#Publisher Control
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
🚀 Exciting news for publishers! Google has updated the Robots Meta Tag documentation to include AI Mode adjustments. Learn how to protect your content and amplify visibility in search results. Check out our latest article for all the details! #SEO #GoogleUpdates #AIMode #DigitalMarketing
#AI Mode#AI Overviews#AI-Powered Search#Content Management#Content Visibility#digital marketing#Gemini 2.0#Google Labs#Google Robots Meta Tag#Max-Snippet Controls#Nosnippet Directive#Online Content#Publisher Control#Query Fan-Out#search engine optimization#Search Features#Search Results#SEO Strategy#Traffic Generation#User Engagement#Website Traffic
1 note
·
View note
Text

Can’t believe we got a crustables reference before the comic even started
#Comic aurora#the mind control trope talk was uploading in mid 2018. Aurora stated getting published at some point in 2019
315 notes
·
View notes
Text
The majority of censorship is self-censorship
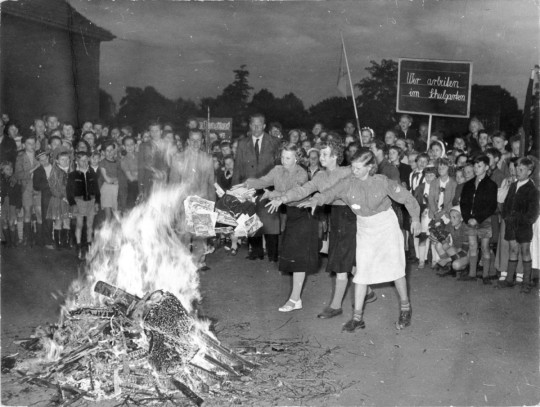

I'm on tour with my new novel The Bezzle! Catch me TONIGHT in SAN DIEGO (Feb 22, Mysterious Galaxy). After that, it's LA (Saturday night, with Adam Conover), Seattle (Monday, with Neal Stephenson), then Portland, Phoenix and more!

I know a lot of polymaths, but Ada Palmer takes the cake: brilliant science fiction writer, brilliant historian, brilliant librettist, brilliant singer, and then some:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/10/monopoly-begets-monopoly/#terra-ignota
Palmer is a friend and a colleague. In 2018, she, Adrian Johns and I collaborated on "Censorship, Information Control, & Information Revolutions from Printing Press to Internet," a series of grad seminars at the U Chicago History department (where Ada is a tenured prof, specializing in the Inquisition and Renaissance forbidden knowledge):
https://ifk.uchicago.edu/research/faculty-fellow-projects/censorship-information-control-information-revolutions-from-printing-press/
The project had its origins in a party game that Ada and I used to play at SF conventions: Ada would describe a way that the Inquisitions' censors attacked the printing press, and I'd find an extremely parallel maneuver from governments, the entertainment industry or other entities from the much more recent history of internet censorship battles.
With the seminars, we took it to the next level. Each 3h long session featured a roster of speakers from many disciplines, explaining everything from how encryption works to how white nationalists who were radicalized in Vietnam formed an armored-car robbery gang to finance modems and Apple ][+s to link up neo-Nazis across the USA.
We borrowed the structure of these sessions from science fiction conventions, home to a very specific kind of panel that doesn't always work, but when it does, it's fantastic. It was a natural choice: after all, Ada and I know each other through science fiction.
Even if you're not an sf person, you've probably heard of the Hugo Awards, the most prestigious awards in the field, voted on each year by attendees of the annual World Science Fiction Convention (Worldcon). And even if you're not an sf fan, you might have heard about a scandal involving the Hugo Awards, which were held last year in China, a first:
https://www.nbcnews.com/news/world/science-fiction-authors-excluded-hugo-awards-china-rcna139134
A little background: each year's Worldcon is run by a committee of volunteers. These volunteers put together bids to host the Worldcon, and canvass Worldcon attendees to vote in favor of their bid. For many years, a group of Chinese fans attempted to field a successful bid to host a Worldcon, and, eventually, they won.
At the time, there were many concerns: about traveling to a country with a poor human rights record and a reputation for censorship, and about the logistics of customary Worldcon attendees getting visas. During this debate, many international fans pointed to the poor human rights record in the USA (which has hosted the vast majority of Worldcons since their inception), and the absolute ghastly rigmarole the US government subjects many foreign visitors to when they seek visas to come to the US for conventions.
Whatever side of this debate you came down on, it couldn't be denied that the Chinese Worldcon rang a lot of alarm-bells. Communications were spotty, and then the con was unceremoniously rescheduled for months after the original scheduled date, without any good explanation. Rumors swirled of Chinese petty officials muscling their way into the con's administration.
But the real alarm bells started clanging after the Hugo Award ceremony. Normally, after the Hugos are given out, attendees are given paper handouts tallying the nominations and votes, and those numbers are also simultaneously published online. Technically, the Hugo committee has a grace period of some weeks before this data must be published, but at every Worldcon I've attended over the past 30+ years, I left the Hugos with a data-sheet in my hand.
Then, in early December, at the very last moment, the Hugo committee released its data – and all hell broke loose. Numerous, acclaimed works had been unilaterally "disqualified" from the ballot. Many of these were written by writers from the Chinese diaspora, but some works – like an episode of Neil Gaiman's Sandman – were seemingly unconnected to any national considerations.
Readers and writers erupted in outrage, demanding to know what had happened. The Hugo administrators – Americans and Canadians who'd volunteered in those roles for many years and were widely viewed as being members in good standing of the community – were either silent or responded with rude and insulting remarks. One thing they didn't do was explain themselves.
The absence of facts left a void that rumors and speculation rushed in to fill. Stories of Chinese official censorship swirled online, and along with them, a kind of I-told-you-so: China should never have been home to a Worldcon, the country's authoritarian national politics are fundamentally incompatible with a literary festival.
As the outrage mounted and the scandal breached from the confines of science fiction fans and writers to the wider world, more details kept emerging. A damning set of internal leaks revealed that it was those long-serving American and Canadian volunteers who decided to censor the ballot. They did so out of a vague sense that the Chinese state would visit some unspecified sanction on the con if politically unpalatable works appeared on the Hugo ballot. Incredibly, they even compiled clumsy dossiers on nominees, disqualifying one nominee out of a mistaken belief that he had once visited Tibet (it was actually Nepal).
There's no evidence that the Chinese state asked these people to do this. Likewise, it wasn't pressure from the Chinese state that caused them to throw out hundreds of ballots cast by Chinese fans, whom they believed were voting for a "slate" of works (it's not clear if this is the case, but slate voting is permitted under Hugo rules).
All this has raised many questions about the future of the Hugo Awards, and the status of the awards that were given in China. There's widespread concern that Chinese fans involved with the con may face state retaliation due to the negative press that these shenanigans stirred up.
But there's also a lot of questions about censorship, and the nature of both state and private censorship, and the relationship between the two. These are questions that Ada is extremely well-poised to answer; indeed, they're the subject of her book-in-progress, entitled Why We Censor: from the Inquisition to the Internet.
In a magisterial essay for Reactor, Palmer stakes out her central thesis: "The majority of censorship is self-censorship, but the majority of self-censorship is intentionally cultivated by an outside power":
https://reactormag.com/tools-for-thinking-about-censorship/
States – even very powerful states – that wish to censor lack the resources to accomplish totalizing censorship of the sort depicted in Nineteen Eighty-Four. They can't go from house to house, searching every nook and cranny for copies of forbidden literature. The only way to kill an idea is to stop people from expressing it in the first place. Convincing people to censor themselves is, "dollar for dollar and man-hour for man-hour, much cheaper and more impactful than anything else a censorious regime can do."
Ada invokes examples modern and ancient, including from her own area of specialty, the Inquisition and its treatment of Gailileo. The Inquistions didn't set out to silence Galileo. If that had been its objective, it could have just assassinated him. This was cheap, easy and reliable! Instead, the Inquisition persecuted Galileo, in a very high-profile manner, making him and his ideas far more famous.
But this isn't some early example of Inquisitorial Streisand Effect. The point of persecuting Galileo was to convince Descartes to self-censor, which he did. He took his manuscript back from the publisher and cut the sections the Inquisition was likely to find offensive. It wasn't just Descartes: "thousands of other major thinkers of the time wrote differently, spoke differently, chose different projects, and passed different ideas on to the next century because they self-censored after the Galileo trial."
This is direct self-censorship, where people are frightened into silencing themselves. But there's another form of censorship, which Ada calls "middlemen censorship." That's when someone other than the government censors a work because they fear what the government would do if they didn't. Think of Scholastic's cowardly decision to pull inclusive, LGBTQ books out of its book fair selections even though no one had ordered them to do so:
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/05/06/books/scholastic-book-racism-maggie-tokuda-hall.html
This is a form of censorship outsourcing, and it "multiplies the manpower of a censorship system by the number of individuals within its power." The censoring body doesn't need to hire people to search everyone's houses for offensive books – it can frighten editors, publishers, distributors, booksellers and librarians into suppressing the books in the first place.
This outsourcing blurs the line between state and private surveillance. Think about comics. After a series of high-profile Congressional hearings about the supposed danger of comics to impressionable young minds, the comics industry undertook a regime of self-censorship, through which the private Comics Code Authority would vet comings for "dangerous" content before allowing its seal of approval to appear on the comics' covers. Distributors and retailers refused to carry books without a CCA stamp, so publishers refused to publish books unless they could get a CCA stamp.
The CCA was unaccountable, capricious – and racist. By the 60s and 70s, it became clear that comic about Black characters were subjected to much tighter scrutiny than comics featuring white heroes. The CCA would reject "a drop of sweat on the forehead of a Black astronaut as 'too graphic' since it 'could be mistaken for blood.'" Every comic that got sent back by the CCA meant long, brutal reworkings by writers and illustrators to get them past the censors.
The US government never censored heroes like Black Panther, but the chain of events that created the CCA "middleman censors" made sure that Black Panther appeared in far fewer comics starring Marvel's most prominent Black character. An analysis of censorship that tries to draw a line between private and public censorship would say that the government played no role in Black Panther's banishment to obscurity – but without Congressional action, Black Panther would never have faced censorship.
This is why attempts to cleanly divide public and private censorship always break down. Many people will tell you that when Twitter or Facebook blocks content they disagree with, that's not censorship, since censorship is government action, and these are private actors. What they mean is that Twitter and Facebook censorship doesn't violate the First Amendment, but it's perfectly possible to infringe on free speech without violating the US Constitution. What's more, if the government fails to prevent monopolization of our speech forums – like social media – and also declines to offer its own public speech forums that are bound to respect the First Amendment, we can end up with government choices that produce an environment in which some ideas are suppressed wherever they might find an audience – all without violating the Constitution:
https://locusmag.com/2020/01/cory-doctorow-inaction-is-a-form-of-action/
The great censorious regimes of the past – the USSR, the Inquisition – left behind vast troves of bureaucratic records, and these records are full of complaints about the censors' lack of resources. They didn't have the manpower, the office space, the money or the power to erase the ideas they were ordered to suppress. As Ada notes, "In the period that Spain’s Inquisition was wildly out of Rome’s control, the Roman Inquisition even printed manuals to guide its Inquisitors on how to bluff their way through pretending they were on top of what Spain was doing!"
Censors have always done – and still do – their work not by wielding power, but by projecting it. Even the most powerful state actors are not powerful enough to truly censor, in the sense of confiscating every work expressing an idea and punishing everyone who creates such a work. Instead, when they rely on self-censorship, both by individuals and by intermediaries. When censors act to block one work and not another, or when they punish one transgressor while another is free to speak, it's tempting to think that they are following some arcane ruleset that defines when enforcement is strict and when it's weak. But the truth is, they censor erratically because they are too weak to censor comprehensively.
Spectacular acts of censorship and punishment are a performance, "to change the way people act and think." Censors "seek out actions that can cause the maximum number of people to notice and feel their presence, with a minimum of expense and manpower."
The censor can only succeed by convincing us to do their work for them. That's why drawing a line between state censorship and private censorship is such a misleading exercise. Censorship is, and always has been, a public-private partnership.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/22/self-censorship/#hugos
#pluralistic#ada palmer#worldcon#hugos#china#science fiction#fanac#publishing#censorship#systems of information control during information revolutions#scholarship
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Remember how you attended destiel wedding 4 years ago? That day you were sitting at the table with... (spin the wheel).
#polls#spn#supernatural#pollsnatural about destiel#destiel#destiel wedding#i know americans are still mostly asleep#but when i make something i always publish it immediately#bc i have no self control#spin the wheel#always forget this tag
194 notes
·
View notes
Note
Pearl answered the question “what games have permanently altered your brain chemistry” with Detroit: Become Human, and I saw four separate people in the host chat mention DBHC
oh snap LKDFJGD It's kinda crazy to think the au is well known enough for chatters to mention it! I'm very honored so many people have seen and enjoy my work <3
At the same time, it makes me kind of anxious for the au to be brought up/brought to the cc's attention since it's it gets very... idk the best word, maybe intense, at times? and I know that's not every CC's cup of tea, especially regarding shipping, since it's present in dbhc. I also know this won't reach everyone who has seen or heard about the au, but I guess it doesn't hurt to just put it out there that I would prefer for dbhc to be kept to this fan space <3 (I also know the CCs probably weren't looking at twitch chat, so it's not a big deal!! it's always just like, a jumpscare to see people call attention to it in cc spaces like WOAH i don't know what you're talking about. erm. who is she never heard of her /silly)
#i know there are ccs on tumblr and i wouldn't be surprised if theres one or two that have seen the au!#it's impossible to expect something publicly published would never reach their eyes#but i definitely don't want people like. *showing* it to ccs yknow#and I can't control people either so I'm aware there's only so much I can do#thank you for bringing it to my attention though :) i appreciate it <3#dbhc ask#ask#staringamassivemistakeintheface#dbhc#I also trust CCs not to go exploring into things that they know could possible make them uncomforable <3#theres a blurry line between my preferences and the reality of the situation where i know stuff happens anyway so it's all good in the end
144 notes
·
View notes
Text



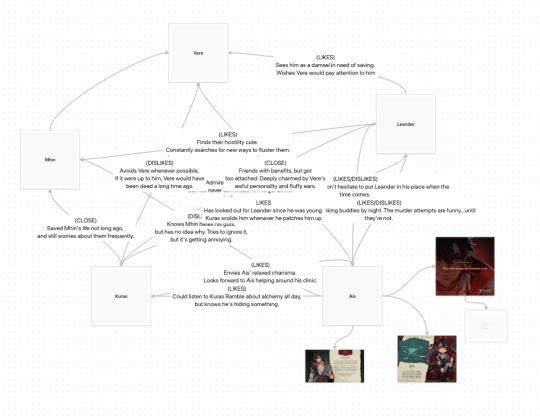
"Hey how's studying going."
Idk but I did make all of this in an hour on Obsidian.
#so each dot is an article that can be linked to other articles.#mindmap explains itself I'm really aiming for corkboard and red string energy#(will this ever be published) noooo because this is just me having fun i fear#touchstarved#touchstarved game#this and a bottle of soju i would love to see what I end up with actually. noting that down for next time I drink in a healthy and controll#environment.
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
The problem with Wikipedia is that it has rendered all other encyclopedias extinct or out of view (the exception are fandom encyclopedias, I guess, but those have their own problems). And people need in-depth information which also isn't highly specific academic papers that only tackle one specific thing in depth without wider context (my main problem when researching, for example, pre-columbian cultures.)
And competitors to Wikipedia like, you know, Encyclopedia Brittanica (I actually read it sometimes, and it's good until it hits you with straight up XIX imperialist apologia) aren't really good either. There is also a drought of encyclopedias in Spanish as all search results are absorbed by Wikipedia, this is why I hoard all sorts of PDFs and books, because the results in Spanish are just Spanish Wikipedia (probably the WORST of all major Wikipedias) and random SEO blogs.
There should be lots of online encyclopedias on different topics written by experts, ideally with some oversight because Wikipedia can be very, very biased when it wants (you can tell some people are really masturbating to Byzantine emperors), but I think this is a lost cause too since Google search, which let's face it, it's 99% of all internet searches, is declining into mush fast. And with AI generated content, things are going to get worse. I think we're honestly reaching a tipping point in the internet regarding access to reliable information.
At the end, my suggestion is that you go and download books, actual published books, and keep your sources broad. Because I think we're reaching a point where information on the internet is going to decline. It won't be lost, it will just be impossible to find unless you do a deep dive, or worse, mumbled into SEO/AI garbage misinformation.
#cosas mias#not that published books are automatically good but at least there are some levels of editing and control that Wikipedia doesn't have#much less all the SEO blogs
270 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mmm I can feel that i am very close to plunging into an "everything I have written is shit and should be burned in a bonfire and I should never touch a word processor again" spiral, I would really rather not, but i also don't know how to stop this train in its tracks.
Fellow writers if you have tips to share re what has worked for you in a similar place in the past they would be much appreciated.
#writing#i fear the solution is to implement a temporary writing ban for a couple of weeks#i suspect i may have been writing feverishly to avoid dealing with a break up#but for that very reason a ban is going to be hard#but mb something like no fic writing for two weeks min and no publishing anything for a month#i was fine when stuff i post was getting good engagement#but you can't rly put that onus on a factor that's totally out of ones control
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
weird as fuck to name and shame a fanfic just because you don’t like it
#that’s someone’s labor of love#they put their own time and hard work into their writing and ur gonna post abt how you hated it?#move on#you control the buttons you press#so press the search bar and try again#and dont go on tumblr or reddit or whatever and post about how you hated it#not everything was written for you#weirdo behavior#it’s fan work#unpaid fan work#you will never catch me shitting on a fan fic just bc i dont like it#published paid media? all day. fan work? never
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
At work my bosses keep bringing up a position I really really want but im not qualified for it and their bosses definitely won't greenlight me for the position so whenever they bring up me being a media specialist I just look at them like this

#LET ME BE THE SCHOOL LIBRARIAAANNNNN#my DREAM JOOOBBBBB#id be happy as a classroom teacher in the meantime and tbh probably more engaged however i want control of that library so bad#id run weekly digital literacy seminars#and bring in the county library#and community resources for financial literacy#and teach them so much about zines and self publishing and ARRHHHHH
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Rook x Observant Reader got even longer. I’m not even talking the current word count which is 39k. I’m talking I have more idea to fit in the end so the entire theme of the fanfic is more wholistic. Yes, there are core themes in this like real novels or short stories. There’s even foreshadowing. I intentionally use story structure to enhance the reader’s experience. I make sure that there’s no scenes that are not there for a reason. If I could take it out of the story and it would still make sense, I’ve banished it to the scrap pile.
I have no idea how this happened. I’m as surprised as everyone else. I’ve been in shock for the past 3 hrs.
Some of these things I didn’t even plan until I looked a little closer and analyzed it and went “oh my god! The parallels!” You’ll get it once you read it.
I’m still in shock but I have to share because wtf. I didn’t plan any of this. It just happened and it’s smart
#baffled#how did i get here#i'm still in shock#brain doesn’t compute#it took like 2 hrs to write the outline/structure for the ending ending#I’m talking we wrap book 7 up#it’s brief because the solution is simple in my opinion#we go for preventative measures here rather than damage control#folks regulate your emotions#go to therapy in a nutshell#she had a great YouTube series on emotional processing#once u read this fanfic you’ll understand how integral it’s become in my life#u could psychoanalyze this#how did this happen#this wasn’t planned#twisted wonderland#twst#twst x reader#pomefiore#fanfic update#rook hunt#twst rook#rook x reader#writing#i feel like this could be publish worthy but it’s a fanfic#can I use this on my resume?#I still don’t know how I got here#I’ve had multiple people tell me that they really like my reader#like move aside romantic interest I want the reader#such a compliment
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
My friend's reactions to reading IDW for the first time pt 2

HOLY SHIT HE CLOCKED THAT IMMEDIATELY 💀💀💀
#for context#prowl got mind controlled like a page and a half before this#it was basically immediate#im cryin#transformers#maccadam#tf idw#transformers idw#idw publishing#robots in disguise#prowl#bombshell
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
I take issue with this idea of Link just "fucking off" and leaving Zelda completely alone before totk. Not even in just a shipping sort of way either, as close friends and him choosing to remain her knight, that makes zero logical sense? It is completely out of character for him?
Link doesn't ever leave Zelda's side. This is canon. "Fucking off" is just not something he does during peace time when he isn't on a heroic quest and being controlled by the player's whims

That's five times it's stated officially somewhere that he is by her side, and that's only the ones I can immediately recall. Botw's full ending and totk's opening together also show us that. We see them together when the story ends and we see them together when it picks back up in the sequel. At no point is it implied they ever parted.
And can we just remember for a second what happens when he's not there, for even a short amount of time, if she is unable to call upon her abilities and therefore defend herself?:

"Fucking off" is a fantastic way to get her killed. The Yiga worship Ganon, there is nobody they want dead more (besides Link), than the last living member of the royal family. They are also not opposed at all to going into villages. They snuck into Kakariko to assassinate Dorian's wife. We just don't see that reflected in gameplay.
Some people will say "it's just his job" to deny they even have a friendship or growth as characters, but want him to... not do the main part of that? "It's just his job" and "he fucked off to the wilderness" are simply not compatible ideas. Either you think Link is just a completely duty-bound mindless command robot or you think he completely doesn't care anymore about that to the point of endangering the person he's supposed to protect. It can't be both at the same time.
Thankfully, it's implied by the wording of master works, the cutscenes and the jpn version that he wants to protect and support her. That this is what he desires, even when the king is dead and he is immediately given the option to not do so anymore. That he is motivated by wanting to see her happy and safe. I'm pretty sure the only way to get him to stop trying to protect her or following her is death, and he has already proven that twice over.
#zelink#tears of the kingdom#link#totk#botw#totk link#botw link#loz#tloz#I wasn't going to publish this post originally but#just had to vent#We play as Link either A) after he woke up after the apocalypse with no memory#or B) after the upheaval when shit hits the fan and Zelda has already been transported to the past#both scenarios where he is literally forced into a survival situation and can't be with her due to the plot#Why apply when we control him to the peaceful off-screen times in-between.#it just doesn't make any sense
735 notes
·
View notes
Text
If anyone is wondering the context of what my Diogenes chicken of actual play is from my previous post, I love to go "Major League Baseball is an actual play" because it pisses so many people off
#other similar chickens are: WWE; Wheel of Fortune; and Big Brother the reality TV series.#mentioning it bc idk when this article will be published and it'll be paywalled anyway (I don't control that) so you all get context
23 notes
·
View notes
Text



actual footage of Maximus surrounded by the flames of my desire for him
#i was so excited to screencap this scene :D#i have multiple sets that i’ll be publishing and i am just#on the floor panting begging for some mercy from him honestly#there has NEVER been such a man#i simp for maximus at every stage of the movie but#general maximus is special#he’s so in control and in charge and strong and capable and competent#and authoritative and powerful and strong and courageous AAHHHHHH#i want him to take charge of me ifyouknowwhatimean#he’s so stunning in these shots#framed by the fires standing among the men he’s killed#mourning for the men he has lost#just taking a moment to realize that he’s survived again and he’s got so much work ahead of him still#but this is his last battle and he’s done now#ohhhh how i wish this had been his last battle#how i wish he had gone home and spent every day in the arms of his family#how i wish he could have brought life from the earth instead of being forced to take even more lives#he is so precious to me#so dear so wonderful so adored#i love him with all my soul#i wish i could be waiting for him in his tent#let him fall asleep in my lap while i stroke his hair and sing to him#I WANT TO LOVE HIM SOMEONE PLEASE LET ME LOVE THIS PERFECT AND PRECIOUS MAN#gladiator#maximus#maximus decimus meridius#gladiator 2000#russell crowe
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
I would say warrior's problems could be solved by having people other than 70 year old white women write the books but at this point I think we're lucky that people are writing them at all.
#genuinely how long do we think till they just fucking ai generate them.#with the absolute nosedive in quality control that publishing has taken lately (ie lightlark)#i honestly think ai work would be slightly more comprehensible than some actual published books I've had the displeasure of reading#i hate to mention non wc on my battle cats blog but it had to be done#erin hunter warriors#warrior cats#warriors#anti ai#publishing
13 notes
·
View notes