#OVERDOSE
Text
"For the first time in decades, public health data shows a sudden and hopeful drop in drug overdose deaths across the U.S.
"This is exciting," said Dr. Nora Volkow, head of the National Institute On Drug Abuse [NIDA], the federal laboratory charged with studying addiction. "This looks real. This looks very, very real."
National surveys compiled by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention already show an unprecedented decline in drug deaths of roughly 10.6 percent. That's a huge reversal from recent years when fatal overdoses regularly increased by double-digit percentages.
Some researchers believe the data will show an even larger decline in drug deaths when federal surveys are updated to reflect improvements being seen at the state level, especially in the eastern U.S.
"In the states that have the most rapid data collection systems, we’re seeing declines of twenty percent, thirty percent," said Dr. Nabarun Dasgupta, an expert on street drugs at the University of North Carolina.
According to Dasgupta's analysis, which has sparked discussion among addiction and drug policy experts, the drop in state-level mortality numbers corresponds with similar steep declines in emergency room visits linked to overdoses.
Dasgupta was one of the first researchers to detect the trend. He believes the national decline in street drug deaths is now at least 15 percent and could mean as many as 20,000 fewer fatalities per year.
"Today, I have so much hope"
After years of wrenching drug deaths that seemed all but unstoppable, some researchers, front-line addiction workers, members of law enforcement, and people using street drugs voiced caution about the apparent trend.
Roughly 100,000 deaths are still occurring per year. Street drug cocktails including fentanyl, methamphetamines, xylazine and other synthetic chemicals are more poisonous than ever.

"I think we have to be careful when we get optimistic and see a slight drop in overdose deaths," said Dan Salter, who heads a federal drug interdiction program in the Atlanta-Carolinas region. "The last thing we want to do is spike the ball."
But most public health experts and some people living with addiction told NPR they believe catastrophic increases in drug deaths, which began in 2019, have ended, at least for now. Many said a widespread, meaningful shift appears underway.
"Some of us have learned to deal with the overdoses a lot better," said Kevin Donaldson, who uses fentanyl and xylazine on the street in Burlington, Vermont.
According to Donaldson, many people using fentanyl now carry naloxone, a medication that reverses most opioid overdoses. He said his friends also use street drugs with others nearby, ready to offer aid and support when overdoses occur.
He believes these changes - a response to the increasingly toxic street drug supply - mean more people like himself are surviving.
"For a while we were hearing about [drug deaths] every other day. When was the last one we heard about? Maybe two weeks ago? That's pretty few and far between," he said.
His experience is reflected in data from the Vermont Department of Health, which shows a 22 percent decline in drug deaths in 2024.
"The trends are definitely positive," said Dr. Keith Humphreys, a nationally respected drug policy researcher at Stanford University. "This is going to be the best year we've had since all of this started."
"A year ago when overdose deaths continued to rise, I was really struggling with hope," said Brad Finegood, who directs the overdose crisis response in Seattle.
Deaths in King County, Washington, linked to all drugs have dropped by 15 percent in the first half of 2024. Fatal overdoses caused by street fentanyl have dropped by 20 percent.
"Today, I have so much hope," Finegood said.
-via NPR, September 18, 2024. Article continues below with an exploration of the whys (mostly unknown) and some absolutely fucking incredible statistics.
Why the sudden and hopeful shift? Most experts say it's a mystery
While many people offered theories about why the drop in deaths is happening at unprecedented speed, most experts agreed that the data doesn't yet provide clear answers.
Some pointed to rapid improvements in the availability and affordability of medical treatments for fentanyl addiction. "Expansion of naloxone and medications for opioid use disorder — these strategies worked," said Dr. Volkow at NIDA.
"We've almost tripled the amount of naloxone out in the community," said Finegood. He noted that one survey in the Seattle area found 85 percent of high-risk drug users now carry the overdose-reversal medication.
Dr. Rahul Gupta, the White House drug czar, said the drop in drug deaths shows a path forward.
"This is the largest decrease on record and the fifth consecutive month of recorded decreases," he said.
Gupta called for more funding for addiction treatment and healthcare services, especially in Black and Native American communities where overdose deaths remain catastrophically high.
"There is no way we're going to beat this epidemic by not focusing on communities that are often marginalized, underserved and communities of color," Gupta said.
"Overdose deaths in Ohio are down 31 percent"
Indeed, in many states in the eastern and central U.S. where improvements are largest, the sudden drop in drug deaths stunned some observers who lived through the darkest days of the fentanyl overdose crisis.
"This year overdose deaths [in Ohio] are down 31 percent," said Dennis Couchon, a harm reduction activist. "The deaths were just plummeting. The data has never moved like this."
"While the mortality data for 2024 is incomplete and subject to change, Ohio is now in the ninth consecutive month of a historic and unexpected drop in overdose deaths," said the organization Harm Reduction Ohio in a statement.
Missouri is seeing a similar trend that appears to be accelerating. After dropping by 10 percent last year, preliminary data shows drug deaths in the state have now fallen roughly 34 percent in the second quarter of 2024.
"It absolutely seems things are going in the right direction, and it's something we should feel pleased about," said Dr. Rachel Winograd, director of addiction science at the University of Missouri St. Louis, who also noted that drug deaths remain too high.
"It feels wonderful and great," said Dr. Mark Levine, head of the Vermont Health Department. "We need encouraging data like this and it will help sustain all of us who are actively involved in trying to have an impact here."
Levine, too, said there's still "plenty of work left to do."" ...
Dasgupta, the researcher at the University of North Carolina, agreed more needs to be done to help people in addiction recover when they're ready.
But he said keeping more people alive is a crucial first step that seemed impossible only a year ago.
"A fifteen or twenty percent [drop in deaths] is a really big number, an enormous impact," he said, calling for more research to determine how to keep the trend going.
"If interventions are what's driving this decline, then let's double down on those interventions."
-article via NPR, September 18, 2024
#some of these statistics are so good I could cry#finally we might have turned the corner#finally we might be able to have the end of this epidemic in sight#cw drugs#cw addiction#substance use#opioid use#naloxone#narcan#addiction#public health#opioid epidemic#united states#north america#fentanyl#harm reduction#good news#hope#opiods#opiod crisis#overdose#tw overdose#drug overdose
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
PSA:
Acetaminophen/paracetamol has a hard stop upper dose limit, above which it becomes extremely toxic.
That limit is 4g (8 “extra strength” (500mg) tablets) in 24 hours (about 2 tablets every 6 hours).
A single dose of 22 extra strength tablets can kill you.
Taking 12 or more tablets per day for more than a week can also kill you (this is about 3 tablets every 6 hours).
Symptoms of overdose take up to 24 hours to manifest, and are fairly difficult to distinguish from other problems. They include abdominal pain (especially right upper quadrant), nausea, malaise, and confusion.
The antidote (n-acetylcystine) must be given within 8hours of ingestion in order to be useful.
After 10 hours the only thing that will work is a liver transplant.
You might think “why would I ever accidentally take so much?”
Well, acetaminophen is in almost everything in the cold/flu/pain aisle. Migraine combos like Excedrin, cold and flu combos like NyQuil, basically anything that says “non-aspirin pain relief”, and anything that’s branded as a fever reducer. It’s all probably acetaminophen/paracetamol.
So the goal of this post is to get you to read the labels on your medications. Because taking taking Tylenol and NyQuil together for a week (like you might if you had the flu) could kill you.
51K notes
·
View notes
Note
what do you mean reverse an overdose? How is that possible?
Hi anon.
So, in my most recent post where I was talking about reversing overdoses, I was talking about Narcan (naloxone).
Narcan is a medicine that can reverse opioid overdoses. It works on any opioids, including fentanyl, heroin, oxy, vicodin, etc. It isn't effective in reversing other kinds of drug overdoses, but would still work to reduce an overdose if your coke has fent in it, for example. It functions by blocking the opioid receptors in your brain and helps restore breathing. Narcan is not a dangerous medication, and it is not harmful to your brain, which means you can be dosed multiple times without increasing harm to your body. The experience of being Narcaned can be pretty fucking shitty, because it basically puts your body in withdrawal super super fast, and you might experience some of the effects of withdrawal like vomiting, body aches and chills, fatigue, etc. But there are not other harmful side effects outside of that. Narcan is safe to give to people of all ages, including children.
Narcan comes in both an nasal spray and intramuscular injections, but it's usually easier to get access to nasal spray. This is what Narcan looks like:

[ID: Someone holding a narcan nasal spray, which has a nozzle that can be placed into someone's nose, and a plunger underneath the nozzle that can be pushed up to administer a dose. Text on the image says: Do not test nasal spray device before use. Each device contains 1 dose of medicine. Each device sprays one time only.]
How to Use Narcan
Identify signs of Overdose
Check for Responsiveness
Administer Narcan
Support (other friends/911/medics)
To administer Narcan, you first need to identify if someone is overdosing. Signs of an opioid overdose can be when someone is unconscious, unresponsive, not breathing or slowly breathing, no pulse or erratic pulse, has pinpoint pupils, and/or has blue lips.
If you see some of these things and think that someone is overdosing, the next step is to check for responsiveness. You can do this by loudly calling the person's name, saying that you are going to Narcan them, gently shaking them, and by performing a sternum rub, which is where you rub your knuckles into the place in someone's chest where their ribs meet. If they're breathing and they respond, even if it's just making noises in response to you or physically pushing your hands away, that can be a sign that you don't need to administer Narcan right away. Still, in that case, it's a really good idea to stay with that person in case that changes. If, and only if, the person is completely unresponsive, you should administer Narcan.
Once you've determined that someone is unresponsive and overdosing, the next step is actually administering Narcan. Narcan comes in packs of two nasal sprays. Take the first nasal spray out of the box, put the nozzle in the person's nose, and press the plunger. If the person is still not responsive after 2-3 minutes, take the other nasal spray out of the box and give them another dose. I try to use the lowest number of doses possible to try to reduce the withdrawal experience, and I stop giving Narcan once someone is breathing and responsive. If they still are not responsive or breathing, and you know how to give rescue breaths, you can start administering rescue breaths. If you have to step away for any reason, turn the person on their side in the recovery position first.
After someone's overdose is reversed, it's really important that whenever possible, someone stays with them for at least an hour afterwards. Narcan is active in the body for about 30-90 minutes, so depending on what someone's original amount of opioids was, they might start overdosing again and need you to give them Narcan again. This is also why it can be important to try not to use again right away, which is really fucking shitty when you're trying to use cause you don't want to be sick, but unfortunately using right away can also put you at risk of overdosing again. When people come back after getting Narcaned, it can be a pretty disorienting and uncomfortable experience. You might not know who Narcaned you or why they're in your space, might be feeling really fucking shitty because of withdrawal, and might want to be left alone. If you've just Narcaned someone, introduce yourself and explain that you just gave them Narcan, listen to what they tell you, empathize with their feelings, respect people's boundaries, and give them space if they ask for it. Understand that they're probably feeling pretty fucking shitty in their body, that it fucking sucks when your high gets ruined, and they (justifiably) might not feel happy about the fact that you Narcaned them.
Pretty much all Narcan trainings will tell you that it's "recommended" to always call 911, but we all know that this is not always actually possible in a lot of situations and that cops always fucking make the situation worse. My policy is that I always, always ask for consent before calling 911 and if someone says no, then we brainstorm other ways of keeping safe and we don't fucking call the cops. If there's a situation where I do need to call 911, I never tell the operator that someone overdosed, because that usually gets them to send out the cops alongside ambulance, which can cause delays to care, put a lot of people at risk, and also put people, including bystanders, in legal danger. If I have to call 911, I say that my friend has collapsed/fainted/isn't breathing and keep it more vague, and when paramedics actually arrive on the scene, that's when I tell them more information about the overdose, what drugs someone took, and how many times I've administered Narcan.
You can get free Narcan a lot of places. Next Distro has resources for getting free Narcan by mail for almost every state. If there's harm reduction orgs in your area, they will have free Narcan. There's also a lot of Department of Health programs for free Narcan. Most pharmacies now also have Narcan available over the counter, but that's usually really fucking expensive and often pretty hard to shoplift cause they keep locking it up.
Even if you don't use drugs and you think that your loved ones don't use drugs, it's super important to have Narcan as a part of your first aid kit and learn how to use it. You never know when you're going to need to use it, and it's super good to be prepared ahead of time, in case your friend/family/neighbor/classmate/coworker ends up overdosing while you're there. Or in case you end up overdosing and having Narcan on you means that bystanders can help support you through it.
Here's a guide that goes a little more in depth into how to use Narcan.
Please feel free to ask if you have any other questions about Narcan or other harm reduction topics!
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
A study conducted by the B.C. Centre for Disease Control has found that prescribing medical-grade opioids dramatically reduced the rates of deaths and overdoses for drug users living in B.C.
The study, published in the British Medical Journal, is described as "the first known instance of a North American province or state providing clinical guidance to physicians and nurse practitioners for prescribing pharmaceutical alternatives to patients at risk of death from the toxic drug supply."
Researchers looked at anonymized health-care data of 5,882 people between March 2020 and August 2021, all of whom had opioid or stimulant use disorder.
Those individuals filled a prescription under the B.C. Risk Mitigation Guide — clinical guidance developed in March 2020 to allow for physical distancing during the COVID-19 pandemic, and to reduce deaths through harm reduction.
Continue Reading
Tagging @politicsofcanada
#cdnpoli#canada#canadian politics#canadian news#british columbia#public health#harm reduction#drug usage#harm reduction works#overdose#research
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

"Globe of Jewels"
It was made around 1869 by order of Nassereddin Shah. Naser al-Din Shah Qajar (1831 – 1896).
It made of 34kg of solid gold and more than 51,000 diamonds, emeralds, rubies and sapphires.
#art#design#luxury#overdose#gold#jewellery#jewelry#luxurious#diamond#globe#earth globe#iran#royal#shah#emerald#ruby#sapphire#qajar#history
401 notes
·
View notes
Text

Overdose, you and me

A sweet bluff
Two steps form hell with me darling, mm
#karly draws#trigun#trigun maximum#vashwood#vash the stampede#nicholas d. wolfwood#natori#overdose#Spotify
207 notes
·
View notes
Text
Casualty S:36 Ep:36 “I need you to stay with me”
#causality#male whumpee#concern#bromance whump#seizure#intubation#chest compressions#held#comfort#hospitalized#bromance#overdose#flatline#electric shock#defibrillator#whump
153 notes
·
View notes
Text





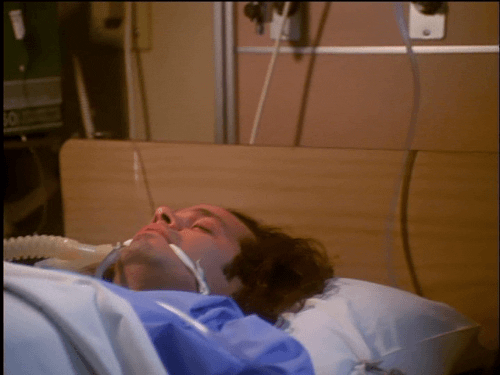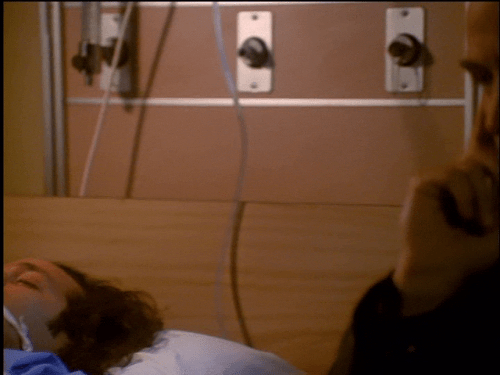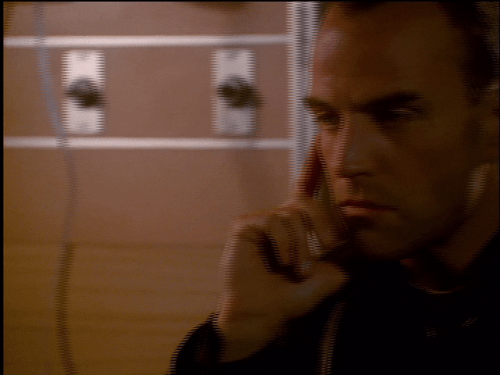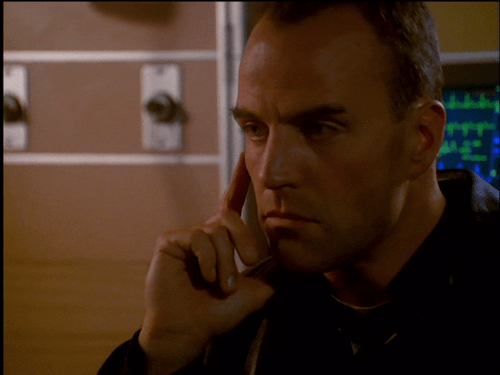
In The Sentinel 2x12, Blair is unwittingly drugged with a powerful hallucinogen that sends him into a violent, disoriented frenzy. Jim manages to calm him down before the overdose kills him.
#the sentinel 1996#whump#bromance whump#bromance#caregiver#worry#aftercare#overdose#drugged#disoriented#collapse#hugging#hospital care#bedside vigil#hurt/comfort#richard burgi#garett maggart
194 notes
·
View notes
Text

71 notes
·
View notes
Text












Casualty - 38x30 - The Last Post
#Don’t come in. Call 999#casualty#rash masum#rashid masum#neet mohan#whump#tw: suicide#tw: suicide attempt#supine#cpr#unconscious#vomiting#tw: vomit#tw: emesis#resus#seizure#resuscitation#intubated#tariq hussein#manpreet bachu#iain dean#michael stevenson#stevie nash#elinor lawless#overdose#drug overdose#cuteguywhump gifs#bbc casualty
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
I am such a burden to everyone around me.
#i am a burden#burden#i am a failure#depressed#sad#depression#sadness#broken#crying#lonely#suicidal#suicide#self hate#self harm#cutting#overdose#i want to die#hurt#🐻#why am i still alive#why am i like this#why am i still here#i want to give up#i’m sorry#i’m not okay#actually disabled#actually autistic#nobody will miss me#nobody needs me#nobody wants me
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo


holding for jongin: day 432 of 641 ~ holding for sehun: day 208 of 639
↳ EXO KAI and SEHUN for OVERDOSE | May 2014
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
The family of an Inuk man who went missing in Ottawa but was found dead last week in Gatineau, Que. is criticizing the Ottawa Police Service for what they say were failures in searching for him.
Tommy Agnetsiak, 30, originally from Pond Inlet, was reported missing in Ottawa in February, his father Robert Agnetsiak told Nunatsiaq News.
On April 6 at around 11 a.m., police in Gatineau, Que., across the Ottawa River from the nation’s capital, received a call from someone who reported seeing a body on the Quebec side of the river, the department’s spokesperson Officer Patrick Kenney said in an email. [...]
“He was missing for a long time and nobody ever saw him ever since. Nobody took it seriously,” Robert Agnetsiak said.
Tragedy has hit the family hard in the last few years. Earlier this year, his daughter overdosed while lying on a couch in an Ottawa apartment and another daughter took her own life a couple of years ago. Tommy was Robert Agnetsiak’s last living child.
Robert said he wants what happened to Tommy to be a warning. Indigenous people are being killed, overdosing, and there needs to be a change. [...]
Continue Reading.
Tagging: @newsfromstolenland, @vague-humanoid
Note from the poster @el-shab-hussein: Please avoid scrolling down to the comments. A lot of victim blaming going on there.
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
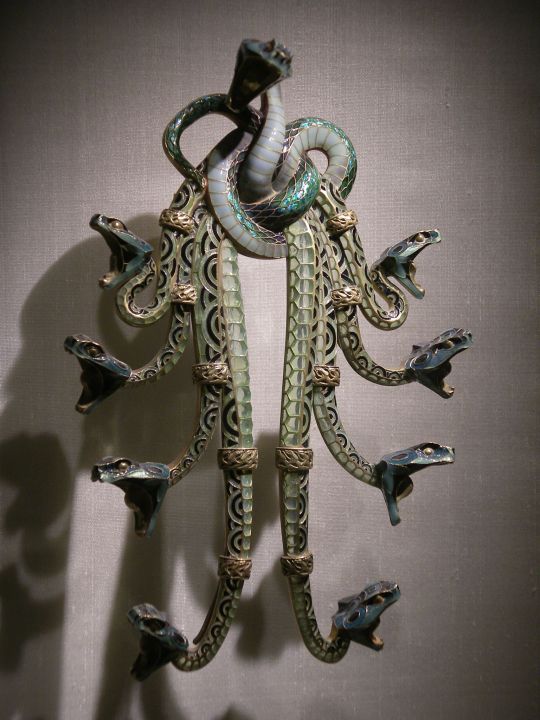

‘Serpents’ corsage ornament by René Lalique, 1889-1900,
A pectoral composed of 9 serpents entwined to form a knot from which the bodies of the other eight fall in a cascade, with the ninth rising in the centre, at the top of the jewel.
Gold and Enamel work,
H. 21 cm; W. 14.3 cm
Gulbenkian Museum
#art#overdose#gold#jewellery#design#jewelry#luxurious#fashion#luxurylifestyle#snake#serpent#ornament#rené lalique#gulbenkian museum#enamel jewelry#enamel#1900s
596 notes
·
View notes
Text








John Constantine, Hellblazer: Dead in America #5 - "One-Way Ticket" (2024)
written by Aaron Campbell
art by John Pearson
#john constantine#constantine#hellblazer#DC#DC comics#wednesday spoilers#spoilers#comic spoilers#drug use#overdose#tw: drug use#tw: overdose
74 notes
·
View notes