#fossil from France
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

Fossil Foraminifera Nummulites laevigatus – Eocene Cuisian Stage, Aisne Valley France – Genuine with COA
Presenting an exquisite fossil specimen of the foraminifera Nummulites laevigatus, a prehistoric marine microorganism from the Eocene epoch. This fossil dates specifically to the Cuisian stage and was discovered in the Aisne Valley near Soissons, France – an area renowned for its well-preserved Paleogene fossils.
Nummulites are large, lenticular foraminifera that thrived in warm shallow seas around 50 million years ago. Their intricate calcareous shells, composed of numerous chambers, are highly prized by both amateur and professional collectors for their scientific importance and distinctive, coin-like appearance (from which the genus gets its name, derived from "nummulus," Latin for "little coin").
Item Details:
Species: Nummulites laevigatus (sometimes referred to as laengryus)
Age: Eocene Epoch, Cuisian stage (~50 million years old)
Location Found: Aisne Valley, Soissons, France
Condition: 100% genuine fossil specimen with exceptional preservation
Scale: Scale cube in photo is 1cm – please refer to image for full size
Photography: What you see is what you get – the exact specimen pictured is the one you will receive
Packaging: Secure and protective packaging
This fossil is an excellent addition to any collection of microfossils or paleontological specimens and is ideal for educational use, display, or gifting. It comes with a Certificate of Authenticity to verify its provenance and authenticity.
We take pride in selecting only high-quality, well-preserved fossils. Each item is handpicked to ensure it meets our rigorous standards.
#Nummulites fossil#foraminifera fossil#Eocene fossil#Cuisian stage#Aisne Valley fossil#Soissons fossil#French fossil#microfossil#marine fossil#fossil specimen#genuine fossil#fossil with certificate#fossil from France#fossil for collection#paleontology#natural history
0 notes
Text

#protect & serve#business#political corruption#politician#corrupt politicians#politics#also all politicians who received campaign contributions from fossil fuel industry in exchange for anti climate policy#politicians#rioters set fire to town hall & clash with cops as protests rage on across france after macron forced pension reform#kill all cops#tw cops#corrupt cops#culture of corruption#all cops are bastards#defund the cops#fuck cops#cops#stop cop city#cop city#copcity#cop#kkkops#kkkop#copsandklangohandinhand#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#neoliberal capitalism
4 notes
·
View notes
Text


precious assemblage
#with sea glass#earthenware from various countries uk cyprus spain n france#stone from aphrodite’s beach#fossils#lil bit of painted pottery i found in a stream in birmingham#soooo many stones with druzy crystals#and lots of pretty shells#tu es à moi
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo
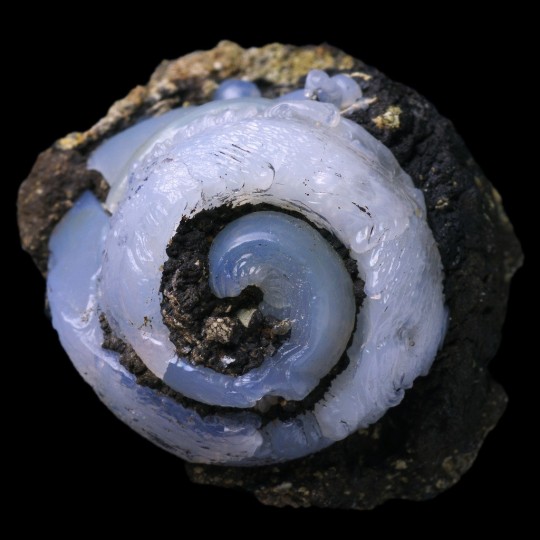
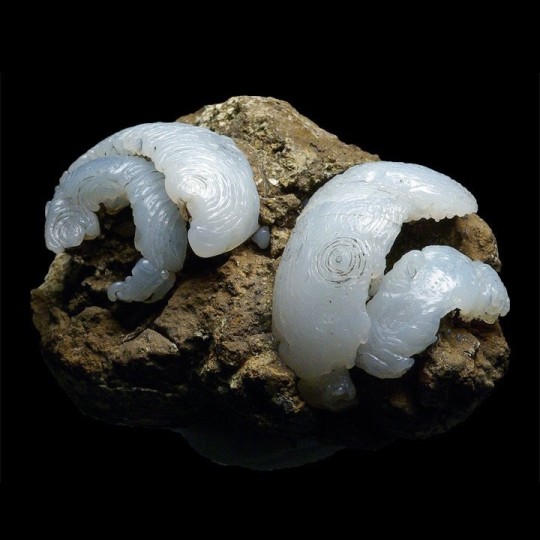
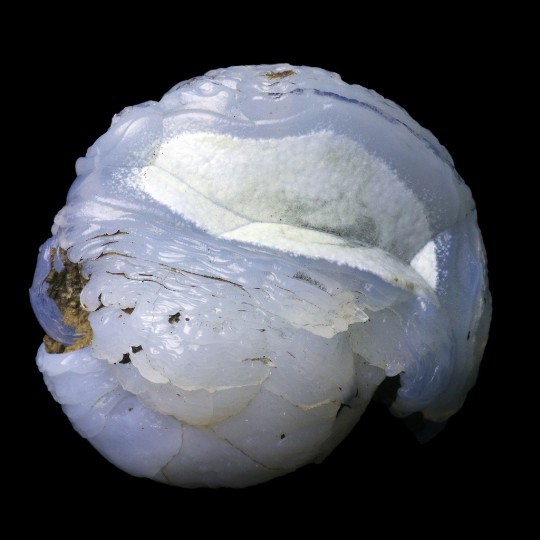
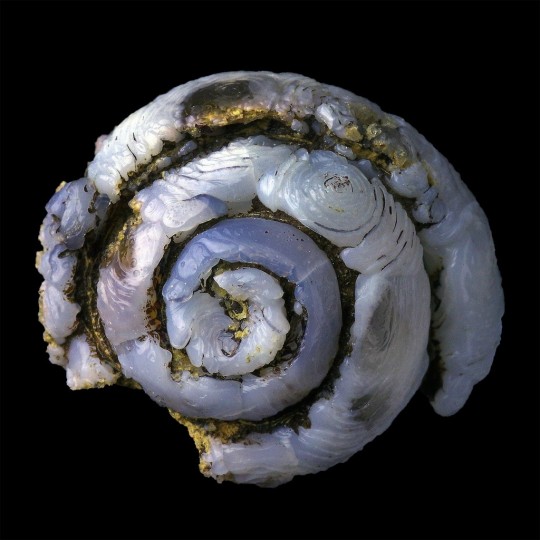




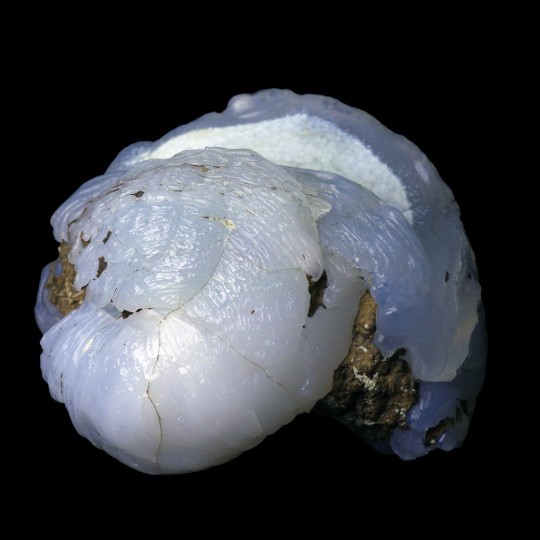


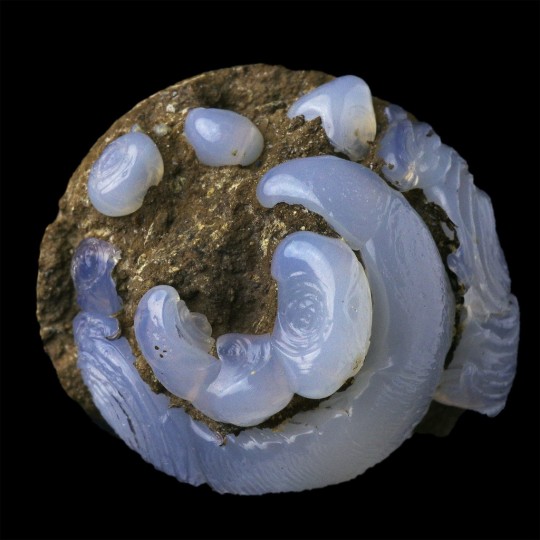


Epigenised (Opal-CT, Lussatite) Helix Ramondi snail fossil, from Dallet, Puy-De-Dôme, France.
#opal-ct#lussatite#epigenised#epigenized#snail#snails#helix ramondi#gastropod#gastropods#animal#animals#fossil#fossils#fossilised#fossilized#ancient#dallet#puy-de-dôme#puy-de-dome#france
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
In 2022, something happened in Britain for the first time in 6,000 years. Deep in the Kent countryside, a wild European bison calf was born as part of the Wilder Blean rewilding project. The last time wild European bison roamed Britain’s landscapes was after the last Ice Age, some 10,000 years ago, so it’s no wonder the calf’s arrival caused a stir. European bison were once a common sight across most of Europe. As the largest herbivore to roam the continent, European bison could be found from France all the way to the tip of the Black Sea in the Ukraine. The fossil record tells us that European bison have been roving the continent since the end of the Paleolithic Ice Age, with the earliest fossils dating back to 9,000 BC.
Now, bison are bouncing back. They have experienced a 166-fold increase in their population in the last 50 years. And these rates of return are not solely the reserve of the mighty bison. Other wild European mammals are also making a roaring comeback, and the speed of their resurgence suggests that wider, rapid natural regeneration is possible with multiple ecological, and therefore human benefits.

From 1960 to 2016, Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber) populations have ballooned 167-fold, from just a few thousand at the start of the 20th century to over 1.2 million wild beavers today. Grey seal populations have also grown by 6,273 percent and the population of Alpine ibex has risen by 417 percent. Eurasian badger populations have doubled, while Eurasian otter populations have tripled.
While these impressive rates of recovery are not reflected across all of Europe’s 250 wild mammal species, they do provide some evidence-based hope that wild mammals can once again flourish across Europe’s diverse and varied landscapes with the right support and policies in place.
The big picture
... Over the last 50 years the fate of some wild mammals across Europe has shifted. Some populations have experienced a rapid and dramatic increase over the last half century, reversing millenia of decline and offering fresh hope that nature can recover – if it’s given the chance.
Brown bear numbers have risen by an average of 44 percent between 1960 and 2016, while the Iberian lynx has seen its population grow by 252 percent. Humpback whales have seen their numbers rise by 37 percent between 1986 to 2016, while the pine marten – a natural predator to the invasive grey squirrel – has seen its population grow by 21 percent from 1986 to 2016. Some reptile species, such as the loggerhead turtle, have seen its numbers grow by 68 percent over the last 40 years.
The most impressive bounce backs, however, are among the beaver and bison – two species that play vital roles within ecosystems. Both beaver and bison populations have seen 167-fold increases over the last 50 years. These mammals help support a rich mosaic of habitats and biodiversity. Wild bison, for instance, trample and wallow in the soil and sand to create niche habitats for plants, insects and lizards, while also playing an important role in the dispersal of seeds.
Context and background
The impressive recovery rates over the past 50 years have been possible due to a shifting cultural and economic context. Alongside this, there is a growing scientific consensus of the importance of small and large mammals for sustaining biodiversity and helping ecosystems flourish. The sheer diversity of mammals, both in terms of their morphology and their roles within ecosystems, is testimony to the functions they perform. From the tiny bumblebee bat, which weighs just two grams, to behemoth blue whales, weighing in at 150,000 kilograms, mammals really do come in all shapes and sizes.

Wild mammals play a variety of leading roles within an ecosystem, from dispersing seeds, pollinating plants and regulating insect populations, to reducing disease transmission and creating niche habitats for other species. The European bison reintroduced to Kent in the UK have already started clearing paths through undergrowth, ripping the bark off trees, and wallowing around in the mud to make space for seeds and other habitats – natural processes that humans would struggle to replicate. Bison and other large herbivores are often labelled ‘ecosystem engineers’ for this very reason – they shape and manage the land they reside on.
Some species of mammals – such as the magical beaver – are considered keystone species due to their ability to shape the ecosystems around them, creating entirely new habitats through building dams where fish, birds and all manner of species can thrive. Other mammals, like bats, act as indicators of healthy and functioning ecosystems. Between 1974 and 2016, Geoffroy’s bat populations have increased 53-fold across Europe.
Wild mammals also have a role to play in reducing the damage and destruction wrought by climate breakdown. In the temperate climate of Europe, large mammals have been proven to reduce the risk of forest and wildfires by creating gaps in vegetation through grazing and trampling. In the summer of 2022, wildfires ravaged Europe, burning the second-largest area on record. As global temperatures continue to rise, wildfires will increase in their frequency and severity. Bolstering the population of large mammals could provide a useful tool in the fight against fires alongside deep and immediate cuts to emissions...
What’s more, the grazing of wild mammals can also help retain the carbon stability of soil over long periods of time. Soil contains vast amounts of carbon – more than all plants and the atmosphere combined – which makes ensuring its stability important for both climate efforts and environmental conservation. Mammals like the alpine ibex, which have seen their numbers grow by 417 percent from 1975 to 2016, are highly effective at stabilising soil carbon within grazing ecosystems.
-via Rapid Transition Alliance, March 29, 2023
#beaver#bison#mammal#ecosystem#ecology#endangered species#europe#united kingdom#kent#wildfires#rewilding#ecosystem restoration#good news#hope#hope posting
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
After watching a random celebrity “What’s in Your Bag?” video, I got curious (or maybe just nosy, lol) and started asking everyone the same question. So, what’s in your bag? Or, if you’re not the type to carry one, what’s in your pockets?
Hi anon ^^
Thank you so much for your question, it's actually a pretty funny one! 🥳 Alright, I'm going to try to satisfy your curiosity by answering in detail.
First, my bag. At the moment, I often use one of these two:

1) Bag from Beara Beara London (Model: Lila)
2) Suede bag found on Vinted for 10€
And now, let's see what's inside the bag. I just emptied my bag on the floor and, as you can see, there's everything and anything. Here's a full picture and some close-ups:



1) Sunglasses. I think they are Prada knock-offs bought on eBay about 10-15 years ago maybe.
2) Hydroalcoholic gel, highly needed in Paris. It's hard to keep your hands clean in this city. 😶
3) First aid kit because I am THAT clumsy and wearing Dr Martens shoes even with big socks has a price (*ouch*)
4) An old pencil and a Funko Harley Queen ballpoint pen (I used it the other day at the bank to sign some documents, you should have seen the face of my banker 👁👄👁)
5) A small personalized case with the initials "P.M" engraved on it, for my lipstick (Rouge Baiser, L'Authentique Le Rouge n°405, if you are interested)
6) House keys with key rings that have witnessed WW2, it seems.
7) Medicine in case of vertigo episodes (Tanganil), we never know 😶
8) A cute brush hidden inside some compact mirror (from Pylones)
9) Wired earphones for my phone (I hate wireless earpods, I prefer the good old wired earphones)
10) A small bottle of perfume, personalized with the monogram "P.M", because I am that extra 🎀
11) My Navigo card (Paris transportation card) inside a Harry Potter card holder found on Aliexpress pour 4€ 🤓
12) Two chestnuts I found at a park last October-November. I still have them in my bag, I have no idea why.
13) Some old receipt from Monoprix (I bought a bottle of Coca Zero, apparently)
14) A card from a Dyptique shop with some perfume sprayed on it. I hate it, I've never understood the whole craze around this brand.
15) My phone, with a home made Liam and Noel Gallagher from Oasis phone case ✌
16) My Karl Lagerfeld wallet featuring Kaaaaarl and Choupette, France's most famous cat.

17) ANNNNNNND I was about to forget the most important thing when I took the picture above, my iPod Touch because yes, Little Miss Fossile Me is still listening to music on her iPod touch. No Apple music, no Spotify, like men, we ride at dawn, like in 2010. 🤓🤘
No book! I don't read in the means of transportation, it gives me headaches so I practically never bring a book or a Kindle with me.
Oh but wait, that's not my only bag, I also have this one for food! So:

1) Totoro lunch bag, present from my friend @vegetadaily 💗
2) Paris 2024 Olympics limited edition lunchbox featuring the one and only Phryge, the official mascot, I love her!
3) Hello Kitty bentô box (lunch box) bought in Japan in 2010
4) Burger-shaped lunch box, bought on Aliexpress, absolutely amazing 😁✨
Et voilà! As I told you, you really have everything and anything in my bag(s).
I hope I answered your question! Have a great day 💗
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
From the article:
For Brother Xavier Boutiot, treasurer of a Benedictine abbeyin central France, pulling the abbey's investments from fossil fuels was an obvious step. Committed to the “Green Church” initiative for four years, the Olivetan monks aimed for consistency in all aspects of their community life. “Financial investments have an ecological impact that is 25 times greater than our daily actions!” emphasized the treasurer. To embark on this ecological and financial transition, the abbey had to scrutinize its investments, which was not straightforward. “The financial world is so opaque for basic investors like us, who don’t have access to all the information,” explained Boutiot. “We called our banks that were not on board with this direction, explained our reasoning, and applied some pressure by saying, ‘Either you support us in this approach, or we’ll switch banks.’” [...] The reasons to divest from fossil fuels are not only ethical but financial: the International Energy Agency predicts fossil fuel use will peak before 2030 and then decline. Religious institutions, managing $3 trillion globally, have divested from fossil fuel companies more than any other sector, aligning their investments with their values.
#divestment#finances#global warming#climate change#climate anxiety#good news#hope#sustainability#environment#ecoanxiety#christianity cw#religion cw#divest
174 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tewkensuchus: King of Punta Peligro
Last month we got our fourth croc of the year and our second notosuchian: Tewkensuchus salamanquensis (Forehead crocodile from the Salamanca Formation), a large-bodied sebecoid from the earliest Paleocene of Argentina. And GODDAMN is it a cool one.
Below some of the fossil material of Tewkensuchus, it doesn't look like much but stay with me for this post.

Starting with the fossil material, Tewkensuchus is admittedly not the most complete sebecid, hell Dentaneosuchus from two years ago is significantly better preserved. Essentially, Tewkensuchus preserves a bit of the skull and a few vertebrae. But the material we do have is exceptional in other ways. Like some European sebecoids, it had a high and broad sagittal crest that extends over its forehead flanked by two broad depressions. Remember the similarity to European sebecoids, thats gonna come back later. Theres also some interesting stuff in how the bony eyebrows, the palpebrals, articulate with the rest of the skull.
What is REALLY weird however is the shape of the postorbitals. Quick anatomy lesson, in crocs the postorbitals form the front corners of the skull table thats located just behind the eyes. They tend to be flat, but in the case of Tewkensuchus they are inclined so that they rise upwards behind the eyes. Now we have plenty of examples of crocodylomorphs with raised squamosals, giving them a somewhat ear-like appearance, but raised postorbitals are a new one.
Below: An artistic interpretation of Tewkensuchus featuring its unique cranial morphology by Manusuchus (give them a follow) from different angles.



One last thing on its anatomy, it was BIG. And I mean big. The team that described Tewkensuchus estimate that its complete skull might have been just over half a meter long, so some 20 inches. This might correspond to a weight of perhaps 300 kg (660 lb), larger than even the largest Cretaceous Baurusuchids.
Now, I hope you remember the part where I said that theres similarities to European sebecoids. Well that sentence has two key points the paper deals with. First of all, the connection to European forms itself. Phylogenetic analysis seems to indicate that despite being found in Patagonia, all its closest relatives are from the Eocene of Europe. These are the recently named giant Dentaneosuchus from France, Bergisuchus from Germany and Iberosuchus (I'll let you figure that one out for yourselves). So after Tewkensuchus disappears South America is inhabited by only distant cousins while its closest relatives show up some 20 million years later on the other side of the Atlantic.
The other noteworthy part of the statement is the use of "Sebecoid" rather than sebecid. That's because of taxonomic back and forth. Essentially, a few previous studies have not included European sebecoids (Bergisuchus and Iberosuchus) within the family Sebecidae, instead featuring them as a separate branch that split off beforehand. In some studies that branch is known as Bergisuchidae, in others they are two branches, you get the idea. Now the description of Dentaneosuchus for instance did away with Bergisuchidae and simply include these European forms within Sebecidae itself. Still as the basalmost members, but given the honor of being at least included. Same goes for Ogresuchus. Well, in the description of Tewkensuchus, we go back to the separate model. So Bergisuchus, Iberosuchus, Dentaneosuchus and Tewkensuchus all form a single not officially named group simply referred to as the "Eurogondwanan clade". This group was placed as the sister family to Sebecidae and together with Ogresuchus the two form the newly named Sebecoidea.
Europe's sebecoids, Dentaneosuchus (art by Joschua Knüppe), Bergisuchus (by Scott Reid) and Iberosuchus (once again Manusuchus)



And this is where we need to address the fact that Tewkensuchus creates a bunch of new problems and makes old ones worse. For starters, it's size. By all accounts its way too big. Keep in mind, this animal appeared some 2 to 3 million years after the extinction of the dinosaurs, an extinction event that is generally thought to have killed everything on land heavier than 10 kilos. And then you get Tewkensuchus with an estimated weight of 300. Well, there's two possible explanations for that. Explanation 1 hinges on the known fact that these rules don't quite apply to semi-aquatic animals. Sure, anything large on land got whiped out, but eusuchian crocodiles managed to survive quite well despite their large size in part because they were partially aquatic. So perhaps Tewkensuchus and sebecoids as a whole underwent an aquatic phase? Well, this would work quite well with what is known as the Sebecia-hypothesis. Essentially, there is some debate on the relationship between sebecids and other notosuchians. Some studies draw a link between them and the similarily terrestrial baurusuchids, placing them in the group Sebecosuchia. Other studies meanwhile believe that sebecids are most closely related to peirosaurids, which in turn are close kin to itasuchids and mahajangasuchids, with both of the latter being more semi-aquatic than other notosuchians. The problem with this is twofold. On the one hand, to my knowledge there has never been any indication that sebecids underwent an aquatic phase and even Cretaceous sebecoids like Ogresuchus from before the impact were clearly terrestrial. The other issue, as nice as this would fit with the Sebecia-hypothesis, this particular study actually recovers the Sebecosuchia model. So there's that.
Personally I don't really buy into this explanation, which takes us to the second possibility. Sebecoids got really jacked really fast. I mean, that's it really. If sebecoids didn't undergo some weird little phase that somehow excempts them from the 10 kilo rule then the only logical answer is that they must have grown to a ridiculous degree the second the dust settled. Do we have evidence for that? Well....kinda but not really no. The closest we have is the fact that Dentaneosuchus from the Eocene clearly reached an enormous size on its own, but that was over 20 million years after the impact. We do at least know that sebecoids were small prior to the KPG thanks to Ogresuchus from Spain, which grew to only a meter in length. But a sample size of one isn't exactly exact proof that all sebecoids were small prior to the impact, especially with shifting phylogenies. The paper itself argues that its most parsimonious that whatever sebecoid crossed the boundry was already fairly large, but time will tell if this holds up. Whatever the case, with a skull half a meter in length it was certainly a formidable predator and a terrifying sight to any unfortunate mammal to cross its path.
Tewkensuchus attacking a startled Monotrematum, a South American monotreme, art by Joschua Knüppe

Finally the last thing to address, paleogeography. It sucks. Moving on. Jokes aside, sebecoid geography was already a pain in the ass. Assuming the sebecosuchian model, sebecoids likely split off from baurusuchids during the Santonian. Mind you this is purely based in the first appearance of baurusuchids, since sebecoids didn't appear for quite a while. Ignoring the problematic Doratodon, the first sebecoid to appear in the fossil record is Ogresuchus in the Maastrichtian of Spain. In the Paleocene we then obviously get Tewkensuchus representing the Eurogondwana clade in Argentina as well as sebecids proper, which seem to be constrained to South America. But then in the Eocene we suddenly have sebecoids in Europe and Africa (for simplicity I'm assuming that Eremosuchus was a sebecoid rather than a sebecid as is traditional). So, how does any of this work? We don't know. I've been breaking my head over how to best explain this without just repeating the paper itself, so let me just say this. Maybe sebecoids originated in South America with baurusuchids, they managed to enter Europe at the very least once giving rise to Ogresuchus, probably via Africa given that its very much undersampled. From there who fucking knows. Maybe Ogresuchus was just one random branch and the two main groups both actually originate in South America. Maybe the Eurogondwana group emmigrating to Europe as well while sebecids proper remained. Maybe the Eurogondwana group originated in Europe and Tewkensuchus simply returned to South America, or maybe they originated in Africa and had members travel west to South America and north to Europe. Or maybe....you get the idea, we don't know. We don't know if they rafted or took land bridges (tho the latter seems more likely), we don't know where certain groups first originated in actuality, we do not know a lot and Tewkensuchus being such a blatant link between Paleocene South America and Europe, which were well separated by that point, raises so many questions.
I imagine this is what this entire last section reads like....

I wish that last segment wasn't as chaotic as it is, but like I said, its a big old confusing mess and it gives me a headachse just thinking about it. So for the time being, its simplest to assume that they split from baurusuchids in South America and then some stuff happened we don't understand. Personally, I'm very much putting my trust in Africa here, I am 100% convinced that some very important stuff went down that we just haven't found yet. But thats just me.
#tewkensuchus#sebecidae#sebecoidea#bergisuchidae#sebecosuchia#evolution#palaeoblr#paleontology#prehistory#pseudosuchia#notosuchia#ziphosuchia#crocodile#croc#paleocene#cenozoic#kpg extinction#long post
130 notes
·
View notes
Text
Archovember 2024 Day 26 - Compsognathus longipes
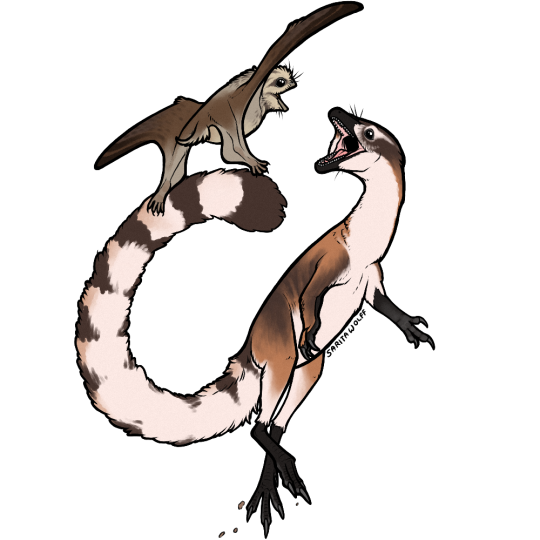

Before it was confirmed that birds were dinosaurs, Compsognathus longipes was regarded as the smallest dinosaur for decades. About the size of a chicken, its name means “elegant/refined/dainty jaw”. It lived in Late Jurassic Europe, found thus far in both Germany and France, with possible teeth also found in Portugal. It was carnivorous, and the remains of small lizards were found preserved in both fossil specimens. They were likely fast, scurrying animals, using their long tails for balance.

In the Late Jurassic, Europe was a dry, tropical archipelago at the edge of the prehistoric Tethys Sea. Both Compsognathus specimens were preserved within lagoons, possibly having died chasing lizards on the beach and then being swept out to sea in a flash flood. The German specimen is known from the Painten Formation, a part of the Solnhofen Limestone. The French specimen was found in limestone on the plateau of Canjuers. One of Compsognathus’ most famous contemporaries is the avialan Archaeopteryx, and the two may have competed over prey. It would have also lived alongside early pterosaurs like Propterodactylus, Rhamphorhynchus, and Anurognathus (as seen above). There were also a diverse variety of turtles, rhynchocephalians, and lizards living here as well, many of which served as prey for this tiny, catlike predator.

This art may be used for educational purposes, with credit, but please contact me first for permission before using my art. I would like to know where and how it is being used. If you don’t have something to add that was not already addressed in this caption, please do not repost this art. Thank you!
#Compsognathus longipes#Compsognathus#compsognathid#theropods#saurischians#dinosaurs#archosaurs#archosauromorphs#reptiles#Archovember#Archovember2024#Dinovember#Dinovember2024#SaritaDrawsPalaeo#Late Jurassic#Germany#France#Portugal#Painten Formation#Solnhofen Limestone#Solnhofen Limestone Formation
149 notes
·
View notes
Text

F is for Flippy (and a fuming furious Fliq) frantically fleeing from fanatic fans at a fall forest festival.
While I was feeling nostalgic over favorite childhood books, I was suddenly in the mood to make an alphabet illustration. Here you'll also find "Flounder fishing for French fries" and "Fix-It Felix fixing a fondue fountain for some foxes and a ferret".
I counted over 60 different F words and things represented here (although I could have also missed some). This includes technicalities like "face", "fur", "finger", "fabric", and "fast". Can you spot them all?
F (character from Mike Salcedo series)
fabric
face
fairy
fairy tale
fall (autumn)
fan (device)
fan (person)
fan art
fanatic
fangs
farm
fast
Felix, Fix-It
fern
ferret
festival
film
film reel
fingers
Finland
firefighter
firefly
firework
first (place)
fish
fishing (verb)
fishing pole / fishing rod
five (both Roman and Arabic)
fix(ing)
flag
flamingo
flee(ing)
Flerovium
Flippy
Fliq(py)
floaty
florist
Flounder
flower
fondue
food
foot / feet
football
footprint
footstool
forest
forget-me-not
fork
fortune teller
fossil
fountain
four
fourteen
fox
foxglove
France / French
Frankenstein's monster
frantic(ally)
fries
frog
fruit
fuming
fur
furious
furniture
429 notes
·
View notes
Text

A 70 Million-Year-Old Titanosaur Dinosaur Skeleton Found in France
A chance discovery made in southern France has revealed a rare specimen — an almost complete dinosaur skeleton found connected from its hind skull to its tail.
The massive fossil came to light in May 2022, after now 25-year-old amateur paleontologist Damien Boschetto and his dog stumbled across something unusual while walking in a forest in Montouliers, France. Boschetto had noticed a cliff edge that had recently collapsed and decided to take a closer look, when he spotted an exposed bone sticking out of the ground, local media outlet France Bleu first reported on February 13.
The Archaeological and Paleontological Cultural Association at the Cruzy Museum, in collaboration with the French National Center for Scientific Research, identified the nearly 10-meter-long (32.8-foot-long) fossil as a Titanosaur skeleton upon excavation. Boschetto, who has been a member of the association for eight years, said that while unearthing dinosaur remains is “always exciting and interesting for scientific research and the understanding of the ecosystems of that time,” finding the bones in their almost original anatomical position is what makes this find extraordinary.
“From a museography point of view, it will make it possible to present to the general public animals almost complete in anatomical positions, which is something great,” Boschetto added via email.
A group of history and archaeology enthusiasts created the Archaeological and Paleontological Cultural Association in 1975 to safeguard the heritage around the village of Cruzy, with several members becoming enlightened amateurs in paleontology due to the areas’ wealth of dinosaur fossils, said Jean-Marc Veyssières, a member of the group and one of the fossil preparers for this discovery. Today, the association is made up of inhabitants of the region, including a few scientists as well as students.
“The most exciting thing was to realize that we had at least one anatomically connected animal and that it was a titanosaur, a long-necked dinosaur,” said Veyssières in an email. “(Boschetto) is an enlightened enthusiast and curious about nature, he spends a lot of time surveying the region in search of new areas. … He became an expert on the Late Cretaceous fauna of our region.”
The association has been excavating the site, which Boschetto referred to as a bone bed, a term used by paleontologists to describe a dense area of animal bones and other fossilized remains, for the past two years. And the newly announced find was not Boschetto’s first.
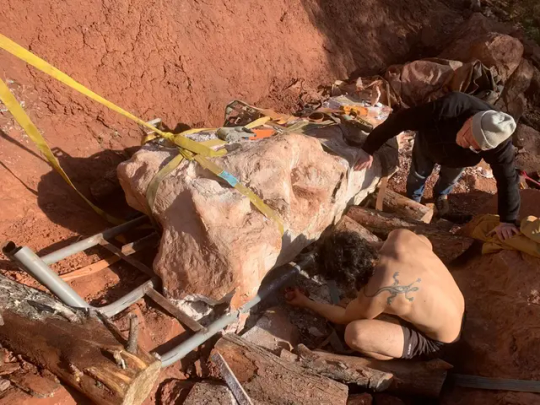
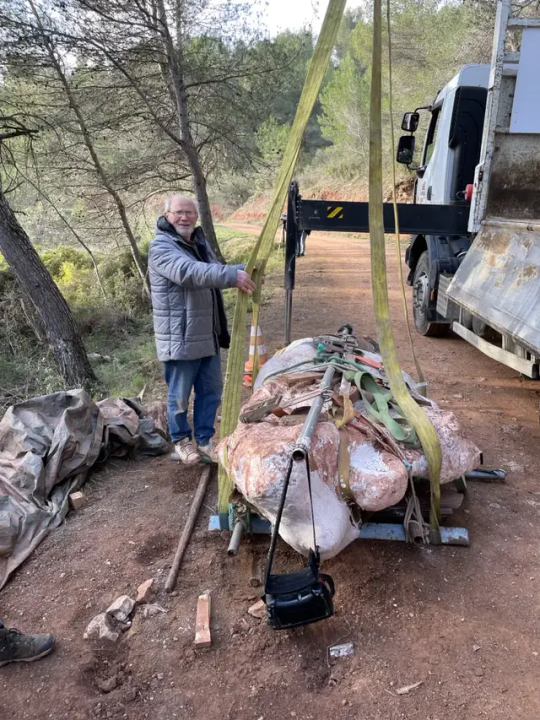
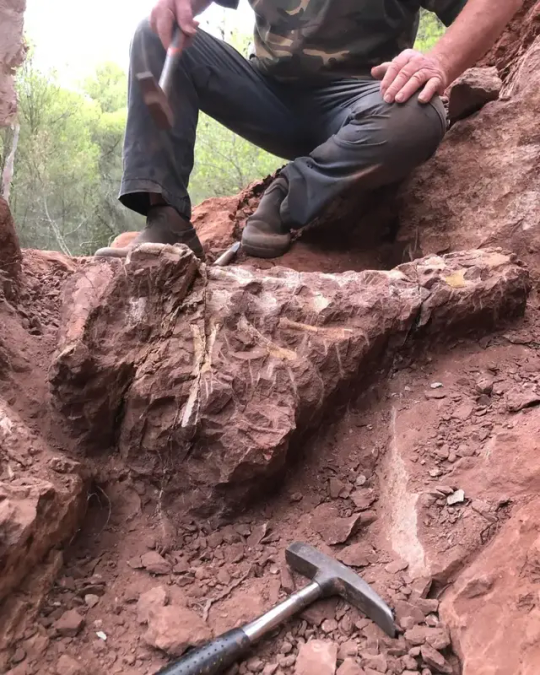



The recently revealed 70% complete Titanosaur skeleton was retrieved during the excavation along with several fossils of various dinosaurs and other vertebrates, including some in anatomical connection and near complete. Other remains identified included those of a Rhabdodon — a herbivore, or plant-eater, like the Titanosaur — and fragments from skeletons of carnivores such as Theropods and crocodiles, according to Boschetto.
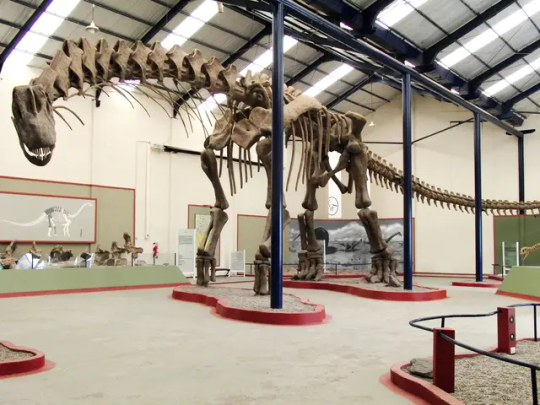
The Titanosaur skeleton currently resides in the Cruzy Museum’s laboratory, where it will be further studied, Veyssières said.
Titanosaur found intact
Researchers estimated the age of the newly discovered fossil to be around 70 to 72 million years old, but Titanosaurs roamed around on four legs from the Late Jurassic Epoch to the end of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 163.5 million to 66 million years ago. Titanosaurs belong to a larger group of dinosaurs known as sauropods, a family of long-necked herbivores that were some of the largest dinosaurs of their time, according to Britannica.
Remains of Titanosaur fossils are widely unearthed in Europe, but few are discovered in anatomical connection, Boschetto said. Finding a skeleton in this connected state suggests that the body was buried before it had entirely decomposed, leaving “some tissues connecting the bones to one another,” said Matthew Carrano, research geologist and curator of Dinosauria at the Smithsonian Institution National Museum of Natural History.


The completeness of the specimen will “make it easier to determine whether it’s a new species or a new specimen of a species that’s already known,” Carrano said in an email. “It will take time to learn all the details about this new specimen, but I’m sure it will provide important new information about this group of dinosaurs.”
The region in which Boschetto discovered the specimen is known to be rich in fossils of dinosaurs and other species living at the same time and is “building one of the largest collections of dinosaurs from the Upper Cretaceous in France,” he said. The association did not publicize the discovery until excavation was complete to protect the archaeological site, he added.
The association plans to continue research on the fossils and to further search the area, and the group’s members hope to obtain the funds to “create a large-scale museum that can accommodate and present these collections,” Boschetto said.
By Taylor Nicioli.



#A 70 Million-Year-Old Titanosaur Dinosaur Skeleton Found in France#Montouliers France#paleontologist#dinosaurs#fossils#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history
416 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Fossil Foraminifera Nummulites laevigatus – Eocene Cuisian Stage, Aisne Valley France – Genuine with COA
Presenting an exquisite fossil specimen of the foraminifera Nummulites laevigatus, a prehistoric marine microorganism from the Eocene epoch. This fossil dates specifically to the Cuisian stage and was discovered in the Aisne Valley near Soissons, France – an area renowned for its well-preserved Paleogene fossils.
Nummulites are large, lenticular foraminifera that thrived in warm shallow seas around 50 million years ago. Their intricate calcareous shells, composed of numerous chambers, are highly prized by both amateur and professional collectors for their scientific importance and distinctive, coin-like appearance (from which the genus gets its name, derived from "nummulus," Latin for "little coin").
Item Details:
Species: Nummulites laevigatus (sometimes referred to as laengryus)
Age: Eocene Epoch, Cuisian stage (~50 million years old)
Location Found: Aisne Valley, Soissons, France
Condition: 100% genuine fossil specimen with exceptional preservation
Scale: Scale cube in photo is 1cm – please refer to image for full size
Photography: What you see is what you get – the exact specimen pictured is the one you will receive
Packaging: Secure and protective packaging
This fossil is an excellent addition to any collection of microfossils or paleontological specimens and is ideal for educational use, display, or gifting. It comes with a Certificate of Authenticity to verify its provenance and authenticity.
We take pride in selecting only high-quality, well-preserved fossils. Each item is handpicked to ensure it meets our rigorous standards.
#Nummulites fossil#foraminifera fossil#Eocene fossil#Cuisian stage#Aisne Valley fossil#Soissons fossil#French fossil#microfossil#marine fossil#fossil specimen#genuine fossil#fossil with certificate#fossil from France#fossil for collection#paleontology#natural history
0 notes
Text
The latest, AI-dedicated server racks contain 72 specialised chips from manufacturer Nvidia. The largest “hyperscale” data centres, used for AI tasks, would have about 5,000 of these racks. And as anyone using a laptop for any period of time knows, even a single chip warms up in operation. To cool the servers requires water – gallons of it. Put all this together, and a single hyperscale data centre will typically need as much water as a town of 30,000 people – and the equivalent amount of electricity. The Financial Times reports that Microsoft is currently opening one of these behemoths somewhere in the world every three days. Even so, for years, the explosive growth of the digital economy had surprisingly little impact on global energy demand and carbon emissions. Efficiency gains in data centres—the backbone of the internet—kept electricity consumption in check. But the rise of generative AI, turbocharged by the launch of ChatGPT in late 2022, has shattered that equilibrium. AI elevates the demand for data and processing power into the stratosphere. The latest version of OpenAI’s flagship GPT model, GPT-4, is built on 1.3 trillion parameters, with each parameter describing the strength of a connection between different pathways in the model’s software brain. The more novel data that can be pushed into the model for training, the better – so much data that one research paper estimated machine learning models will have used up all the data on the internet by 2028. Today, the insatiable demand for computing power is reshaping national energy systems. Figures from the International Monetary Fund show that data centres worldwide already consume as much electricity as entire countries like France or Germany. It forecasts that by 2030, the worldwide energy demand from data centres will be the same as India’s total electricity consumption.
30 May 2025
81 notes
·
View notes
Text

A sketch study of Arthropleura armata, the monstrous cow-sized Late Carboniferous-Early Permian millipede which could grow up to 2.5 meters long and 50-55 cm wide, lived about 346-290 million years ago in Europe and North America, and is the largest terrestrial arthropod ever to have lived, and an impression of an individual leaving behind a trackway in its open woodland habitat somewhere in what is now central France as a Meganeura monyi flies by in the foreground.
Newly-described juvenile specimens from the Montceau-les-Mines fossil site of eastern France reveal that Arthropleura’s facial anatomy was different from those of modern millipedes and that the monster myriapod forms the sister group of the centipede-millipede crown group.
References: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adp6362
#arthropleura#paleozoic#paleoartists on tumblr#paleoartwork#paleoart#palaeoart#palaeoblr#palaeontology#paleontology#paleontologie#paleoartist#carboniferous#meganeura#arthropods#arthropod#arthropoda
99 notes
·
View notes
Text


From September 20 to 27, tens of thousands will take to the streets to denounce the causes of climate change and call on governments to address what may be the most drastic crisis facing humanity in the 21st century. These mass actions will showcase the growing anger of a new generation that has known nothing but crisis, war, and the threat of environmental collapse. We have prepared the following text as a flier encouraging climate activists to consider how to interrupt the causes of climate change via direct action rather than petitioning the state to solve the problem for us. Please print these out and distribute them at climate protests and everywhere else you can.
Finally, people are filling the streets to call on governments to address the climate crisis, the most serious threat facing humanity in the 21st century. This is long overdue. But what good will it do to petition the same sector of society that created this problem? Time and again, we have learned that the state does not exist to serve our needs but to protect those who are profiting on the causes of this crisis.
The most effective way to pressure politicians and executives to address the climate crisis is to show that whatever they fail to do, we will do ourselves. This means moving beyond symbolic displays of “non-violence” to build the capacity to shut down the fossil fuel economy ourselves. No amount of media attention or progressive rhetoric can substitute for this. If we fail to build this capacity, we can be sure that the timeline for the transition to less destructive technologies will be set by those who profit on the fossil fuel economy.
Several examples from recent social movements show that we have the power to shut down the economy ourselves.
In 2011–2012, the Occupy Movement demonstrated that tens of thousands of people could make decisions without top-down organization, meeting their needs collectively and carrying out massive demonstrations. On one day of action, participants shut down ports up and down the West Coast, confirming that coordinated blockades can disrupt the global supply chain of energy and commodities.
In 2016, people converged to fight the Dakota Access Pipeline, a corporate project threatening Native land and water. Tens of thousands established a network of camps to block construction, demonstrating a new way to live and fight together. The Obama administration canceled the pipeline, causing many occupiers to go home, but the Trump administration reinstated it—confirming that we must never count on the government to do anything for us.
In France, occupiers blocked the construction of a new airport at la ZAD, the “Zone to Defend.” Farmers teamed up with anarchists and environmentalists, establishing an autonomous village that provided infrastructure for the struggle. After years of struggle, the French government gave up and canceled the airport.
We have seen train blockades in a variety of struggles. In Olympia, Washington, anarchists blocked trains carrying fracking proppants in 2016 and in 2017, forcing the company to stop transporting the commodity. In Harlan County, Kentucky, coal miners have blocked a coal-carrying train after the Black Jewel company refused to pay wages they owed to workers. It only takes a few dozen people to shut down a key node in the supply chains of the global fossil fuel economy. Imagine what we could do on a bigger scale!
Governments serve to protect the economy from those it exploits. The state exists to evict, to police, to wage war, to oppress, and above all to defend the property of the wealthy few. The perils of climate change have been known for years, but governments have done little in response, focusing instead on fighting wars for oil, militarizing their borders to keep out climate refugees, and attacking the social movements that could bring about the sort of systemic change that is our only hope of survival.
The capitalist economy is literally killing us. Let’s begin the process of shutting it down.
Another end of the world is possible!
#crimethinc#climate crisis#direct action#ecology#environment#anarchism#revolution#climate change#resistance#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#anarchy works#environmentalism
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
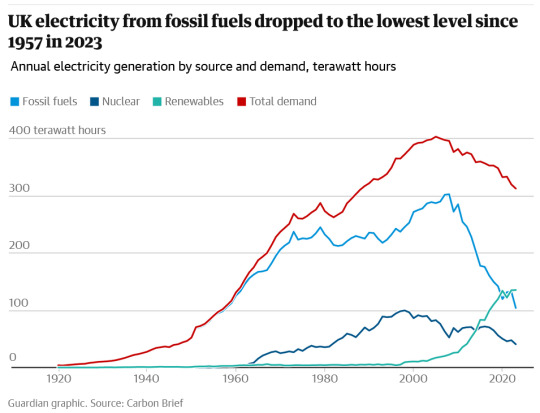
"The amount of electricity generated by the UK’s gas and coal power plants fell by 20% last year, with consumption of fossil fuels at its lowest level since 1957.
Not since Harold Macmillan was the UK prime minister and the Beatles’ John Lennon and Paul McCartney met for the first time has the UK used less coal and gas.
The UK’s gas power plants last year generated 31% of the UK’s electricity, or 98 terawatt hours (TWh), according to a report by the industry journal Carbon Brief, while the UK’s last remaining coal plant produced enough electricity to meet just 1% of the UK’s power demand or 4TWh.
Fossil fuels were squeezed out of the electricity system by a surge in renewable energy generation combined with higher electricity imports from France and Norway and a long-term trend of falling demand.
Higher power imports last year were driven by an increase in nuclear power from France and hydropower from Norway in 2023. This marked a reversal from 2022 when a string of nuclear outages in France helped make the UK a net exporter of electricity for the first time.
Carbon Brief found that gas and coal power plants made up just over a third of the UK’s electricity supplies in 2023, while renewable energy provided the single largest source of power to the grid at a record 42%.
It was the third year this decade that renewable energy sources, including wind, solar, hydro and biomass power, outperformed fossil fuels [in the UK], according to the analysis. Renewables and Britain’s nuclear reactors, which generated 13% of electricity supplies last year, helped low-carbon electricity make up 55% of the UK’s electricity in 2023.
[Note: "Third year this decade" refers to the UK specifically, not global; there are several countries that already run on 100% renewable energy, and more above 90% renewable. Also, though, there have only been four years this decade so far! So three out of four is pretty good!]
Dan McGrail, the chief executive of RenewableUK, said the data shows “the central role that wind, solar and other clean power sources are consistently playing in Britain’s energy transition”.
“We’re working closely with the government to accelerate the pace at which we build new projects and new supply chains in the face of intense global competition, as everyone is trying to replicate our success,” McGrail said.
Electricity from fossil fuels was two-thirds lower in 2023 compared with its peak in 2008, according to Carbon Brief. It found that coal has dropped by 97% and gas by 43% in the last 15 years.
Coal power is expected to fall further in 2024 after the planned shutdown of Britain’s last remaining coal plant in September. The Ratcliffe on Soar coal plant, owned by the German utility Uniper, is scheduled to shut before next winter after generating power for over 55 years.
Renewable energy has increased sixfold since 2008 as the UK has constructed more wind and solar farms, and the large Drax coal plant has converted some of its generating units to burn biomass pellets.
Electricity demand has tumbled by 22% since its peak in 2005, according to the data, as part of a long-term trend driven by more energy efficient homes and appliances as well as a decline in the UK’s manufacturing sector.
Demand for electricity is expected to double as the UK aims to cut emissions to net zero by 2050 because the plan relies heavily on replacing fossil fuel transport and heating with electric alternatives.
In recent weeks [aka at the end of 2023], offshore wind developers have given the green light to another four large windfarms in UK waters, including the world’s largest offshore windfarm at Hornsea 3, which will be built off the North Yorkshire coast by Denmark’s Ørsted."
-via The Guardian, January 2, 2024
#uk#united kingdom#england#scotland#wales#northern ireland#electricity#renewables#renewable energy#climate change#sustainability#hope posting#green energy#fossil fuels#oil#coal#solar power#wind power#environment#climate action#global warming#air pollution#climate crisis#good news#hope
396 notes
·
View notes