#SQL Insert
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Database design and management course and Assignment help

Contact me through : [email protected]
I will provide advice and assistance in your database and system design course. I will handle everything including;
Normalization
Database design (ERD, Use case, concept diagrams etc)
Database development (SQL and Sqlite)
Database manipulation
Documentation
#database assignment#assignment help#SQL#sqlserver#Microsoft SQL server#INSERT#UPDATE#DELETE#CREATE#college student#online tutoring#online learning#assignmentwriting#Access projects#Database and access Final exams
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Logo Sql Insert Into LG_XT1001_001 Parlogref
DELETE LG_XT1001_001;INSERT INTO LG_XT1001_001 (PARLOGREF,MERKEZ,DEPO2 )SELECTITM.LOGICALREF,(SELECT SUM(ONHAND) FROM LV_001_XX_STINVTOT WHERE STOCKREF=ITM.LOGICALREF AND INVENNO=0) AS MERKEZ,(SELECT SUM(ONHAND) FROM LV_001_XX_STINVTOT WHERE STOCKREF=ITM.LOGICALREF AND INVENNO=2) AS DEPO2 FROM LG_001_ITEMS ITMWHERE CARDTYPE<>22 Logo Malzemeler ana ekranına eklenen ek depolardaki stok…
0 notes
Text
The Performance Trade-offs Between SELECT * INTO and SELECT THEN INSERT in T-SQL
In the realm of SQL Server development, understanding the intricacies of query optimization can drastically impact the performance of your applications. A common scenario that developers encounter involves deciding between using SELECT * INTO to create and populate a temporary table at the beginning of a stored procedure versus first creating a temp table and then populating it with a SELECT…
View On WordPress
#efficient data handling in SQL#query optimization techniques#SELECT INTO vs INSERT#SQL Server temp tables#T-SQL performance optimization#TempTable
0 notes
Text
if i'm being honest i don't really give a shit about the discourse of whether 09 is good or bad DID rep nor do i give a shit about how his DID manifests. i find that what makes him interesting isn't a label for a set of symptoms but rather his expression of those symptoms cultivated by the world he was raised in and how he responds or continues those behaviours. it's honestly more interesting to analyze the overarching systems in society that assisted in developing Mikoto Kayano into a murderer.
how different would he be if Japanese society were more open about emotions and struggles? how different would he be if he were receiving mental health treatment? would he still become a murderer and, if so, what made those mental health treatments ineffective? if he had been hired at another japanese company that didn't follow black company practices, would he still have become a murderer? if so, why? what were the factors that made an average, young adult become a murderer? so on so forth.
honestly the fetish this fandom has on his dissociated self that gives the illusion of multiplicity — when, in reality, he's a singular whole that is fragmented; cracks lined with dissociative barriers, chiseled by continuous stress — detracts from the complexity of his character and writing, flanderizing him into a prop of DID that the fandom puppets into theatrics of stigmatization that same fans claim to "educate" against when, in truth, spout blasé hearsays encrypted with a DIDcore-lese that does nothing for communicating information about the disorder and, instead, excludes and dissuades the general population that that supposed "education" is directed towards.
"Mikoto's a system from the interactive music project MILGRAM. His alter, 'John', murdered a bunch of people on the train."
so there's a program called "Mikoto" and you named the SQL table "John" with the ALTER command that somehow murdered a bunch of people. did the train running the Mikoto program malfunction because of some zero day error with the John table?
"'He has Dissociative Identity Disorder. John's a protector and Mikoto's the host."
so is this Mikoto guy some vessel or something for some supernatural ouija board summon and the John guy is like the familiar or bodyguard summoned? is their character just that? a job and occupation? that sounds boring. and what do those jobs have to do with a disorder on dissociation? are you talking about something like "occupation disorder" or "stuck-in-their-work-self disorder"? or is this some DnD homebrew class type?
what purpose does inaccessible language have if you're trying to educate the average person who isn't familiar with those online community terms that aren't even universal terms in literature nor research? and how are these terms even relevant to discussing Mikoto's character when the concepts it supposedly encompasses aren't universal nor applicable to all possible subjective presentations that a human brain can develop? and yet the fandom, and much of the online mental disorder community, treats those sociolect terms as an axiom — a universal truth, universal terms — and the lack of adherence to that speech is seen as wrong or sin.
"[insert link to some website claiming to have info on DID] is a good website if you wanna read up on what DID is!!"
and then that supposed resource uses highly specialized, nonuniversal, sociolect terms that is jargon to those who are only familiar with layman terms which makes the "information" — if it even is faithfully derived from research — seem like further jargon rather than a comprehensible source for educating.
applying this to Mikoto's character, those who aren't already acquainted with how he's spoken about likely view discussions or comments on him as indecipherable jargon thus it must mean Mikoto's character is just jargon thus not well-written or boring because according to the bubble of jargon people describe this guy with: Mikoto Kayano = computer program system + dnd classes or some chuunibyou alter ego personality savior complex + party hoster or vessel for some supernatural thing + mechanical switch that states 0 or 1 + going through some mitosis split
how does any of that relate to dissociation? people have made DID symptoms so convoluted, yet structured that convolutedness through terms and expressions that sound like some Gary Sue Ebony Dementia Darkness Raven trope that completely detracts from the fact that it's a dissociation disorder rather than a roleplay character form.
have people even considered the fact that if Mikoto had never been imprisoned, he, nor anyone, would even know he has DID— if he even counts as having DID? if how his brain works regarding how he handles stress doesn't impact his life negatively- even if he has all the symptoms of DID if how his brain works regarding how he handles stress doesn't cause disorder for him, he wouldn't have dissociative identity disorder.
the less people view Mikoto as the "alters guy", the more complex understandings can be gathered and discussed within the fandom. the more people view Mikoto as the "average, normal guy who committed a murder, but why? what caused an average, hardworking guy to commit the most grievous sin of murder?", the better the range of insight and curiosity into what shapes a person and the factors in their world — a reflection of our present reality — at play which interact and weave with one another to shape and respond to its members; the opposite of cutting off the fluidity and interwovenness Mikoto has with people and environments outside of his self that people constrain him to, that prison cell of a single label characteristic: "DID".
conclusion: for the love of torch novelgram, let's talk about Mikoto Kayano like the multifaceted, complex, shaped-by-the-socioeconomic-stratae-of-the-world-he-is-part-of-and-interacts-with well-written character he is.
#mikoto kayano#milgram#milgram 09#milgram mikoto#idk just a tired yap bc srsly does anyone actually have something to say about 09 that isn't just some theatrical fixation on his disorder#./009/concat
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
Structured Query Language (SQL): A Comprehensive Guide
Structured Query Language, popularly called SQL (reported "ess-que-ell" or sometimes "sequel"), is the same old language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. Developed in the early 1970s by using IBM researchers Donald D. Chamberlin and Raymond F. Boyce, SQL has when you consider that end up the dominant language for database structures round the world.
Structured query language commands with examples
Today, certainly every important relational database control system (RDBMS)—such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and SQLite—uses SQL as its core question language.
What is SQL?
SQL is a website-specific language used to:
Retrieve facts from a database.
Insert, replace, and delete statistics.
Create and modify database structures (tables, indexes, perspectives).
Manage get entry to permissions and security.
Perform data analytics and reporting.
In easy phrases, SQL permits customers to speak with databases to shop and retrieve structured information.
Key Characteristics of SQL
Declarative Language: SQL focuses on what to do, now not the way to do it. For instance, whilst you write SELECT * FROM users, you don’t need to inform SQL the way to fetch the facts—it figures that out.
Standardized: SQL has been standardized through agencies like ANSI and ISO, with maximum database structures enforcing the core language and including their very own extensions.
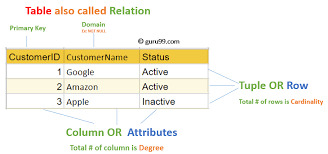
Relational Model-Based: SQL is designed to work with tables (also called members of the family) in which records is organized in rows and columns.
Core Components of SQL
SQL may be damaged down into numerous predominant categories of instructions, each with unique functions.
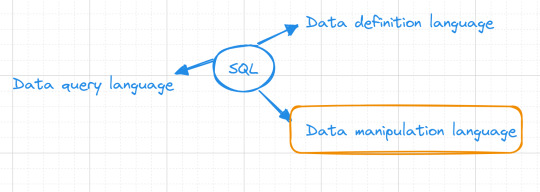
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands are used to outline or modify the shape of database gadgets like tables, schemas, indexes, and so forth.
Common DDL commands:
CREATE: To create a brand new table or database.
ALTER: To modify an present table (add or put off columns).
DROP: To delete a table or database.
TRUNCATE: To delete all rows from a table but preserve its shape.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE TABLE personnel (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
call VARCHAR(one hundred),
income DECIMAL(10,2)
);
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands are used for statistics operations which include inserting, updating, or deleting information.
Common DML commands:
SELECT: Retrieve data from one or more tables.
INSERT: Add new records.
UPDATE: Modify existing statistics.
DELETE: Remove information.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
INSERT INTO employees (id, name, earnings)
VALUES (1, 'Alice Johnson', 75000.00);
three. Data Query Language (DQL)
Some specialists separate SELECT from DML and treat it as its very own category: DQL.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT name, income FROM personnel WHERE profits > 60000;
This command retrieves names and salaries of employees earning more than 60,000.
4. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL instructions cope with permissions and access manage.
Common DCL instructions:
GRANT: Give get right of entry to to users.
REVOKE: Remove access.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON personnel TO john_doe;
five. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL commands manage transactions to ensure data integrity.
Common TCL instructions:
BEGIN: Start a transaction.
COMMIT: Save changes.
ROLLBACK: Undo changes.
SAVEPOINT: Set a savepoint inside a transaction.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
BEGIN;
UPDATE personnel SET earnings = income * 1.10;
COMMIT;
SQL Clauses and Syntax Elements
WHERE: Filters rows.
ORDER BY: Sorts effects.
GROUP BY: Groups rows sharing a assets.
HAVING: Filters companies.
JOIN: Combines rows from or greater tables.
Example with JOIN:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT personnel.Name, departments.Name
FROM personnel
JOIN departments ON personnel.Dept_id = departments.Identity;
Types of Joins in SQL
INNER JOIN: Returns statistics with matching values in each tables.
LEFT JOIN: Returns all statistics from the left table, and matched statistics from the right.
RIGHT JOIN: Opposite of LEFT JOIN.
FULL JOIN: Returns all records while there is a in shape in either desk.
SELF JOIN: Joins a table to itself.
Subqueries and Nested Queries
A subquery is a query inside any other query.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
SELECT name FROM employees
WHERE earnings > (SELECT AVG(earnings) FROM personnel);
This reveals employees who earn above common earnings.
Functions in SQL
SQL includes built-in features for acting calculations and formatting:
Aggregate Functions: SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MAX(), MIN()
String Functions: UPPER(), LOWER(), CONCAT()
Date Functions: NOW(), CURDATE(), DATEADD()
Conversion Functions: CAST(), CONVERT()
Indexes in SQL
An index is used to hurry up searches.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON employees(call);
Indexes help improve the performance of queries concerning massive information.
Views in SQL
A view is a digital desk created through a question.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
CREATE VIEW high_earners AS
SELECT call, salary FROM employees WHERE earnings > 80000;
Views are beneficial for:
Security (disguise positive columns)
Simplifying complex queries
Reusability
Normalization in SQL
Normalization is the system of organizing facts to reduce redundancy. It entails breaking a database into multiple related tables and defining overseas keys to link them.
1NF: No repeating groups.
2NF: No partial dependency.
3NF: No transitive dependency.
SQL in Real-World Applications
Web Development: Most web apps use SQL to manipulate customers, periods, orders, and content.
Data Analysis: SQL is extensively used in information analytics systems like Power BI, Tableau, and even Excel (thru Power Query).
Finance and Banking: SQL handles transaction logs, audit trails, and reporting systems.
Healthcare: Managing patient statistics, remedy records, and billing.
Retail: Inventory systems, sales analysis, and consumer statistics.
Government and Research: For storing and querying massive datasets.
Popular SQL Database Systems
MySQL: Open-supply and extensively used in internet apps.
PostgreSQL: Advanced capabilities and standards compliance.
Oracle DB: Commercial, especially scalable, agency-degree.
SQL Server: Microsoft’s relational database.
SQLite: Lightweight, file-based database used in cellular and desktop apps.
Limitations of SQL
SQL can be verbose and complicated for positive operations.
Not perfect for unstructured information (NoSQL databases like MongoDB are better acceptable).
Vendor-unique extensions can reduce portability.
Java Programming Language Tutorial
Dot Net Programming Language
C ++ Online Compliers
C Language Compliers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok more complaining abt work
More technically capable but genuinely sweet but also power hungry coworker keeps seeing other people (me) getting assigned to projects or working on things and then secretly tackles them herself IF she's interested and then makes no indication that she's working on it to the people assigned. So then we end up with these parallel solutions/reports and its like ????? I know you're "just trying to help" but the constant undercurrent is that we (I) am simply not to be trusted to be able to resolve anything and she needs to be the one to swoop in and save the day with her thing. It would be one thing if she was asked or if she was like hey can i join in? But no, us lesser mortals have to just be in a weird one-sided competition for things that just duplicate efforts!!!!!!!
Add to that the fact that she like WILLFULLY makes data architecture decisions that play specifically to HER strengths/certifications (she got our developers to provide the data UNSTRUCTURED so now we ALL need to get oracle drivers installed and need to learn SQL when she happily ALREADY has them installed and is used to SQL (none of us are data scientists or developers btw) so now she's the ONLY one w access to the data from the application) its like. Ok you clearly believe you are the ONLY one driving this unit or doing anything and unless anyone else is a coder we are basically useless. She keeps saying "i'll have to teach you SQL" like i haven't already gotten MEYE cert in it???? And then making off-hand remarks like "i need to build this so its easy for you to use it" like ms ma'am you are part of THIS team IM not your customer im your team member!!!!!!!!! OH AND WE HAVE ACTIAL DEVELOPERS FOR THE JOB YOU KEEP INSERTING YOURSELF INTO!!!!!!!!!!!!!
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQL Fundamentals #2: SQL Data Manipulation
In our previous database exploration journey, SQL Fundamentals #1: SQL Data Definition, we set the stage by introducing the "books" table nestled within our bookstore database. Currently, our table is empty, Looking like :
books
| title | author | genre | publishedYear | price |
Data manipulation

Now, let's embark on database interaction—data manipulation. This is where the magic happens, where our "books" table comes to life, and we finish our mission of data storage.
Inserting Data
Our initial task revolves around adding a collection of books into our "books" table. we want to add the book "The Great Gatsby" to our collection, authored F. Scott Fitzgerald. Here's how we express this in SQL:
INSERT INTO books(title, author, genre, publishedYear, price) VALUES('The Great Gatsby', 'F. Scott Fitzgerald', 'Classic', 1925, 10.99);
Alternatively, you can use a shorter form for inserting values, but be cautious as it relies on the order of columns in your table:
INSERT INTO books VALUES('The Great Gatsby', 'F. Scott Fitzgerald', 'Classic', 1925, 10.99);
Updating data
As time goes on, you might find the need to modify existing data in our "books" table. To accomplish this, we use the UPDATE command.For example :
UPDATE books SET price = 12.99 WHERE title = 'The Great Gatsby';
This SQL statement will locate the row with the title "The Great Gatsby" and modify its price to $12.99.
We'll discuss the where clause in (SQL fundamentals #3)
Deleting data
Sometimes, data becomes obsolete or irrelevant, and it's essential to remove it from our table. The DELETE FROM command allows us to delete entire rows from our table.For example :
DELETE FROM books WHERE title = 'Moby-Dick';
This SQL statement will find the row with the title "Moby-Dick" and remove it entirely from your "books" table.
To maintain a reader-friendly and approachable tone, I'll save the discussion on the third part of SQL, which focuses on data querying, for the upcoming post. Stay tuned ...
#studyblr#code#codeblr#javascript#java development company#study#progblr#programming#studying#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#webdev#website#tech#sql#sql course#mysql#datascience#data#backend
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQL GitHub Repositories
I’ve recently been looking up more SQL resources and found some repositories on GitHub that are helpful with learning SQL, so I thought I’d share some here!
Guides:
s-shemee SQL 101: A beginner’s guide to SQL database programming! It offers tutorials, exercises, and resources to help practice SQL
nightFuryman SQL in 30 Days: The fundamentals of SQL with information on how to set up a SQL database from scratch as well as basic SQL commands
Projects:
iweld SQL Dictionary Challenge: A SQL project inspired by a comment on this reddit thread https://www.reddit.com/r/SQL/comments/g4ct1l/what_are_some_good_resources_to_practice_sql/. This project consists of creating a single file with a column of randomly selected words from the dictionary. For this column, you can answer the various questions listed in the repository through SQL queries, or develop your own questions to answer as well.
DevMountain SQL 1 Afternoon: A SQL project where you practice inserting querying data using SQL. This project consists of creating various tables and querying data through this online tool created by DevMountain, found at this link https://postgres.devmountain.com/.
DevMountain SQL 2 Afternoon: The second part of DevMountain’s SQL project. This project involves intermediate queries such as “practice joins, nested queries, updating rows, group by, distinct, and foreign key”.
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Remediation of SQLi
Defense Option 1: Prepared Statements (with Parameterized Queries)
Prepared statements ensure that an attacker is not able to change the intent of a query, even if SQL commands are inserted by an attacker. In the safe example below, if an attacker were to enter the userID of tom' or '1'='1, the parameterized query would not be vulnerable and would instead look for a username which literally matched the entire string tom' or '1'='1.
Defense Option 2: Stored Procedures
The difference between prepared statements and stored procedures is that the SQL code for a stored procedure is defined and stored in the database itself, and then called from the application.
Both of these techniques have the same effectiveness in preventing SQL injection so it is reasonable to choose which approach makes the most sense for you. Stored procedures are not always safe from SQL injection. However, certain standard stored procedure programming constructs have the same effect as the use of parameterized queries when implemented safely (the stored procedure does not include any unsafe dynamic SQL generation) which is the norm for most stored procedure languages.
Defense Option 3: Allow-List Input Validation
Various parts of SQL queries aren't legal locations for the use of bind variables, such as the names of tables or columns, and the sort order indicator (ASC or DESC). In such situations, input validation or query redesign is the most appropriate defense. For the names of tables or columns, ideally those values come from the code, and not from user parameters.
But if user parameter values are used to make different for table names and column names, then the parameter values should be mapped to the legal/expected table or column names to make sure unvalidated user input doesn't end up in the query. Please note, this is a symptom of poor design and a full rewrite should be considered if time allows.
Defense Option 4: Escaping All User-Supplied Input
This technique should only be used as a last resort, when none of the above are feasible. Input validation is probably a better choice as this methodology is frail compared to other defenses and we cannot guarantee it will prevent all SQL Injection in all situations.
This technique is to escape user input before putting it in a query and usually only recommended to retrofit legacy code when implementing input validation isn't cost effective.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Breaking Homework Barriers: Journey to Database Brilliance

In the fast-paced world of academia, students often find themselves grappling with the intricacies of database management and SQL homework. The challenges posed by these assignments can be daunting, leaving many seeking a guiding light to navigate the complexities of database design, queries, and optimization. If you're one of those students desperately searching for "help with mySQL homework," you've come to the right place. This blog will serve as your roadmap, guiding you through the journey to unlock the secrets of database brilliance.
Unraveling the Mysteries of mySQL Homework
Help with mySQL homework is more than just a search query; it's a plea for assistance in unraveling the mysteries of structured query language and database management systems. As you embark on your academic quest, you'll encounter challenges that test your understanding of data modeling, SQL syntax, and the nuances of optimizing database performance. Fear not, for every hurdle you face is an opportunity to grow and master the art of database design.
Navigating the Database Landscape
To embark on this journey, it's crucial to understand the landscape you're navigating. Databases are the backbone of modern applications, storing and managing vast amounts of information. SQL, or Structured Query Language, serves as the key to interacting with these databases, allowing you to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data seamlessly. However, the road to becoming proficient in SQL can be winding, filled with challenges that demand attention to detail and a deep understanding of database concepts.
The Role of Expert Guidance
In your quest for database brilliance, seeking expert guidance is akin to having a seasoned navigator on your journey. Platforms like DatabaseHomeworkHelp.com are designed to provide comprehensive help with mySQL homework. These services offer a lifeline for students drowning in assignments, providing expert assistance that goes beyond mere completion to ensure understanding and mastery of database principles.
Tailored Solutions for Individual Needs
One size does not fit all, especially when it comes to mastering database concepts. Help with mySQL homework should be tailored to your individual needs and learning style. A reliable service will not only assist with assignment completion but also provide detailed explanations, clarifying doubts and reinforcing your understanding of SQL. This personalized approach is the key to breaking down barriers and fostering true brilliance in database management.
Overcoming Common Challenges
As you delve into the world of databases, you'll likely encounter common challenges that can be stumbling blocks in your academic journey. Whether it's understanding normalization, crafting complex queries, or optimizing database performance, expert assistance can make all the difference. These challenges, when conquered with the right guidance, become stepping stones to a deeper understanding of database management.
Building a Foundation for Future Success
The journey to database brilliance is not just about completing assignments; it's about building a solid foundation for future success. The skills you acquire in navigating SQL and database design will prove invaluable in real-world scenarios. As industries increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, your proficiency in database management will set you apart in the job market.
Embracing the Learning Process
Every stumble, every challenge, and every "help with mySQL homework" query is an integral part of your learning process. Embrace the journey, knowing that each assignment is an opportunity to enhance your skills. Don't shy away from seeking assistance when needed, as it's a sign of strength to recognize your limitations and actively work towards overcoming them.
Conclusion: Your Path to Database Brilliance
In conclusion, the journey to database brilliance is not a solitary one; it's a collaborative effort that involves seeking guidance, overcoming challenges, and embracing the learning process. When faced with the complexities of SQL homework, remember that help with mySQL homework is readily available. Take advantage of the resources at your disposal, and soon you'll find yourself not just completing assignments but mastering the art of database management. Your path to brilliance starts now.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQL Temporary Table | Temp Table | Global vs Local Temp Table
Q01. What is a Temp Table or Temporary Table in SQL? Q02. Is a duplicate Temp Table name allowed? Q03. Can a Temp Table be used for SELECT INTO or INSERT EXEC statement? Q04. What are the different ways to create a Temp Table in SQL? Q05. What is the difference between Local and Global Temporary Table in SQL? Q06. What is the storage location for the Temp Tables? Q07. What is the difference between a Temp Table and a Derived Table in SQL? Q08. What is the difference between a Temp Table and a Common Table Expression in SQL? Q09. How many Temp Tables can be created with the same name? Q10. How many users or who can access the Temp Tables? Q11. Can you create an Index and Constraints on the Temp Table? Q12. Can you apply Foreign Key constraints to a temporary table? Q13. Can you use the Temp Table before declaring it? Q14. Can you use the Temp Table in the User-Defined Function (UDF)? Q15. If you perform an Insert, Update, or delete operation on the Temp Table, does it also affect the underlying base table? Q16. Can you TRUNCATE the temp table? Q17. Can you insert the IDENTITY Column value in the temp table? Can you reset the IDENTITY Column of the temp table? Q18. Is it mandatory to drop the Temp Tables after use? How can you drop the temp table in a stored procedure that returns data from the temp table itself? Q19. Can you create a new temp table with the same name after dropping the temp table within a stored procedure? Q20. Is there any transaction log created for the operations performed on the Temp Table? Q21. Can you use explicit transactions on the Temp Table? Does the Temp Table hold a lock? Does a temp table create Magic Tables? Q22. Can a trigger access the temp tables? Q23. Can you access a temp table created by a stored procedure in the same connection after executing the stored procedure? Q24. Can a nested stored procedure access the temp table created by the parent stored procedure? Q25. Can you ALTER the temp table? Can you partition a temp table? Q26. Which collation will be used in the case of Temp Table, the database on which it is executing, or temp DB? What is a collation conflict error and how you can resolve it? Q27. What is a Contained Database? How does it affect the Temp Table in SQL? Q28. Can you create a column with user-defined data types (UDDT) in the temp table? Q29. How many concurrent users can access a stored procedure that uses a temp table? Q30. Can you pass a temp table to the stored procedure as a parameter?
#sqlinterview#sqltemptable#sqltemporarytable#sqltemtableinterview#techpointinterview#techpointfundamentals#techpointfunda#techpoint#techpointblog
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discord Bot: Devlog #0
I've never done done anything like this before but I just wanted to share some of the things I've been learning about. This is also like my second tumblr post so please bear with me.
I've recently been working on this discord bot that lets users earn points and such. It's very basic, but I'm using it to learn a little SQL and JavaScript (even though I hate it).
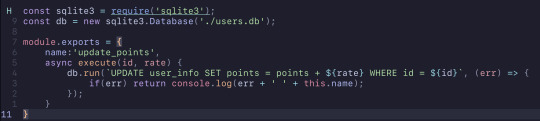
I had written this little piece of code that updates the amount of points a user has by the provided rate. However, a problem will of course occur if the user doesn't exist in the table.
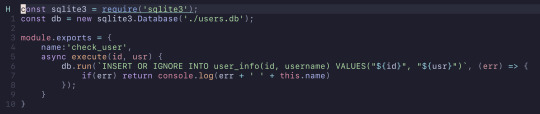
So I created this verifier to check if the user exists in the table, and if they don't it would insert them into the table.

Put together, this is what it looks like. Both functions were wrapped in sqlite3's serialize function to ensure that they would execute the queries to the db sequentially. However, this did not work as intended. Sqlite3's serialize function doesn't really "extend" into each of the function and it would simply just run asynchronously like normal. This meant that if the user didn't exist, it would sometimes (most of the time) try to update the non-existent user's points and then it would check and insert the user into the table.
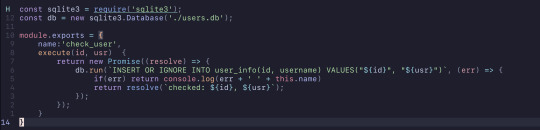
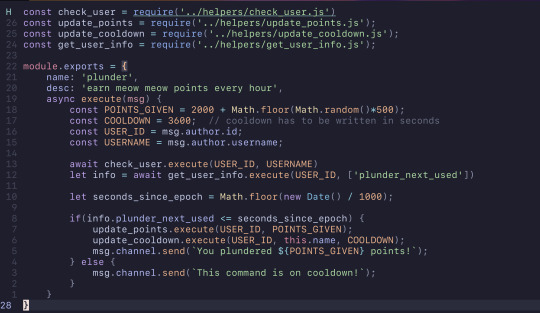
Ignoring all of the extra features added, this was fixed using async/await with promises. The check_user function now returns a promise and in combination of using await in the now async function, plunder, it works perfectly. The function has to wait for the promise that check_user returns to resolve before moving forward with the code. The update_points function didn't need to be asynchronous as nothing else in the function really relied on it.
I just wanted to share me learning about async/await and promises in JavaScript. Thanks for reading!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Efficient Data Import in SQL Server 2022: BCP vs. BULK INSERT vs. OPENROWSET
Ever found yourself swimming in an ocean of data, wondering the best way to import it into your SQL Server? You’re not alone. SQL Server 2022 comes to the rescue with a trio of tools designed to streamline this process: BCP, BULK INSERT, and OPENROWSET. Each has its unique flair for handling data, and I’m here to guide you through choosing the right tool for the job with some handy T-SQL…
View On WordPress
#BCP command examples#BULK INSERT SQL tutorial#Efficient database management SQL#OPENROWSET usage guide#SQL Server 2022 data import
0 notes
Text
Image description: screencap of Mastodon post from user [email protected] with the following text: A valiant effort has been made by Little Tim this year, who for some reason has decided to change his name to Tim'); INSERT INTO [NiceList] SELECT * FROM [NaughtyList];--
HO HO HO! Nice try Tim. I don't use #SQL, I use several dozen interconnected #Excel spreadsheets, like a professional.
End image description.
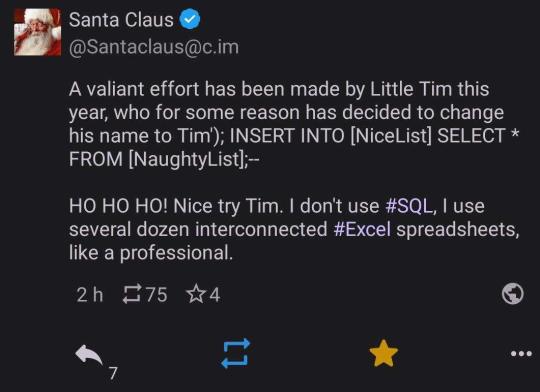
#'like a professional' BRUH#*haunted by flashbacks to the tangled web of Excel spreadsheets that were used to keep track of production for consumables*
20K notes
·
View notes
Text
🚀 Professional Database Designer | Expert in ERD & Data Modeling 🚀
Struggling to visualize your database structure? I create clear, efficient Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) that simplify complex data and improve your system’s performance.
🔹 Tailored ERD designs for your unique business needs 🔹 Support for Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL & more 🔹 Scalable and optimized database models 🔹 Detailed documentation & expert consultation included
Let’s turn your data into a powerful asset!
👉 Hire me on PeoplePerHour now: https://www.peopleperhour.com/hourlie/professional-database-designer-erd/524486
DatabaseDesign #ERDDesign #DataModeling #DataArchitecture #DatabaseExpert #SQLDatabase #DataManagement #TechSolutions #PeoplePerHour #FreelancerLife #ITConsulting #BusinessIntelligence #DataDriven #SoftwareDevelopment #CustomDatabase #DataEngineering #DatabaseConsultant #TechFreelancer #DatabaseOptimization #DataVisualization #SystemDesign #CloudDatabase #TechSupport
0 notes
Text
How Secure Are Internet of Things (IoT) Devices in 2025?

From smart homes anticipating your every need to industrial sensors optimizing manufacturing lines, Internet of Things (IoT) devices have seamlessly integrated into our lives, promising unparalleled convenience and efficiency. In 2025, are these interconnected gadgets truly secure, or are they opening up a Pandora's Box of vulnerabilities?
The truth is, IoT security is a complex and often concerning landscape. While significant progress is being made by some manufacturers and regulatory bodies, many IoT devices still pose substantial risks, largely due to a race to market that often prioritizes features and cost over robust security.
The Allure vs. The Alarms: Why IoT Devices Are Often Vulnerable
The promise of IoT is immense: automation, data-driven insights, remote control. The peril, however, lies in how easily these devices can become entry points for cyberattacks, leading to privacy breaches, network compromise, and even physical harm.
Here's why many IoT devices remain a security headache:
Weak Default Credentials & Lack of Updates:
The Problem: Many devices are still shipped with easily guessable default usernames and passwords (e.g., "admin/admin," "user/123456"). Even worse, many users never change them. This is the single easiest way for attackers to gain access.
The Challenge: Unlike smartphones or laptops, many IoT devices lack clear, robust, or frequent firmware update mechanisms. Cheaper devices often receive no security patches at all after purchase, leaving critical vulnerabilities unaddressed for their entire lifespan.
Insecure Network Services & Open Ports:
The Problem: Devices sometimes come with unnecessary network services enabled or ports left open to the internet, creating direct pathways for attackers. Poorly configured remote access features are a common culprit.
The Impact: Remember the Mirai botnet? It famously exploited vulnerable IoT devices with open ports and default credentials to launch massive Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Lack of Encryption (Data In Transit & At Rest):
The Problem: Data transmitted between the device, its mobile app, and the cloud often lacks proper encryption, making it vulnerable to eavesdropping (Man-in-the-Middle attacks). Sensitive data stored directly on the device itself may also be unencrypted.
The Risk: Imagine your smart speaker conversations, security camera footage, or even health data from a wearable being intercepted or accessed.
Insecure Hardware & Physical Tampering:
The Problem: Many IoT devices are designed with minimal physical security. Easily accessible debug ports (like JTAG or UART) or lack of tamper-resistant enclosures can allow attackers to extract sensitive data (like firmware or encryption keys) directly from the device.
The Threat: With physical access, an attacker can potentially rewrite firmware, bypass security controls, or extract confidential information.
Vulnerabilities in Accompanying Apps & Cloud APIs:
The Problem: The web interfaces, mobile applications, and cloud APIs used to control IoT devices are often susceptible to common web vulnerabilities like SQL Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), or insecure authentication.
The Loophole: Even if the device itself is somewhat secure, a flaw in the control app or cloud backend can compromise the entire ecosystem.
Insufficient Privacy Protections:
The Problem: Many IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal and sensitive data (e.g., location, habits, biometrics) without always providing clear consent mechanisms or robust data handling policies. This data might then be shared with third parties.
The Concern: Beyond direct attacks, the sheer volume of personal data collected raises significant privacy concerns, especially if it falls into the wrong hands.
Supply Chain Risks:
The Problem: Vulnerabilities can be introduced at any stage of the complex IoT supply chain, from compromised components to insecure firmware inserted during manufacturing.
The Fallout: A single compromised component can affect thousands or millions of devices, as seen with some supply chain attacks in the broader tech industry.
The Elephant in the Room: Why Securing IoT is Hard
Diversity & Scale: The sheer number and variety of IoT devices (from tiny sensors to complex industrial machines) make a "one-size-fits-all" security solution impossible.
Resource Constraints: Many devices are low-power, low-cost, or battery-operated, limiting the computational resources available for robust encryption or security features.
Long Lifespans: Unlike phones, many IoT devices are expected to operate for years, even decades, long after manufacturers might cease providing support or updates.
Patching Complexity: Pushing updates to millions of geographically dispersed devices, sometimes with limited connectivity, is a logistical nightmare.
Consumer Awareness: Many consumers prioritize convenience and price over security, often unaware of the risks they introduce into their homes and networks.
Towards a More Secure IoT in 2025: Your Shield & Their Responsibility
While the challenges are significant, there's a collective effort towards a more secure IoT future. Here's what needs to happen and what you can do:
For Manufacturers (Their Responsibility):
Security by Design: Integrate security into the entire product development lifecycle from day one, rather than as an afterthought.
Secure Defaults: Ship devices with unique, strong, and randomly generated default passwords.
Robust Update Mechanisms: Implement easy-to-use, automatic, and regular firmware updates throughout the device's lifecycle.
Clear End-of-Life Policies: Communicate transparently when support and security updates for a device will cease.
Secure APIs: Design secure application programming interfaces (APIs) for cloud communication and mobile app control.
Adhere to Standards: Actively participate in and adopt industry security standards (e.g., ETSI EN 303 645, IoT Security Foundation guidelines, PSA Certified). Regulatory pushes in Europe (like the Cyber Resilience Act) and elsewhere are driving this.
For Consumers & Businesses (Your Shield):
Change Default Passwords IMMEDIATELY: This is your absolute first line of defense. Make them strong and unique.
Network Segmentation: Isolate your IoT devices on a separate Wi-Fi network (a "guest" network or a VLAN if your router supports it). This prevents a compromised IoT device from accessing your main computers and sensitive data.
Keep Firmware Updated: Regularly check for and apply firmware updates for all your smart devices. If a device doesn't offer updates, reconsider its use.
Disable Unused Features: Turn off any unnecessary ports, services, or features on your IoT devices to reduce their attack surface.
Research Before You Buy: Choose reputable brands with a track record of security and clear privacy policies. Read reviews and look for security certifications.
Strong Wi-Fi Security: Ensure your home Wi-Fi uses WPA2 or, ideally, WPA3 encryption with a strong, unique password.
Be Mindful of Data Collected: Understand what data your devices are collecting and how it's being used. If the privacy policy isn't clear or feels invasive, reconsider the device.
Physical Security: Secure physical access to your devices where possible, preventing easy tampering.
Regular Monitoring (for Businesses): Implement tools and processes to monitor network traffic from IoT devices for unusual or suspicious activity.
In 2025, the convenience offered by IoT devices is undeniable. However, their security is not a given. It's a shared responsibility that demands both diligence from manufacturers to build secure products and vigilance from users to deploy and manage them safely.
0 notes