#geoinformatics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


The dark and cozy times have arrived! 🍂
#studyblr#intern#geoinformatics#geography#study#desk#uni#motivation#mine#study setup#studying#study aesthetic#master of science
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why I care about history so much

Okay, because I have been asked about this a lot: No, I am not a historian. And I am not studying religion or mythology either. In fact I did my first masters degree in economics and currently am working on my second degree in geoinformatics. So... why do I write so much about history?
So, the easy answer is: I am autistic. I hyperfocus on history.
But there is also a more complicated answer to this.
See, what I want to do with my life is actually to work in science communication and especially work towards this with climate change and ecology. That is also why I do geoinformatics, because part of that is actually using maps and software to communicate this kind of information.
And here is the thing where history comes in. See, we often act as if the social science and the STEM fields are super far apart and super different. But I am going to tell you: They are not. Because it is all connected.
Climate change is the best example. There is a "history of climate change" as in a history of how we found out it was happening and how the fossil fuel tried to bury it. Climate change is also a topic where social science do intersect a lot of STEM stuff. How people behave in groups, how people interact with information, an how to communicate information is important for this.
A funny thing happened yesterday. I have one class this semester called "Geoinformatics in Society", which is kinda about this: How to use geoinformatics to communicate information to people. Yesterday the professor showed us some examples of this. One of them was a graphic showing a very abstract version of change over time of the life expectancy of countries between 1800 and 2015. And the prof was asking us about storytelling in it and what we could see. And me, who again has a hyperfocus on history, looked at it: "Oh, yeah, here we see the polio vaccine being given out. Oh, and there is the Spanish flu happening. These are the world wars. Oh, there was a famine hitting China." And so on. Because... well, those things intersect. The reason why life expectancy rose is largely to be attributed to science - but also to societal factors. These things intersect.
The professor in question is doing research on this kinda stuff. Which is something that people in my area do research on. So, yeah, it intersects.
But there is another reason, too. I am trans, queer and disabled. As such I experience a lot of marginalization and discrimination. And... well, understanding that is also just a need for me. And you need to understand history to understand that.
And when it comes to this... Well, you cannot just look at one thing in history and say "Oh, yeah, this is why this is happening." Because, well, so many factors play into it. Like, sure, there is Nazism playing into it. And eugenics. But you cannot look at either without looking at both the Enlightenment movement and colonialism. And well, you cannot look at those without looking at the crusades and the spice trade. And those? Well, you cannot talk about those without Byzantium. And for those you need to understand Rome and then... well, you get what I am getting at, right?
Everything is intersecting. And I think... I think understanding that is important.
#personal#history#autism#neurodivergent#hyperfixation#stem#science#science communication#sociology#geoinformatics
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Careers in Geography - From Cartographer to Urban Planner
Welcome to "No Herd Mentality" Today, we're exploring exciting careers in geography. Ever wondered who makes maps or plans cities. We'll introduce you to cartographers, urban planners, and more. These professionals use geography to improve our world, from designing better places to live to protecting the environment. If you love maps, technology, and nature, a career in geography might be perfect for you. Stay tuned to learn how you can turn your passion for geography into a fulfilling job.
#geography#subjectstream#career#careerguidance#careercounselling#humanities#liberalarts#subjectchoice#ecocomics#politicalscience#geoinformatics#GeographyCareer#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#youtube#cartography#forestry#geoinformatics#gps#image processing#hydrology#gis#earth science#mapping
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Project "ML.Satellite": Image Parser
In order to speed up the "manufacturing" of the training dataset as much as possible, extreme automation is necessary. Hence, the next step was to create a semi-automatic satellite multispectral Image Parser.
Firstly, it should carve the smaller pieces from the big picture and adjust them linearly, providing radiometrical rescaling, since spectrometer produces somewhat distorted results compared to the actual radiance of the Earth's surface. These "pieces" will comprise the dataset. It was proposed to "manufacture" about 400 such "pieces" in a 500 by 500 "pixels" format.
P.S.: Below are example images of the procedure described above. (Novaya Zemlya Archipelago)
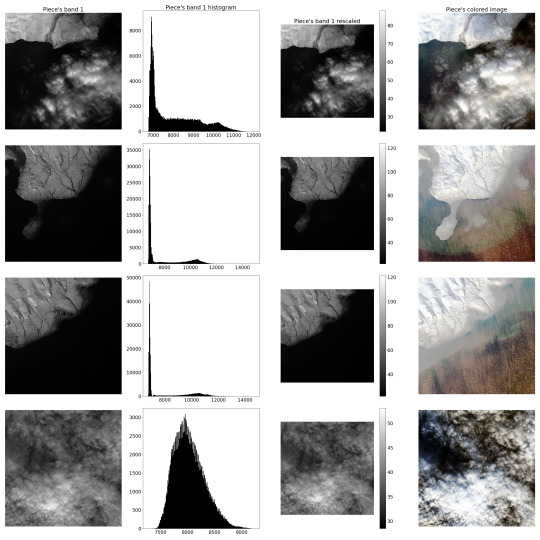
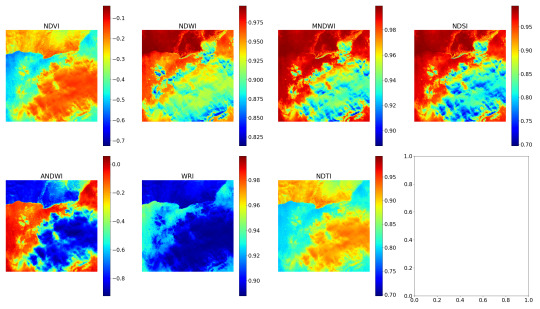
Secondly, it should calculate some remote sensing indexes. For this task, a list of empirical indexes was taken: NDVI, NDWI, MNDWI, NDSI, ANDWI (alternatively calculated NDWI), WRI and NDTI. Only several of them were useful for the project purposes.
P.S.2: The following are example images of the indexing procedure.
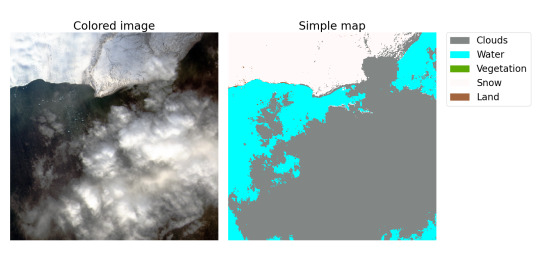
Lastly, it should compute the "labels" for the "pieces" describing a schematic map of the territory on image splitting this territory into several types according to the calculated indexes. To simplify segmentation, in our project, a territory can consist only of the following types: Clouds, Water (seas, oceans, rivers, lakes…), Vegetation (forests, jungles…), Snow and Land (this class includes everything else). And, of course, Parser should save the processed dataset and labels.
P.S.3: Below are sample image of a colored "piece" and a simple map based on the label assigned to this "piece". Map may seem a drop inaccurate and it's not surprising, since as far as I know, indexes are empirical and by definition cannot be precise. As a result, if it is possible to create a sufficiently accurate model that predicts analytical classification, then it may be possible to create a model that classifies optical images better than analytics.
#student project#machine learning#neural network#ai#artificial intelligence#computer vision#image segmentation#segmentation task#satellite#remote sensing#optical sensors#geoinformatics
0 notes
Text


screenshots from a mapping seminar i took this fall
0 notes
Text
GIS Services in Canada
GIS services are crucial for RS Solar CAD Group's operations, aiding in site selection, solar panel placement, and infrastructure planning. Our offerings include spatial analysis, data visualization, and custom mapping solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of solar energy projects. With our expertise, RS Solar CAD Group can optimize their designs, minimize environmental impact, and maximize energy production efficiency.
Our Services include Solar Design Services | GIS | CAD/Drafting | BIM | Project management | Civil Engineering | MEP | Permit plan set
To know more contact us Email: [email protected]/ [email protected] or calling / Whatsapp at +919958060424
#gis#geospatial#mapping#geography#cartography#geodata#spatialanalysis#geoinformatics#geospatialintelligence#geospatialtechnology#permit#proposals#engineeringstamp#solar#solarenergy#solarpower#solarinstallation#usa#usajobs#california#washington#oregon#nevada#idaho#montana#arizona#utah#colorado#newmexico#texas
0 notes
Text
Geoinformatics Colleges in India: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you passionate about geospatial technology and its applications? Do you want to pursue a career in geoinformatics? If so, you've come to the right place! In this article, we will explore the top geoinformatics colleges in India and provide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision about your future.

What is Geoinformatics?
Before we dive into the details of geoinformatics colleges in India, let's first understand what geoinformatics is all about. Geoinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that combines geography, geology, computer science, and information technology to analyse and interpret spatial data. It involves the use of various tools and techniques to collect, store, process, analyse, and visualise geographic information.
Courses offered for Geoinformatics
If you're interested in pursuing a career in geoinformatics, it's important to know what courses are available and what they entail. Here are some geoinformatics course details offered by geoinformatics colleges in India:
1. Bachelor's Degree in Geoinformatics
A bachelor's degree in geoinformatics is the first step towards building a successful career in this field. This course typically spans over three to four years and covers a wide range of topics such as GIS (Geographic Information System), remote sensing, spatial analysis, database management, and cartography. Some colleges also offer specialised courses in areas like environmental management and urban planning.
2. Master's Degree in Geoinformatics
If you want to further enhance your knowledge and skills in geoinformatics, you can pursue a master's degree in this field. A master's degree program usually lasts for two years and provides advanced training in areas such as geospatial data analysis, geodatabase design, web mapping, and geospatial programming. Many colleges also offer research opportunities for students who wish to delve deeper into specific topics.
3. Diploma/Certificate Courses
Apart from bachelor's and master's degree programs, there are also several diploma and certificate courses available for those who want to gain specialised knowledge in specific areas of geoinformatics. These short-term courses focus on topics such as remote sensing applications, GIS software, and spatial data analysis.
Top Geoinformatics Colleges in India
Now that we have a basic understanding of geoinformatics and its course details, let's take a look at some of the top geoinformatics colleges in India:
Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS)
Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS), located in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, is another renowned institute that offers excellent programs in remote sensing and geoinformatics. The institute is affiliated with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) and provides world-class training and research opportunities to students.
National Institute of Technology (NIT) Warangal
National Institute of Technology (NIT) Warangal offers a comprehensive program in geoinformatics at both undergraduate and postgraduate levels. The institute has state-of-the-art facilities, well-equipped laboratories, and experienced faculty members who are actively involved in research projects.
Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics (SIG)
Located in Pune, Maharashtra, SIG is one of the premier institutes for geoinformatics education in India. It offers a variety of undergraduate, postgraduate, and diploma programs in geoinformatics. The institute has a state-of-the-art infrastructure, experienced faculty members, and strong industry connections, making it an ideal choice for aspiring geospatial professionals.
Scope of Geoinformatics
After completing your education in geoinformatics, you'll have a wide range of career opportunities to explore. Here are some possible MSc geoinformatics scopes:
1. GIS Analyst: As a GIS analyst, you'll be responsible for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting geographic data using GIS software.
2. Remote Sensing Specialist: Remote sensing specialists use satellite imagery and other remote sensing techniques to gather information about the Earth's surface.
3. Spatial Data Scientist: Spatial data scientists analyze spatial data using statistical techniques to derive meaningful insights.
4. Urban Planner: Urban planners use geospatial technology to develop plans for land use, transportation systems, and urban development.
5. Environmental Consultant: Environmental consultants assess the impact of human activities on the environment using geospatial tools.
These are just a few examples of the career paths you can pursue with an MSc degree in geoinformatics. The demand for skilled professionals in this field is growing rapidly, both in India and abroad.
Conclusion
Geoinformatics is a fascinating field that offers exciting career opportunities for those who are passionate about spatial data analysis and interpretation. By pursuing a degree in geoinformatics from one of the top colleges mentioned above, you’ll gain the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in this field. We recommend SIG from Pune as it offers the perfect blend of education and experience you need for your career ahead.
Remember to thoroughly research each college’s curriculum, faculty expertise, infrastructure, and industry connections before making a decision. Good luck with your academic journey!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Geoinformatics, Geodynamos & Superchrons: Will Humanity Survive Next Geomagnetic Pole Flip?

© Photo: Dr. Gary A. Glatzmaier, Los Alamos National Laboratory
The magnetic North Pole’s accelerating march toward Russia from Canada has fascinated and frightened millions of people around the world in recent years amid the prospect of a complete reversal of Earth’s Dipole Magnetic field. The director of the Russian Academy of Sciences’ Geophysical Center delves into the processes taking place under our feet.
The force generating the magnetic field shielding us from deadly solar winds has a fascinating life of its own, and one definitely worth exploring more closely if humanity is to get a fundamental understanding of the planet we call home, according to Veteran Russian Geophysicist, Geoinformatics Expert and Schmidt Institute of Physics of the Earth Head Researcher Anatoly Solovyov.
“The task of geoinformatics is to develop mathematical tools capable of handling the immense quantities of information that we began receiving recently thanks to modern networks digitally recording various natural process,” Dr. Solovyov explained.
“The ability to obtain new knowledge by processing large, often heterogeneous data from different disciplines in the field of Earth sciences, be it geomagnetism, gravity field anomalies, seismological observations, tsunamis,” and other phenomena, including the study of rapid fluctuations in Earth’s magnetic field has become possible only with modern technology and computing power, the academic said.
“Until recently, the characteristic temporal variations in the magnetic field were subject to study measured in centuries, with magnetic field reversals measured in the hundreds of thousands of years. With the advent of modern magnetic field recording systems, rapid variations in the magnetic field have been detected on characteristic time scales of one to ten years,” Solovyev noted. “We’ve learned to record such changes in the magnetic field – caused mainly by processes occurring at the boundary of the Earth’s liquid core, the mantle. We can observer them on the surface of Earth and from near-Earth space using high-precision geomagnetic observatories and low-orbit satellite systems.”

Dr. Anatoly Alexandrovich Solovyev, Geophysicist, Specialist in Geoinformatics, Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Corresponding Member and Professor with the Russian Academy of Sciences. © Sputnik/Olga Merzlyakova
Earth Geomagnetic Poles’ Past…..and Future
Solovyev, coauthor of the Atlas of the Earth’s Magnetic Field, a comprehensive 2012 study of the evolution of Earth’s magnetic field from the years 1500 to 2010, and a top scholar involved in the creation of geomagnetic monitoring centers, says these observatories provide scientists the ability to study the temporal variability of Earths’ magnetic field over long periods of time.
“Modern models allow us to reconstruct the magnetic field not only of the past 500 years, but over tens of thousands of years, based on paleomagnetic and archeomagnetic data. We can say that, for example, that the movement of the North Magnetic Pole has significantly accelerated recently, and there is speculation that an inversion can be expected in the near future,” the academic explained.
Of course, there are counterarguments to the pole flip thesis, Solovyev noted.
“For example, 40,000 years ago, the Laschamp event geomagnetic excursion occurred when the dipole axis deviated significantly from the rotation axis. Thus, the North Magnetic Pole can shift to angles of 30-40 degrees, with this process accompanied by a major weakening of the magnetic field. 40,000 years ago, it weakened several times over compared to its present intensity. Nevertheless, everything later returned to its normal place.”
“On the scale we’re talking about, this is related to processes occurring in the liquid core. These have not been fully studied yet, because we only have indirect data. There’s actually very little data. Modern field observation systems were introduced only in the late 1980s, when digital data recordings became possible. Vector-based measurements using low-earth orbit satellites began to be conducted systematically only in the late 1990s, so a thorough reconstruction of the processes occurring in the liquid core, especially over such large intervals, is only possible using theoretical approximations,” Dr. Solovyev explained.
On top of that, it’s an issue of computing power, according to the academic. “For example, one of the latest achievements in the field of numerical modeling of such processes was the possibility to recreate variations associated with rapid changes to the magnetic field – so-called geomagnetic jerks, something achieved only in the last 50 years.”
Scientists have some idea about how the redistribution of magnetic flux occurs at the boundary of the liquid core and mantle, and theoretical concepts explaining the recent acceleration of the movement of the North Magnetic Pole in Russia’s direction, Solovyev said.
Life-Giving Force Shielding the Earth
As for the creation of Earth’s magnetic field itself, scientists postulate that the heterogeneity of states in the Earth’s mantle led to the non-stationary processes that generate the magnetic field.
“They are affected, in particular, by the Coriolis force, thermal convection, compositional convection. Such heterogeneities in Earth’s depths have apparently given rise to process of the creation of the geodynamo and its consequent maintenance,” Solovyev noted, referring to the theory about the mechanisms through which celestial bodies, including Earth, generate their magnetic fields.
“Geophysics is largely a science dedicated to heterogeneities and anomalies, starting with the fact that our planet consists of core-shells that are heterogeneous both in their composition and state of aggregation…In order to start up the dynamo in the form we see today, there must be a solid and a liquid core. The dynamo’s operating modes change depending on the radio of radii of the inner and outer cores. As the inner core grows, the dynamo’s operating modes (inversion frequency and intensity) also change,” the academic said.
In turn, the magnetic sphere contributed to the formation of life on Earth, given its role shielding us from the deadly effects of solar radiation.
At the same time, powerful magnetic storms can have an indirect impact on human health, with the dense flow of high-speed solar winds affecting the magnetosphere, in turn affecting atmospheric pressure, blood pressure, hormonal background, and various environmental factors.
Then, there is solar radiation. “At high altitudes, where high-energy particles penetrate close to the Earth’s surface and can reach the altitude of commercial aviation, the influence of precisely this radiation plan can be felt. Therefore, the [Russian] Space Weather Prediction Center provides a forecast for the level of geomagnetic activity on the Earth’s surface, including for the benefit of aviation. The trajectory of transpolar flights is adjusted accordingly depending on space weather. After all, in a powerful magnetic storm, a human being at such an altitude could receive a dose of radiation in one hour comparable to the average annual dose of radiation,” Solovyev noted.
Humans Adopt to Survive
Humanity has evolved by adapting to the natural changes in our geomagnetic environment over past millennia, and Dr. Solovyev is confident the species can adapt to abrupt changes in the magnetic field, should they take place once again.
“[Such changes] will not happen instantly. On a geological scale, it’s an instant, but on the scale we’re accustomed to, it’s quite a significant period of time, amounting to thousands of years, with the duration of the inversion itself lasting several thousand years…The magnetic field will gradually weaken. We have no documentary evidence about what will accompany this. Perhaps our species will be preserved, because the ionosphere and atmosphere will remain. Currents will be generated in the ionosphere, acting as a kind of shield in relation to those harmful particles flying toward us from the Sun, and may well protect us from solar radiation.”
Flips in the geomagnetic poles occur an average of 500,000 years or so, with the last one taking place about 750,000 years ago.
“No one knows when to expect the next one. It does not happen regularly. Moreover, periods know as superchrons were discovered when no inversion would occur for millions of years, with the field maintaining some fixed polarity. We know of three such superchrons,” Solovyev pointed out.
With homo erectus dating back about two million years, and the last inversion taking place three quarters of a million years ago, that means that the last time a pole flip occurred, it didn’t wipe out our ancestors.
More Data Can Lead to Fundamental Discoveries
Solovyev and his colleagues worked to build the Rotkovets Geobiosphere station in Popovka, Arkhangelsk region in 2012, providing researchers with pristine data free of electromagnetic interference and allowing for a range of geophysical observations.
“Since I have a background in engineering education, although it is a mathematical one, I would like to significantly expand the network of magnetic field observations using observatories of the highest class. This would make it possible to study the subtle effects in the change of the Earth’s magnetic field over a long-term basis,” Solovyev stressed.
With this knowledge, humanity would gain “information about the structure and arrangement of our planet. This is undoubtedly of fundamental importance,” he added.
“We will be able, for example, to study in greater detail the movement of the Magnetic North Pole, around which all the most intense changes in the magnetic field occur and, as a result, the most negative effects of space weather are observed. We’ll be able to adjust the trajectories of aircraft, be prepared for the impact of solar radiation on satellite systems. It’s a wide range of problems, from purely theoretical to important applied aspects,” Dr. Solovyev summed up.
— Sputnik International | Sunday August 18, 2024
#Geoinformatics | Geodynamos | Superchrons#Humanity | Survival#Geomagnetic#Pole Flip#Russian 🇷🇺 | Geophysicist | Geoinformatics | Expert | Schmidt Institute of Physics of the Earth | Head Researcher | Anatoly Solovyov.#Earth | Dipole | Magnetic Field#Russian🇷🇺| Academy of Sciences | Geophysical#Beyond Politics#Science & Tech Earth#North Pole#Russia 🇷🇺#Magnetic Poles#Magnetic 🧲 Field#Magnetic 🧲 North Pole
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Advance your career with IGMPI’s industry-oriented PG Diploma in Geoinformatics. Learn GIS, remote sensing, spatial data analysis & more. Enroll online today!
Enroll in the Post Graduate Diploma in Geoinformatics offered by IGMPI – a government-recognized institute. This distance learning course provides in-depth knowledge of GIS, remote sensing, spatial data analysis, and practical tools used in geosciences and urban planning. Ideal for professionals in geography, environmental science, agriculture, and infrastructure sectors.
#Geoinformatics course India#PG Diploma in Geoinformatics#GIS course online#IGMPI Geoinformatics program#remote sensing training#spatial data analysis course#GIS distance learning#Geoinformatics certification India#GIS and mapping course#online Geoinformatics diploma
0 notes
Text


don’t forget to do fun things in life
#studyblr#geography#study#desk#uni#motivation#mine#study setup#studying#study aesthetic#geo#geoinformatics
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discussion about possible group project at uni, concerning using GIS to teach about history (specifically the crusades).
Fellow student: "That would be a lot of research work."
Me: "Oh, not for me. For me that isn't work. Historical research is more like relaxation to me."
I mean, really people. Leave me for two days in the local historical library with some tea, and I am a very happy little alpaca.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
M.sc Geoinformatics in India
Pursue M.Sc Geoinformatics in India at Sangam University and master GIS, remote sensing, and spatial data technologies. This program prepares you for careers in urban planning, environmental science, and geospatial analytics. With industry-aligned curriculum, hands-on training, and expert faculty, Sangam University is the ideal choice for aspiring geoinformatics professionals.
0 notes
Text
youtube
#mapping#image processing#hydrology#gps#gis#earth science#geoinformatics#cartography#forestry#youtube#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Project "ML.Satellite": Launch
The new semester brings to me a new ML project. A prerequisite for getting a good grade for a mandatory data analysis course is to create the beneficial neural network of medium complexity. Thus, I started a project "Machine learning model for the terrain segmentation".
The idea of project is to train a model which could divide the multispectral satellite images into parts by type of terrain (to mark where land and water are in the image, where forest and snow are, etc.) An analytical solution for this task does exist, but it appears to be empirical in nature. And it would be really nice to devise a model independent of this solution. But I haven't been able to find a useful dataset for such a task, therefore this task is getting more and more difficult since I need to create such a dataset. First of all, this dataset will be created using an analytical solution, so the goal changes from trying to beat the analytical solution to trying to catch up with the existing solution. The resulting dataset will be published by the end of the project.
The dataset will be "manufactured" using the data from the Landsat 8 satellite. It provides the images of 11 bands with an aspect size of about 5000-10000 "pixels", excluding the 8th band of doubled size.
P.S.: Below is an example of an image band reduced in size by 10 times.
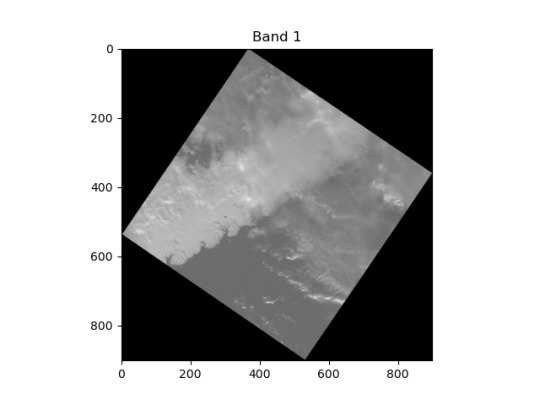
#new project#student project#machine learning#neural network#ai#artificial intelligence#computer vision#image segmentation#segmentation task#satellite#remote sensing#optical sensors#geoinformatics
0 notes
Text
M.Sc Geoinformatics in India
Sangam University is a renowned institution offering top-notch education across streams. With cutting-edge facilities and learned faculty, it provides an enriching academic experience. Sangam's M.Sc Geoinformatics program is one of the best in India, equipping students with advanced geographic information skills. The university's focus on practical training, industry exposure, and holistic development makes it a prime choice for students seeking M.Sc Geoinformatics in India.
0 notes