#mobile ui testing tools
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How AI is Shaping the Future of Web Automation Testing
Introduction:
Briefly introduce the role of AI in transforming industries.
Highlight its emerging impact on web automation testing.
Enhancing Test Automation Efficiency
Discuss how AI optimizes test case generation and execution.
Mention AI-powered tools for smart test script creation.
Self-Healing Test Scripts
Explain how AI helps maintain test scripts by dynamically adapting to UI changes.
Reduce the need for manual script updates.
Advanced Defect Detection
Highlight AI’s ability to identify patterns and anomalies.
Leverage predictive analytics for proactive bug fixing.
Improved Test Coverage with AI
Discuss how AI ensures comprehensive test coverage.
Utilize machine learning to prioritize high-risk areas for testing.
Future of Web Testing with AI
Explore emerging trends like autonomous testing and AI-driven test analytics.
Discuss potential integration of AI with DevOps.
Conclusion:
Summarize the advantages of AI in web testing.
Encourage embracing AI to stay competitive in QA.
#web automation testing#web ui testing#ui automation testing#web api test tool#web application testing#web app performance testing#mobile app testing#app testing#mobile application testing#mobile automation testing tools#mobile ui testing tools#api test automation
0 notes
Text

Why SwiftUI Should Be Your First Choice for iOS Apps in 2024 | Elite Iphone Devs
Learn about the reasons why SwiftUI stands out as the premier framework for iOS app development in 2024. Compare its simplicity in design and layout, superior performance, capabilities in user interaction and animation, cross-platform compatibility, robust testing tools, anticipated future trends, strong community support, and proven real-world successes. Make an educated choice to adopt SwiftUI and streamline the development of your apps while ensuring they are future-proof.
#SwiftUI#iOS app development#mobile app frameworks#benefits of SwiftUI#iOS UI design#application development#optimizing performance#app animations#iOS device compatibility#testing and debugging tools#future technology trends#developer support#real-world examples
0 notes
Text

2 MORE DAYS EVERYONE!!
LS here. Today I'm going to talk about my favorite thing: UI design. When it's good, it's utterly invisible, but when it's bad, everyone notices!
There were definitely some hurdles and hiccups in the UI design of the demo. Part of it was me being unfamiliar with my tools, part of it was not understanding some of the in-built features of the sugarcube twine template. Since then I've brushed up on my JS and restructured things to make the game more intuitive.
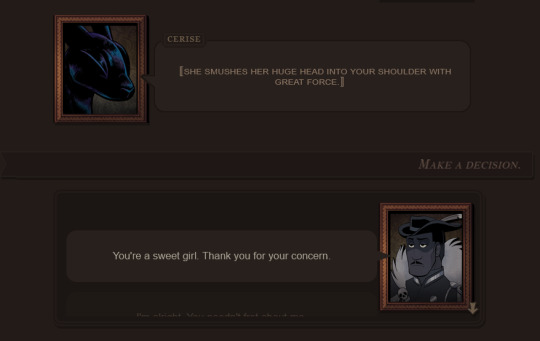
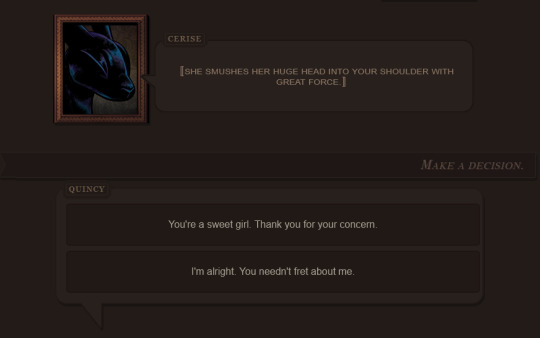
First up, we now have two different options for the choice menu! By default, the game displays the "scrolling list" as seen on the left. Using either touch controls or your mouse scroll wheel, you can cycle through the available options before making your choice... or if your device lacks touch/wheel options (or you dislike needless UI animation), you can set the choice menu to "static list" and have your options display in a plain list.


Next is the top bar! At first glance, the buttons might look the same as they did in the demo, but they are not. Yes, the larger of the two still leads to a (new) character summary, but the smaller button now opens the new glossary rather than than being a redundant link to the inventory.
The glossary is a small feature a few readers suggested and it does exactly what it says. It combs through the current passage and looks for vocabulary words which may be unfamiliar to readers.
As always, the glossary feature is meant to be a convenience for readers who may have taken breaks in their playthrough and would like a refresher. It's an anti-frustration feature, not "homework!"
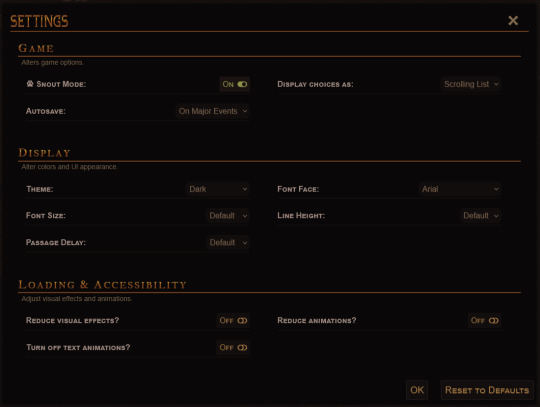
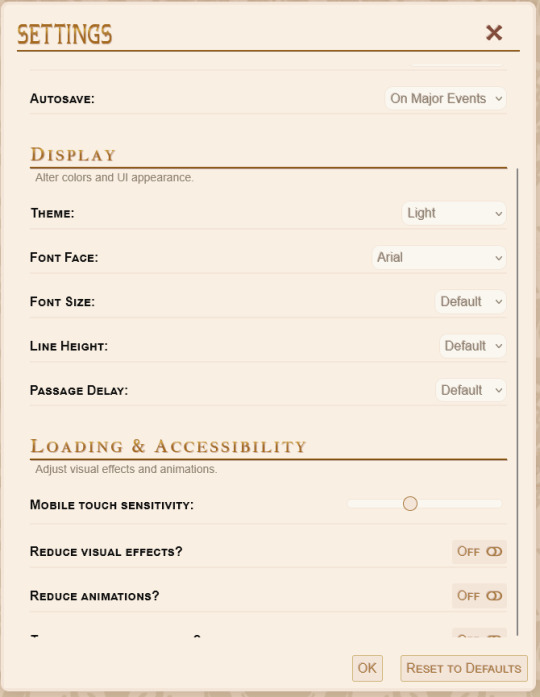
The settings menu is much like it was before, but with a few new features. Changing the theme now changes the UI popups as well as the main layout, so no more white text on dark backgrounds for light theme users! Mobile users will also be happy to learn that you can adjust touch sensitivity - this should hopefully fix some of the issues with people triggering the touch menu when scrolling down the page.
(The touch sensitivity range given in the menu might be tweaked later though - I've only had a few people test mobile for me so my perception of "the average mobile device" has a lot of holes in it. Mobile users, you'll have to let me know if the range is too great/too small to be useful!)
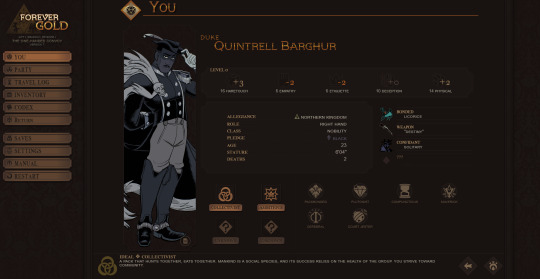
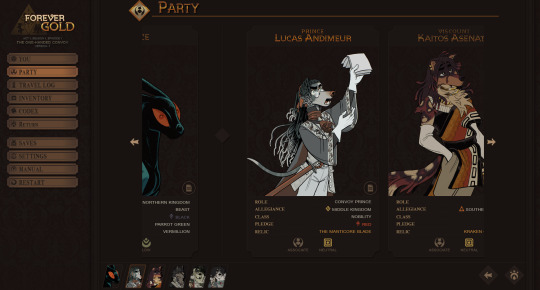
The "You" page has been separated from the Party menu and overhauled. This was mentioned in a previous post, so I'll move on to how the Party menu has been restructured!
Wanting to have as much information as possible easily available, I did away with the individual subpages in favor of these smaller summaries you can scroll through (using touch, mousewheel, or buttons).
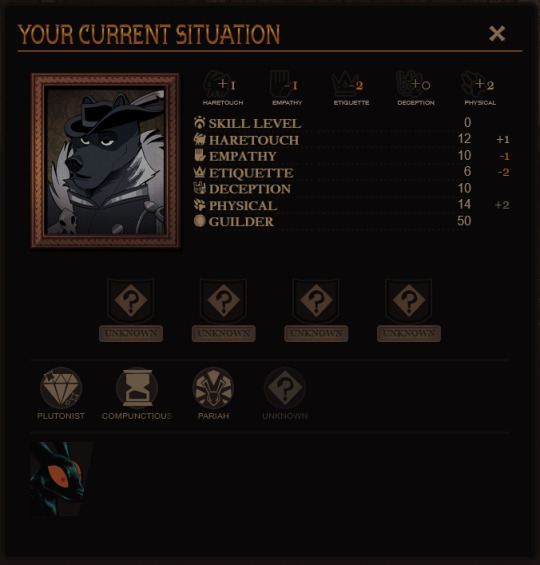
The longer, unclear lists of companion thoughts are now represented by almost equally vague relationship icons. The left icon gives you an overview on "what" your relationship is, while the right icon gives you an idea of its "tone." Broadly speaking, "low tension" relationships are ones where the given companion and Quincy largely agree, and "high tension" relations are ones where you do not. A friendship with high tension might manifest as a cheeky rivalry, while a low-tension enemy might be someone who resents Quincy but stays polite for the sake of shared goals.
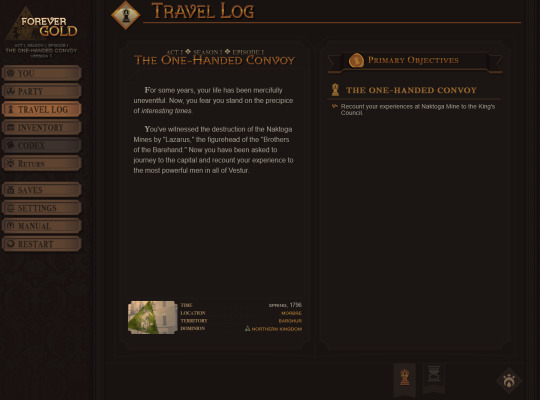
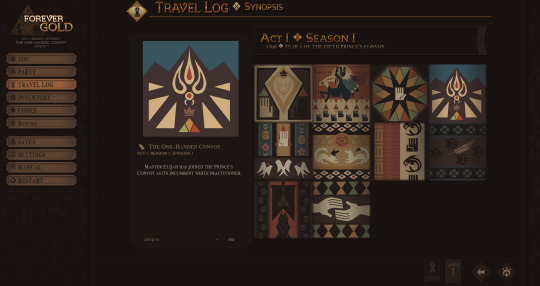
The travel log has gotten a similar retool for ease of use. We've chosen to drop the framing of "quests" in favor of plainly listed "tasks." Itemizing story events as "quests" was a sort of holdover from early development, when we were still conceptualizing what "gameplay" for an IF story like this would even look like, but as development progressed, it became clear that was kind of an overcomplication.
The timeline on the synopsis page has also been done away with in favor of this woven history log which tracks the beginning/ending of arcs and some big ticket player choices. You can scroll through the squares for a brief reminder of what you did in your specific playthrough!
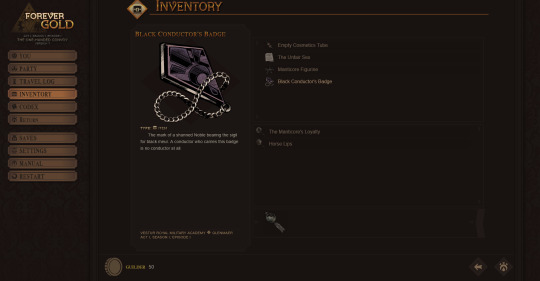
The inventory has been redone to better reflect how we're putting the inventory system to use in-game. Doing away with "notes," we now have three categories of inventory item: actual items, Quincy's observations, and oaths. What is an oath? You'll just have to find out!
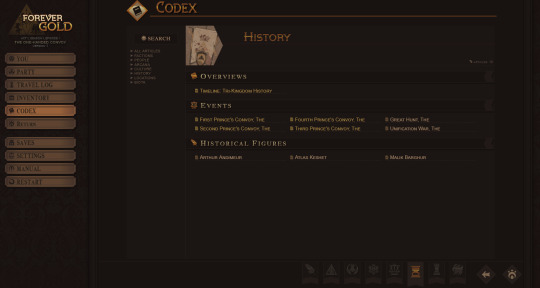
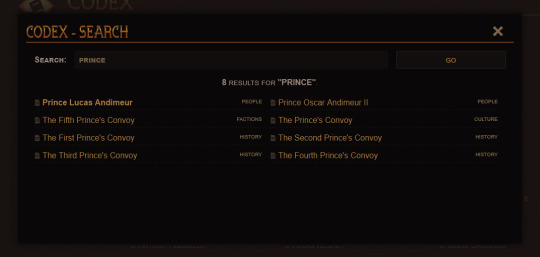
The codex has received a ton of QoL updates - namely, better options for navigation and a simple search function. We've also altered the categories somewhat and reassessed what "deserves" an article and what should exist as an amendment to a larger article, as - for example - giving each and every named location a codex entry like we originally planned would very quickly spin out of control and overwhelm players. We hope the end result is a cleaner codex experience!
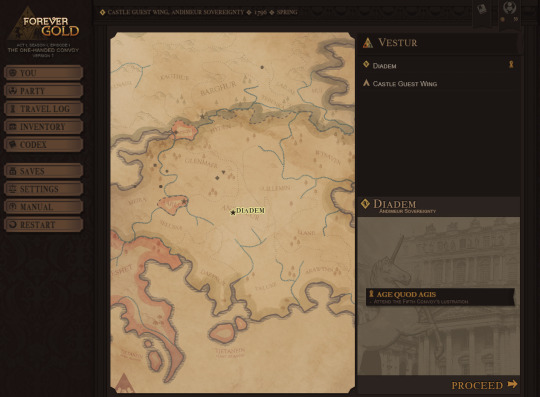
And, finally, we have the retooled map. Instead of awkwardly navigating submenus, we now have one huge map with everything on it! The player can navigate by either clicking the points on the map or the list of available locations. A selected location will display in the corner, and list any active story tasks associated with that location.
And that's all for today's post! We're so close to release, and I can't wait to hear everyone's thoughts on what we've made!
-LS
#forever gold#if game#interactive fiction#twine if#twine game#twine story#twine wip#twine#twine interactive fiction#episode 1 announcement
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Progress update: stuff
I've been pretty quiet lately because I've been slowly working on an android app of my own outside of work. Still a long way to go before it's finished, but baby steps.
It's an app where you can make custom beading patterns easily with mobile UI in mind. The only other one I've seen on the android store was this really old one with only two stars because they hide 90% of the features behind a paywall while calling it a free app.
While I like using the Beadographer website it has its limits and is designed for computers in mind rather than touch screens. Trying to use it on a phone can be a bit annoying.
Right now I have a basic grid set up for square stitch and loom stitch with the ability to select colors, color/clear beads on tap, add rows/columns, and pan/zoom in using two finger touch. I plan on adding more features including the following:
Drag your finger over several beads to color them at once rather than have to tap them individually.
Templates for several styles including peyote, brick, herringbone, right angle weave, different circular peyote stitches, and others.
Auto save patterns in progress.
Can store multiple patterns.
Create and save custom colors to use between projects.
Tools like undo/redo, rotate the canvas, select and drag, color picker, image import, and mirror.
Export patterns as png files.
Available different kinds of beads (toho, miyuki, etc)
I know this isn't most peoples' cup of tea but I'm really excited to try and complete this, and maybe even get it on the app store :D
My biggest worry is how I'm going to handle the circular peyote patterns since they don't conform to grids as easily as other styles would due to increases. The rest seems easy enough albeit long and tedious to develop and test for everything.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
That post from like a month ago (I was planning to write this the day after and then immediately forgot and this has been in drafts since lol) about web devs not having some basic knowledge of the web has been stuck in my brain for a while because they are correct as I said in the notes but it's the landscape of web dev right now that's causing it and I don't see it stopping anytime soon.
I've been a professional Front End Dev for just over 7 years at this point (now a UX Dev working on a design system), and while I have a good chunk of experience under my belt, I've gotten to the point where I realize just how much shit I do not know and it's a LOOOOT.
The current landscape of web dev is that most projects and products are robust web apps that, in the absolute best case scenario, are gonna require, at minimum:
User experience research and work (UX)
User interface design (UI)
Front end with accessibility and mobile responsiveness (I am here)
Front end interactions and state management (JS engineers)
Backend database and API work
Backend infrastructure work (including setting up the dev and QA test environments)
QA testing
Developer experience to make sure devs/engineers are working efficiently with the tools they have
I'm sure I've missed some roles here, but you can see why people end up specializing when they work on bigger projects and products. The web is so unbelievably JavaScript heavy nowadays that all these specializations are Kind Of Required™, but that's absolute best case scenario. A lot of companies simply do not have the budget (or desire) to fill all these roles. So then you have a bunch of people who are kinda okay to mediocre at multiple of these things instead focusing on being good at one or two things. And then put in timeline requirements. AND THEN you have some companies who have different philosophies on how to build their core product: some are very UX focused and will put time into making sure that's present, others are not and will not care about UX in the slightest and thus those roles may not exist there at all. And...well things aren't going to be as quality as you expect when you consider all of those points.
The web is full of applications now that require a lot more expertise in different fields than just a basic static site with no data. That's not to say static sites don't exist or have no place anymore, tho. But this is where we are. It sucks.
#web#web dev#web development#front end development#back end development#ui design#ux design#html#CSS#JavaScript#career
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Zoe and Coffee
Out traveling again for a family event.
This artwork is also a test run of my art / mixed media skills on mobile devices / mobile software. Photographed with and drawn on my new iPad Air and Apple Pencil Pro; using Procreate. Outside the small learning curve of the UI and lack of a wand tool (as far as I’m aware), I feel almost right at home with Procreate as I do with CSP on my desktop, given the numerous tools (especially with the various brushes) and layers / layer options.
#zoe and coffee#original character#the commodities#zoe#mixed media#photography#hotel#digital art#procreate#coffee#art#artists on tumblr
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
React Native Auto Code Application Development: The Smart Way to Build Mobile Apps
Introduction to React Native Auto Code Application Development
React Native auto code application development is changing the way mobile apps are built. Developers now use intelligent automation tools to generate code quickly and accurately. This speeds up development, reduces errors, and improves the overall quality of applications.
Auto code development with React Native is ideal for startups, agencies, and enterprises aiming to deliver high-quality apps fast.
youtube
Benefits of React Native Auto Code Application Development
1. Speed Up Development Cycles Automation tools handle repetitive tasks instantly. Developers can focus on building unique features rather than wasting time on boilerplate code.
2. Maintain Consistent Code Quality Auto-generated code follows consistent standards. This consistency improves code readability and eases future maintenance.
3. Reduce Human Errors By automating setup and structure, auto code tools minimize the chances of introducing bugs during the initial stages.
4. Enhance Developer Productivity Developers spend more time solving real problems and less time writing repetitive components.
5. Cost-Effective App Creation Faster development with fewer mistakes leads to lower project costs. This allows businesses to scale faster without ballooning budgets.
Popular Tools for React Native Auto Code Development
Ignite CLI Ignite offers pre-configured templates and plugins, making it easy to set up scalable projects instantly.
Hygen Hygen is a simple yet powerful code generator that helps teams maintain consistent coding standards with minimal setup.
Plop.js Plop.js allows developers to create custom generators for components, screens, and more, saving hours on manual coding.
Draftbit Draftbit provides a visual builder for React Native apps. Developers can create screens visually and export production-ready code.
Steps to Implement Auto Code in Your React Native Project
Step 1: Select the right auto code tools based on your project size and complexity. Step 2: Install and configure the tools within your development environment. Step 3: Create templates for commonly used components and screens. Step 4: Generate code structures automatically with simple commands. Step 5: Customize and enhance the generated code to meet unique business needs.
Following a structured approach ensures that automation becomes an asset, not a liability.
Challenges of Auto Code Application Development
1. Initial Learning Curve Some auto code tools require initial time investment for setup and training.
2. Over-Template Dependency Too much reliance on templates can sometimes limit creativity and flexibility.
3. Need for Regular Updates Auto code tools need constant updates to stay compatible with the latest React Native versions.
Developers can overcome these challenges with proper training and proactive tool management.
Best Practices for React Native Auto Code Development
- Use Automation for Repetitive Tasks Only Rely on auto code tools for repetitive elements but custom-build critical business logic manually.
- Keep Templates Updated Ensure all code generation templates are updated regularly to match new coding practices.
- Conduct Regular Code Reviews Even auto-generated code should undergo strict code reviews to maintain quality standards.
- Train Developers Continually Keep teams updated with the latest automation practices and tool updates for maximum efficiency.
Future of React Native Auto Code Application Development
The future points toward more AI-driven automation. Smart assistants will suggest code, build UI components, and even test functionalities automatically. React Native developers who embrace automation today will gain a competitive edge tomorrow.
Innovation combined with automation will define the next era of mobile app development.
Conclusion
React Native auto code application development offers a smarter, faster, and more efficient path to building world-class mobile apps. It helps developers minimize repetitive work, deliver projects quicker, and ensure consistent quality across platforms.
By integrating automation thoughtfully, businesses can create better apps and reach the market faster. React Native auto code development isn't just the future—it's the present.
Read More:
Ai Auto code
AI Wave maker
Rapid low code application development platform
Low code platform Enterprise software for application development
Low code application development platform or Low code platform for application development
What is Low code app development platforms
Composable low code isvs
Java-based low code platform
Composable isvs
RAD studio-Rapid application development software platform
APAAS-application platform as a service
Cloud Low code application development platform
Legacy application modernization solutions
React-native cross-platform mobile application development platform
Compare Wavemaker vs Outsystems vs mendix vs power apps — low code alternatives and its pricing
New and fast application development platform
Rapid application development model or RAD model
Low-code for consumable Banking and financial Low-code platform solutions
Internal api vs external apis
Rapid application development vs SDLC Platform
Custom Enterprise low code application development platform
Legacy enterprise application Modernization Platform
Embedded banking and Finance, Low-Code and the Emerging Face of Adaptability
BAAS- Low code Banking as a service
Composable Low code banking solutions
Telecom low code platform
Alternative to Xamarin and Cordova
Wavemaker Low code
Legacy application modernization platform
Cross-Platform React Native Mobile App Development Platform
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which is better full stack development or testing?

Full Stack Development vs Software Testing: Which Career Path is Right for You?
In today’s rapidly evolving IT industry, choosing the right career path can be challenging. Two popular options are Full Stack Development and Software Testing. Both of these fields offer unique opportunities and cater to different skill sets, making it essential to assess which one aligns better with your interests, goals, and long-term career aspirations.
At FirstBit Solutions, we take pride in offering a premium quality of teaching, with expert-led courses designed to provide real-world skills. Our goal is to help you know, no matter which path you choose. Whether you’re interested in development or testing, our 100% unlimited placement call guarantee ensures ample job opportunities. In this answer, we’ll explore both career paths to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding Full Stack Development
What is Full Stack Development?
Full Stack Development involves working on both the front-end (client-side) and back-end (server-side) of web applications. Full stack developers handle everything from designing the user interface (UI) to managing databases and server logic. They are versatile professionals who can oversee a project from start to finish.
Key Skills Required for Full Stack Development
To become a full stack developer, you need a diverse set of skills, including:
Front-End Technologies: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are the fundamental building blocks of web development. Additionally, proficiency in front-end frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js is crucial for creating dynamic and responsive web interfaces.
Back-End Technologies: Understanding back-end programming languages like Node.js, Python, Ruby, Java, or PHP is essential for server-side development. Additionally, knowledge of frameworks like Express.js, Django, or Spring can help streamline development processes.
Databases: Full stack developers must know how to work with both SQL (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL) and NoSQL (e.g., MongoDB) databases.
Version Control and Collaboration: Proficiency in tools like Git, GitHub, and agile methodologies is important for working in a collaborative environment.
Job Opportunities in Full Stack Development
Full stack developers are in high demand due to their versatility. Companies often prefer professionals who can handle both front-end and back-end tasks, making them valuable assets in any development team. Full stack developers can work in:
Web Development
Mobile App Development
Enterprise Solutions
Startup Ecosystems
The flexibility to work on multiple layers of development opens doors to various career opportunities. Moreover, the continuous rise of startups and digital transformation initiatives has further fueled the demand for full stack developers.
Benefits of Choosing Full Stack Development
High Demand: The need for full stack developers is constantly increasing across industries, making it a lucrative career choice.
Versatility: You can switch between front-end and back-end tasks, giving you a holistic understanding of how applications work.
Creativity: If you enjoy creating visually appealing interfaces while also solving complex back-end problems, full stack development allows you to engage both creative and logical thinking.
Salary: Full stack developers typically enjoy competitive salaries due to their wide skill set and ability to handle various tasks.
Understanding Software Testing
What is Software Testing?
Software Testing is the process of evaluating and verifying that a software product or application is free of defects, meets specified requirements, and functions as expected. Testers ensure the quality and reliability of software by conducting both manual and automated tests.
Key Skills Required for Software Testing
To succeed in software testing, you need to develop the following skills:
Manual Testing: Knowledge of testing techniques, understanding different testing types (unit, integration, system, UAT, etc.), and the ability to write test cases are fundamental for manual testing.
Automated Testing: Proficiency in tools like Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, or Cucumber is essential for automating repetitive test scenarios and improving efficiency.
Attention to Detail: Testers must have a keen eye for identifying potential issues, bugs, and vulnerabilities in software systems.
Scripting Knowledge: Basic programming skills in languages like Java, Python, or JavaScript are necessary to write and maintain test scripts for automated testing.
Job Opportunities in Software Testing
As the demand for high-quality software increases, so does the need for skilled software testers. Companies are investing heavily in testing to ensure that their products perform optimally in the competitive market. Software testers can work in:
Manual Testing
Automated Testing
Quality Assurance (QA) Engineering
Test Automation Development
With the rise of Agile and DevOps methodologies, the role of testers has become even more critical. Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines rely on automated testing to deliver reliable software faster.
Benefits of Choosing Software Testing
Job Security: With software quality being paramount, skilled testers are in high demand, and the need for testing professionals will only continue to grow.
Quality Assurance: If you have a knack for perfection and enjoy ensuring that software works flawlessly, testing could be a satisfying career.
Automated Testing Growth: The shift toward automation opens up new opportunities for testers to specialize in test automation tools and frameworks, which are essential for faster releases.
Flexibility: Testing provides opportunities to work across different domains and industries, as almost every software product requires thorough testing.
Full Stack Development vs Software Testing: A Comparative Analysis
Let’s break down the major factors that could influence your decision:
Factors
Full Stack Development
Software Testing
Skills
Proficiency in front-end and back-end technologies, databases
Manual and automated testing, attention to detail, scripting
Creativity
High – involves creating and designing both UI and logic
Moderate – focuses on improving software through testing and validation
Job Roles
Web Developer, Full Stack Engineer, Mobile App Developer
QA Engineer, Test Automation Engineer, Software Tester
Career Growth
Opportunities to transition into senior roles like CTO or Solution Architect
Growth towards roles in automation and quality management
Salary
Competitive with wide-ranging opportunities
Competitive, with automation testers in higher demand
Demand
High demand due to increasing digitalization and web-based applications
Consistently high, especially in Agile/DevOps environments
Learning Curve
Steep – requires mastering multiple languages and technologies
Moderate – requires a focus on testing tools, techniques, and automation
Why Choose FirstBit Solutions for Full Stack Development or Software Testing?
At FirstBit Solutions, we provide comprehensive training in both full stack development and software testing. Our experienced faculty ensures that you gain hands-on experience and practical knowledge in the field of your choice. Our 100% unlimited placement call guarantee ensures that you have ample opportunities to land your dream job, no matter which course you pursue. Here’s why FirstBit is your ideal training partner:
Expert Trainers: Learn from industry veterans with years of experience in development and testing.
Real-World Projects: Work on real-world projects that simulate industry scenarios, providing you with the practical experience needed to excel.
Job Assistance: Our robust placement support ensures you have access to job openings with top companies.
Flexible Learning: Choose from online and offline batch options to fit your schedule.
Conclusion: Which Career Path is Right for You?
Ultimately, the choice between full stack development and software testing comes down to your personal interests, skills, and career aspirations. If you’re someone who enjoys building applications from the ground up, full stack development might be the perfect fit for you. On the other hand, if you take satisfaction in ensuring that software is of the highest quality, software testing could be your calling.
At FirstBit Solutions, we provide top-notch training in both fields, allowing you to pursue your passion and build a successful career in the IT industry. With our industry-aligned curriculum, expert guidance, and 100% placement call guarantee, your future is in good hands.
So, what are you waiting for? Choose the course that excites you and start your journey toward a rewarding career today!
#education#programming#tech#technology#training#python#full stack developer#software testing#itservices#java#.net#.net developers#datascience
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Key Challenges in Mobile Automation Testing and How to Overcome Them
Mobile automation testing presents several challenges due to the wide variety of devices, operating systems, and configurations in the mobile ecosystem. One primary challenge is device fragmentation—with numerous models, screen sizes, and OS versions, ensuring consistent test results across devices can be complex. Overcoming this requires using device farms or cloud-based testing solutions, such as BrowserStack or AWS Device Farm, to cover a broader range of devices and environments.
Another challenge is handling mobile-specific conditions like varying network speeds, device orientation, and battery constraints, which can affect app performance. Simulating these conditions in test environments ensures the app behaves reliably for real-world users.
Test script instability can also occur, often due to UI changes across app versions. Using stable locators and adopting practices like modular test design can help prevent frequent test failures due to minor UI updates.
Automation tool selection is crucial too, as not all mobile test automation tools support every platform or app type. Frameworks like Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest are popular for handling different needs.
Addressing these challenges with robust strategies and reliable tools enables teams to maintain high-quality, reliable mobile apps that perform well across various devices and conditions.
#mobile app testing#mobile app test automation#mobile automation#mobile app testing tools#ios testing#mobile performance testing#mobile device testing#mobile app usability testing#mobile ui testing tools
0 notes
Text
Transforming Digital Landscapes: The Excellence of Corusview IT Services.

In today's fast-paced digital world, having a reliable and innovative technology partner is crucial for businesses aiming to stay ahead. Corusview IT Services, a leading web development company, stands out by offering top-tier software, web and mobile application development services. With a commitment to quality, reliability, and global reach, Corusview IT Services ensures that clients receive exceptional value for their investments.
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, businesses often face a myriad of challenges when it comes to web, mobile, and software development. Navigating these hurdles can be daunting, but the right technology partner can turn these challenges into opportunities.
Common challenges in Digital development:
Complexity and integration challenges
Web Development: Building dynamic, responsive, and user-friendly websites that effortlessly integrate with existing systems can be quite intricate.
Mobile Development: Creating mobile applications that function seamlessly across various devices and platforms while delivering an excellent user experience poses a significant challenge.
Software Development: Developing custom software solutions that need to integrate with multiple other applications and databases often results in compatibility issues.
Staying current with technology
The fast-paced nature of technological advancements makes it challenging for businesses to remain up-to-date with the latest trends and tools.
Ensuring digital solutions are scalable and future-proof demands continuous investment and specialized expertise.
User experience and design
Developing an intuitive and engaging user experience is essential for the success of any digital product.
Subpar design and usability can result in low user engagement and satisfaction.
Security and compliance
Maintaining the security of digital solutions and adhering to regulatory requirements is a critical concern. Data breaches and security vulnerabilities can have significant consequences for businesses.
How Corusview IT Services can assist:
Corusview IT Services provides a broad range of solutions specifically crafted to tackle these challenges and support businesses in thriving within the digital landscape.
Expert web development
Custom web development: Tailored solutions crafted to fit your unique business requirements.
Content Management Systems (CMS): User-friendly systems that simplify website updates and maintenance.
Cutting-Edge Mobile App Development
Mobile App Creation: Bespoke apps designed to meet the needs of diverse industries.
Cross-Platform Solutions: Strategies that extend your app’s reach and boost its effectiveness across different platforms.
Ongoing Updates and Support: Regular enhancements and maintenance to keep your app fresh, secure, and up-to-date.
User-centric designs
UX and UI Innovation: Creating immersive and visually appealing designs tailored to enhance user interaction.
Prototyping and Usability Testing: Developing and refining prototypes to ensure optimal functionality and user satisfaction.
Ongoing Enhancement: Continuously evolving designs based on user feedback to maintain relevance and effectiveness.
Pioneering Technology and Innovation
Forefront of technological advancements, embracing the latest innovations to deliver state-of-the-art solutions.
Cutting-edge technology ensures your digital products are not only scalable and future-ready but also perfectly in tune with the latest market trends.
Rigorous Quality Assurance:
Implementing comprehensive quality assurance processes to ensure that every solution meets the highest standards of performance and reliability.
At Corusview IT Services, we’re dedicated to helping businesses tackle digital development challenges and achieve their ambitions. Whether you need a cutting-edge website, a bespoke software solution, or a trailblazing mobile app, our skilled team is here to provide top-notch results.
Elevate your digital game with us and witness the transformative power of our solutions. Learn more about how we can boost your company’s digital presence by visiting www.corusview.com.
#it services#technology#web development#mobile development#software development#software development company#web app development#mobile application development#digital marketing#services
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role of a Frontend Developer: Crafting Engaging User Experiences
In the digital age, the frontend developer plays a pivotal role in creating the online experiences we interact with every day. From websites to mobile apps, these professionals are responsible for shaping how users interact with digital products, ensuring that every click, scroll, and swipe is smooth and intuitive. But what exactly does a frontend developer do, and why is their role so critical in today's tech-driven world?
What Is a Frontend Developer?
A frontend developer is responsible for the visual and interactive elements of a website or application that users interact with directly. They bridge the gap between design and technology, translating a designer’s vision into functional, responsive, and user-friendly interfaces. Unlike backend developers, who focus on the server-side aspects, frontend developers specialize in client-side development, working with tools and technologies that directly impact the user experience.
Key Responsibilities of a Frontend Developer
The main job of a frontend developer is to ensure that users can easily navigate, interact with, and enjoy the digital product. Here’s a breakdown of their core responsibilities:
Turning Design into Code: Frontend developers take the visual designs created by UI/UX designers and bring them to life using code. They ensure that what users see on their screen aligns with the intended look and feel, while also making sure it’s functional across different devices and screen sizes.
Responsive Design: With users accessing websites from various devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and desktops, frontend developers focus on responsive design. This means building websites that automatically adjust to fit different screen sizes and orientations, offering an optimal experience regardless of the device.
Optimizing Performance: A key part of a frontend developer’s job is making sure that websites load quickly and perform smoothly. They optimize images, manage scripts, and streamline code to ensure fast loading times, as slow websites can lead to user frustration and high bounce rates.
Implementing Interactivity: Frontend developers add interactive elements like animations, hover effects, and dropdown menus that enhance the user experience. By using JavaScript and frameworks like React or Vue.js, they make websites dynamic and engaging, going beyond static designs.
Cross-Browser Compatibility: Websites need to work consistently across different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.), and frontend developers are responsible for ensuring this compatibility. They test websites in multiple environments to fix any bugs or inconsistencies in the design or functionality.
Core Skills of a Frontend Developer
To excel as a frontend developer, there are several technical skills and tools that are essential:
HTML/CSS: These are the building blocks of web development. HTML structures the content, while CSS styles it, ensuring that it looks polished and visually appealing.
JavaScript: This programming language allows developers to add interactive elements, like form validation, dynamic content updates, and animations, making websites more engaging.
Frameworks and Libraries: Frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js help developers build complex web applications efficiently by providing pre-built structures and components.
Version Control (Git): Collaboration is key in web development, and version control tools like Git allow frontend developers to track changes, collaborate with other developers, and manage different versions of the project code.
Responsive Design & CSS Frameworks: Developers often use frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS to ensure that their websites are responsive and adaptable to all devices.
The Evolving Role of Frontend Developers
As technology continues to evolve, the role of a frontend developer is expanding. Today, the line between frontend and backend development is becoming increasingly blurred, with many frontend developers expected to have some knowledge of backend technologies (a role often referred to as "full-stack development").
Additionally, the rise of progressive web apps (PWAs) and headless CMS architectures has introduced new ways of thinking about frontend development. Frontend developers are now focusing on creating experiences that go beyond the browser, delivering high-performance, native-like experiences on the web.
Another area of growing importance for frontend developers is accessibility. Ensuring that websites are usable by people with disabilities is not just a legal requirement but a responsibility for developers who want to create inclusive digital experiences. This involves using semantic HTML, providing keyboard navigability, and designing with screen readers in mind.
Why Frontend Developers Are Crucial for Business Success
Frontend developers play a critical role in shaping the user experience, which directly impacts the success of a digital product. A well-designed, fast, and user-friendly website or application can increase engagement, boost conversion rates, and enhance brand perception.
For businesses, the user interface is often the first point of contact with potential customers. If a website is slow, difficult to navigate, or visually unappealing, users are likely to leave, costing the business potential sales or leads. Frontend developers ensure that the website or app not only looks great but also performs optimally, keeping users engaged and satisfied.
Conclusion
In the modern digital landscape, frontend developers are essential to creating seamless, engaging, and high-performance online experiences. Their unique combination of technical skills and creative problem-solving allows them to transform designs into functional, responsive, and dynamic websites. As the demand for intuitive digital products continues to grow, the role of the frontend developer will only become more integral to business success and the evolution of web technologies.
4o
You said:
is ko english ma kr do "A o A Sir aj 3 outreach sy bat hoi or YTC k Backlinks Create KIa "
ChatGPT said:
ChatGPT
"Hello Sir, today I had discussions with 3 outreach contacts and created backlinks for YTC."
4o
You said:
ma gmail pr richout kr raha ho mujy ya masg aya ha is ka mujy koi replly kro "Thanks for reaching out. We charge $59 for submission. Let me know what you think."
ChatGPT said:
ChatGPT
You can reply with a polite and professional message like this:
Subject: Re: Submission Inquiry
Hi [Recipient's Name],
Thank you for your response and for providing the pricing details. I appreciate the information. I'll take this into consideration and get back to you shortly with my decision.
Best regards, [Your Name] [Your Position] [Your Company]
This keeps the conversation open while allowing you time to decide.
4o
You said:
Write A Article on "Front End Developer"
ChatGPT said:
ChatGPT
Title: The Role of a Front-End Developer: Crafting the Digital Experience
In today’s fast-paced digital world, websites and applications are the primary touchpoints for businesses and users. The seamless experiences we enjoy on websites—from smooth navigation to responsive design—are largely due to the efforts of front-end developers. But what exactly does a front-end developer do, and why is their role crucial in building user-friendly, efficient digital products?
What is a Front-End Developer?
A front-end developer is a professional who focuses on the client-side development of a website or application. This means they work on the part of the website that users directly interact with. While the back-end (server-side) handles the logic and data storage, the front-end is responsible for what users see and how they interact with a site.
In essence, front-end developers translate design mockups into functional websites or applications using code. They combine the worlds of design, user experience (UX), and coding to ensure a smooth, responsive, and visually appealing user interface (UI).
Key Responsibilities of a Front-End Developer
The role of a front-end developer goes beyond just coding a website. It involves understanding user needs, optimizing for performance, and ensuring the digital product works flawlessly across various devices and browsers. Here are the key responsibilities of a front-end developer:
Translating Designs into Code: Front-end developers take designs created by web designers and bring them to life using programming languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They ensure the design translates accurately into a functioning webpage or application, maintaining the visual fidelity of the design while ensuring usability.
Ensuring Responsiveness: In today’s multi-device world, websites need to work across desktops, tablets, and smartphones. Front-end developers make sure websites are responsive, meaning they adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and orientations.
Implementing Interactivity: Interactivity is key to user engagement. Front-end developers use JavaScript and related frameworks to add interactive elements like animations, sliders, form validations, and dynamic content updates, making the user experience more engaging.
Optimizing Performance: Fast loading times are critical for user satisfaction and SEO. Front-end developers optimize images, minimize code, and ensure efficient loading of assets to create websites that load quickly and perform smoothly.
Cross-Browser Compatibility: Websites need to work consistently across different browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Front-end developers ensure that websites function correctly and look the same on all browsers, addressing any quirks or inconsistencies.
Maintaining Website Accessibility: Front-end developers also focus on making websites accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. They implement practices like semantic HTML, ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) attributes, and keyboard navigation to create an inclusive user experience.
Essential Skills for a Front-End Developer
To excel as a front-end developer, professionals need a combination of technical skills, creativity, and attention to detail. Below are some of the key skills required:
HTML/CSS: These are the foundational languages of front-end development. HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) structures content on the web, while CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) defines how that content looks in terms of layout, color, fonts, and design.
JavaScript: JavaScript is a powerful scripting language used to add interactivity to a website. With JavaScript, developers can create dynamic content, handle user events, and interact with back-end data in real-time.
Responsive Design: Knowledge of responsive design is crucial to ensure that websites and apps work seamlessly across all devices. Tools like Bootstrap or media queries in CSS help developers create adaptive layouts that fit all screen sizes.
Frameworks and Libraries: Modern front-end developers often use libraries and frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js to build more complex web applications efficiently. These tools provide pre-built components and structures to speed up development.
Version Control (Git): Front-end developers often work in teams, and version control tools like Git allow them to track changes in code, collaborate with others, and ensure the codebase remains organized.
Cross-Browser Development: Each browser interprets code slightly differently, so front-end developers must test their websites across various browsers and devices to ensure compatibility.
The Importance of Front-End Developers in Business
In today’s digital economy, a company’s website or mobile app is often the first point of contact with customers. Whether it’s an e-commerce platform, a SaaS application, or a simple company webpage, the user experience can significantly impact brand perception and business outcomes.
Front-end developers ensure that these digital touchpoints are engaging, easy to navigate, and visually appealing, which can directly influence user engagement and conversion rates. A well-designed website that loads quickly, functions smoothly, and offers a seamless user experience can set a business apart from its competitors.
Moreover, front-end developers are key players in building websites optimized for SEO (Search Engine Optimization). Fast-loading, mobile-friendly, and well-structured websites tend to rank higher on search engines, driving more organic traffic to the site.
Front-End Development and Emerging Technologies
As technology evolves, so does the role of the front-end developer. The rise of progressive web apps (PWAs), single-page applications (SPAs), and headless CMS (Content Management Systems) has created new challenges and opportunities for front-end developers.
PWAs allow websites to function like native apps, offering offline capabilities and faster load times. Front-end developers need to integrate these features while maintaining the flexibility of a website.
SPAs load a single HTML page and dynamically update content as the user interacts with the app, creating a more fluid experience. This requires front-end developers to have expertise in frameworks like React and Angular.
Headless CMS decouples the front-end from the back-end, giving front-end developers more control over how content is presented. This allows for greater flexibility in design and user interaction.
Conclusion
The role of a front-end developer is crucial in shaping the digital experience. By combining technical expertise with creativity, front-end developers bring designs to life, ensuring that websites are not only visually appealing but also functional, responsive, and user-friendly. In a world where the digital experience can make or break a business, front-end developers are key players in driving online success.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transforming Businesses with DI Solutions: Innovative IT Expertise
Transform your business with DI Solutions

In the ever-evolving digital landscape, businesses must harness cutting-edge technology to remain competitive. At DI Solutions, we specialize in driving business transformation through advanced IT solutions and expert services. Our dedication to innovation and excellence has empowered numerous clients to achieve their goals and excel in their industries.
Innovative IT Solutions DI Solutions excels in providing tailored IT solutions that meet each client's unique needs. Our services include custom software development, mobile app creation, web development, and UI/UX design. By leveraging the latest technologies, we deliver state-of-the-art solutions that enhance growth and efficiency.
Expert Team of Professionals Our team consists of highly skilled professionals—creative designers, experienced developers, and strategic problem-solvers. We emphasize continuous learning to stay at the forefront of industry trends and technological advancements, ensuring that our clients receive the most effective and innovative solutions.
Global Reach and Impact
With over a decade of experience, DI Solutions has made a significant impact globally, partnering with more than 120 clients across North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. Our extensive global presence demonstrates our capability to provide exceptional IT services that address diverse business needs.
Client-Centric Approach
At DI Solutions, clients are central to our mission. We take the time to understand their business objectives, challenges, and requirements, enabling us to deliver customized solutions that surpass expectations. Our client-centric approach ensures we provide not just what is needed but what drives success and growth.
Comprehensive IT Services
Our service offerings include:
Custom Software Development: Tailored software solutions for optimal efficiency and performance.
Mobile App Development: Innovative mobile applications for Android and iOS platforms.
Web Development: Expert web development to create responsive and user-friendly websites.
UI/UX Design: Engaging user interfaces that enhance the overall user experience.
Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing to ensure the highest quality standards.
DevOps Services: Streamlined operations through integrated cultural philosophies, practices, and tools.

Join Hands with DI Solutions
Partner with DI Solutions to harness the power of innovative IT expertise. Whether you’re a startup aiming to establish a presence or an established business seeking new heights, we have the solutions and expertise to propel you forward.
For more information, visit our website or contact us directly. Let’s embark on a journey of transformation and growth together.
Transform your business with DI Solutions – where innovation meets excellence.
Contact Us Website: https://disolutions.net/ Email: [email protected] , Call: 91-9904566590 , B-301, 307, 406 Apex Commercial Center, Varachha Road, Nr. Yash Plaza, Surat, Gujarat,India-395006.
youtube
#disolutions #DI Solutions #Hire Angular.js Developers #Hire React.js Developers #Hire Vue.js Developers #Hire UI/UX Developers #Hire .NET Developers #Hire Node.js Developers #Hire Laravel/PHP Developers #Hire Android Developers #Hire IOS Developers #Hire Ionic Developers #Hire React Native Developers #Hire Full Stack Developers #Hire MERN Stack Developers #Hire MEAN Stack Developers #Mobile App Development #Web Development #UI/UX Design #Quality Assurance #DevOps Services
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I will do mobile app, website, dashboard, software, design, UX UI design with Figma, photoshp or xd
Fiverr Gig link : https://www.fiverr.com/s/Ajjml4
UI Design
UI design involves creating the user interface of a digital product, focusing on its visual elements and layout.
UI/UX Design
UI/UX design combines user interface and user experience design to create a seamless and user-friendly digital product.
Mobile App Design
Mobile app design is the process of creating the visual elements and layout for a mobile application.
App Design
App design refers to the overall design of an application, encompassing both its user interface and user experience.
Figma
Figma is a popular design and prototyping tool used by designers and teams for creating digital designs and collaborating on projects.
Mobile App UI
Mobile app UI design focuses specifically on the user interface elements of a mobile application.
UX Design
UX design, or user experience design, involves creating a positive and efficient experience for users when interacting with a digital product.
Mobile App
A mobile app is a software application designed to run on mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
App UI Design
App UI design focuses on the visual elements and layout of the user interface within an application.
UI/UX
UI/UX combines user interface and user experience design to ensure a product is both visually appealing and user-friendly.
Website Design
Website design involves creating the visual elements and layout for a website.
UX UI Design
UX UI design combines user experience and user interface design to create an optimal user interaction with a digital product.
Figma Design
Figma design refers to the design work done using the Figma design and prototyping tool.
UX
UX, or user experience, focuses on enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability and accessibility of a digital product.
UI
UI, or user interface, pertains to the visual elements and layout that users interact with in a digital product.
Prototype
A prototype is a preliminary model of a digital product used for testing and evaluation before full development.
User Interface
The user interface (UI) is the point of interaction between the user and a digital product.
UX UI
UX UI combines user experience and user interface design to create a cohesive and user-friendly product.
Mobile UI Design
Mobile UI design focuses on creating the visual elements and layout specifically for mobile devices.
App UI UX
App UI UX design combines user interface and user experience design for an application.
Web UI Design
Web UI design involves creating the visual elements and layout for web applications and websites.
User Experience
User experience (UX) refers to the overall experience a user has while interacting with a digital product.
Web Design
Web design is the process of creating the visual elements and layout for websites.
Mobile UI
Mobile UI encompasses the visual elements and layout specifically designed for mobile devices.
Website UI Design
Website UI design focuses on creating the user interface for websites.
Mobile Design
Mobile design involves designing for mobile devices, including both UI and UX considerations.
Landing Page Design
Landing page design focuses on creating a compelling and conversion-friendly webpage for marketing purposes.
Wireframe
A wireframe is a visual representation of the layout and structure of a digital product, used as a blueprint for design and development.
Figma App Design
Figma app design refers to using the Figma tool for designing mobile and web applications.
Wireframe Design
Wireframe design involves creating visual blueprints of digital products to plan their layout and structure.
UI UX Designer
A UI/UX designer specializes in both user interface and user experience design.
Website
A website is a collection of webpages accessible on the internet, designed for various purposes.
Web UI UX
Web UI/UX design combines user interface and user experience principles for web-based products.
Adobe XD
Adobe XD is a design and prototyping tool used for creating user interfaces and experiences.
Website UI
Website UI refers to the user interface elements of a website.
Dashboard UI UX
Dashboard UI/UX design involves creating user-friendly and informative dashboards for data visualization.
Application
An application (app) is a software program designed to perform specific tasks or functions on a digital device.
Responsive Design
Responsive design ensures that a digital product adapts and functions well on various screen sizes and devices.
Dashboard Design
Dashboard design focuses on creating visually appealing and functional dashboards for data presentation.
iOS
iOS is the operating system developed by Apple for their mobile devices such as iPhones and iPads.
Mobile
Mobile refers to devices like smartphones and tablets that are portable and typically run on mobile operating systems.
Android
Android is the operating system developed by Google for a wide range of mobile devices.
Web App Design
Web app design involves designing the user interface and user experience for web-based applications.
Website UX
Website UX focuses on optimizing the user experience of a website to meet user needs and expectations.
App
An app, short for application, is a software program designed for specific functions or tasks.
Design
Design encompasses the process of creating visual and functional elements for a product or project.
Web UI
Web UI refers to the user interface elements of a web-based product or application.
App Screenshots
App screenshots are images captured from a mobile app to showcase its features and design.
App Prototype
An app prototype is a preliminary model of a mobile application used for testing and demonstration.
App UI
App UI refers to the user interface elements within a mobile application.
App Development
App development involves the process of creating and building software applications.
Web Application
A web application is a software program accessed and used through a web browser.
NFT Website Design
NFT website design focuses on creating websites for buying, selling, and trading non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
App Mockup
An app mockup is a static representation of an application's user interface, used for design and presentation purposes.
UI Website Design
UI website design involves creating the user interface elements for a website.
UI UX Website
UI/UX website design combines user interface and user experience principles for web-based products.
Landing Page UI
Landing page UI design focuses on creating the user interface elements of a landing page.
Android App UI
Android app UI design involves designing the user interface for applications on the Android platform.
PSD Design
PSD design refers to creating design layouts and elements using Adobe Photoshop (PSD) files.
#Certainly#here are the points with the “hax” tag added:#UI Design#UI/UX Design#Mobile App Design#App Design#Figma#Mobile App UI#UX Design#Mobile App#App UI Design#UI/UX#Website Design#UX UI Design#Figma Design#UX#UI#Prototype#User Interface#UX UI#Mobile UI Design#App UI UX#Web UI Design#User Experience#Web Design#Mobile UI#Website UI Design#Mobile Design#Landing Page Design#Wireframe
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Front-End Development: Building the Interface of the Future
Front-end development is at the heart of creating user-friendly and visually appealing websites. It involves translating designs into code and ensuring that web applications are responsive and interactive. In this article, we explore the key aspects of front-end development, essential skills, and emerging trends in the field.
What is Front-End Development?
Front-end development focuses on the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) aspects of web development. It involves creating the part of the website that users see and interact with, using a combination of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Core Technologies
HTML (HyperText Markup Language): HTML is the foundation of web pages, defining the structure and content, such as headings, paragraphs, and images.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): CSS is used to style and layout web pages, controlling aspects like colors, fonts, and spacing to create an attractive and consistent look.
JavaScript: JavaScript adds interactivity and dynamic content to web pages, enabling features like form validation, animations, and user input handling.
Popular Frameworks and Libraries
React: A JavaScript library for building fast and dynamic user interfaces, particularly single-page applications.
Angular: A comprehensive framework for building large-scale applications with a structured and modular approach.
Vue.js: A flexible framework that is easy to integrate into projects and focuses on the view layer of applications.
The Role of a Front-End Developer
Turning Designs into Code
Front-end developers take designs created by UI/UX designers and turn them into code. This involves creating HTML for structure, CSS for styling, and JavaScript for functionality, ensuring the design is faithfully implemented and functional across various devices and browsers.
Ensuring Responsiveness
With the growing use of mobile devices, it’s crucial that websites work well on screens of all sizes. Front-end developers ensure that web applications are responsive, meaning they adapt smoothly to different screen resolutions and orientations.
Optimizing Performance
Performance optimization is key in front-end development. Developers reduce file sizes, minimize load times, and implement lazy loading for images and videos to enhance the user experience.
Maintaining Cross-Browser Compatibility
A successful front-end developer ensures that web applications work consistently across different browsers. This involves testing and resolving compatibility issues to provide a uniform experience.
Implementing Accessibility
Making web content accessible to people with disabilities is a critical aspect of front-end development. Developers adhere to accessibility standards and best practices to ensure that everyone can use the website effectively.
Essential Skills for Front-End Developers
Mastery of Core Technologies
Proficiency in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is fundamental. Front-end developers must be able to write clean, efficient code that is both maintainable and scalable.
Familiarity with Modern Frameworks
Knowledge of modern frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js is crucial for building contemporary web applications. These tools facilitate the creation of complex, dynamic interfaces.
Version Control with Git
Version control systems like Git are essential for tracking changes in the codebase and collaborating with other developers. Mastery of Git allows for efficient project management and collaboration.
Understanding of UX/UI Design
An understanding of UX/UI principles helps developers create user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing interfaces. This includes knowledge of user behavior, usability testing, and design basics.
Problem-Solving and Debugging
Front-end development often involves troubleshooting issues related to layout, functionality, and performance. Strong problem-solving skills are essential to identify and resolve these challenges efficiently.
Emerging Trends in Front-End Development
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs combine the best features of web and mobile applications, offering fast loading times, offline capabilities, and push notifications. They provide a native app-like experience within the browser.
WebAssembly
WebAssembly allows developers to run high-performance code in web browsers. It enables complex applications like games and video editors to run efficiently on the web, expanding the possibilities of front-end development.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Server-side rendering improves the loading speed of web pages and enhances SEO. Frameworks like Next.js (for React) facilitate SSR, making it easier to build fast and search-friendly applications.
Single Page Applications (SPAs)
SPAs load a single HTML page and dynamically update the content as users interact with the application. This approach provides a smoother user experience, similar to that of a desktop application.
Component-Based Development
Modern frameworks emphasize component-based architecture, where UI elements are built as reusable components. This modular approach enhances maintainability and scalability.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Integrating AI and machine learning into front-end development enables the creation of smarter, more personalized applications. Features like chatbots, recommendation engines, and voice recognition can significantly enhance user engagement.
#FrontEndDevelopment#WebDevelopment#UIUXDesign#HTML#CSS#JavaScript#ReactJS#Angular#VueJS#ResponsiveDesign#WebDesign#UserExperience#WebPerformance#WebAccessibility#SinglePageApplication#ProgressiveWebApp#WebDevelopmentTrends#ModernWebDev#FrontendFrameworks#CodeNewbie#LearnToCode#WebDevCommunity#CodingLife#TechTrends#WebComponents#WebAssembly#ServerSideRendering#DigitalDesign#UIComponents#WebOptimization
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Digital marketing online course in Mohali and Chandigarh | Param digital marketing
Digital Marketing Course – Learn Online and Save Money
Below is an outline of an online digital marketing course content. This content is a general guideline and can be adapted and expanded based on the specific needs of the course and the level of expertise of the learners. Learn Advanced Digital Marketing with DKI and DSA Ads only in 29999/– now – Join Now
Digital marketing online course in Mohali and Chandigarh.

Understanding digital marketing and its importance
Evolution of digital marketing
Digital marketing vs. traditional marketing
Key concepts and terminology
Book Class Now
Module 2: Website Planning and Development
Importance of a website in digital marketing
Domain registration and hosting
Website design principles and best practices
User experience (UX) and user interface (UI)
Mobile responsiveness and optimization
Introduction to Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress
Module 3: Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Want to join click here
Understanding search engines and how they work
On-page SEO: Keyword research, Density and Proximity, meta tags and Description, headings, content and image optimization
Off-page SEO: Link building, backlinks, and domain authority, DA/PA Checking
Technical SEO: Website speed, site structure, and crawlability, Mobile Friendly, Security
Local SEO and Google My Business Page Optimization
Module 4: Content Marketing
Importance of quality content writing in the digital landscape
Creating a content writing strategy
Types of content: blog posts, articles, infographics, videos, etc.
Content promotion and distribution
Content analytics and measuring success
Module 5: Social Media Marketing
Overview of major social media platforms (Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, Pinterest, Tumblr etc.)
Creating a social media strategy
Social media advertising and sponsored posts, Event Creating
Building and engaging with an online community
Social media analytics and performance tracking
Module 6: Email Marketing
Building an email marketing list
Creating effective email campaigns
Email marketing tools and platforms
Personalization and segmentation
Analyzing email marketing performance
Module 7: Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
Introduction to PPC Advertising and Google Ads
Creating PPC campaigns and ad groups
Keyword research and selection
Ad copywriting and A/B testing
Bid strategies and budget management
Module 8: Display and Banner Advertising
Understanding display advertising and its formats
Display advertising platforms (Google Display Network, etc.)
Targeting options for display ads
Designing effective banner ads
Display ad performance tracking and optimization
Module 9: Video Marketing
The rise of video content in digital marketing
Creating engaging video content
Video SEO and optimizing for platforms like YouTube
Video advertising and sponsored content
Analyzing video marketing metrics
Module 10: Analytics and Data-driven Marketing
Introduction to marketing analytics
Setting up Google Analytics and understanding key metrics
Data analysis for decision-making
A/B testing and conversion rate optimization (CRO)
Customer journey and attribution modeling
Module 11: Mobile Marketing
Mobile marketing trends and opportunities
Mobile app marketing and optimization
SMS marketing and push notifications
Mobile advertising and location-based marketing
Mobile analytics and tracking
Module 12: Digital Marketing Strategy and Planning
Developing a comprehensive digital marketing strategy
Integrating various digital marketing channels
Budget allocation and resource planning
Measuring ROI and KPIs for digital campaigns
Case studies and real-world examples
Module 13: Legal and Ethical Considerations
Privacy and data protection laws (e.g., GDPR)
Ethical practices in digital marketing
Dealing with online reviews and reputation management
Handling customer data responsibly
Module 14: Emerging Trends in Digital Marketing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning in marketing
Voice search and voice-activated devices
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) marketing
Influencer marketing and social media trends
Future outlook and staying ahead in the digital marketing landscape
Module 15: Final Project and Certification
Capstone project applying concepts learned throughout the course
Presentations and feedback sessions
Issuance of course completion certificates
Remember that this is just a general outline, and the content and depth of each module can be adjusted to suit the course’s duration, audience level, and objectives. Additionally, including practical exercises, case studies, and hands-on projects will enhance the learning experience. We provide 100% Job Placement after completion of Course.
Digital marketing online course in Mohali and Chandigarh.
#digital marketing#online marketing#seo services#search engine optimization#mohali#chandigarh#tricity#learning#education#student#university#jobseekers#college#online courses
3 notes
·
View notes