#chmod number calculator
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

Another optional column is superuser. This column denotes the special setuid, setgid and sticky flags. Chmod Calculator possesses two modes of usage, one is symbolic and the other absolute. Symbolic allows you to remove, add, or set a particular mode while having other modes unchanged. This is achieved by using operators and letters. But, in absolute mode, you can overrule the existing permission with a new value. This new value is a three digit number. Chmod Calculator 4 digits allowed four-digit codes, as well.
try right now: http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#Chmod Command Calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#convert for free#chmod calculator free#Online free Calculator#calculator#calculate#Online Calculator#chmod number calculator
0 notes
Link
Introduction
Hello, freeCodeCamp readers. I hope I can bring you some great coding content for inspiration, education and of course, fun! In this tutorial, we will learn about keyword density and how to build a tool that can calculate keyword density with Laravel. The web tool will allow us to paste in a full page of HTML. Then, magic will be executed to give us a precise keyword density score. In a quick summary, here are some basic skills we will touch upon whilst building the tool.
Laravel routes, controllers, and views
Laravel layouts
HTML & forms
JQuery & Ajax
Some native PHP
A bit of SEO!
What is keyword density?
If you have your own website or blog, you possibly already know what keyword density is. For those who don't know what it means I will give a short and sweet explanation below. Keyword density is a calculation of word or keyword occurrences usually in a large piece of text. The density is reported in a percentage which is simply calculated with the following formula. KeywordDensity = (Keyword Count / Word Count) * 100
Why is this important?
Keyword density is a key factor in the Google search engine algorithm. It is widely thought that a good keyword density for optimising web pages for Google rankings is around 3.5%. If the percentage is higher, for example 20%, then this could be seen as 'keyword stuffing' and therefore could badly affect your Google search rankings. So, that is a minuscule lesson on SEO and to give you a bit of context of what we are trying to build.
Building a Keyword Density Tool with Laravel
This tutorial will presume we are all starting with a fresh Laravel build enabling anyone to follow on from any particular point. (Apologies if the beginning sections are telling you to suck eggs!) Also, just for further context, I'm building this on MacOS with XAMPP locally.
Prerequisites
A PHP environment installed and access to the root directory
Composer installed
Your favourite code editor that interprets PHP, HTML, CSS & JS.
With all of these prerequisites checked off, we can now get our hands dirty.
Creating Our Laravel App
First of all we need to download and install a fresh Laravel build. Follow the steps below to achieve this.
Open your command line interface at the root directory of your web server, for example XAMPP/xamppfiles/htdocs/
Run the following command and let composer do it's magic
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel KeywordDensityApp
Top Tip: If you are working on MacOS, then check out the following steps to enable permissions on the Laravel storage folder.
Navigate to your CLI to the project folder ('KeywordDensityApp')
Run the following command
sudo chmod -R 777 storage/*
Adding a controller and view
Now that we have the basics out of the way, we can start to build our controller and web page that will allow a user to paste in and analyse some HTML. We can create a new controller in two ways: via the PHP artisan command line helper or simply by creating with your code editor. Feel free to use any of the below methods, just make sure the controller matches
Create controller with PHP artisan
php artisan make:controller ToolController
Create controller with code editor
Locate the following - ProjectFolder/App/Http/Controllers
Create a new .php file named ToolController
Make sure this newly created file has the following contents:
<?php namespace App\Http\Controllers; use Illuminate\Http\Request; class ToolController extends Controller { // }
Now let's create the view.
Create view with code editor
Locate view folder under ProjectFolder/resources/views
Create a new folder named tool
Create a new view PHP file named index.blade.php
Now let's create a layout file
With most Laravel applications, you will want to build a layouts file so that you don't have to repeat lots of HTML over and over to get the same design across the board. This layout is pretty basic, using a simple Bootstrap template and has a @yield call to the 'content' area which we will utilise in our views. In addition, there's a @yield call to 'scripts' which we will utilise later.
Locate view folder under ProjectFolder/resources/views
Create a new folder here named layouts
Create a new file named master.blade.php
Add the following code to the file
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=""> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Keyword Density Tool</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.4.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-Vkoo8x4CGsO3+Hhxv8T/Q5PaXtkKtu6ug5TOeNV6gBiFeWPGFN9MuhOf23Q9Ifjh" crossorigin="anonymous"> <!-- Fonts --> <link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Nunito:200,600" rel="stylesheet"> <meta name="csrf-token" content=""> <style> body {padding-top: 5em;} </style> </head> <body> <nav class="navbar navbar-expand-md navbar-dark bg-dark fixed-top"> <a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Keyword Density App</a> <button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarsExampleDefault" aria-controls="navbarsExampleDefault" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation"> <span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span> </button> <div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarsExampleDefault"> <ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto"> <li class="nav-item"> <a class="nav-link" href="/">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a> </li> <li class="nav-item active"> <a class="nav-link" href="">Tool</a> </li> </ul> </div> </nav> <main role="main" class="container mt-3"> @yield('content') </main><!-- /.container --> <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/umd/popper.min.js"></script> <script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.4.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script> @yield('scripts') </body> </html>
Extend our views to use the layout file
Let us now use the newly created layouts file in both our welcome view and tool index view. Follow these steps to extend to the layout.
Add the following code to both ProjectFolder/resources/views/welcome.blade.php and ProjectFolder/resources/views/tool/index.blade.php
@extends('layouts.master') @section('content') @endsection
Try rendering the index page of the tool directory, for example localhost/tool. It should look something like below.

Basic view layout
Linking up the Controller, Route, & View
Now that we have a controller and view we need to first define a route and second add a return view method to the controller.
Define the route
Locate web routes file under ProjectFolder/routes/web.php
Add the following code to the bottom of the file:
Route::get('/tool', 'ToolController@index')->name('KDTool');
Create the new controller method
Now, go back to your ToolController and add the following function:
public function index() { return view('tool.index'); }
Feel free to change the view names, route URLs, or controller functions to your personal liking. Just make sure they all match up and the page renders.
Building up our tool view
Now, with our earlier set up of views and layout files, we can start to add the content in the form of HTML that we are going to need. It will consist of nothing more than some text, textarea input form, and a submit button. Add the following HTML to the content section of the ProjectFolder/resources/views/tool/index.blade.php file.
<form id="keywordDensityInputForm"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="keywordDensityInput">HTML or Text</label> <textarea class="form-control" id="keywordDensityInput" rows="12"></textarea> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary mb-2">Get Keyword Densities</button> </form>
The view should now render like this:
Keyword Density Tool View with Text Area input
Creating the bridge between the front end and the back end
Now, we pretty much have everything we need on the front end: a simple input text area where users can paste in their plain text or HTML. What's missing is the logic for when the button is pressed 'Get Keyword Densities'. This bridging logic will essentially do the following.
Listen for clicks on the Get Keyword Density Button
Grab the contents of the non-empty text area input
Use JQuery Ajax to send the data to the backend to be processed and await a response.
When the response is passed back, handle the data and create a HTML table with the human-readable statistics (keyword density).
Front end
To do this we will use an in-page script which we can inject using the @section tag. Add the following to the tool/index.blade.php view, after the content section.
@section ('scripts') <script> $('#keywordDensityInputForm').on('submit', function (e) { // Listen for submit button click and form submission. e.preventDefault(); // Prevent the form from submitting let kdInput = $('#keywordDensityInput').val(); // Get the input if (kdInput !== "") { // If input is not empty. // Set CSRF token up with ajax. $.ajaxSetup({ headers: { 'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="csrf-token"]').attr('content') } }); $.ajax({ // Pass data to backend type: "POST", url: "/tool/calculate-and-get-density", data: {'keywordInput': kdInput}, success: function (response) { // On Success, build a data table with keyword and densities if (response.length > 0) { let html = "<table class='table'><tbody><thead>"; html += "<th>Keyword</th>"; html += "<th>Count</th>"; html += "<th>Density</th>"; html += "</thead><tbody>"; for (let i = 0; i < response.length; i++) { html += "<tr><td>"+response[i].keyword+"</td>"; html += "<td>"+response[i].count+"</td>"; html += "<td>"+response[i].density+"%</td></tr>"; } html += "</tbody></table>"; $('#keywordDensityInputForm').after(html); // Append the html table after the form. } }, }); } }) </script> @endsection
This entire script that we inject will handle all of the numbered list items above. What is left to do is handle the data coming in on the back end side of things.
Back end
Firstly, before we go any further with coding, we need to handle the fact that both plain text and HTML can be submitted. For this we can use a nifty tool to help us out. html2text is the perfect PHP library for this use case, so it's time we install it. html2text does exactly what it says on the tin, converts HTML markup to plain text. Luckily, this package has a composer install command, so enter the following command into the CLI on the projects root directory.
composer require html2text/html2text
Now, our backend controller is going to receive either HTML or plain text in requests firing from the HTML form we created in our view. We now need to make the route to handle this call and to route the call to the specific controller that will work the magic. Add the following PHP to the web.php routes file:
Route::post('/tool/calculate-and-get-density', 'ToolController@CalculateAndGetDensity');
Secondly, add the following to ToolController.php file:
public function CalculateAndGetDensity(Request $request) { if ($request->isMethod('GET')) { } }
OK, so the stage is set. Let's code in the magic that will calculate the keyword density and return the data. Firstly, add use statement is required for the newly installed html2text package. Add the following to the top of the ToolController.php, just below other use statements:
use Html2Text\Html2Text;
Then we need to handle the get parameter that is to be passed in, making sure it's not set and then converting the parameter of content to plain text. Refactor the CalculateAndGetDensity function to look like below:
public function CalculateAndGetDensity(Request $request) { if ($request->isMethod('GET')) { if (isset($request->keywordInput)) { // Test the parameter is set. $html = new Html2Text($request->keywordInput); // Setup the html2text obj. $text = $html->getText(); // Execute the getText() function. } } }
Now that we have a variable to hold all of the text stripped for the keywordInput parameter, we can go ahead and start to calculate density. We need to handle the following:
Determine the total count of words
Analyse the textual string and convert it to a key value array (the key being the keyword, the value being the occurrence of the word)
Sort into order by descending with the biggest occurrence first in the array
Loop over the key and value array, pushing the values to a new array with an additional field of 'density' which utilises the keyword density formula we looked at earlier in the article. This formula will use the value (occurrence) and the total word count.
Finally, to return the data
Refactor the function to look like the following, taking note of the comments:
public function CalculateAndGetDensity(Request $request) { if ($request->isMethod('GET')) { if (isset($request->keywordInput)) { // Test the parameter is set. $html = new Html2Text($request->keywordInput); // Setup the html2text obj. $text = strtolower($html->getText()); // Execute the getText() function and convert all text to lower case to prevent work duplication $totalWordCount = str_word_count($text); // Get the total count of words in the text string $wordsAndOccurrence = array_count_values(str_word_count($text, 1)); // Get each word and the occurrence count as key value array arsort($wordsAndOccurrence); // Sort into descending order of the array value (occurrence) $keywordDensityArray = []; // Build the array foreach ($wordsAndOccurrence as $key => $value) { $keywordDensityArray[] = ["keyword" => $key, // keyword "count" => $value, // word occurrences "density" => round(($value / $totalWordCount) * 100,2)]; // Round density to two decimal places. } return $keywordDensityArray; } } }
Note: The beauty of html2text is that it doesn't really care if it's converting HTML or plain text in the first place, so we don't need to worry if a user submits either. It will still churn out plain text.
Putting it to the test
Finally, we are ready to test the tool, wahoo! Go ahead and render the tool index view (localhost/tool).
Now, you can go to any website of your choice on the web, load a page from that site, right click and click view source.
Copy the entire contents and come back to the tool.
Paste the contents into the text area and click the Get Keyword Densities button.
Await the response and check out the table of keyword densities!
Check out my example below which uses the HTML of this page.
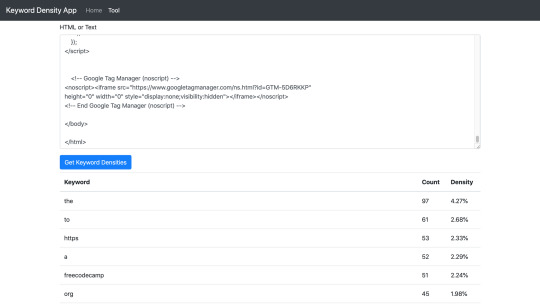
Keyword Density Tool & Table of keywords
And that is it!
Summary
In this article we learned how to build a Laravel application from scratch. It touched on some of the different parts of the full stack in development such as JQuery, PHP, HTML etc. Hopefully, with the understanding of this application, the same methodology can be used to build something else, perhaps bigger and better.
Possible further developments
The keyword density tool currently takes 'stop' words into account. Stop words are known to be ignored by Googles crawlers. Words such as it, the, as, and a. Looking at the tool screenshot above, you can see that they are used a lot! Further development could be carried out to filter the stop words and only calculate density on the non-stop words which is potentially a better view for SEO scoring.
0 notes
Text
Common administrator responsibilities on Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora for PostgreSQL databases
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) and Amazon Aurora as fully managed relational database services. With a few commands, you can have your production database instance up and running on AWS. An online database frees the database administrator (DBA) from many maintenance and management tasks. However, there are a few significant responsibilities to be aware of. This post discusses the DBA tasks to perform on Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL and Aurora with PostgreSQL-compatible databases. As a DBA, you face daily pressure to deliver value to your business across many fronts. Maintaining the right platform for running mission-critical databases is becoming increasingly difficult. Maintenance is also a challenging job. The launch of Amazon RDS and Aurora has vastly reduced the time you spend on tasks like installation, configuration, monitoring, and security. Nevertheless, you must still carry out several critical tasks: several of them daily, a few weekly, and some only at the time of Amazon RDS or Aurora installation (at the time of instance creation). Some of the administrative tasks that you must carry out include: Configuring the parameter group Managing IP traffic using a security group Auditing the database log files Maintenance and management activities Planning backup and recovery strategies User management Monitoring the database Configuring the parameter group The data directory of an on-premises PostgreSQL cluster contains the configuration file postgresql.conf. You can manage the parameters through this configuration file. Similarly, for Amazon RDS and Aurora PostgreSQL instances, you manage the parameters through a parameter group. Before you create a new Amazon RDS and Aurora instance, customize your DB parameter group. For more information about creating a new parameter group, modifying the parameters, and attaching it to the instance, see Working with DB Parameter Groups. If you do not have a customized parameter group at the time of creation, you can perform an instance restart. Replace the default DB parameter group with the custom parameter group, which allows the customized parameters to take effect. The following overview describes which parameters you should turn on for optimal performance: Enter the following logging parameters: log_autovacuum_min_duration 0 log_checkpoints '1' log_connection '1' log_disconnection '1' log_min_duration_statement '' log_temp_files '1' log_statement='ddl' rds.force_autovacuum_logging_level='log' Enter the following autovacuum parameters: autovacuum_max_workers autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay Enter the following as other parameters: random_page_cost default_statistics_target shared_preload_libraries='pg_hint_plan, pg_stat_statements' Managing IP traffic using a security group In Amazon RDS and Aurora, the security group controls the traffic in and out of the instance. It controls both incoming and outgoing traffic by applying appropriate rules to the security group. For example, the following screenshot shows how you can allow PG traffic from your applications to the database via port 5432: Do not open your database to the world by using 0.0.0.0/0. Auditing the database log files The busier your database is, the higher the number of transactions. The more transactions, the more logs it generates. The more log files, the more complicated it becomes to extract specific information from those log files. Most DBAs review their log files as a last resort, but you should turn to them frequently for the ERROR, FATAL, WARNING, and HINTS messages they contain. It is vital to check and audit the log files regularly. When it becomes difficult to analyze the log files every day due to size, you can use pgBadger, which is available on GitHub. pgBadger is an open-source PostgreSQL log analyzing tool that generates HTML reports from your PostgreSQL log file. By default, RDS and Aurora instances retain logs for 3–7 days. Run custom bash scripts to download the log files locally or to an Amazon EC2 instance or an Amazon S3 bucket to maintain log files for a longer period. To install and generate pgBadger reports, complete the following steps: Sign in to the AWS Management Console and create one EC2 RHEL or CentOS instance. Download the pgdg repo on Amazon EC2. To install, enter the following code: sudo yum install ftp://ftp.pbone.net/mirror/apt.sw.be/redhat/7.3/en/i386/rpmforge/RPMS/perl-Text-CSV_XS-0.65-1.rh7.rf.i386.rpm perl perl-devel sudo yum install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm sudo yum install pgbadger -y This post tested the preceding steps on RHEL 7 with pgdg-10 (PostgreSQL repo). To generate the report, complete the following steps: Download the PostgreSQL log files from Amazon RDS or Aurora to Amazon EC2 and run pgBadger. Enable the logging parameters in your DB parameter group. Schedule a cron job to download the log files to an appropriate location on Amazon EC2 and generate the pgBadger report. Download and convert your log files with the following code: #This Script helps to download the Postgres log files from cloud and store it on EC2. ## 1. Delete the logs and pgBadger reports older than 3 days. ## 2. Download the latest Postgres log from Amazon RDS instance: . ## 3. Generate the pgBadger report for newly downloaded log file. #create pgBadger dir under /home/ec2-user mkdir -p /home/ec2-user/pgBadger, # mkdir -p /home/ec2-user/pgBadger/logs , mkdir -p /home/ec2-user/pgBadger/reports #Use must install pgbadger and it should be in path. #Here is link for pgbadger installation: https://github.com/darold/pgbadger #Install awscli on EC2 instance set the env (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/topic/config-vars.html) # to download the log files. home_dir="/home/postgres/pgBadger" logDir="/home/postgres/pgBadger/logs" rptDir="/var/www/pgbadger" identifier='' date=`date -d "-1 days" +%Y-%m-%d` sudo find $logDir -name '*.log.*' -type f -mtime 0 -exec rm {} ; sudo find $rptDir -name 'postgresql*.html' -type f -mtime +10 -exec rm {} ; sudo mkdir -p $logDir/$date sudo chown -R postgres:postgres $logDir/$date #how to generate pgbadger report #Install pgbadger on EC2 . To install, follow the link: https://github.com/darold/pgbadger for i in `seq -w 00 23` do sudo aws rds download-db-log-file-portion --db-instance-identifier $identifier --log-file-name error/postgresql.log.$date-$i --starting-token 0 --output text > $logDir/$date/postgresql.log.$date-$i done if [ $? -eq 0 ] ; then sudo pgbadger --prefix '%t:%r:%u@%d:[%p]:' $logDir/$date/*.log.* -o $rptDir/postgresql.$date.html -f stderr #-f $logDir/*.log.* sudo chmod -R 777 $rptDir/postgresql.$date.html if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then #mailx -s "Successfully Generated the pgbadger report for Date: $date" echo "Successfully Generated the pgbadger report for Date: $date" else #mailx -s "UNSUCESSFUL GENERATION of pgbadger report for Date: $date" echo "Successfully Generated the pgbadger report for Date: $date" fi gzip -r9 $logDir/$date fi This script generates the pgbadger report that you can use to analyze the activities performed on the database. For a sample pgBadger report, see postgres_sample. Maintenance and management activities A remote database still requires maintenance. The following section discusses autovacuuming, the VACUUM ANALYZE command, and long-running queries and sessions. Autovacuuming Query slowness due to table or index bloat is one of the most common scenarios in PostgreSQL. Amazon RDS and Aurora enable autovacuuming by default to reduce this bloat. As you manage slowdown, keep the following in mind: Autovacuum holds a less-priority lock on the table. It might cancel its own job when another high-priority operation wants to acquire a lock on the table. The same table can become a candidate for repeated autovacuums, which causes other tables to remain bloated. Because these are the common scenarios in PostgreSQL, you should tune your autovacuum parameter properly. If tuning does not work, you must schedule a manual vacuum/analyze script. Based on the frequency of the bloat, you can decide whether to perform VACUUM ANALYZE, VACUUM FULL, or PG_REPACK. Scheduling VACUUM ANALYZE To keep the stats updated, remove bloat in reused space, and avoid the transaction wraparound, schedule VACUUM ANALYZE on your database. VACUUM removes the bloat and avoids transaction wraparound. ANALYZE helps to update the database stats, which helps the planner generate good plans for queries. Before you proceed, you should understand the differences between VACUUM ANALYZE, VACUUM FULL, and PG_REPACK. VACUUM ANALYZE – Removes the bloat from the tables and indexes and updates the tables’ statistics. This is a non-locking operation; you can run it at a table level or database level. It cleans the bloated pages but does not reclaim the space. VACUUM FULL – Writes the entire content of the table into a new disk file and releases the wasted space back to OS. This causes a table-level lock on the table and slow speeds. Avoid using VACUUM FULL on a high-load system. PG_REPACK – Writes the entire content of the table into a new disk file and releases the wasted space back to OS and does it online without holding the lock on the table. It is faster than VACUUM FULL, and Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS support it as an extension. Instead of re-indexing or performing a VACUUM FULL, you should use PG_REPACK to back up. PG_REPACK is available as an extension in Amazon Aurora for PostgreSQL and Amazon RDS PostgreSQL. The following code calculates the bloat and extra space that bloated pages occupy: SELECT current_database(), schemaname, tblname, bs*tblpages AS real_size, (tblpages-est_tblpages)*bs AS extra_size, CASE WHEN tblpages - est_tblpages > 0 THEN 100 * (tblpages - est_tblpages)/tblpages::float ELSE 0 END AS extra_ratio, fillfactor, CASE WHEN tblpages - est_tblpages_ff > 0 THEN (tblpages-est_tblpages_ff)*bs ELSE 0 END AS bloat_size, CASE WHEN tblpages - est_tblpages_ff > 0 THEN 100 * (tblpages - est_tblpages_ff)/tblpages::float ELSE 0 END AS bloat_ratio, is_na -- , (pst).free_percent + (pst).dead_tuple_percent AS real_frag FROM ( SELECT ceil( reltuples / ( (bs-page_hdr)/tpl_size ) ) + ceil( toasttuples / 4 ) AS est_tblpages, ceil( reltuples / ( (bs-page_hdr)*fillfactor/(tpl_size*100) ) ) + ceil( toasttuples / 4 ) AS est_tblpages_ff, tblpages, fillfactor, bs, tblid, schemaname, tblname, heappages, toastpages, is_na -- , stattuple.pgstattuple(tblid) AS pst FROM ( SELECT ( 4 + tpl_hdr_size + tpl_data_size + (2*ma) - CASE WHEN tpl_hdr_size%ma = 0 THEN ma ELSE tpl_hdr_size%ma END - CASE WHEN ceil(tpl_data_size)::int%ma = 0 THEN ma ELSE ceil(tpl_data_size)::int%ma END ) AS tpl_size, bs - page_hdr AS size_per_block, (heappages + toastpages) AS tblpages, heappages, toastpages, reltuples, toasttuples, bs, page_hdr, tblid, schemaname, tblname, fillfactor, is_na FROM ( SELECT tbl.oid AS tblid, ns.nspname AS schemaname, tbl.relname AS tblname, tbl.reltuples, tbl.relpages AS heappages, coalesce(toast.relpages, 0) AS toastpages, coalesce(toast.reltuples, 0) AS toasttuples, coalesce(substring( array_to_string(tbl.reloptions, ' ') FROM 'fillfactor=([0-9]+)')::smallint, 100) AS fillfactor, current_setting('block_size')::numeric AS bs, CASE WHEN version()~'mingw32' OR version()~'64-bit|x86_64|ppc64|ia64|amd64' THEN 8 ELSE 4 END AS ma, 24 AS page_hdr, 23 + CASE WHEN MAX(coalesce(null_frac,0)) > 0 THEN ( 7 + count(*) ) / 8 ELSE 0::int END + CASE WHEN tbl.relhasoids THEN 4 ELSE 0 END AS tpl_hdr_size, sum( (1-coalesce(s.null_frac, 0)) * coalesce(s.avg_width, 1024) ) AS tpl_data_size, bool_or(att.atttypid = 'pg_catalog.name'::regtype) OR count(att.attname) <> count(s.attname) AS is_na FROM pg_attribute AS att JOIN pg_class AS tbl ON att.attrelid = tbl.oid JOIN pg_namespace AS ns ON ns.oid = tbl.relnamespace LEFT JOIN pg_stats AS s ON s.schemaname=ns.nspname AND s.tablename = tbl.relname AND s.inherited=false AND s.attname=att.attname LEFT JOIN pg_class AS toast ON tbl.reltoastrelid = toast.oid WHERE att.attnum > 0 AND NOT att.attisdropped AND tbl.relkind = 'r' GROUP BY 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10, tbl.relhasoids ORDER BY 2,3 ) AS s ) AS s2 ) AS s3; You receive the following code as output: current_database | schemaname | tblname | real_size | extra_size | extra_ratio | fillfactor | bloat_size | bloat_ratio | is_na ------------------+--------------------+-------------------------+------------+------------+------------------+------------+------------+------------------+------- postgres | public | sample_table | 1565351936 | 239951872 | 15.3289408267611 | 100 | 239951872 | 15.3289408267611 | f To reclaim the space, run VACUUM FULL or PG_REPACK: Postgres# vacuum full analyze sample_table; After you run VACUUM FULL, the query returns something similar to the following output: current_database | schemaname | tblname | real_size | extra_size | extra_ratio | fillfactor | bloat_size | bloat_ratio | is_na ------------------+--------------------+-------------------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+------------+------------+--------------------+------- postgres | public | sample_table | 41746432 | 24576 | 0.0588697017268446 | 100 | 24576 | 0.0588697017268446 | f VACUUM FULL and re-indexing are locking operations that block other sessions, but PG_REPACK is an online method to reorganize the tables and indexes. You can query the pg_stat_all_tables and pg_stat_user_tables to check the last autovacuum or manual vacuum execution. For example, see the following code: SELECT schemaname,relname as table_name, last_vacuum, last_analyze, last_autovacuum, last_autoanalyze, n_live_tup,n_dead_tup from pg_stat_user_tables; You receive the following code as output: schemaname | table_name | last_vacuum | last_analyze | last_autovacuum | last_autoanalyze | n_live_tup | n_dead_tup ------------+-------------+-------------+--------------+-----------------+-------------------------------+------------+------------ public | vacuum_test | | | | 2019-01-23 06:44:56.257586+00 | 13671089 | 0 You can also use this code: SELECT schemaname, relname as table_name, last_vacuum, last_analyze, last_autovacuum, last_autoanalyze, n_live_tup, n_dead_tup from pg_stat_all_tables; You receive the following code as output: schemaname | table_name | last_vacuum | last_analyze | last_autovacuum | last_autoanalyze | n_live_tup | n_dead_tup --------------------+----------------+-------------------------------+-------------------------------+--------------------+------------------+------------+------------ information_schema | sql_sizing | 2019-01-23 07:05:06.524004+00 | 2019-01-23 07:05:06.52429+00 | | | 23 | 0 To run VACUUM ANALYZE on a table, enter the following code: Vacuum analyze ; To run VACUUM ANALYZE on the database, enter the following code: Vacuum analyze verbose; Only the superuser or database owner can run a vacuum on system tables. If substantial bloat in system tables causes performance degradation, or when you must free up bloated space to the disk, you must run VACUUM FULL. Only run this command outside of business hours, because it locks the tables on which it runs. To check the transactional age of the database, enter the following code: SELECT datname, age(datfrozenxid) from pg_database order by age(datfrozenxid) desc limit 20; To prevent transaction wraparound issues in the database, enter the following code: Vacuum freeze; The autovacuum process can also perform these activities, and it is highly recommended that you keep it enabled. Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL has autovacuuming enabled by default. Make sure that you tune the autovacuum parameters to best suit your requirements. In Amazon RDS, the parameter rds.adaptive_autovacuum helps automatically tune the autovacuum parameters whenever the database exceeds the transaction ID thresholds. Enter the following code to check if autovacuum is running in PostgreSQL version 9.6 and above: SELECT datname, usename, pid, waiting, current_timestamp - xact_start AS xact_runtime, query FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE upper(query) like '%VACUUM%' ORDER BY xact_start; Long-running queries and sessions To terminate queries that have run for a long time or are blocking another session, check the PID of the query from the pg_stat_activity table. To kill the query, run the following commands. To cancel the query without disconnecting the connection, enter the following code: SELECT pg_cancel_backend(pid); To terminate the connection and cancel all other queries in that connection, enter the following code: SELECT pg_terminate_backend(pid); To cancel the running queries, always use PG_CANCEL_BACKEND. If the query is stuck and locking other processes, you can use PG_TERMINATE_BACKEND. After termination, you might need to re-run the session again to establish the connection. Planning backup and recovery strategies Unlike on-premises databases, which require manual backup and recovery, Aurora for PostgreSQL and RDS PostgreSQL instances have built-in features to automate backups using snapshots. You must enable these during the creation of the Amazon RDS or Aurora instance. Amazon RDS creates a storage volume snapshot to back up the entire database instance. When you create a DB snapshot, you must identify which DB instance you want to back up, and then give your DB snapshot a name so you can restore from it later. The amount of time it takes to create a snapshot varies depends on the size of your databases. For more information, see Restoring from a DB Snapshot. User management User management is one of the most critical admin tasks, and you must perform it with utmost care. When you create a new Amazon RDS PostgreSQL or Aurora for PostgreSQL instance, it creates an RDS_SUPERUSER role. This is similar to the PostgreSQL user of a typical PostgreSQL instance, but with a few limitations. You can manage users that connect to the database by setting appropriate permission levels. In a default PostgreSQL environment, you can manage user connection through the pg_hba.conf file, but in Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL, you must use GRANT/REVOKE. You can also assign access and privileges to users at a schema level or table level. You can decide on what kind of privileges you want to provide to the users. For more information, see Managing PostgreSQL users and roles. Monitoring the database Monitoring is an integral part of maintaining the reliability, availability, and performance of Amazon RDS and your AWS solutions. Collect monitoring data from all the parts of your AWS solution so that you can debug a multi-point failure if one occurs. One of the major tasks is to set up a detailed level of monitoring for your Amazon RDS and Aurora instances. Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS offer two types of monitoring by default: Amazon CloudWatch and Amazon RDS Performance Insights. Monitoring with CloudWatch CloudWatch offers the following metrics available for Amazon RDS and Aurora PostgreSQL: High CPU or RAM consumption Disk space consumption Network traffic Database connections IOPS metrics Maximum Used Transaction IDs Queue Depth For more information, see Monitoring Amazon Aurora DB Cluster Metrics. CloudWatch has many metrics available to monitor the health of the Amazon RDS and Aurora instances at the hardware level. However, you must configure Amazon SNS (alarm) on each metric. Monitoring with Performance Insights Amazon RDS Performance Insights employs lightweight data collection methods without impacting the performance of your applications to tune the database for performance. Performance Insights offers the following metrics: OS metrics: CPU Utilization – Wait, Idle, Steal, Nice Disk I/O – Read KbPS, Write IOsPS Load Average Swap – Cached, Free, Total Database metrics: Cache – blocks hit, buffers allocated Checkpoint – Checkpoint timed, buffers checkpoint, checkpoint write latency For more information, see Performance Insights for Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL. Summary This post shared a few common administrator responsibilities on Amazon RDS and Aurora for PostgreSQL databases. This provides a basic framework that you can implement on your test and production workloads. The post also highlights logging and log auditing for better management of the instances. If you have questions or comments about this post, post your thoughts in the comments. About the Author John Solomon is a Consultant with AWS Global Competency Center India, working closely with customers who are migrating from on-premises to the AWS Cloud. He is an AWS certified speaker and speaks at various meetups, breakout sessions, webinars, etc. He is an ardent member of the PostgreSQL community and works as a database administrator for PostgreSQL databases. https://probdm.com/site/MjI4MDE
0 notes
Link
New to Kali Linux ? or to Linux world at all ... welcome to this new experience i'm sure you will enjoy once you start to try ... and why not to try over and over we are learning at end and this is the most Important part of it, commands and commands almost everything in Linux need a command we are not in Windows to click we are in Linux to write! so here is a list for some of the basic commands for Kali Linux
If you are looking for Linux Chart Sheet Check this post
lets start with details of commands : 1.Command: ls The command “ls” stands for (List Directory Contents), List the contents of the folder, be it file or folder, from which it runs. The most common options are -a (all files) and -l (long or details) Tab completion is supported and may be configured with .inputrc When output to file the files are listed one per line. By default, colour is not used to distinguish types of files. That is equivalent to using --color=none. Using the --color option without the optional WHEN argument is equivalent to using --color=always. With --color=auto, color codes are output only if standard output is connected to a terminal (tty).
ls
A.Command “ls -a“, list the content of folder, including hidden files the hidden files is colored blue 2. Command: lsblk The “lsblk” stands for (List Block Devices), print block devices by their assigned name (but not RAM) on the standard output in a tree-like fashion.
lsblk
The “lsblk -l” command list block devices in ‘list‘ structure (not tree like fashion). Note: lsblk is very useful and easiest way to know the name of New Usb Device you just plugged in, especially when you have to deal with disk/blocks in terminal. 3. Command: sudo he “sudo” (super user do) command allows a permitted user to execute a command as the superuser or another user, as specified by the security policy in the sudoers list.
1sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tualatrix/ppa
Note: sudo allows user to borrow superuser privileged, while a similar command ‘su‘ allows user to actually log in as superuser. Sudo is safer than su. It is not advised to use sudo or su for day-to-day normal use, as it can result in serious error if accidentally you did something wrong, that’s why a very popular saying in Linux community is: “To err is human, but to really foul up everything, you need root password.” 4. Command: mkdir The “mkdir” (Make directory) command create a new directory with name path. However is the directory already exists, it will return an error message “cannot create folder, folder already exists”.
1 mkdir Kalitut
Note: Directory can only be created inside the folder, in which the user has write permission. mkdir: cannot create directory `Kalitut‘: File exists (Don’t confuse with file in the above output, you might remember what i said at the beginning – In Linux every file, folder, drive, command, scripts are treated as file). 5.Command: chmod The Linux “chmod” command stands for (change file mode bits). chmod changes the file mode (permission) of each given file, folder, script, etc.. according to mode asked for. There exist 3 types of permission on a file (folder or anything but to keep things simple we will be using file).
123Read (r)=4 Write(w)=2 Execute(x)=1
So if you want to give only read permission on a file it will be assigned a value of ‘4‘, for write permission only, a value of ‘2‘ and for execute permission only, a value of ‘1‘ is to be given. For read and write permission 4+2 = ‘6‘ is to be given, ans so on. Now permission need to be set for 3 kinds of user and usergroup. The first is owner, then usergroup and finally world.
1rwxr-x--x abc.sh
Here the root’s permission is rwx (read, write and execute). usergroup to which it belongs, is r-x (read and execute only, no write permission) and for world is –x (only execute). To change its permission and provide read, write and execute permission to owner, group and world.
1chmod 777 abc.sh
only read and write permission to all three.
1chmod 666 abc.sh
read, write and execute to owner and only execute to group and world.
1chmod 711 abc.sh
Note: one of the most important command useful for sysadmin and user both. On a multi-user environment or on a server, this command comes to rescue, setting wrong permission will either makes a file inaccessible or provide unauthorized access to someone. 6.Command: tar The “tar” command is a Tape Archive is useful in creation of archive, in a number of file format and their extraction.
123 tar -zxvf abc.tar.gz (Remember 'z' for .tar.gz) tar -jxvf abc.tar.bz2 (Remember 'j' for .tar.bz2) tar -cvf archieve.tar.gz(.bz2) /path/to/folder/abc
Note: A ‘tar.gz‘ means gzipped. ‘tar.bz2‘ is compressed with bzip which uses a better but slower compression method. 7. Command: cp The “copy” stands for (Copy), it copies a file from one location to another location.
1cp /home/user/Downloads abc.tar.gz /home/user/Desktop
Note: cp is one of the most commonly used command in shell scripting and it can be used with wildcard characters (Describe in the above block), for customised and desired file copying. 8. Command: mv The “mv” command moves a file from one location to another location.
1mv /home/user/Downloads abc.tar.gz /home/user/Desktop
Note: mv command can be used with wildcard characters. mv should be used with caution, as moving of system/unauthorised file may lead to security as well as breakdown of system. 9.Command: pwd The command “pwd” (print working directory), prints the current working directory with full path name from terminal.
1 pwd /home/user/Desktop
Note: This command won’t be much frequently used in scripting but it is an absolute life saver for newbie who gets lost in terminal in their early connection with nux. (Linux is most commonly referred as nux or nix). 10. Command: cd Finally, the frequently used “cd” command stands for (change directory), it change the working directory to execute, copy, move write, read, etc. from terminal itself.
123 cd /home/user/Desktop pwd /home/user/Desktop
Note: cd comes to rescue when switching between directories from terminal. “Cd ~” will change the working directory to user’s home directory, and is very useful if a user finds himself lost in terminal. “Cd ..” will change the working directory to parent directory (of current working directory). Now i will leave you with few more commends File Operations: pwd Print Name Of Current/Working Directory The pwd is an acronym for print working directory. The pwd command is considered as one of the most frequently used commands on Linux, AIX, HP-UX, *BSD, and other UNIX like operating systems along with the ls, and cd commands. It can be used for the following purposes under Apple OS X or UNIX or Linux operating systems: => Find the full path to the current directory. => Store the full path to the current directory in the shell variable. => Verify the absolute path. => Verify the physical path i.e exclude . cd Changing The Working Directory cp Copy Files Or Directory rm Remove Files And Directory ls List Of Directory Contents mkdir Make Directory cat Concatenate Files And Print On Standard Output mv Move Files chmod Change Files Permissions Know Your System uname Print System Information who Show Who Is Logged On cal Displays Calculator date Print System Date And Time df Report File System Disk Space Usage du Estimate File Space Usage ps Displays Information Of Current Active Processes kill Allows To Kills Process clear Clear The Terminal Screen cat /proc/cpuinfo Cpuinfo Display CPU Information cat /proc/meminfo Display Memory Information Compression tar Store and Extract Files From An Archive File gzip Compress Or Decompress Named Files Network ifconfig To Config Network Interface ping Check Other System are reachable from The Host System wget Download Files From Network ssh Remote Login Program ftp Download/Upload Files From/To Remote System last Displays List Of Last Logged In User telnet Used To Communicate With Another Host Using THe Telnet Protocol Searching Files grep Search Files(s) For Specific Text find Search For Files In A Directory Hierarchy locate Find Files By Name
0 notes
Photo

New Post has been published on https://www.techy360.com/2017/11/29/linux-bash-script-step-step-guide/
Linux Bash Script Step By Step Guide , You Will Love It
Today we are going to talk about bash scripting or shell scripting and how to write your first bash script. Actually, they are called shell scripts in general, but we are going to call them bash scripts because we are going to use bash among the other Linux shells.
There are zsh, tcsh, ksh and other shells.
In the previous posts, we saw how to use the bash shell and how to use Linux commands.
The concept of a bash script is to run a series of Commands to get your job done.
To run multiple commands in a single step from the shell, you can type them on one line and separate them with semicolons.
pwd ; whoami
Actually, this is a bash script!!
The pwd command runs first, displaying the current working directory then the whoami command runs to show the currently logged in users.
You can run multiple commands as much as you wish, but with a limit. You can determine your max args using this command.
getconf ARG_MAX
Well, What about putting the commands into a file, and when we need to run these commands we run that file only. This is called a bash script.
First, make a new file using the touch command. At the beginning of any bash script, we should define which shell we will use because there are many shells on Linux, bash shell is one of them.
Bash Script Shebang
The first line you type when writing a bash script is the (#!) followed by the shell you will use.
#! <=== this sign is called shebang. #!/bin/bash
If you use the pound sign (#) in front of any line in your bash script, this line will be commented which means it will not be processed, but, the above line is a special case . This line defines what shell we will use, which is bash shell in our case.
The shell commands are entered one per line like this:
#!/bin/bash # This is a comment pwd whoami
You can type multiple commands on the same line but you must separate them with semicolons, but it is preferable to write commands on separate lines, this will make it simpler to read later.
Set Script Permission
After writing your bash script, save the file.
Now, set that file to be executable, otherwise, it will give you permissions denied. You can review how to set permissions using chmod command.
chmod +x ./myscript
Then try run it by just typing it in the shell:
./myscript
And Yes, it is executed.
Print Messages
As we know from other posts, printing text is done by echo command.
Edit our file and type this:
#!/bin/bash # our comment is here echo "The current directory is:" pwd echo "The user logged in is:" whoami
Perfect! Now we can run commands and display text using echo command.
If you don’t know echo command or how to edit a file I recommend you to view previous articles about basic Linux commands
Using Variables
Variables allow you to store information to use it in your script.
You can define 2 types of variables in your bash script:
Environment variables
User variables
Environment Variables
Sometimes you need to interact with system variables, you can do this by using environment variables.
#!/bin/bash # display user home echo "Home for the current user is: $HOME"
Notice that we put the $HOME system variable between double quotations, and it prints the home variable correctly.
What if we want to print the dollar sign itself?
echo "I have $1 in my pocket"
Because variable $1 doesn’t exist, it won’t work. So how to overcome that?
You can use the escape character which is the backslash before the dollar sign like this:
echo "I have $1 in my pocket"
Now it works!!
User Variables
Also, you can set and use your custom variables in the script.
You can call user variables in the same way like this:
#!/bin/bash
# User variables grade=5 person="Adam" echo "$person is a good boy, he is in grade $grade" chmod +x myscript ./myscript
Command Substitution
You can extract information from the result of a command using command substitution.
You can perform command substitution with one of the following methods:
The backtick character (`).
The $() format.
Make sure when you type backtick character, it is not the single quotation mark.
You must enclose the command with two backticks like this:
mydir=`pwd`
Or the other way:
mydir=$(pwd)
So the script could be like this:
#!/bin/bash mydir=$(pwd) echo $mydir
The output of the command will be stored in mydir variable.
Math calculation
You can perform basic math calculations using $(( 2 + 2 )) format:
#!/bin/bash var1=$(( 5 + 5 )) echo $var1 var2=$(( $var1 * 2 )) echo $var2
Just that easy.
if-then-else Statement
The if-then-else statement takes the following structure:
if command then do something else do another thing fi
If the first command runs and returns zero; which means success, it will not hit the commands after the else statement, otherwise, if the if statement returns non-zero; which means the statement condition fails, in this case, the shell will hit the commands after else statement.
#!/bin/bash user=anotherUser if grep $user /etc/passwd then echo "The user $user Exists" else echo "The user $user doesn’t exist" fi
We are doing good till now, keep moving.
Now, what if we need more else statements.
Well, that is easy, we can achieve that by nesting if statements like this:
if condition1 then commands elif condition2 then commands fi
If the first command return zero; means success, it will execute the commands after it, else if the second command return zero, it will execute the commands after it, else if none of these return zero, it will execute the last commands only.
#!/bin/bash user=anotherUser if grep $user /etc/passwd then echo "The user $user Exists" elif ls /home then echo "The user doesn’t exist" fi
You can imagine any scenario here, maybe if the user doesn’t exist, create a user using the useradd command or do anything else.
Numeric Comparisons
You can perform a numeric comparison between two numeric values using numeric comparison checks like this:
number1 -eq number2 Checks if number1 is equal to number2.
number1 -ge number2 Checks if number1 is bigger than or equal number2.
number1 -gt number2 Checks if number1 is bigger than number2.
number1 -le number2 Checks if number1 is smaller than or equal number2.
number1 -lt number2 Checks if number1 is smaller than number2.
number1 -ne number2 Checks if number1 is not equal to number2.
As an example, we will try one of them and the rest is the same.
Note that the comparison statement is in square brackets as shown.
#!/bin/bash num=11 if [ $num -gt 10] then echo "$num is bigger than 10" else echo "$num is less than 10" fi
The num is greater than 10 so it will run the first statement and prints the first echo.
String Comparisons
You can compare strings with one of the following ways:
string1 = string2 Checks if string1 identical to string2.
string1 != string2 Checks if string1 is not identical to string2.
string1 < string2 Checks if string1 is less than string2.
string1 > string2 Checks if string1 is greater than string2.
-n string1 Checks if string1 longer than zero.
-z string1 Checks if string1 is zero length.
We can apply string comparison on our example:
#!/bin/bash user ="Hello" if [$user = $USER] then echo "The user $user is the current logged in user" fi
One tricky note about the greater than and less than for string comparisons, they MUST be escaped with the backslash because if you use the greater-than symbol only, it shows wrong results.
So you should do it like that:
#!/bin/bash v1=text v2="another text" if [ $v1 > "$v2" ] then echo "$v1 is greater than $v2" else echo "$v1 is less than $v2" fi
It runs but it gives this warning:
./myscript: line 5: [: too many arguments
To fix it, wrap the $vals with a double quotation, forcing it to stay as one string like this:
#!/bin/bash v1=text v2="another text" if [ $v1 > "$v2" ] then echo "$v1 is greater than $v2" else echo "$v1 is less than $v2" fi
One important note about greater than and less than for string comparisons. Check the following example to understand the difference:
#!/bin/bash v1=Hello v2=Hello if [ $v1 > $v2 ] then echo "$v1 is greater than $v2" else echo "$v1 is less than $v2" fi
sort myfile Hello Hello
The test condition considers the lowercase letters bigger than capital letters. Unlike the sort command which does the opposite.
The test condition is based on the ASCII order, while the sort command is based on the numbering orders from the system settings.
File Comparisons
You can compare and check for files using the following operators:
-d my_file Checks if its a folder.
-e my_file Checks if the file is available.
-f my_file Checks if its a file.
-r my_file Checks if it’s readable.
my_file –nt my_file2 Checks if my_file is newer than my_file2.
my_file –ot my_file2 Checks if my_file is older than my_file2.
-O my_file Checks if the owner of the file and the logged user match.
-G my_file Checks if the file and the logged user have the idetical group.
As they imply, you will never forget them.
Let’s pick one of them and take it as an example:
#!/bin/bash mydir=/home/Hello if [ -d $mydir ] then echo "Directory $mydir exists" cd $mydir ls else echo "NO such file or directory $mydir" fi
We are not going to type every one of them as an example. You just type the comparison between the square brackets as it is and complete you script normally.
There are some other advanced if-then features but let’s make it in another post.
That’s for now. I hope you enjoy it and keep practicing more and more.
Thank you.
0 notes
Text
find Linux Command
find
find [pathnames] [conditions]
An extremely useful command for finding particular groups of files (numerous examples follow this description). find descends the directory tree beginning at each pathname and locates files that meet the specified conditions. The default pathname is the current directory. The most useful conditions include -name and -type (for general use), -exec and -size (for advanced use), and -mtime and -user (for administrators). Conditions may be grouped by enclosing them in \( \) (escaped parentheses), negated with !, given as alternatives by separating them with -o, or repeated (adding restrictions to the match; usually only for -name, -type, or -perm). Note that "modification" refers to editing of a file's contents, whereas "change" means a modification, or permission or ownership changes. In other words, -ctime is more inclusive than -atime or -mtime.
Conditions and actions
-amin +n| -n| n Find files last accessed more than n (+n), less than n (-n), or exactly n minutes ago. -anewer file Find files that were accessed after file was last modified. Affected by -follow when after -follow on the command line. -atime +n| -n| n Find files that were last accessed more than n (+n), less than n (-n), or exactly n days ago. Note that find changes the access time of directories supplied as pathnames. -cmin +n| -n| n Find files last changed more than n (+n), less than n (-n), or exactly n minutes ago. -cnewer file Find files that were changed after they were last modified. Affected by -follow when after -follow on the command line. -ctime +n| -n| n Find files that were changed more than n (+n), less than n (-n), or exactly n days ago. A change is anything that changes the directory entry for the file, such as a chmod. -daystart Calculate times from the start of the day today, not 24 hours ago. -depth Descend the directory tree, skipping directories and working on actual files first, and then the parent directories. Useful when files reside in unwritable directories (e.g., when using find with cpio). -empty Continue if file is empty. Applies to regular files and directories. -exec command{ } \ ; Run the Linux command, from the starting directory on each file matched by find (provided command executes successfully on that file—i.e., returns a 0 exit status). When command runs, the argument { } substitutes the current file. Follow the entire sequence with an escaped semicolon (\;). In some shells, the braces may need to be escaped as well. -false Return false value for each file encountered. -follow Follow symbolic links and track the directories visited (don't use with -type l). -fstype type Match files only on type filesystems. Acceptable types include minix, ext, ext2, xia, msdos, umsdos, vfat, proc, nfs, iso9660, hpfs, sysv, smb, and ncpfs. -gid num Find files with numeric group ID of num. -group gname Find files belonging to group gname. gname can be a group name or a group ID number. -ilname pattern A case-insensitive version of -lname. -iname pattern A case-insensitive version of -name. -inum n Find files whose inode number is n. -ipath pattern A case-insensitive version of -path. -iregex pattern A case-insensitive version of -regex. -links n Find files having n links. -lname pattern Search for files that are symbolic links, pointing to files named pattern. pattern can include shell metacharacters and does not treat / or . specially. The match is case-insensitive. -maxdepth num Do not descend more than num levels of directories. -mindepth num Begin applying tests and actions only at levels deeper than num levels. -mmin +n| -n| n Find files last modified more than n (+n), less than n (-n), or exactly n minutes ago. -mount, -xdev Search only for files that reside on the same filesystem as pathname. -mtime +n| -n| n Find files that were last modified more than n (+n), less than n (-n), or exactly n days ago. A modification is a change to a file's data. -name pattern Find files whose names match pattern. Filename metacharacters may be used but should be escaped or quoted. -newer file Find files that were modified more recently than file; similar to -mtime. Affected by -follow only if it occurs after -follow on the command line. -nogroup The file's group ID does not correspond to any group. -noleaf Normally, find assumes that each directory has at least two hard links that should be ignored (a hard link for its name and one for "."--i.e., two fewer "real" directories than its hard link count indicates). -noleaf turns off this assumption, a useful practice when find runs on non-Unix-style filesystems. This forces find to examine all entries, assuming that some might prove to be directories into which it must descend (a time-waster on Unix). -nouser The file's user ID does not correspond to any user. -ok command { }\; Same as -exec, but prompts user to respond with y before command is executed. -path pattern Find files whose names match pattern. Expect full pathnames relative to the starting pathname (i.e., do not treat / or . specially). -perm nnn Find files whose permission flags (e.g., rwx) match octal number nnn exactly (e.g., 664 matches -rw-rw-r--). Use a minus sign before nnn to make a "wildcard" match of any unspecified octal digit (e.g., -perm -600 matches -rw-******, where * can be any mode). -print Print the matching files and directories, using their full pathnames. Return true. This is the default behavior. -regex pattern Like -path, but uses grep-style regular expressions instead of the shell-like globbing used in -name and -path. -size n[c] Find files containing n blocks, or if c is specified, n characters long. -type c Find files whose type is c. c can be b (block special file), c (character special file), d (directory), p (fifo or named pipe), l (symbolic link), s (socket), or f (plain file). -user user Find files belonging to user (name or ID).
Examples
List all files (and subdirectories) in your home directory: find $HOME -print List all files named chapter1 in the /work directory: find /work -name chapter1 List all files beginning with memo owned by ann: find /work -name 'memo*' -user ann -print Search the filesystem (begin at root) for manpage directories: find / -type d -name 'man*' -print Search the current directory, look for filenames that don't begin with a capital letter, and send them to the printer: find . \! -name '[A-Z] *' -exec lpr { }\; Find and compress files whose names don't end with .gz: gzip `find . \! -name '*.gz' -print` Remove all empty files on the system (prompting first): find / -size 0 -ok rm { } \; Search the system for files that were modified within the last two days (good candidates for backing up): find / -mtime -2 -print Recursively grep for a pattern down a directory tree: find /book -print | xargs grep '[Nn] utshell' If the files kt1 and kt2 exist in the current directory, their names can be printed with the command: $ find . -name 'kt[0-9] ' ./kt1 ./kt2 Since the command prints these names with an initial ./ path, you need to specify the ./ when using the -path option: $ find . -path './kt[0-9] ' ./kt1 ./kt2 The -regex option uses a complete pathname, like -path, but treats the following argument as a regular expression rather than a glob pattern (although in this case the result is the same): $ find . -regex './kt[0-9] ' ./kt1 ./kt2
from Java Tutorials Corner http://ift.tt/2w9k32V via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
Real Estate Agency Portal Script Développeur
New Post has been published on http://www.developpeur.ovh/1026/
Real Estate Agency Portal
1900+ Happy users! Thank You So Much!
Frontend user login and property submission
Test R-T-L
Documentation
Technical documentation, Knowledge base, FAQ, Support center
Application is based on CodeIgniter PHP framework, if you know CodeIgniter you can easily customize the system.
CodeIgniter is a very simple framework with the best documentation ever seen, so you can easy learn it.
Script was born to be ahead in innovation and at the peak of the real estate portal solutions, specifically designed for easy customization and use.
The script is so awesome that there are several clones on the market (with public confession), you can not make a mistake if you buy the original version
Why is Real estate agency portal script your best choice for real estate business?
You can earn money providing listing and featured submissions for visitors on portal with PayPal/Cash/Bank transfer payment support
You can earn money with Google AdSense or other similar service
You can add custom fields (textareas, inputs, dropdowns, upload) / Indoor amenities / Outdoor amenities / distances direct from Admin interface (No programming skills needed)
Top notch multilanguage (Backend+Frontend) features like auto-translating with MyMemory API service and Google translator (manually corrections are also supported), RTL, look this extra simplicity, try administration!
Real multicurrency support ( different currency and different price on different language and different purposes Sale/Rent )
Exclusive innovation on results filtering (Very simple, intuitive and powerful), you must try this on our live preview!
Supported front-end and backend user-types/roles with submissions: Admin, Agent and front-end Agent/User with admin verification
Front-end Facebook login for extra lazy guys
Each agent/agency and user have public profile page with all listings, logo can be listed on homepage
Enquires system for you and your agents in administration
Extra easy to use, drag & drop multi image upload, reorder images, pages, fields
Innovative drag & drop Menu and pages builder with logical page structure embedded
Check in / check out dates for rental purpose.
Backup your database and files direct from administration
Easy to make new custom theme, Bootstrap responsive example with 6 color styles provided and nice documentation
Track your visitors with Google Analytics
Based on Codeigniter, so if you know it you can easy customize anything you want
Incredible support, documentation, knowledge base, FAQ section and quick answering on any issue!
If at least one of the answers is yes, see the application and you’ll love it.
Add/Edit, Drag & drop any field, Indoor/outdoor amenities, distances, or custom fields like Floor etc. with icons of course.
New innovation with visual rectangle drawing search!
Exclusive innovation on results filtering (Very simple, intuitive and powerful), you must try this on our live preview!
Earn money with submission and featured listings (Cash/Bank transfer also supported) for frontend users, Adsense and similar services is also supported
More then 60+ languages supported with auto-translate feature based on MyMemory API and Google translator
Native multilanguage support
Support all world currencies in listings (can be different based on langauge) and all PayPal supported currencies for PayPal payments
Easy location entering
Auto-suggest based on City, County, Zip
Easy search form template customization
Visual energy efficient and gas emissions plugin
Walkscore plugin integrated
Drag & Drop files/images for multiple upload or reorder
Custom upload fields like plan image company image etc…
Search for properties near your address
Facebook login for lazy guys
Facebook comments social plugin integrated
Agent/admin stars rating and views counter for each property
Extra color examples with demo picker for test
Portal website or full-screen map
Grid or List Layout
What People Are Saying About Real Estate Agency Portal
Extendable with many addons and themes
Download Package
Source JS
Source CSS
Source PHP files
Documentation
Preview example and bootstrap theme examples
Server requirements
PHP version 5.6 or newer
MySQL (4.1+)
Changelog
1.6.0 – 9 November 16
Update to PHP 5.6 as required
offline page support
visual search form builder
Links on slider
some responsive design improvements
address/gps not required
date field type
dropdown multiple field type
is_features for api added
more number format supported for price
profile social links added to property preview
external links improvements
live results counters on sidebar search
search and remove multiple inquiries
user search by email in admin
Update instructions from 1.5.9: extract all files except ”/files” folder and ”/application/config” folder and update database by running updater script: index.php/updater
1.5.9 – 2 July 16
HTTPS issues
PHP7 compatibility improvements
agent description fix
added http://schema.org/LocalBusiness
lite caching feature, for fast loading menu, property, agent pages
recaptcha support
user/admin menu improvements, quick links to edit page
searchable dropdown elements, designed for large number of listings, tested with 100.000
danish flag renamed
custom fields for user profile
map pin markers and amenities icons now can be uploaded via admin
Renamed badget to badge
Hints on property submission form for each field
Updater improvements
Last edit IP saved in database
Update instructions from 1.5.8: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database by running updater script: index.php/updater
1.5.8 – 20 February 16
Admin dashboard map translation parameter support
Single website link for homepage in all menu items
inquiries search in admin, same as user/properties
Favicon icon upload
Watermark upload via admin
Property submission disabled feature via admin
Facebook comments widget translations
Commercial google translate api support
Title and link on slider images
Breadcrumb added
customsearch2 template with price scales example
api improvements for external app support
[FIX] change color fix for some login pages
[FIX] double markers when adding property on frontend
[FIX] Fixes in result items
[FIX] External modules compatibility
[FIX] Missing translation on editproperty
Update instructions from 1.5.7: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database by running updater script: index.php/updater
1.5.7 – 27 December 15
Field hidden on preview page fix
Spanish and Italian language files update, thanks to E.B.
Image cutter and resizer
Pagination on agent profile page
Update instructions from 1.5.6: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database by running updater script: index.php/updater
1.5.6 – 25 October 15
Persian language updated, Thanks to S.G.!
Google translations API updated
Disabled removing last ADMIN
New email your property waiting for activation
New email you property is activated by ADMIN/AGENT
Agent video upload field
“cookie warning for EU” now translatable
Rectangle size depends on zoom index
Google-maps controls reposition
Profile page with pagination
Agent other estates pagination
Dropdown language menu version
Delete multiple properties at once for admin
Upload marker icon/image in bootstrap2-responsive template
Update instructions from 1.5.5: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database by running updater script: index.php/updater
1.5.5 – 6 August 15
map popup as widget
translation files zip export
property inquiry form auto populated for logged users
Czech keyboard fix for numeric inputs
Installation error reporting improvement
Validation improvements for non-existing coordinates
Script news hidden for agent
mail & widgets & templates code editor
Mortgage calculator module support (cost additionally)
admin map fixed location support
all emails now have template files
Numerical filtering range enable in database
Facebook share buttons to top on property preview
Only search header template added
Modules in administration
Beta feature: Searching parameters and pagination added to URL, can be enabled with: $config[‘enable_ajax_url’] = TRUE;
Facebook login updated for api v2.4 support, with adding: $config[‘facebook_api_version’] = ‘2.4’;
check chmod on installation and adding languages
Database problem with special chars in password fixed
Update instructions from 1.5.4: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database by running updater script: index.php/updater
1.5.4 – 25 May15
Serbian language added, thanks to R.M.!
Installation disabled if database is not empty
Updater, disable clicking 2 times on update button
tidy HTML fixer integrated into auto translator
Admin marker issue, double markers fixed
Backup issue can’t be restored fixed
Add notice to recommend cpanel backups as well
Disable FAQ configurator parameter added
Few settings moved from cms_config.php to administration
My messages added for frontend agents/users
Benchmarking tools
Tested and optimized with 10.000 properties
Performance improvements also in backend/admin
Multi-domain support (different domain for different language)
Agent description added on agent profile page
?search=zagreb now filter also map results
Header template can be changed via admin
Footer template can be changed via admin
On translate files, also translate content if same exists
Properties search in admin
Payment can be disabled
Depended fields (Specific inputs hidden for land or other type of property)
Company info added to preview page
Last script news, tips, instructions added to dashboard
Update instructions from 1.5.3: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database by running new updater script: index.php/updater
1.5.3 – 8 March 15
Website link in administration
Configurator improvement
Suffix/Prefix added into property submission forms
Hide copy to other language if only one language is in system
Property preview button in admin page
Reduce register fields configuration
GPS coordinates and Email validation in Settings->Company contact form
Set current language fix in administration
Performance improvements for website with more then 1000 properties
Plan image now showing on non-default languages even if added only for default language…
RTL improvements
Autodetect user language from browser (2 chars) and redirect to language if exists
Required validation added to fields
Paginations ajax url if accessing from google redirected to homepage.
Restricted mode added so only loged user can see page, cms_config.php: // $config[‘enable_restricted_mode’] = TRUE;
estates database structure changes and performance improvements
Map now limited to 100 properties for default preview
Auto-update script for database update
Additional sitemap data like lastmod and changefreq
Rectangle search added to map view
Agent estates on property preview limited to 6
Language tabs always on top when edit property in administration
Improvement on file uploading and deleting validation
Walkscore plugin added to property page
Croatian translations updated
Frequently asked questions added to administration directly
Update instructions from 1.5.2: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database by running new updater script: index.php/updater
1.5.2 BETA – 29 December 14
Carousel images improvement for property view, vertical centered, thanks to I.R.
Hide category feature on property preview page, thanks to Y.P.
Translation feature for pages and estate content, thanks to S.L.
Translation and copy to other lang feature added to frontend submission
More translation improvements on file translations
Additional color theme, WHITE
Upload field type for custom uplaods and property plan image uploading
All button added to frontend search, thanks to M.V.
Energy efficient plugin, thanks to S.L. and P.B.
New configuration possibilities: // $config[‘contrast_captcha_enabled’] = TRUE; // $config[‘logout_redirection_uri’] = ’’;
Configurator check captcha folder for writing permissions
var scrollWheelEnabled = false; configuration added to head.php
Agent / User search in administration, Thanks to V.S.
ID added to property preview page
HTML email formating example added
Field “I Agree To The Terms & Conditions” added when submitting property on frontend, thanks to V.S.
Auto created marker when adding new property, simplified gps entering…
Confirmation email on registration
Print button adden on print preview
Marker popup on click or mouseover, configurable, default changed to click…
RSS feature, http://real-estate.iwinter.com.hr/index.php/api/rss/en
JSON export API feature, http://real-estate.iwinter.com.hr/index.php/api/json/en
[FIX] Frontend user profile image ordering
[FIX] Frontend user my properties title link
[FIX] Backend tables responsive on mobile devices
[FIX] Autocomplete disabled on smart search input field
[FIX] MyMemory translation api
Update instructions from 1.5.1: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.5.2.sql.
1.5.1 – 8 October 14
Facebook comments on property
Featured icon
Ownership filed added
Views counter on property details and results
Rent inc., Rent excl. prices field added
Reviews pro (agent & admin) and Additional module support for user reviews
Persian language added (For Iran, Afganistan, Tajikistan), Thanks to Amin T.
Russian translation updated, Thanks to YRIX
Arabic language added, Thanks to Bassam A.
RTL improvements, Thanks to Amin T.
DB update debug table
Populated enquire form fields based on session
Validation on languages improved, show language
Edit profile for frontend users
Showroom on sitemap improvement
Fix, Captcha sometime returns wrong captcha
Fix, Few small fixes, for rent prices on homepage
Update instructions from 1.5.0: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.5.1.sql.
Please don’t forget to make a backup!
1.5.0 – 16 August 14
Google AdSense support added in Admin, earn additional money with your website
PayPal payment for featured, earn more extra money!
Facebook login
Carousel slider improvement with thumbnail image
Backup module added, for images and database
Inovative results filtering on homepage
MyMemory and Google free translation API integrated for translation language files
Category ‘Distances from’ examples added (Beach, Train, Metro, Bus, Pharmacies, Bakery, Restourant, Coffee shop…)
Amenities categorized example to Indoor/Outdoor amenities
Field Floor added as new example for option
Currency and other fields now can be prefixed also… (for pounds etc…)
Print version added on view property
Additional Agents listing page template example
Cash option / Withdrawal payment added, after payment admin can activate property manually
Agencies example added to homepage, bottom
Main menu beginner version with more left menu items in administration
icons added in edit property for frontend and backend
Prices for featured listing and activation available on registration/login page
Added flag icon in frontend languages menu
On one language pages, menu is now hidden
Custom map and black design added to demo as default
Latest articles/news/blog posts added to homepage example
Add prefix for options
Map added on slideshow bottom
Icons added to results listing
page_featured.php prices example added
Validation for dropdown option added (same number of values for each language)
Logo in footer definition moved from css to HTML , so easily can be detected and changed…
Watermark on ads and slideshow module removed and disabled size restrictions
Profile and Property page, now agents estates are ordered from newest…
Copy to all languages feature improvements (Copy numeric and empty values)
cms_config.php new parameter, $config[‘disable_responsive’] = TRUE;
Update instructions from 1.4.9: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.5.0.sql. Additional, you should copy facebook.php to your ?/application/config? folder
Please don’t forget to make a backup!
1.4.9 – 19 July 14
Hotfixed, collapse menu added
PayPal payment feature for property/listing activation, monetize your website now!
Captcha on frontend forms
Agent profile page
Forget password feature
Order by price in results
Private pages, for logged users only, Thanks to S. Lopez!
Agents pagination and search feature included
Listing expiry date added
Purchase code checker added to configurator script
Featured properties now have border and colored address in results
Articles/News/Blog SEO uri-s
Gallery added to ‘page_homepage.php’
File repository added to property view
Admin search, show not_activated warning now
Properties on same address gmap view improvement
Menu item without link feature added, just enter ’#’ into keywords of wanted page
Upload images watermark issue with small images fixed
Quote in title characted issue fixed for new added properties
Non-responsive template version removed
Few minor fixes and improvements included
cms_config.php new parameter, $config[‘cookie_warning_enabled’] = TRUE; // For EU countries
cms_config.php new parameter, $config[‘custom_map_center’] = ‘27.175015, 78.042155’; // For fixed map center
cms_config.php new parameter, $config[‘show_not_available_amenities’] = TRUE;
cms_config.php new parameter, $config[‘all_results_default’] = TRUE; // To show all results on homepage by default, no purpose selected
cms_config.php new parameter, $config[‘reactivation_enabled’] = TRUE; // Property must be activated again after changes
Update instructions from 1.4.8: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.9.sql.
Because of purchase code checker, you must add following to your ‘applicationconfigcms_config.php’:
$config['codecanyon_username'] = 'your_codecanyon_username'; $config['codecanyon_code'] = 'your_purchase_code';
Where to find purchase code?
If you using customized template without captcha, then you need add $config[‘captcha_disabled’] = true; in your ‘applicationconfigcms_config.php’
1.4.8 – 21 May 14
Frontend listings change order from publish_date ASC to DESC
My location button feature on Google Map
Dutch translation added, Thanks to Floris w.!
Add embed video field added
seo-godaddy.htaccess added
robots.txt example added
Customization on purple theme example
Custom Map translation added
URL transitions for few new languages added: Czech, Mongolian, Ukrainian, Belorussian, Russian, Thanks to Dima!
Hidden pages, not visible in menu
Fixed, Zoom images on iPad mini
Fixed, Homepage slideshow pagination
Fixed, address characters on contact page error cause map crash
Fixed, Agent can become admin
Fixed, pagination sometimes show plain JSON
Update instructions from 1.4.7: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.8.sql.
1.4.7 – 21 April 14 (Hotfixed)
Additional Color variation theme examples (Orange, Purple, Black) with demo preview
Articles page type added with template example
Custom map style example added in, ‘templatesbootstrap2-responsivecomponentshead.php’ —More custom maps can be found on http://snazzymaps.com
Clickable cluster event added to cluster config
RTL test added to live demo, http://iwinter.com.hr/real-estate/index.php?test=rtl
seo-v2.htaccess mod_rewrite configuration added
When all options are not translated, dropdown’s doesn’t work, fiexd
Email export file spaced in Windows notepad, fixed
Hotfixed:
Agent interface, show just agent properties
Blank screen on some localhost installations
Update SQL script issue
Update instructions from 1.4.6: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.7.sql.
1.4.6 – 6 April 14
3 Color variations theme examples (Red, Green, Blue) with demo preview —If you want to specify color, in ‘application/config/cms_config.php’ add line $config[‘color’] = ‘red’;
Beta frontend RTL support (If someone knows well RTL, please let me know)
Template parameter added is_rtl…/is_rtl for RTL customization in template
Search query added, example: http://iwinter.com.hr/real-estate/index.php?search=zagreb
URI characters transformation, added for turkish language.
Featured properties template example added
Hidden amenities category added
Property options values_correction validation added, when user enter spaces
Language admin translation fixed for $ character
Update instructions from 1.4.5: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.6.sql.
1.4.5 – 23 March 14
Clustering, Map InfoWindow AutoPan, Draggable now configurable in responsive theme
Login link added
SMTP configuration added to ‘applicationlibrariesMY_Email.php’
configuration to change URI ‘property’->’listing’: – Add $config[‘listing_uri’] = ‘listing’; to cms_config.php
External link supported now, you just need to add page to menu and your link with ‘http’ included to keywords
Featured properties listing on top of results now
Footer and Header template saparated
DateTimePicker translation added
GPS data format validation added
Rename ‘Visible in frontend’ => ‘Visible in frontend submission’.
Simplify badget translations, just images in badgets folder
Performance issue on edit property when you have >=100 options on >=3 languages improved…
Generate_sitemap fix and performance improvements…
Enquire message length limitation removed
Opera Browser responsive menu fix
Login failure in rare situations (after 2 hour of inactivity) fixed
Update instructions from 1.4.4: extract all files except ?/files? folder and ?/application/config? folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.5.sql. There are few new fields in frontend translation files, so you need to translate this new fields for your language.
1.4.4 – 9 March 14
German language pack added. Thanks to Sassun Mirzakhanyan!
“Changes are saved” message added when saving properties/pages in admin and frontend.
Email alerts on new not actiated property from user
Facebook/social code embed in admin
Selected property change icon to red color
Homepage show first option purpose results, and not “Sale” based on template name
Watermark support for specific images format
Update instructions from 1.4.3: extract all files except ”/files” folder and ”/application/config” folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.4.sql
1.4.3 – 3 March 14
Responsive Frontend demo template example!
Language file translation feature now available in admin, no more file editing!
Fullscreen Map template example
Activate/deactivate all user properties feature in administration
Tag estate_data_icon added for property template
InfoWindow added to property map, with GPS and address
Route suggestion added to property
Marker icon based by property type in Admin
Noreply email added to settings
Frontend zoom parameter added to settings
Admin estates and users pagination, default 20 per page
Frontend results loading indicator, and effect slideEffect removed
Tag featured_properties…/featured_properties added to template
CSS icons height fix in general amenities
General amenities and property title in results, fixed height defined in CSS
Options problems with order fixed
Hotfix:
Turkish language files added, thanks to Turan Ta?k?n Sabah!
Hidden languages not visible in sitemap (Please save any page, just for sitemap update)
Gallery image blueimp script updated to new version
Few iOS7 Safari issue fixed
Spanish translation added, Thanks to Luis Eduardo Miralles!
Map just remove markers if no results on search, no change of location.
Slideshow responsive improvement
Responsive menu improvement for small devices
Available languages listing when adding new language
Few mini-fixes/mini-improvements in frontend and backend
hash function detection improvements fur server that doesn’t support hash function
Language edit limitation to hide all languages (One must always be visible)
Language edit fix for unique language detection
Russian language pack added, Thanks toAndrew!
Search properties near wanted addres
Update instructions from 1.4.2: extract all files except ”/files” folder and ”/application/config” folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.3.sql
1.4.2 – 24 February 14
Map Location Marker for property type added
Auto-suggest for County, City, Zip (List only available)
Refresh map markers based on search results, also can be disabled ( var mapRefresh = false; )
Icon examples added to property amenities
Auto-resize normal-size images to 1024×768
Sitemap generator improvements
Improvement in auto-tab selection by title ( Sale and Rent example provided, user asks for Newlunches )
Disable auto-drag on map example, in customsearch template file
Links Back to web-page / admin-interface
Hard lock for options implemented, for elements that should not be removed
has_page_images…/has_page_images integrated to template
Upload progressbar css improvement
GoDaddy fix for delete images
Translation for email subject added
Few mini-bugs fixed and mini-improvements in backend and frontend
For amenities if tag exists, has_option_#…/has_option_#
Update instructions from 1.4.1: extract all files except ”/files” folder and ”/application/config” folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.2.sql
1.4.1 – 18 February 14
Auto-search when click on property purpose (Rent, Sale, …), example added to page_customsearch.php
Option locked feature (For options that requiring template customisations)
Option Frontend visible feature (For options that will be hidden on frontend submission)
Button for copy data (dropdown, checkboxes) to other languages if you want this
Server that doesn’t support HTTP DELETE method issues, fixed
“application” and “system” folder outside default path now supported, for security
Database port added to configurator
Contact form ‘settings’ issue fixed
Add language, validation-improvement
Few bug fixed and mini-improvements in backend, frontend and sitemap
Update instructions from 1.4: extract all files except ”/files” folder and ”/application/config” folder and update database, in phpmyadmin select database and import update-1.4.1.sql.
1.4 – 12 February 14
Drop-down search-field for category General amenities template example, page_customsearch.php
Search tab manipulation-example added to template example, page_customsearch.php
Export user list feature in administration, can be used for insert/import to newslatter script like MailChimp
Added template parameters (last_estates_num, array last_estates) and template example to show last 3 added
properties, page_customsearch.php
“short_open_tag=On” is no longer necessary
Update from jQuery-1.8.2 to jQuery-1.8.3, fix frontend issues in Opera Browser.
Page visual editor height in “code mode” issue fixed
Few bugs in backend and frontend fixed, when adding new property and no agent is selected, changing language in property, language files missing errors
Configurator improvements, check for writable files/folders
Update instructions from 1.3: extract all files except ”/files” folder and ”/application/config” folder.
1.3 – 8 February 14
URI optimization, from “frontend/property/” to “property/“
Logo link url issue fixed
Hidden date-range in admin for non-rental properties now is empty
not hidden, because it can be usable if admin/agent want to edit enquire->change property that can be rentable
Zip code example added, searchable
Search filter improvements for numerical values, examples for Max price, Min price, Bathrooms, Bedrooms
No more jQuery customization needed for new standard search fields, just add it to form by HTML
Checkbox support and example added to search-form
Added template parameters (options_values_li_#)
Admin dashboard design improvements for non-validated properties label
Admin map not showing all properties error fixed
Search form HTML template moved to components
Android 4.x HTML fix for h2 tags
General amenities that is not available show with X, instead of hidden
Frontend JS optimisations
1.2 – 3 February 14
Email validation for Enquire form in frontend property
Language problem with url fixed
#.Uu4ba_tklH8 removed from URL in theme example
Google maps translated based on lang_code added to theme example
IE8 issue with frontend map fixed
Database Host and Database Driver added to configurator
1.1 ? 28 January 14
Property Sale and Rent in same time example
Option suffix field, usage example for currency, area etc…
Added template parameters for suffix (options_suffix_#, category_options_#->option_suffix, has_option_#, is_purpose_rent, is_purpose_sale)
Example with more currency used, price for rent and sale
Different price for sale and rent
New, sold, action badget added to theme example
Configurator security fixes (Old passwords after update will not work!)
For rental purpose, check_in / check_out date fields in Enquire form.
Energy efficiency field added to theme example
Front end submition with activate feature for admin (alpha version)
1.0 ? 17 January 14
Initial release
Thanks!
If you enjoy this application please rate & share it! If you are rating it with less than 5 stars please drop me a mail why it didn?t achieve a full score and what could be improved in your opinion.
Counter
Voir sur Codecanyon
Real Estate Agency Portal
0 notes
Photo

WHAT IS CHMOD AND CHMOD CALCULATOR
Operating systems like those of Linux and Unix have a set of rules. They determine file access priorities. It rules out who can access a particular file and how freely they can access it. Such commands or access rules are known as file permissions. The command that can reset the file permissions is called chmod. It is short for ‘change mode.’ It is a type of command computing and also a system call for Linux and Unix-like systems. It changes file permissions to file objects or directories. They can be prioritized between the user, group, and others.
Try right now: http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#Chmod Command Calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#convert for free#chmod calculator free#Online Calculator#chmod calculator online#calculator#Online free Calculator#chmod number calculator#actual chmod calculator#linux permissions#linux permissions calculator#chmod change permissions#chmod recursive directories and files#chmod recursive mac#chmod recursive directory
0 notes
Text
CHMOD CALCULATOR- THE NEW TREND! | OnvertForFree

Why Chose Chmod Calculator?
Chmod Calculator is a tool for finding the numeric or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux server. It has three compulsory columns
1) Owner
2) Group
3) Other
Also, it has three modes:
1) Read
2) Write
3) Execute.
Another optional column is superuser. This column denotes the special setuid, setgid and sticky flags. Chmod Calculator possesses two modes of usage, one is symbolic and the other absolute. Symbolic allows you to remove, add, or set a particular mode while having other modes unchanged. This is achieved by using operators and letters. But, in absolute mode, you can overrule the existing permission with a new value. This new value is a three digit number. Chmod Calculator 4 digits allowed four-digit codes, as well.
use right now : http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
Benefits OF CHMOD CALCULATOR
Chmod Calculator generates the code which is readable, writeable and executable by everyone. Generally, Linux permission users face problems such as not being able to upload a file or modify a document due to not getting permissions. To overcome this, the Webmaster would need to change the Chmod code. Unix systems have a file control mechanism which decides who can access a file or a folder and what they can do to it. Fine control mechanism has two parts: "classes" and "permissions" which determine who can access the file and how respectively. Unix permission users can also use this. Hence, obtain the online chmod calc today!
How to use CHMOD CALCULATOR
The Chmod Calculator has three classes, namely, owner, group and other. Owner is the creator of the file. Group, whereas, contains a bunch of users sharing similar permissions and user privileges. Other, however, symbolizes the general public. This calculator has three permissions which go as read, write and execute. Read indicates the action of merely viewing the file and being unable to modify it. When applied to a folder, one can't delete or modify any files in it, but they can view it. In the write, you can edit or modify files and for the folder, remove or add files to it. Execute is mostly accessed when there is a need to run a file. Combining the classes and permissions will allow you to control who can access the data and what they can do to it. Chmod examples are various in numbers and can be used according to need. Chmod Calc is, therefore, a widely used calculator. Likewise, Chmod Mode Calculator allows you to access Linux permission calculators. Chmod Calc can also aid Unix Permissions Calculators!
Why OPT FOR CHOMAD CALCULATOR
Chmod Calculator makes your life as a webmaster easier. Go use it now to make it easier for you to read, write and execute.
CONVERT FOR FREE- THE BEST SITE FOR RELIABLE CHOMAD CALCULATORS!
This site can be used to convert or calculate almost anything. Finding a specific conversion is attainable with its on-site search. Easy to use on all platforms and browsers with a simple and straightforward interface, online conversion is a mobile-friendly site. It has conversions sorted in categories and alphabetical order. Helpful in everything from calculating the exchange rate of currency to finding the day of a specific date to figuring the Chmod code and more are the uses of this site. It is a useful site which is easy to use for everyone.
use right now : http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#linux chmod calculator#Convert For free#Online Calculator#chmod calculator online#chmod permissions#unix permissions chart#chmod number calculator
0 notes
Text
CHANGE FILE PERMISSIONS EASILY WITH ONLINE CHMOD CALCULATOR | Convert For Free

WHAT IS CHMOD AND CHMOD CALCULATOR
Operating systems like those of Linux and Unix have a set of rules. They determine file access priorities. It rules out who can access a particular file and how freely they can access it. Such commands or access rules are known as file permissions. The command that can reset the file permissions is called chmod. It is short for ‘change mode.’ It is a type of command computing and also a system call for Linux and Unix-like systems. It changes file permissions to file objects or directories. They can be prioritized between the user, group, and others.
User, group and others are three classes of users. The owner of the file objects is known as the ‘user.’ The group means the members of the group owning that file. Others or public are anyone other than the two categories which can view the file.
Try right now
Convert for free chmod calculator is a Linux permissions calculator. It is a chmod calculator four digits and is trusted by many. It generates values in octal or symbolic figures. The codes change file permissions. Octal characters are numbers, and symbolic or alphanumeric includes both letters and digits. The chmod mode calculator calculates octal or alphanumeric codes for users. The generated codes can then be applied to relevant files. Chmod calc provides an easy solution to users online, free of cost to change file permissions.
HOW TO USE THE CHMOD CALCULATOR 4 DIGIT
Convert for free has an easy, simple to use chmod calculator. Generating codes is quick. Here is a guide on how to use this:
● It has three mandatory formats
○ They include read, write and execute.
● It has three columns. a fourth special addition being a Unix permissions calculator as well
○ They are the owner, group, and others. The special feature is a superuser column. It helps to point out the stupid, setgid, and sticky flags. It is a unique feature.
● The chmod calculator has two modes provided to all users worldwide.
○ They are
■ Symbolic mode: It allows users to utilize operators and alphabets. Setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. It meanwhile also enable them to leave remaining modes unchanged. The symbolic mode allows users to add, delete or set particular modes.
■ Absolute mode: it kets all users to override the current file permissions. And re-write it completely. It lets users calculate a new three-digit unit.
CHMOD EXAMPLE: WHY CHMOD CALCULATOR IS THE BEST
A few common octal and alphanumeric chmod examples are:
664 or -rw-r--r-- web content and pictures viewed by surfers.
666 or -rw-rw-rw- This symbolizes the log files or pages.
755 or - rwxr-xr-x perl scripts to make them executable.
One of the many benefits of this chmod calculator is that it is free of cost and available online. To all of its users, it has helped make file permissions easier to change. It is open to anyone that needs it online. It is quick to use and generates codes in seconds. Get coding with chmod calculator today!
Convert For Free- Best Solution For Chmod Calculator
This website provides an easy-to-use interference. Make your task a piece of cake by visiting Convert For Free! Access the best Chmod Calculator in just a few clicks!
Website: http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod mode calculator#chmod calc#linux chmod calculator#chmod calculator free#Convert For free#unix chmod calculator#chmod code generator#chmod number calculator#chmod calculator online#chmod command calculator#unix permissions chart#chmod calculator 4 digit#use chmod calculator
0 notes
Text
Online Chmod Calculator | Free & Easy To Use Converter

CHMOD Calculator is a free that lets you check boxes which tell you what number to use to CHMOD a file for access.
Try it right now: http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#Chmod Command Calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#convert#convert for free#converter#Online Calculator#Online#chmod calculator online#Online free Calculator#Smart Conversion
0 notes
Photo

Convert for free chmod calculator is a Linux permissions calculator. It is a chmod calculator four digits and is trusted by many. It generates values in octal or symbolic figures. The codes change file permissions. Octal characters are numbers, and symbolic or alphanumeric includes both letters and digits. The chmod mode calculator calculates octal or alphanumeric codes for users. The generated codes can then be applied to relevant files. Chmod calc provides an easy solution to users online, free of cost to change file permissions.
URL: http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#linux chmod calculator#Convert For free#Online Calculator#chmod calculator free#chmod calculator 4 digit#actual chmod calculator#easy to use chmod calculator#chmod calculator online#try chmod calculator#digital chmod calculator#chmod permissions
0 notes
Text
CHANGE FILE PERMISSIONS EASILY WITH ONLINE CHMOD CALCULATOR

WHAT IS CHMOD AND CHMOD CALCULATOR
Operating systems like those of Linux and Unix have a set of rules. They determine file access priorities. It rules out who can access a particular file and how freely they can access it. Such commands or access rules are known as file permissions. The command that can reset the file permissions is called chmod. It is short for ‘change mode.’ It is a type of command computing and also a system call for Linux and Unix-like systems. It changes file permissions to file objects or directories. They can be prioritized between the user, group, and others.
User, group and others are three classes of users. The owner of the file objects is known as the ‘user.’ The group means the members of the group owning that file. Others or public are anyone other than the two categories which can view the file.
Try for free http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
Convert for free chmod calculator is a Linux permissions calculator. It is a chmod calculator four digits and is trusted by many. It generates values in octal or symbolic figures. The codes change file permissions. Octal characters are numbers, and symbolic or alphanumeric includes both letters and digits. The chmod mode calculator calculates octal or alphanumeric codes for users. The generated codes can then be applied to relevant files. Chmod calc provides an easy solution to users online, free of cost to change file permissions.
HOW TO USE THE CHMOD CALCULATOR 4 DIGIT
Convert for free has an easy, simple to use chmod calculator. Generating codes is quick. Here is a guide on how to use this:
● It has three mandatory formats
○ They include read, write and execute.
● It has three columns. a fourth special addition being a Unix permissions calculator as well
○ They are owner, group, and others. The special feature is a superuser column. It helps to point out the setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. It is a unique feature.
● The chmod calculator has two modes provided to all users worldwide.
○ They are
■ Symbolic mode: It allows users to utilize operators and alphabets. Setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. It meanwhile also enable them to leave remaining modes unchanged. The symbolic mode allows users to add, delete or set particular modes.
■ Absolute mode: it kets all users to override the current file permissions. And re-write it completely. It lets users calculate a new three-digit unit.
CHMOD EXAMPLE: WHY CHMOD CALCULATOR IS THE BEST
A few common octal and alphanumeric chmod examples are:
664 or -rw-r--r-- web content and pictures viewed by surfers.
666 or -rw-rw-rw- This symbolizes the log files or pages.
755 or - rwxr-xr-x perl scripts to make them executable.
One of the many benefits of this chmod calculator is that it is free of cost and available online. To all of its users, it has helped make file permissions easier to change. It is open to anyone that needs it online. It is quick to use and generates codes in seconds. Get coding with chmod calculator today!
Convert For Free- Best Solution For Chmod Calculator
This website provides an easy-to-use interference. Make your task a piece of cake by visiting Convert For Free! Access the best Chmod Calculator in just a few clicks!
Try for free http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calculator free#Convert For free#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#linux chmod calculator
0 notes
Photo

CHMOD Calculator is a free that lets you check boxes which tell you what number to use to CHMOD a file for access. Try it right now.
URL: http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#linux chmod calculator#chmod calculator free#Convert For free#Online Calculator#Image#Text#Link
0 notes
Photo

CHMOD Calculator is a free that lets you check boxes which tell you what number to use to CHMOD a file for access. Try today.
URL: http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#linux chmod calculator#Convert For free#use chmod calculator#chmod calculator free#chmod code generator#chmod calculator 4 digit#actual chmod calculator
0 notes
Photo

Online Chmod Calculator | Free & Easy To Use Converter
CHMOD Calculator is a free that lets you check boxes which tell you what number to use to CHMOD a file for access. Try it right now.
URL: http://www.convertforfree.com/chmod-calculator/
#chmod calculator#free chmod calculator#chmod calc#chmod mode calculator#linux chmod calculator#unix chmod calculator#use chmod calculator#chmod calculator free#Convert For free#chmod code generator#chmod calculator 4 digit#actual chmod calculator#easy to use chmod calculator
0 notes