba traffic through the firewall:
sudo ufw allow samba
Finally restart the Samba service:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
At this point we'll be able to access to the pool, browse its contents, and read and write to it from Windows. But there's one more thing left to do, Windows doesn't natively support the ZFS file systems and will read the used/available/total space in the pool incorrectly. Windows will read available space as total drive space, and all used space as null. This leads to Windows only displaying a dwindling amount of "available" space as the drives are filled. We can fix this! Functionally this doesn't actually matter, we can still write and read to and from the disk, it just makes it difficult to tell at a glance the proportion of used/available space, so this is an optional step but one I recommend (this step is also unnecessary if you're just using a single external drive). What we're going to do is write a little shell script in #bash. Open nano with the terminal with the command:
nano
Now insert the following code:
#!/bin/bash CUR_PATH=`pwd` ZFS_CHECK_OUTPUT=$(zfs get type $CUR_PATH 2>&1 > /dev/null) > /dev/null if [[ $ZFS_CHECK_OUTPUT == *not\ a\ ZFS* ]] then IS_ZFS=false else IS_ZFS=true fi if [[ $IS_ZFS = false ]] then df $CUR_PATH | tail -1 | awk '{print $2" "$4}' else USED=$((`zfs get -o value -Hp used $CUR_PATH` / 1024)) > /dev/null AVAIL=$((`zfs get -o value -Hp available $CUR_PATH` / 1024)) > /dev/null TOTAL=$(($USED+$AVAIL)) > /dev/null echo $TOTAL $AVAIL fi
Save the script as "dfree.sh" to /home/"yourlinuxusername" then change the ownership of the file to make it executable with this command:
sudo chmod 774 dfree.sh
Now open smb.conf with sudo again:
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
Now add this entry to the top of the configuration file to direct Samba to use the results of our script when Windows asks for a reading on the pool's used/available/total drive space:
[global]
dfree command = /home/"yourlinuxusername"/dfree.sh
Save the changes to smb.conf and then restart Samba again with the terminal:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
Now there’s one more thing we need to do to fully set up the Samba share, and that’s to modify a hidden group permission. In the terminal window type the following command:
usermod -a -G sambashare “yourlinuxusername”
Then restart samba again:
sudo systemctl restart smbd
If we don’t do this last step, everything will appear to work fine, and you will even be able to see and map the drive from Windows and even begin transferring files, but you'd soon run into a lot of frustration. As every ten minutes or so a file would fail to transfer and you would get a window announcing “0x8007003B Unexpected Network Error”. This window would require your manual input to continue the transfer with the file next in the queue. And at the end it would reattempt to transfer whichever files failed the first time around. 99% of the time they’ll go through that second try, but this is still all a major pain in the ass. Especially if you’ve got a lot of data to transfer or you want to step away from the computer for a while.
It turns out samba can act a little weirdly with the higher read/write speeds of RAIDz arrays and transfers from Windows, and will intermittently crash and restart itself if this group option isn’t changed. Inputting the above command will prevent you from ever seeing that window.
The last thing we're going to do before switching over to our Windows PC is grab the IP address of our Linux machine. Enter the following command:
hostname -I
This will spit out this computer's IP address on the local network (it will look something like 192.168.0.x), write it down. It might be a good idea once you're done here to go into your router settings and reserving that IP for your Linux system in the DHCP settings. Check the manual for your specific model router on how to access its settings, typically it can be accessed by opening a browser and typing http:\\192.168.0.1 in the address bar, but your router may be different.
Okay we’re done with our Linux computer for now. Get on over to your Windows PC, open File Explorer, right click on Network and click "Map network drive". Select Z: as the drive letter (you don't want to map the network drive to a letter you could conceivably be using for other purposes) and enter the IP of your Linux machine and location of the share like so: \\"LINUXCOMPUTERLOCALIPADDRESSGOESHERE"\"zpoolnamegoeshere"\. Windows will then ask you for your username and password, enter the ones you set earlier in Samba and you're good. If you've done everything right it should look something like this:

You can now start moving media over from Windows to the share folder. It's a good idea to have a hard line running to all machines. Moving files over Wi-Fi is going to be tortuously slow, the only thing that’s going to make the transfer time tolerable (hours instead of days) is a solid wired connection between both machines and your router.
Step Six: Setting Up Remote Desktop Access to Your Server
After the server is up and going, you’ll want to be able to access it remotely from Windows. Barring serious maintenance/updates, this is how you'll access it most of the time. On your Linux system open the terminal and enter:
sudo apt install xrdp
Then:
sudo systemctl enable xrdp
Once it's finished installing, open “Settings” on the sidebar and turn off "automatic login" in the User category. Then log out of your account. Attempting to remotely connect to your Linux computer while you’re logged in will result in a black screen!
Now get back on your Windows PC, open search and look for "RDP". A program called "Remote Desktop Connection" should pop up, open this program as an administrator by right-clicking and selecting “run as an administrator”. You’ll be greeted with a window. In the field marked “Computer” type in the IP address of your Linux computer. Press connect and you'll be greeted with a new window and prompt asking for your username and password. Enter your Ubuntu username and password here.
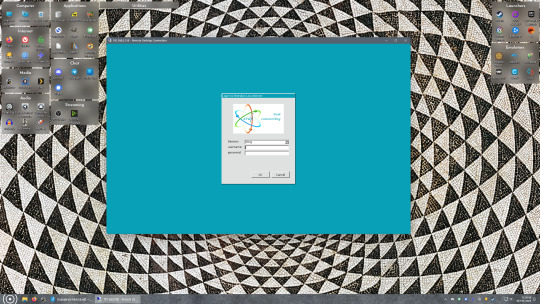
If everything went right, you’ll be logged into your Linux computer. If the performance is sluggish, adjust the display options. Lowering the resolution and colour depth do a lot to make the interface feel snappier.
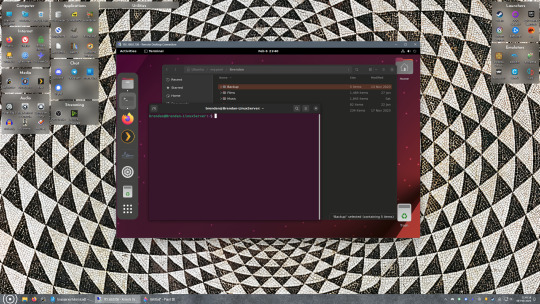
Remote access is how we're going to be using our Linux system from now, barring edge cases like needing to get into the BIOS or upgrading to a new version of Ubuntu. Everything else from performing maintenance like a monthly zpool scrub to checking zpool status and updating software can all be done remotely.
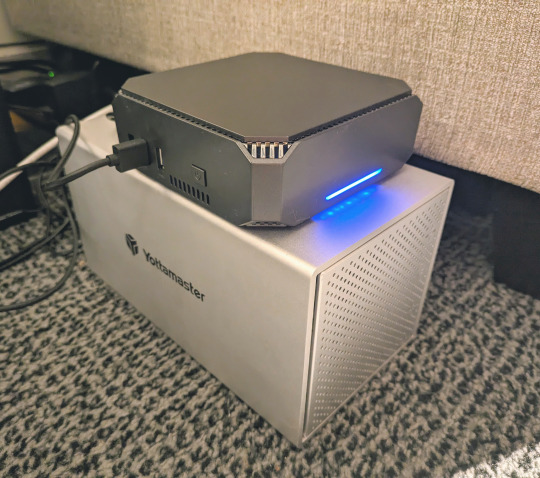

This is how my server lives its life now, happily humming and chirping away on the floor next to the couch in a corner of the living room.
Step Seven: Plex Media Server/Jellyfin
Okay we’ve got all the ground work finished and our server is almost up and running. We’ve got Ubuntu up and running, our storage array is primed, we’ve set up remote connections and sharing, and maybe we’ve moved over some of favourite movies and TV shows.
Now we need to decide on the media server software to use which will stream our media to us and organize our library. For most people I’d recommend Plex. It just works 99% of the time. That said, Jellyfin has a lot to recommend it by too, even if it is rougher around the edges. Some people run both simultaneously, it’s not that big of an extra strain. I do recommend doing a little bit of your own research into the features each platform offers, but as a quick run down, consider some of the following points:
Plex is closed source and is funded through PlexPass purchases while Jellyfin is open source and entirely user driven. This means a number of things: for one, Plex requires you to purchase a “PlexPass” (purchased as a one time lifetime fee $159.99 CDN/$120 USD or paid for on a monthly or yearly subscription basis) in order to access to certain features, like hardware transcoding (and we want hardware transcoding) or automated intro/credits detection and skipping, Jellyfin offers some of these features for free through plugins. Plex supports a lot more devices than Jellyfin and updates more frequently. That said, Jellyfin's Android and iOS apps are completely free, while the Plex Android and iOS apps must be activated for a one time cost of $6 CDN/$5 USD. But that $6 fee gets you a mobile app that is much more functional and features a unified UI across platforms, the Plex mobile apps are simply a more polished experience. The Jellyfin apps are a bit of a mess and the iOS and Android versions are very different from each other.
Jellyfin’s actual media player is more fully featured than Plex's, but on the other hand Jellyfin's UI, library customization and automatic media tagging really pale in comparison to Plex. Streaming your music library is free through both Jellyfin and Plex, but Plex offers the PlexAmp app for dedicated music streaming which boasts a number of fantastic features, unfortunately some of those fantastic features require a PlexPass. If your internet is down, Jellyfin can still do local streaming, while Plex can fail to play files unless you've got it set up a certain way. Jellyfin has a slew of neat niche features like support for Comic Book libraries with the .cbz/.cbt file types, but then Plex offers some free ad-supported TV and films, they even have a free channel that plays nothing but Classic Doctor Who.
Ultimately it's up to you, I settled on Plex because although some features are pay-walled, it just works. It's more reliable and easier to use, and a one-time fee is much easier to swallow than a subscription. I had a pretty easy time getting my boomer parents and tech illiterate brother introduced to and using Plex and I don't know if I would've had as easy a time doing that with Jellyfin. I do also need to mention that Jellyfin does take a little extra bit of tinkering to get going in Ubuntu, you’ll have to set up process permissions, so if you're more tolerant to tinkering, Jellyfin might be up your alley and I’ll trust that you can follow their installation and configuration guide. For everyone else, I recommend Plex.
So pick your poison: Plex or Jellyfin.
Note: The easiest way to download and install either of these packages in Ubuntu is through Snap Store.
After you've installed one (or both), opening either app will launch a browser window into the browser version of the app allowing you to set all the options server side.
The process of adding creating media libraries is essentially the same in both Plex and Jellyfin. You create a separate libraries for Television, Movies, and Music and add the folders which contain the respective types of media to their respective libraries. The only difficult or time consuming aspect is ensuring that your files and folders follow the appropriate naming conventions:
Plex naming guide for Movies
Plex naming guide for Television
Jellyfin follows the same naming rules but I find their media scanner to be a lot less accurate and forgiving than Plex. Once you've selected the folders to be scanned the service will scan your files, tagging everything and adding metadata. Although I find do find Plex more accurate, it can still erroneously tag some things and you might have to manually clean up some tags in a large library. (When I initially created my library it tagged the 1963-1989 Doctor Who as some Korean soap opera and I needed to manually select the correct match after which everything was tagged normally.) It can also be a bit testy with anime (especially OVAs) be sure to check TVDB to ensure that you have your files and folders structured and named correctly. If something is not showing up at all, double check the name.
Once that's done, organizing and customizing your library is easy. You can set up collections, grouping items together to fit a theme or collect together all the entries in a franchise. You can make playlists, and add custom artwork to entries. It's fun setting up collections with posters to match, there are even several websites dedicated to help you do this like PosterDB. As an example, below are two collections in my library, one collecting all the entries in a franchise, the other follows a theme.

My Star Trek collection, featuring all eleven television series, and thirteen films.
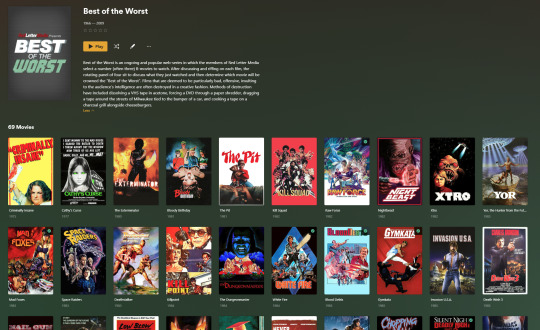
My Best of the Worst collection, featuring sixty-nine films previously showcased on RedLetterMedia’s Best of the Worst. They’re all absolutely terrible and I love them.
As for settings, ensure you've got Remote Access going, it should work automatically and be sure to set your upload speed after running a speed test. In the library settings set the database cache to 2000MB to ensure a snappier and more responsive browsing experience, and then check that playback quality is set to original/maximum. If you’re severely bandwidth limited on your upload and have remote users, you might want to limit the remote stream bitrate to something more reasonable, just as a note of comparison Netflix’s 1080p bitrate is approximately 5Mbps, although almost anyone watching through a chromium based browser is streaming at 720p and 3mbps. Other than that you should be good to go. For actually playing your files, there's a Plex app for just about every platform imaginable. I mostly watch television and films on my laptop using the Windows Plex app, but I also use the Android app which can broadcast to the chromecast connected to the TV in the office and the Android TV app for our smart TV. Both are fully functional and easy to navigate, and I can also attest to the OS X version being equally functional.
Part Eight: Finding Media
Now, this is not really a piracy tutorial, there are plenty of those out there. But if you’re unaware, BitTorrent is free and pretty easy to use, just pick a client (qBittorrent is the best) and go find some public trackers to peruse. Just know now that all the best trackers are private and invite only, and that they can be exceptionally difficult to get into. I’m already on a few, and even then, some of the best ones are wholly out of my reach.
If you decide to take the left hand path and turn to Usenet you’ll have to pay. First you’ll need to sign up with a provider like Newshosting or EasyNews for access to Usenet itself, and then to actually find anything you’re going to need to sign up with an indexer like NZBGeek or NZBFinder. There are dozens of indexers, and many people cross post between them, but for more obscure media it’s worth checking multiple. You’ll also need a binary downloader like SABnzbd. That caveat aside, Usenet is faster, bigger, older, less traceable than BitTorrent, and altogether slicker. I honestly prefer it, and I'm kicking myself for taking this long to start using it because I was scared off by the price. I’ve found so many things on Usenet that I had sought in vain elsewhere for years, like a 2010 Italian film about a massacre perpetrated by the SS that played the festival circuit but never received a home media release; some absolute hero uploaded a rip of a festival screener DVD to Usenet. Anyway, figure out the rest of this shit on your own and remember to use protection, get yourself behind a VPN, use a SOCKS5 proxy with your BitTorrent client, etc.
On the legal side of things, if you’re around my age, you (or your family) probably have a big pile of DVDs and Blu-Rays sitting around unwatched and half forgotten. Why not do a bit of amateur media preservation, rip them and upload them to your server for easier access? (Your tools for this are going to be Handbrake to do the ripping and AnyDVD to break any encryption.) I went to the trouble of ripping all my SCTV DVDs (five box sets worth) because none of it is on streaming nor could it be found on any pirate source I tried. I’m glad I did, forty years on it’s still one of the funniest shows to ever be on TV.
Part Nine/Epilogue: Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr and Overseerr
There are a lot of ways to automate your server for better functionality or to add features you and other users might find useful. Sonarr, Radarr, and Lidarr are a part of a suite of “Servarr” services (there’s also Readarr for books and Whisparr for adult content) that allow you to automate the collection of new episodes of TV shows (Sonarr), new movie releases (Radarr) and music releases (Lidarr). They hook in to your BitTorrent client or Usenet binary newsgroup downloader and crawl your preferred Torrent trackers and Usenet indexers, alerting you to new releases and automatically grabbing them. You can also use these services to manually search for new media, and even replace/upgrade your existing media with better quality uploads. They’re really a little tricky to set up on a bare metal Ubuntu install (ideally you should be running them in Docker Containers), and I won’t be providing a step by step on installing and running them, I’m simply making you aware of their existence.
The other bit of kit I want to make you aware of is Overseerr which is a program that scans your Plex media library and will serve recommendations based on what you like. It also allows you and your users to request specific media. It can even be integrated with Sonarr/Radarr/Lidarr so that fulfilling those requests is fully automated.
And you're done. It really wasn't all that hard. Enjoy your media. Enjoy the control you have over that media. And be safe in the knowledge that no hedgefund CEO motherfucker who hates the movies but who is somehow in control of a major studio will be able to disappear anything in your library as a tax write-off.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text









Hotmail service was founded by Sabeer Bhatia and Jack Smith, and was one of the first webmail services on the Internet along with Four11's RocketMail (later Yahoo! Mail). It was commercially launched on July 4, 1996, symbolizing "freedom" from ISP-based email and the ability to access a user's inbox from anywhere in the world. The name "Hotmail" was chosen out of many possibilities ending in "-mail" as it included the letters HTML, the markup language used to create web pages (to emphasize this, the original type casing was "HoTMaiL"). The limit for free storage was 2 MB. Hotmail was initially backed by venture capital firm Draper Fisher Jurvetson. By December 1997, it reported more than 8.5 million subscribers. Hotmail initially ran under Solaris for mail services and Apache on FreeBSD for web services, before being partly converted to Microsoft products, using Windows Services for UNIX in the migration path.
Hotmail was sold to Microsoft in December 1997 for a reported $400 million (~$705 million in 2023), and it joined the MSN group of services. The sale had been preceded by a major incident in 1997 where all email was lost for 25% of mailboxes. Hotmail quickly gained in popularity as it was localized for different markets around the globe, and became the world's largest webmail service with more than 30 million active members reported by February 1999.
Hotmail originally ran on a mixture of FreeBSD and Solaris operating systems. A project was started to move Hotmail to Windows 2000. In June 2001, Microsoft claimed this had been completed; a few days later they retracted the statement and admitted that the DNS functions of the Hotmail system were still reliant on FreeBSD. In 2002 Hotmail still ran its infrastructure on UNIX servers, with only the front-end converted to Windows 2000. Later development saw the service tied with Microsoft's web authentication scheme, Microsoft Passport (now Microsoft account), and integration with Microsoft's instant messaging and social networking programs, MSN Messenger and MSN Spaces (later Windows Live Messenger and Windows Live Spaces, respectively).
#hotmail#msn#90s www#90s web#90s internet#vintage internet#vintage computing#outlook#microsoft#Bandcamp
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

Okay ^_^
So for those who don’t know (most people (especially on here)) Foxhole is a mmo(rp?)g played as an (eternal) series of open-form matches (wars) between two factions on a 36-hexagon(best) map grid, each of which is a server that fits about 250 players, so a war might be fought by about 2-4k people at once, but in a (frontline) hex it’s sort of a rotating 100-on-100 match. Your faction wins the war when you take X(~=28)/36 hex capitals slash *prozd voice* victory points
Probably the most important thing in Foxhole, though, is that basically every single thing in the game is made by players. Every trench is dug by someone, every bunker base is dug out, fortified with materials that were refined from scrap that was mined at one of the dozens of scrap fields, crated up and hauled to the front. Every rifle and every bullet was made out of the same reprocessed scrap, every truck, tank, barge, destroyer, battleship. (Well, not quite- there’s actually about a half dozen types of resources all used and processed into more and more advanced materials at, you guessed it, player-built facilities)
Because of this, there are absolutely massive benefits to specialization and division of labor. A regiment (clan) dedicated purely to logistics will be orders of magnitude better at turning their time into usable equipment. It’s simply not worth doing things not at scale. Not only are there duplicate paths that let you use for better outgoing production efficiency, collecting resources at peak hours is going to lead to you competing with dozens of other players, but an Australian can have basically free access to resource spawns.
All of this is sort of adjacent to the main point of why I wanted to write this. You’ll notice I haven’t really talked about the combat at all. It’s a twin stick shooter basically. Probably not what you expected! It’s fun though, there’s skill, it feels appropriate for the interwar period aesthetics, etc. But it doesn’t matter! Shooting dudes on the frontline is simultaneously the only reason the game exists and literally pointless. New players will spawn in on the frontline, fight over a broken bridge for 6 hours straight, have a great time, and have contributed literally NOTHING.
Right now, in the current war, about 3 weeks in, in the center of the map there’s been a fight that has stagnated since day 2 or 3 of the war at the outskirts of a city.
Six Hundred And Seventy Five Thousand player deaths have occurred.
Zero territory has been captured.
So obviously, nothing ever happens, the game is impossible to push in, etc. Except wars very much do progress and end! Like I said, we’re only 3 weeks into this war. There’s been like 4 or 5 wars since the year started. So how do you actually do something? I mean, you’re not gonna brute force it. You can’t die 675k times on your own.
For better or for worse, the answer is in game mechanics. When you capture an enemy base (player-built or map town) by destroying and rebuilding it, you get 25% of the supplies in it, but more importantly, you reset its defensive tech progress. Map bases start out with all their tech, player built with none, but if you capture (“tap”) it, all that progress is gone, and it takes IRL days to re-tech it. Things like garrisoned houses in cities, seaports and stockpiles, advanced construction materials for bunkers, anti-tank and artillery counterbattery emplacements, your ability to build all of that goes away. What this does is turn the area into a no-mans-land (often filled with artillery craters and rubble). This type of frontline is impossible to really effectively hold while it is frontline, hence no-mans-land, but you can push through it. When you tap a town with a storage depot full of supplies in it, even if you don’t hold the town you knock all their private supplies public, and more importantly, you stop them from getting to any of it for at least 2 days, even if they retake and hold the town (which they now have to do without all those supplies!!)
Everything in Foxhole is about time. You want to make sure you are using your time in a way that has the biggest multiplier of your time spent to enemy time destroyed. Every time you kill someone, their respawn costs 16 salvage, plus the cost of all their extra gear, plus the time it took to refine all that, drive it up to the front, etc. This actually ends up being a piddling amount- you have to kill like a hundred people to deal even one logi truck worth of time-damage to the enemy, and at a hot frontline, a logi will be rolling up every 3-5 min. This is why shooting dudes does not win the war.
For a long time, my regi’s philosophy was to go directly after the juicy, valuable Enemy Gamer Time directly- we’d camp out a klick behind an enemy base, shoot up logi drivers as they shuffle up to the frontline, steal their truck, and send someone to sneak it back to our frontlines and deliver the supplies. Here too though, you run into time problems. This ie a fantastic strat with 3-5 players. A few good partisans (the community’s somewhat inaccurate term for logi interception and backline harassment) make a fantastic impact in terms of player time spent per player time destroyed/recovered. But they saturate quickly- if you have 3 people holding a road, you can probably stop 75% of trucks, 5, 95%, but beyond that you’re investing tons of extra player time for almost no gain. Any time you hit 6 people camping a road, you should immediately mitose and hit two roads with three people. Once you saturate all or even most of the roads to a base, extra partisans do nothing! Your td/ts goes to shit!
So if you’re a big group, you also lose efficiency by being big. Same effect with partisans happens with tanks- if the terrain doesn’t let all your tanks frontline, you’re wasting those tanks time. These independent saturation effects make multitasking more important. If you have 40 people in hex, you should have, yknow, 18 doing tanks, 8 doing arty, 10 doing infantry, and four doing logi/building up the front. Each of these activities is a force multiplier on the other, but you end up with everyone doing the same thing in 80% of clan ops. I partially blame discord for this, because it doesn’t have whisper functionality, and you really need like a command comms channel where all the squad leaders can talk to each other.
Some regis can pull this off, sure, but it’s rare. Making best use of player time is just a really multifaceted issue that has both exogenous and endogenous constraints.
#i have a lot more to say but this is long enough already.#maybe i’ll edit together a better part 2 that communicates my beliefs on time usage and how it differs from other games#that could have broader appeal#effortpost
7 notes
·
View notes
Text


@ BUNAAPOM ∎ CONDUCTOR POM - POM, a major NON - PLAYABLE CHARACTER of HONKAI: STAR RAIL, closed & affiliated with GNOSTIC HYMNS. written & cherished by ELIX or BARELY [ EIGHTEEN + ANY PRNS + EST ] ! notes on portrayal, rules, & official story continuity under the cut, with important links here: [ RECORDS ROOM + CONDUCTOR'S PAGE + TALENTS ]
notes.
i. MORE ABOUT ELIX & BARELY: an english lit college student that was once, and still is, sporadically online. can be contacted through TUMBLR IMS or DISCORD DMS, with a small preference for the latter, though i am both in the server as 'elix' and open for private messages.
∎ A MAJOR NOTE, briefly, but i do not, and likely will never, touch another hoyoverse game for a few reasons [ mainly, the lack of storage space & burn - out from said games ], so to stay updated, i tend to cling to recorded playthroughs, watch my sibling stream, or turn to written records. basically, varying forms of osmosis. and because of this, i want to apologize in advance for any lapses in memory or information. so far, i am caught up on HONKAI: STAR RAIL, and am still catching up on smaller storylines in GENSHIN IMPACT and HONKAI IMPACT 3RD.
ii. MORE ABOUT POM - POM: the small but mighty conductor, and ▇▇▇, of the astral express, serving as a major npc for the events of honkai: star rail. while their origins and background are unknown, they've proven to be a necessity on the express, unmistakably cherished by both it and the crew of nameless that board it. usually, can be found fussing over small tasks in the parlor car, or dancing in front of the phonograph.
∎ A MAJOR NOTE, despite the wealth of portals mysteriously appearing in and outside of the astral express, POM - POM IS STILL BOUND TO THE CONFINES OF THE TRAIN. this has not, and likely will not, change until something or someone crazy happens in the main storyline of the game. so, unfortunately, this vastly limits the interactions pom - pom is able to have on the dashboard. [ which caters this his overwhelming loneliness, so i'm game! ] ALL THREADS AND ASKS HAVE TO BE SET IN THE ASTRAL EXPRESS, or near it, for it to be considered canon. which also means that pom - pom cannot participate in any events hosted by GNOSTICHYMNS unless certain lengths are taken on my side for inclusion. [ EX. parking the astral express, doors open, right outside of whatever festival is being held so pom - pom can be handed street food :thumbsup: ]
iii. POST FORMATTING: small, double - spaced text. colored, bolded dialogue. little to no icon usage due to laziness. will always match a partner in length but not formatting, unless it is their preference that i change the font size and reduce the spacing for accessibility. never be afraid to ask this of me! i'll do my best to remember and check pages beforehand though, just in case.
iv. INBOX & INTERACTIONS: always open, no matter the content! if you’d like to turn an ask into a thread, please do, and do not worry for approval. i welcome all and any interactions, especially impulsive and random ones. the astral express will always open its doors for a hello!
v. CONTENT & TRIGGER WARNINGS: no serious content warnings, only vague inclinations to GRIEF, DEATH, and an all-encompassing, unrecognized LONELINESS. i can do my best to lessen the extent of any aforementioned themes upon being asked. however, on behalf of my triggers, i ask for IMAGES of SPIDERS, HEAVY GORE, and EYE TRAUMA to be tagged, please and thank you.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
A free image hosting solution for AO3 and elsewhere - A Tutorial (mobile-friendly!)
See the demo site made from this template IN ACTION: https://hotlink-archive-template.pages.dev/
This guide is for an easy, mobile-friendly way to host files for hotlinking on AO3 or elsewhere, using github and cloudflare pages.
I've encountered far too many dead links in fanfics and forums simply because a hosting service decided to dump older files, or they decided to change their TOS to no longer allow hotlinking or certain kinds of content (nsfw, fictional graphic content). See Optional Steps for even more options.
This is an easy, barebones way to permanently host images that you don't want deleted unexpectedly or that you can't host elsewhere. (Emphasis on barebones. This will not be a nice portfolio style site. Unless you decide to code that yourself!) You can follow the link above for an example of this type of site.
It is also EASY to upload and use on mobile devices after initial setup!
Tools you will need:
Cloudflare Pages/Workers is a free to use static site hosting service. This will publish your files and make them available online. This will publish your files and make them available online. There is a limit to the amount of data you can upload for free, but you can pay for proper hosting if you want to exceed it.
Github is a code sharing/storage platform. Your files will go here first before being published on Pages. You can edit and upload files through your browser at github.com, or through Github Desktop, a program you install on your computer. There are limits to Github repositories, but they are also generous (suggested 1GB to 5GB per repo).
Basic Setup
1. Create a github account
2. Copy this template repository hotlink-archive-template
Your website will be contained in a repository, a place where all the files and the revision history for your project are stored.
This template repository uses an "Action" (using python) to automatically create a "home" page with an Index of all the files in your repository every time it is updated.
NOTE: I recommend you set your repository to Private. Github's history feature is extensive, so if you have sensitive content or think you might want to delete something later, it will be hard to get rid of it completely once it's been committed and publicly available.
3. Enable Action permissions
In order for the Action script to work, you need to give Actions permission to read and write in your repository.
Within your repository, go to the tab Settings > Actions > General > Workflow Permissions

4. Create a Cloudflare account
5. Create a Pages (or Workers) project and link it to your Github repository
Your Pages project will create the front end of the site where the images will be displayed. You will be able to link those images to other platforms like AO3.
You can create either a Workers or Pages project by going to Add > Pages (or Workers). Name your project WISELY! This name will be your site's URL.
Workers vs. Pages
Workers is subsuming Pages on Cloudflare and now has all the same static hosting capabilities, in addition to its original server-side processing services. If you'd like to, read more about this.
While Workers has similar capabilities, I recommend Pages for this project. Pages has the added bonus of a cleaner URL if you do not have your own domain: “MySite.pages.dev” in Pages vs Workers' “MySite.username.workers.dev”
You will be prompted to import an existing Git repository. You will need to give it access to your Github to do this.

Select the repository on your Github you made for your project, then hit "Begin Setup".
Name your project WISELY! This name will be your site's URL.
You do not need to change any settings on the next page, so hit "Save and Deploy". Your image hosting site will now be live!
The URL will be "https://ProjectName.pages.dev". It may take a few minutes to become accessible.
Now you're done with the basic setup!
How to Add files
You can add any files you want to link to on AO3/elsewhere through mobile, desktop browser, or the Github desktop program!
Here is how to do it on Github.com:
Open up the repository that you made (it can be found at github.com/username/repositoryname). You will see a list of folders and files that are in that repository.
Click into the folder "fan-stuff".
In the top right, go Add file > Upload files and drag in the images you want added. You will need to name the images BEFORE you upload them, as there is not an easy renaming feature within Github's browser interface.
In the Commit changes box, choose a title for what action you are doing. This will help you backtrack uploads if needed.
For example, it could be "Uploaded Batman Art". Make sure it's set to "commit directly to the main branch", then commit those changes. This will upload the files.
Now, if you visit your site, you will see your uploaded image under the "fan-stuff" folder!
To embed/link your image, navigate to your file on your Pages site and copy the URL in the address bar. This URL is what you will use to embed your photo (using HTML or "add image as URL" tools some sites have).
Continue onto More Setup to customize your site and implement more advanced settings. See Tips/Troubleshooting if you're running into problems.
More Setup
Perform site customization/advanced setup with Github Desktop on your PC
Github’s web UI is great, but it has major limitations. I highly recommend that you use Github Desktop during the initial setup, as well as when you want to make major organizational changes to your files/site. Once you have everything set, though, you can use Github in your browser to upload whatever files you want to hotlink at the moment.
Download Github Desktop and “clone” (download a copy of) the repository you made.
This is the best time to rename/rearrange folders + files, etc.
There are other methods in the Troubleshooting section if you need, but Github Desktop is by far the easiest way
see Adding/Renaming Folders for important info on how to properly rename/add folders
see About the Index Page for how to customize your Index pages
Once you’re done editing, “push” (upload) all the changes you made to your online Github repository.
Having some sort of text editor like Notepad++ is useful for editing any code, the automatic color-coding is very helpful. You can edit in plain old Notepad as well, it just won’t look as nice.
About the Index Page
The template repository uses a python Action to automatically create an HTML "home" page with an Index of ALL the files in the folder every time it is updated.
This is particularly convenient for mobile use, as you can upload a file, and the python action automatically updates the Index page.
If you don’t want this, just disable the “create-index” Action and delete the .py files. You can just type in the file locations to get to each file, or you can manually maintain an home/Index page yourself, which isn't hard if you know some basic HTML and can remember to do it consistently.
Also note that if you wish to change any of the content on your Index pages, you must edit the "index.py" file, not the "index.html" file. The "index.html" file gets re-written every time the "create-index" Action is run in order to keep the file index up to date.
Adding/Renaming/Deleting Folders
Disclaimer: This is a bit convoluted because I am extremely unqualified to be working with python OR HTML. There’s probably an easy way to do this, but I don’t have the skill to do it, and most of the stuff here is copied from stuff I found around. If you know a better way to do things, please let me know, it’d make my life easier too!
Adding or renaming folders involves some extra steps.
1. The "index.py" file inside the folder needs to be edited to match the parent folder name.
The place you need to do this is found near the top of the file (highlighted below)

2. Then the outer-most "create-index.py" file needs to be updated to match the new name as well. If you’ve added a new folder, duplicate and adjust the code to match.
The place you need to do this is found at the bottom (highlighted below)

If you don’t need any folders at all, great! Just delete them and their contents! No need to edit any files. (Don’t delete “index.html” or “create-index.py” or “.github/workflows”!)
If you would like to have these folders for later use, leave them as-is and simply edit the index files.
The relevant lines of code at the bottom of "create-index.py" like in the previous step for renaming folders. You may delete this code, or comment it out (using # at the beginning of a line will make it “invisible” to the computer)
Then, add the folder’s name to the “exclusions” list at the top of the "create-index.py" file so that it doesn’t show up on your Index page (highlighted below)

You can also use this same concept to create "invisible" files/folders. Any files/folders included in the "exclusions" list in "(create-)index.py" will not be listed on the Index page, however they can still be found through the direct URL to the file.
On the flipside, this means simply hiding the file/folder from the Index page does not get rid of the file from your site. Anyone who has the URL will be able to find that file unless you remove it, or move its location to change the URL
Tips/Troubleshooting
(Re)name your files before uploading
It’s not possible to rename image/media files on Github’s web UI (it is possible with the local Git program). The "create-index" Action lists out the names of your files exactly, so you will end up with ugly strings of numbers and letters on your Index page if you don't rename them, which is terrible to look at and also plain old CONFUSING to navigate.
So if you're uploading on mobile or through Github on browser, name your files with easy to remember and distinctive filenames before you go ahead and upload them. This makes everything much easier, and it makes your Index page look nice :)
My website isn’t updating when I edit my Github repository!
Check to see if your Pages is retrieving from the correct branch, and if it has automatic deployments enabled.

Can’t see your Github repository when trying to link it on Cloudflare?
Check your Github applications Repository Access settings. Go to your ACCOUNT Settings > Integrations - Applications > Cloudflare > Repository Access

Index action is failing!
Go back to step 3 in Basic Setup and check if you’ve given Actions permission to read and write. If that’s not the issue, check to see if you’ve set up your "index.py" files correctly. The folder names should correspond to the parent folders, and the "create-index.py" file in the outer-most folder should have the correct folder names at the VERY BOTTOM.
How do I rename a folder (or move a file) in Github’s web UI?
It isn’t possible to directly rename a folder in Github’s web UI, doing it using Git on your computer is the most foolproof way to do it. But there is a way (except for media files).
Go into the folder you want to rename and select a file such as “index.html” and enter the “edit” mode.
Go to the file name and backspace until you can edit the parent folder name as well. This will create a new folder with the new name.
You’ll have to do this to every file in the folder until they’re all in the new folder.
Unfortunately, you can’t do this with media files like png/jpg/etc, because entering the “edit” mode on a photo “breaks” it somehow, and bye-bye image :’) (Don’t worry if this happens, just don’t commit the change or roll it back in your history).
Optional Steps
Make deployment (semi-)Manual
You can play with cloudflare and github to make deployment of your site a manual step you have to trigger, instead of automatic with each commit (default setting). This is a safeguard in case you accidentally make a change or delete something from your github, it won't affect your website.
Deploy w/ Branches
You could do a semi-automatic deployment with a "Production" branch on your github that is separate from the branch you edit. This creates an extra step before anything is published on Cloudflare. A safeguard against accidental changes/deletion of sorts :)

Go to Settings > Build tab > Branch Control
Choose your Production Branch (MAIN or CLOUDFLARE) and enable (or disable) automatic deployments
If you choose MAIN, every change you commit to MAIN will be published to Pages
If you choose CLOUDFLARE, any changes you make to MAIN will not show up on your Pages site until you Pull from MAIN to CLOUDFLARE
To Pull changes from MAIN to CLOUDFLARE, go to your github repository
Above your files on the Left, you will see a toggle to choose which branch you are on.
Choose Cloudflare. There will be a message like "This branch is 7 commits ahead of, 2 commits behind main." Click "2 commits behind"
Click "Create a Pull Request". Then click "Merge Pull Request". If everything is correct, this should trigger a build on your Cloudflare
Deploy w/ Github Actions
Or you can create a manual command that you have to enter on github to trigger a deployment on cloudflare. If you're paranoid about anything happening to your site due to a mishap on the Github side, this is a safe choice. Unless you manually trigger the command, your Pages site will be completely untouched no matter if something happens to your repo.
This can be done in many ways, I think the most straightforward is with Deploy Hooks (maybe in conjunction with Actions if you want to make it mobile-friendly), and might be a bit complicated, but not too hard to figure out with some Google-fu.
Here’s some links I think will be useful (note: I don’t use this method, so these haven’t been tested)
Manual trigger action tutorial
How to configure Github webooks
Storing Locally instead of on Github
Although this guide is written with Cloudflare's Github integration in mind, particularly for easy online/mobile access, you can also keep your files locally on your PC and directly upload your assets onto your Pages project. This gives you full control over what happens to your files. (Keeping backups is a good idea. You can still use Github Desktop to do this, just keep your repository on your PC.)
Simply clone/download the repository as it is, customize it as you like, and create a NEW Pages project on Cloudflare, using "Direct Upload" to upload your files
Once you have connected a Pages project with Github, there is no way to change the deployment method to Direct Upload or vice versa. Direct Upload is also not available for Workers.
One thing that will NOT work the same is the "create-index" Action that only works on Github.
I have made a "create-index.exe" that will execute the "create-index.py" files in the exact same way as they would work with the Action. You do not have to install python for this to work (if I did everything right). Simply run "create-index.exe" whenever you make a change and want to update the "index.html" files
Remember, this is EXACTLY THE SAME as the "create-index" Action, meaning you have to edit each "index.py" file when you rename folders, add a folder, want to exclude a file from the Index page, etc. (See Adding/Renaming Folders for how to do this)
Find me on Bluesky. Or if you have a problem, open an Issue on this project :)
I'll try to answer your questions as best I can! But really, I am the most amateur of amateurs and figured this all out using Google, so I might not be of much help ^^;
I also recommend Squidge Images (an offshoot of Squidge.org) as a fairly trustworthy alternative. However, Squidge Images does have some additional rules that Squidge does not, and what crosses the line is at their discretion.
I also posted this over on AO3!
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scrollkeeper's Case



High res versions of the art, a Foundry VTT module, and other formats, as well as a full compendium of our 100+ items can be found on our Patreon
While some fumble about with paper and ink, I’ve found that it’s time to move beyond that old chestnut and into a brand new cashew. I’m moving over to completely magical storage these days. Sure, it takes a little bit to get used to the conversion, but it’s so much easier and none of the power is lost in the transition. Now you can have all of those scrolls in one easily accessible magical storage device. Not sure what to call it yet, but I was thinking of personalizing it a bit. Put an “i” in front of it or something.
If you want to see more of our items you can check us out on our Website, Twitter, Pinterest, Tumblr, Bluesky, Threads or Instagram where we post them regularly. You can also find us at our Discord server where you can hang out and chat with the community.
#digital art#dnd#dnd homebrew#dnd5e#dnd 5e art#dungeons and dragons#fantasy art#fantasy illustration#magic item#ttrpg#pathfinder2e#pathfinder
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Over nearly a decade, the hacker group within Russia's GRU military intelligence agency known as Sandworm has launched some of the most disruptive cyberattacks in history against Ukraine's power grids, financial system, media, and government agencies. Signs now point to that same usual suspect being responsible for sabotaging a major mobile provider for the country, cutting off communications for millions and even temporarily sabotaging the air raid warning system in the capital of Kyiv.
On Tuesday, a cyberattack hit Kyivstar, one of Ukraine's largest mobile and internet providers. The details of how that attack was carried out remain far from clear. But it “resulted in essential services of the company’s technology network being blocked,” according to a statement posted by Ukraine’s Computer Emergency Response Team, or CERT-UA.
Kyivstar's CEO, Oleksandr Komarov, told Ukrainian national television on Tuesday, according to Reuters, that the hacking incident “significantly damaged [Kyivstar's] infrastructure [and] limited access.”
“We could not counter it at the virtual level, so we shut down Kyivstar physically to limit the enemy's access,” he continued. “War is also happening in cyberspace. Unfortunately, we have been hit as a result of this war.”
The Ukrainian government hasn't yet publicly attributed the cyberattack to any known hacker group—nor have any cybersecurity companies or researchers. But on Tuesday, a Ukrainian official within its SSSCIP computer security agency, which oversees CERT-UA, pointed out in a message to reporters that a group known as Solntsepek had claimed credit for the attack in a Telegram post, and noted that the group has been linked to the notorious Sandworm unit of Russia's GRU.
“We, the Solntsepek hackers, take full responsibility for the cyber attack on Kyivstar. We destroyed 10 computers, more than 4 thousand servers, all cloud storage and backup systems,” reads the message in Russian, addressed to Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy and posted to the group's Telegram account. The message also includes screenshots that appear to show access to Kyivstar's network, though this could not be verified. “We attacked Kyivstar because the company provides communications to the Ukrainian Armed Forces, as well as government agencies and law enforcement agencies of Ukraine. The rest of the offices helping the Armed Forces of Ukraine, get ready!”
Solntsepek has previously been used as a front for the hacker group Sandworm, the Moscow-based Unit 74455 of Russia's GRU, says John Hultquist, the head of threat intelligence at Google-owned cybersecurity firm Mandiant and a longtime tracker of the group. He declined, however, to say which of Solntsepek’s network intrusions have been linked to Sandworm in the past, suggesting that some of those intrusions may not yet be public. “It's a group that has claimed credit for incidents we know were carried out by Sandworm,” Hultquist says, adding that Solntsepek's Telegram post bolsters his previous suspicions that Sandworm was responsible. "Given their consistent focus on this type of activity, it's hard to be surprised that another major disruption is linked to them.”
If Solntsepek is a front for Sandworm, it would be far from the first. Over its years of targeting Ukrainian infrastructure, the GRU unit has used a wide variety of covers, hiding behind false flags such as independent hacktivist groups and cybercriminal ransomware gangs. It even attempted to frame North Korea for its attack on the 2018 Winter Olympics.
Today, Kyivstar countered some of Solntsepek's claims in a post on X, writing that “we assure you that the rumors about the destruction of our ‘computers and servers’ are simply fake.” The company had also written on the platform that it hoped to restore its network's operations by Wednesday, adding that it's working with the Ukrainian government and law enforcement agencies to investigate the attack. Kyivstar's parent company, Veon, headquartered in Amsterdam, didn't respond to WIRED's request for more information.
While the fog of war continues to obscure the exact scale of the Kyivstar incident, it already appears to be one of the most disruptive cyberattacks to have hit Ukraine since Russia's full-scale invasion began in February 2022. In the year that followed, Russia launched more data-destroying wiper attacks on Ukrainian networks than have been seen anywhere else in the world in the history of computing, though most have had far smaller effects than the Kyivstar intrusion. Other major Russian cyberattacks to hit Ukraine over the past 20 months include a cyberattack that crippled thousands of Viasat satellite modems across the country and other parts of Europe, now believed to have been carried out by the GRU. Another incident of cybersabotage, which Mandiant attributes to Sandworm specifically, caused a blackout in a Ukrainian city just as it was being hit by missile strikes, potentially hampering defensive efforts.
It's not yet clear if the Kyivstar attack—if it was indeed carried out by a Russian state-sponsored hacker group—was merely intended to sow chaos and confusion among the company's customers, or if it had a more specific tactical intention, such as disguising intelligence-gathering within Kyivstar's network, hampering Ukrainian military communications, or silencing its alerts to civilians about air raids.
“Telecoms offer intelligence opportunities, but they're also very effective targets for disruption," says Mandiant's Hultquist. “You can cause significant disruption to people's lives. And you can even have military impacts.”
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
November 15, 2023
By Jonathan Mahler, James B. Stewart, and Benjamin Mullin
(The New York Times Magazine) — It was April 2022, and David Zaslav had just closed the deal of a lifetime. From the helm of his relatively small and unglamorous cable company, Discovery, he had taken control of a sprawling entertainment conglomerate that included perhaps the most storied movie studio on the planet, Warner Brothers. The longtime New Yorker had always loved movies, and against the advice of several media peers, he had moved to Hollywood and taken over Jack Warner’s historic office, hauling the old mogul’s desk out of storage and topping it off with an old-time handset telephone. So far things were going great. He had met all the stars and players, was widely feted as the next in line to save the eternally struggling industry and was well into the process of renovating a landmark house in Beverly Hills. “You’re the dog that caught the bus,” the billionaire octogenarian cable pioneer John Malone, one of Discovery’s largest shareholders, told him. All he needed to do now was pay back the $56 billion in debt that he piled onto the new company to make the deal happen.
Money is never just lying around Hollywood, and the town was still reeling from the pandemic. But that was OK. Zaslav had set a “synergy target” — cost cuts, essentially — of $3 billion in the next two years, and now, with the clock ticking, he got to work. To help, he had brought along his chief financial officer from Discovery, an amateur pilot and former McKinsey consultant named Gunnar Wiedenfels. As spring turned to summer, they laid off hundreds of workers, shuttered or reorganized divisions and suspended or canceled hundreds of millions of dollars’ worth of programming. Anything we don’t think is awesome, Zaslav told executives, stop production right now. Turn the cameras off.
Cuts are the norm after a merger, but Zaslav and Wiedenfels were pushing things hard, and in sometimes unorthodox directions. By shelving several nearly completed projects — including the animated, direct-to-streaming movie “Scoob!: Holiday Haunt,” and the fourth season of the postapocalyptic TV series “Snowpiercer” — they saved millions in postproduction and marketing costs, as well as residuals down the line, and they locked in hefty tax breaks up front. Like so much of what happened in Hollywood, all this was reminiscent of a Hollywood production — in this case, the beloved 1967 Mel Brooks comedy “The Producers.” There, the producers, Max Bialystock and Leopold Bloom, realized that under the right circumstances, a producer could make more money with a flop than a hit. For Zaslav and Wiedenfels, the money would come from making sure that no one would get to see the shows in the first place.
Then they came for “Batgirl.” The big-ticket streaming project had just finished filming in Scotland when Zaslav took over, and he and Wiedenfels had immediately identified it as a target — a “free ball,” as Zaslav described it to several colleagues. The audience test scores for a very early cut were not encouraging. Still, a number of executives warned him not to shelve it. “Batgirl” was a $90 million entry in a multibillion-dollar universe of movies and television shows based on DC Comics. Michael Keaton was reprising his role as Batman, and sequels were already in the works. Plenty of movies had tested poorly but still earned millions. Killing an all-but-completed movie would alienate the people Zaslav — or at least Hollywood — needed most: the people who made the movies. It was to no avail. On Aug. 2, the word came down: “Batgirl” was dead.
As predicted, the backlash was immediate and emotional. Stunned, the film’s up-and-coming directors, Adil El Arbi and Bilall Fallah, tried to look at their footage, but their access to the production server was denied. The head of the DC unit, Walter Hamada, who was not consulted on the decision, asked to be released from his contract and would leave before the end of the year. Courtenay Valenti, one of the most respected development executives at Warner Brothers, was equally devastated and would be gone in a matter of weeks, ending a 33-year run at the studio. The news dominated the Hollywood trades for days. Under fire, Zaslav defended the decision in an earnings call with analysts, saying he shelved “Batgirl” to protect the DC brand. More quietly, Zaslav also sought cover in the authority of Bryan Lourd, the powerful co-chairman of Creative Artists Agency and a leading arbiter of Hollywood mores. As Zaslav told it to several associates, Lourd had supported the decision, observing that it wasn’t in the interest of C.A.A. clients, like the film’s star, Leslie Grace, to be associated with a bad movie. But a C.A.A. spokeswoman denied that. “Bryan Lourd was not consulted in advance of the studio’s move to cancel ‘Batgirl,’” she said.
At Discovery, producers referred to having their budgets slashed as “getting Gunnared,” and Wiedenfels maintains a hard-boiled, McKinsey-esque attitude toward the bottom line. “It’s hard work,” he says. “You don’t make friends.” Zaslav, a born salesman who would prefer to make friends, is more reflective. “You do sometimes get bloodied,” he said in a wide-ranging interview at Warner Brothers Discovery’s corporate headquarters in New York. But business is business. “We have made unpopular decisions because they were necessary.”
That joke about selling to Saudi Arabia in the end. Just... no.
#David Zaslav#Warner Bros.#Warner Bros. Discovery#WBD#CNN#TCM#SaveTCM#Discovery Channel#WGA#SAG AFTRA#SAG#labor#Barbie#DCEU#Batgirl#The Flash#Wizarding World#Harry Potter#Steven Spielberg#Cannes Film Festival#The New York Times#The New York Times Magazine#news
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Comprehensive Guide to Web Development, Data Management, and More
Introduction
Everything today is technology driven in this digital world. There's a lot happening behind the scenes when you use your favorite apps, go to websites, and do other things with all of those zeroes and ones — or binary data. In this blog, I will be explaining what all these terminologies really means and other basics of web development, data management etc. We will be discussing them in the simplest way so that this becomes easy to understand for beginners or people who are even remotely interested about technology. JOIN US
What is Web Development?
Web development refers to the work and process of developing a website or web application that can run in a web browser. From laying out individual web page designs before we ever start coding, to how the layout will be implemented through HTML/CSS. There are two major fields of web development — front-end and back-end.
Front-End Development
Front-end development, also known as client-side development, is the part of web development that deals with what users see and interact with on their screens. It involves using languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create the visual elements of a website, such as buttons, forms, and images. JOIN US
HTML (HyperText Markup Language):
HTML is the foundation of all website, it helps one to organize their content on web platform. It provides the default style to basic elements such as headings, paragraphs and links.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets):
styles and formats HTML elements. It makes an attractive and user-friendly look of webpage as it controls the colors, fonts, layout.
JavaScript :
A language for adding interactivity to a website Users interact with items, like clicking a button to send in a form or viewing images within the slideshow. JOIN US
Back-End Development
The difference while front-end development is all about what the user sees, back end involves everything that happens behind. The back-end consists of a server, database and application logic that runs on the web.
Server:
A server is a computer that holds website files and provides them to the user browser when they request it. Server-Side: These are populated by back-end developers who build and maintain servers using languages like Python, PHP or Ruby.
Database:
The place where a website keeps its data, from user details to content and settings The database is maintained with services like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB. JOIN US
Application Logic —
the code that links front-end and back-end It takes user input, gets data from the database and returns right informations to front-end area.

Why Proper Data Management is Absolutely Critical
Data management — Besides web development this is the most important a part of our Digital World. What Is Data Management? It includes practices, policies and procedures that are used to collect store secure data in controlled way.
Data Storage –
data after being collected needs to be stored securely such data can be stored in relational databases or cloud storage solutions. The most important aspect here is that the data should never be accessed by an unauthorized source or breached. JOIN US
Data processing:
Right from storing the data, with Big Data you further move on to process it in order to make sense out of hordes of raw information. This includes cleansing the data (removing errors or redundancies), finding patterns among it, and producing ideas that could be useful for decision-making.
Data Security:
Another important part of data management is the security of it. It refers to defending data against unauthorized access, breaches or other potential vulnerabilities. You can do this with some basic security methods, mostly encryption and access controls as well as regular auditing of your systems.
Other Critical Tech Landmarks
There are a lot of disciplines in the tech world that go beyond web development and data management. Here are a few of them:
Cloud Computing
Leading by example, AWS had established cloud computing as the on-demand delivery of IT resources and applications via web services/Internet over a decade considering all layers to make it easy from servers up to top most layer. This will enable organizations to consume technology resources in the form of pay-as-you-go model without having to purchase, own and feed that infrastructure. JOIN US
Cloud Computing Advantages:
Main advantages are cost savings, scalability, flexibility and disaster recovery. Resources can be scaled based on usage, which means companies only pay for what they are using and have the data backed up in case of an emergency.
Examples of Cloud Services:
Few popular cloud services are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These provide a plethora of services that helps to Develop and Manage App, Store Data etc.
Cybersecurity
As the world continues to rely more heavily on digital technologies, cybersecurity has never been a bigger issue. Protecting computer systems, networks and data from cyber attacks is called Cyber security.
Phishing attacks, Malware, Ransomware and Data breaches:
This is common cybersecurity threats. These threats can bear substantial ramifications, from financial damages to reputation harm for any corporation.
Cybersecurity Best Practices:
In order to safeguard against cybersecurity threats, it is necessary to follow best-practices including using strong passwords and two-factor authorization, updating software as required, training employees on security risks.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) represent the fastest-growing fields of creating systems that learn from data, identifying patterns in them. These are applied to several use-cases like self driving cars, personalization in Netflix.
AI vs ML —
AI is the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way we would consider “smart”. Machine learning is a type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that provides computers with the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. JOIN US
Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: some common applications include Image recognition, Speech to text, Natural language processing, Predictive analytics Robotics.
Web Development meets Data Management etc.
We need so many things like web development, data management and cloud computing plus cybersecurity etc.. but some of them are most important aspects i.e. AI/ML yet more fascinating is where these fields converge or play off each other.
Web Development and Data Management
Web Development and Data Management goes hand in hand. The large number of websites and web-based applications in the world generate enormous amounts of data — from user interactions, to transaction records. Being able to manage this data is key in providing a fantastic user experience and enabling you to make decisions based on the right kind of information.
E.g. E-commerce Website, products data need to be saved on server also customers data should save in a database loosely coupled with orders and payments. This data is necessary for customization of the shopping experience as well as inventory management and fraud prevention.
Cloud Computing and Web Development
The development of the web has been revolutionized by cloud computing which gives developers a way to allocate, deploy and scale applications more or less without service friction. Developers now can host applications and data in cloud services instead of investing for physical servers.
E.g. A start-up company can use cloud services to roll out the web application globally in order for all users worldwide could browse it without waiting due unavailability of geolocation prohibited access.
The Future of Cybersecurity and Data Management
Which makes Cybersecurity a very important part of the Data management. The more data collected and stored by an organization, the greater a target it becomes for cyber threats. It is important to secure this data using robust cybersecurity measures, so that sensitive information remains intact and customer trust does not weaken. JOIN US
Ex: A healthcare provider would have to protect patient data in order to be compliant with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) that is also responsible for ensuring a degree of confidentiality between a provider and their patients.
Conclusion
Well, in a nutshell web-developer or Data manager etc are some of the integral parts for digital world.
As a Business Owner, Tech Enthusiast or even if you are just planning to make your Career in tech — it is important that you understand these. With the progress of technology never slowing down, these intersections are perhaps only going to come together more strongly and develop into cornerstones that define how we live in a digital world tomorrow.
With the fundamental knowledge of web development, data management, automation and ML you will manage to catch up with digital movements. Whether you have a site to build, ideas data to manage or simply interested in what’s hot these days, skills and knowledge around the above will stand good for changing tech world. JOIN US
#Technology#Web Development#Front-End Development#Back-End Development#HTML#CSS#JavaScript#Data Management#Data Security#Cloud Computing#AWS (Amazon Web Services)#Cybersecurity#Artificial Intelligence (AI)#Machine Learning (ML)#Digital World#Tech Trends#IT Basics#Beginners Guide#Web Development Basics#Tech Enthusiast#Tech Career#america
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Full-Stack Web Development In 7 days Ebook
Title: Full-Stack Web Development in 7 Days: Your Comprehensive Guide to Building Dynamic Websites
Introduction: Are you eager to embark on a journey to become a full-stack web developer? Look no further! In this comprehensive ebook, "Full-Stack Web Development in 7 Days," we will guide you through the fundamental concepts and practical skills necessary to build dynamic websites from front to back. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced programmer looking to expand your skill set, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to kickstart your journey as a full-stack web developer in just one week.
Day 1: Introduction to Web Development:
Understand the foundations of web development, including the client-server architecture and HTTP protocol.
Learn HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—the building blocks of any web application.
Dive into the basics of responsive web design and create your first static webpage.
Day 2: Front-End Development:
Explore the world of front-end development frameworks like Bootstrap and learn how to build responsive and visually appealing user interfaces.
Master JavaScript libraries such as jQuery to add interactivity and dynamic elements to your web pages.
Gain hands-on experience with front-end frameworks like React or Angular to create robust single-page applications.
Day 3: Back-End Development:
Discover the essentials of back-end development using popular programming languages like Python, JavaScript (Node.js), or Ruby.
Learn about server-side frameworks such as Express, Django, or Ruby on Rails to build powerful back-end applications.
Connect your front-end and back-end components, enabling them to communicate and exchange data seamlessly.
Day 4: Databases and Data Management:
Dive into the world of databases and understand the difference between relational and NoSQL databases.
Learn how to work with popular databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB.
Implement database integration into your web applications, enabling data storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
Day 5: API Development and Integration:
Explore the fundamentals of RESTful APIs and their role in modern web development.
Build your own APIs using frameworks like Express or Flask to expose data and functionality to external applications.
Integrate third-party APIs, such as social media APIs or payment gateways, to enhance the functionality of your web applications.
Day 6: Security and Performance Optimization:
Understand common security vulnerabilities in web applications and learn how to protect against them.
Implement authentication and authorization mechanisms to secure user data and control access.
Optimize your web applications for performance, including techniques like caching, code minification, and server-side rendering.
Day 7: Deployment and Continuous Integration:
Learn how to deploy your web applications to a hosting platform or a cloud infrastructure like AWS, Azure, or Heroku.
Set up continuous integration and deployment workflows using tools like Git, GitHub, and Docker.
Finalize your full-stack web development journey by exploring best practices for maintenance, troubleshooting, and scalability.
Conclusion: "Full-Stack Web Development in 7 Days" provides a structured and comprehensive roadmap to help you become a proficient full-stack web developer within a week. By following this ebook, you will gain a solid foundation in front-end and back-end development, databases, APIs, security, performance optimization, and deployment. Get ready to unleash your creativity and embark on an exciting career in web development. Start your journey today and unlock the endless possibilities of building dynamic and interactive websites.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

I can't find the exact one but one of my favorite childhood CD holders looked something like the above. It was a plastic transparent-but-not-see-through drawer that you opened by pushing into the front to pop it open, and then the front part would pop forwards a little to make it easier to access.
The inside was a bunch of soft sleeves attached to the drawer that you could sort your CDs into. I remember not having very much room and pushing CDs together and very carefully sliding them in to avoid scratching them because I was a child and couldn't just go out and buy new CD holders.
That, combined with spindles like this:

And books like in the original post were everywhere in my home.
And let me tell you: I preferred the floppy disks so much. I had a bunch of 3½" floppy disks (the kind where they're hard plastic and only the internal diskette is still floppy, vs the older kinds where the whole thing was floppy) and they were so nice because they were much easier to store safely, could be rewritten multiple times, and just felt really great to use (the ker-klunk when sliding them in, the ker-pop when ejecting them).

Not nearly as much storage space but files were so small back then. CDs were more for storing larger archival data (backups) and software (installers, games), and floppies were how I moved files around between computers. How I shared them.
I never used zip drives or any of that family. I didn't need that much storage space.

But man I really would love to go to an era where the evolution of the ZIP drive, the Clik drive, was the norm.

Mainly for aesthetic reasons. I think USB drives are fine, but they don't have the satisfying clicks and ejects.
More than anything, though, I wish that people still relied on physical media the way they used to. Now everything's being sent around in cloud storage servers, and backed up to cloud storage servers, and lost in cloud storage server sync failures...
Physical media was so much more under your own control. You didn't have to worry about people tracking what you were doing (even if you think you're not breaking any laws, trust me when I say you'll end up with a record if anybody truly audited your life against the books; so many things that seem intuitively fine are either breach of contract from an EULA you didn't read well enough or surprisingly criminal). You didn't have to worry about the cloud service going offline. Or losing internet.
Electricity was out? As long as you had a generator, those files were still accessible. (I didn't have a generator... couldn't install one in the condos I grew up in, which sucked considering the amount of power outages.)
Internet is so much less reliable by comparison. Cloud providers even less so.
Sure, you had to keep your physical media in the right conditions. The right temperature, humidity, etc. But in my opinion, that's much easier than making sure that your account is secure at all times.
IDK. This sort of thing is why I'm a big fan of Cassette Futurism era of Cyberpunk. The modern Internet-focused Cyberpunk narratives are great for writing dystopian fiction, but the old "haha I stored your soul on a mini CD" era has so much aesthetic appeal and comfort to me.

#compact disk#data storage#floppy disk#zip drive#clik drive#Wishing for certain aspects of a bygone era but not other aspects of it because honestly I think life is better now it's just there are#certain things I would've liked to develop in a different direction
38K notes
·
View notes
Text
Aria Telecom: Your Trusted Cloud Based Doctor Appointment System in Canada
In today’s digital-first world, efficiency and accessibility in healthcare are more important than ever. Long queues, telephone delays, and manual scheduling are not just outdated—they compromise patient care. That’s why modern clinics, hospitals, and medical practices are turning to smart solutions like Aria Telecom’s Cloud Based Doctor Appointment System in Canada, designed to simplify scheduling, reduce administrative burden, and enhance the patient experience.
Whether you manage a private clinic or a public healthcare network, digitizing your appointment process ensures better control, higher patient satisfaction, and fewer no-shows. And with Aria Telecom’s cloud infrastructure, your system is always secure, available, and scalable.
Why Choose a Cloud-Based Appointment System?
A cloud-based solution means your scheduling system isn’t restricted to one computer or clinic. Doctors, staff, and patients can access it from anywhere—be it a mobile device, tablet, or desktop.
As a trusted provider of a Cloud Based Doctor Appointment System in Canada, Aria Telecom offers:
24/7 booking access for patients
Automated appointment confirmations and reminders
Easy rescheduling and cancellation options
Integrated doctor availability calendar
HIPAA and PIPEDA-compliant cloud storage
All appointments, updates, and patient interactions are securely logged in real-time, reducing errors and miscommunication.
Key Features of Aria Telecom’s Appointment Platform
🗓️ Smart Booking Interface
Patients can easily book, view, and manage appointments via web portal or mobile app. Available time slots update in real time.
🔄 Auto Notifications
Patients receive SMS and email reminders to reduce no-shows and late cancellations.
🩺 Multi-Doctor and Multi-Clinic Support
Ideal for small practices or large healthcare networks. Manage multiple doctors’ calendars under a unified system.
🔐 Secure Canadian Hosting
Our cloud platform is hosted on Canadian servers, ensuring full PIPEDA compliance and patient data privacy.
📊 Admin Dashboard
Admins can track booking trends, manage workloads, and generate reports with a few clicks.
Perfect for Canadian Healthcare Providers
Whether you’re a private practitioner in Toronto or a clinic in British Columbia, our Cloud Based Doctor Appointment System in Canada is built to serve:
Solo doctors and specialists
Multi-specialty clinics
Diagnostic and pathology labs
Mental health and therapy centers
Provincial healthcare groups and public hospitals
It integrates seamlessly with existing EHRs and patient record systems to create a smooth operational flow.
Success Story: Quebec-Based Medical Group
A growing network of dermatology clinics in Quebec faced scheduling chaos due to phone-based appointment systems. Long hold times and miscommunication were affecting both patients and front-desk staff.
After adopting Aria Telecom’s solution:
Patient booking increased by 35% in the first 3 months
Missed appointments dropped by over 40%
Staff reported 60% less time spent on scheduling-related tasks
This highlights why Aria Telecom is a go-to name for a reliable Cloud Based Doctor Appointment System in Canada.
Designed with Compliance and Security in Mind
Your patient data is sensitive. Our cloud infrastructure ensures that it stays secure and fully compliant with Canadian healthcare laws:
Encrypted data at rest and in transit
Canadian data center hosting
Role-based access for doctors, admin staff, and patients
Full PIPEDA and HIPAA alignment
Daily backups and activity audit logs
Why Aria Telecom?
Aria Telecom brings over two decades of experience in telecom and healthcare IT solutions. Choosing us means:
🚀 Quick deployment and onboarding
📞 24/7 technical support
🔧 Custom branding and integration
💡 Scalable plans for clinics of all sizes
🤝 A technology partner that evolves with you
We’re not just giving you software—we’re helping you offer smarter, faster, and safer care.
#DoctorAppointmentSystem#CloudHealthcareCanada#AriaTelecomSolutions#PatientBookingMadeEasy#DigitalHealthCanada
0 notes
Text
Aligning BI Strategy with Microsoft’s Analytics Stack
In today’s data-driven world, aligning your Business Intelligence (BI) strategy with a robust analytics ecosystem is no longer optional—it’s essential. Microsoft’s analytics stack, centered around Power BI, Azure Synapse Analytics, and the broader Azure Data Services, offers a scalable, unified platform that can transform how organizations gather insights, make decisions, and achieve business goals.
For enterprises transitioning from Tableau to Power BI, integrating with Microsoft’s analytics stack is more than a technical shift—it’s a strategic opportunity.
Why Microsoft’s Analytics Stack?
Microsoft’s stack is designed with synergy in mind. Power BI serves as the front-end visualization tool, while Azure Synapse Analytics acts as the powerhouse for data integration, big data analytics, and real-time processing. Azure Data Factory, Azure Data Lake, and SQL Server complement the environment by enabling seamless data movement, storage, and management.
Aligning with this ecosystem empowers organizations to:
Unify data access and governance
Leverage native AI and machine learning
Streamline collaboration via Microsoft 365 integration
Improve performance with cloud-scale analytics
Key Considerations for BI Strategy Alignment
1. Define Strategic Goals Clearly Start with identifying what you want to achieve—whether it’s real-time reporting, predictive analytics, or better self-service BI. Microsoft’s platform offers the flexibility to scale BI initiatives based on maturity and business priorities.
2. Optimize Data Architecture Unlike Tableau’s more visual-centric architecture, Power BI thrives in a model-driven environment. Organizations should design dataflows and models to fully leverage Power BI’s DAX capabilities, semantic layers, and integration with Azure SQL and Synapse.
3. Leverage Azure Synapse for Enterprise-Scale Analytics Synapse enables unified analytics over big data and structured data. When aligned with Power BI, it removes data silos and allows for direct querying of large datasets, which enhances performance and reduces duplication.
4. Automate with Azure Data Factory A well-aligned BI strategy includes efficient ETL processes. Azure Data Factory helps automate pipelines and data transformations that feed clean data into Power BI for analysis, reducing manual effort and errors.
5. Prioritize Governance and Security With Microsoft Purview and Power BI's Row-Level Security (RLS), organizations can ensure data compliance and user-level control over access. This becomes increasingly vital during and after a migration from platforms like Tableau.
A Strategic Migration Opportunity
For those moving from Tableau to Power BI, aligning with Microsoft’s full analytics stack opens doors to advanced capabilities previously underutilized. Tools like Pulse Convert by OfficeSolution help automate and optimize this migration process, ensuring that your data assets, dashboards, and logic align smoothly with Power BI’s architecture.
Final Thoughts
Aligning your BI strategy with Microsoft’s analytics stack isn't just a move to a new tool—it’s an investment in a future-ready, scalable, and intelligent data ecosystem. Whether you're migrating from Tableau or building from scratch, OfficeSolution is here to guide you in leveraging the full potential of Microsoft's platform for long-term analytics success.
0 notes