#Information Theory
Text
hmmm the current dose of brain meds has successfully tamped down the SAD but i think it might not be a good idea to keep it up for too long bc i am now fighting the delusion that i have made some kind of Brilliant Breakthrough In Theoretical Physics And Also Biology Maybe
(i am not a physicist, I can't do math for shit, i have skimmed a few wikipedia articles that i mostly did not understand. this is almost certainly either some timecube shit or something that has already been considered and discarded by people who actually knew what the fuck they were talking about lmao)
but hey if there's any physicists out there who need a break from their thesis or w/e and want to have a laugh, this is for you! maybe explaining why it's wrong will help un-stick your brain or smth, i'm always happy to be a rubber duck 🤓

so yeah i mostly just need to put this out there so i can stop thinking about it lmao, but if you want to take time out of your day to explain physics to a complete noob i do love learning whatever i can about this stuff 😅
#physics#science#information theory#idek which disciplines are the ones that apply to this even#particle physics#?#there's probably a whole branch of ppl who study Time Shit specifically#and the origins of life etc#mad respect to y'all#and sorry 2 bother you lol
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Unaccountability Machine
Information Theory and The Machine of the Economy
"things went off the rails starting in about 1970 when everyone decided that the way they were going to deal with complexity was basically to ignore it and to assume that the free market would solve all the problems because people you know from Hayek onwards in the economics profession have always regarded the market as being a magic all-purpose computer..."

"it's really weird that a profession that's based on the idea that there's no such thing as a free lunch is always so happy to help itself to an informational version of exactly the same that thing ... that the market is this giant information processing and decision making machine"
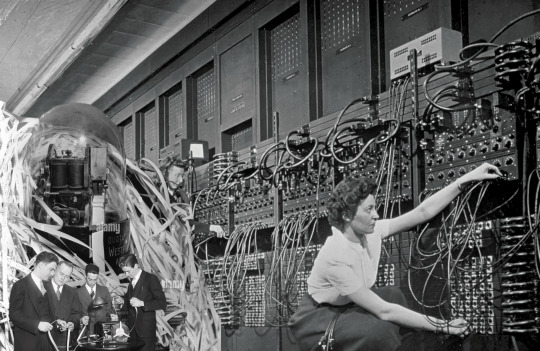
"the great tragedy of our friend Hayek is that he was thinking in a very sophisticated way about information in the economy but he was doing it in the 1920s and 30s and the concept of information Theory did not exist then"
"you know all of Hayek's works on information in the economy were before Alan Turing they were before Kurt Godel... they were before Shannon you know the concept of information was not on a sound kind of rigorous mathematic basis when he was doing these things"

"unfortunately all the economists who came after Hayek presumed that information in the economy was a solved problem. It was a done deal. "
"It was the Socialist calculation problem everything that was interesting to say about it had been said in 1928 and so they never really got to grips with the idea that information is a quantity and as equally as important as balancing supply and demand is the ability to balance the information generated by the environment."

"the kind of chaos and variety and variability you know of the world with the capacity of the system that's meant to be regulating and managing that environment to process it because if those if your information balance sheet isn't balancing then the system has become unregulated and then not only is it going to go out of control but also because it's unregulated you cannot assume that your actions to try to control it are going to push it back to a steady state"

"it's quite often the case that you'll be pushing it out of equilibrium and you'll be causing you know what they call what you'd recognize as oscillation if it happened in an engineering framework because you're working on a broken model of reality..."

"and you know that's kind of my diagnosis of a lot of the state that we've got to which is that we're just working on a broken or insufficient model of reality and as a result very often we're making policy interventions that are just pushing things further away from our desired State without us really knowing that we're doing that"
"The way in which the economics profession ignored most
of the work done in information theory is striking. It ignored
its own traditions relating to uncertainty and decision-making,
instead ploughing ahead with a frighteningly simplistic view of
the world in which everything could be reduced to a single goal
of shareholder value maximisation."
- Dan Davies - The Unaccountability Machine
youtube

#the unaccountability machine#friedrich hayek#information theory#control theory#stafford beer#norbert weiner#dan davies#management cybernetics#cybernetics#cybernetic#marshall mcluhan#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is Evolution an Entropic Process?
The traditional view of entropy as disorder might not fully capture the relationship between life and the universe's fundamental forces. A closer look reveals a surprising relationship: evolution, the process driving the diversity and complexity of life, may itself be an entropic process.
Entropy, a key concept in thermodynamics, traditionally represents the measure of disorder in a system leading to an imagined perspective of flatness. However, from a statistical mechanics standpoint, entropy also quantifies the number of possible states a system can occupy. In this broader sense, a system with more complexity—characterized by a greater variety of components and interactions—holds the potential for more states, thereby possessing higher entropy.
Evolution through natural selection is fundamentally about changes—specifically, genetic variations that increase an organism's adaptability to its environment. Each genetic change, adaptation, or mutation that survives the harsh sieve of natural selection adds layers of complexity to life's blueprint. More complexity means more potential states and interactions, which translates to higher entropy. Thus, as species evolve and ecosystems diversify, they potentially increase the entropy of the biological system.
Evolution isn't just a genetic process; it involves significant energy and information flow changes. These transformations, as organisms become more adapted and ecosystems more intricate, lead to greater dispersal and utilization of energy. As species evolve, they explore and embody more microstates of energy distribution, suggesting that evolution might be one of nature’s pathways to maximizing entropy.
If evolution is indeed an entropic process, this provides a novel lens through which to view life's development: not merely as a fight for survival against entropy but as an integral part of the broader entropic trends of the universe. Life, in its myriad forms, isn’t just undergoing evolution; it is being driven by and facilitating the universe's intrinsic march towards higher entropy and complexity.
This perspective can reshapes understanding of the partnership between evolution and entropy. It posits life as a creation of and a dynamic participant in the universe's entropic unfolding, actively exploring new states of being and complexity. As such life could be seen as a natural consequence of entropy which includes consciousness itself.
#entropy#science#information theory#systems thinking#complex adaptive systems#complexity#physics#life#evolution
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Abstract
Deep neural networks (DNNs) are often used for text classification due to their high accuracy. However, DNNs can be computationally intensive, requiring millions of parameters and large amounts of labeled data, which can make them expensive to use, to optimize, and to transfer to out-of-distribution (OOD) cases in practice. In this paper, we propose a non-parametric alternative to DNNs that’s easy, lightweight, and universal in text classification: a combination of a simple compressor like gzip with a k-nearest-neighbor classifier. Without any training parameters, our method achieves results that are competitive with non-pretrained deep learning methods on six in-distribution datasets. It even outperforms BERT on all five OOD datasets, including four low-resource languages. Our method also excels in the few-shot setting, where labeled data are too scarce to train DNNs effectively. Code is available at https://github.com/bazingagin/npc_gzip.
(July 2023 – pdf)
“this paper's nuts. for sentence classification on out-of-domain datasets, all neural (Transformer or not) approaches lose to good old kNN on representations generated by.... gzip” [x]

CLASSICAL ML SWEEP
#machine learning#programming#deep learning#nlp#neural networks#information theory#my uploads#my uploads (unjank)#transformer models#gzip#knn#k nearest neighbors
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Who is Claude Shannon?
Anyone in IT will have heard of Alan Turing and Tim Berners-Lee. The majority of developers will know about Ada Lovelace. But what about Claude Shannon? Well, I have to admit that I didn’t until I had time to watch the documentary film The Bit Player. I am shocked I’d never come across Shannon’s name before, given the importance of his work.
So what did he do? Well, Claude was responsible for…

View On WordPress
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

2 notes
·
View notes
Text

this is a very strange SF story, between cyberpunk and Thomas Pynchon
Fantasy & Science Fiction v073n05 (1987 11) (LennyS aMouse) : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
#paul di filippo#science fiction#science fiction literature#cyberpunk#paranoia#information theory#cybernetics
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Yes. The coveted job title: ancestor of many distinguished people.
#idk what to tag#claude shannon#information theory#Wikipedia#thomas edison#john ogden#american#inventors#scientists#dark academia#stuff#mathematics#mathblr
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Structure Leads to Information
How Structure Leads to Information
The importance of structure in physics and other branches of science cannot be overstated. Stucture is knowledge, structure is understanding. By structure we intend a map, or a graph, which reflects how information travels within a given system. In other words, we looking at the topology of all the interdependencies between the various actors, agents, or simply data channels, which compose or…

View On WordPress
#Complexity#complexity management#complexity map#entropy#information#information theory#shannon#structured information#uncertainty
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Entropy transformers
What is the relationship between information, causation, and entropy?
The other day, I was reading a post from Corey S. Powell on how we are all ripples of information. I found it interesting because it resonated with my own understanding of information (i.e. it flattered my biases). We both seem to see information as something active rather than passive. In my case I see it fundamentally…
0 notes
Text
transistor2tnanslator is a research group dedicated to finding solutions to problems that isolate humans.
We believe communication and ideas are two completely separate things.
We want to remove any and all barriers to connecting with another person.
Some areas of interest:
Natural Language
Accessibility
Information Theory
“Language is but a vehicle for ideas”
#science#communication#research#humans#accessibility#information theory#connection#t2t#translation#translator#computer science#cs#collab
1 note
·
View note
Text
Life does have meaning. Meaning is all around you. But there isn't a meaning of life, for at least two reasons:
(1) because there is a limit on the observable universe, and we'd need all the information to be able to extract the complete meaning - we will never have all the information; and
(2) while the meaning of life is out there, it's almost certainly just unintelligible nonsense. Like if you took the average (centroid) word out of all the words in the dictionary, it'd probably be a nonword, or at a minimum, reveal nothing interesting. Dhuidjh. K. Now what?
0 notes
Text
Theseus - Life-sized magnetic mouse
Year: 1950
Creator: Claude Shannon
Video: AT&T Website - (Original Bell Labs)
"one of the world’s first examples of machine learning: a robotic maze-solving mouse known as Theseus. The Theseus of ancient Greek mythology navigated a minotaur’s labyrinth and escaped by following a thread he’d used to mark his path. But Shannon’s electromechanical toy was able to “remember” its path with the help of telephone relay switches.
As the film begins, Shannon’s wheeled mouse methodically explores its surroundings—a 25-square maze. Shannon tells viewers that the maze’s metal walls can be freely rearranged, so Theseus must use a small computing machine to learn the layout anew each time. But the mouse, a tiny wooden device containing a bar magnet and adorned with wire whiskers, is “far too small” to contain a computing machine, he says. Instead, the machinery is hidden beneath the floor of the maze, a series of telephone relay circuits he has repurposed to do something that they had never done before: learn." - MIT Technology Review
#ai#ai research#artificial intelligence#machine learning#claude shannon#information theory#bell labs#cybernetic#cybernetics
1 note
·
View note
Text
Universal Heat Death Revisited: A Happy Ending
Introduction to Entropy and State Variability
Entropy, traditionally understood in thermodynamics as a measure of disorder, is actually proportional to the number of possible configurations (states) a system can take. As entropy increases, so too does the system's state variability, a term we use to describe the diversity of potential states available to a system.
Misconceptions About the Universe’s Configuration
It's essential to clarify that while the universe increases in entropy, implying more potential states, it exists in only one configuration at any given moment. As entropy expands the range of possible states, the likelihood of more complex configurations also increases. This relationship suggests that each moment in the universe is not just a step towards disorder but potentially towards greater complexity.
Heat Death and Complexity
The concept of the heat death of the universe suggests an end state of maximum entropy, characterized by a uniform and useless distribution of energy. Traditional views equate this state with simplicity and inertness. However, as state variability rises with entropy, the complexity of possible states, including energy distributions, also increases. This raises a critical question: Is a universe at maximum entropy necessarily simple, or could it be complex in unexpected ways?
Complexity in Human Terms
Consider the complexity of a human being versus a pile of its molecular constituents. The human organism exhibits a higher state of complexity and thus requires more information for its description. If state complexity and state variability both scale with entropy, then phenomena like life itself are not merely surviving entropy but are direct manifestations and drivers of it. This challenges the traditional view of life as a struggle against entropy. Instead, life—through its myriad forms and functions—can be seen as an agent that harnesses and even accelerates the entropic processes, facilitating the universe's exploration of new and more complex states.
Information, Entropy, and Work
To further understand this, we can examine the relationship between information, entropy, and the capacity to perform work. While the classical view holds that no work can be done at the point of heat death due to the uniformity of energy, an alternative perspective considers the role of information in directing energy to perform work. Information theory suggests that even in a high-entropy state, where traditional work is impossible, random fluctuations of energy might still occur. These fluctuations, within a universe at maximum entropy, can lead to localized increases in complexity even as the overall system remains in a state of equilibrium due to decreases in complexity elsewhere.
Conclusion: A New Perspective on Entropy and the Universe
Thus, understanding entropy as a creative rather than destructive force offers a more optimistic view of the universe's fate. It suggests that the universe, driven by entropy, continually evolves into states of greater complexity and novelty, not despite entropy but because of it. This view encourages us to reconsider our perspective on the universe, not as marching towards a cold, inert end but as evolving through a dynamic interplay of complex structures and processes, revealing an ongoing narrative of transformation, destruction and creativity.
Call to Embrace a Holistic View
In embracing this holistic and dynamic perspective, we might better appreciate the intricate interdependencies and the ultimate unity of the cosmos, where every end is potentially the beginning of new forms of order and complexity even when no work can be done.
#entropy#physics#philosophy#science#complex adaptive systems#systems thinking#systemsthinking#heat death of the universe#information theory#complexity
0 notes
Text
I went down a research rabbit hole today. I'm a firm believer that agent-based modeling is possible now that we have an abundance of computing resources and that AI could be smaller and more efficient if we could figure out how to get them to communicate and cooperate, like how parts of our brain do.
So I started reading a review about opponent modeling techniques and how it's used in negotiation modeling. (Learning about the opponent in automated bilateral negotiation: a comprehensive survey of opponent modeling techniques by Baarslag, Hendrikx, Hendriks, & Jonker). They're already using a lot of techniques like this in e-commerce and auctions. Part of it is an information game, like Clue. Time is an important factor since the benefits of negotiation cannot be realized until after the final round of negotiation and many agents experience time pressure. There's a Bayesian learning SO which makes me unbelievably happy. You can use time-series forecasting to help your strategy. Another key is learning about your opponent which is ties back to the information game idea. I find it both upsetting and comforting that problems can be simplified by guessing what an opponent will do. I have a love/hate relationship with heuristics. What I find really crazy, though, is somehow there are negotiating agents that are domain-independent. (SO to whoever made agents specific to playing Diplomacy. It's an addictive game.)
Anyway, because the action and outcome spaces are so huge, I feel like it would be a great exploratory space for small neural networks. I like Primer's YouTube videos that explore population dynamics. They did one video simulating an economy, and I'd love to see something similar where you have little blobs running around trying to sell things to each other (since that's where most of the research has been done) and see what strategies they learn. That would be so interesting to watch.
0 notes
Text
You aren't disconnected from your feelings or weak for not performing your emotions "properly". Our culture presses us to justify ourselves because the greater system loves itself more than the individual.
1 note
·
View note